7c3d68fc4e810b719f777038559ddca7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 FADE: Secure Overlay Cloud Storage with File Assured Deletion Yang Tang 1, Patrick P. C. Lee 1, John C. S. Lui 1, Radia Perlman 2 1 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 2 Intel Labs Secure. Comm 2010 1
FADE: Secure Overlay Cloud Storage with File Assured Deletion Yang Tang 1, Patrick P. C. Lee 1, John C. S. Lui 1, Radia Perlman 2 1 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 2 Intel Labs Secure. Comm 2010 1
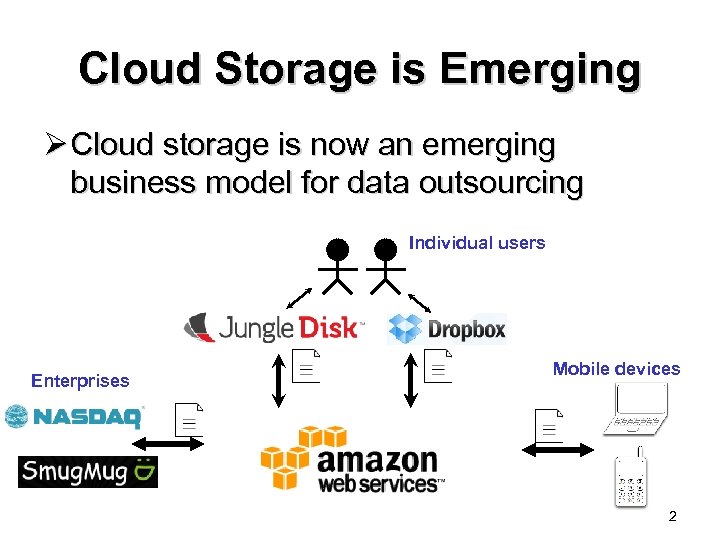 Cloud Storage is Emerging Ø Cloud storage is now an emerging business model for data outsourcing Individual users Enterprises Mobile devices 2
Cloud Storage is Emerging Ø Cloud storage is now an emerging business model for data outsourcing Individual users Enterprises Mobile devices 2
 Case Studies Ø Smugmug: hosting terabytes of photos since 2006 • Savings: USD 500 K per year as in 2006 • More savings are expected with more photos Ø NASDAQ: hosting historical market data since 2008 Ø More clients are found on: http: //aws. amazon. com/solutions/case-studies/ References: • http: //don. blogs. smugmug. com/2006/11/10/amazon-s 3 -show-me-the-money/ • http: //www. infoq. com/articles/nasdaq-case-study-air-and-s 3? 3
Case Studies Ø Smugmug: hosting terabytes of photos since 2006 • Savings: USD 500 K per year as in 2006 • More savings are expected with more photos Ø NASDAQ: hosting historical market data since 2008 Ø More clients are found on: http: //aws. amazon. com/solutions/case-studies/ References: • http: //don. blogs. smugmug. com/2006/11/10/amazon-s 3 -show-me-the-money/ • http: //www. infoq. com/articles/nasdaq-case-study-air-and-s 3? 3
 Implications of Cloud Storage Ø Cloud storage will be a cost-saving business solution: • Save cost for unused storage • Save technical support for data backups • Save electric power and maintenance costs for data centers Ø Yet, as a cloud client, how do we provide security guarantees for outsourced data? 4
Implications of Cloud Storage Ø Cloud storage will be a cost-saving business solution: • Save cost for unused storage • Save technical support for data backups • Save electric power and maintenance costs for data centers Ø Yet, as a cloud client, how do we provide security guarantees for outsourced data? 4
 Security Challenges Ø Can we protect outsourced data from improperly accessed? • Unauthorized users must not access our data • We don’t want cloud providers to mine our data for their marketing purposes Ø We need access control: • Only authorized parties can access outsourced data 5
