4e9f71f5ee11e62c48e3ca4a13291c41.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65
 Facing the Challenges of M 2 M Security and Privacy Phil Hawkes Principal Engineer at Qualcomm Inc. phawkes@qti. qualcomm. com one. M 2 M www. onem 2 m. org 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 1
Facing the Challenges of M 2 M Security and Privacy Phil Hawkes Principal Engineer at Qualcomm Inc. phawkes@qti. qualcomm. com one. M 2 M www. onem 2 m. org 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 1
 Overview • one. M 2 M Architecture: a quick review • Challenges 1. Large variety of scenarios 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy • Solutions A. Secure communication B. Remote provisioning C. Access control policies • Future Challenges 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 2
Overview • one. M 2 M Architecture: a quick review • Challenges 1. Large variety of scenarios 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy • Solutions A. Secure communication B. Remote provisioning C. Access control policies • Future Challenges 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 2
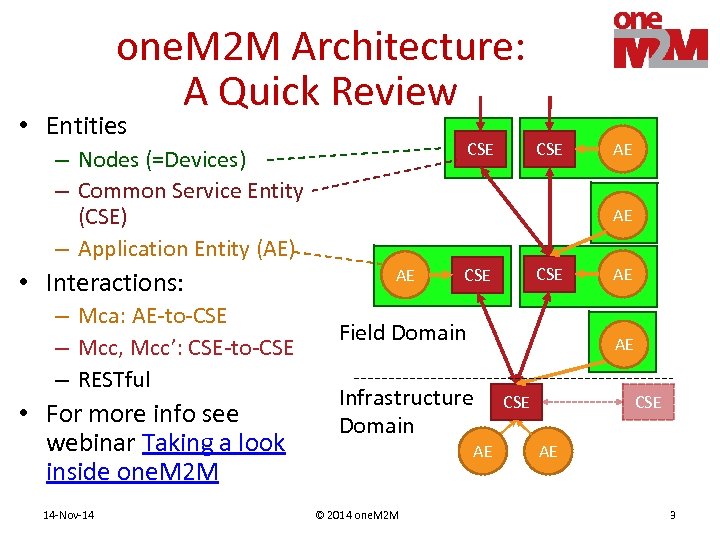 one. M 2 M Architecture: A Quick Review • Entities CSE – Nodes (=Devices) – Common Service Entity (CSE) – Application Entity (AE) • Interactions: – Mca: AE-to-CSE – Mcc, Mcc’: CSE-to-CSE – RESTful • For more info see webinar Taking a look inside one. M 2 M 14 -Nov-14 CSE AE AE AE CSE Field Domain AE Infrastructure Domain AE © 2014 one. M 2 M AE CSE AE 3
one. M 2 M Architecture: A Quick Review • Entities CSE – Nodes (=Devices) – Common Service Entity (CSE) – Application Entity (AE) • Interactions: – Mca: AE-to-CSE – Mcc, Mcc’: CSE-to-CSE – RESTful • For more info see webinar Taking a look inside one. M 2 M 14 -Nov-14 CSE AE AE AE CSE Field Domain AE Infrastructure Domain AE © 2014 one. M 2 M AE CSE AE 3
 Challenges 1. Large variety of scenarios 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 4
Challenges 1. Large variety of scenarios 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 4
 Challenges 1. Large variety of deployments – “Assets” that need protecting can be unique to a deployment • Content confidentiality, content integrity, anonymity, traffic efficiency – Environment can be unique to a deployment • Does wired or wireless transport layer provide adequate security? • Tamper-resistance considerations – (Continued on next slide) 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 5
Challenges 1. Large variety of deployments – “Assets” that need protecting can be unique to a deployment • Content confidentiality, content integrity, anonymity, traffic efficiency – Environment can be unique to a deployment • Does wired or wireless transport layer provide adequate security? • Tamper-resistance considerations – (Continued on next slide) 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 5
 Challenges 1. Large variety of deployments (continued) – Variety of authentication scenarios • Pre-shared Key provisioned to both by end-points • PKI/Certificates (asymmetric cryptography) • Centralized authentication 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 6
