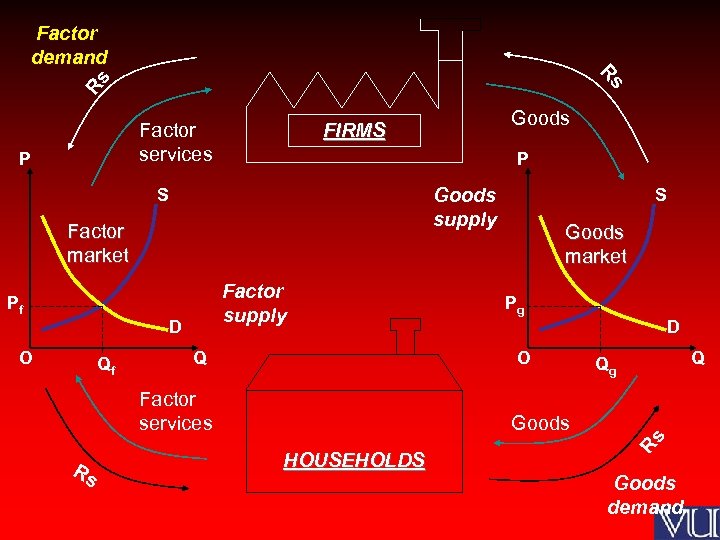
 Factor demand s Rs R Factor services P Goods supply S Factor market Factor supply Pf D O Qf Q Goods market Pg D O Factor services Rs S Q Qg Goods HOUSEHOLDS Rs P Goods FIRMS Goods demand
Factor demand s Rs R Factor services P Goods supply S Factor market Factor supply Pf D O Qf Q Goods market Pg D O Factor services Rs S Q Qg Goods HOUSEHOLDS Rs P Goods FIRMS Goods demand
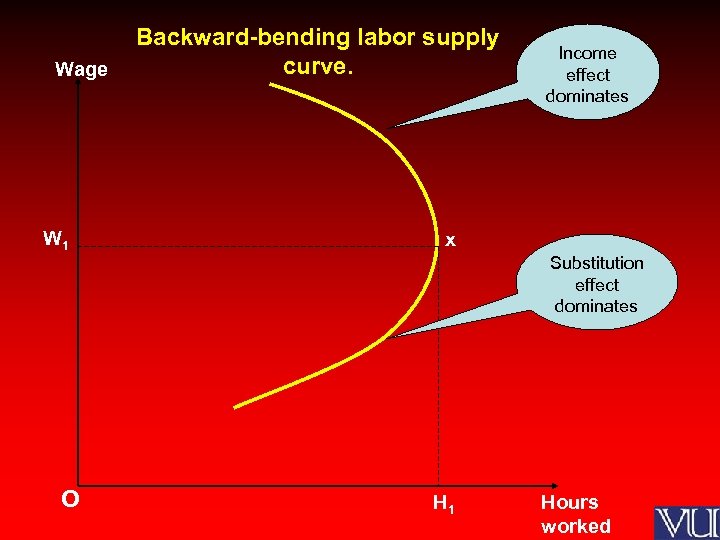 Wage W 1 Backward-bending labor supply curve. Income effect dominates x Substitution effect dominates O H 1 Hours worked
Wage W 1 Backward-bending labor supply curve. Income effect dominates x Substitution effect dominates O H 1 Hours worked
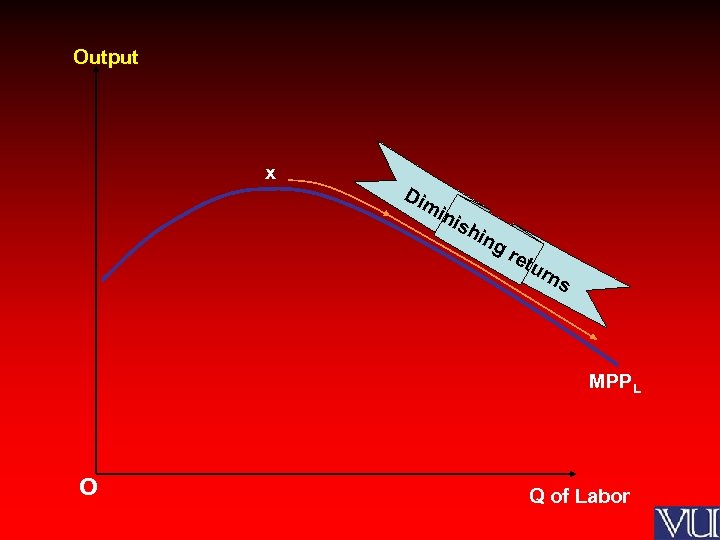 Output x Dim ini sh ing ret urn s MPPL O Q of Labor
Output x Dim ini sh ing ret urn s MPPL O Q of Labor
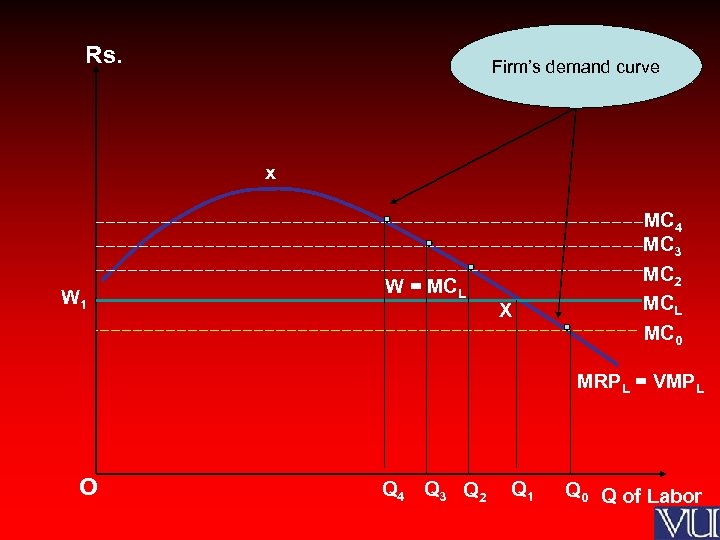 Rs. Firm’s demand curve x W 1 W = MCL X MC 4 MC 3 MC 2 MCL MC 0 MRPL = VMPL O Q 4 Q 3 Q 2 Q 1 Q 0 Q of Labor
Rs. Firm’s demand curve x W 1 W = MCL X MC 4 MC 3 MC 2 MCL MC 0 MRPL = VMPL O Q 4 Q 3 Q 2 Q 1 Q 0 Q of Labor
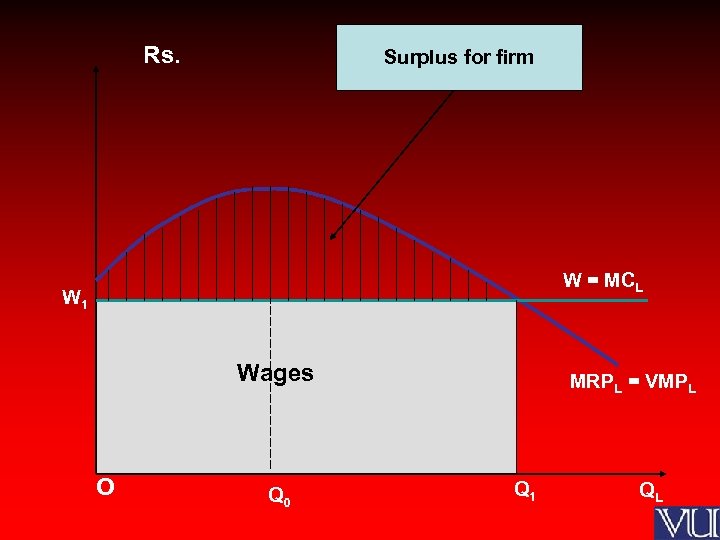 Rs. Surplus for firm W = MCL W 1 Wages O Q 0 MRPL = VMPL Q 1 QL