Security Challenges Ø Can we protect outsourced data from improperly accessed? • Unauthorized users must not access our data • We don’t want cloud providers to mine our data for their marketing purposes Ø We need access control: • Only authorized parties can access outsourced data 5
 Security Challenges Ø Can we reliably remove data from cloud? • We don’t want backups to exist after pre-defined time • e. g. , to avoid future exposure due to data breach or error management of operators • If an employee quits, we want to remove his/her data • e. g. , to avoid legal liability Ø Cloud makes backup copies. We don’t know if all backup copies are reliably removed. Ø We need assured deletion: • Data becomes inaccessible upon requests of deletion 6
Security Challenges Ø Can we reliably remove data from cloud? • We don’t want backups to exist after pre-defined time • e. g. , to avoid future exposure due to data breach or error management of operators • If an employee quits, we want to remove his/her data • e. g. , to avoid legal liability Ø Cloud makes backup copies. We don’t know if all backup copies are reliably removed. Ø We need assured deletion: • Data becomes inaccessible upon requests of deletion 6
 Previous Work Ø Cryptographic protection on outsourced data storage [Ateniese et al. , Secure. Comm’ 08; Wang et al. , CCSW’ 09] • Require new protocol support on the cloud infrastructure Ø Security solutions compatible with existing cloud (e. g. , Cumulus, Jungle. Disk) [Yun et al. , CCSW’ 09; Vrable et al. , To. S’ 09] • No guarantees of reliable deletion of data 7
Previous Work Ø Cryptographic protection on outsourced data storage [Ateniese et al. , Secure. Comm’ 08; Wang et al. , CCSW’ 09] • Require new protocol support on the cloud infrastructure Ø Security solutions compatible with existing cloud (e. g. , Cumulus, Jungle. Disk) [Yun et al. , CCSW’ 09; Vrable et al. , To. S’ 09] • No guarantees of reliable deletion of data 7
![Previous Work Ø Perlman’s Ephemerizer [NDSS’ 07] … … • A file is encrypted Previous Work Ø Perlman’s Ephemerizer [NDSS’ 07] … … • A file is encrypted](https://present5.com/presentation/7c3d68fc4e810b719f777038559ddca7/image-8.jpg) Previous Work Ø Perlman’s Ephemerizer [NDSS’ 07] … … • A file is encrypted with a data key expiration date • The data key is further encrypted with a time-based control key • The control key is deleted when expiration time is reached • The control key is maintained by a separate key manager (aka Ephemerizer) Ø Weaknesses: • Target only time-based assured deletion • No fine-grained control of different file access policies • No implementation 8