Challenges 1. Large variety of deployments (continued) – Variety of authentication scenarios • Pre-shared Key provisioned to both by end-points • PKI/Certificates (asymmetric cryptography) • Centralized authentication 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 6
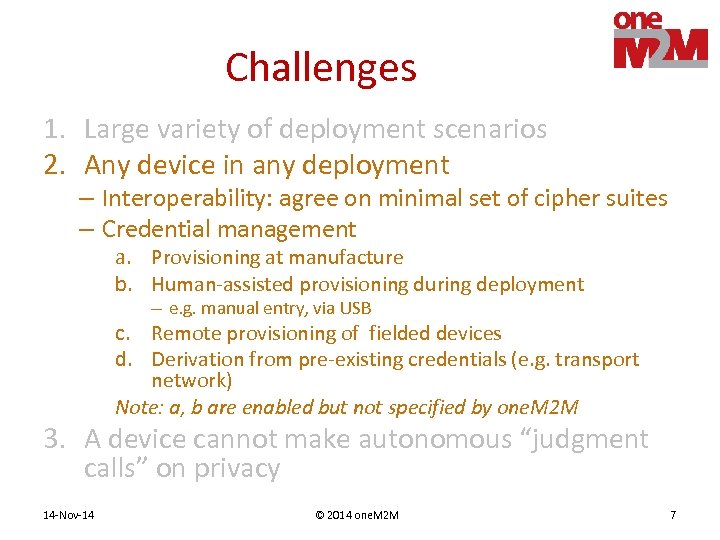 Challenges 1. Large variety of deployment scenarios 2. Any device in any deployment – Interoperability: agree on minimal set of cipher suites – Credential management a. Provisioning at manufacture b. Human-assisted provisioning during deployment – e. g. manual entry, via USB c. Remote provisioning of fielded devices d. Derivation from pre-existing credentials (e. g. transport network) Note: a, b are enabled but not specified by one. M 2 M 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 7
Challenges 1. Large variety of deployment scenarios 2. Any device in any deployment – Interoperability: agree on minimal set of cipher suites – Credential management a. Provisioning at manufacture b. Human-assisted provisioning during deployment – e. g. manual entry, via USB c. Remote provisioning of fielded devices d. Derivation from pre-existing credentials (e. g. transport network) Note: a, b are enabled but not specified by one. M 2 M 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 7
 Challenges 1. Large variety of scenarios 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy – M 2 M/Io. T may expose information about our lives without our awareness – Privacy = who can access information about me – CSE needs to determine: “Should I allow access? ” – Can’t ask human to make case-by-case judgment call – CSE needs clear rules 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 8
Challenges 1. Large variety of scenarios 2. Any device in any deployment 3. A device cannot make autonomous “judgment calls” on privacy – M 2 M/Io. T may expose information about our lives without our awareness – Privacy = who can access information about me – CSE needs to determine: “Should I allow access? ” – Can’t ask human to make case-by-case judgment call – CSE needs clear rules 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 8
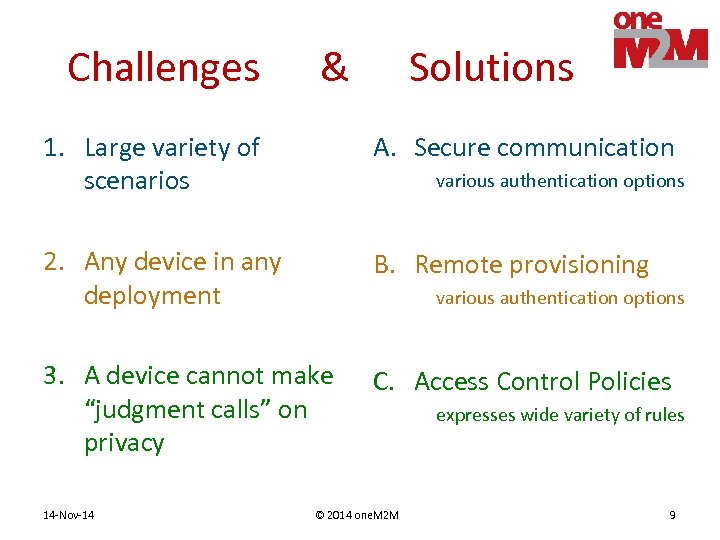 Challenges & Solutions 1. Large variety of scenarios A. Secure communication 2. Any device in any deployment B. Remote provisioning 3. A device cannot make “judgment calls” on privacy C. Access Control Policies 14 -Nov-14 various authentication options © 2014 one. M 2 M expresses wide variety of rules 9
Challenges & Solutions 1. Large variety of scenarios A. Secure communication 2. Any device in any deployment B. Remote provisioning 3. A device cannot make “judgment calls” on privacy C. Access Control Policies 14 -Nov-14 various authentication options © 2014 one. M 2 M expresses wide variety of rules 9
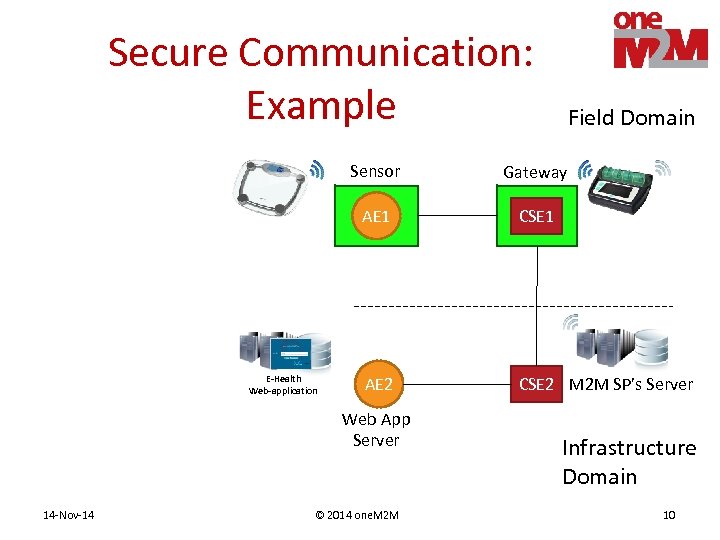 Secure Communication: Example Field Domain Sensor AE 1 E-Health Web-application Gateway CSE 1 AE 2 CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 10
Secure Communication: Example Field Domain Sensor AE 1 E-Health Web-application Gateway CSE 1 AE 2 CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 10
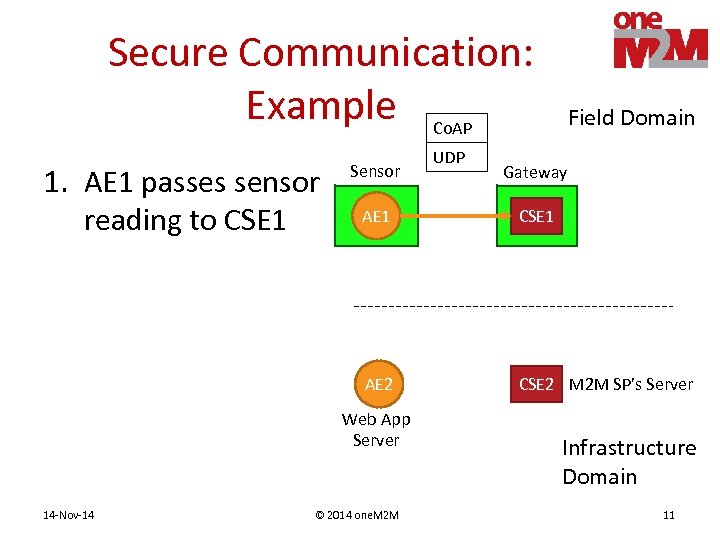 Secure Communication: Example Co. AP 1. AE 1 passes sensor reading to CSE 1 Sensor UDP Field Domain Gateway AE 1 CSE 1 AE 2 CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 11
