all.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 64
 Farrakhov Ayrat English Teaching Material for students of Engineering Specialties RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES • • • Biogas Solar Wind Geothermal Hydro Wave Thermal Nuclear Equipment Famous People
Farrakhov Ayrat English Teaching Material for students of Engineering Specialties RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES • • • Biogas Solar Wind Geothermal Hydro Wave Thermal Nuclear Equipment Famous People
 Renewable sources Renewable energy is an alternative to fossil fuels and nuclear power, and was commonly called alternative energy in the 1970 s and 1980 s. Scientists have advanced a plan to power 100% of the world's energy with wind, hydroelectric, and solar power by the year 2030, recommending renewable energy subsidies and a price on carbon reflecting its cost for flood and related expenses. Wind This type of energy harnesses the power of the wind to propel the blades of wind turbines. These turbines cause the rotation of magnets, which creates electricity. Wind towers are usually built together on wind farms. Hydroelectric The Gordon Dam in Tasmania is a large conventional dammed-hydro facility, with an installed capacity of up to 430 MW. In hydro energy, the gravitational descent of a river is compressed from a long run to a single location with a dam or a flume. This creates a location where concentrated pressure and flow can be used to turn turbines or water wheels, which drive a mechanical mill or an electric generator. In some cases with hydroelectric dams, there are unexpected results. One study shows that a hydroelectric dam in the Amazon has 3. 6 times larger greenhouse effect per KHour than electricity production from oil, due to large scale emission of methane from decaying organic material though this is most significant as river valleys are initially flooded, and are of much less consequence for more boreal dams. This effect applies in particular to dams created by simply flooding a large area, without first clearing it of vegetation. There are however investigations into underwater turbines that do not require a dam. And pumped-storage hydroelectricity can use water reservoirs at different altitudes to store wind and solar power.
Renewable sources Renewable energy is an alternative to fossil fuels and nuclear power, and was commonly called alternative energy in the 1970 s and 1980 s. Scientists have advanced a plan to power 100% of the world's energy with wind, hydroelectric, and solar power by the year 2030, recommending renewable energy subsidies and a price on carbon reflecting its cost for flood and related expenses. Wind This type of energy harnesses the power of the wind to propel the blades of wind turbines. These turbines cause the rotation of magnets, which creates electricity. Wind towers are usually built together on wind farms. Hydroelectric The Gordon Dam in Tasmania is a large conventional dammed-hydro facility, with an installed capacity of up to 430 MW. In hydro energy, the gravitational descent of a river is compressed from a long run to a single location with a dam or a flume. This creates a location where concentrated pressure and flow can be used to turn turbines or water wheels, which drive a mechanical mill or an electric generator. In some cases with hydroelectric dams, there are unexpected results. One study shows that a hydroelectric dam in the Amazon has 3. 6 times larger greenhouse effect per KHour than electricity production from oil, due to large scale emission of methane from decaying organic material though this is most significant as river valleys are initially flooded, and are of much less consequence for more boreal dams. This effect applies in particular to dams created by simply flooding a large area, without first clearing it of vegetation. There are however investigations into underwater turbines that do not require a dam. And pumped-storage hydroelectricity can use water reservoirs at different altitudes to store wind and solar power.
 Solar power involves using solar cells to convert sunlight into electricity, using sunlight hitting solar thermal panels to convert sunlight to heat water or air, using sunlight hitting a parabolic mirror to heat water (producing steam), or using sunlight entering windows for passive solar heating of a building. It would be advantageous to place solar panels in the regions of highest solar radiation. In the Phoenix, Arizona area, for example, the average annual solar radiation is 5. 7 k. W·h/(m²·day), or 2. 1 MW·h/(m²·yr). Electricity demand in the continental U. S. is 3. 7× 1012 k. W·h per year. Thus, at 20% efficiency, an area of approximately 3500 square miles (3% of Arizona's land area) would need to be covered with solar panels to replace all current electricity production in the US with solar power. The average solar radiation in the United States is 4. 8 k. W·h/(m²·day), but reaches 8– 9 k. Wh/m²/day in parts of the Southwest. China is increasing worldwide silicon wafer capacity for photovoltaics to 2, 000 metric tons by July 2008, and over 6, 000 metric tons by the end of 2010. Significant international investment capital is flowing into China to support this opportunity. China is building large subsidized off-the-grid solarpowered cities in Huangbaiyu and Dongtan Eco City. Much of the design was done by Americans such as William Mc. Donough.
Solar power involves using solar cells to convert sunlight into electricity, using sunlight hitting solar thermal panels to convert sunlight to heat water or air, using sunlight hitting a parabolic mirror to heat water (producing steam), or using sunlight entering windows for passive solar heating of a building. It would be advantageous to place solar panels in the regions of highest solar radiation. In the Phoenix, Arizona area, for example, the average annual solar radiation is 5. 7 k. W·h/(m²·day), or 2. 1 MW·h/(m²·yr). Electricity demand in the continental U. S. is 3. 7× 1012 k. W·h per year. Thus, at 20% efficiency, an area of approximately 3500 square miles (3% of Arizona's land area) would need to be covered with solar panels to replace all current electricity production in the US with solar power. The average solar radiation in the United States is 4. 8 k. W·h/(m²·day), but reaches 8– 9 k. Wh/m²/day in parts of the Southwest. China is increasing worldwide silicon wafer capacity for photovoltaics to 2, 000 metric tons by July 2008, and over 6, 000 metric tons by the end of 2010. Significant international investment capital is flowing into China to support this opportunity. China is building large subsidized off-the-grid solarpowered cities in Huangbaiyu and Dongtan Eco City. Much of the design was done by Americans such as William Mc. Donough.
 Biomass, agricultural Sugar cane residue can be used as a biofuel Biomass production involves using garbage or other renewable resources such as corn or other vegetation to generate electricity. When garbage decomposes, the methane produced is captured in pipes and later burned to produce electricity. Vegetation and wood can be burned directly to generate energy, like fossil fuels, or processed to form alcohols. Vegetable oil is generated from sunlight, H 2 O, and CO 2 by plants. It is safer to use and store than gasoline or diesel as it has a higher flash point. Straight vegetable oil works in diesel engines if it is heated first. Vegetable oil can also be transesterified to make biodiesel, which burns like normal diesel. Geothermal energy harnesses the heat energy present underneath the Earth. Two wells are drilled. One well injects water into the ground to provide water. The hot rocks heat the water to produce steam. The steam that shoots back up the other hole(s) is purified and is used to drive turbines, which power electric generators. When the water temperature is below the boiling point of water a binary system is used. A low boiling point liquid is used to drive a turbine and generator in a closed system similar to a refrigeration unit running in reverse. There also natural sources of geothermal ennergy some can come from volcanoes, geysers, hot springs, and steam vents. Tidal power can be extracted from Moon-gravity-powered tides by locating a water turbine in a tidal current, or by building impoundment pond dams that admit-or-release water through a turbine. The turbine can turn an electrical generator, or a gas compressor, that can then store energy until needed. Coastal tides are a source of clean, free, renewable, and sustainable energy.
Biomass, agricultural Sugar cane residue can be used as a biofuel Biomass production involves using garbage or other renewable resources such as corn or other vegetation to generate electricity. When garbage decomposes, the methane produced is captured in pipes and later burned to produce electricity. Vegetation and wood can be burned directly to generate energy, like fossil fuels, or processed to form alcohols. Vegetable oil is generated from sunlight, H 2 O, and CO 2 by plants. It is safer to use and store than gasoline or diesel as it has a higher flash point. Straight vegetable oil works in diesel engines if it is heated first. Vegetable oil can also be transesterified to make biodiesel, which burns like normal diesel. Geothermal energy harnesses the heat energy present underneath the Earth. Two wells are drilled. One well injects water into the ground to provide water. The hot rocks heat the water to produce steam. The steam that shoots back up the other hole(s) is purified and is used to drive turbines, which power electric generators. When the water temperature is below the boiling point of water a binary system is used. A low boiling point liquid is used to drive a turbine and generator in a closed system similar to a refrigeration unit running in reverse. There also natural sources of geothermal ennergy some can come from volcanoes, geysers, hot springs, and steam vents. Tidal power can be extracted from Moon-gravity-powered tides by locating a water turbine in a tidal current, or by building impoundment pond dams that admit-or-release water through a turbine. The turbine can turn an electrical generator, or a gas compressor, that can then store energy until needed. Coastal tides are a source of clean, free, renewable, and sustainable energy.
 Fossil fuels The Moss Landing Power Plant burns natural gas to produce electricity in California. Gas flare from an oil refinery. Fossil fuels sources burn coal or hydrocarbon fuels, which are the remains of the decomposition of plants and animals. There are three main types of fossil fuels: coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Another fossil fuel, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), is principally derived from the production of natural gas. Heat from burning fossil fuel is used either directly for space heating and process heating, or converted to mechanical energy for vehicles, industrial processes, or electrical power generation. Greenhouse gas emissions result from fossil fuel-based electricity generation. Currently governments subsidize fossil fuels by an estimated $500 billion a year. Nuclear Diablo Canyon Power Plant Nuclear power station. Fission Nuclear power stations use nuclear fission to generate energy by the reaction of uranium-235 inside a nuclear reactor. The reactor uses uranium rods, the atoms of which are split in the process of fission, releasing a large amount of energy. The process continues as a chain reaction with other nuclei. The energy heats water to create steam, which spins a turbine generator, producing electricity.
Fossil fuels The Moss Landing Power Plant burns natural gas to produce electricity in California. Gas flare from an oil refinery. Fossil fuels sources burn coal or hydrocarbon fuels, which are the remains of the decomposition of plants and animals. There are three main types of fossil fuels: coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Another fossil fuel, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), is principally derived from the production of natural gas. Heat from burning fossil fuel is used either directly for space heating and process heating, or converted to mechanical energy for vehicles, industrial processes, or electrical power generation. Greenhouse gas emissions result from fossil fuel-based electricity generation. Currently governments subsidize fossil fuels by an estimated $500 billion a year. Nuclear Diablo Canyon Power Plant Nuclear power station. Fission Nuclear power stations use nuclear fission to generate energy by the reaction of uranium-235 inside a nuclear reactor. The reactor uses uranium rods, the atoms of which are split in the process of fission, releasing a large amount of energy. The process continues as a chain reaction with other nuclei. The energy heats water to create steam, which spins a turbine generator, producing electricity.
 Gas in Crisis? 1. To which countries does your country export its gas? Read this newspaper article and discuss the questions. The world is changing fast. There is an energy crisis on the horizon for Europe. If we take natural gas as an example it would seem at first glance that countries such as Norway, Britain and the Netherlands have sufficient gas reserves to supply Europe for some time to come. However, this is misleading; most of these reserves will be used up over the next ten to twenty years. Even if more deposits are found in the North Sea or the Atlantic Ocean the problem will still not be solved. The continent must turn to Russia where there are huge quantities of gas underground. This country is in the happy position of being the gas giant of the world. Other nations are also approaching Moscow to cover their energy requirements. The economies of countries such as China and India are expanding dramatically and they are going to need massive amounts of energy, which includes gas. Will there be enough of this commodity to satisfy the needs of Asia and Europe? This is by no means certain, and the consequence could be a shortage of gas imports, which could lead to power cuts in some European countries in the future. There is one other source of gas - LNG, liquefied natural gas. This is transported by ship from such places as the Arabian Peninsula. Nevertheless, it is questionable if these supplies can ever be a realistic alternative to gas which is imported by pipeline; the simple fact is that the volumes shipped would never meet demand. People are therefore right to be worried. Political leaders and companies must tackle this issue; we need a secure and reliable supply of gas for the long term. This inevitably means that wholesale prices will soar, but this is still better than the nightmare scenario of freezing in our homes or having no power for our industry. 2. Discuss with your group. Is there really a gas crisis? What do you think? What about oil and coal? Do you think there will be enough reserves for the future? How do you think China will develop its economy and how will it power its industry? How can your country ensure gas supplies? 3. Watch the video about alternative source of gas.
Gas in Crisis? 1. To which countries does your country export its gas? Read this newspaper article and discuss the questions. The world is changing fast. There is an energy crisis on the horizon for Europe. If we take natural gas as an example it would seem at first glance that countries such as Norway, Britain and the Netherlands have sufficient gas reserves to supply Europe for some time to come. However, this is misleading; most of these reserves will be used up over the next ten to twenty years. Even if more deposits are found in the North Sea or the Atlantic Ocean the problem will still not be solved. The continent must turn to Russia where there are huge quantities of gas underground. This country is in the happy position of being the gas giant of the world. Other nations are also approaching Moscow to cover their energy requirements. The economies of countries such as China and India are expanding dramatically and they are going to need massive amounts of energy, which includes gas. Will there be enough of this commodity to satisfy the needs of Asia and Europe? This is by no means certain, and the consequence could be a shortage of gas imports, which could lead to power cuts in some European countries in the future. There is one other source of gas - LNG, liquefied natural gas. This is transported by ship from such places as the Arabian Peninsula. Nevertheless, it is questionable if these supplies can ever be a realistic alternative to gas which is imported by pipeline; the simple fact is that the volumes shipped would never meet demand. People are therefore right to be worried. Political leaders and companies must tackle this issue; we need a secure and reliable supply of gas for the long term. This inevitably means that wholesale prices will soar, but this is still better than the nightmare scenario of freezing in our homes or having no power for our industry. 2. Discuss with your group. Is there really a gas crisis? What do you think? What about oil and coal? Do you think there will be enough reserves for the future? How do you think China will develop its economy and how will it power its industry? How can your country ensure gas supplies? 3. Watch the video about alternative source of gas.
 What is Biogas is generated from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. Biogas is generated in landfill sites since organic matter such as domestic food and garden waste is buried and compressed in a dark oxygen free environment. For decades after a landfill site is filled biogas continues to be generated and released into the atmosphere. Biogas is made up primarily of Methane and Carbon Dioxide, but can also contain small quantities of Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Hydrogen Sulphide, and even Oxygen. With processing biogas can be cleaned up to make a substitute for natural gas which can therefore be pumped to homes and businesses for cooking and heating etc. There are big industrial biogas power plants as well as the small biogas plants for individual households. Collecting and Using Biogas has to be collected from landfill sites by drilling gas wells. Historically it was just flamed (i. e. burnt off) but now more and more landfills are collecting the gas generated for power generation. Some sites have even built dedicated Anaerobic Digesters to generate larger quantites of methane-rich biogas more quickly and to reduce the volume of the waste to be buried. Biogas can be used to power vehicles. There is a biogas powered trains in Sweden running between Linkoeping and Vaestervik which is powered with gas generated from cow waste and sewage. From well to the vehicle diesel generates 20 times more carbon dioxide than biogas. Biogas also has no pariculate emissions and generates one-fifth as much nitrous oxide emissions as diesel. The Modern Importance of Biogas The use of biogas is increasing rapidly today for a number of reasons: Fuel costs have been rising steadily for a number of years and the taxation burden increases as well, leading to a double load for the user to bear. Attempts are now being made to improve the use of renewable energy sources. The gas produced, mainly methane, is one of the major causes of the greenhouse effect. The production is possible in small scale sites, obviating the need to supply energy to outlying areas. Even a very basic construction using mostly used materials will produce gas if a few simple design rules are followed. The gas produced and the slurry being fermented are corrosive. This means that some of the fittings must be made of corrosion-proof material. Plastic can be used for many things, but where pressure and sunlight are involved, then stainless steel may be needed. Again, as the gas is corrosive due to the presence of hydrogen sulphide and other impurities, it may have to be collected in a stainless steel tank in some cases. The cost for such materials is high and may be prohibitive, but larger industrial systems will be forced to go in this direction to get a useful working life. Stainless steel is not cheap, but it has properties that make its use essential sometimes. Answer the questions: • What is biogas? • Why is biogas corrosive? • Why has the use of biogas increased recently? • What is the biogas made of? • How can you use biogas?
What is Biogas is generated from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. Biogas is generated in landfill sites since organic matter such as domestic food and garden waste is buried and compressed in a dark oxygen free environment. For decades after a landfill site is filled biogas continues to be generated and released into the atmosphere. Biogas is made up primarily of Methane and Carbon Dioxide, but can also contain small quantities of Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Hydrogen Sulphide, and even Oxygen. With processing biogas can be cleaned up to make a substitute for natural gas which can therefore be pumped to homes and businesses for cooking and heating etc. There are big industrial biogas power plants as well as the small biogas plants for individual households. Collecting and Using Biogas has to be collected from landfill sites by drilling gas wells. Historically it was just flamed (i. e. burnt off) but now more and more landfills are collecting the gas generated for power generation. Some sites have even built dedicated Anaerobic Digesters to generate larger quantites of methane-rich biogas more quickly and to reduce the volume of the waste to be buried. Biogas can be used to power vehicles. There is a biogas powered trains in Sweden running between Linkoeping and Vaestervik which is powered with gas generated from cow waste and sewage. From well to the vehicle diesel generates 20 times more carbon dioxide than biogas. Biogas also has no pariculate emissions and generates one-fifth as much nitrous oxide emissions as diesel. The Modern Importance of Biogas The use of biogas is increasing rapidly today for a number of reasons: Fuel costs have been rising steadily for a number of years and the taxation burden increases as well, leading to a double load for the user to bear. Attempts are now being made to improve the use of renewable energy sources. The gas produced, mainly methane, is one of the major causes of the greenhouse effect. The production is possible in small scale sites, obviating the need to supply energy to outlying areas. Even a very basic construction using mostly used materials will produce gas if a few simple design rules are followed. The gas produced and the slurry being fermented are corrosive. This means that some of the fittings must be made of corrosion-proof material. Plastic can be used for many things, but where pressure and sunlight are involved, then stainless steel may be needed. Again, as the gas is corrosive due to the presence of hydrogen sulphide and other impurities, it may have to be collected in a stainless steel tank in some cases. The cost for such materials is high and may be prohibitive, but larger industrial systems will be forced to go in this direction to get a useful working life. Stainless steel is not cheap, but it has properties that make its use essential sometimes. Answer the questions: • What is biogas? • Why is biogas corrosive? • Why has the use of biogas increased recently? • What is the biogas made of? • How can you use biogas?
 EXTRA ENERGY FROM BIOGAS 1. Read the text and answer the questions. Sakunthaladev Kathiravetpillai is 31 years old and lives with her husband four children in Vattavaan, a rural district of Sri Lanka. The family incomes from the sale of milk from their cows. Each day Sakunthaldev and her daughters used to spend several hours collecting wood for cooking and heating water. Practical Action were able to help the family by showing them how the waste from their cows could provide them with all the energy they need. The construction of a biogas plant at their home has transformed their lives. The plant produces methane gas from animal dung by adding water to the waste and letting it ferment. This gas produced can then be used to provide energy for cooking and lighting. Sakunthaladev, freed from the daily drudgery of firewood collection, now has more time to spend on activities that generate income for the family. Also the organic waste from the plant improves the productivity of their vegetable garden. Sakunthaladev’s husband has become skilled at installing and maintaining the biogas plant, making him crucial for the development of other plants in the area. In order to help make biogas a more widely used fuel Practical Action is also now working on setting standards for biogas systems in Sri Lanka and Nepal. • What is the main income of this family? • How does the biogas ease their life? • What is biogas used for? • What organization helped to install biogas? • Where does this family live? 2. Translate the sentences: 1. Биогазовая установка является источником энергии. 2. Биогаз получают из отходов. 3. Биогаз состоит из метана и пропана. 4. Закрой клапан, пахнет газом. 5. У тебя есть биогаз? 3. Watch the video. 4. Discussion. Let’s make a conference. Every one suppose to make his own biogas project. Give name to your company and prove to local authorities the necessity of biogas station and get the needed license.
EXTRA ENERGY FROM BIOGAS 1. Read the text and answer the questions. Sakunthaladev Kathiravetpillai is 31 years old and lives with her husband four children in Vattavaan, a rural district of Sri Lanka. The family incomes from the sale of milk from their cows. Each day Sakunthaldev and her daughters used to spend several hours collecting wood for cooking and heating water. Practical Action were able to help the family by showing them how the waste from their cows could provide them with all the energy they need. The construction of a biogas plant at their home has transformed their lives. The plant produces methane gas from animal dung by adding water to the waste and letting it ferment. This gas produced can then be used to provide energy for cooking and lighting. Sakunthaladev, freed from the daily drudgery of firewood collection, now has more time to spend on activities that generate income for the family. Also the organic waste from the plant improves the productivity of their vegetable garden. Sakunthaladev’s husband has become skilled at installing and maintaining the biogas plant, making him crucial for the development of other plants in the area. In order to help make biogas a more widely used fuel Practical Action is also now working on setting standards for biogas systems in Sri Lanka and Nepal. • What is the main income of this family? • How does the biogas ease their life? • What is biogas used for? • What organization helped to install biogas? • Where does this family live? 2. Translate the sentences: 1. Биогазовая установка является источником энергии. 2. Биогаз получают из отходов. 3. Биогаз состоит из метана и пропана. 4. Закрой клапан, пахнет газом. 5. У тебя есть биогаз? 3. Watch the video. 4. Discussion. Let’s make a conference. Every one suppose to make his own biogas project. Give name to your company and prove to local authorities the necessity of biogas station and get the needed license.
 Read the text Answer the question 1 What is wood waste? 2 What country produces more waste than any other country? 3 How much trash is thrown every day by Americans? 4 Can you use the wood waste to produce electricity? 5 What is biomass? Wood Waste The most common form of biomass is wood. For thousands of years people have burned wood for heating and cooking. Wood was the main source of energy in the United States and the rest of the world until the mid-1800 s. Wood continues to be a major source of energy in much of the developing world. Translate into English 1 Биомасса – это горючий материал. 2 Пластик и другие синтетические материалы не являются биомассой. 3 Органические отходы содержат энергию. 4 Дрова - это биомасса. 5 Люди используют дрова для обогрева и приготовления пищи. In the United States, wood and wood waste (bark, sawdust, wood chips, and wood scrap) provide about 2% of the energy we use today. About 84% of the wood and wood waste fuel used in the United States is consumed by industry, electric power producers, and commercial businesses. The rest, mainly wood, is used in homes for heating and cooking. Many manufacturing plants in the wood and paper products industry use wood waste to produce their own steam and electricity. This saves these companies money because they don't have to dispose of their waste products and they don't have to buy as much electricity. Energy from Garbage, often called municipal solid waste (MSW), is the source of about 10% of the total biomass energy consumed in the United States. MSW contains biomass (or biogenic) materials like paper, cardboard, food scraps, grass clippings, leaves, wood, and leather products, and other nonbiomass combustible materials, mainly plastics and other synthetic materials made from petroleum. Americans produce more and more waste each year. In 1960, the average American threw away 2. 7 pounds of trash a day. Today, each American throws away about 4. 5 pounds of trash every day. What are we going to do with all our trash? One solution is to burn it. (Burning is sometimes called combustion. ) Organic waste is waste that is made from plant or animal products. All organic waste contains energy. People have burned one type of organic material — wood — for hundreds of thousands of years. Ancient peoples burned wood to keep themselves warm and to cook their food.