Previous Work Ø Perlman’s Ephemerizer [NDSS’ 07] … … • A file is encrypted with a data key expiration date • The data key is further encrypted with a time-based control key • The control key is deleted when expiration time is reached • The control key is maintained by a separate key manager (aka Ephemerizer) Ø Weaknesses: • Target only time-based assured deletion • No fine-grained control of different file access policies • No implementation 8
![Previous Work Ø Vanish [USENIX’ 09] • Divide the data key into many key Previous Work Ø Vanish [USENIX’ 09] • Divide the data key into many key](https://present5.com/presentation/7c3d68fc4e810b719f777038559ddca7/image-9.jpg) Previous Work Ø Vanish [USENIX’ 09] • Divide the data key into many key shares • Store key shares in nodes of a deployed P 2 P network • Nodes remove key shares that reside in cache for 8 hours Ø Weaknesses: • Time-based, no fine-grained control 9
Previous Work Ø Vanish [USENIX’ 09] • Divide the data key into many key shares • Store key shares in nodes of a deployed P 2 P network • Nodes remove key shares that reside in cache for 8 hours Ø Weaknesses: • Time-based, no fine-grained control 9
 Our Work FADE: a secure overlay cloud storage system with file assured deletion Ø Design of FADE: • work atop today’s cloud as an overlay • achieve protection from a cloud client’s perspective, no changes on the cloud provider side Ø Security of FADE: • Fine-grained file assured deletion: files are permanently inaccessible based on policies 10
Our Work FADE: a secure overlay cloud storage system with file assured deletion Ø Design of FADE: • work atop today’s cloud as an overlay • achieve protection from a cloud client’s perspective, no changes on the cloud provider side Ø Security of FADE: • Fine-grained file assured deletion: files are permanently inaccessible based on policies 10
 Our Work Ø We propose a new policy-based file assured deletion scheme that reliably deletes files of revoked file access policies Ø We implement a working prototype of FADE atop Amazon S 3 Ø We empirically evaluate the performance overhead of FADE atop Amazon S 3 11
Our Work Ø We propose a new policy-based file assured deletion scheme that reliably deletes files of revoked file access policies Ø We implement a working prototype of FADE atop Amazon S 3 Ø We empirically evaluate the performance overhead of FADE atop Amazon S 3 11
