389fe20eb2c2b854fad0deeef3438e44.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Fast Modeling Techniques for C 4 ISR Problems John Furman The MITRE Corporation Mc. Lean, Virginia, USA 3 September 2004 MITRE 1

The Challenge How do you calculate the impact of C 4 ISR* systems on Force Effectiveness? System Technical Performance N IO Distributed Functional Processes & IM Performance High Dimensionality (Options & Factors) Relationship to Operational Effectiveness MITRE Cognition and Human Factors *C 4 ISR: An older acronym for Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance 2

The Taxonomy of C 4 ISR Analysis Mission Branch (Impact of Info Delivery) Mo. FE Mo. CE Comparison of Avail Information & Decisions Taken Force Operational Outcome Tactical or Operational Task Performance Based on Info Delivery Communications Mo. P MITRE Decision Branch (Choice & Outcome) Synthesis, Fusion, Human Cognition Access Timeliness Quantity System Performance Persistence Mo. FE Mo. CE Perception Quality Mo. P 3

Basic Principles • Identify Fundamental Operational Issues ü “Drivers” --- most challenging aspects (hard problem) ü Critical Factors for operational execution ü What must I do to succeed? What is a “successful” outcome? • Model to Support Analysis ü Based on comprehensive understanding of problem domain ü Rapid-response: idea to execution in days or weeks ü Focus on critical variables and processes (can’t do everything) • Analyze to Examine the KEY Issues ü Task analysis ü Linkages among tasks ü Time dependencies ü Parametric representations of performance ü Quantitative measures for outcomes ü Influence diagrams as the primary technique Simple, understandable, parametric MITRE 4
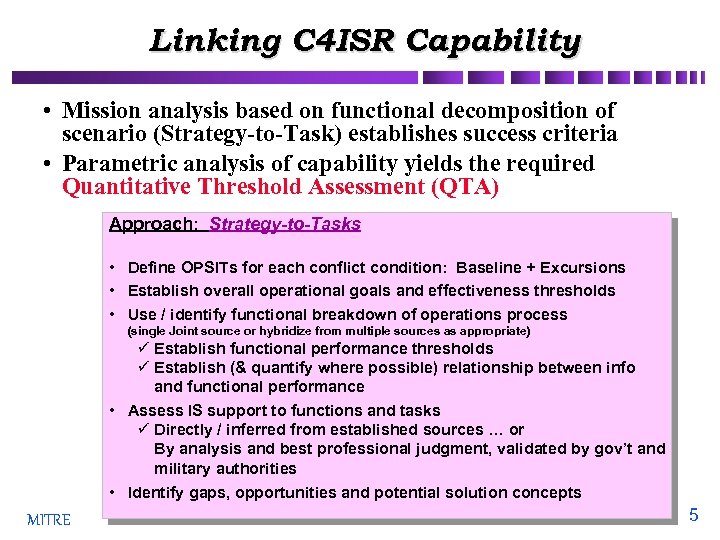
Linking C 4 ISR Capability • Mission analysis based on functional decomposition of scenario (Strategy-to-Task) establishes success criteria • Parametric analysis of capability yields the required Quantitative Threshold Assessment (QTA) Approach: Strategy-to-Tasks • Define OPSITs for each conflict condition: Baseline + Excursions • Establish overall operational goals and effectiveness thresholds • Use / identify functional breakdown of operations process (single Joint source or hybridize from multiple sources as appropriate) ü Establish functional performance thresholds ü Establish (& quantify where possible) relationship between info and functional performance • Assess IS support to functions and tasks ü Directly / inferred from established sources … or By analysis and best professional judgment, validated by gov’t and military authorities • Identify gaps, opportunities and potential solution concepts MITRE 5
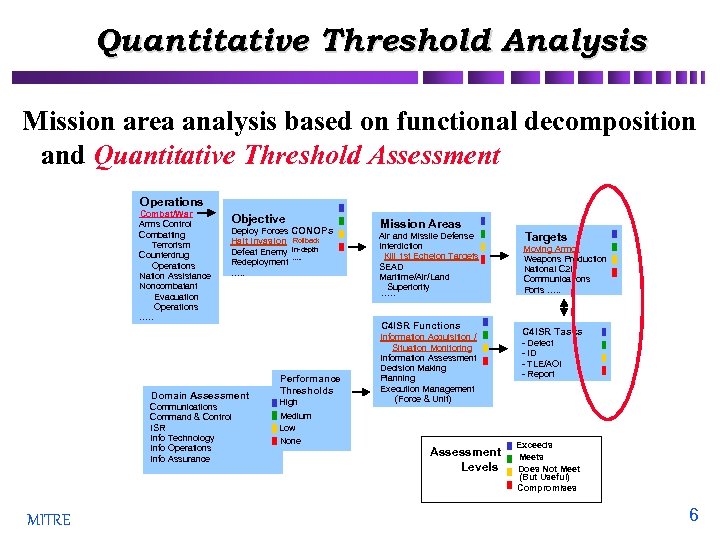
Quantitative Threshold Analysis Mission area analysis based on functional decomposition and Quantitative Threshold Assessment Operations Combat/War Arms Control Combatting Terrorism Counterdrug Operations Nation Assistance Noncombatant Evacuation Operations …. . Objective Deploy Forces CONOPs Halt Invasion Rollback Defeat Enemy In-depth …. . Redeployment …. . Domain Assessment Communications Command & Control ISR Info Technology Info Operations Info Assurance MITRE Mission Areas Air and Missile Defense Interdiction Kill 1 st Echelon Targets SEAD Maritime/Air/Land Superiority …. . C 4 ISR Functions Performance Thresholds High Medium Low None Information Acquisition / Situation Monitoring Information Assessment Decision Making Planning Execution Management (Force & Unit) Assessment Levels Targets Moving Armor Weapons Production National C 2 I Communications Ports …. . C 4 ISR Tasks - Detect - ID - TLE/AOI - Report Exceeds Meets Does Not Meet (But Useful) Compromises 6