Read the text Answer the question 1 What is wood waste? 2 What country produces more waste than any other country? 3 How much trash is thrown every day by Americans? 4 Can you use the wood waste to produce electricity? 5 What is biomass? Wood Waste The most common form of biomass is wood. For thousands of years people have burned wood for heating and cooking. Wood was the main source of energy in the United States and the rest of the world until the mid-1800 s. Wood continues to be a major source of energy in much of the developing world. Translate into English 1 Биомасса – это горючий материал. 2 Пластик и другие синтетические материалы не являются биомассой. 3 Органические отходы содержат энергию. 4 Дрова - это биомасса. 5 Люди используют дрова для обогрева и приготовления пищи. In the United States, wood and wood waste (bark, sawdust, wood chips, and wood scrap) provide about 2% of the energy we use today. About 84% of the wood and wood waste fuel used in the United States is consumed by industry, electric power producers, and commercial businesses. The rest, mainly wood, is used in homes for heating and cooking. Many manufacturing plants in the wood and paper products industry use wood waste to produce their own steam and electricity. This saves these companies money because they don't have to dispose of their waste products and they don't have to buy as much electricity. Energy from Garbage, often called municipal solid waste (MSW), is the source of about 10% of the total biomass energy consumed in the United States. MSW contains biomass (or biogenic) materials like paper, cardboard, food scraps, grass clippings, leaves, wood, and leather products, and other nonbiomass combustible materials, mainly plastics and other synthetic materials made from petroleum. Americans produce more and more waste each year. In 1960, the average American threw away 2. 7 pounds of trash a day. Today, each American throws away about 4. 5 pounds of trash every day. What are we going to do with all our trash? One solution is to burn it. (Burning is sometimes called combustion. ) Organic waste is waste that is made from plant or animal products. All organic waste contains energy. People have burned one type of organic material — wood — for hundreds of thousands of years. Ancient peoples burned wood to keep themselves warm and to cook their food.
 Biogas Generator Basic Principles What Is Biogas? Biogas is actually a mixture of gases, usually carbon dioxide and methane. It is produced by a few kinds of microorganisms, usually when air or oxygen is absent. (The absence of oxygen is called “anaerobic conditions. ”) Animals that eat a lot of plant material, particularly grazing animals such as cattle, produce large amounts of biogas. The biogas is produced not by the cow or elephant, but by billions of microorganisms living in its digestive system. Biogas also develops in bogs and at the bottom of lakes, where decaying organic matter builds up under wet and anaerobic conditions. Plant-eating animals such as bison release large amounts of biogas to the atmosphere. Biogas is a Form of Renewable Energy Flammable biogas can be collected using a simple tank, as shown here. Animal manure is stored in a closed tank where the gas accumulates. It makes an excellent fuel for cook stoves and furnaces, and can be used in place of regular natural gas, which is a fossil fuel. A microscope photo of the methane-producing bacteria. Photo courtesy of University of Florida, Agricultural and Biological Engineering Department Biogas is a form of renewable energy, because Besides being able to live without oxygen, it is produced with the help of growing plants. methaneproducing microorganisms have It makes an excellent fuel for cook stoves and another special feature: They are among the very few creatures that can digest cellulose, the furnaces, and can be used in place of regular main ingredient of plant fi bres. Another special natural gas, which is a fossil fuel. feature of these organisms is that they are very Biogas is considered to be a source of renewable energy. This is because the sensitive to conditions in their environment, production of biogas depends on the supply of such as temperature, acidity, the amount of grass, which usually grows back each year. water, etc. Biogas is a Form of Renewable By comparison, the natural gas used in most Energy Flammable biogas can be collected of our homes is not considered a form of using a simple tank, as shown here. Animal manure is stored in a closed tank where the gas renewable energy. Natural gas formed from the fos accumulates.
Biogas Generator Basic Principles What Is Biogas? Biogas is actually a mixture of gases, usually carbon dioxide and methane. It is produced by a few kinds of microorganisms, usually when air or oxygen is absent. (The absence of oxygen is called “anaerobic conditions. ”) Animals that eat a lot of plant material, particularly grazing animals such as cattle, produce large amounts of biogas. The biogas is produced not by the cow or elephant, but by billions of microorganisms living in its digestive system. Biogas also develops in bogs and at the bottom of lakes, where decaying organic matter builds up under wet and anaerobic conditions. Plant-eating animals such as bison release large amounts of biogas to the atmosphere. Biogas is a Form of Renewable Energy Flammable biogas can be collected using a simple tank, as shown here. Animal manure is stored in a closed tank where the gas accumulates. It makes an excellent fuel for cook stoves and furnaces, and can be used in place of regular natural gas, which is a fossil fuel. A microscope photo of the methane-producing bacteria. Photo courtesy of University of Florida, Agricultural and Biological Engineering Department Biogas is a form of renewable energy, because Besides being able to live without oxygen, it is produced with the help of growing plants. methaneproducing microorganisms have It makes an excellent fuel for cook stoves and another special feature: They are among the very few creatures that can digest cellulose, the furnaces, and can be used in place of regular main ingredient of plant fi bres. Another special natural gas, which is a fossil fuel. feature of these organisms is that they are very Biogas is considered to be a source of renewable energy. This is because the sensitive to conditions in their environment, production of biogas depends on the supply of such as temperature, acidity, the amount of grass, which usually grows back each year. water, etc. Biogas is a Form of Renewable By comparison, the natural gas used in most Energy Flammable biogas can be collected of our homes is not considered a form of using a simple tank, as shown here. Animal manure is stored in a closed tank where the gas renewable energy. Natural gas formed from the fos accumulates.
 Biogas Generator silized remains of plants and animals-a process that took millions of years. These resources do not “grow back” in a time scale that is meaningful for humans. Biogas is Not New People have been using biogas for over 200 years. In the days before electricity, biogas was drawn from the underground sewer pipes in London and burned in street lamps, which were known as “gaslights. ” In many parts of the world, biogas is used to heat and light homes, to cook, and even to fuel buses. It is collected from large-scale sources such as landfi lls and pig barns, and through small domestic or community systems in many villages. For more information about biogas, read the backgrounder entitled Biomass Energy. Build It! The apparatus you are going to build uses a discarded 18 litre water container as the “digester. ” A mixture of water and animal manure will generate the methane, which you will collect in a plastic balloon. The 18 litre water container performs the same task as the stomach of a livestock animal by providing the warm, wet conditions favored by the bacteria that make the methane. Safety Precautions. The main hazards in this activity are from sharp tools such as tubing cutters and scissors. Exercise caution while using any tool. There is no risk of explosion due to the leakage of methane because the gas develops so slowly that it dissipates long before it can reach fl ammable concentrations in room air. Exercise th normal precautions in the use of Bunsen burners: keep hair and clothing away from the burner while it is lit. Tools • Tubing cutter • Scissors • Adjustable wrench • Rubber gloves • Electric drill with ¼” bit, or cork borer • Hot glue gun, with glue sticks • Electrical or duct tape • Sandpaper (metal fi le will also work) Materials • Used 18 L clear plastic water bottle • Large Mylar helium balloon Plastic water bottle cap (with the “no-spill” insert-see photo) • Copper tubing (40 cm long, 6. 5 mm (1/4”) inside diameter) • T-connector for plastic tubing (barbed, 6 mm or ¼” long) • 1 cork (tapered, 23 mm long) • Clear vinyl tubing (1. 5 m long, 4 mm or ¼-inch inside diameter) • 2 barb fi ttings (¼” x ¼”) • Ball valve (1/4”) • 6 -8 L manure pellets (goat, sheep, llama, rabbit, or other ruminant) • Rubber gloves • Large plastic funnel (can be made from a 4 L plastic milk jug with bottom removed) • Wooden dowelling or stick (30 to 50 cm long, 2 -3 cm thick) The materials and tools you’ll need to build a biogas generator.
Biogas Generator silized remains of plants and animals-a process that took millions of years. These resources do not “grow back” in a time scale that is meaningful for humans. Biogas is Not New People have been using biogas for over 200 years. In the days before electricity, biogas was drawn from the underground sewer pipes in London and burned in street lamps, which were known as “gaslights. ” In many parts of the world, biogas is used to heat and light homes, to cook, and even to fuel buses. It is collected from large-scale sources such as landfi lls and pig barns, and through small domestic or community systems in many villages. For more information about biogas, read the backgrounder entitled Biomass Energy. Build It! The apparatus you are going to build uses a discarded 18 litre water container as the “digester. ” A mixture of water and animal manure will generate the methane, which you will collect in a plastic balloon. The 18 litre water container performs the same task as the stomach of a livestock animal by providing the warm, wet conditions favored by the bacteria that make the methane. Safety Precautions. The main hazards in this activity are from sharp tools such as tubing cutters and scissors. Exercise caution while using any tool. There is no risk of explosion due to the leakage of methane because the gas develops so slowly that it dissipates long before it can reach fl ammable concentrations in room air. Exercise th normal precautions in the use of Bunsen burners: keep hair and clothing away from the burner while it is lit. Tools • Tubing cutter • Scissors • Adjustable wrench • Rubber gloves • Electric drill with ¼” bit, or cork borer • Hot glue gun, with glue sticks • Electrical or duct tape • Sandpaper (metal fi le will also work) Materials • Used 18 L clear plastic water bottle • Large Mylar helium balloon Plastic water bottle cap (with the “no-spill” insert-see photo) • Copper tubing (40 cm long, 6. 5 mm (1/4”) inside diameter) • T-connector for plastic tubing (barbed, 6 mm or ¼” long) • 1 cork (tapered, 23 mm long) • Clear vinyl tubing (1. 5 m long, 4 mm or ¼-inch inside diameter) • 2 barb fi ttings (¼” x ¼”) • Ball valve (1/4”) • 6 -8 L manure pellets (goat, sheep, llama, rabbit, or other ruminant) • Rubber gloves • Large plastic funnel (can be made from a 4 L plastic milk jug with bottom removed) • Wooden dowelling or stick (30 to 50 cm long, 2 -3 cm thick) The materials and tools you’ll need to build a biogas generator.
 Biogas Generator Sources Water bottle: Many hardware and grocery stores now sell purifi ed water that they bottle on site. They often collect containers that can no longer be refi lled because of dirt or damage to the bottle. These unrefi llable bottles are frequently available for free. Ask to speak to the clerk in charge of refi lling bottles. Ask for a used cap as well. 3. Test the tube to be sure air can enter and leave the balloon freely, by blowing a little in through the tube. The balloon should infl ate with little or no resistance, and the air should be able to escape easily through the tube. 4. Securely tape the neck of the balloon to the tube as shown in the illustration. Mylar balloons: Check with any local fl orist or novelty store. Tubing, valves, T-connectors, barb fi ttings: Check at your local hardware or plumbing supply store. Manure: If you do not know someone who has domesticated rabbits, sheep, llamas or other similar pellet-producing animals, you can often purchase sheep or steer manure by the bag at your local garden center. A. Prepare the biogas collection system 1. Cut a 20 cm piece of copper tubing. Round off the sharp edges of the freshly cut tubing using sandpaper or a metal fi le. 2. The Mylar balloon has a sleeve-like valve that prevents helium from escaping once it is fi lled. This sleeve will help form a leak-proof seal around the rigid tubing. Push the tubing into the neck of the balloon, past the end of the sleeve, leaving about 2 cm protruding from the neck of the balloon, as shown below. Taping the neck. 5. Using a drill or cork borer, make a small (4 mm) hole in the center of the stopper. Add a few drops of hot glue around and inside the hole and insert the stem of the ¼-inch Tadapter into the cork. Gluing cork. Inserting copper tubing.
Biogas Generator Sources Water bottle: Many hardware and grocery stores now sell purifi ed water that they bottle on site. They often collect containers that can no longer be refi lled because of dirt or damage to the bottle. These unrefi llable bottles are frequently available for free. Ask to speak to the clerk in charge of refi lling bottles. Ask for a used cap as well. 3. Test the tube to be sure air can enter and leave the balloon freely, by blowing a little in through the tube. The balloon should infl ate with little or no resistance, and the air should be able to escape easily through the tube. 4. Securely tape the neck of the balloon to the tube as shown in the illustration. Mylar balloons: Check with any local fl orist or novelty store. Tubing, valves, T-connectors, barb fi ttings: Check at your local hardware or plumbing supply store. Manure: If you do not know someone who has domesticated rabbits, sheep, llamas or other similar pellet-producing animals, you can often purchase sheep or steer manure by the bag at your local garden center. A. Prepare the biogas collection system 1. Cut a 20 cm piece of copper tubing. Round off the sharp edges of the freshly cut tubing using sandpaper or a metal fi le. 2. The Mylar balloon has a sleeve-like valve that prevents helium from escaping once it is fi lled. This sleeve will help form a leak-proof seal around the rigid tubing. Push the tubing into the neck of the balloon, past the end of the sleeve, leaving about 2 cm protruding from the neck of the balloon, as shown below. Taping the neck. 5. Using a drill or cork borer, make a small (4 mm) hole in the center of the stopper. Add a few drops of hot glue around and inside the hole and insert the stem of the ¼-inch Tadapter into the cork. Gluing cork. Inserting copper tubing.
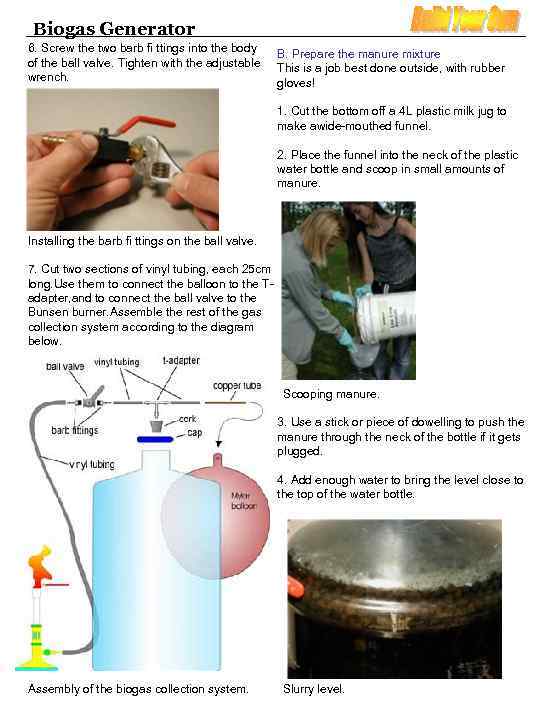 Biogas Generator 6. Screw the two barb fi ttings into the body of the ball valve. Tighten with the adjustable wrench. B. Prepare the manure mixture This is a job best done outside, with rubber gloves! 1. Cut the bottom off a 4 L plastic milk jug to make awide-mouthed funnel. 2. Place the funnel into the neck of the plastic water bottle and scoop in small amounts of manure. Installing the barb fi ttings on the ball valve. 7. Cut two sections of vinyl tubing, each 25 cm long. Use them to connect the balloon to the Tadapter, and to connect the ball valve to the Bunsen burner. Assemble the rest of the gas collection system according to the diagram below. Scooping manure. 3. Use a stick or piece of dowelling to push the manure through the neck of the bottle if it gets plugged. 4. Add enough water to bring the level close to the top of the water bottle. Assembly of the biogas collection system. Slurry level.
Biogas Generator 6. Screw the two barb fi ttings into the body of the ball valve. Tighten with the adjustable wrench. B. Prepare the manure mixture This is a job best done outside, with rubber gloves! 1. Cut the bottom off a 4 L plastic milk jug to make awide-mouthed funnel. 2. Place the funnel into the neck of the plastic water bottle and scoop in small amounts of manure. Installing the barb fi ttings on the ball valve. 7. Cut two sections of vinyl tubing, each 25 cm long. Use them to connect the balloon to the Tadapter, and to connect the ball valve to the Bunsen burner. Assemble the rest of the gas collection system according to the diagram below. Scooping manure. 3. Use a stick or piece of dowelling to push the manure through the neck of the bottle if it gets plugged. 4. Add enough water to bring the level close to the top of the water bottle. Assembly of the biogas collection system. Slurry level.
 Biogas Generator 5. Use the stick to stir up the manure and water mixture, releasing any bubbles of air that might be trapped. 6. Clean up carefully. Use soap and wash hands thoroughly. C. Final Set-up 1. Snap the cap onto the top of the manurefilled 18 litre water bottle. 2. Be sure the ball valve is closed, but that gas moving from the water bottle can pass freely through the T-adapter to the balloon. Use caution when testing the biogas. 1. First, open the clamp or valve so that biogas can flow back from the balloon to the Bunsen burner. 2. Have a friend squeeze the Mylar balloon gently while you attempt to light the Bunsen burner with a match or spark igniter. 3. Set the biogas 3. If your Bunsen burner ignites, your biogas generator in a generator is a success! warm location, such as over a Completed biogas generator. heat register or radiator or in a sunlit window. If the biogas Questions generator is placed in a window, be sure to 1. Why is biogas considered a source of wrap the outside of the container in black renewable energy? plastic or construction paper, to discourage 2. In what appliances or to what uses algae from growing inside the bottle. Could biogas be applied? 3. What are some of the practical Limitations to using biogas as an energy Test It! source on a large scale? For the fi rst few weeks, your biogas generator 4. Where in Canada would biogas be a will produce mainly carbon dioxide. When the Viable alternative to fossil fuels? aerobic bacteria use up all the oxygen inside the 5. Why do you not want photosynthetic bottle, the anaerobic bacteria, which make Algae (see Part C, # 3) growing in your methane, can take over. It can take up to a month for the generator to start making biogas “digester”? with enough methane to be fl ammable. When gas begins to accumulate in the balloon, test it by attempting to light the Bunsen burner: Contact us at: education@pembina. org
Biogas Generator 5. Use the stick to stir up the manure and water mixture, releasing any bubbles of air that might be trapped. 6. Clean up carefully. Use soap and wash hands thoroughly. C. Final Set-up 1. Snap the cap onto the top of the manurefilled 18 litre water bottle. 2. Be sure the ball valve is closed, but that gas moving from the water bottle can pass freely through the T-adapter to the balloon. Use caution when testing the biogas. 1. First, open the clamp or valve so that biogas can flow back from the balloon to the Bunsen burner. 2. Have a friend squeeze the Mylar balloon gently while you attempt to light the Bunsen burner with a match or spark igniter. 3. Set the biogas 3. If your Bunsen burner ignites, your biogas generator in a generator is a success! warm location, such as over a Completed biogas generator. heat register or radiator or in a sunlit window. If the biogas Questions generator is placed in a window, be sure to 1. Why is biogas considered a source of wrap the outside of the container in black renewable energy? plastic or construction paper, to discourage 2. In what appliances or to what uses algae from growing inside the bottle. Could biogas be applied? 3. What are some of the practical Limitations to using biogas as an energy Test It! source on a large scale? For the fi rst few weeks, your biogas generator 4. Where in Canada would biogas be a will produce mainly carbon dioxide. When the Viable alternative to fossil fuels? aerobic bacteria use up all the oxygen inside the 5. Why do you not want photosynthetic bottle, the anaerobic bacteria, which make Algae (see Part C, # 3) growing in your methane, can take over. It can take up to a month for the generator to start making biogas “digester”? with enough methane to be fl ammable. When gas begins to accumulate in the balloon, test it by attempting to light the Bunsen burner: Contact us at: education@pembina. org
 End of Biogas Lesson • Пройти тестирование • Вернуться на начало
End of Biogas Lesson • Пройти тестирование • Вернуться на начало
 Heating With the Sun's Energy S olar thermal (heat) energy is often used for heating water used in homes and swimming pools and for heating the insides of buildings ("space heating"). Solar space heating systems can be classified as passive or active. Passive space heating is what happens to your car on a hot summer day. The sun's rays heat up the inside of your car. In buildings, the air is circulated past a solar heat surface and through the building by convection (meaning that less dense warm air tends to rise while denser cool air moves downward). No mechanical equipment is needed for passive solar heating systems Active require a collector to absorb and collect solar radiation . Fans or pumps are used to circulate the heated air or heat absorbing fluid. Active systems often include some type of energy storage system. Solar Collectors Are Either Nonconcentrating or Concentrating collectors - The collector area (the area that intercepts the Nonconcentrating solar radiation) is the same as the absorber area (the area absorbing the radiation). Flatplate collectors are the most common type of nonconcentrating collector and are used when temperatures below about 200°F are sufficient. They are often used for heating buildings. There are many flat-plate collector designs but generally all consist of: A flat-plate absorber that intercepts and absorbs the solar energy A transparent cover(s) that allows solar energy to pass through but reduces heat loss from the absorber A heat-transport fluid (air or water) flowing through tubes to remove heat from the absorber, and a heat insulating backing -the area intercepting the solar radiation is greater, sometimes Concentrating collectors hundreds of times greater, than the absorber area. 1 Read the text. 2 Answer the following questions. 1. What device do you have at your home that uses solar energy? 2. What is required to collect sun’s energy? 3. Is the energy of the sun renewable? 4. What devices use solar energy? 3 Translate into English. 1. Дом может быть обогреваем энергией солнца. 2. Солнечные лучи преобразуются в энергию. 3. Электричество, получаемое от солнца очень дешевое. 4. Охладителем в солнечных коллекторах служит вода. 5. Насос используется для циркуляции воздуха. 4 Watch the video.