Rs. Surplus for firm W = MCL W 1 Wages O Q 0 MRPL = VMPL Q 1 QL
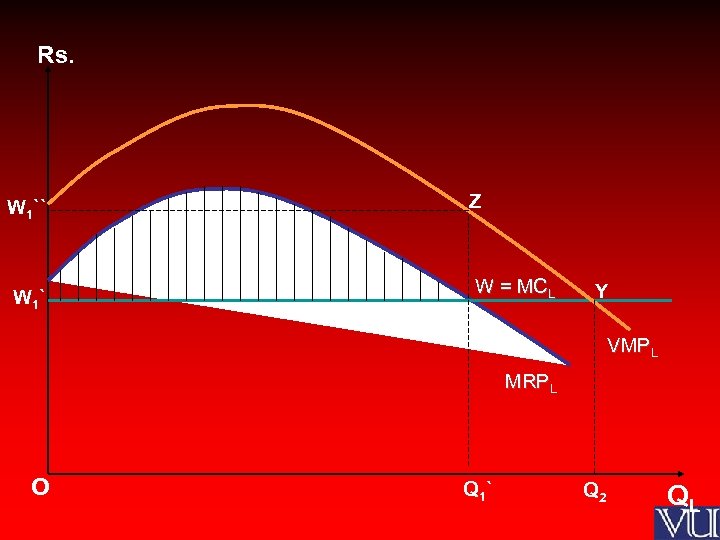 Rs. Z W 1`` W 1 ` W = MCL Y X VMPL MRPL O Q 1 ` Q 2 QL
Rs. Z W 1`` W 1 ` W = MCL Y X VMPL MRPL O Q 1 ` Q 2 QL
 Discounting • Rate of discount = 10% • The formula for discounting is as follows: Xi PV = Σ i (1+ r) i where PV is present value Xi is earnings from the investment in the year i r is the rate of discount Σ is the sum over i, of the discounted earnings. i
Discounting • Rate of discount = 10% • The formula for discounting is as follows: Xi PV = Σ i (1+ r) i where PV is present value Xi is earnings from the investment in the year i r is the rate of discount Σ is the sum over i, of the discounted earnings. i
 Present value of machine that generates Rs. 1, 000 for four years and then sold as scrap for Rs. 1, 000 at the end of year 4? Year 2 Year 1 = 1, 000 1. 1 = 909 1 + 1, 000 1. 1 + 826 2 Year 3 + 1, 000 1. 1 + 751 3 Year 4 + 2, 000 1. 1 + 4 1366 = Rs. 3852 If machine costs less than this then Buy, otherwise don’t Buy. Net present value = PV – Purchase cost