 Policy-based File Assured Deletion Ø Each file is associated with a data key and a file access policy Ø Each policy is associated with a control key Ø All control keys are maintained by a key manager Ø When a policy is revoked, its respective control key will be removed from the key manager 12
Policy-based File Assured Deletion Ø Each file is associated with a data key and a file access policy Ø Each policy is associated with a control key Ø All control keys are maintained by a key manager Ø When a policy is revoked, its respective control key will be removed from the key manager 12
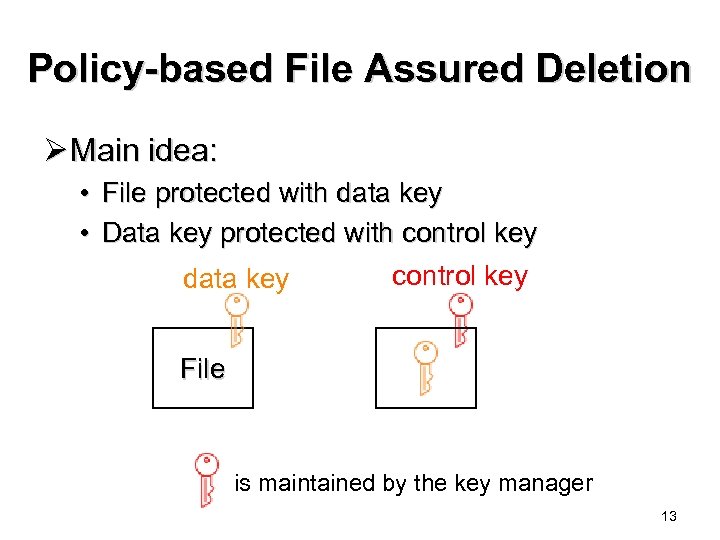 Policy-based File Assured Deletion Ø Main idea: • File protected with data key • Data key protected with control key data key File is maintained by the key manager 13
Policy-based File Assured Deletion Ø Main idea: • File protected with data key • Data key protected with control key data key File is maintained by the key manager 13
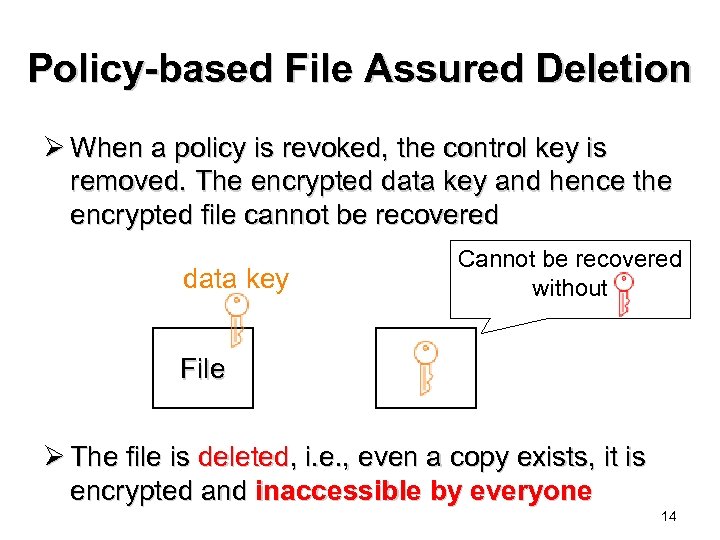 Policy-based File Assured Deletion Ø When a policy is revoked, the control key is removed. The encrypted data key and hence the encrypted file cannot be recovered data key Cannot be recovered without File Ø The file is deleted, i. e. , even a copy exists, it is encrypted and inaccessible by everyone 14
Policy-based File Assured Deletion Ø When a policy is revoked, the control key is removed. The encrypted data key and hence the encrypted file cannot be recovered data key Cannot be recovered without File Ø The file is deleted, i. e. , even a copy exists, it is encrypted and inaccessible by everyone 14
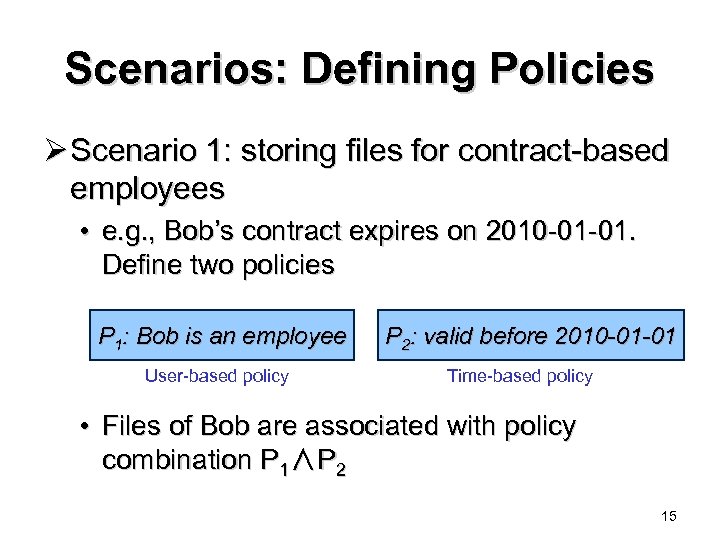 Scenarios: Defining Policies Ø Scenario 1: storing files for contract-based employees • e. g. , Bob’s contract expires on 2010 -01 -01. Define two policies P 1: Bob is an employee User-based policy P 2: valid before 2010 -01 -01 Time-based policy • Files of Bob are associated with policy combination P 1∧P 2 15
Scenarios: Defining Policies Ø Scenario 1: storing files for contract-based employees • e. g. , Bob’s contract expires on 2010 -01 -01. Define two policies P 1: Bob is an employee User-based policy P 2: valid before 2010 -01 -01 Time-based policy • Files of Bob are associated with policy combination P 1∧P 2 15
 Scenarios: Defining Policies Ø Scenario 2: switching a cloud provider • Define a customer-based policy P: customer of cloud provider X • • All files outsourced on X are tied with policy P If the company switches to a new cloud provider, it simply revokes policy P 16