Heating With the Sun's Energy S olar thermal (heat) energy is often used for heating water used in homes and swimming pools and for heating the insides of buildings ("space heating"). Solar space heating systems can be classified as passive or active. Passive space heating is what happens to your car on a hot summer day. The sun's rays heat up the inside of your car. In buildings, the air is circulated past a solar heat surface and through the building by convection (meaning that less dense warm air tends to rise while denser cool air moves downward). No mechanical equipment is needed for passive solar heating systems Active require a collector to absorb and collect solar radiation . Fans or pumps are used to circulate the heated air or heat absorbing fluid. Active systems often include some type of energy storage system. Solar Collectors Are Either Nonconcentrating or Concentrating collectors - The collector area (the area that intercepts the Nonconcentrating solar radiation) is the same as the absorber area (the area absorbing the radiation). Flatplate collectors are the most common type of nonconcentrating collector and are used when temperatures below about 200°F are sufficient. They are often used for heating buildings. There are many flat-plate collector designs but generally all consist of: A flat-plate absorber that intercepts and absorbs the solar energy A transparent cover(s) that allows solar energy to pass through but reduces heat loss from the absorber A heat-transport fluid (air or water) flowing through tubes to remove heat from the absorber, and a heat insulating backing -the area intercepting the solar radiation is greater, sometimes Concentrating collectors hundreds of times greater, than the absorber area. 1 Read the text. 2 Answer the following questions. 1. What device do you have at your home that uses solar energy? 2. What is required to collect sun’s energy? 3. Is the energy of the sun renewable? 4. What devices use solar energy? 3 Translate into English. 1. Дом может быть обогреваем энергией солнца. 2. Солнечные лучи преобразуются в энергию. 3. Электричество, получаемое от солнца очень дешевое. 4. Охладителем в солнечных коллекторах служит вода. 5. Насос используется для циркуляции воздуха. 4 Watch the video.
 • Photovoltaic Systems 1. Answer the questions: 1. What is the application of photovoltaic systems? 2. Can the solar panels reduce your electricity bill? 3. Are they harmful for environment? 4. Do they look gorgeous? 5. Would you install them on our own house? The area of photovoltaic systems involves the technology and the study of solar panels. It is with such ingenuity that we are able to continue moving forward with the use of such an abundance of alternative renewable energy. Photovoltaic panels make the process very easy for homeowners and business owners to be able to implement the concept into their own lives. • As a result, they are able to save a great deal of money that they would have to pay for electricity. They are also able to feel good that they are doing something very positive for their environment. Instead of having to worry about the amount of electricity they consume they can freely use it. That is a breath of fresh air since we live in a world of electronic gadgets. • With all of the information circulating out there about photovoltaic systems, they have become a very common part of new designs for buildings and homes. This is often due to governments offering incentives to the contractors to put them in place. It is a better idea than having to put them in later on which costs more time and money. From a business perspective, this is a great way to cut down overhead expenses. Even a landlord can reduce the monthly bill he gets for electricity on behalf of his tenants. • These photovoltaic panels also look gorgeous, so you don’t have to worry that they are going to bring down the value of the structure they are placed on. In fact, the opposite is very true. The value of the location is going to increase due to the fact that anyone buying it will be able to save money on the electricity that they consume. You can take a look at a video featuring them on a home at. . • The installation of photovoltaic panels should be done by a professional. However, there are many contractors out there that offer such services. You can contact them for a free estimate if you want to get them installed on an existing location. You can also speak to contractors about photovoltaic systems for any new structure you would like to have them take part in building. • There is no doubt that turning to alternative renewable resources such as the sun for electricity makes sense. Being able to capture it to fulfill our ongoing need for electricity can be accomplished with photovoltaic systems. This is definitely an investment that will save you money and protect our nonrenewable resources. 2. Discuss what is more advantageous use of wind power of solar power in your area?
• Photovoltaic Systems 1. Answer the questions: 1. What is the application of photovoltaic systems? 2. Can the solar panels reduce your electricity bill? 3. Are they harmful for environment? 4. Do they look gorgeous? 5. Would you install them on our own house? The area of photovoltaic systems involves the technology and the study of solar panels. It is with such ingenuity that we are able to continue moving forward with the use of such an abundance of alternative renewable energy. Photovoltaic panels make the process very easy for homeowners and business owners to be able to implement the concept into their own lives. • As a result, they are able to save a great deal of money that they would have to pay for electricity. They are also able to feel good that they are doing something very positive for their environment. Instead of having to worry about the amount of electricity they consume they can freely use it. That is a breath of fresh air since we live in a world of electronic gadgets. • With all of the information circulating out there about photovoltaic systems, they have become a very common part of new designs for buildings and homes. This is often due to governments offering incentives to the contractors to put them in place. It is a better idea than having to put them in later on which costs more time and money. From a business perspective, this is a great way to cut down overhead expenses. Even a landlord can reduce the monthly bill he gets for electricity on behalf of his tenants. • These photovoltaic panels also look gorgeous, so you don’t have to worry that they are going to bring down the value of the structure they are placed on. In fact, the opposite is very true. The value of the location is going to increase due to the fact that anyone buying it will be able to save money on the electricity that they consume. You can take a look at a video featuring them on a home at. . • The installation of photovoltaic panels should be done by a professional. However, there are many contractors out there that offer such services. You can contact them for a free estimate if you want to get them installed on an existing location. You can also speak to contractors about photovoltaic systems for any new structure you would like to have them take part in building. • There is no doubt that turning to alternative renewable resources such as the sun for electricity makes sense. Being able to capture it to fulfill our ongoing need for electricity can be accomplished with photovoltaic systems. This is definitely an investment that will save you money and protect our nonrenewable resources. 2. Discuss what is more advantageous use of wind power of solar power in your area?
 1. Read the text A solar dish/engine system uses concentrating solar collectors that track the sun, so they always point straight at the sun and concentrate the solar energy at the focal point of the dish. A solar dish's concentration ratio is much higher than a solar trough's, typically over 2, 000, with a working fluid temperature over 1380°F. The power-generating equipment used with a solar dish can be mounted at the focal point of the dish, making it well suited for remote operations or, as with the solar trough, the energy may be collected from a number of installations and converted to electricity at a central point. The engine in a solar dish/engine system converts heat to mechanical power by compressing the working fluid when it is cold, heating the compressed working fluid, and then expanding the fluid through a turbine or with a piston to produce work. The engine is coupled to an electric generator to convert the mechanical power to electric 2. Answer the questions: 1) What is solar dish? 2) For what is used the solar dish? 3) Have you ever seen solar dish? 4) What does engine system convert? 5) Does the solar dish have a turbine? 3. Translate into English: 1) Сегодня не солнечно 2) Солнце является источником энергии 3) Свет приходит от солнца 4) Вчера солнце не светило 5) Температура жидкости выше 100 градусов 4. Watch the video about solar power plant in Spain
1. Read the text A solar dish/engine system uses concentrating solar collectors that track the sun, so they always point straight at the sun and concentrate the solar energy at the focal point of the dish. A solar dish's concentration ratio is much higher than a solar trough's, typically over 2, 000, with a working fluid temperature over 1380°F. The power-generating equipment used with a solar dish can be mounted at the focal point of the dish, making it well suited for remote operations or, as with the solar trough, the energy may be collected from a number of installations and converted to electricity at a central point. The engine in a solar dish/engine system converts heat to mechanical power by compressing the working fluid when it is cold, heating the compressed working fluid, and then expanding the fluid through a turbine or with a piston to produce work. The engine is coupled to an electric generator to convert the mechanical power to electric 2. Answer the questions: 1) What is solar dish? 2) For what is used the solar dish? 3) Have you ever seen solar dish? 4) What does engine system convert? 5) Does the solar dish have a turbine? 3. Translate into English: 1) Сегодня не солнечно 2) Солнце является источником энергии 3) Свет приходит от солнца 4) Вчера солнце не светило 5) Температура жидкости выше 100 градусов 4. Watch the video about solar power plant in Spain
 Future Energy Technology With rising fuel costs, climate change concerns and a growing demand for electricity, renewable energy resources such as solar power are becoming an increasingly valuable part of the world's energy mix. Around the globe, businesses and homeowners are harnessing the power of the earth's most abundant natural resource - sunlight - to provide energy using solar power. Solar thermal energy is a technology for harnessing solar energy for heat. • Most renewable energy comes either directly or indirectly from the sun. Solar energy can be used directly for heating and lighting, for generating electricity and a variety of commercial and industrial uses. • Solar power describes a number of methods of harnessing energy from the light of the Sun. It has been present in many traditional building methods for centuries, but has become of increasing interest in developed countries as the environmental costs and limited supply of other power sources such as fossil fuels are realized. It is already in widespread use where other power supplies are absent, such as in remote locations and in space. • Solar energy can be stored at high temperatures using molten salts. Solar thermal power plants use the sun's rays to heat a fluid to very high temperatures. The fluid is then circulated through pipes so it can transfer its heat to water to produce steam. The steam, in turn, is converted into mechanical energy in a turbine and into electricity by a conventional generator coupled to the turbine. • The three main types of solar thermal power systems are: parabolic trough, solar dish, solar power tower. • Solar cells are devices that convert light energy directly into electrical energy. You may have seen small solar cells in calculators. Larger arrays of solar cells are used to power road signs in remote areas, and even larger arrays are used to power satellites in orbit around Earth. • Solar panels do not generate electricity, but rather they heat up water. They are often located on the roofs of buildings where they can receive heat energy from the sun. The diagram outlines how they work. • 4. Watch the video. 2. Match the device shown with it’s name: Parabolic trough Solar dish Solar power tower 3. Answer the question: 1. What does solar thermal plant use to produce power ? 2. What are three main types of solar thermal power systems ? 3. Is there generator in solar power plant ? 4. How is steam produced in solar power plant? 5. Have you ever seen the solar panels? House powered entirely by Sun
Future Energy Technology With rising fuel costs, climate change concerns and a growing demand for electricity, renewable energy resources such as solar power are becoming an increasingly valuable part of the world's energy mix. Around the globe, businesses and homeowners are harnessing the power of the earth's most abundant natural resource - sunlight - to provide energy using solar power. Solar thermal energy is a technology for harnessing solar energy for heat. • Most renewable energy comes either directly or indirectly from the sun. Solar energy can be used directly for heating and lighting, for generating electricity and a variety of commercial and industrial uses. • Solar power describes a number of methods of harnessing energy from the light of the Sun. It has been present in many traditional building methods for centuries, but has become of increasing interest in developed countries as the environmental costs and limited supply of other power sources such as fossil fuels are realized. It is already in widespread use where other power supplies are absent, such as in remote locations and in space. • Solar energy can be stored at high temperatures using molten salts. Solar thermal power plants use the sun's rays to heat a fluid to very high temperatures. The fluid is then circulated through pipes so it can transfer its heat to water to produce steam. The steam, in turn, is converted into mechanical energy in a turbine and into electricity by a conventional generator coupled to the turbine. • The three main types of solar thermal power systems are: parabolic trough, solar dish, solar power tower. • Solar cells are devices that convert light energy directly into electrical energy. You may have seen small solar cells in calculators. Larger arrays of solar cells are used to power road signs in remote areas, and even larger arrays are used to power satellites in orbit around Earth. • Solar panels do not generate electricity, but rather they heat up water. They are often located on the roofs of buildings where they can receive heat energy from the sun. The diagram outlines how they work. • 4. Watch the video. 2. Match the device shown with it’s name: Parabolic trough Solar dish Solar power tower 3. Answer the question: 1. What does solar thermal plant use to produce power ? 2. What are three main types of solar thermal power systems ? 3. Is there generator in solar power plant ? 4. How is steam produced in solar power plant? 5. Have you ever seen the solar panels? House powered entirely by Sun
 • We've used the Sun for drying clothes and food for thousands of years, but only recently have we been able to use it for generating power. The Sun is 150 million kilometres away, and amazingly powerful. Just the tiny fraction of the Sun's energy that hits the Earth (around a hundredth of a millionth of a percent) is enough to meet all our power needs many times over. In fact, every minute, enough energy arrives at the Earth to meet our demands for a whole year - if only we could harness it properly. Currently in the UK there are grants available to help you install solar power in your home. How it works: There are three main ways that we use the Sun's energy: 1 Solar Cells (really called "photovoltaic", "PV" or "photoelectric" cells) that convert light directly into electricity. In a sunny climate, you can get enough power to run a 100 W light bulb from just one square metre of solar panel. This was originally developed in order to provide electricity for satellites, but these days many of us own calculators powered by solar cells.
• We've used the Sun for drying clothes and food for thousands of years, but only recently have we been able to use it for generating power. The Sun is 150 million kilometres away, and amazingly powerful. Just the tiny fraction of the Sun's energy that hits the Earth (around a hundredth of a millionth of a percent) is enough to meet all our power needs many times over. In fact, every minute, enough energy arrives at the Earth to meet our demands for a whole year - if only we could harness it properly. Currently in the UK there are grants available to help you install solar power in your home. How it works: There are three main ways that we use the Sun's energy: 1 Solar Cells (really called "photovoltaic", "PV" or "photoelectric" cells) that convert light directly into electricity. In a sunny climate, you can get enough power to run a 100 W light bulb from just one square metre of solar panel. This was originally developed in order to provide electricity for satellites, but these days many of us own calculators powered by solar cells.
 • This helps out your central heating system, and cuts your fuel bills. However, with the basic type of panel shown in the diagram you must drain the water out to stop the panels freezing in the winter. Some manufacturers have systems that do this automatically. Solar water heating is easily worthwhile in places like California and Australia, where you get lots of sunshine. Mind you, as technology improves it's becoming worthwhile in the UK. Here's a more advanced type of solar water heating panel. The suppliers claim that in the UK it can supply 90% of a typical home's hot water needs from April to November. This "Thermomax" panel is made of a set of glass tubes. Each contains a metal plate with a blue-ish coating to help it absorb solar energy from IR to UV, so that even in diffuse sunlight you get a decent output. The air has been removed from the glass tubes to reduce heat loss, rather like a thermos flask. Up the back of the metal plate is a "heat pipe", which looks like a copper rod but contains a liquid that transfers heat very quickly to the top of the glass tube. A water pipe runs across the top of the whole thing and picks up the heat from the tubes. Solar water heating, where heat from the Sun is used to heat water in glass panels on your roof. This means you don't need to use so much gas or electricity to heat your water at home. Water is pumped through pipes in the panel. The pipes are painted black, so they get hotter when the Sun shines on them. The water is pumped in at the bottom so that convection helps the flow of hot water out of the top.
• This helps out your central heating system, and cuts your fuel bills. However, with the basic type of panel shown in the diagram you must drain the water out to stop the panels freezing in the winter. Some manufacturers have systems that do this automatically. Solar water heating is easily worthwhile in places like California and Australia, where you get lots of sunshine. Mind you, as technology improves it's becoming worthwhile in the UK. Here's a more advanced type of solar water heating panel. The suppliers claim that in the UK it can supply 90% of a typical home's hot water needs from April to November. This "Thermomax" panel is made of a set of glass tubes. Each contains a metal plate with a blue-ish coating to help it absorb solar energy from IR to UV, so that even in diffuse sunlight you get a decent output. The air has been removed from the glass tubes to reduce heat loss, rather like a thermos flask. Up the back of the metal plate is a "heat pipe", which looks like a copper rod but contains a liquid that transfers heat very quickly to the top of the glass tube. A water pipe runs across the top of the whole thing and picks up the heat from the tubes. Solar water heating, where heat from the Sun is used to heat water in glass panels on your roof. This means you don't need to use so much gas or electricity to heat your water at home. Water is pumped through pipes in the panel. The pipes are painted black, so they get hotter when the Sun shines on them. The water is pumped in at the bottom so that convection helps the flow of hot water out of the top.
 Solar Furnaces use a huge array of mirrors to concentrate the Sun's energy into a small space and produce very high temperatures. There's one at Odeillo, in France, used for scientific experiments. It can achieve temperatures up to 3, 000 degrees Celsius. Solar furnaces are basically huge "solar cookers". A solar cooker can be used in hot countries to cook food. This one is in the UK, making tea and coffee, although it does take a long time! Watch the video
Solar Furnaces use a huge array of mirrors to concentrate the Sun's energy into a small space and produce very high temperatures. There's one at Odeillo, in France, used for scientific experiments. It can achieve temperatures up to 3, 000 degrees Celsius. Solar furnaces are basically huge "solar cookers". A solar cooker can be used in hot countries to cook food. This one is in the UK, making tea and coffee, although it does take a long time! Watch the video
 End of Solar Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
End of Solar Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
 Wind Power Translate into Russian. Wind power can be an excellent complement to a solar power system. Here in West Taxes, when the sun isn't shining, the wind is usually blowing. Building a wind generator from scratch is not that difficult of a project. You will need a shop with basic power and hand tools, and some degree of dedication. Large wind generators of 2000 Watts and up are a major project needing very strong construction. But smaller ones in the 700 -1000 Watt, 8 -11 foot range can be built fairly easily! Wind is an emissions and waste-free resource. Prices range from $500 to $5000 for small-scale wind turbines ranging from 300 w up to 5 Kw. In the year 2012, the wind industry is expected for the first time to offer 1 million jobs. Discussion. Suppose the government of your area wants to choose where to invest money either to wind industry or to solar power industry. Represent your projects. Each member of the team suppose to say something. The team that wins the tender gets excellent marks. 1. What are the advantages of the wind power? 2. What are the disadvantages of the wind power? 3. What are the advantages of solar power? 4. What are the disadvantages of solar power? 5. What would you choose? Watch the video.
Wind Power Translate into Russian. Wind power can be an excellent complement to a solar power system. Here in West Taxes, when the sun isn't shining, the wind is usually blowing. Building a wind generator from scratch is not that difficult of a project. You will need a shop with basic power and hand tools, and some degree of dedication. Large wind generators of 2000 Watts and up are a major project needing very strong construction. But smaller ones in the 700 -1000 Watt, 8 -11 foot range can be built fairly easily! Wind is an emissions and waste-free resource. Prices range from $500 to $5000 for small-scale wind turbines ranging from 300 w up to 5 Kw. In the year 2012, the wind industry is expected for the first time to offer 1 million jobs. Discussion. Suppose the government of your area wants to choose where to invest money either to wind industry or to solar power industry. Represent your projects. Each member of the team suppose to say something. The team that wins the tender gets excellent marks. 1. What are the advantages of the wind power? 2. What are the disadvantages of the wind power? 3. What are the advantages of solar power? 4. What are the disadvantages of solar power? 5. What would you choose? Watch the video.
 History of Wind Power Since ancient times, people have harnessed the wind's energy. Over 5, 000 years ago, the ancient Egyptians used wind to sail ships on the Nile River. Later, people built windmills to grind wheat and other grains. The earliest known windmills were in Persia (now called Iran). These early windmills looked like large paddle wheels. Centuries later, the people of Holland improved the basic design of the windmill. They gave it propeller-type blades, still made with sails. Holland's windmills are world renowned. American colonists used windmills to grind wheat and corn, to pump water, and to cut wood at sawmills. As late as the 1920 s, Americans used small windmills to generate electricity in rural areas without electric service. When power lines began to transport electricity to rural areas in the 1930 s, local windmills were used less and less, though they can still be seen on some Western ranches. The oil shortages of the 1970 s changed the energy picture for the Country and the world. It created an interest in alternative energy sources, paving the way for the re-entry of the windmill to generate electricity. In the early 1980 s, wind energy really took off in California, partly because of State policies that encouraged renewable energy sources. In the 1970 s, oil shortages pushed the development of alternative energy sources. In the 1990 s, the push came from a renewed concern for the environment in response to scientific studies indicating potential changes to the global climate if the use of fossil fuels continues to increase. Wind energy is an economical power resource in many areas of the country. Wind is a clean fuel; wind power plants (also called wind farms) produce no air or water pollution because no fuel is burned to generate electricity. Growing concern about emissions from fossil fuel generation, increased government support, and higher costs for fossil fuels (especially natural gas and coal) have helped wind power capacity in the United States grow substantially over the past 10 years. The most serious environmental drawbacks to wind machines may be their negative effect on wild bird populations and the visual impact on the landscape. To some, the glistening blades of windmills on the horizon are an eyesore; to others, they're a beautiful alternative to conventional power plants. Read the text and answer 1 the following questions. 1. Where were the first windmills? 2. How did Egyptians use the power of the wind? 3. Why did the interest in alternative energy sources renew? 4. Can the wind energy replace conventional power plants? 5. What is the bad environmental impact of wind power plants? 2 Translate into English: 1. Ветер это чистое топливо. 2. Ветер является возобновляемым природным ресурсом. 3. Ископаемое топливо заканчивается. 4. Я интересуюсь ветряными электростанциями. 5. Ты интересуешься производством электричества из ветра?
History of Wind Power Since ancient times, people have harnessed the wind's energy. Over 5, 000 years ago, the ancient Egyptians used wind to sail ships on the Nile River. Later, people built windmills to grind wheat and other grains. The earliest known windmills were in Persia (now called Iran). These early windmills looked like large paddle wheels. Centuries later, the people of Holland improved the basic design of the windmill. They gave it propeller-type blades, still made with sails. Holland's windmills are world renowned. American colonists used windmills to grind wheat and corn, to pump water, and to cut wood at sawmills. As late as the 1920 s, Americans used small windmills to generate electricity in rural areas without electric service. When power lines began to transport electricity to rural areas in the 1930 s, local windmills were used less and less, though they can still be seen on some Western ranches. The oil shortages of the 1970 s changed the energy picture for the Country and the world. It created an interest in alternative energy sources, paving the way for the re-entry of the windmill to generate electricity. In the early 1980 s, wind energy really took off in California, partly because of State policies that encouraged renewable energy sources. In the 1970 s, oil shortages pushed the development of alternative energy sources. In the 1990 s, the push came from a renewed concern for the environment in response to scientific studies indicating potential changes to the global climate if the use of fossil fuels continues to increase. Wind energy is an economical power resource in many areas of the country. Wind is a clean fuel; wind power plants (also called wind farms) produce no air or water pollution because no fuel is burned to generate electricity. Growing concern about emissions from fossil fuel generation, increased government support, and higher costs for fossil fuels (especially natural gas and coal) have helped wind power capacity in the United States grow substantially over the past 10 years. The most serious environmental drawbacks to wind machines may be their negative effect on wild bird populations and the visual impact on the landscape. To some, the glistening blades of windmills on the horizon are an eyesore; to others, they're a beautiful alternative to conventional power plants. Read the text and answer 1 the following questions. 1. Where were the first windmills? 2. How did Egyptians use the power of the wind? 3. Why did the interest in alternative energy sources renew? 4. Can the wind energy replace conventional power plants? 5. What is the bad environmental impact of wind power plants? 2 Translate into English: 1. Ветер это чистое топливо. 2. Ветер является возобновляемым природным ресурсом. 3. Ископаемое топливо заканчивается. 4. Я интересуюсь ветряными электростанциями. 5. Ты интересуешься производством электричества из ветра?