Secure Communication: Example Co. AP 1. AE 1 passes sensor reading to CSE 1 Sensor UDP Field Domain Gateway AE 1 CSE 1 AE 2 CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 11
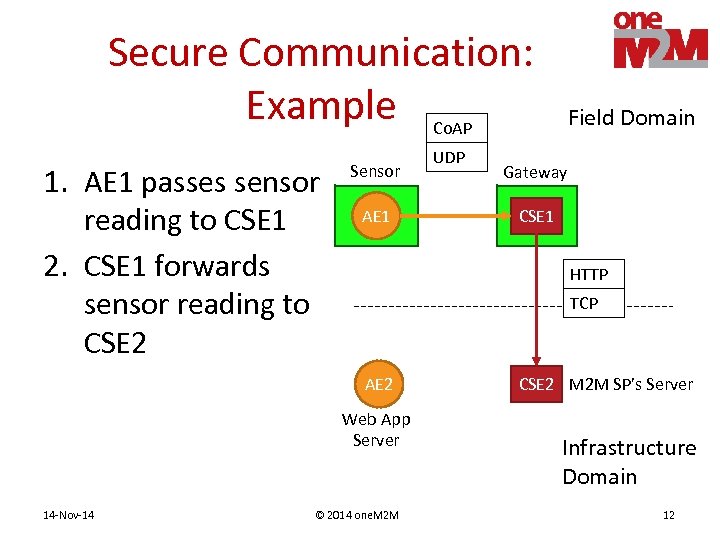 Secure Communication: Example Co. AP 1. AE 1 passes sensor reading to CSE 1 2. CSE 1 forwards sensor reading to CSE 2 Sensor AE 1 Gateway CSE 1 HTTP TCP AE 2 Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 UDP Field Domain © 2014 one. M 2 M CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Infrastructure Domain 12
Secure Communication: Example Co. AP 1. AE 1 passes sensor reading to CSE 1 2. CSE 1 forwards sensor reading to CSE 2 Sensor AE 1 Gateway CSE 1 HTTP TCP AE 2 Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 UDP Field Domain © 2014 one. M 2 M CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Infrastructure Domain 12
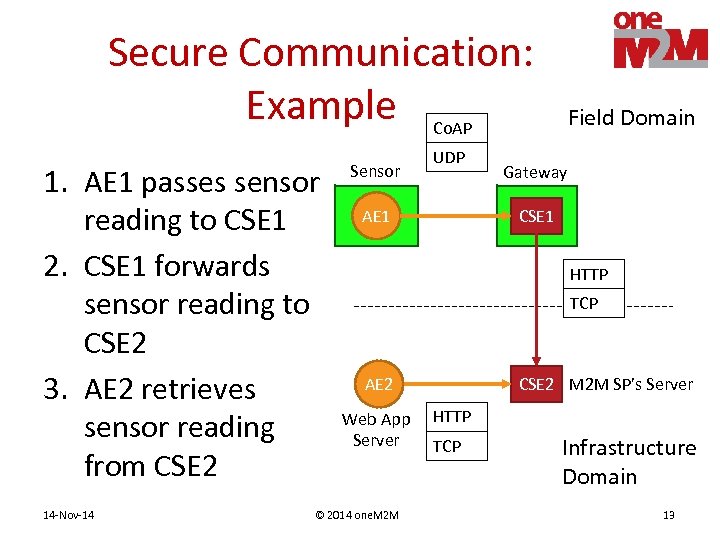 Secure Communication: Example Co. AP 1. AE 1 passes sensor reading to CSE 1 2. CSE 1 forwards sensor reading to CSE 2 3. AE 2 retrieves sensor reading from CSE 2 14 -Nov-14 Sensor UDP AE 1 Field Domain Gateway CSE 1 HTTP TCP CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server AE 2 Web App Server © 2014 one. M 2 M HTTP TCP Infrastructure Domain 13
Secure Communication: Example Co. AP 1. AE 1 passes sensor reading to CSE 1 2. CSE 1 forwards sensor reading to CSE 2 3. AE 2 retrieves sensor reading from CSE 2 14 -Nov-14 Sensor UDP AE 1 Field Domain Gateway CSE 1 HTTP TCP CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server AE 2 Web App Server © 2014 one. M 2 M HTTP TCP Infrastructure Domain 13
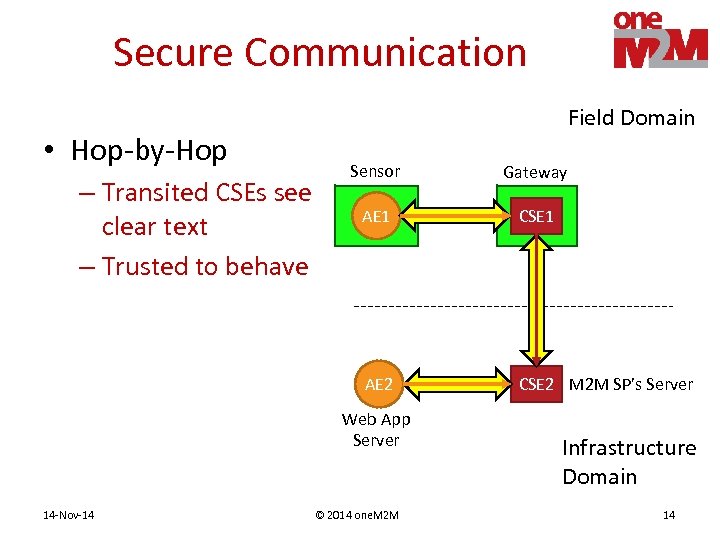 Secure Communication • Hop-by-Hop Field Domain Gateway AE 1 CSE 1 AE 2 – Transited CSEs see clear text – Trusted to behave Sensor CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 14
Secure Communication • Hop-by-Hop Field Domain Gateway AE 1 CSE 1 AE 2 – Transited CSEs see clear text – Trusted to behave Sensor CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 14
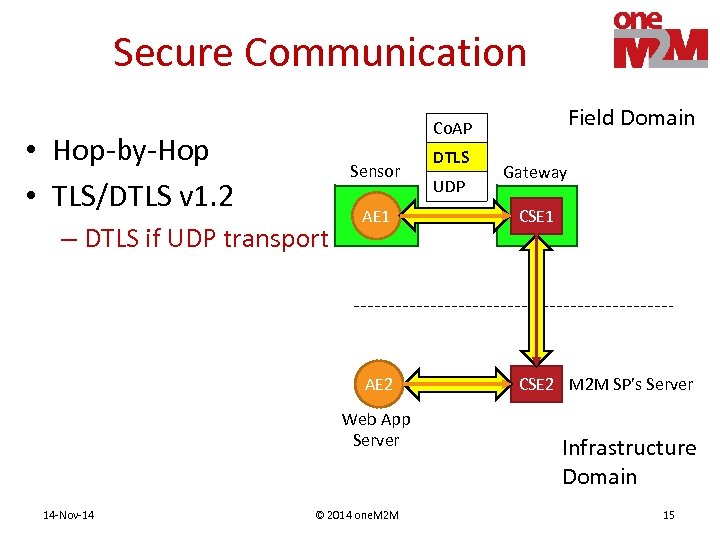 Secure Communication Field Domain Co. AP • Hop-by-Hop • TLS/DTLS v 1. 2 Sensor DTLS UDP Gateway CSE 1 AE 2 – DTLS if UDP transport AE 1 CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 15
Secure Communication Field Domain Co. AP • Hop-by-Hop • TLS/DTLS v 1. 2 Sensor DTLS UDP Gateway CSE 1 AE 2 – DTLS if UDP transport AE 1 CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 15
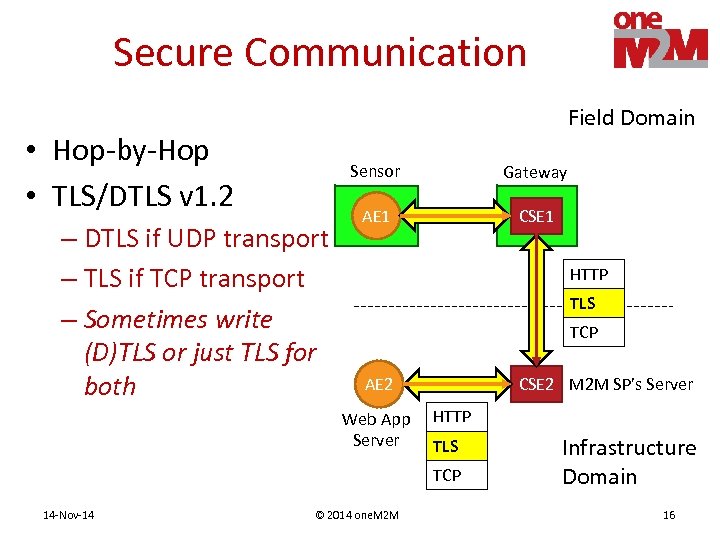 Secure Communication Field Domain • Hop-by-Hop • TLS/DTLS v 1. 2 Sensor – DTLS if UDP transport – TLS if TCP transport – Sometimes write (D)TLS or just TLS for both Gateway AE 1 CSE 1 HTTP TLS TCP CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server AE 2 Web App Server HTTP TLS TCP 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 16
Secure Communication Field Domain • Hop-by-Hop • TLS/DTLS v 1. 2 Sensor – DTLS if UDP transport – TLS if TCP transport – Sometimes write (D)TLS or just TLS for both Gateway AE 1 CSE 1 HTTP TLS TCP CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server AE 2 Web App Server HTTP TLS TCP 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M Infrastructure Domain 16
