791ce38e0d60b056567d220abc8666df.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Factors that determine exchange rates. Forecasting future exchange rates. Foreign exchange risk and its management.
Factors that determine exchange rates. Forecasting future exchange rates. Foreign exchange risk and its management.
 Foreign Exchange (FX) Rates SPO T RA TE (S 0 ) = $/FX WHICH IS A U. S. DIRECT QUO TE (AND A FX INDIR ECT QUOTE) S 0 = $1. 35/ € IS THE SP OT RATE FOR EURO…TO BE EXCHA NG ED W ITHIN 2 BUSINESS DAYS.
Foreign Exchange (FX) Rates SPO T RA TE (S 0 ) = $/FX WHICH IS A U. S. DIRECT QUO TE (AND A FX INDIR ECT QUOTE) S 0 = $1. 35/ € IS THE SP OT RATE FOR EURO…TO BE EXCHA NG ED W ITHIN 2 BUSINESS DAYS.
 Change in Exchange Rates S 0 = $1. 36/€ S 1 = $1. 38/€ The dollar has depreciated against the euro OR the euro has appreciated against the dollar. Devaluation and revaluation are the terms used when exchange rates are fixed as opposed to floating.
Change in Exchange Rates S 0 = $1. 36/€ S 1 = $1. 38/€ The dollar has depreciated against the euro OR the euro has appreciated against the dollar. Devaluation and revaluation are the terms used when exchange rates are fixed as opposed to floating.
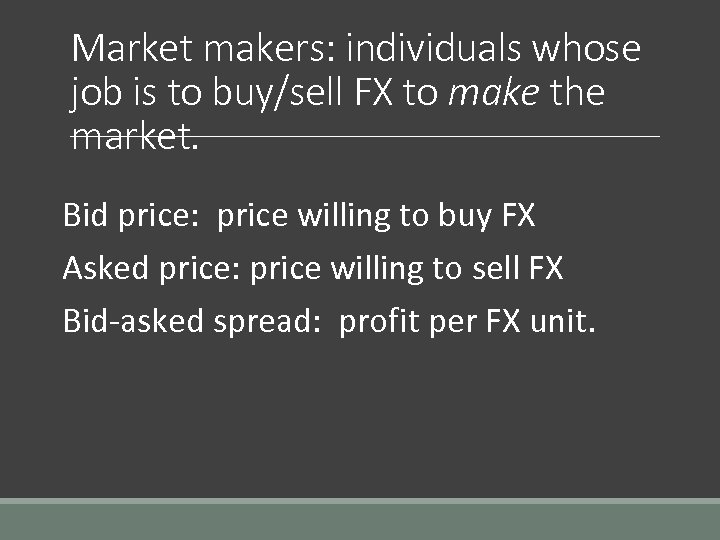 Market makers: individuals whose job is to buy/sell FX to make the market. Bid price: price willing to buy FX Asked price: price willing to sell FX Bid-asked spread: profit per FX unit.
Market makers: individuals whose job is to buy/sell FX to make the market. Bid price: price willing to buy FX Asked price: price willing to sell FX Bid-asked spread: profit per FX unit.
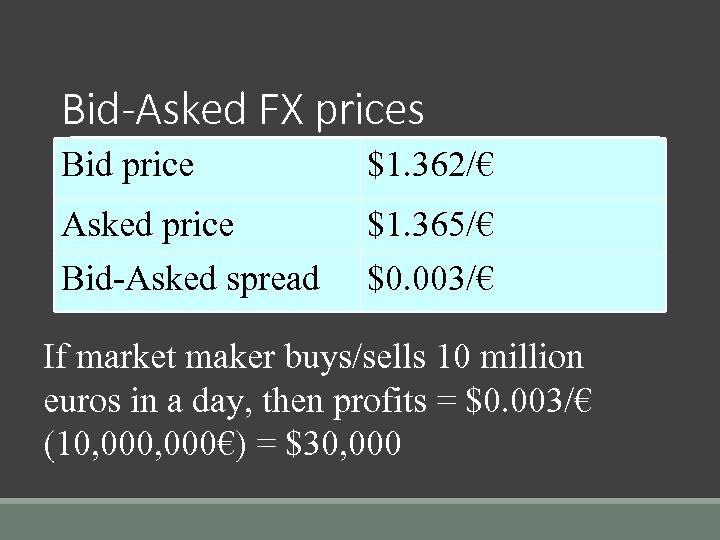 Bid-Asked FX prices Bid price $1. 362/€ Asked price Bid-Asked spread $1. 365/€ $0. 003/€ If market maker buys/sells 10 million euros in a day, then profits = $0. 003/€ (10, 000€) = $30, 000
Bid-Asked FX prices Bid price $1. 362/€ Asked price Bid-Asked spread $1. 365/€ $0. 003/€ If market maker buys/sells 10 million euros in a day, then profits = $0. 003/€ (10, 000€) = $30, 000
 Objective of market maker: avoid being long or short FX Long FX buy > sell accumulate Short buy < sell need to acquire FX from another trader
Objective of market maker: avoid being long or short FX Long FX buy > sell accumulate Short buy < sell need to acquire FX from another trader
 How does a market maker know how to change FX prices in response to changes in world supply and demand?