Scenarios: Defining Policies Ø Scenario 2: switching a cloud provider • Define a customer-based policy P: customer of cloud provider X • • All files outsourced on X are tied with policy P If the company switches to a new cloud provider, it simply revokes policy P 16
 Lessons Learned Ø Policy-based file-assured deletion enables to have a fine-grained control of how to delete files Ø Similar to Attribute-Based Encryption (ABE) • ABE focuses on accessing data and distribute keys to users that satisfy attributes (policies) • We focus on deleting data, and need to manage/delete keys in a centralized manner 17
Lessons Learned Ø Policy-based file-assured deletion enables to have a fine-grained control of how to delete files Ø Similar to Attribute-Based Encryption (ABE) • ABE focuses on accessing data and distribute keys to users that satisfy attributes (policies) • We focus on deleting data, and need to manage/delete keys in a centralized manner 17
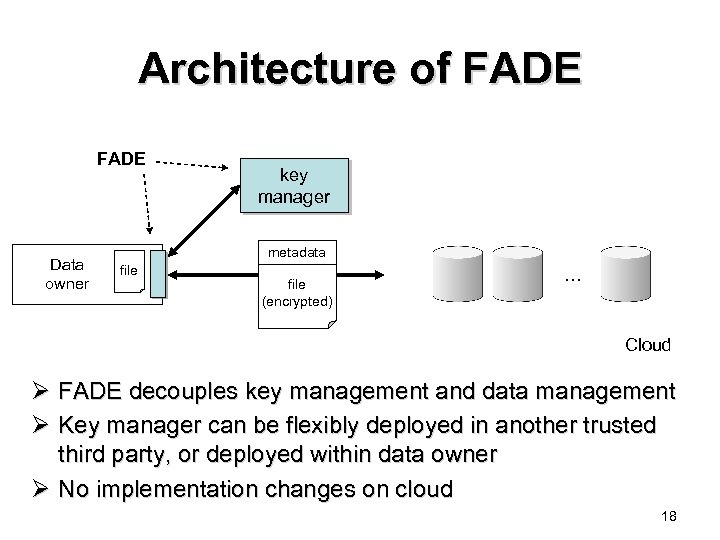 Architecture of FADE Data owner key manager metadata file (encrypted) … Cloud Ø FADE decouples key management and data management Ø Key manager can be flexibly deployed in another trusted third party, or deployed within data owner Ø No implementation changes on cloud 18
Architecture of FADE Data owner key manager metadata file (encrypted) … Cloud Ø FADE decouples key management and data management Ø Key manager can be flexibly deployed in another trusted third party, or deployed within data owner Ø No implementation changes on cloud 18
 Threat Models and Assumptions Ø File assured deletion is achieved • If we request to delete a file, it is inaccessible Ø Key manager is minimally trusted • can reliably remove keys of revoked policies • can be compromised, but only files with active policies can be recovered Ø Data owner forms an authenticated channel with key manager for key management operations 19
Threat Models and Assumptions Ø File assured deletion is achieved • If we request to delete a file, it is inaccessible Ø Key manager is minimally trusted • can reliably remove keys of revoked policies • can be compromised, but only files with active policies can be recovered Ø Data owner forms an authenticated channel with key manager for key management operations 19
 Key Management Operations Ø Idea: use key management operations to decide how files are accessed while achieving file assured deletion Ø Basic operations for data outsourcing: • • File upload File download Policy revocation Policy renewal Ø Built on RSA 20