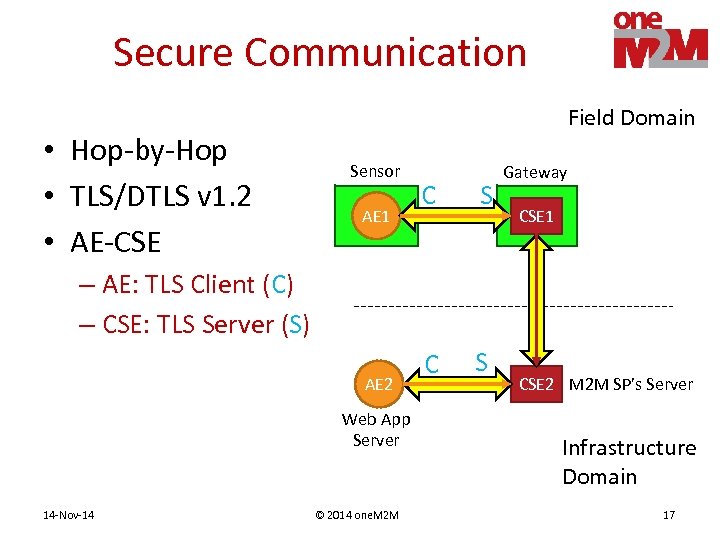 Secure Communication • Hop-by-Hop • TLS/DTLS v 1. 2 • AE-CSE Field Domain Sensor AE 1 C S Gateway CSE 1 – AE: TLS Client (C) – CSE: TLS Server (S) AE 2 Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Infrastructure Domain 17
Secure Communication • Hop-by-Hop • TLS/DTLS v 1. 2 • AE-CSE Field Domain Sensor AE 1 C S Gateway CSE 1 – AE: TLS Client (C) – CSE: TLS Server (S) AE 2 Web App Server 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Infrastructure Domain 17
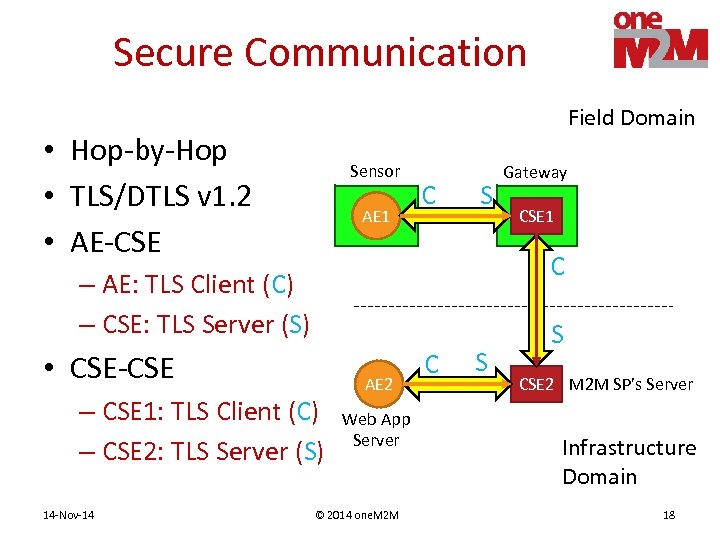 Secure Communication Field Domain • Hop-by-Hop • TLS/DTLS v 1. 2 • AE-CSE Sensor AE 1 C S CSE 1 C – AE: TLS Client (C) – CSE: TLS Server (S) • CSE-CSE – CSE 1: TLS Client (C) – CSE 2: TLS Server (S) 14 -Nov-14 Gateway AE 2 Web App Server © 2014 one. M 2 M C S S CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Infrastructure Domain 18
Secure Communication Field Domain • Hop-by-Hop • TLS/DTLS v 1. 2 • AE-CSE Sensor AE 1 C S CSE 1 C – AE: TLS Client (C) – CSE: TLS Server (S) • CSE-CSE – CSE 1: TLS Client (C) – CSE 2: TLS Server (S) 14 -Nov-14 Gateway AE 2 Web App Server © 2014 one. M 2 M C S S CSE 2 M 2 M SP’s Server Infrastructure Domain 18
 Authentication Options • Pre-Shared Key (PSK) – TLS Client & Server provisioned with a shared key# • Certificate – TLS Client & Server both have certificates • M 2 M Authentication Function (MAF) – MAF operated by 3 rd Party or M 2 M Service Provider – TLS Client and MAF provisioned with a shared key# – MAF assists authentication of TLS Client & Server #This 14 -Nov-14 shared key can be remotely provisioned © 2014 one. M 2 M 19
Authentication Options • Pre-Shared Key (PSK) – TLS Client & Server provisioned with a shared key# • Certificate – TLS Client & Server both have certificates • M 2 M Authentication Function (MAF) – MAF operated by 3 rd Party or M 2 M Service Provider – TLS Client and MAF provisioned with a shared key# – MAF assists authentication of TLS Client & Server #This 14 -Nov-14 shared key can be remotely provisioned © 2014 one. M 2 M 19
 Certificates • Somewhat aligned with Co. AP Security RFC 7252 • X. 509/PKIX (RFC 5280) • Raw. Public. Key Certificates – Contains only X. 509 Subject. Public. Key. Info element – Suits less complex deployments & debugging • Certificates chaining to a trust anchor. E. g. – Device Certificate (e. g. manufacturer issued) – M 2 M SP issued certificate identifying CSE or AE 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 20
Certificates • Somewhat aligned with Co. AP Security RFC 7252 • X. 509/PKIX (RFC 5280) • Raw. Public. Key Certificates – Contains only X. 509 Subject. Public. Key. Info element – Suits less complex deployments & debugging • Certificates chaining to a trust anchor. E. g. – Device Certificate (e. g. manufacturer issued) – M 2 M SP issued certificate identifying CSE or AE 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 20