Common Modeling Approach • Parametric system dynamics modeling • Implemented in easily available tools ü Analytica™, Mat. Lab, Mathematica, Python, Smalltalk, Sim. Py ü Open-source when appropriate (cost, risk, or response time) MITRE Mission analysis based on functional decomposition and quantitative threshold assessment 7

Example Model Concept Maritime Engagement Model - MEM Approach • Posit evolution of adversaries, forces and capabilities • Lay down adversary forces into defense zones • Time dynamic, 2 -sided, parametric calculation of expected damage • If E(damage) < tolerance threshold, then access to zone is obtained on day N • Forecast force lethality vs. ground mobile targets relative to “complete access” Simple MITRE --- Aggregate --- Rapid 8

MEM Top-level Structure Modules contain a process (collection of nodes) Attrition of Threat Forces, Capabilities, Disposition & CONOPs Attrition of US Forces US Maritime Forces, Disposition, Capabilities & CONOPs Defense Zones Analysis Case • Decision nodes • Chance nodes • Result nodes • Data MITRE Access Achieved by US Forces E( KPD) / Max( KPD) Combat Power 9
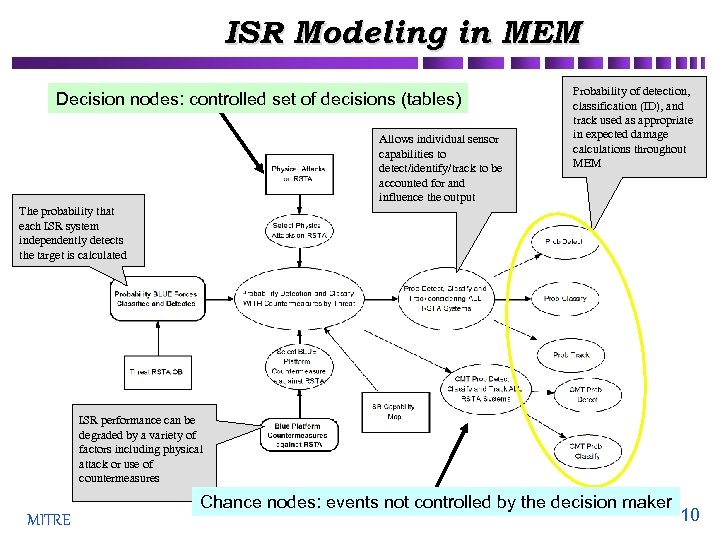
ISR Modeling in MEM Decision nodes: controlled set of decisions (tables) Allows individual sensor capabilities to detect/identify/track to be accounted for and influence the output Probability of detection, classification (ID), and track used as appropriate in expected damage calculations throughout MEM The probability that each ISR system independently detects the target is calculated ISR performance can be degraded by a variety of factors including physical attack or use of countermeasures MITRE Chance nodes: events not controlled by the decision maker 10