Key Management Operations Ø Idea: use key management operations to decide how files are accessed while achieving file assured deletion Ø Basic operations for data outsourcing: • • File upload File download Policy revocation Policy renewal Ø Built on RSA 20
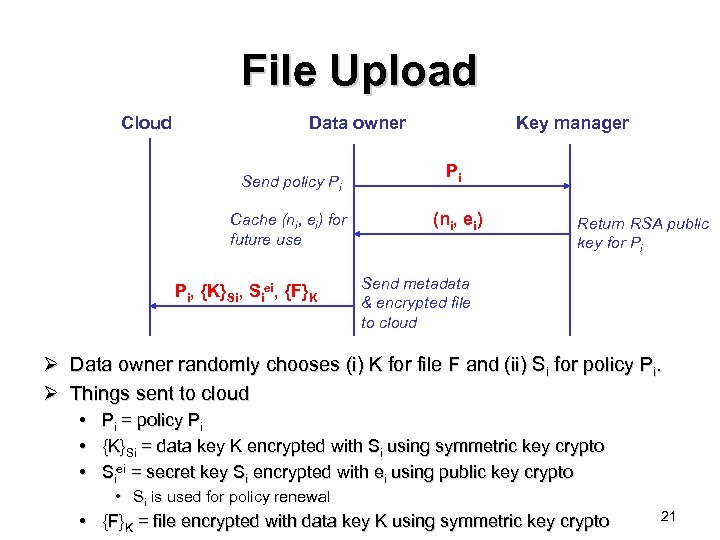 File Upload Cloud Data owner Send policy Pi Cache (ni, ei) for future use Pi, {K}Si, Siei, {F}K Key manager Pi (ni, ei) Return RSA public key for Pi Send metadata & encrypted file to cloud Ø Data owner randomly chooses (i) K for file F and (ii) Si for policy Pi. Ø Things sent to cloud • Pi = policy Pi • {K}Si = data key K encrypted with Si using symmetric key crypto • Siei = secret key Si encrypted with ei using public key crypto • Si is used for policy renewal • {F}K = file encrypted with data key K using symmetric key crypto 21
File Upload Cloud Data owner Send policy Pi Cache (ni, ei) for future use Pi, {K}Si, Siei, {F}K Key manager Pi (ni, ei) Return RSA public key for Pi Send metadata & encrypted file to cloud Ø Data owner randomly chooses (i) K for file F and (ii) Si for policy Pi. Ø Things sent to cloud • Pi = policy Pi • {K}Si = data key K encrypted with Si using symmetric key crypto • Siei = secret key Si encrypted with ei using public key crypto • Si is used for policy renewal • {F}K = file encrypted with data key K using symmetric key crypto 21
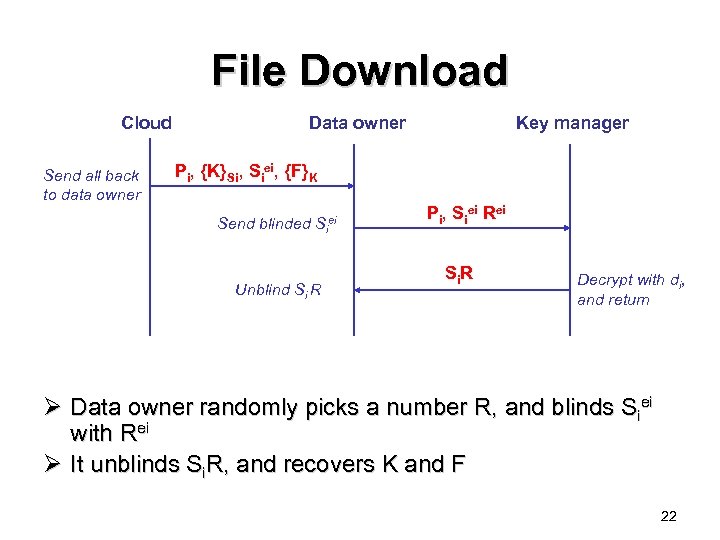 File Download Cloud Send all back to data owner Data owner Key manager Pi, {K}Si, Siei, {F}K Send blinded Siei Unblind Si R Pi, Siei Rei Si. R Decrypt with di, and return Ø Data owner randomly picks a number R, and blinds Siei with Rei Ø It unblinds Si. R, and recovers K and F 22
File Download Cloud Send all back to data owner Data owner Key manager Pi, {K}Si, Siei, {F}K Send blinded Siei Unblind Si R Pi, Siei Rei Si. R Decrypt with di, and return Ø Data owner randomly picks a number R, and blinds Siei with Rei Ø It unblinds Si. R, and recovers K and F 22
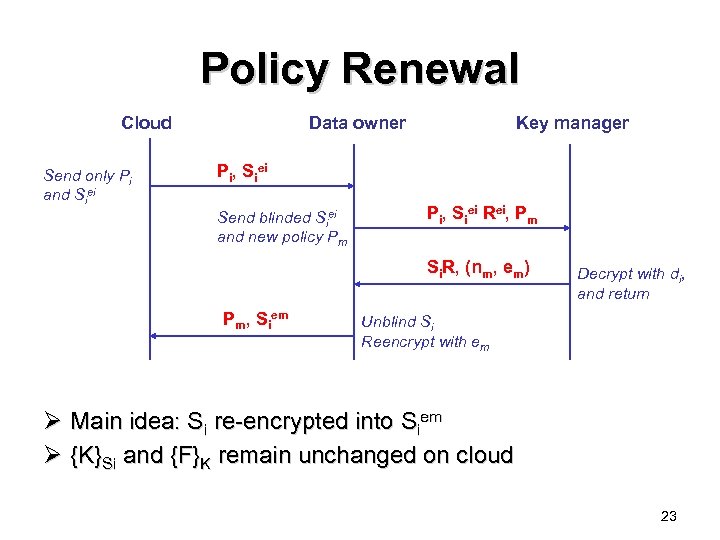 Policy Renewal Cloud Send only Pi and Siei Data owner Key manager Pi, Siei Send blinded Siei and new policy Pm Pi, Siei Rei, Pm Si. R, (nm, em) Pm, Siem Decrypt with di, and return Unblind Si Reencrypt with em Ø Main idea: Si re-encrypted into Siem Ø {K}Si and {F}K remain unchanged on cloud 23