Present value of machine that generates Rs. 1, 000 for four years and then sold as scrap for Rs. 1, 000 at the end of year 4? Year 2 Year 1 = 1, 000 1. 1 = 909 1 + 1, 000 1. 1 + 826 2 Year 3 + 1, 000 1. 1 + 751 3 Year 4 + 2, 000 1. 1 + 4 1366 = Rs. 3852 If machine costs less than this then Buy, otherwise don’t Buy. Net present value = PV – Purchase cost
 A typical information product Online economics course Q TC MC AC 50 50, 000 100 50, 000 150 50, 000 200 50, 000 250 50, 000 300 50, 000 0 0 500 330 250 200 166
A typical information product Online economics course Q TC MC AC 50 50, 000 100 50, 000 150 50, 000 200 50, 000 250 50, 000 300 50, 000 0 0 500 330 250 200 166
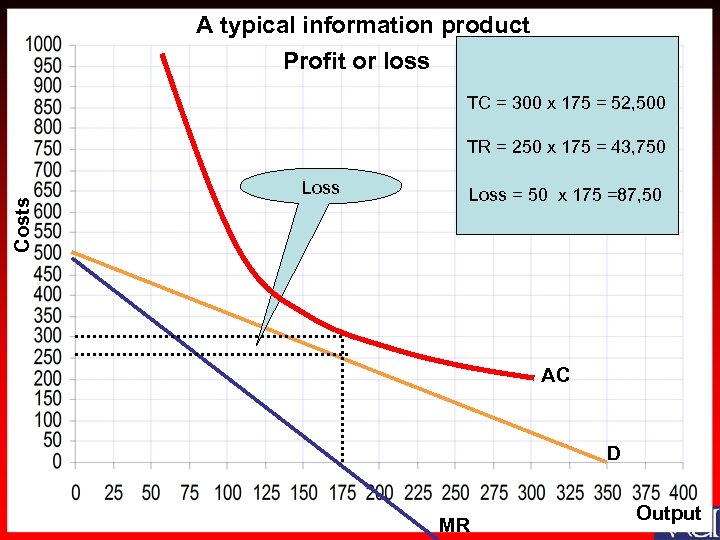 A typical information product Profit or loss TC = 300 x 175 = 52, 500 Costs TR = 250 x 175 = 43, 750 Loss = 50 x 175 =87, 50 AC D MR Output
A typical information product Profit or loss TC = 300 x 175 = 52, 500 Costs TR = 250 x 175 = 43, 750 Loss = 50 x 175 =87, 50 AC D MR Output
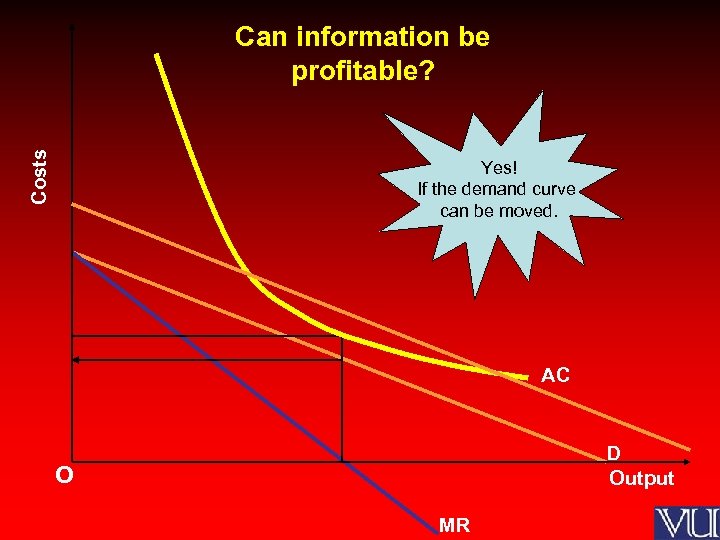 Costs Can information be profitable? Yes! If the demand curve can be moved. AC D Output O MR
Costs Can information be profitable? Yes! If the demand curve can be moved. AC D Output O MR