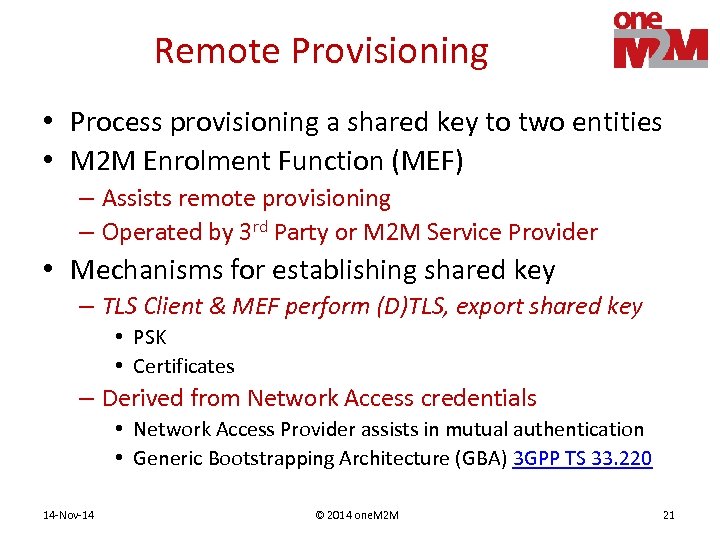 Remote Provisioning • Process provisioning a shared key to two entities • M 2 M Enrolment Function (MEF) – Assists remote provisioning – Operated by 3 rd Party or M 2 M Service Provider • Mechanisms for establishing shared key – TLS Client & MEF perform (D)TLS, export shared key • PSK • Certificates – Derived from Network Access credentials • Network Access Provider assists in mutual authentication • Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA) 3 GPP TS 33. 220 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 21
Remote Provisioning • Process provisioning a shared key to two entities • M 2 M Enrolment Function (MEF) – Assists remote provisioning – Operated by 3 rd Party or M 2 M Service Provider • Mechanisms for establishing shared key – TLS Client & MEF perform (D)TLS, export shared key • PSK • Certificates – Derived from Network Access credentials • Network Access Provider assists in mutual authentication • Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA) 3 GPP TS 33. 220 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 21
 Access Control Requirements • one. M 2 M uses a RESTful architecture – API: request to perform an operation on a resource – Operations: Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete – Webinar Taking a look inside one. M 2 M has more info • CSEs can’t make resource access judgement calls • CSE need clear rules dictating, for each resource – WHO (which CSEs and AEs) are authorized to access, – WHAT operations (see above), and under… – WHICH circumstances (e. g. time, location of entity) 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 22
Access Control Requirements • one. M 2 M uses a RESTful architecture – API: request to perform an operation on a resource – Operations: Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete – Webinar Taking a look inside one. M 2 M has more info • CSEs can’t make resource access judgement calls • CSE need clear rules dictating, for each resource – WHO (which CSEs and AEs) are authorized to access, – WHAT operations (see above), and under… – WHICH circumstances (e. g. time, location of entity) 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 22
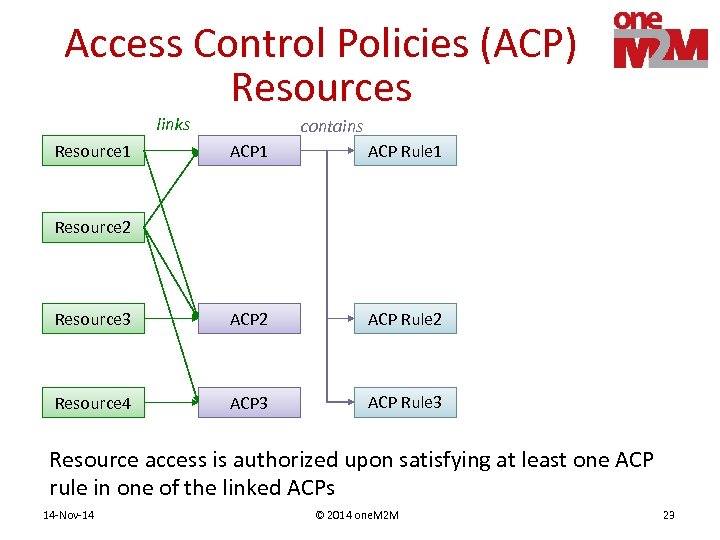 Access Control Policies (ACP) Resources links Resource 1 contains ACP 1 ACP Rule 1 Resource 3 ACP 2 ACP Rule 2 Resource 4 ACP 3 ACP Rule 3 Resource 2 Resource access is authorized upon satisfying at least one ACP rule in one of the linked ACPs 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 23
Access Control Policies (ACP) Resources links Resource 1 contains ACP 1 ACP Rule 1 Resource 3 ACP 2 ACP Rule 2 Resource 4 ACP 3 ACP Rule 3 Resource 2 Resource access is authorized upon satisfying at least one ACP rule in one of the linked ACPs 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 23
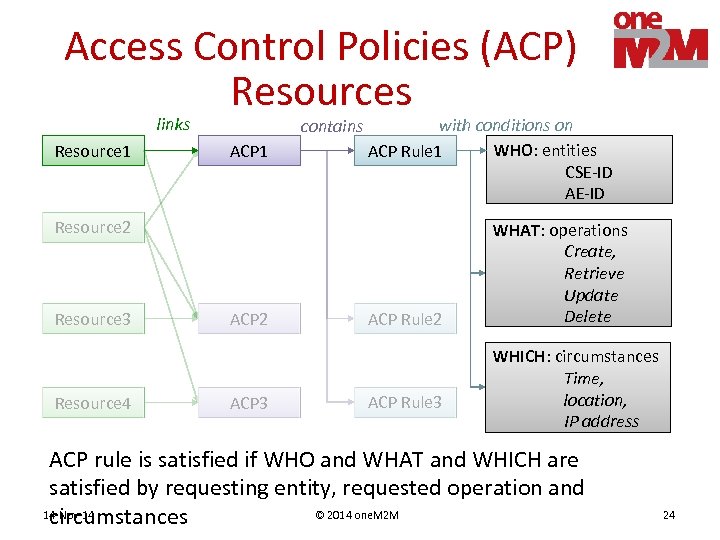 Access Control Policies (ACP) Resources links Resource 1 contains ACP 1 with conditions on WHO: entities ACP Rule 1 CSE-ID AE-ID Resource 2 Resource 3 Resource 4 ACP 2 ACP 3 ACP Rule 2 ACP Rule 3 WHAT: operations Create, Retrieve Update Delete WHICH: circumstances Time, location, IP address ACP rule is satisfied if WHO and WHAT and WHICH are satisfied by requesting entity, requested operation and 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M circumstances 24