Policy Renewal Cloud Send only Pi and Siei Data owner Key manager Pi, Siei Send blinded Siei and new policy Pm Pi, Siei Rei, Pm Si. R, (nm, em) Pm, Siem Decrypt with di, and return Unblind Si Reencrypt with em Ø Main idea: Si re-encrypted into Siem Ø {K}Si and {F}K remain unchanged on cloud 23
 Policy Revocation Ø Revoke policy Pi • Key manager removes all keys (ni, ei, di) • All files tied with policy Pi become inaccessible 24
Policy Revocation Ø Revoke policy Pi • Key manager removes all keys (ni, ei, di) • All files tied with policy Pi become inaccessible 24
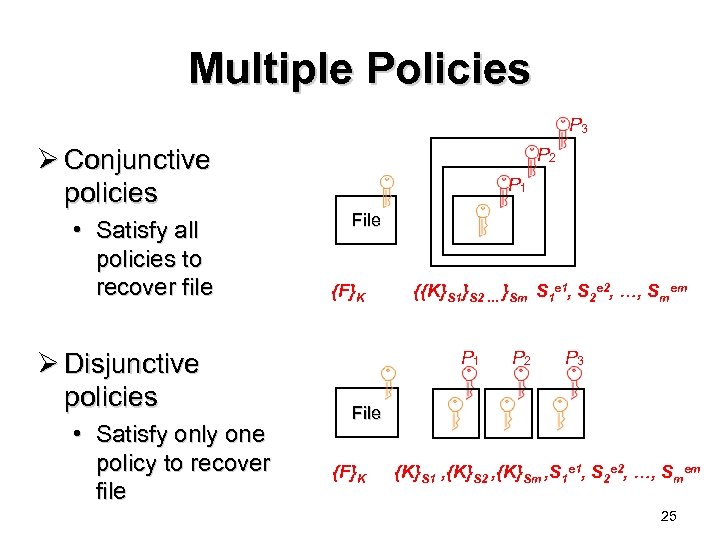 Multiple Policies P 3 Ø Conjunctive policies • Satisfy all policies to recover file Ø Disjunctive policies • Satisfy only one policy to recover file P 2 P 1 File {F}K {{K}S 1}S 2 … }Sm S 1 e 1, S 2 e 2, …, Smem P 1 P 2 P 3 File {F}K {K}S 1 , {K}S 2 , {K}Sm , S 1 e 1, S 2 e 2, …, Smem 25
Multiple Policies P 3 Ø Conjunctive policies • Satisfy all policies to recover file Ø Disjunctive policies • Satisfy only one policy to recover file P 2 P 1 File {F}K {{K}S 1}S 2 … }Sm S 1 e 1, S 2 e 2, …, Smem P 1 P 2 P 3 File {F}K {K}S 1 , {K}S 2 , {K}Sm , S 1 e 1, S 2 e 2, …, Smem 25
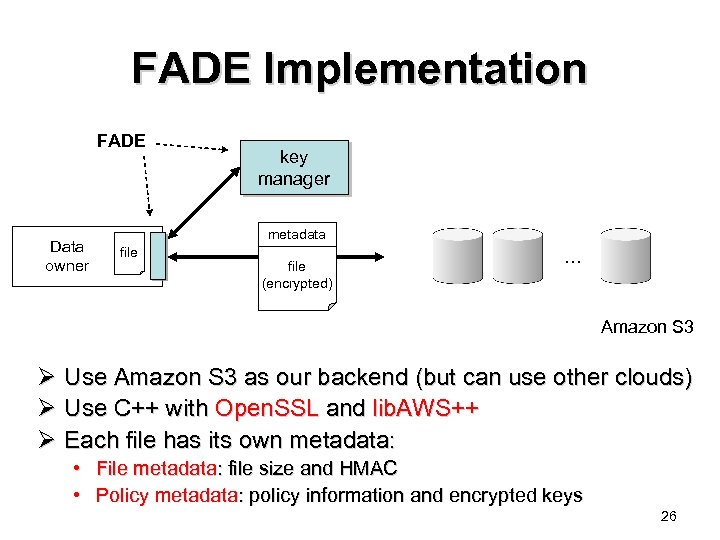 FADE Implementation FADE Data owner key manager metadata file (encrypted) … Amazon S 3 Ø Use Amazon S 3 as our backend (but can use other clouds) Ø Use C++ with Open. SSL and lib. AWS++ Ø Each file has its own metadata: • File metadata: file size and HMAC • Policy metadata: policy information and encrypted keys 26
FADE Implementation FADE Data owner key manager metadata file (encrypted) … Amazon S 3 Ø Use Amazon S 3 as our backend (but can use other clouds) Ø Use C++ with Open. SSL and lib. AWS++ Ø Each file has its own metadata: • File metadata: file size and HMAC • Policy metadata: policy information and encrypted keys 26
 Interfaces of Data Owner Ø Interfaces to interact with cloud: • • Upload(file, policy) Download(file) Delete(policy) Renew(file, new_policy) Ø Can be exported as library APIs for other implementations of data owner 27
Interfaces of Data Owner Ø Interfaces to interact with cloud: • • Upload(file, policy) Download(file) Delete(policy) Renew(file, new_policy) Ø Can be exported as library APIs for other implementations of data owner 27
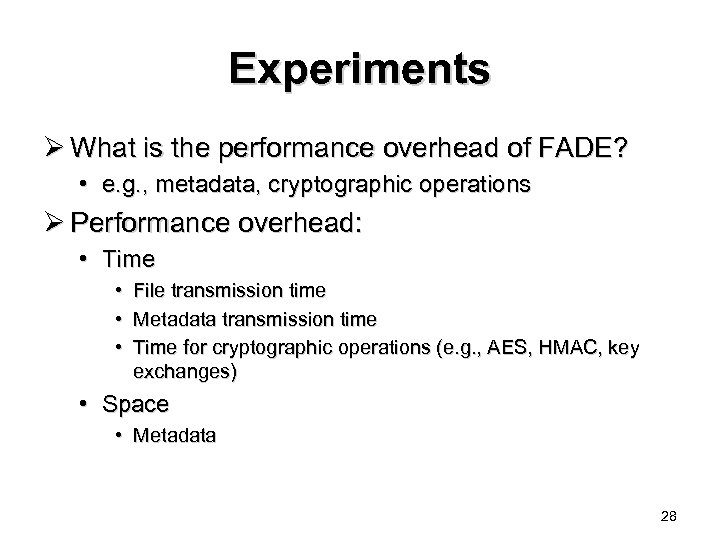 Experiments Ø What is the performance overhead of FADE? • e. g. , metadata, cryptographic operations Ø Performance overhead: • Time • File transmission time • Metadata transmission time • Time for cryptographic operations (e. g. , AES, HMAC, key exchanges) • Space • Metadata 28