 International Wind Power Read 1. Мельницы используют в сельском хозяйстве. the text and answer the following questions. Most of the wind power plants in the world are located in Europe and in the United States where government programs have helped support wind power development. As of 2008, the United States ranks first in the world in wind power capacity, followed by Germany, Spain, and China. Denmark ranks ninth in the world in wind power capacity, but generates about 20% of its electricity from wind. Conditions are well suited along much of the coasts of the United States to use wind energy. However, there are people oppose putting turbines just offshore, near the coastlines. However, there are people who think the wind turbines will spoil the view of the ocean. Right now, there is a plan to build an offshore wind plant off the coast of Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Wind is a renewable energy source that does not pollute, so some people see it as a good alternative to fossil fuels. There are two types of wind machines (turbines) used today, based on the direction of the rotating shaft (axis): horizontal-axis wind machines and vertical-axis wind machines. The size of wind machines varies widely. Small turbines used to power a single home or business may have a capacity of less than 100 kilowatts. Some large commercial-sized turbines may have a capacity of 5 million watts, or 5 megawatts. Larger turbines are often grouped together into wind farms that provide power to the electrical grid. Most wind machines being used today are the horizontal-axis type. 2. Использование возобновляемых природных ресурсов выгодно для экономики. Translate into English: 3. Необходимо сократить выброс опасных газов в атмосферу. 4. Ветроэнергетические установки не загрязняют окружающую среду. 5. Ты можешь сделать ветряную турбину? Answer the questions. 1. What is a windmill? 2. What are advantages of using wind power plants? 3. How much energy from wind is produced in Denmark? 4. Do you want to make your own windmill? 5. How many kilowatts does your family consume every day?
International Wind Power Read 1. Мельницы используют в сельском хозяйстве. the text and answer the following questions. Most of the wind power plants in the world are located in Europe and in the United States where government programs have helped support wind power development. As of 2008, the United States ranks first in the world in wind power capacity, followed by Germany, Spain, and China. Denmark ranks ninth in the world in wind power capacity, but generates about 20% of its electricity from wind. Conditions are well suited along much of the coasts of the United States to use wind energy. However, there are people oppose putting turbines just offshore, near the coastlines. However, there are people who think the wind turbines will spoil the view of the ocean. Right now, there is a plan to build an offshore wind plant off the coast of Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Wind is a renewable energy source that does not pollute, so some people see it as a good alternative to fossil fuels. There are two types of wind machines (turbines) used today, based on the direction of the rotating shaft (axis): horizontal-axis wind machines and vertical-axis wind machines. The size of wind machines varies widely. Small turbines used to power a single home or business may have a capacity of less than 100 kilowatts. Some large commercial-sized turbines may have a capacity of 5 million watts, or 5 megawatts. Larger turbines are often grouped together into wind farms that provide power to the electrical grid. Most wind machines being used today are the horizontal-axis type. 2. Использование возобновляемых природных ресурсов выгодно для экономики. Translate into English: 3. Необходимо сократить выброс опасных газов в атмосферу. 4. Ветроэнергетические установки не загрязняют окружающую среду. 5. Ты можешь сделать ветряную турбину? Answer the questions. 1. What is a windmill? 2. What are advantages of using wind power plants? 3. How much energy from wind is produced in Denmark? 4. Do you want to make your own windmill? 5. How many kilowatts does your family consume every day?
 Wind Power Read the text. Wind power is the leader in wholesale renewable electricity production in the United States. Total installed U. S. wind power capacity was 9, 149 megawatts at the beginning of 2006, according to the American Wind Energy Association. A large part of this— 2, 420 megawatts—was installed in 2005, and an estimated 3, 000 megawatts is planned for installation in 2006. With recent technological advances, the price competitiveness of wind generation versus natural gas has improved, supporting continued growth. In addition, the U. S. federal government offers companies a production tax credit for wind power equal to about 1. 9 cents per watt-hour. This has been a powerful incentive to attract tax-oriented investors, such as utility companies, into wind farm ownership. The original market for wind power was Denmark in the late 1990 s, followed by Germany. Today, the hot markets are Spain, Italy, France, the United Kingdom, and India. But wind power is available almost everywhere. Answer the questions. 1. What is the leader in the electricity production in US? 2. What is the wind farm? 3. Where is the original market of wind power? 4. What is the total capacity of all wind power plant in US? 5. Does the government attract to wind power plant ownership? Translate into English. 1. Цены на электричество повышаются. 2. Ветер есть везде. 3. Государство стимулирует развитие ветряной энергетики. 4. Ветряные генераторы не сложно установить. 5. Ветер вчера не дул. Watch the video.
Wind Power Read the text. Wind power is the leader in wholesale renewable electricity production in the United States. Total installed U. S. wind power capacity was 9, 149 megawatts at the beginning of 2006, according to the American Wind Energy Association. A large part of this— 2, 420 megawatts—was installed in 2005, and an estimated 3, 000 megawatts is planned for installation in 2006. With recent technological advances, the price competitiveness of wind generation versus natural gas has improved, supporting continued growth. In addition, the U. S. federal government offers companies a production tax credit for wind power equal to about 1. 9 cents per watt-hour. This has been a powerful incentive to attract tax-oriented investors, such as utility companies, into wind farm ownership. The original market for wind power was Denmark in the late 1990 s, followed by Germany. Today, the hot markets are Spain, Italy, France, the United Kingdom, and India. But wind power is available almost everywhere. Answer the questions. 1. What is the leader in the electricity production in US? 2. What is the wind farm? 3. Where is the original market of wind power? 4. What is the total capacity of all wind power plant in US? 5. Does the government attract to wind power plant ownership? Translate into English. 1. Цены на электричество повышаются. 2. Ветер есть везде. 3. Государство стимулирует развитие ветряной энергетики. 4. Ветряные генераторы не сложно установить. 5. Ветер вчера не дул. Watch the video.
 The turbine was very cheap to build, the most expensive part being the secondhand tape drive motor which cost $25. The voltage conversion kit cost $24 a couple of years back, and the rest of the material was free. The water pipe was salvaged second-hand from a building site, while the aluminum sheet was from some old signs I found in my workshop after we moved in. The only other expenses were a dollar or two worth of paint and rivets and $5 for a bag of concrete. The output voltage of the generator is actually quite low at the speeds it is likely to turn at attached to a Savonius rotor. At 200 RPM the output is only about four or five volts. While this is obviously not enough to charge a 12 volt battery by itself, a bit of clever circuitry solved the problem. The one I used I already had from another disused project, so I tested it and found that it would output the required 13. 8 volts from as little as four volts in. This kit was originally bought from Jaycar Electronics, who no longer sell it, but they do have a pre-built module called a solar power converter, cat# AA-0259, that will take an input voltage from one to ten volts and charge a 12 volt battery—perfect for uses such as this. At under 200 RPM I was getting full charging voltage, with available current increasing as rotor speed increased. The circuit was housed in a box and slid down inside the tube before the generator and end cap were fitted. The cables from the output of the circuit run down inside the mast and out of a sealed hole at the bottom, through some flexible conduit to the box containing the gate opener circuitry. The mast and turbine were both painted green to help them blend in with their surroundings. The photos show the turbine before its paint job. To prevent water getting into the generator bearing, a skirt will be attached around the perimeter of the bottom of the turbine. The DC motor fitted to the plastic end cap which holds it to the mast. Front view of the motor. Note threaded holes in the face plate. This rear view shows the three plastic angle sections used to make the motor a tight fit in the mast. Here you can see the whole motor and rotor assembly before fitting to the mast and painting. Note how the vanes in the top section are rotated 90° to those in the bottom section, and the motor does not yet have the plastic angle sections attached. Discuss what is easier to build wind, biogas, solar or hydro power generator. What is cheaper and more profitable?
The turbine was very cheap to build, the most expensive part being the secondhand tape drive motor which cost $25. The voltage conversion kit cost $24 a couple of years back, and the rest of the material was free. The water pipe was salvaged second-hand from a building site, while the aluminum sheet was from some old signs I found in my workshop after we moved in. The only other expenses were a dollar or two worth of paint and rivets and $5 for a bag of concrete. The output voltage of the generator is actually quite low at the speeds it is likely to turn at attached to a Savonius rotor. At 200 RPM the output is only about four or five volts. While this is obviously not enough to charge a 12 volt battery by itself, a bit of clever circuitry solved the problem. The one I used I already had from another disused project, so I tested it and found that it would output the required 13. 8 volts from as little as four volts in. This kit was originally bought from Jaycar Electronics, who no longer sell it, but they do have a pre-built module called a solar power converter, cat# AA-0259, that will take an input voltage from one to ten volts and charge a 12 volt battery—perfect for uses such as this. At under 200 RPM I was getting full charging voltage, with available current increasing as rotor speed increased. The circuit was housed in a box and slid down inside the tube before the generator and end cap were fitted. The cables from the output of the circuit run down inside the mast and out of a sealed hole at the bottom, through some flexible conduit to the box containing the gate opener circuitry. The mast and turbine were both painted green to help them blend in with their surroundings. The photos show the turbine before its paint job. To prevent water getting into the generator bearing, a skirt will be attached around the perimeter of the bottom of the turbine. The DC motor fitted to the plastic end cap which holds it to the mast. Front view of the motor. Note threaded holes in the face plate. This rear view shows the three plastic angle sections used to make the motor a tight fit in the mast. Here you can see the whole motor and rotor assembly before fitting to the mast and painting. Note how the vanes in the top section are rotated 90° to those in the bottom section, and the motor does not yet have the plastic angle sections attached. Discuss what is easier to build wind, biogas, solar or hydro power generator. What is cheaper and more profitable?
 The generator I used was actually a large permanent magnet DC motor from an old vertical computer tape drive. These are very robust, well built motors about the size of a large car starter motor. They are simple and reliable, and as generators are extremely efficient— connecting one to a torch bulb causes the bulb to be blown by a quick flick of the shaft! The rotor slides directly onto the end of the motor shaft, and is held in place with a stainless steel bolt. In this design, I decided to see if I could do away with having a top bearing. The bearings in the tape drive motor are at least as strong as the average car alternator bearing, and the local bearing shop gave me specs that indicate that most bearings this size will take a radial load (the load the wind would place on the bearing) of up to 450 kg, and an axial load (the load from the rotor’s weight) of up to 45 kg. This was heaps for my uses, so I decided to leave out the top bearing and see how the turbine went. Answer the questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What was the mast made of? What generator did the author use for wind turbine? How did the author fasten the mast? Could you make the wind turbine yourself? What do you think would it be profitable to make a wind generator in our area? Translate into English. This was made from a 2200 mm length of 150 mm diameter PVC water pipe, just like the rotor. In sections this diameter and this length, PVC pipe is quite rigid. The pipe was buried about 400 mm into a hole and concreted into place. The mast does still flex a bit in a strong wind and if this proves to be a problem it can easily be made rigid by filling with concrete. The generator is mounted to the top of the pole by means of a stormwater pipe endcap. The face of the generator has four screw holes, so it was just a matter of drilling corresponding holes into the end cap, and one much larger hole in the centre for the shaft. By itself, this would not have been strong enough, as the end cap would have flexed and eventually broken through, so I attached three short braces made from 25 x 3 plastic angle to the other end of the generator. These were fixed to the motor using machine screws into the bottom end plate, and point out away from the centre of the generator. The overall diameter of the circle they make is the same as that of the inside of the pipe, so that when the generator is slid into the pipe the whole assembly is quite solid. Watch the video. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Прикрепи генератор сюда. Закрути эту деталь. Трубу нужно забетонировать. Генератор внутри трубы. Конструкция достаточно прочная.
The generator I used was actually a large permanent magnet DC motor from an old vertical computer tape drive. These are very robust, well built motors about the size of a large car starter motor. They are simple and reliable, and as generators are extremely efficient— connecting one to a torch bulb causes the bulb to be blown by a quick flick of the shaft! The rotor slides directly onto the end of the motor shaft, and is held in place with a stainless steel bolt. In this design, I decided to see if I could do away with having a top bearing. The bearings in the tape drive motor are at least as strong as the average car alternator bearing, and the local bearing shop gave me specs that indicate that most bearings this size will take a radial load (the load the wind would place on the bearing) of up to 450 kg, and an axial load (the load from the rotor’s weight) of up to 45 kg. This was heaps for my uses, so I decided to leave out the top bearing and see how the turbine went. Answer the questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What was the mast made of? What generator did the author use for wind turbine? How did the author fasten the mast? Could you make the wind turbine yourself? What do you think would it be profitable to make a wind generator in our area? Translate into English. This was made from a 2200 mm length of 150 mm diameter PVC water pipe, just like the rotor. In sections this diameter and this length, PVC pipe is quite rigid. The pipe was buried about 400 mm into a hole and concreted into place. The mast does still flex a bit in a strong wind and if this proves to be a problem it can easily be made rigid by filling with concrete. The generator is mounted to the top of the pole by means of a stormwater pipe endcap. The face of the generator has four screw holes, so it was just a matter of drilling corresponding holes into the end cap, and one much larger hole in the centre for the shaft. By itself, this would not have been strong enough, as the end cap would have flexed and eventually broken through, so I attached three short braces made from 25 x 3 plastic angle to the other end of the generator. These were fixed to the motor using machine screws into the bottom end plate, and point out away from the centre of the generator. The overall diameter of the circle they make is the same as that of the inside of the pipe, so that when the generator is slid into the pipe the whole assembly is quite solid. Watch the video. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Прикрепи генератор сюда. Закрути эту деталь. Трубу нужно забетонировать. Генератор внутри трубы. Конструкция достаточно прочная.
 End of Wind Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
End of Wind Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
 Renewable Energy Hydropower 1. Read the text. Hydropower is one of the most efficient spheres of the electric power industry. Hydro-resources are renewable and the most environmentally friendly source of energy, use of which allows emissions into the atmosphere from thermal electric power plants to be reduced and reserves of hydrocarbon fuel to be saved for future generations. Apart from its immediate purpose – production of electric power – hydropower resolves a number of additional tasks of extreme importance for society and the state. The direct benefits include creation of drinking and industrial water supply systems, development of navigation, creation of irrigation systems for agricultural purposes, fishbreeding, and regulation of fluvial flow for the purpose of combating high water and floods and thereby ensuring the safety of the population. Hydropower constitutes an infrastructure for the activities and development of a whole series of vital branches of the economy and the country as a whole. Each hydro-electric power plant brought on line becomes an economic growth centre for the region in which it is located, with production facilities clustering around it, industry developing and new jobs being created. The Golden Age of Russia’s hydro-electric power industry was between 1930 and the 1990 s. Previously, in Russia and the USSR, there had been only very few hydroplants and the total installed capacity of turbogenerator units in the USSR was no more than 600, 000 k. Wh in 1930. Sixty years later, our country was second only to the USA in terms of installed HPP capacity (65 million k. Wh) and came in after the USA and Canada only in terms of electric power produced by HPPs (233 billion k. Wh/year). Russia now has 102 hydropower plants in operation, with a capacity of over 100 MW. The total installed capacity of HPP turbogenerator units in Russia today amounts to approximately 45 million k. W (5 th place in the world), with an output in the order of 165 billion k. Wh/year (also 5 th place) – while HPP account for no more than 21% of Russia’s total electric power production. At the same time, in terms of hydropower resources economic potential Russia takes second place in the world (about 852 billion k. Wh, after China), but in terms of the degree of their development – 20% – it is way behind virtually all the developed countries and even many developing ones. The respective figures for France and Switzerland, for instance, are over 90%, for Canada and Norway – 70%, and for the USA and Brazil – 50%.
Renewable Energy Hydropower 1. Read the text. Hydropower is one of the most efficient spheres of the electric power industry. Hydro-resources are renewable and the most environmentally friendly source of energy, use of which allows emissions into the atmosphere from thermal electric power plants to be reduced and reserves of hydrocarbon fuel to be saved for future generations. Apart from its immediate purpose – production of electric power – hydropower resolves a number of additional tasks of extreme importance for society and the state. The direct benefits include creation of drinking and industrial water supply systems, development of navigation, creation of irrigation systems for agricultural purposes, fishbreeding, and regulation of fluvial flow for the purpose of combating high water and floods and thereby ensuring the safety of the population. Hydropower constitutes an infrastructure for the activities and development of a whole series of vital branches of the economy and the country as a whole. Each hydro-electric power plant brought on line becomes an economic growth centre for the region in which it is located, with production facilities clustering around it, industry developing and new jobs being created. The Golden Age of Russia’s hydro-electric power industry was between 1930 and the 1990 s. Previously, in Russia and the USSR, there had been only very few hydroplants and the total installed capacity of turbogenerator units in the USSR was no more than 600, 000 k. Wh in 1930. Sixty years later, our country was second only to the USA in terms of installed HPP capacity (65 million k. Wh) and came in after the USA and Canada only in terms of electric power produced by HPPs (233 billion k. Wh/year). Russia now has 102 hydropower plants in operation, with a capacity of over 100 MW. The total installed capacity of HPP turbogenerator units in Russia today amounts to approximately 45 million k. W (5 th place in the world), with an output in the order of 165 billion k. Wh/year (also 5 th place) – while HPP account for no more than 21% of Russia’s total electric power production. At the same time, in terms of hydropower resources economic potential Russia takes second place in the world (about 852 billion k. Wh, after China), but in terms of the degree of their development – 20% – it is way behind virtually all the developed countries and even many developing ones. The respective figures for France and Switzerland, for instance, are over 90%, for Canada and Norway – 70%, and for the USA and Brazil – 50%.
 Hydropower Basics Energy From Moving Water l l l l l Hydropower Generates Electricity Hydropower is the renewable energy source that produces the most electricity in the United States. It accounted for 6% of total U. S. electricity generation and 67% of generation from renewables in 2008. Hydropower Relies on the Water Cycle Understanding the water cycle is important to understanding hydropower. In the water cycle: Solar energy heats water on the surface, causing it to evaporate. This water vapor condenses into clouds and falls back onto the surface as precipitation (rain, snow, etc. ). The water flows through rivers back into the oceans, where it can evaporate and begin the cycle over again. Mechanical Energy Is Harnessed from Moving Water The amount of available energy in moving water is determined by its flow or fall. Swiftly flowing water in a big river, like the Columbia River that forms the border between Oregon and Washington, carries a great deal of energy in its flow. Water descending rapidly from a very high point, like Niagara Falls in New York, also has lots of energy in its flow. In either instance, the water flows through a pipe, or penstock, then pushes against and turns blades in a turbine to spin a generator to produce electricity. In a run-of-the-river system, the force of the current applies the needed pressure, while in a storage system, water is accumulated in reservoirs created by dams, then released as needed 2. Answer the questions 1) How is determined the energy potential for the dam? 2) What sites have the best energy potential? 3) Is hydropower renewable energy? 4) Is there a dam in Udmurtia? 5) Is the energy from dam cheaper than from the fossil fuel? 3. Translate into English 1) Газ есть на камее. 2) Гидроэнергетика- это возобновляемый энергетический источник. 3) В России существует много ГЭС. 4) Электричество вырабатывается по средствам тока воды через турбину. 5)Гидроэнергетика хорошо развивается в России 4. Watch the video.
Hydropower Basics Energy From Moving Water l l l l l Hydropower Generates Electricity Hydropower is the renewable energy source that produces the most electricity in the United States. It accounted for 6% of total U. S. electricity generation and 67% of generation from renewables in 2008. Hydropower Relies on the Water Cycle Understanding the water cycle is important to understanding hydropower. In the water cycle: Solar energy heats water on the surface, causing it to evaporate. This water vapor condenses into clouds and falls back onto the surface as precipitation (rain, snow, etc. ). The water flows through rivers back into the oceans, where it can evaporate and begin the cycle over again. Mechanical Energy Is Harnessed from Moving Water The amount of available energy in moving water is determined by its flow or fall. Swiftly flowing water in a big river, like the Columbia River that forms the border between Oregon and Washington, carries a great deal of energy in its flow. Water descending rapidly from a very high point, like Niagara Falls in New York, also has lots of energy in its flow. In either instance, the water flows through a pipe, or penstock, then pushes against and turns blades in a turbine to spin a generator to produce electricity. In a run-of-the-river system, the force of the current applies the needed pressure, while in a storage system, water is accumulated in reservoirs created by dams, then released as needed 2. Answer the questions 1) How is determined the energy potential for the dam? 2) What sites have the best energy potential? 3) Is hydropower renewable energy? 4) Is there a dam in Udmurtia? 5) Is the energy from dam cheaper than from the fossil fuel? 3. Translate into English 1) Газ есть на камее. 2) Гидроэнергетика- это возобновляемый энергетический источник. 3) В России существует много ГЭС. 4) Электричество вырабатывается по средствам тока воды через турбину. 5)Гидроэнергетика хорошо развивается в России 4. Watch the video.