Access Control Policies (ACP) Resources links Resource 1 contains ACP 1 with conditions on WHO: entities ACP Rule 1 CSE-ID AE-ID Resource 2 Resource 3 Resource 4 ACP 2 ACP 3 ACP Rule 2 ACP Rule 3 WHAT: operations Create, Retrieve Update Delete WHICH: circumstances Time, location, IP address ACP rule is satisfied if WHO and WHAT and WHICH are satisfied by requesting entity, requested operation and 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M circumstances 24
 one. M 2 M Security Documents • TR-0008 “Analysis of Security Solutions for the one. M 2 M System” http: //onem 2 m. org/images/files/deliverables/one. M 2 M_TR-0008 -Security-V 1_0_0. doc • TS-0003 “Security Solutions” http: //onem 2 m. org/images/files/deliverables/TS-0003 -Security_Solutions-V-2014 -08. pdf • Latest versions available from ftp: //ftp. onem 2 m. org/Work%20 Programme/WI 0007/ 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 25
one. M 2 M Security Documents • TR-0008 “Analysis of Security Solutions for the one. M 2 M System” http: //onem 2 m. org/images/files/deliverables/one. M 2 M_TR-0008 -Security-V 1_0_0. doc • TS-0003 “Security Solutions” http: //onem 2 m. org/images/files/deliverables/TS-0003 -Security_Solutions-V-2014 -08. pdf • Latest versions available from ftp: //ftp. onem 2 m. org/Work%20 Programme/WI 0007/ 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 25
 Limitations of initial release • A “minimum deployable solution” addressing short term needs • Focus: Vertically deployed industrial applications – Centralized client-server architectures – Most devices have limited number of static connections – Deployments are managed by skilled workforce – Nodes are trusted to behave • Our solutions meet these needs while having a place in future M 2 M/Io. T (consumer) scenarios 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 26
Limitations of initial release • A “minimum deployable solution” addressing short term needs • Focus: Vertically deployed industrial applications – Centralized client-server architectures – Most devices have limited number of static connections – Deployments are managed by skilled workforce – Nodes are trusted to behave • Our solutions meet these needs while having a place in future M 2 M/Io. T (consumer) scenarios 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 26
 Future Challenges • Decentralization – Increasingly complex interactions • Sharing Information between deployments • Complex authentication and authorization scenarios • Confidentiality & integrity concerns – Unskilled Consumers managing their “Things” • Technological Challenges: – End-to-End (multi-hop) message security – Many connections per device – Authentication & Authorization mechanisms 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 27
Future Challenges • Decentralization – Increasingly complex interactions • Sharing Information between deployments • Complex authentication and authorization scenarios • Confidentiality & integrity concerns – Unskilled Consumers managing their “Things” • Technological Challenges: – End-to-End (multi-hop) message security – Many connections per device – Authentication & Authorization mechanisms 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 27