ISR Systems Modeled Categorization ensures proper consideration of all systems EO / IR Space Commercial Adversary Ally Missile Launch Det. Air TACAIR Recce MPA UAV Radar SIGINT Scientific Adversary Ally Gov’t Owned TACAIR Recce MPA UAV Acoustic TACAIR ESM MPA UAV Monitor shore / straits Ground Monitor shore / straits Counter-battery Radar Monitoring networks IADS / ATC Sea FPB D-E sub Merchantman Patrol D-E sub Acoustic D-E sub Space - Commercial EO/IR Other / Cyber Space - Adversary Ally EO/IR Space – EO/IR Space - Missile Launch Detect EO/IR Space - Scientific Radar Space - Adversary Ally Radar Space – Radar Space - Adversary Ally SIGINT Space – SIGINT Air - TACAIR RECCE EO/IR Air - MPA EO/IR Air - UAV EO/IR Air - TACAIR RECCE Radar Air - MPA Radar Air - UAV Radar Air - TACAIR ESM SIGINT Air - MPA SIGINT Air - UAV SIGINT MITRE Ground - Monitor Shore/Straits EO/IR Ground - Monitor Shore/Straits Radar Ground - OTH Radar Ground - Counter-Battery Radar Ground - IADS/ATC Radar Ground - SIGINT Ground - Offensive EW Sea - Fast Patrol Boat EO/IR Sea - Diesel Electric Sub EO/IR Sea - Modern Diesel Electric Sub EO/IR Sea - Merchantman Radar Sea - Patrol Craft Radar Sea - Patrol SIGINT Sea - Diesel Electric Sub SIGINT Sea - Modern Diesel Electric Sub SIGINT Sea - Sea Bed Acoustic Sea - Diesel Electric Sub Acoustic Systems can be categorized by time to expedite portfolio analysis 11
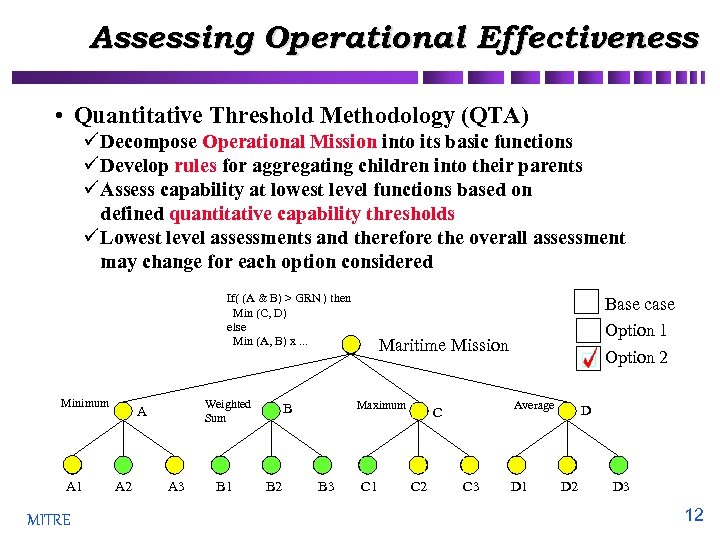
Assessing Operational Effectiveness • Quantitative Threshold Methodology (QTA) ü Decompose Operational Mission into its basic functions ü Develop rules for aggregating children into their parents ü Assess capability at lowest level functions based on defined quantitative capability thresholds ü Lowest level assessments and therefore the overall assessment may change for each option considered If( (A & B) > GRN ) then Min (C, D) else Min (A, B) x. . . Minimum A 1 MITRE Weighted Sum A A 2 A 3 B 1 B 2 Maritime Mission Maximum B B 3 Base case Option 1 Option 2 C 1 Average C C 2 C 3 D 1 D D 2 D 3 12