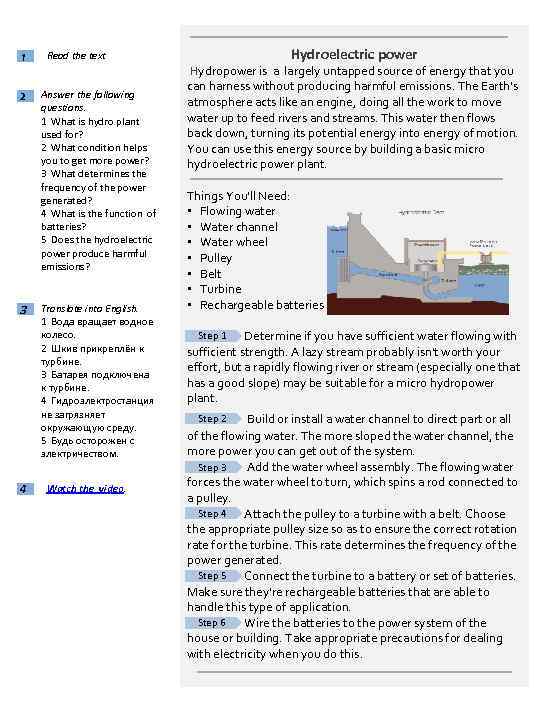 1 2 3 4 Read the text Answer the following questions. 1 What is hydro plant used for? 2 What condition helps you to get more power? 3 What determines the frequency of the power generated? 4 What is the function of batteries? 5 Does the hydroelectric power produce harmful emissions? Translate into English. 1 Вода вращает водное колесо. 2 Шкив прикреплён к турбине. 3 Батарея подключена к турбине. 4 Гидроэлектростанция не загрязняет окружающую среду. 5 Будь осторожен с электричеством. Watch the video. Hydroelectric power Hydropower is a largely untapped source of energy that you can harness without producing harmful emissions. The Earth's atmosphere acts like an engine, doing all the work to move water up to feed rivers and streams. This water then flows back down, turning its potential energy into energy of motion. You can use this energy source by building a basic micro hydroelectric power plant. Things You'll Need: • Flowing water • Water channel • Water wheel • Pulley • Belt • Turbine • Rechargeable batteries Step 1 Determine if you have sufficient water flowing with sufficient strength. A lazy stream probably isn't worth your effort, but a rapidly flowing river or stream (especially one that has a good slope) may be suitable for a micro hydropower plant. Step 2 Build or install a water channel to direct part or all of the flowing water. The more sloped the water channel, the more power you can get out of the system. Step 3 Add the water wheel assembly. The flowing water forces the water wheel to turn, which spins a rod connected to a pulley. Step 4 Attach the pulley to a turbine with a belt. Choose the appropriate pulley size so as to ensure the correct rotation rate for the turbine. This rate determines the frequency of the power generated. Step 5 Connect the turbine to a battery or set of batteries. Make sure they're rechargeable batteries that are able to handle this type of application. Step 6 Wire the batteries to the power system of the house or building. Take appropriate precautions for dealing with electricity when you do this.
1 2 3 4 Read the text Answer the following questions. 1 What is hydro plant used for? 2 What condition helps you to get more power? 3 What determines the frequency of the power generated? 4 What is the function of batteries? 5 Does the hydroelectric power produce harmful emissions? Translate into English. 1 Вода вращает водное колесо. 2 Шкив прикреплён к турбине. 3 Батарея подключена к турбине. 4 Гидроэлектростанция не загрязняет окружающую среду. 5 Будь осторожен с электричеством. Watch the video. Hydroelectric power Hydropower is a largely untapped source of energy that you can harness without producing harmful emissions. The Earth's atmosphere acts like an engine, doing all the work to move water up to feed rivers and streams. This water then flows back down, turning its potential energy into energy of motion. You can use this energy source by building a basic micro hydroelectric power plant. Things You'll Need: • Flowing water • Water channel • Water wheel • Pulley • Belt • Turbine • Rechargeable batteries Step 1 Determine if you have sufficient water flowing with sufficient strength. A lazy stream probably isn't worth your effort, but a rapidly flowing river or stream (especially one that has a good slope) may be suitable for a micro hydropower plant. Step 2 Build or install a water channel to direct part or all of the flowing water. The more sloped the water channel, the more power you can get out of the system. Step 3 Add the water wheel assembly. The flowing water forces the water wheel to turn, which spins a rod connected to a pulley. Step 4 Attach the pulley to a turbine with a belt. Choose the appropriate pulley size so as to ensure the correct rotation rate for the turbine. This rate determines the frequency of the power generated. Step 5 Connect the turbine to a battery or set of batteries. Make sure they're rechargeable batteries that are able to handle this type of application. Step 6 Wire the batteries to the power system of the house or building. Take appropriate precautions for dealing with electricity when you do this.
 Sayano– Shushenskaya hydroelectric power station accident occurred on 17 August 2009(08: 13 AM local time), when an explosion brought down the ceiling of the station’s turbine hall, leading to the flooding of the turbine hall and engine room. Accident There was a loud bang from turbine № 2. The turbine cover shot up and the rotor with weight 920 tons also shot out of its seat. After this water spouted from the cavity of the turbine into the machinery hall. As a result, the machinery hall and rooms below its level were flooded. As of 9 September, 74 people were found dead while 1 person is listed as missing but probably also dead. On 19 August, the mourning day was announced in Khakassia. Rus. Hydro declared 25 August a day of mourning at the company. A festival in the city of Abakan on 22 August was canceled. Due to the accident, the town of Cheryomushki has banned Power supply the sale of strong alcoholic beverages. Power generation from the station ceased completely following the incident, with the resulting blackout in residential areas being alleviated by diverting power from other plants. Aluminium smelters in Sayanogorsk and Khakassia were completely cut off from the grid before power supplies were replaced using alternate power sources. Power to blacked out areas was fully restored by 19 August 2009. Although smelters continue to work at their normal rate, RUSAL warned that in the longer term it may lose up to 500, 000 tons of aluminum output due to the power shortage, and called for accelerating the construction of the Boguchany hydroelectric power station to replace lost generating capacity. It is expected that electricity prices will have to increase after the disaster. 1 The accident caused an oil spill, releasing at least 40 tonnes of transformer oil which spread over 80 km downstream of Yenisei. The oil spill during the approximately 2 -3 hour cutoff of river flow when all the Environmental impact gates of the dam were closed, killed 400 tons of cultivated trout in two riverside fisheries, with its impact on wildlife as yet unassessed. By 19: 00 local time on 19 August 2009, the 15 km-long spill had reached Ust-Abakan, where it was cordoned off with floating barriers and chemical sorbents. The oil spill was fully removed by 25 August 2009. The Russian government will pay compensation of 1 million rubles to the each victim's family, and 100, 000 rubles to each survivor, while Rus. Hydro will pay a further 1 million rubles in compensation. Compensation Questions: Who is the owner of this hydro power plant? What business suffered most? How many people were killed? Was there any environmental implication? What is the amount of financial help to every victim family? 2 Discuss: Can you live without electricity?
Sayano– Shushenskaya hydroelectric power station accident occurred on 17 August 2009(08: 13 AM local time), when an explosion brought down the ceiling of the station’s turbine hall, leading to the flooding of the turbine hall and engine room. Accident There was a loud bang from turbine № 2. The turbine cover shot up and the rotor with weight 920 tons also shot out of its seat. After this water spouted from the cavity of the turbine into the machinery hall. As a result, the machinery hall and rooms below its level were flooded. As of 9 September, 74 people were found dead while 1 person is listed as missing but probably also dead. On 19 August, the mourning day was announced in Khakassia. Rus. Hydro declared 25 August a day of mourning at the company. A festival in the city of Abakan on 22 August was canceled. Due to the accident, the town of Cheryomushki has banned Power supply the sale of strong alcoholic beverages. Power generation from the station ceased completely following the incident, with the resulting blackout in residential areas being alleviated by diverting power from other plants. Aluminium smelters in Sayanogorsk and Khakassia were completely cut off from the grid before power supplies were replaced using alternate power sources. Power to blacked out areas was fully restored by 19 August 2009. Although smelters continue to work at their normal rate, RUSAL warned that in the longer term it may lose up to 500, 000 tons of aluminum output due to the power shortage, and called for accelerating the construction of the Boguchany hydroelectric power station to replace lost generating capacity. It is expected that electricity prices will have to increase after the disaster. 1 The accident caused an oil spill, releasing at least 40 tonnes of transformer oil which spread over 80 km downstream of Yenisei. The oil spill during the approximately 2 -3 hour cutoff of river flow when all the Environmental impact gates of the dam were closed, killed 400 tons of cultivated trout in two riverside fisheries, with its impact on wildlife as yet unassessed. By 19: 00 local time on 19 August 2009, the 15 km-long spill had reached Ust-Abakan, where it was cordoned off with floating barriers and chemical sorbents. The oil spill was fully removed by 25 August 2009. The Russian government will pay compensation of 1 million rubles to the each victim's family, and 100, 000 rubles to each survivor, while Rus. Hydro will pay a further 1 million rubles in compensation. Compensation Questions: Who is the owner of this hydro power plant? What business suffered most? How many people were killed? Was there any environmental implication? What is the amount of financial help to every victim family? 2 Discuss: Can you live without electricity?
 Micro Hydro Power Plant Micro hydro power is probably the least common of the three readily used renewable energy sources, but it has the potential to produce the most power, more reliably than solar or wind power if you have the right site. This means having access to a river or creek that has a high enough flow to produce useable power for a good part of the year. Many creeks and rivers are permanent, ie, they never dry up, and these are the most suitable for micro-hydro power production. A micro hydro turbine can take several forms, the most widely recognized of which would be the water wheel, used extensively for grain grinding up until this century. Waterwheels are still used in some situations that do not require a fast-spinning turbine, such as for pumping water. However, other type of turbines have become quite common. The most common of these newer turbines is the Pelton wheel, which is basically a series of cups attached to a hub. A jet of water is aimed at the cups, and the resulting force on the cups causes the turbine to spin. Other types of turbines include the Turgo, Crossflow and various axial flow turbines, where the shaft through the center of the turbine runs in the same direction as the water flow, much like a boat propeller Water turbines have many advantages over solar panels or wind turbines, the most obvious of which is that they produce power continuously, 24 hours per day. However, they also have some associated problems or requirements. The most important of these is correct sitting of the turbine and associated equipment so as to cause the least environmental damage as possible. Placing a large concrete dam across a creek or river can do considerable damage to the surrounding ecology. A general rule of thumb is to not divert more than 20% of the water flow of the creek through your turbine, and to return any diverted water back to the creek just below the turbine. Answer the questions to the text: 1) Why do people build dams across a river? 2) What advantages has the hydro power over the solar and wind power plant ? 3) What is the necessary condition for hydro power plant? 4) What is the most important rule for the hydro power plant using? Translate into English: 1)Микро гидроэнергетика имеет большой потенциал 2)Водяные колеса используются для вращения турбины 3) Струя воды вращает колесо 4)Гидростанция работает 24 часа в сутки 5)Сколько ГЭС в Удмуртии?
Micro Hydro Power Plant Micro hydro power is probably the least common of the three readily used renewable energy sources, but it has the potential to produce the most power, more reliably than solar or wind power if you have the right site. This means having access to a river or creek that has a high enough flow to produce useable power for a good part of the year. Many creeks and rivers are permanent, ie, they never dry up, and these are the most suitable for micro-hydro power production. A micro hydro turbine can take several forms, the most widely recognized of which would be the water wheel, used extensively for grain grinding up until this century. Waterwheels are still used in some situations that do not require a fast-spinning turbine, such as for pumping water. However, other type of turbines have become quite common. The most common of these newer turbines is the Pelton wheel, which is basically a series of cups attached to a hub. A jet of water is aimed at the cups, and the resulting force on the cups causes the turbine to spin. Other types of turbines include the Turgo, Crossflow and various axial flow turbines, where the shaft through the center of the turbine runs in the same direction as the water flow, much like a boat propeller Water turbines have many advantages over solar panels or wind turbines, the most obvious of which is that they produce power continuously, 24 hours per day. However, they also have some associated problems or requirements. The most important of these is correct sitting of the turbine and associated equipment so as to cause the least environmental damage as possible. Placing a large concrete dam across a creek or river can do considerable damage to the surrounding ecology. A general rule of thumb is to not divert more than 20% of the water flow of the creek through your turbine, and to return any diverted water back to the creek just below the turbine. Answer the questions to the text: 1) Why do people build dams across a river? 2) What advantages has the hydro power over the solar and wind power plant ? 3) What is the necessary condition for hydro power plant? 4) What is the most important rule for the hydro power plant using? Translate into English: 1)Микро гидроэнергетика имеет большой потенциал 2)Водяные колеса используются для вращения турбины 3) Струя воды вращает колесо 4)Гидростанция работает 24 часа в сутки 5)Сколько ГЭС в Удмуртии?
 1 Read the advertisement about micro hydro power plant and find the factual information and an opinion. The water motor The Campo Nuevo Water motor is the only modern turbine designed to drive common machines directly with waterpower. It converts waterpower directly into mechanical power at a highly efficient 80 -85%. 2 Discuss with a partner. 1 Would you build a micro hydro power plant yourself? 2 What are the necessary things for that? 3 Is there a brook or a river in the place you live? 4 What is more profitable hydro or wind power plant? 5 If you started production of your own micro hydro power plants would it be marketable? 3 Watch the video. The Water motor has a patented switch that allows instant on/off power control. This unique feature makes it practical and safe to run machines directly with waterpower. The combination of high efficiency and power control makes it possible to use much smaller waterpower sources than ever before. Although water-power has been in use for thousands of years, with the Water motor small scale waterpower has become a vast new natural energy resource. Most of the common machines used in workshops, industry, and farms are driven by motors of only 4. 5 - 5 horsepower. The Water motor will produce this amount of power at an extremely low cost and with a minimum of ecological disruption.
1 Read the advertisement about micro hydro power plant and find the factual information and an opinion. The water motor The Campo Nuevo Water motor is the only modern turbine designed to drive common machines directly with waterpower. It converts waterpower directly into mechanical power at a highly efficient 80 -85%. 2 Discuss with a partner. 1 Would you build a micro hydro power plant yourself? 2 What are the necessary things for that? 3 Is there a brook or a river in the place you live? 4 What is more profitable hydro or wind power plant? 5 If you started production of your own micro hydro power plants would it be marketable? 3 Watch the video. The Water motor has a patented switch that allows instant on/off power control. This unique feature makes it practical and safe to run machines directly with waterpower. The combination of high efficiency and power control makes it possible to use much smaller waterpower sources than ever before. Although water-power has been in use for thousands of years, with the Water motor small scale waterpower has become a vast new natural energy resource. Most of the common machines used in workshops, industry, and farms are driven by motors of only 4. 5 - 5 horsepower. The Water motor will produce this amount of power at an extremely low cost and with a minimum of ecological disruption.
 Types of Hydropower Plants Most hydropower plants are conventional in design, meaning they use one-way water flow to generate electricity. There are two categories of conventional plants, run-of-river and storage plants. Run-of-river plants—These plants use little, if any, stored water to provide water flow through the turbines. Although some plants store a day or week's worth of water, weather changes—especially seasonal changes—cause runof-river plants to experience significant fluctuations in power output. Storage plants—These plants have enough storage capacity to off-set seasonal fluctuations in water flow and provide a constant supply of electricity throughout the year. Large dams can store several years worth of water. Pumped Storage In contrast to conventional hydropower plants, pumped storage plants reuse water. After water initially produces electricity, it flows from the turbines into a lower reservoir located below the dam. During off-peak hours (periods of low energy demand), some of the water is pumped into an upper reservoir and reused during periods of peakdemand. Building Hydropower Plants Most hydropower plants are built through federal or local agencies as part of a multipurpose project. In addition to generating electricity, dams and reservoirs provide flood control, water supply, irrigation, transportation, recreation and refuges for fish and birds. Private utilities also build hydropower plants, although not as many as government agencies. Hydropower is a clean, domestic and renewable source of energy. Hydropower plants provide inexpensive electricity and produce no pollution. And, unlike other energy sources such as fossil fuels, water is not destroyed during the production of electricity—it can be reused for other purposes. Hydropower plants can significantly impact the surrounding area—reservoirs can cover towns, scenic locations and farmland, as well as affect fish and wildlife habitat. To mitigate impact on migration patterns and wildlife habitats, dams maintain a steady stream flow and can be designed or retrofitted with fish ladders and fish ways to help fish migrate upstream to spawn. The best sites for hydroelectric plants are swift-flowing rivers or steams, mountainous regions and areas with heavy rainfall. Only 20 percent of potential U. S. hydro-power has been developed, but unfavorable terrain and environmental concerns make many sites unsuitable for hydropower plants. However, since only 2, 400 of the nation's 80, 000 dams are currently used for hydropower, new projects do not necessarily require building new dams—many existing dams can be retrofitted to produce electricity. At existing hydropower plants, advanced technologies can be installed to increase efficiently and energy production. 1. Answer the questions. 1)What types of hydro power plants do you know? 2)What are the benefits of hydro power plants? 3)Have you ever been to the hydro power plant? 4)What is the difference between conventional hydro power plant and pumped one? 5)Is there a way to help fish to migrate upstream through the hydro power plant constructions? 2. Translate into English. 1)Большая ГЭС может вырабатывать до 10000 мегаватт электричества. 2)Рыбе трудно перебраться через платину. 3)Дамбы служат для хранения воды. 4)ГЭС может служить для разведения рыбы. 5)Микро ГЭС можно построить самому. 3. Watch the video.
Types of Hydropower Plants Most hydropower plants are conventional in design, meaning they use one-way water flow to generate electricity. There are two categories of conventional plants, run-of-river and storage plants. Run-of-river plants—These plants use little, if any, stored water to provide water flow through the turbines. Although some plants store a day or week's worth of water, weather changes—especially seasonal changes—cause runof-river plants to experience significant fluctuations in power output. Storage plants—These plants have enough storage capacity to off-set seasonal fluctuations in water flow and provide a constant supply of electricity throughout the year. Large dams can store several years worth of water. Pumped Storage In contrast to conventional hydropower plants, pumped storage plants reuse water. After water initially produces electricity, it flows from the turbines into a lower reservoir located below the dam. During off-peak hours (periods of low energy demand), some of the water is pumped into an upper reservoir and reused during periods of peakdemand. Building Hydropower Plants Most hydropower plants are built through federal or local agencies as part of a multipurpose project. In addition to generating electricity, dams and reservoirs provide flood control, water supply, irrigation, transportation, recreation and refuges for fish and birds. Private utilities also build hydropower plants, although not as many as government agencies. Hydropower is a clean, domestic and renewable source of energy. Hydropower plants provide inexpensive electricity and produce no pollution. And, unlike other energy sources such as fossil fuels, water is not destroyed during the production of electricity—it can be reused for other purposes. Hydropower plants can significantly impact the surrounding area—reservoirs can cover towns, scenic locations and farmland, as well as affect fish and wildlife habitat. To mitigate impact on migration patterns and wildlife habitats, dams maintain a steady stream flow and can be designed or retrofitted with fish ladders and fish ways to help fish migrate upstream to spawn. The best sites for hydroelectric plants are swift-flowing rivers or steams, mountainous regions and areas with heavy rainfall. Only 20 percent of potential U. S. hydro-power has been developed, but unfavorable terrain and environmental concerns make many sites unsuitable for hydropower plants. However, since only 2, 400 of the nation's 80, 000 dams are currently used for hydropower, new projects do not necessarily require building new dams—many existing dams can be retrofitted to produce electricity. At existing hydropower plants, advanced technologies can be installed to increase efficiently and energy production. 1. Answer the questions. 1)What types of hydro power plants do you know? 2)What are the benefits of hydro power plants? 3)Have you ever been to the hydro power plant? 4)What is the difference between conventional hydro power plant and pumped one? 5)Is there a way to help fish to migrate upstream through the hydro power plant constructions? 2. Translate into English. 1)Большая ГЭС может вырабатывать до 10000 мегаватт электричества. 2)Рыбе трудно перебраться через платину. 3)Дамбы служат для хранения воды. 4)ГЭС может служить для разведения рыбы. 5)Микро ГЭС можно построить самому. 3. Watch the video.
 End of Hydro Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
End of Hydro Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
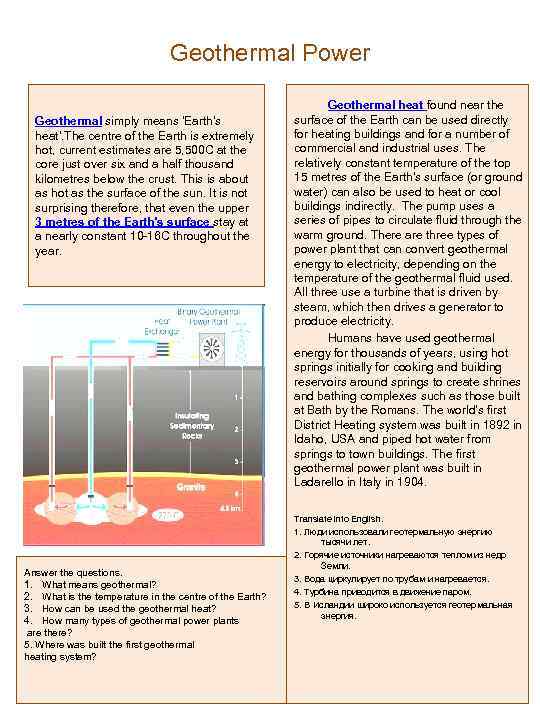 Geothermal Power Geothermal simply means 'Earth's heat'. The centre of the Earth is extremely hot, current estimates are 5, 500 C at the core just over six and a half thousand kilometres below the crust. This is about as hot as the surface of the sun. It is not surprising therefore, that even the upper 3 metres of the Earth's surface stay at a nearly constant 10 -16 C throughout the year. Geothermal simply means 'Earth's heat'. The centre of the Earth is extremely hot, current estimates are 5, 500 C at the core just over six and a half thousand kilometres below the crust. This is about as hot as the surface of the sun. It is not surprising therefore, that even the upper 3 metres of the Earth's surface stay at a nearly constant 10 -16 C throughout the year. Answer the questions. 1. What means geothermal? 2. What is the temperature in the centre of the Earth? 3. How can be used the geothermal heat? 4. How many types of geothermal power plants are there? 5. Where was built the first geothermal heating system? Geothermal heat found near the surface of the Earth can be used directly for heating buildings and for a number of commercial and industrial uses. The relatively constant temperature of the top 15 metres of the Earth's surface (or ground water) can also be used to heat or cool buildings indirectly. The pump uses a series of pipes to circulate fluid through the warm ground. There are three types of power plant that can convert geothermal energy to electricity, depending on the temperature of the geothermal fluid used. All three use a turbine that is driven by steam, which then drives a generator to produce electricity. Humans have used geothermal energy for thousands of years, using hot springs initially for cooking and building reservoirs around springs to create shrines and bathing complexes such as those built at Bath by the Romans. The world's first District Heating system was built in 1892 in Idaho, USA and piped hot water from springs to town buildings. The first geothermal power plant was built in Ladarello in Italy in 1904. Translate into English. 1. Люди использовали геотермальную энергию тысячи лет. 2. Горячие источники нагреваются теплом из недр Земли. 3. Вода циркулирует по трубам и нагревается. 4. Турбина приводится в движение паром. 5. В Исландии широко используется геотермальная энергия.