How does a market maker know how to change FX prices in response to changes in world supply and demand?
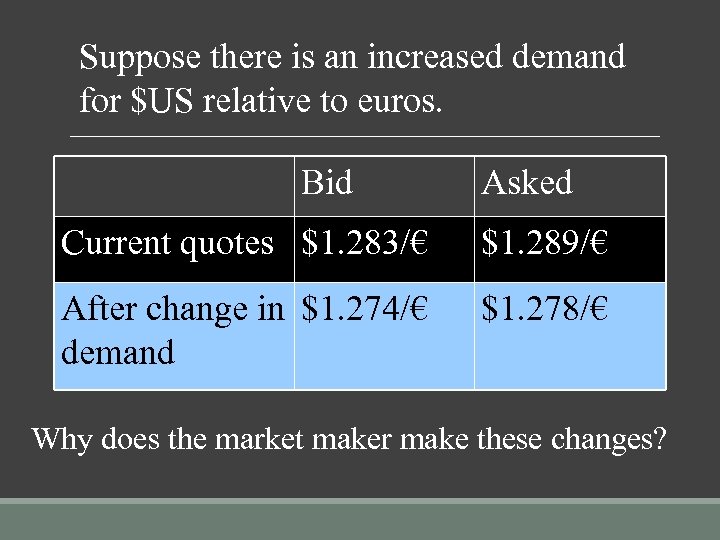 Suppose there is an increased demand for $US relative to euros. Bid Asked Current quotes $1. 283/€ $1. 289/€ After change in $1. 274/€ demand $1. 278/€ Why does the market maker make these changes?
Suppose there is an increased demand for $US relative to euros. Bid Asked Current quotes $1. 283/€ $1. 289/€ After change in $1. 274/€ demand $1. 278/€ Why does the market maker make these changes?
 Forward Rates (F): rate set today to be paid in 30, 60, 90, or 180 days. ANNUALIZED FORWARD PREMIUM (OR DISCOUNT) = [(F- S )/ S 0 ](12/N)100% 0 WHERE N = NUMBER OF MONTHS IN THE FORWARD CONTRACT.
Forward Rates (F): rate set today to be paid in 30, 60, 90, or 180 days. ANNUALIZED FORWARD PREMIUM (OR DISCOUNT) = [(F- S )/ S 0 ](12/N)100% 0 WHERE N = NUMBER OF MONTHS IN THE FORWARD CONTRACT.
 Forward premium: the forward value of the FX is higher than the spot: S = $1. 35/€; F = $1. 40/€ so the euro is selling at a forward premium Forward discount: the forward value of the FX is lower than the spot: S = $1. 35/€; F = $1. 30/€ so the euro is selling at a forward discount
Forward premium: the forward value of the FX is higher than the spot: S = $1. 35/€; F = $1. 40/€ so the euro is selling at a forward premium Forward discount: the forward value of the FX is lower than the spot: S = $1. 35/€; F = $1. 30/€ so the euro is selling at a forward discount
 Forward rate is an unbiased estimate of future spot rates known as the unbiased forward rate condition: Ft = E(St)
Forward rate is an unbiased estimate of future spot rates known as the unbiased forward rate condition: Ft = E(St)
 Interest Rate Parity (IRP) IRP simply means that the rate of return on a domestic investment will be equal to the rate of return on a foreign investment. The relationship occurs because investors take part in covered interest arbitrage also known as a forward hedge.
Interest Rate Parity (IRP) IRP simply means that the rate of return on a domestic investment will be equal to the rate of return on a foreign investment. The relationship occurs because investors take part in covered interest arbitrage also known as a forward hedge.
