4bcabe6e9a148a443e9fc6ae2313ccd9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Fantabulous Friday, Aug. 28 th Agenda: 1. Warm-Up/Healthy Note 2. The Declaration of Independence 3. Wrap-up / collect warm-ups Home Fun: 1. Finish copying FN: The American Constitution 2. Title Page Warm-Up What does a healthy breakfast look like and why is it important that you eat one? 3 -5 sentences

Why Breakfast Matters Why You Should Eat a Healthy Breakfast • Breakfast is the most important meal of the day. Breakfast provides you with the energy and nutrients that lead to increased concentration in the classroom. • Studies show that breakfast can be important in maintaining a healthy body weight. • Hunger sets in long before it's time for lunch, but because it's not convenient to eat properly, many people who have not eaten breakfast snack on foods that are high in fat and sugar. • People who skip breakfast are unlikely to make up their daily requirement for some vitamins and minerals that a simple breakfast would have provided. • Breakfast provides energy for the activities during the morning and helps to prevent that midmorning slump. Tips on Eating a Quick and Healthy Breakfast • Pick 2 -3 foods, including at least one from each of the following food groups: -bread and grain (i. e. cereal, toast, muffin) -milk and milk product (i. e. low-fat yogurt, low-fat milk) -fruit or vegetable group (i. e bananas, apples, carrots) • Pick up portable breakfast items when at the grocery store. You should buy foods like fruit, low -fat yogurt, whole grain breakfast bars, or granola bars for those mornings when you have to eat breakfast on the go. • Replace or accompany that morning cup of coffee with a glass of orange juice or milk. • Make an omelet! You can shorten preparation time by chopping up your vegetables ahead of time. • Get up 15 minutes earlier. You can fix and consume a healthy breakfast in 15 minutes or less. • Plan ahead to eat breakfast. This means you should decide what you are going to eat for breakfast before the next morning. You can save time by putting out the box of cereal or cutting up some fruit the night before

Mighty Mustang Monday, Aug. 31 st Agenda: 1. Warm-Up 2. FN: The American Constitution 3. Constitution Chart Home Fun: 1. Work on Title Page Warm-Up Review the Grievance of the Declaration of Independence. Which of them do you think was the most important issue for the Colonists to fight for? Why? 3 -5 sentences

Terrific Tuesday, Sept. 1 st Agenda: 1. Warm-Up 2. FN: The American Constitution 3. Constitution Chart Home Fun: 1. Work on notebook 1. Highlight information in your notes 2. Work on title page 3. Tape in documents 4. Finish vocab or any inc. assignments Warm-Up As you watch the video you will need to take down at least 4 points.

The American Constitution Standard 11. 1 – Analyze the sig. events that lead to the development of our nation and its attempts to realize its guiding philosophies. EQ - How did the Constitution change the 5 power of the national government?

the articles of confederation, 1781 -1788 • Our 1 st government was created in a way that it couldn’t take people’s rights. • The Nation couldn’t raise taxes or an army. • The government only lasted a few years. • It was a really terrible government, but it was OUR terrible government. 6

the articles of confederation, 1781 -1788 • States were like their own little countries • Sort of like the European Union • All 13 states got one vote. • Each state had its own unique money • The expression "not worth a Continental" arose when the new, American, paper notes essentially became worthless due to severe inflation toward the end of the Rev. War 7

shays’ rebellion, 1786 • An armed uprising in Massachusetts (MA) makes many people realize that the government was too weak • Daniel Shays was a Revolutionary war veteran who lost his farm because he fell behind on his farm payments. • His excuse was that he wasn’t working his farm because he was fighting the British. • The bank said too bad…and uh thanks for the liberty. • After the uprising 12 states agreed to meet in Philadelphia, PA. • Rhode Island did not send a delegate 8

the constitutional convention, 1787 • The states’ delegates met in PA to fix the Articles of Confederation • They met from May to September and it was ridiculously hot and humid and the delegates all wore wool and wigs. It was supposedly super miserable (and smelly). • They realized they needed a stronger national government. • They immediately gave up on the Articles of Confederation and started over. • Two major plans were submitted. 9

Wonderful Wednesday, Sept. 2 nd Agenda: 1. Warm-Up 2. FN: The American Constitution / Graphic org. 3. Review Graphic Org 4. Wrap-Up Home Fun: 1. Finish Constitution graphic organizer 2. Study guide questions 1 -10 Warm-Up Take 4 notes from the video – We are going to watch it twice, you will take notes the second time.

The Constitutional Convention, 1787 • Virginia Plan • James Madison suggested a two-house legislature with membership based on each state’s population. • The small states hated it. • Mostly this was based on British Parliament and Virginia’s state congress. • New Jersey Plan • This plan suggested a single-house congress in which each state had an equal vote. • The large states hated it. • Basically this was just the Articles of Confederation all over again. CSS 11. 1. 2