Geothermal Power Geothermal simply means 'Earth's heat'. The centre of the Earth is extremely hot, current estimates are 5, 500 C at the core just over six and a half thousand kilometres below the crust. This is about as hot as the surface of the sun. It is not surprising therefore, that even the upper 3 metres of the Earth's surface stay at a nearly constant 10 -16 C throughout the year. Geothermal simply means 'Earth's heat'. The centre of the Earth is extremely hot, current estimates are 5, 500 C at the core just over six and a half thousand kilometres below the crust. This is about as hot as the surface of the sun. It is not surprising therefore, that even the upper 3 metres of the Earth's surface stay at a nearly constant 10 -16 C throughout the year. Answer the questions. 1. What means geothermal? 2. What is the temperature in the centre of the Earth? 3. How can be used the geothermal heat? 4. How many types of geothermal power plants are there? 5. Where was built the first geothermal heating system? Geothermal heat found near the surface of the Earth can be used directly for heating buildings and for a number of commercial and industrial uses. The relatively constant temperature of the top 15 metres of the Earth's surface (or ground water) can also be used to heat or cool buildings indirectly. The pump uses a series of pipes to circulate fluid through the warm ground. There are three types of power plant that can convert geothermal energy to electricity, depending on the temperature of the geothermal fluid used. All three use a turbine that is driven by steam, which then drives a generator to produce electricity. Humans have used geothermal energy for thousands of years, using hot springs initially for cooking and building reservoirs around springs to create shrines and bathing complexes such as those built at Bath by the Romans. The world's first District Heating system was built in 1892 in Idaho, USA and piped hot water from springs to town buildings. The first geothermal power plant was built in Ladarello in Italy in 1904. Translate into English. 1. Люди использовали геотермальную энергию тысячи лет. 2. Горячие источники нагреваются теплом из недр Земли. 3. Вода циркулирует по трубам и нагревается. 4. Турбина приводится в движение паром. 5. В Исландии широко используется геотермальная энергия.
 Geothermal Basics What Is Geothermal Energy? The word geothermal comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). So, geothermal energy is heat from within the Earth. We can recover this heat as steam or hot water and use it to heat buildings or generate electricity. Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source because the heat is continuously produced inside the Earth. Geothermal energy is generated in the Earth's core. Temperatures hotter than the sun's surface are continuously produced inside the Earth by the slow decay of radioactive particles, a process that happens in all rocks. Earth has a number of different layers: • The core itself has two layers: a solid iron core and an outer core made of very hot melted rock, called magma. core and is about 1, 800 miles thick. It is made up of magma and rock. • The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth, the land that forms the continents and ocean floors. It can be 3 to 5 miles thick under the oceans and 15 to 35 miles thick on the continents. The Earth's crust is broken into pieces called plates. Magma comes close to the Earth's surface near the edges of these plates. This is where volcanoes occur. The lava that erupts from volcanoes is partly magma. Deep underground, the rocks and water absorb the heat from this magma. The temperature of the rocks and water gets hotter and hotter as you go deeper underground. People around the world use geothermal energy to heat their homes and to produce electricity by digging deep wells and pumping the heated underground water or steam to the surface. We can also make use of the stable temperatures near the surface of the Earth to heat and cool buildings. Answer the questions to the text: Translate into English: 1) What is geothermal energy? 2) Where do volcanos occur? 3) What is the fire ring? 4) What are the core's layers? 5) What is the depth of the crust? 1)Магма находится глубоко внизу 2)Геотермальная энергия используется для обогрева домов и выработки электричества 3)Подземная вода нагревает пар 4)Ядро состоит из двух слоев. 5)Геотермальная энергия-это возобновляемый источник энергии
Geothermal Basics What Is Geothermal Energy? The word geothermal comes from the Greek words geo (earth) and therme (heat). So, geothermal energy is heat from within the Earth. We can recover this heat as steam or hot water and use it to heat buildings or generate electricity. Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source because the heat is continuously produced inside the Earth. Geothermal energy is generated in the Earth's core. Temperatures hotter than the sun's surface are continuously produced inside the Earth by the slow decay of radioactive particles, a process that happens in all rocks. Earth has a number of different layers: • The core itself has two layers: a solid iron core and an outer core made of very hot melted rock, called magma. core and is about 1, 800 miles thick. It is made up of magma and rock. • The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth, the land that forms the continents and ocean floors. It can be 3 to 5 miles thick under the oceans and 15 to 35 miles thick on the continents. The Earth's crust is broken into pieces called plates. Magma comes close to the Earth's surface near the edges of these plates. This is where volcanoes occur. The lava that erupts from volcanoes is partly magma. Deep underground, the rocks and water absorb the heat from this magma. The temperature of the rocks and water gets hotter and hotter as you go deeper underground. People around the world use geothermal energy to heat their homes and to produce electricity by digging deep wells and pumping the heated underground water or steam to the surface. We can also make use of the stable temperatures near the surface of the Earth to heat and cool buildings. Answer the questions to the text: Translate into English: 1) What is geothermal energy? 2) Where do volcanos occur? 3) What is the fire ring? 4) What are the core's layers? 5) What is the depth of the crust? 1)Магма находится глубоко внизу 2)Геотермальная энергия используется для обогрева домов и выработки электричества 3)Подземная вода нагревает пар 4)Ядро состоит из двух слоев. 5)Геотермальная энергия-это возобновляемый источник энергии
 Where Geothermal Energy is Found The ring of fire goes around the edges of the Pacific. The map shows that volcanic activity occurs around the Pacific rim. Naturally occurring large areas of hydrothermal resources are called geothermal reservoirs. Most geothermal reservoirs are deep underground with no visible clues showing above ground. But geothermal energy sometimes finds its way to the surface in the form of: volcanoes and fumaroles, hot springs, geysers. Watch the video about geothermal plant in Nicaragua. Most Geothermal Resources Are Near Plate Boundaries The most active geothermal resources are usually found along major plate boundaries where earthquakes and volcanoes are concentrated. Most of the geothermal activity in the world occurs in an area called the Ring of Fire. This area encircles the Pacific Ocean. When magma comes close to the surface, it heats ground water found trapped in porous rock or water running along fractured rock surfaces and faults. These features are called hydrothermal. They have two common ingredients: water (hydro) and heat(thermal). Geologists use various methods to look for geothermal reservoirs. Drilling a well and testing the temperature deep underground is the most reliable method for finding a geothermal reservoir. U. S. Geothermal Is Mostly in the West Most of the geothermal reservoirs in the United States are located in the western States and Hawaii. California generates the most electricity from geothermal energy. "The Geysers" dry steam reservoir in northern California is the largest known dry steam field in the world and has been producing electricity since 1960. Answer the questions to the text: Translate into English: 1) Why does volcanic activity occur at the fire ring? 2) What are the forms of geothermal energy? 3) What does hydrothermal mean? 4) What is the most common source of electricity in California? 5) What is the way of locating of a geothermal reservoir? 1)Самые активные геотермальные ресурсы находятся там, где вулканы и землетрясения сконцентрированы. 2)Магма находится близко к поверхности 3)Калифорния производит электричество 4)Подземная вода нагревает пар 5)Вода испаряется
Where Geothermal Energy is Found The ring of fire goes around the edges of the Pacific. The map shows that volcanic activity occurs around the Pacific rim. Naturally occurring large areas of hydrothermal resources are called geothermal reservoirs. Most geothermal reservoirs are deep underground with no visible clues showing above ground. But geothermal energy sometimes finds its way to the surface in the form of: volcanoes and fumaroles, hot springs, geysers. Watch the video about geothermal plant in Nicaragua. Most Geothermal Resources Are Near Plate Boundaries The most active geothermal resources are usually found along major plate boundaries where earthquakes and volcanoes are concentrated. Most of the geothermal activity in the world occurs in an area called the Ring of Fire. This area encircles the Pacific Ocean. When magma comes close to the surface, it heats ground water found trapped in porous rock or water running along fractured rock surfaces and faults. These features are called hydrothermal. They have two common ingredients: water (hydro) and heat(thermal). Geologists use various methods to look for geothermal reservoirs. Drilling a well and testing the temperature deep underground is the most reliable method for finding a geothermal reservoir. U. S. Geothermal Is Mostly in the West Most of the geothermal reservoirs in the United States are located in the western States and Hawaii. California generates the most electricity from geothermal energy. "The Geysers" dry steam reservoir in northern California is the largest known dry steam field in the world and has been producing electricity since 1960. Answer the questions to the text: Translate into English: 1) Why does volcanic activity occur at the fire ring? 2) What are the forms of geothermal energy? 3) What does hydrothermal mean? 4) What is the most common source of electricity in California? 5) What is the way of locating of a geothermal reservoir? 1)Самые активные геотермальные ресурсы находятся там, где вулканы и землетрясения сконцентрированы. 2)Магма находится близко к поверхности 3)Калифорния производит электричество 4)Подземная вода нагревает пар 5)Вода испаряется
 Geothermal Energy & the Environment Read the text and answer the questions. • Do geothermal power plants turn fuel to generate electricity? • Is there any CO 2 emission from geothermal power plant? • Are geothermal power plants harmful for environment? • What is the most famous geyser park in USA? • Is there a famous geyser park in Russia? Yellowstone National Park Geothermal power plants do not burn fuel to generate electricity, so their emission levels are very low. They release less than 1% of the carbon dioxide emissions of a fossil fuel plant. Geothermal plants use scrubber systems to clean the air of hydrogen sulfide that is naturally found in the steam and hot water. The environmental impact of geothermal energy depends on how it is being used. Direct use and heating applications have almost no negative impact on the environment. Geothermal plants emit 97% less acid rain-causing sulfur compounds than are emitted by fossil fuel plants. After the steam and water from a geothermal reservoir have been used, they are injected back into the Earth. Geothermal features in national parks, such as geysers and fumaroles in Yellowstone National Park, are protected by law, to prevent them from being disturbed. Translate into English: • Геотермальные электростанции не загрязняют окружающую среду. • Есть ли негативное влияние на окружающую среду от геотермальных электростанций? • В России нет геотермальной электростанции. • Геотермальная станция производит электричество, используя энергию Земли. • На Камчатке есть гейзеры.
Geothermal Energy & the Environment Read the text and answer the questions. • Do geothermal power plants turn fuel to generate electricity? • Is there any CO 2 emission from geothermal power plant? • Are geothermal power plants harmful for environment? • What is the most famous geyser park in USA? • Is there a famous geyser park in Russia? Yellowstone National Park Geothermal power plants do not burn fuel to generate electricity, so their emission levels are very low. They release less than 1% of the carbon dioxide emissions of a fossil fuel plant. Geothermal plants use scrubber systems to clean the air of hydrogen sulfide that is naturally found in the steam and hot water. The environmental impact of geothermal energy depends on how it is being used. Direct use and heating applications have almost no negative impact on the environment. Geothermal plants emit 97% less acid rain-causing sulfur compounds than are emitted by fossil fuel plants. After the steam and water from a geothermal reservoir have been used, they are injected back into the Earth. Geothermal features in national parks, such as geysers and fumaroles in Yellowstone National Park, are protected by law, to prevent them from being disturbed. Translate into English: • Геотермальные электростанции не загрязняют окружающую среду. • Есть ли негативное влияние на окружающую среду от геотермальных электростанций? • В России нет геотермальной электростанции. • Геотермальная станция производит электричество, используя энергию Земли. • На Камчатке есть гейзеры.
 Wave power 1. Read the text. Wave power is the energy that could be generated using the power of the waves. The energy that the waves have or produce is converted into other forms of energy such as electricity. Wave energy is a renewable source of energy. Wave energy can be efficiently used for electricity generation. There are four very important factors that should be considered in choosing a place that is suitable for the installation of a wave farm: they are wave height, wave speed, wave length, and water density. First of all, the waves that will be used in the conversion should be of proper height. The same principle applies with wave speed and wave length. The longer the waves, the faster they could get. The faster the waves are, the more energy they could produce. On the matter of water density, the denser the water, the more buoyant force the buoys will experience. A good and effective wave farm should also be located near a place that is ready to receive and utilize the electricity it could generate. Otherwise, there would be no use for the electricity generated. 2. Answer the questions. -What is the wave power? -Is it renewable energy? -What are the most important factors for wave power plant installation? -Is it possible to make wave power farm in local lake?
Wave power 1. Read the text. Wave power is the energy that could be generated using the power of the waves. The energy that the waves have or produce is converted into other forms of energy such as electricity. Wave energy is a renewable source of energy. Wave energy can be efficiently used for electricity generation. There are four very important factors that should be considered in choosing a place that is suitable for the installation of a wave farm: they are wave height, wave speed, wave length, and water density. First of all, the waves that will be used in the conversion should be of proper height. The same principle applies with wave speed and wave length. The longer the waves, the faster they could get. The faster the waves are, the more energy they could produce. On the matter of water density, the denser the water, the more buoyant force the buoys will experience. A good and effective wave farm should also be located near a place that is ready to receive and utilize the electricity it could generate. Otherwise, there would be no use for the electricity generated. 2. Answer the questions. -What is the wave power? -Is it renewable energy? -What are the most important factors for wave power plant installation? -Is it possible to make wave power farm in local lake?
 End of Geothermal Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
End of Geothermal Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
 Fossil fuel power plant Read the text. Mohave Power Station, a 1, 580 MW coal power plant near Laughlin. Nevada, out of service since 2005 due to environmental restrictions. A fossil-fuel power plant is a power plant that burns fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas or petroleum (oil) to produce electricity. Fossil-fuel power plants are designed on a large scale for continuous operation. In many countries, such plants provide most of the electrical energy used. Fossil fuel power plants have some kind of rotating machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operate an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small isolated plants, a reciprocating internal combustion engine. Some thermal plants have the intermediate step of using the heat from combustion to produce steam, reducing overall efficiency of electricity production. All plants use the drop between the high pressure and temperature of the steam or combusting fuel and the lower pressure of the atmosphere or condensing vapor in the steam turbine. What do you think about global warming. Is it truth or myth? Byproducts of power thermal plant operation need to be considered in both the design and operation. Waste heat due to the finite efficiency of the power cycle, when not recovered and sold as steam or hot water, must be released to the atmosphere, often using a cooling tower, or river or lake water as a cooling medium, especially for condensing steam. The flue gas from combustion of the fossil fuels is discharged to the air; this contains carbon dioxide and water vapor, as well as other substances such as nitrogen, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and (in the case of coal-fired plants) fly ash and mercury. Solid waste ash from coal-fired boilers must also be removed, although some coal ash can be recycled for building materials. Fossil fueled power stations are major emitters of greenhouse gases (GHG) which according to the consensus of scientific organizations are a major contributor to the global warming observed over the last 100 years. Brown coal emits 3 times as much GHG as natural gas, black coal emits twice as much. Efforts exist to use carbon capture and storage of emissions but these are not expected to be available on a commercial scale and economically viable basis by 2025. Answer the questions. 1. What is the fossil fuel? 2. What fuel contributes more to GHG? 3. What are the substances of gas emition? 4. What is the main produce of thermal plant? 5. What are the byproducts of thermal plants? 6. What does fossil fuel power plant use for its work? 7. What heats the water? 8. How do they cool the steam? 9. What does pulverizer do?
Fossil fuel power plant Read the text. Mohave Power Station, a 1, 580 MW coal power plant near Laughlin. Nevada, out of service since 2005 due to environmental restrictions. A fossil-fuel power plant is a power plant that burns fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas or petroleum (oil) to produce electricity. Fossil-fuel power plants are designed on a large scale for continuous operation. In many countries, such plants provide most of the electrical energy used. Fossil fuel power plants have some kind of rotating machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operate an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small isolated plants, a reciprocating internal combustion engine. Some thermal plants have the intermediate step of using the heat from combustion to produce steam, reducing overall efficiency of electricity production. All plants use the drop between the high pressure and temperature of the steam or combusting fuel and the lower pressure of the atmosphere or condensing vapor in the steam turbine. What do you think about global warming. Is it truth or myth? Byproducts of power thermal plant operation need to be considered in both the design and operation. Waste heat due to the finite efficiency of the power cycle, when not recovered and sold as steam or hot water, must be released to the atmosphere, often using a cooling tower, or river or lake water as a cooling medium, especially for condensing steam. The flue gas from combustion of the fossil fuels is discharged to the air; this contains carbon dioxide and water vapor, as well as other substances such as nitrogen, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and (in the case of coal-fired plants) fly ash and mercury. Solid waste ash from coal-fired boilers must also be removed, although some coal ash can be recycled for building materials. Fossil fueled power stations are major emitters of greenhouse gases (GHG) which according to the consensus of scientific organizations are a major contributor to the global warming observed over the last 100 years. Brown coal emits 3 times as much GHG as natural gas, black coal emits twice as much. Efforts exist to use carbon capture and storage of emissions but these are not expected to be available on a commercial scale and economically viable basis by 2025. Answer the questions. 1. What is the fossil fuel? 2. What fuel contributes more to GHG? 3. What are the substances of gas emition? 4. What is the main produce of thermal plant? 5. What are the byproducts of thermal plants? 6. What does fossil fuel power plant use for its work? 7. What heats the water? 8. How do they cool the steam? 9. What does pulverizer do?
 Fossil Fuel Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and natural gas, are non-renewable sources of energy. Dominion's fossil-fueled power stations generate more than 40 percent of the power provided to its customers. Advanced technologies, top-quality training and a dedicated workforce are the keys to being a pacesetter in fossil-fuel generation. Since coal-fired power stations produce gases and airborne particles known as fly ash, Dominion has a comprehensive approach to protecting the environment. Its power stations use a variety of techniques to reduce harmful emissions, including electrostatic precipitators and systems that reduce nitrogen oxide, such as selective catalytic reduction. The coal (or oil or gas) is burned in a furnace. The furnace heats water in a boiler. This generates super heated steam that turns turbines. The steam is then cooled in cooling towers and condensed back into water to be returned to the boiler, reducing heat loss as much as possible. Some steam has to be released in the cooling process; that’s the source of those big white clouds coming out of the power station cooling towers. Here’s a picture of the process: Fossil fuel power plants produce the electricity which is the lifeblood of the developed nation, and we all rely heavily on it in our daily lives. The majority of current power stations run on fossil fuels. While solar energy power stations are being developed around the world on commercial scales, it is true to say that over 70% of every developed nation’s energy comes from fossil fuel electricity generation. In Australia, over 90% of our electricity is sourced in this way. We can reduce the amount of pollution from the power stations by using less electricity. While we are still operating the majority of our power stations as fossil fuel power plants this is crucial; lower energy demands mean less pollution.
Fossil Fuel Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and natural gas, are non-renewable sources of energy. Dominion's fossil-fueled power stations generate more than 40 percent of the power provided to its customers. Advanced technologies, top-quality training and a dedicated workforce are the keys to being a pacesetter in fossil-fuel generation. Since coal-fired power stations produce gases and airborne particles known as fly ash, Dominion has a comprehensive approach to protecting the environment. Its power stations use a variety of techniques to reduce harmful emissions, including electrostatic precipitators and systems that reduce nitrogen oxide, such as selective catalytic reduction. The coal (or oil or gas) is burned in a furnace. The furnace heats water in a boiler. This generates super heated steam that turns turbines. The steam is then cooled in cooling towers and condensed back into water to be returned to the boiler, reducing heat loss as much as possible. Some steam has to be released in the cooling process; that’s the source of those big white clouds coming out of the power station cooling towers. Here’s a picture of the process: Fossil fuel power plants produce the electricity which is the lifeblood of the developed nation, and we all rely heavily on it in our daily lives. The majority of current power stations run on fossil fuels. While solar energy power stations are being developed around the world on commercial scales, it is true to say that over 70% of every developed nation’s energy comes from fossil fuel electricity generation. In Australia, over 90% of our electricity is sourced in this way. We can reduce the amount of pollution from the power stations by using less electricity. While we are still operating the majority of our power stations as fossil fuel power plants this is crucial; lower energy demands mean less pollution.
 End of Fossil Fuel Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
End of Fossil Fuel Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
 The Nuclear Fission Power Plant Fuel Assembly Containing a Number of Fuel Rods A typical nuclear reactor has a few main parts. Inside the "core" where the nuclear reactions take place are the fuel rods and assemblies, the control rods, the moderator, and the coolant. Outside the core are the turbines, the heat exchanger, and part of the cooling system. The fuel assemblies are collections of fuel rods. These rods are each about 3. 5 meters (11. 48 feet) long. They are each about a centimeter in diameter. These are grouped into large bundles of a couple hundred rods called fuel assemblies, which are then placed in the reactor core. Inside each fuel rod are hundreds of pellets of uranium fuel stacked end to end. Another component of the reactor is the moderator. The moderator serves to slow down the high speed neutrons "flying" all around the reactor core. If a neutron is moving too fast, and thus is at a high-energy state, it passes right through the 235 U nucleus. It must be slowed down to be captured by the nucleus and to induce fission. The most common moderator is water, but sometimes it can be another material. The job of the coolant is to absorb the heat from the reaction. The most common coolant used in nuclear power plants today is water. In actuality, in many reactor designs the coolant and the moderator are one and the same. The coolant water is heated by the nuclear reactions going on inside the core. However, this heated water does not boil because it is kept at an extremely intense pressure, thus raising its boiling point above the normal 100° Celsius. The heated water rises up and passes through another part of the reactor, the heat exchanger. The moderator/coolant water is radioactive, so it can not leave the inner reactor containment. Its heat must be transferred to non-radioactive water, which can then be sent out of the reactor shielding. This is done through the heat exchanger, which works by moving the radioactive water through a series of pipes that are wrapped around other pipes. The metallic pipes conduct the heat from the moderator to the normal water. After the hot water has passed through the turbine, some of its energy is changed into electricity. However, the water is still very hot. It must be cooled somehow. Many nuclear power plants used steam towers to cool this water with air. These are generally the buildings that people associate with nuclear power plants. At reactors that do not have towers, the clean water is purified and dumped into the nearest body of water, and cool water is pumped in to replace it. Answer the questions: 1)What are the main parts of nuclear reactor? 2)What is the most common coolant? 3)How do they cool the water? 4)What is used to raise the boiling point of water& 5)What is the boiling point of water?