 Consider the following investment opportunities U. S. investor has $1. 2 million to invest. US 90 -day CDs are 4%; Swiss 90 -day CDs are 7%. Spot rate: S 0 = $0. 60/CHF 90 -day forward rate: F 90 = $0. 60/CHF. Objective: Maximize 90 -day return.
Consider the following investment opportunities U. S. investor has $1. 2 million to invest. US 90 -day CDs are 4%; Swiss 90 -day CDs are 7%. Spot rate: S 0 = $0. 60/CHF 90 -day forward rate: F 90 = $0. 60/CHF. Objective: Maximize 90 -day return.
 If everyone invests in the Swiss CD, the CHF should appreciate in the spot market and depreciate in the forward market relative to the $US…WHY? Suppose now the we have: S 0 = $0. 605/CHF; F 90 = $0. 595/CHF US 90 -day Rh = 4. 0%; Swiss 90 -day Rf = 7. 0%
If everyone invests in the Swiss CD, the CHF should appreciate in the spot market and depreciate in the forward market relative to the $US…WHY? Suppose now the we have: S 0 = $0. 605/CHF; F 90 = $0. 595/CHF US 90 -day Rh = 4. 0%; Swiss 90 -day Rf = 7. 0%
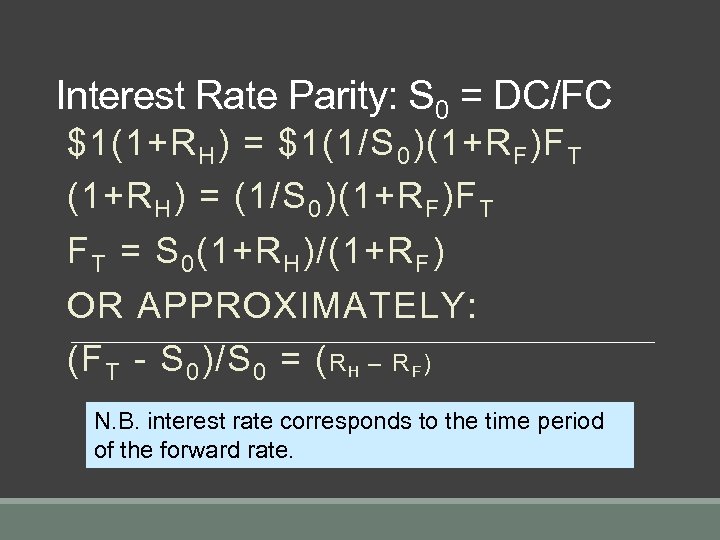 Interest Rate Parity: S 0 = DC/FC $1(1+R H ) = $1(1/S 0 )(1+R F )F T (1+R H ) = (1/S 0 )(1+R F )F T = S 0 (1+R H )/(1+R F ) OR APPROXIMATELY: (F T - S 0 )/S 0 = ( R H – R F ) N. B. interest rate corresponds to the time period of the forward rate.
Interest Rate Parity: S 0 = DC/FC $1(1+R H ) = $1(1/S 0 )(1+R F )F T (1+R H ) = (1/S 0 )(1+R F )F T = S 0 (1+R H )/(1+R F ) OR APPROXIMATELY: (F T - S 0 )/S 0 = ( R H – R F ) N. B. interest rate corresponds to the time period of the forward rate.
 What forward rate would be set under the following conditions? U. S. 90 -day Rh= 4. 0% Swiss 90 -day Rf= 7. 0% So = $0. 60/CHF Ft = ? ? ? How does the forward discount/premium relate to the interest rate differential?
What forward rate would be set under the following conditions? U. S. 90 -day Rh= 4. 0% Swiss 90 -day Rf= 7. 0% So = $0. 60/CHF Ft = ? ? ? How does the forward discount/premium relate to the interest rate differential?