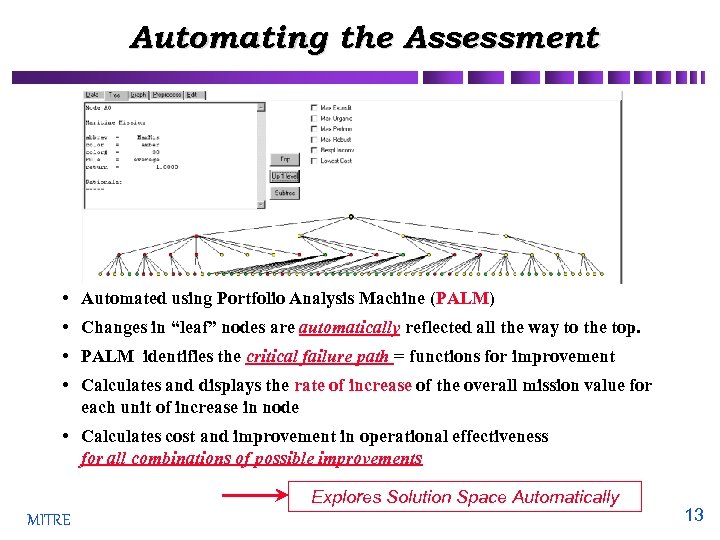
Automating the Assessment • Automated using Portfolio Analysis Machine (PALM) • Changes in “leaf” nodes are automatically reflected all the way to the top. • PALM identifies the critical failure path = functions for improvement • Calculates and displays the rate of increase of the overall mission value for each unit of increase in node • Calculates cost and improvement in operational effectiveness for all combinations of possible improvements Explores Solution Space Automatically MITRE 13
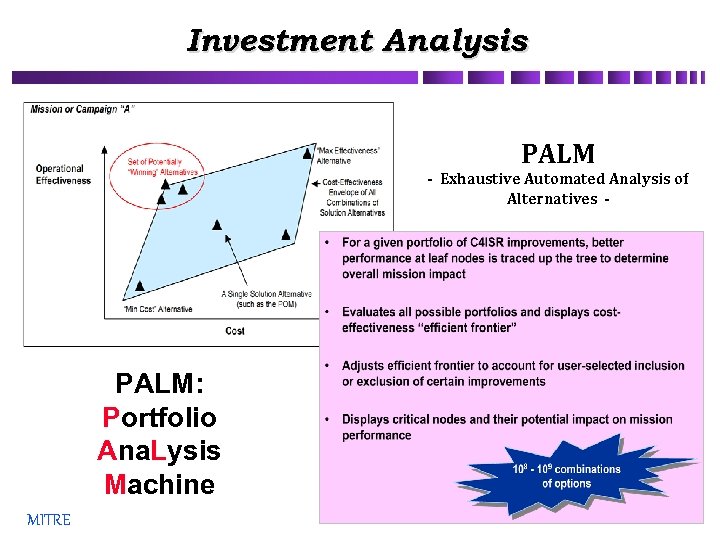
Investment Analysis PALM - Exhaustive Automated Analysis of Alternatives - PALM: Portfolio Ana. Lysis Machine MITRE 14
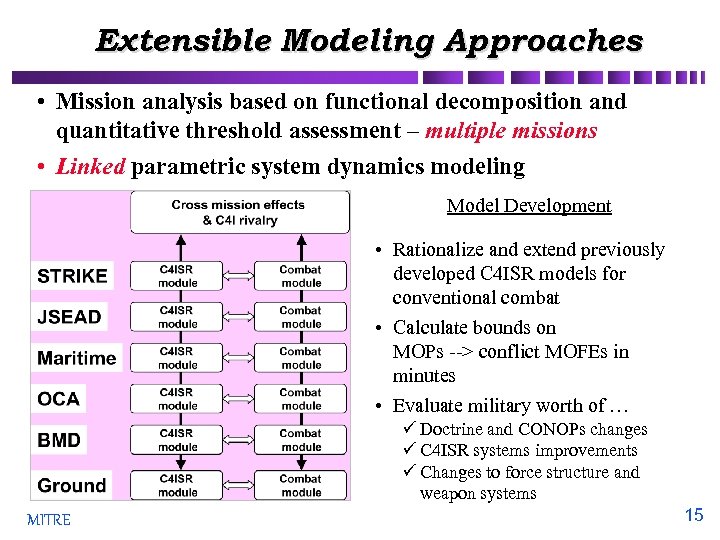
Extensible Modeling Approaches • Mission analysis based on functional decomposition and quantitative threshold assessment – multiple missions • Linked parametric system dynamics modeling Model Development • Rationalize and extend previously developed C 4 ISR models for conventional combat • Calculate bounds on MOPs --> conflict MOFEs in minutes • Evaluate military worth of … ü Doctrine and CONOPs changes ü C 4 ISR systems improvements ü Changes to force structure and weapon systems MITRE 15

Analytic Rigor • Measure C 4 ISR effectiveness • Quantify performance: üComparative performance § “System A performs 3 times as well as system B. ” üAbsolute performance § “System A is likely to meet 65 of 85 percent of capability needs. ” • Assess capability needs üEvaluates options at the mission or operation level üRecommends solutions that address § § MITRE Future risk tradeoffs, Force management, Warfighting capabilities, and Economic limitations 16
389fe20eb2c2b854fad0deeef3438e44.ppt