The Nuclear Fission Power Plant Fuel Assembly Containing a Number of Fuel Rods A typical nuclear reactor has a few main parts. Inside the "core" where the nuclear reactions take place are the fuel rods and assemblies, the control rods, the moderator, and the coolant. Outside the core are the turbines, the heat exchanger, and part of the cooling system. The fuel assemblies are collections of fuel rods. These rods are each about 3. 5 meters (11. 48 feet) long. They are each about a centimeter in diameter. These are grouped into large bundles of a couple hundred rods called fuel assemblies, which are then placed in the reactor core. Inside each fuel rod are hundreds of pellets of uranium fuel stacked end to end. Another component of the reactor is the moderator. The moderator serves to slow down the high speed neutrons "flying" all around the reactor core. If a neutron is moving too fast, and thus is at a high-energy state, it passes right through the 235 U nucleus. It must be slowed down to be captured by the nucleus and to induce fission. The most common moderator is water, but sometimes it can be another material. The job of the coolant is to absorb the heat from the reaction. The most common coolant used in nuclear power plants today is water. In actuality, in many reactor designs the coolant and the moderator are one and the same. The coolant water is heated by the nuclear reactions going on inside the core. However, this heated water does not boil because it is kept at an extremely intense pressure, thus raising its boiling point above the normal 100° Celsius. The heated water rises up and passes through another part of the reactor, the heat exchanger. The moderator/coolant water is radioactive, so it can not leave the inner reactor containment. Its heat must be transferred to non-radioactive water, which can then be sent out of the reactor shielding. This is done through the heat exchanger, which works by moving the radioactive water through a series of pipes that are wrapped around other pipes. The metallic pipes conduct the heat from the moderator to the normal water. After the hot water has passed through the turbine, some of its energy is changed into electricity. However, the water is still very hot. It must be cooled somehow. Many nuclear power plants used steam towers to cool this water with air. These are generally the buildings that people associate with nuclear power plants. At reactors that do not have towers, the clean water is purified and dumped into the nearest body of water, and cool water is pumped in to replace it. Answer the questions: 1)What are the main parts of nuclear reactor? 2)What is the most common coolant? 3)How do they cool the water? 4)What is used to raise the boiling point of water& 5)What is the boiling point of water?
 Types of nuclear weapons There are two basic types of nuclear weapon. The first type produces its explosive energy through nuclear fission reactions alone. Such fission weapons are commonly referred to as atomic bombs or atom bombs (abbreviated as A-bombs), though their energy comes specifically from the nucleus of the atom. In fission weapons, a mass of fissile material (enriched uranium or plutonium) is assembled into a supercritical mass—the amount of material needed to start an exponentially growing nuclear chain reaction—either by shooting one piece of sub-critical material into another (the "gun" method) or by compressing a sub-critical sphere of material using chemical explosives to many times its original density (the "implosion" method). The latter approach is considered more sophisticated than the former and only the latter approach can be used if the fissile material is plutonium. A major challenge in all nuclear weapon designs is to ensure that a significant fraction of the fuel is consumed before the weapon destroys itself. The amount of energy released by fission bombs can range from the equivalent of less than a ton of TNT upwards of 500, 000 tons (500 kilotons) of TNT. Discussion. What do you think is the third world war inevitable? And if so will it be nuclear? Translate into Russian. • 1)Уран-это топливо для АЭС. • 2)Ядро находится внутри реактора. • 3)Металлические трубы проводят тепло. • 4)Вода очищается. • 5)Ты не радиоактивен? The basics of the Teller–Ulam design for a hydrogen bomb: a fission bomb uses radiation to compress and heat a separate section of fusion fuel. The second basic type of nuclear weapon produces a large amount of its energy through nuclear fusion reactions. Such fusion weapons are generally referred to as thermonuclear weapons or more colloquially as hydrogen bombs (abbreviated as H-bombs), as they rely on fusion reactions between isotopes of hydrogen (deuterium and tritium). However, all such weapons derive a significant portion, and sometimes a majority, of their energy from fission (including fission induced by neutrons from fusion reactions). Unlike fission weapons, there are no inherent limits on the energy released by thermonuclear weapons. Only six countries—United States, Russia, United Kingdom, People's Republic of China, France and India—have conducted thermonuclear weapon tests. Whether India has detonated a "true, " multi-staged thermonuclear weapon is controversial.
Types of nuclear weapons There are two basic types of nuclear weapon. The first type produces its explosive energy through nuclear fission reactions alone. Such fission weapons are commonly referred to as atomic bombs or atom bombs (abbreviated as A-bombs), though their energy comes specifically from the nucleus of the atom. In fission weapons, a mass of fissile material (enriched uranium or plutonium) is assembled into a supercritical mass—the amount of material needed to start an exponentially growing nuclear chain reaction—either by shooting one piece of sub-critical material into another (the "gun" method) or by compressing a sub-critical sphere of material using chemical explosives to many times its original density (the "implosion" method). The latter approach is considered more sophisticated than the former and only the latter approach can be used if the fissile material is plutonium. A major challenge in all nuclear weapon designs is to ensure that a significant fraction of the fuel is consumed before the weapon destroys itself. The amount of energy released by fission bombs can range from the equivalent of less than a ton of TNT upwards of 500, 000 tons (500 kilotons) of TNT. Discussion. What do you think is the third world war inevitable? And if so will it be nuclear? Translate into Russian. • 1)Уран-это топливо для АЭС. • 2)Ядро находится внутри реактора. • 3)Металлические трубы проводят тепло. • 4)Вода очищается. • 5)Ты не радиоактивен? The basics of the Teller–Ulam design for a hydrogen bomb: a fission bomb uses radiation to compress and heat a separate section of fusion fuel. The second basic type of nuclear weapon produces a large amount of its energy through nuclear fusion reactions. Such fusion weapons are generally referred to as thermonuclear weapons or more colloquially as hydrogen bombs (abbreviated as H-bombs), as they rely on fusion reactions between isotopes of hydrogen (deuterium and tritium). However, all such weapons derive a significant portion, and sometimes a majority, of their energy from fission (including fission induced by neutrons from fusion reactions). Unlike fission weapons, there are no inherent limits on the energy released by thermonuclear weapons. Only six countries—United States, Russia, United Kingdom, People's Republic of China, France and India—have conducted thermonuclear weapon tests. Whether India has detonated a "true, " multi-staged thermonuclear weapon is controversial.
 Nuclear Power 1. Read the text. Nuclear power is possibly the most contentious and emotive of all methods of energy production, due to the nature of the material involved and long term consequences of accidents. Nuclear power stations currently produce about 14% of Britain's electricity. There has been a significant drop in this figure since 2006 (around 20%) because several nuclear plants have been shut down for repairs for extended periods. Uranium is a naturally occurring radioactive element, left over from Earth's formation. It can be used in nuclear power production because if a free neutron collides with the nucleus of a Uranium atom, the nucleus splits (fission) into two smaller atoms plus one free neutron. This free neutron can then cause another fission to occur (a chain reaction). As the two new atoms weigh less than the original Uranium atom, an enormous amount of energy is also released. The energy produced by the splitting of the Uranium nucleus in the power plant (the reactor) is used as a heat source. This turns water into steam, which drives a turbine. The turbine spins a generator to produce electricity. The reactor is sealed inside concrete and steel to prevent radioactive gases and fluids leaking from the plant. Calder Hall, Cumbria, was the world's first nuclear power station to produce electricity. It opened in 1956. Currently there are nineteen reactors operating in Britain with many due to close over the coming years. The British Government confirmed in 2008 that it would back a new generation of nuclear power stations. John Hutton, former Secretary of State for Business Enterprise and Regulatory Reform told Parliament that the case in favour of nuclear power was “compelling” and that he hoped the first new station would be up and running well before 2020. 3. Translate into Russian. Белоярская АЭС первая в СССР. Россия строит новые АЭС. Атомная реакция началась. Свободные нейтроны сталкиваются в ядром урана. Ядро раскалывается на два маленьких атома. 4. Discuss if we need a NPP in Udmurtia? The Sedan test from 1962 formed a crater 100 m (330 ft) deep with a diameter of about 390 m (1, 300 ft), as a means of investigating the possibilities of using peaceful nuclear explosions for large-scale earth moving. 2. Answer the questions. 1. How much energy is produced in UK by the nuclear power plant? 2. What is the fuel foe NPP? 3. What is used to prevent radiation from leaking the reactor? 4. When was built the first nuclear reactor? 5. Where is the first Russian NPP?
Nuclear Power 1. Read the text. Nuclear power is possibly the most contentious and emotive of all methods of energy production, due to the nature of the material involved and long term consequences of accidents. Nuclear power stations currently produce about 14% of Britain's electricity. There has been a significant drop in this figure since 2006 (around 20%) because several nuclear plants have been shut down for repairs for extended periods. Uranium is a naturally occurring radioactive element, left over from Earth's formation. It can be used in nuclear power production because if a free neutron collides with the nucleus of a Uranium atom, the nucleus splits (fission) into two smaller atoms plus one free neutron. This free neutron can then cause another fission to occur (a chain reaction). As the two new atoms weigh less than the original Uranium atom, an enormous amount of energy is also released. The energy produced by the splitting of the Uranium nucleus in the power plant (the reactor) is used as a heat source. This turns water into steam, which drives a turbine. The turbine spins a generator to produce electricity. The reactor is sealed inside concrete and steel to prevent radioactive gases and fluids leaking from the plant. Calder Hall, Cumbria, was the world's first nuclear power station to produce electricity. It opened in 1956. Currently there are nineteen reactors operating in Britain with many due to close over the coming years. The British Government confirmed in 2008 that it would back a new generation of nuclear power stations. John Hutton, former Secretary of State for Business Enterprise and Regulatory Reform told Parliament that the case in favour of nuclear power was “compelling” and that he hoped the first new station would be up and running well before 2020. 3. Translate into Russian. Белоярская АЭС первая в СССР. Россия строит новые АЭС. Атомная реакция началась. Свободные нейтроны сталкиваются в ядром урана. Ядро раскалывается на два маленьких атома. 4. Discuss if we need a NPP in Udmurtia? The Sedan test from 1962 formed a crater 100 m (330 ft) deep with a diameter of about 390 m (1, 300 ft), as a means of investigating the possibilities of using peaceful nuclear explosions for large-scale earth moving. 2. Answer the questions. 1. How much energy is produced in UK by the nuclear power plant? 2. What is the fuel foe NPP? 3. What is used to prevent radiation from leaking the reactor? 4. When was built the first nuclear reactor? 5. Where is the first Russian NPP?
 Nuclear weapon A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter; a modern thermonuclear weapon weighing little more than a thousand kilograms can produce an explosion comparable to the detonation of more than a billion kilograms of conventional high explosive. Thus, even single small nuclear devices no larger than traditional bombs can devastate an entire city by blast, fire and radiation. Nuclear weapons are considered weapons of mass destruction, and their use and control has been a major focus of international relations policy since their debut. In the history of warfare, only two nuclear weapons have been detonated offensively, both near the end of World War II. The first was detonated on the morning of 6 August 1945, when the United States dropped a uranium gun-type device code-named "Little Boy" on the Japanese city of Hiroshima. The second was detonated three days later when the United States dropped a plutonium implosion-type device code-named "Fat Man" on the city of Nagasaki, Japan. These bombings resulted in the immediate deaths of an estimated 80, 000 people (mostly civilians) from injuries sustained from the explosion. When factoring in deaths from long-term effects of ionizing radiation and acute radiation sickness, the total death toll is estimated at 120, 000. The use of these weapons remains controversial. Since the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings, nuclear weapons have been detonated on over two thousand occasions for testing purposes and demonstration purposes. A few states have possessed such weapons or are suspected of seeking them. The only countries known to have detonated nuclear weapons—and that acknowledge possessing such weapons—are (chronologically) the United States, the Soviet Union (succeeded as a nuclear power by Russia), the United Kingdom, France, the People's Republic of China, India, Pakistan, and North Korea. Israel is also widely believed to possess nuclear weapons, though it does not acknowledge having them. Answer the questions. Translate into Russian. 1. What is the nuclear weapon? 2. What is the result of nuclear explosion? 3. When was used the nuclear weapon? 4. Where was used the nuclear weapon? 5. What country used the nuclear weapon? 1. Атомное оружие использовалось против Японии. 2. Последствия атомного взрыва ужасны. 3. Бомбы были взорваны в конце 2 мировой войны. 4. Японские города пострадали от оружия массового поражения. 5. Некоторые страны обладают атомным оружием. Discuss: Is the nuclear war inevitable in future? Watch the video.
Nuclear weapon A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter; a modern thermonuclear weapon weighing little more than a thousand kilograms can produce an explosion comparable to the detonation of more than a billion kilograms of conventional high explosive. Thus, even single small nuclear devices no larger than traditional bombs can devastate an entire city by blast, fire and radiation. Nuclear weapons are considered weapons of mass destruction, and their use and control has been a major focus of international relations policy since their debut. In the history of warfare, only two nuclear weapons have been detonated offensively, both near the end of World War II. The first was detonated on the morning of 6 August 1945, when the United States dropped a uranium gun-type device code-named "Little Boy" on the Japanese city of Hiroshima. The second was detonated three days later when the United States dropped a plutonium implosion-type device code-named "Fat Man" on the city of Nagasaki, Japan. These bombings resulted in the immediate deaths of an estimated 80, 000 people (mostly civilians) from injuries sustained from the explosion. When factoring in deaths from long-term effects of ionizing radiation and acute radiation sickness, the total death toll is estimated at 120, 000. The use of these weapons remains controversial. Since the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings, nuclear weapons have been detonated on over two thousand occasions for testing purposes and demonstration purposes. A few states have possessed such weapons or are suspected of seeking them. The only countries known to have detonated nuclear weapons—and that acknowledge possessing such weapons—are (chronologically) the United States, the Soviet Union (succeeded as a nuclear power by Russia), the United Kingdom, France, the People's Republic of China, India, Pakistan, and North Korea. Israel is also widely believed to possess nuclear weapons, though it does not acknowledge having them. Answer the questions. Translate into Russian. 1. What is the nuclear weapon? 2. What is the result of nuclear explosion? 3. When was used the nuclear weapon? 4. Where was used the nuclear weapon? 5. What country used the nuclear weapon? 1. Атомное оружие использовалось против Японии. 2. Последствия атомного взрыва ужасны. 3. Бомбы были взорваны в конце 2 мировой войны. 4. Японские города пострадали от оружия массового поражения. 5. Некоторые страны обладают атомным оружием. Discuss: Is the nuclear war inevitable in future? Watch the video.
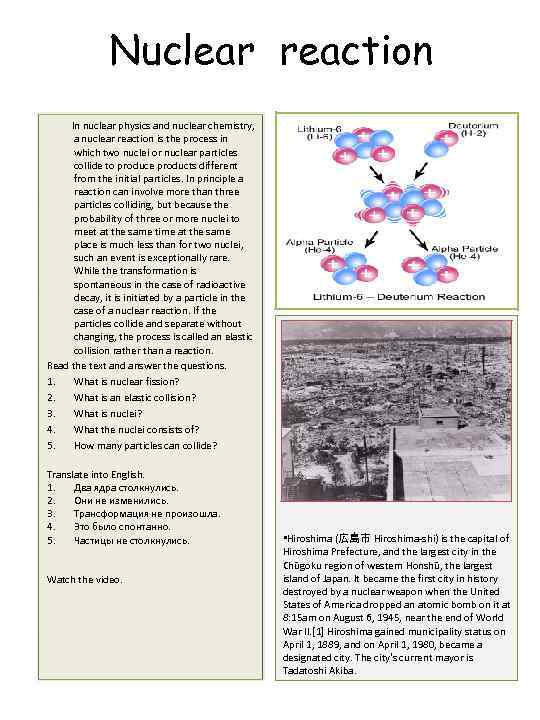 Nuclear reaction In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is the process in which two nuclei or nuclear particles collide to produce products different from the initial particles. In principle a reaction can involve more than three particles colliding, but because the probability of three or more nuclei to meet at the same time at the same place is much less than for two nuclei, such an event is exceptionally rare. While the transformation is spontaneous in the case of radioactive decay, it is initiated by a particle in the case of a nuclear reaction. If the particles collide and separate without changing, the process is called an elastic collision rather than a reaction. Read the text and answer the questions. 1. What is nuclear fission? 2. What is an elastic collision? 3. What is nuclei? 4. What the nuclei consists of? 5. How many particles can collide? Translate into English. 1. Два ядра столкнулись. 2. Они не изменились. 3. Трансформация не произошла. 4. Это было спонтанно. 5. Частицы не столкнулись. Watch the video. • Hiroshima (広島市 Hiroshima-shi) is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture, and the largest city in the Chūgoku region of western Honshū, the largest island of Japan. It became the first city in history destroyed by a nuclear weapon when the United States of America dropped an atomic bomb on it at 8: 15 am on August 6, 1945, near the end of World War II. [1] Hiroshima gained municipality status on April 1, 1889, and on April 1, 1980, became a designated city. The city's current mayor is Tadatoshi Akiba.
Nuclear reaction In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is the process in which two nuclei or nuclear particles collide to produce products different from the initial particles. In principle a reaction can involve more than three particles colliding, but because the probability of three or more nuclei to meet at the same time at the same place is much less than for two nuclei, such an event is exceptionally rare. While the transformation is spontaneous in the case of radioactive decay, it is initiated by a particle in the case of a nuclear reaction. If the particles collide and separate without changing, the process is called an elastic collision rather than a reaction. Read the text and answer the questions. 1. What is nuclear fission? 2. What is an elastic collision? 3. What is nuclei? 4. What the nuclei consists of? 5. How many particles can collide? Translate into English. 1. Два ядра столкнулись. 2. Они не изменились. 3. Трансформация не произошла. 4. Это было спонтанно. 5. Частицы не столкнулись. Watch the video. • Hiroshima (広島市 Hiroshima-shi) is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture, and the largest city in the Chūgoku region of western Honshū, the largest island of Japan. It became the first city in history destroyed by a nuclear weapon when the United States of America dropped an atomic bomb on it at 8: 15 am on August 6, 1945, near the end of World War II. [1] Hiroshima gained municipality status on April 1, 1889, and on April 1, 1980, became a designated city. The city's current mayor is Tadatoshi Akiba.
 Little Boy "Little Boy" was the codename of the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945 by the Boeing B-29 Superfortress Enola Gay, piloted by Colonel Paul Tibbets of the 393 d Bombardment Squadron, Heavy, of the United States Army Air Forces. It was the first atomic bomb to be used as a weapon. The second, the "Fat Man", was dropped three days later on Nagasaki. The weapon was developed by the Manhattan Project during World War II. It derived its explosive power from the nuclear fission of uranium 235. The Hiroshima bombing was the second artificial nuclear explosion in history, after the Trinity test, and the first uranium-based detonation. Approximately 600 milligrams of mass were converted into energy. It exploded with a destructive power equivalent to between 13 and 18 kilotons of TNT (54 and 75 TJ) (estimates vary) and killed approximately 140, 000 people. Its design was not tested in advance, unlike the more complex plutonium bomb (Fat Man). The available supply of enriched uranium was very small at that time, and it was felt that the simple design of a uranium "gun" type bomb was so sure to Answer the questions. work that there was no need to test it at full scale. 1. What was the first bombs code Small-scale experiments were used to determine name? the critical mass and other properties. 2. What was the second bomb code A major challenge in all nuclear weapon designs name? is to ensure that a significant fraction of the fuel is 3. What are the cities bombed? consumed before the weapon destroys itself. 4. How many people were killed? The amount of energy released by fission bombs 5. What was the first testing of can range from the equivalent of less than a ton of nuclear weapon in history? TNT upwards of 500, 000 tons (500 kilotons) of TNT. Discussion. What do you think is it necessary to have for Russia nuclear weapon? Watch the video.
Little Boy "Little Boy" was the codename of the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945 by the Boeing B-29 Superfortress Enola Gay, piloted by Colonel Paul Tibbets of the 393 d Bombardment Squadron, Heavy, of the United States Army Air Forces. It was the first atomic bomb to be used as a weapon. The second, the "Fat Man", was dropped three days later on Nagasaki. The weapon was developed by the Manhattan Project during World War II. It derived its explosive power from the nuclear fission of uranium 235. The Hiroshima bombing was the second artificial nuclear explosion in history, after the Trinity test, and the first uranium-based detonation. Approximately 600 milligrams of mass were converted into energy. It exploded with a destructive power equivalent to between 13 and 18 kilotons of TNT (54 and 75 TJ) (estimates vary) and killed approximately 140, 000 people. Its design was not tested in advance, unlike the more complex plutonium bomb (Fat Man). The available supply of enriched uranium was very small at that time, and it was felt that the simple design of a uranium "gun" type bomb was so sure to Answer the questions. work that there was no need to test it at full scale. 1. What was the first bombs code Small-scale experiments were used to determine name? the critical mass and other properties. 2. What was the second bomb code A major challenge in all nuclear weapon designs name? is to ensure that a significant fraction of the fuel is 3. What are the cities bombed? consumed before the weapon destroys itself. 4. How many people were killed? The amount of energy released by fission bombs 5. What was the first testing of can range from the equivalent of less than a ton of nuclear weapon in history? TNT upwards of 500, 000 tons (500 kilotons) of TNT. Discussion. What do you think is it necessary to have for Russia nuclear weapon? Watch the video.