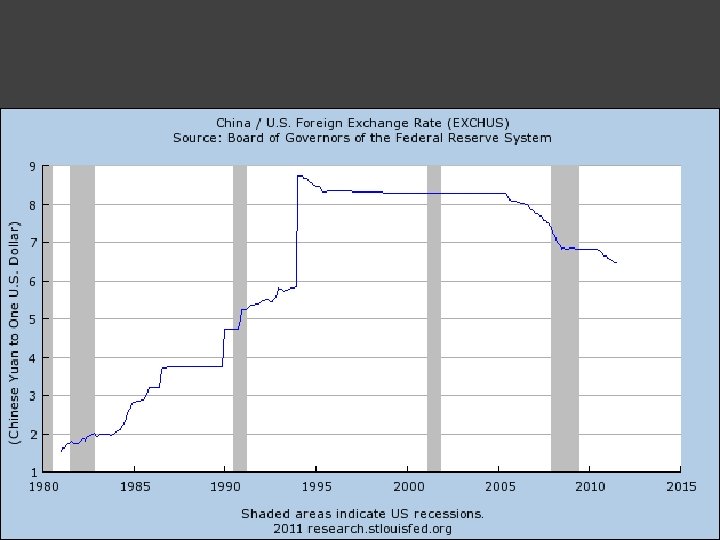
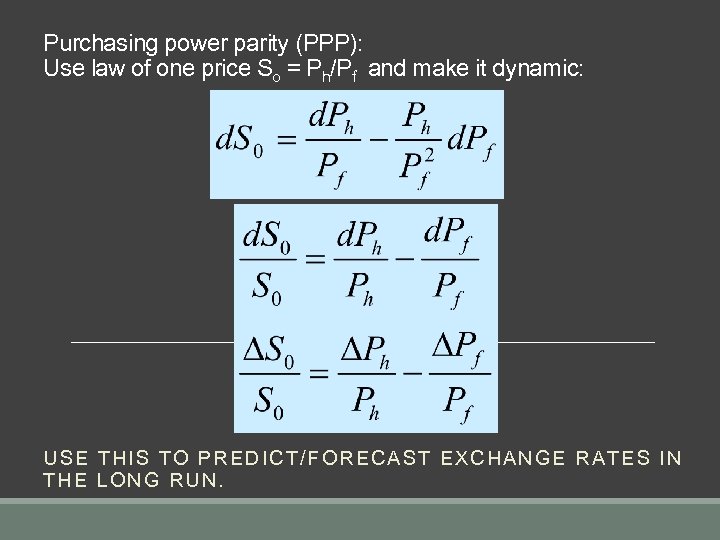 Purchasing power parity (PPP): Use law of one price So = Ph/Pf and make it dynamic: USE THI S TO PREDIC T/FORECAST EXCHANGE RATE S IN THE LONG RUN.
Purchasing power parity (PPP): Use law of one price So = Ph/Pf and make it dynamic: USE THI S TO PREDIC T/FORECAST EXCHANGE RATE S IN THE LONG RUN.
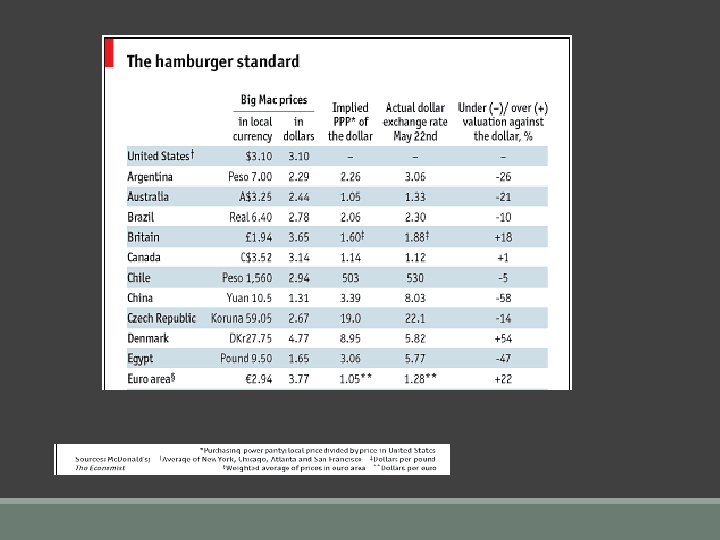
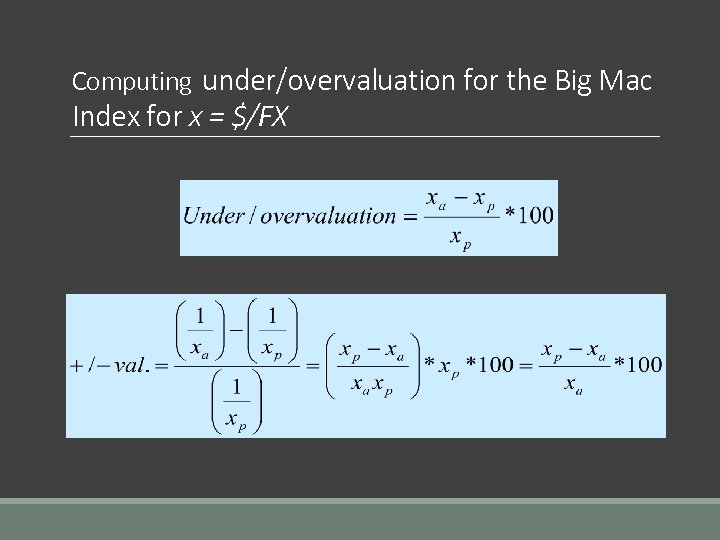 Computing under/overvaluation for the Big Mac Index for x = $/FX
Computing under/overvaluation for the Big Mac Index for x = $/FX
 SUPPOSE YOUR COMPANY’S CURRENCY IS U. S. DOLLARS. TODAY IS JANUARY 8 TH, 2014 AND YOU ARE SHORT 850, 000 EURO – IN OTHER WORDS, YOU OWE 850, 000 EURO TO ANOTHER COMPANY. THE EURO PAYMENT IS DUE IN 90 DAYS ON APRIL 8, 2014. THE CURRENT SPOT RATE FOR EURO IS $1. 26/EURO AND THE EURO IS CURRENTLY SELLING AT A 1. 3 PERCENT 90 -DAY FORWARD DISCOUNT. • 90 -DAY INTEREST RATES ARE: • DEPOSITS: U. S. 3. 2%; EURO 2. 9% • LOANS: U. S. 4. 3%; EURO 4. 2% ASSUME YOUR COMPANY DOES NOT CURRENTLY HAVE THE FUNDS FOR THE LIABILITY BUT EXPECTS TO HAVE ADEQUATE CASH FLOW IN 90 DAYS. DISCUSS THE RISKS AND HEDGING POSSIBILITIES.
SUPPOSE YOUR COMPANY’S CURRENCY IS U. S. DOLLARS. TODAY IS JANUARY 8 TH, 2014 AND YOU ARE SHORT 850, 000 EURO – IN OTHER WORDS, YOU OWE 850, 000 EURO TO ANOTHER COMPANY. THE EURO PAYMENT IS DUE IN 90 DAYS ON APRIL 8, 2014. THE CURRENT SPOT RATE FOR EURO IS $1. 26/EURO AND THE EURO IS CURRENTLY SELLING AT A 1. 