 Conclusion: Challenges & Solutions 1. Large variety of scenarios A. Secure communication 2. Any device in any deployment B. Remote provisioning 3. A device cannot make “judgment calls” on privacy C. Access Control Policies 14 -Nov-14 various authentication options © 2014 one. M 2 M expresses wide variety of rules 28
Conclusion: Challenges & Solutions 1. Large variety of scenarios A. Secure communication 2. Any device in any deployment B. Remote provisioning 3. A device cannot make “judgment calls” on privacy C. Access Control Policies 14 -Nov-14 various authentication options © 2014 one. M 2 M expresses wide variety of rules 28
 Join us for the next webinar “On Management, Abstraction & Semantics” by Dr. Yongjing Zhang Standard Research Project Lead at Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd 27 November 2014 at 0700 UTC http: //www. onem 2 m. org/btchannel. cfm 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 29
Join us for the next webinar “On Management, Abstraction & Semantics” by Dr. Yongjing Zhang Standard Research Project Lead at Huawei Technologies Co. , Ltd 27 November 2014 at 0700 UTC http: //www. onem 2 m. org/btchannel. cfm 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 29
 Check out the recorded webinars “How standardization enables the next internet evolution” by Marc Jadoul Strategic Marketing Director, Alcatel-Lucent “Taking a look inside” by Nicolas Damour Senior Manager for Business and Innovation Development, Sierra Wireless http: //www. onem 2 m. org/btchannel. cfm 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 30
Check out the recorded webinars “How standardization enables the next internet evolution” by Marc Jadoul Strategic Marketing Director, Alcatel-Lucent “Taking a look inside” by Nicolas Damour Senior Manager for Business and Innovation Development, Sierra Wireless http: //www. onem 2 m. org/btchannel. cfm 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 30
 Join us at the one. M 2 M showcase event • One. M 2 M project partners, rationale and goals • One. M 2 M Service Layer Specification release • Showcase demos that demonstrate one. M 2 M “live" 9 December 2014, Sophia-Antipolis, France (free of charge, but online registration is required) http: //www. onem 2 m. org/Showcase Followed by the ETSI M 2 M workshop 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 31
Join us at the one. M 2 M showcase event • One. M 2 M project partners, rationale and goals • One. M 2 M Service Layer Specification release • Showcase demos that demonstrate one. M 2 M “live" 9 December 2014, Sophia-Antipolis, France (free of charge, but online registration is required) http: //www. onem 2 m. org/Showcase Followed by the ETSI M 2 M workshop 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 31
 Q&A 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 32
Q&A 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 32
 Backup Slides 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 33
Backup Slides 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 33
 PSK-Based Authentication Server Client 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 34
PSK-Based Authentication Server Client 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 34
