 Factoring is a financial transaction in which a business sells its accounts receivable (i. e. , invoices) to a third party (called a factor) at a discount.
Factoring is a financial transaction in which a business sells its accounts receivable (i. e. , invoices) to a third party (called a factor) at a discount.
 Functions financing the supply of goods, credit insurance, account of the condition of accounts receivable and work with debtors to timely payment.
Functions financing the supply of goods, credit insurance, account of the condition of accounts receivable and work with debtors to timely payment.
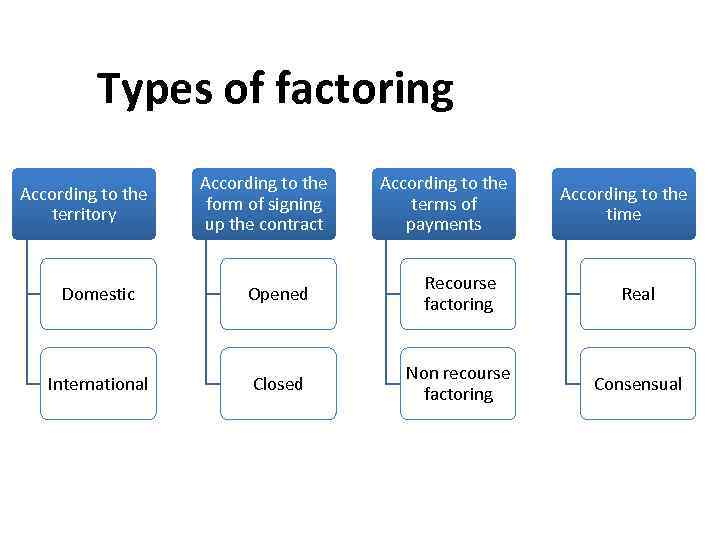 Types of factoring According to the territory According to the form of signing up the contract According to the terms of payments According to the time Domestic Opened Recourse factoring Real International Closed Non recourse factoring Consensual
Types of factoring According to the territory According to the form of signing up the contract According to the terms of payments According to the time Domestic Opened Recourse factoring Real International Closed Non recourse factoring Consensual
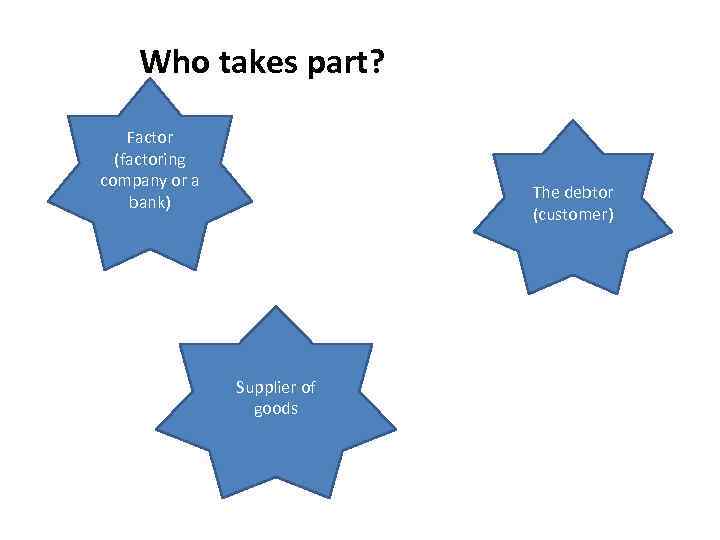 Who takes part? Factor (factoring company or a bank) The debtor (customer) Supplier of goods
Who takes part? Factor (factoring company or a bank) The debtor (customer) Supplier of goods
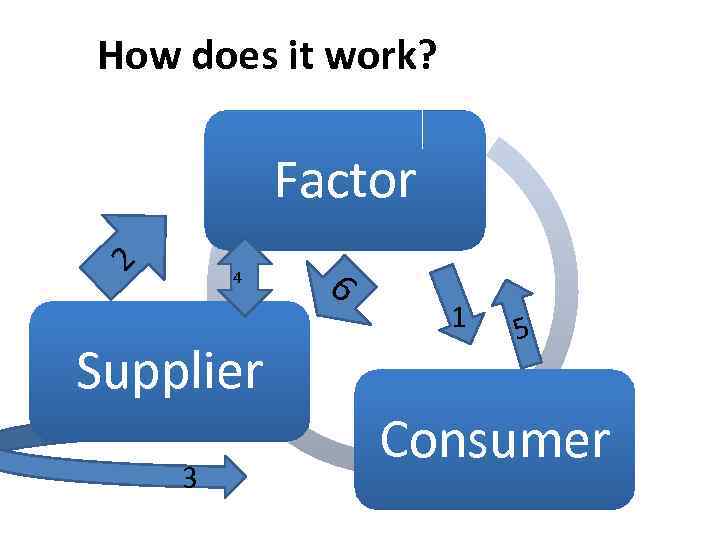 How does it work? Factor 2 4 Supplier 3 6 1 5 Consumer
How does it work? Factor 2 4 Supplier 3 6 1 5 Consumer
 1. Factor analyzes debtor 2. Sign a contract 3. Supplier ships the goods to the buyer on credit terms. 4. Factor funds up to 100% of the supplies under the security for the debtor 5. Debtor pays the supply to the factor 6. Factor takes the rest of payment to the supplier, less the factoring commission (a bill for factoring services).
1. Factor analyzes debtor 2. Sign a contract 3. Supplier ships the goods to the buyer on credit terms. 4. Factor funds up to 100% of the supplies under the security for the debtor 5. Debtor pays the supply to the factor 6. Factor takes the rest of payment to the supplier, less the factoring commission (a bill for factoring services).
 pros Supplier can immediately get from the factor payment for shipped goods, allowing him not to wait for payment from the buyer and plan their cash flow. Risk reduction Compared with lending factoring has a number of significant advantages. and cons: Obtain financing on factoring sometimes is very difficult
pros Supplier can immediately get from the factor payment for shipped goods, allowing him not to wait for payment from the buyer and plan their cash flow. Risk reduction Compared with lending factoring has a number of significant advantages. and cons: Obtain financing on factoring sometimes is very difficult
 In the case of non-delivery of debtor, factor pays for it Receivables, as a rule, does not exceed 180 days. International factoring contract is signed between the supplier and the factoring company in the vendor. The contract describes the scheme of work, terms of service and responsibility of the parties. Factoring company, as opposed to the bank assesses not only the solvency (платежеспособность)of the client, to apply for funding, as paying its debtors (ie, the client can not meet the requirements for bank credit, and get funding).
In the case of non-delivery of debtor, factor pays for it Receivables, as a rule, does not exceed 180 days. International factoring contract is signed between the supplier and the factoring company in the vendor. The contract describes the scheme of work, terms of service and responsibility of the parties. Factoring company, as opposed to the bank assesses not only the solvency (платежеспособность)of the client, to apply for funding, as paying its debtors (ie, the client can not meet the requirements for bank credit, and get funding).