The Constitutional Convention, 1787 • Great Compromise • Roger Sherman suggested a twohouse legislature. • The upper house would have equal votes (two) and the lower house would be based on population. • Three-Fifths Compromise • Southern states wanted to include slaves in their populations. • In the end they could count them but only as three-fifths of a person. • By the Civil War, 2/3 of the population of South Carolina were slaves. CSS 11. 1. 2
what’s in the constitution? • Federalism divides power between the national (federal) government and the state governments. • Separation of Powers • They created three branches of government: legislative, judicial, and executive. • Separation of Church and State • The government can’t tax churches and churches can’t get involved in politics. 13
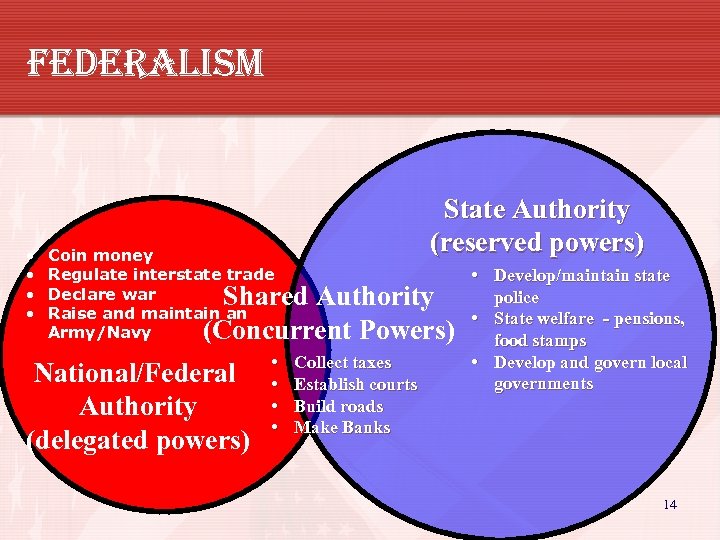
federalism • • State Authority (reserved powers) Coin money Regulate interstate trade Declare war Raise and maintain an Army/Navy Shared Authority (Concurrent Powers) National/Federal Authority (delegated powers) • • Collect taxes Establish courts Build roads Make Banks • Develop/maintain state police • State welfare - pensions, food stamps • Develop and govern local governments 14

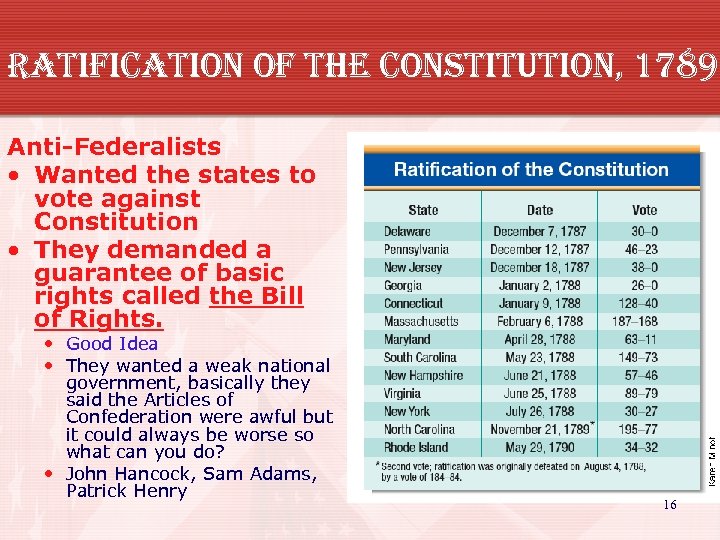
ratification of the constitution, 1789 • 9 of 13 states had to ratify (accept) the Constitution for it to be law. • Federalists wanted the states to vote for the Constitution. • They wrote essays called “the Federalist Papers” and held parades to drum up support for their side. They won. • They wanted a strong president and more national power than state power. • James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, George Washington, Ben Franklin 15
ratification of the constitution, 1789 Anti-Federalists • Wanted the states to vote against Constitution • They demanded a guarantee of basic rights called the Bill of Rights. • Good Idea • They wanted a weak national government, basically they said the Articles of Confederation were awful but it could always be worse so what can you do? • John Hancock, Sam Adams, Patrick Henry 16

the new nation • George Washington was elected the first President and John Adams was the first Vice President. • Washington had to “invent” how to be President • In 1789, only white, land owning men had the ability to vote in most states • Very few votes overall: • Delaware 3% of the population • Georgia 5% • New York 3% • Rhode Island 0. 7%. 17

the new nation • Whiskey Rebellion, 1794 • The government raised taxes on the production of whiskey which PA farmers refused to pay. • Whiskey- concentrated liquid corn • Easier to transport and store • Urban vs rural politics • Washington led 15, 000 federal soldiers to make them pay and proved that the new government was strong. • This was the opposite of Shays Rebellion 18

the first Political Parties • Federalists • Alexander Hamilton supported federal authority. • national bank, a high tariff, industry • Democratic-Republicans • Thomas Jefferson supported the states’ having more authority. • state banks, a low tariff, farmers 19

alien and sedition acts, 1798 • John Adams, a Federalist, made it illegal to express opinions considered dangerous to the government (sedition). • The Act raised the residency requirements for citizenship (voting). • Most new immigrants were becoming Democratic-Republicans. • Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions, 1798 • Thomas Jefferson argued that the states should ignore any laws that violated the Constitution. • This argument, called nullification, led to the 20 Civil War.

marbury v. madison, 1803 • Arguably, the MOST important Supreme Court cases in American history. • Marbury was appointed by John Adams at the end of his presidency but had to get his license to be a judge from the new president Thomas Jefferson. • James Madison refused to hand over the papers because he thought Marbury’s appointment was illegal. • Created - Judicial Review • The right of the Supreme Court to declare acts of the Congress and the president as unconstitutional. 21
4bcabe6e9a148a443e9fc6ae2313ccd9.ppt