 1 Answer the following questions. 1 2 3 4 5 What are environmental implications of this disaster? When did It happen? What was the causes of this incident? How many people were evacuated? Can somebody live in Chernobyl now? Translate into English. 1 Нужно выключить реактор. 2 В результате катастрофы пострадало много людей. 3 Атомные электростанции служат для выработки электроэнергии. 4 Была проведена срочная эвакуация. 5 Радиоактивные отходы попали в атмосферу. The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine. It is considered the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. During the daytime of 25 April 1986, reactor 4 was scheduled to be shut down. An experiment was scheduled to test a potential safety emergency core cooling feature during the shutdown procedure. Another regional power station unexpectedly went off-line, so Chernobyl was producing more power than usual to compensate. Then the day shift workers decided not to do the test. No-one ever told the night time staff not to do it, so they tried to perform the test. There is a lot of controversy of what happened next, but something went wrong. On April 26, 1986, reactor number four at the Chernobyl plant, had a meltdown. The resulting fire sent a plume of radioactive fallout into the atmosphere and over an extensive geographical area, including the nearby town of Pripyat. The plume drifted over Europe, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Large areas in Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia had to be evacuated. Causes According to the analysis, the main cause of the accident was the operators' actions. Another view was that the reactor had a dangerously large positive void coefficient. But the human factor had to be considered as a major element in causing the accident. Effects In the aftermath of the accident, 237 people suffered from acute radiation sickness, of whom 31 died within the first three months. Most of these were fire and rescue workers trying to bring the accident under control, who were not fully aware of how dangerous exposure to the radiation in the smoke was. Some 135, 000 people were evacuated from the area, including 50, 000 from Pripyat. 10 individuals have already died of cancer as a result of the disaster. Radiation causes Physical Health Effects such as Down's syndrome, Neural tube defects, the Dnepr River reservoir system, one of the largest surface water systems in Europe. The radioactive contamination of aquatic systems therefore became a major issue in the immediate aftermath of the accident. After the disaster, four square kilometers of pine forest in the immediate vicinity of the reactor turned reddish-brown and died, earning the name of the "Red Forest". Some animals in the worst-hit areas also died or stopped reproducing. There is a 17 -mile Exclusion Zone around Chernobyl where officially nobody is allowed to live, but people do. Farming or any other type of agricultural industry would be dangerous
1 Answer the following questions. 1 2 3 4 5 What are environmental implications of this disaster? When did It happen? What was the causes of this incident? How many people were evacuated? Can somebody live in Chernobyl now? Translate into English. 1 Нужно выключить реактор. 2 В результате катастрофы пострадало много людей. 3 Атомные электростанции служат для выработки электроэнергии. 4 Была проведена срочная эвакуация. 5 Радиоактивные отходы попали в атмосферу. The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine. It is considered the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. During the daytime of 25 April 1986, reactor 4 was scheduled to be shut down. An experiment was scheduled to test a potential safety emergency core cooling feature during the shutdown procedure. Another regional power station unexpectedly went off-line, so Chernobyl was producing more power than usual to compensate. Then the day shift workers decided not to do the test. No-one ever told the night time staff not to do it, so they tried to perform the test. There is a lot of controversy of what happened next, but something went wrong. On April 26, 1986, reactor number four at the Chernobyl plant, had a meltdown. The resulting fire sent a plume of radioactive fallout into the atmosphere and over an extensive geographical area, including the nearby town of Pripyat. The plume drifted over Europe, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Large areas in Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia had to be evacuated. Causes According to the analysis, the main cause of the accident was the operators' actions. Another view was that the reactor had a dangerously large positive void coefficient. But the human factor had to be considered as a major element in causing the accident. Effects In the aftermath of the accident, 237 people suffered from acute radiation sickness, of whom 31 died within the first three months. Most of these were fire and rescue workers trying to bring the accident under control, who were not fully aware of how dangerous exposure to the radiation in the smoke was. Some 135, 000 people were evacuated from the area, including 50, 000 from Pripyat. 10 individuals have already died of cancer as a result of the disaster. Radiation causes Physical Health Effects such as Down's syndrome, Neural tube defects, the Dnepr River reservoir system, one of the largest surface water systems in Europe. The radioactive contamination of aquatic systems therefore became a major issue in the immediate aftermath of the accident. After the disaster, four square kilometers of pine forest in the immediate vicinity of the reactor turned reddish-brown and died, earning the name of the "Red Forest". Some animals in the worst-hit areas also died or stopped reproducing. There is a 17 -mile Exclusion Zone around Chernobyl where officially nobody is allowed to live, but people do. Farming or any other type of agricultural industry would be dangerous
 End of Nuclear Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
End of Nuclear Power Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
 Boilers hang from reinforced steel joists in the boiler house which are like big hollow boxes. The boiler house can be 220 m long, 60 m high, and 55 m wide. The boiler walls are formed by 53 kilometers of 6. 25 cm bore tubing. Inside these tubes, extremely pure water is converted by heat into steam at high pressure. The steam is then super-heated to 568 degrees Celsius A modern 500 MW boiler can consume over 200 tones of coal per hour and is capable of delivering l, 522, 727 kgs of steam per hour at a pressure of 1967 x 10 -4 Pascal's. To transfer large quantities of steam from the boiler to the turbine, the steam must travel at very high speeds (200 -300 Km/hr), In the case of problems the steam flow must be halted immediately. This is done by placing a valve close to the turbine. The valve's hydraulic systems ensure that it can close in a fraction of a second, ensuring that the turbine does not over speed. As temperatures rise and fall so the pipes expand contract 5 and therefore cannot be too solidly enclosed. To allow expansion, pipes must be shaped so that internal stresses do not cause buckling. This can be done by providing loops in the pipe. The amount by which a pipe expands depends on it's length. A 100 m pipe, having it's temperature increased by 500 ' would expand by approximately 5 meters (1/200 th of its length). Exercise 1: Answer the questions. 1. What can be the size of a boiler? 2. To what temperature can be heated the steam in the boiler? 3. What speed is necessary for the steam to travel to turbine? 4. What device is used to halt the steam? 5. Does the water expands or contracts when being cooled? Exercise 2: Translate into English. 1. Трубы переносят пар. 2. Клапан нужен для закрытия. 3. Металл расширяется при нагревании. 4. Закрой клапан, плохо пахнет. 5. У тебя есть доля секунды? Exercise 3: Discuss with the partner. What would happen with the fish if the water had contracted at low temperatures? Can smoking and other bad habits cause the stroke or heart attack? If it can why?
Boilers hang from reinforced steel joists in the boiler house which are like big hollow boxes. The boiler house can be 220 m long, 60 m high, and 55 m wide. The boiler walls are formed by 53 kilometers of 6. 25 cm bore tubing. Inside these tubes, extremely pure water is converted by heat into steam at high pressure. The steam is then super-heated to 568 degrees Celsius A modern 500 MW boiler can consume over 200 tones of coal per hour and is capable of delivering l, 522, 727 kgs of steam per hour at a pressure of 1967 x 10 -4 Pascal's. To transfer large quantities of steam from the boiler to the turbine, the steam must travel at very high speeds (200 -300 Km/hr), In the case of problems the steam flow must be halted immediately. This is done by placing a valve close to the turbine. The valve's hydraulic systems ensure that it can close in a fraction of a second, ensuring that the turbine does not over speed. As temperatures rise and fall so the pipes expand contract 5 and therefore cannot be too solidly enclosed. To allow expansion, pipes must be shaped so that internal stresses do not cause buckling. This can be done by providing loops in the pipe. The amount by which a pipe expands depends on it's length. A 100 m pipe, having it's temperature increased by 500 ' would expand by approximately 5 meters (1/200 th of its length). Exercise 1: Answer the questions. 1. What can be the size of a boiler? 2. To what temperature can be heated the steam in the boiler? 3. What speed is necessary for the steam to travel to turbine? 4. What device is used to halt the steam? 5. Does the water expands or contracts when being cooled? Exercise 2: Translate into English. 1. Трубы переносят пар. 2. Клапан нужен для закрытия. 3. Металл расширяется при нагревании. 4. Закрой клапан, плохо пахнет. 5. У тебя есть доля секунды? Exercise 3: Discuss with the partner. What would happen with the fish if the water had contracted at low temperatures? Can smoking and other bad habits cause the stroke or heart attack? If it can why?
 Refrigerati on Refrigeration is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space, or from a substance, and moving it to a place where it is unobjectionable. The primary purpose of refrigeration is lowering the temperature of the enclosed space or substance and then maintaining that lower temperature. The term cooling refers generally to any natural or artificial process by which heat is dissipated. The process of artificially producing extreme cold temperatures is referred to as cryogenics. Cold is the absence of heat, hence in order to decrease a temperature, one "removes heat", rather than "adding cold. " In order to satisfy the Second Law of Thermodynamics, some form of work must be performed to accomplish this. This work is traditionally done by mechanical work but can also be done by magnetism, laser or other means.
Refrigerati on Refrigeration is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space, or from a substance, and moving it to a place where it is unobjectionable. The primary purpose of refrigeration is lowering the temperature of the enclosed space or substance and then maintaining that lower temperature. The term cooling refers generally to any natural or artificial process by which heat is dissipated. The process of artificially producing extreme cold temperatures is referred to as cryogenics. Cold is the absence of heat, hence in order to decrease a temperature, one "removes heat", rather than "adding cold. " In order to satisfy the Second Law of Thermodynamics, some form of work must be performed to accomplish this. This work is traditionally done by mechanical work but can also be done by magnetism, laser or other means.
 A refrigerator (often called a "fridge" for short) is a cooling appliance comprising a thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump—chemical or mechanical means—to transfer heat from it to the external environment, cooling the contents to a temperature below ambient. Refrigerators are extensively used to store foods which spoil from bacterial growth if not refrigerated. A device described as a "refrigerator" maintains a temperature a few degrees above the freezing point of water; a similar device which maintains a temperature below the freezing point of water is called a "freezer. " The refrigerator is a relatively modern invention among kitchen appliances. It replaced the icebox, which had been a common household appliance for almost a century and a half prior. For this reason, a refrigerator is sometimes referred to as an «icebox» . Answer the questions. What is cold? What is darkness? What is refrigeration? Why does the food get spoiled? What is the difference between fridge and freezer? Translate into English. Холодильник - это бытовой прибор. Люди используют холодильники. Закрой холодильник, холодно. Для того чтобы понизить температуру, нужно удалить тепло. Вода замерзла.
A refrigerator (often called a "fridge" for short) is a cooling appliance comprising a thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump—chemical or mechanical means—to transfer heat from it to the external environment, cooling the contents to a temperature below ambient. Refrigerators are extensively used to store foods which spoil from bacterial growth if not refrigerated. A device described as a "refrigerator" maintains a temperature a few degrees above the freezing point of water; a similar device which maintains a temperature below the freezing point of water is called a "freezer. " The refrigerator is a relatively modern invention among kitchen appliances. It replaced the icebox, which had been a common household appliance for almost a century and a half prior. For this reason, a refrigerator is sometimes referred to as an «icebox» . Answer the questions. What is cold? What is darkness? What is refrigeration? Why does the food get spoiled? What is the difference between fridge and freezer? Translate into English. Холодильник - это бытовой прибор. Люди используют холодильники. Закрой холодильник, холодно. Для того чтобы понизить температуру, нужно удалить тепло. Вода замерзла.
 End of Equipment Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
End of Equipment Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 Вариант 2 • Вернуться на начало
 SAKHAROV 1. Translate into English. 1) Сахаров изобрел водородную бомбу 2) Сахарову вручили премию Сталина 3) Водородная бомбаэто ужасное оружие 4) Сахаров был выдающимся физиком 5)Это изобретение опасно 2. Answer the questions. 1)Who was Andrey Sakharov? 2)When was he born? 3)What did he invent? 4) Why was he sorry about his invention? 5) Did he have any problems in his life? Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov was born on May 21, 1921, in Moscow. His father, named Dmitri Ivanovich Sakharov, was a distinguished scientist, a writer of science, and a pedagogy. He also had a hobby of playing piano for silent films and at home. His mother, named Ekaterina Alekseevna was the daughter of a distinguished General, Aleksei Sophiano, who was a Greek. Russian aristocrat in Moscow. Young Andrei Sakharov was a voracious reader. He graduated from high school with excellence. From 1938, Sakharov studied physics at Moscow State University. He graduated 'cum laude' in 1942, while the university was evacuated in Ashkhabad, Turkmenistan during WWII. Sakharov made a number of inventions for the Soviet military industry during the Second World War. He earned his Ph. D. in 1947 and was included in the top-secret Soviet thermonuclear research group under Igor Tamm. In 1949 -50 Sakharov became the co-inventor of the controlled hydrogen reaction. Today he is known as "the father of the Soviet hydrogen bomb. " He was secretly awarded the State Prize by Joseph Stalin, who had a personal meeting with Sakharov and Lavrenti Beria, the chief of NKVD/KGB. After giving the hydrogen bomb to Joseph Stalin Sakharov himself went through a dramatic moral transformation. He wrote in his 'Memoirs' that from 1952 -1961 he grew to realization that his invention is extremely harmful in the hands of politicians, and it caused him a serious moral pain. Sakharov rose to become a staunch opponent of the nuclear tests and made a political statement in 1961, causing anger from Nikita Khrushchev. During the Cuban missile crisis, Sakharov had a clear vision of the danger that his mighty invention may cause in the hands of undereducated career politicians, who exterminated millions of their own people. Sakharov raised his voice in 1966 -1967 in defense of the political prisoners in the USSR; at a time when Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn was terrorized by the KGB.
SAKHAROV 1. Translate into English. 1) Сахаров изобрел водородную бомбу 2) Сахарову вручили премию Сталина 3) Водородная бомбаэто ужасное оружие 4) Сахаров был выдающимся физиком 5)Это изобретение опасно 2. Answer the questions. 1)Who was Andrey Sakharov? 2)When was he born? 3)What did he invent? 4) Why was he sorry about his invention? 5) Did he have any problems in his life? Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov was born on May 21, 1921, in Moscow. His father, named Dmitri Ivanovich Sakharov, was a distinguished scientist, a writer of science, and a pedagogy. He also had a hobby of playing piano for silent films and at home. His mother, named Ekaterina Alekseevna was the daughter of a distinguished General, Aleksei Sophiano, who was a Greek. Russian aristocrat in Moscow. Young Andrei Sakharov was a voracious reader. He graduated from high school with excellence. From 1938, Sakharov studied physics at Moscow State University. He graduated 'cum laude' in 1942, while the university was evacuated in Ashkhabad, Turkmenistan during WWII. Sakharov made a number of inventions for the Soviet military industry during the Second World War. He earned his Ph. D. in 1947 and was included in the top-secret Soviet thermonuclear research group under Igor Tamm. In 1949 -50 Sakharov became the co-inventor of the controlled hydrogen reaction. Today he is known as "the father of the Soviet hydrogen bomb. " He was secretly awarded the State Prize by Joseph Stalin, who had a personal meeting with Sakharov and Lavrenti Beria, the chief of NKVD/KGB. After giving the hydrogen bomb to Joseph Stalin Sakharov himself went through a dramatic moral transformation. He wrote in his 'Memoirs' that from 1952 -1961 he grew to realization that his invention is extremely harmful in the hands of politicians, and it caused him a serious moral pain. Sakharov rose to become a staunch opponent of the nuclear tests and made a political statement in 1961, causing anger from Nikita Khrushchev. During the Cuban missile crisis, Sakharov had a clear vision of the danger that his mighty invention may cause in the hands of undereducated career politicians, who exterminated millions of their own people. Sakharov raised his voice in 1966 -1967 in defense of the political prisoners in the USSR; at a time when Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn was terrorized by the KGB.
 FIELD THEORIES When he was 81, Tesla stated he had completed a "dynamic theory of gravity". He stated that it was "worked out in all details" and that he hoped to soon give it to the world. The theory was never published. The bulk of theory was developed between 1892 and 1894, during the period that he was conducting experiments with high frequency and high potential electromagnetism and patenting devices for their use. Reminiscent of Mach's principle, Tesla stated in 1925 that: There is no thing endowed with life—from man, who is enslaving the elements, to the nimblest creature—in all this world that does not sway in its turn. Whenever action is born from force, though it be infinitesimal, the cosmic balance is upset and the universal motion results. Tesla was critical of Einstein's relativity work, calling it: magnificent mathematical garb which fascinates, dazzles and makes people blind to the underlying errors. The theory is like a beggar clothed in purple whom ignorant people take for a king. . . its exponents are brilliant men but they are metaphysicists rather than scientists. . . Tesla also argued: I hold that space cannot be curved, for the simple reason that it can have no properties. It might as well be said that God has properties. He has not, but only attributes and these are of our own making. Of properties we can only speak when dealing with matter filling the space. To say that in the presence of large bodies space becomes curved is equivalent to stating that something can act upon nothing. I, for one, refuse to subscribe to such a view.
FIELD THEORIES When he was 81, Tesla stated he had completed a "dynamic theory of gravity". He stated that it was "worked out in all details" and that he hoped to soon give it to the world. The theory was never published. The bulk of theory was developed between 1892 and 1894, during the period that he was conducting experiments with high frequency and high potential electromagnetism and patenting devices for their use. Reminiscent of Mach's principle, Tesla stated in 1925 that: There is no thing endowed with life—from man, who is enslaving the elements, to the nimblest creature—in all this world that does not sway in its turn. Whenever action is born from force, though it be infinitesimal, the cosmic balance is upset and the universal motion results. Tesla was critical of Einstein's relativity work, calling it: magnificent mathematical garb which fascinates, dazzles and makes people blind to the underlying errors. The theory is like a beggar clothed in purple whom ignorant people take for a king. . . its exponents are brilliant men but they are metaphysicists rather than scientists. . . Tesla also argued: I hold that space cannot be curved, for the simple reason that it can have no properties. It might as well be said that God has properties. He has not, but only attributes and these are of our own making. Of properties we can only speak when dealing with matter filling the space. To say that in the presence of large bodies space becomes curved is equivalent to stating that something can act upon nothing. I, for one, refuse to subscribe to such a view.
 Albert Einstein was born at Ulm, in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879. Six weeks later the family moved to Munich, where he later on began his schooling at the Luitpold Gymnasium. Later, they moved to Italy and Albert continued his education at Aarau, Switzerland in 1896 he entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich to be trained as a teacher in physics and mathematics. In 1901, the year he gained his diploma, he acquired Swiss citizenship and, as he was unable to find a teaching post, he accepted a position as technical assistant in the Swiss Patent Office. In 1905 he obtained his doctor's degree. During his stay at the Patent Office , and in his spare time, he produced much of his remarkable work and in 1908 he was appointed Privatdozent in Berne. In 1909 he became Professor Extraordinary at Zurich, in 1911 Professor of Theoretical Physics at Prague, returning to Zurich in the following year to fill a similar post. In 1914 he was appointed Director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Physical Institute and Professor in the University of Berlin. He became a German citizen in 1914 and remained in Berlin until 1933 when he renounced his citizenship for political reasons and emigrated to America to take the position of Professor of Theoretical Physics at Princeton*. He became a United States citizen in 1940 and retired from his post in 1945.
Albert Einstein was born at Ulm, in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879. Six weeks later the family moved to Munich, where he later on began his schooling at the Luitpold Gymnasium. Later, they moved to Italy and Albert continued his education at Aarau, Switzerland in 1896 he entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich to be trained as a teacher in physics and mathematics. In 1901, the year he gained his diploma, he acquired Swiss citizenship and, as he was unable to find a teaching post, he accepted a position as technical assistant in the Swiss Patent Office. In 1905 he obtained his doctor's degree. During his stay at the Patent Office , and in his spare time, he produced much of his remarkable work and in 1908 he was appointed Privatdozent in Berne. In 1909 he became Professor Extraordinary at Zurich, in 1911 Professor of Theoretical Physics at Prague, returning to Zurich in the following year to fill a similar post. In 1914 he was appointed Director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Physical Institute and Professor in the University of Berlin. He became a German citizen in 1914 and remained in Berlin until 1933 when he renounced his citizenship for political reasons and emigrated to America to take the position of Professor of Theoretical Physics at Princeton*. He became a United States citizen in 1940 and retired from his post in 1945.
 James Watt was born on 19 January 1736 in Greenock, Renfrewshire, a seaport on the Firth of Clyde. His father was a shipwright, ship owner and contractor, and served as the town's chief baillie, while his mother, Agnes Muirhead, came from a distinguished family and was well educated. Both were Presbyterians and strong Covenanters. Watt's grandfather, Thomas Watt, was a mathematics teacher and baillie to the Baron of Cartsburn. Watt did not attend school regularly; initially he was mostly schooled at home by his mother but later he attended Greenock grammar school. He exhibited great manual dexterity and an aptitude for mathematics, although Latin and Greek failed to interest him. When he was 18, his mother died and his father's health began to fail. Watt travelled to London to study instrument-making for a year, then returned to Scotland, settling in the major commercial city of Glasgow intent on setting up his own instrument-making business. However, because he had not served at least seven years as an apprentice, the Glasgow Guild of Hammermen (which had jurisdiction over any artisans using hammers) blocked his application, despite there being no other mathematical instrument makers in Scotland. Watt was saved from this impasse by the arrival of astronomical instruments to the University of Glasgow that required expert attention. Watt restored them to working order and was remunerated. These instruments were eventually installed in the Macfarlane Observatory. Subsequently three professors offered him the opportunity to set up a small workshop within the university. It was established in 1758 and one of the professors, the physicist and chemist Joseph Black, became Watt's friend.
James Watt was born on 19 January 1736 in Greenock, Renfrewshire, a seaport on the Firth of Clyde. His father was a shipwright, ship owner and contractor, and served as the town's chief baillie, while his mother, Agnes Muirhead, came from a distinguished family and was well educated. Both were Presbyterians and strong Covenanters. Watt's grandfather, Thomas Watt, was a mathematics teacher and baillie to the Baron of Cartsburn. Watt did not attend school regularly; initially he was mostly schooled at home by his mother but later he attended Greenock grammar school. He exhibited great manual dexterity and an aptitude for mathematics, although Latin and Greek failed to interest him. When he was 18, his mother died and his father's health began to fail. Watt travelled to London to study instrument-making for a year, then returned to Scotland, settling in the major commercial city of Glasgow intent on setting up his own instrument-making business. However, because he had not served at least seven years as an apprentice, the Glasgow Guild of Hammermen (which had jurisdiction over any artisans using hammers) blocked his application, despite there being no other mathematical instrument makers in Scotland. Watt was saved from this impasse by the arrival of astronomical instruments to the University of Glasgow that required expert attention. Watt restored them to working order and was remunerated. These instruments were eventually installed in the Macfarlane Observatory. Subsequently three professors offered him the opportunity to set up a small workshop within the university. It was established in 1758 and one of the professors, the physicist and chemist Joseph Black, became Watt's friend.
 End of Famous People Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 • Вернуться на начало
End of Famous People Lesson • Пройти тестирование Вариант 1 • Вернуться на начало