3 PERCENT 90 -DAY FORWARD DISCOUNT. • 90 -DAY INTEREST RATES ARE: • DEPOSITS: U. S. 3. 2%; EURO 2. 9% • LOANS: U. S. 4. 3%; EURO 4. 2% ASSUME YOUR COMPANY DOES NOT CURRENTLY HAVE THE FUNDS FOR THE LIABILITY BUT EXPECTS TO HAVE ADEQUATE CASH FLOW IN 90 DAYS. DISCUSS THE RISKS AND HEDGING POSSIBILITIES.
 Suppose your company’s currency is U. S. dollars. Today is January 8 th, 2014 and you are long 850, 000 euro – in other words, you are owed 850, 000 euro from another company. The euro payment will be received in 90 days on April 8, 2014. The current spot rate for euro is $1. 26/euro and the euro is currently selling at a 1. 3 percent 90 -day forward discount. • 90 -day interest rates are: • Deposits: U. S. 3. 2%; Euro 2. 9% • Loans: U. S. 4. 3%; Euro 4. 2% Discuss the risks and hedging possibilities.
Suppose your company’s currency is U. S. dollars. Today is January 8 th, 2014 and you are long 850, 000 euro – in other words, you are owed 850, 000 euro from another company. The euro payment will be received in 90 days on April 8, 2014. The current spot rate for euro is $1. 26/euro and the euro is currently selling at a 1. 3 percent 90 -day forward discount. • 90 -day interest rates are: • Deposits: U. S. 3. 2%; Euro 2. 9% • Loans: U. S. 4. 3%; Euro 4. 2% Discuss the risks and hedging possibilities.
 Read through the following: International capital budgeting (you did this on the project) Exchange rate risk
Read through the following: International capital budgeting (you did this on the project) Exchange rate risk