Experiments Ø What is the performance overhead of FADE? • e. g. , metadata, cryptographic operations Ø Performance overhead: • Time • File transmission time • Metadata transmission time • Time for cryptographic operations (e. g. , AES, HMAC, key exchanges) • Space • Metadata 28
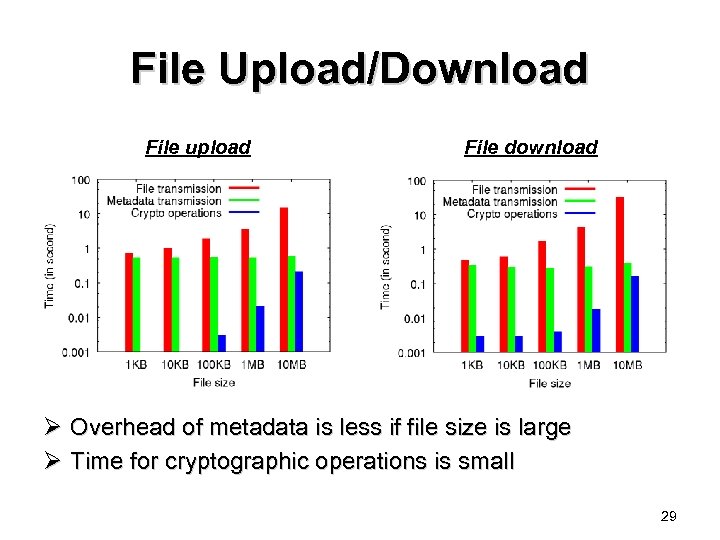 File Upload/Download File upload File download Ø Overhead of metadata is less if file size is large Ø Time for cryptographic operations is small 29
File Upload/Download File upload File download Ø Overhead of metadata is less if file size is large Ø Time for cryptographic operations is small 29
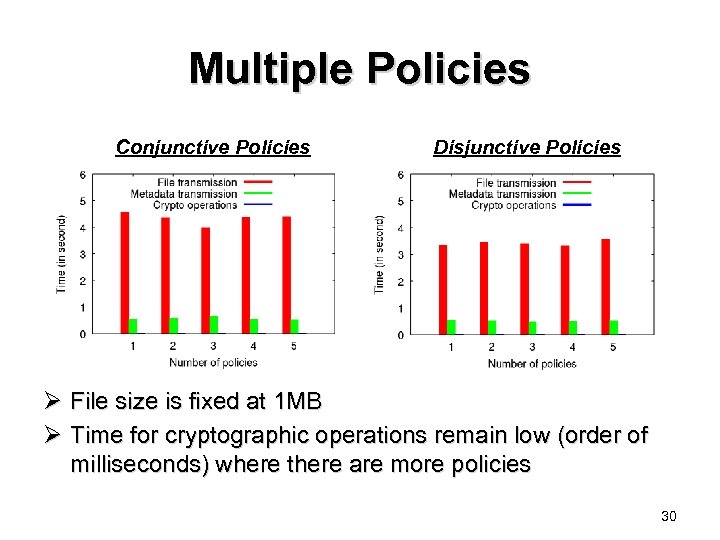 Multiple Policies Conjunctive Policies Disjunctive Policies Ø File size is fixed at 1 MB Ø Time for cryptographic operations remain low (order of milliseconds) where there are more policies 30
Multiple Policies Conjunctive Policies Disjunctive Policies Ø File size is fixed at 1 MB Ø Time for cryptographic operations remain low (order of milliseconds) where there are more policies 30
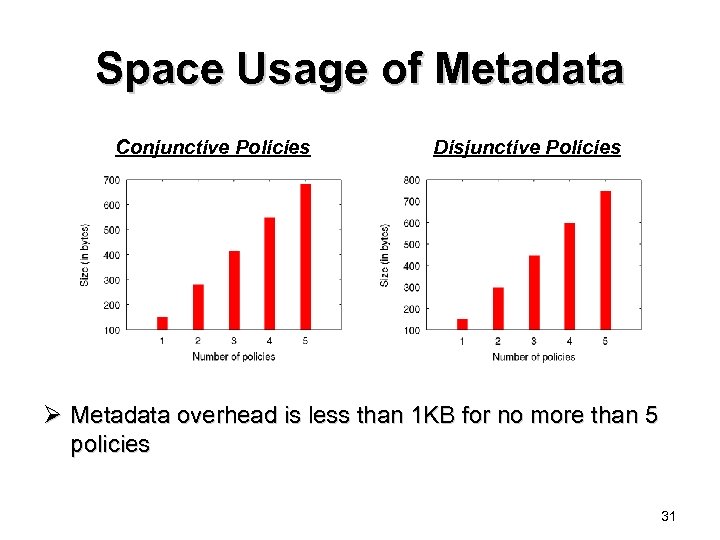 Space Usage of Metadata Conjunctive Policies Disjunctive Policies Ø Metadata overhead is less than 1 KB for no more than 5 policies 31
Space Usage of Metadata Conjunctive Policies Disjunctive Policies Ø Metadata overhead is less than 1 KB for no more than 5 policies 31
 Conclusions Ø FADE, an overlay cloud storage system with access control and assured deletion Ø Cryptographic operations for policy-based file assured deletion Ø Implement a FADE prototype atop Amazon S 3 Ø FADE works in practice 32
Conclusions Ø FADE, an overlay cloud storage system with access control and assured deletion Ø Cryptographic operations for policy-based file assured deletion Ø Implement a FADE prototype atop Amazon S 3 Ø FADE works in practice 32
 Future Work Ø Quorum scheme of multiple key managers • Threshold secret sharing • k out of n key shares to recover keys Ø Integration with ABE for communication between data owner and key managers Ø Optimization of storage • Operations for a batch of files rather than individual files 33
Future Work Ø Quorum scheme of multiple key managers • Threshold secret sharing • k out of n key shares to recover keys Ø Integration with ABE for communication between data owner and key managers Ø Optimization of storage • Operations for a batch of files rather than individual files 33
 Source Code Ø Source code available at: • http: //ansrlab. cse. cuhk. edu. hk/software/fade/ 34
Source Code Ø Source code available at: • http: //ansrlab. cse. cuhk. edu. hk/software/fade/ 34