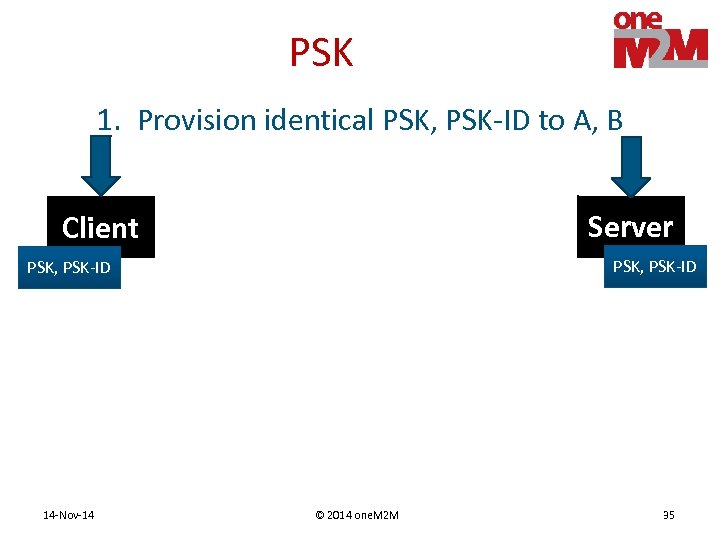 PSK 1. Provision identical PSK, PSK-ID to A, B Server Client PSK, PSK-ID 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 35
PSK 1. Provision identical PSK, PSK-ID to A, B Server Client PSK, PSK-ID 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 35
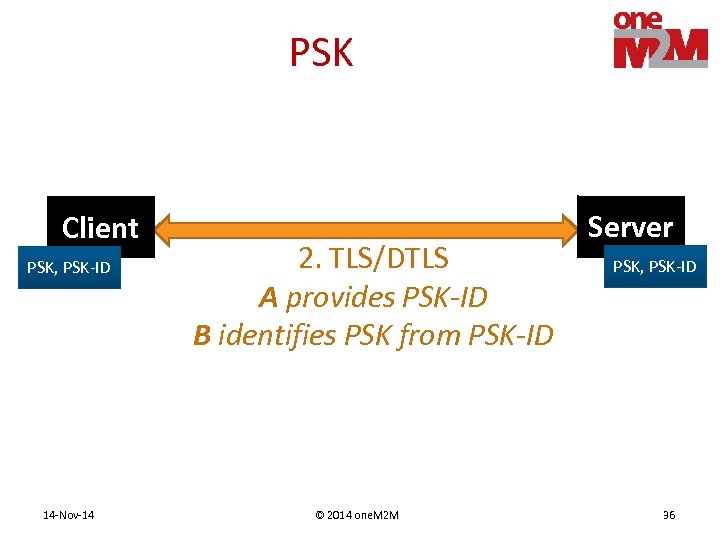 PSK Client PSK, PSK-ID 14 -Nov-14 2. TLS/DTLS A provides PSK-ID B identifies PSK from PSK-ID © 2014 one. M 2 M Server PSK, PSK-ID 36
PSK Client PSK, PSK-ID 14 -Nov-14 2. TLS/DTLS A provides PSK-ID B identifies PSK from PSK-ID © 2014 one. M 2 M Server PSK, PSK-ID 36
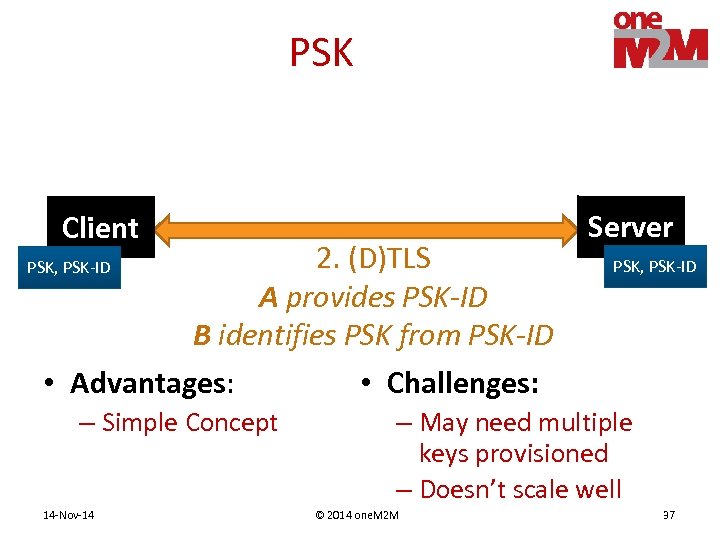 PSK Client PSK, PSK-ID 2. (D)TLS A provides PSK-ID B identifies PSK from PSK-ID • Advantages: – Simple Concept 14 -Nov-14 Server PSK, PSK-ID • Challenges: – May need multiple keys provisioned – Doesn’t scale well © 2014 one. M 2 M 37
PSK Client PSK, PSK-ID 2. (D)TLS A provides PSK-ID B identifies PSK from PSK-ID • Advantages: – Simple Concept 14 -Nov-14 Server PSK, PSK-ID • Challenges: – May need multiple keys provisioned – Doesn’t scale well © 2014 one. M 2 M 37
 PKI/Certificate-Based Authentication Client 14 -Nov-14 Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 38
PKI/Certificate-Based Authentication Client 14 -Nov-14 Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 38
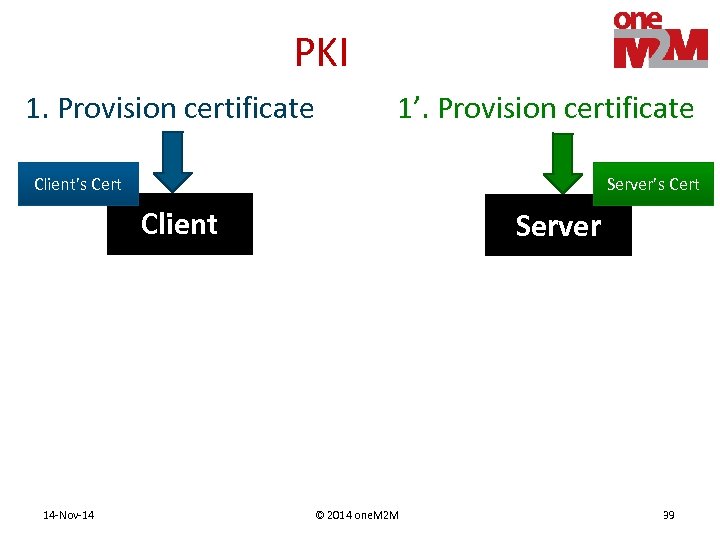 PKI 1. Provision certificate 1’. Provision certificate Client’s Cert Server’s Cert Client 14 -Nov-14 Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 39
PKI 1. Provision certificate 1’. Provision certificate Client’s Cert Server’s Cert Client 14 -Nov-14 Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 39
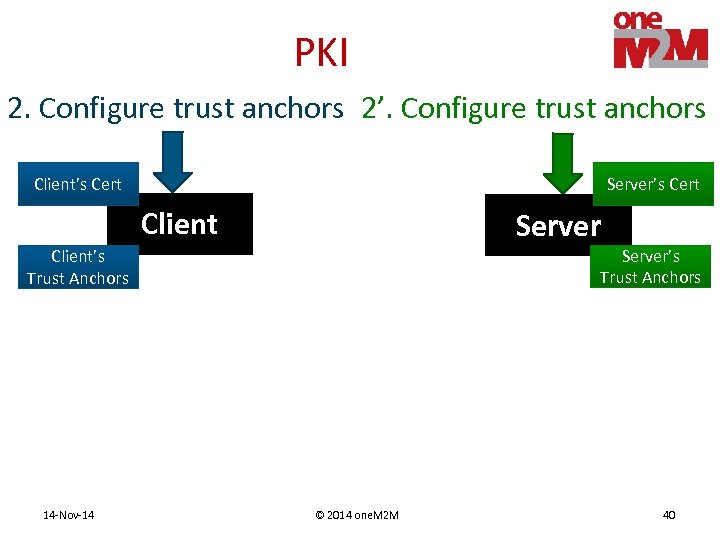 PKI 2. Configure trust anchors 2’. Configure trust anchors Client’s Cert Server’s Cert Client Server’s Trust Anchors Client’s Trust Anchors 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 40
PKI 2. Configure trust anchors 2’. Configure trust anchors Client’s Cert Server’s Cert Client Server’s Trust Anchors Client’s Trust Anchors 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 40
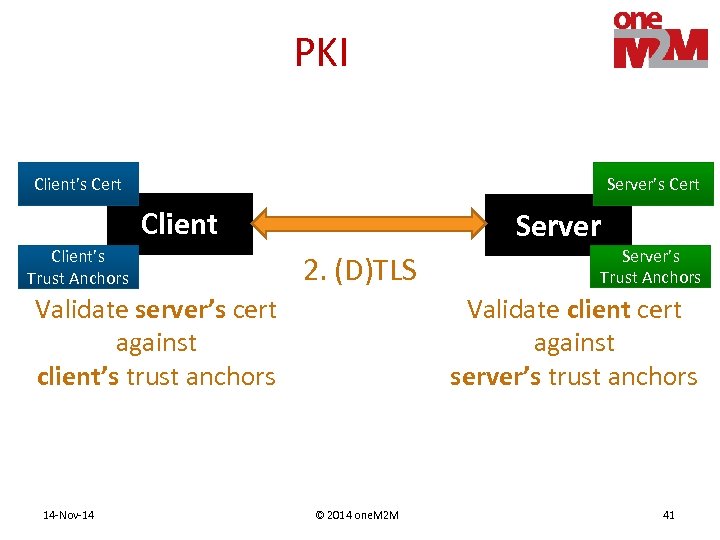 PKI Client’s Cert Server’s Cert Client’s Trust Anchors Server 2. (D)TLS Validate server’s cert against client’s trust anchors 14 -Nov-14 Server’s Trust Anchors Validate client cert against server’s trust anchors © 2014 one. M 2 M 41
PKI Client’s Cert Server’s Cert Client’s Trust Anchors Server 2. (D)TLS Validate server’s cert against client’s trust anchors 14 -Nov-14 Server’s Trust Anchors Validate client cert against server’s trust anchors © 2014 one. M 2 M 41
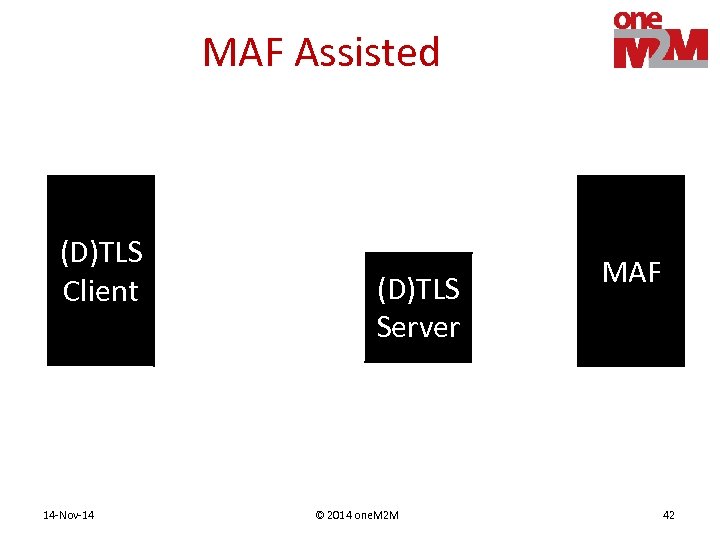 MAF Assisted (D)TLS Client 14 -Nov-14 (D)TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M MAF 42
MAF Assisted (D)TLS Client 14 -Nov-14 (D)TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M MAF 42
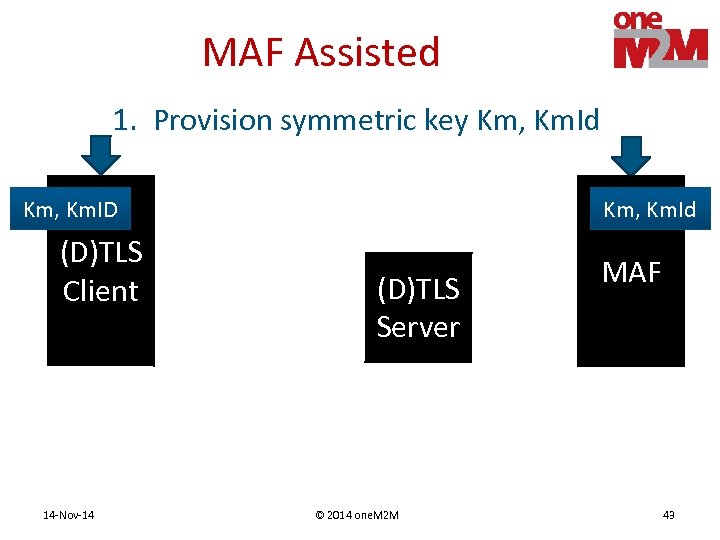 MAF Assisted 1. Provision symmetric key Km, Km. Id Km, Km. ID (D)TLS Client 14 -Nov-14 Km, Km. Id (D)TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M MAF 43
MAF Assisted 1. Provision symmetric key Km, Km. Id Km, Km. ID (D)TLS Client 14 -Nov-14 Km, Km. Id (D)TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M MAF 43
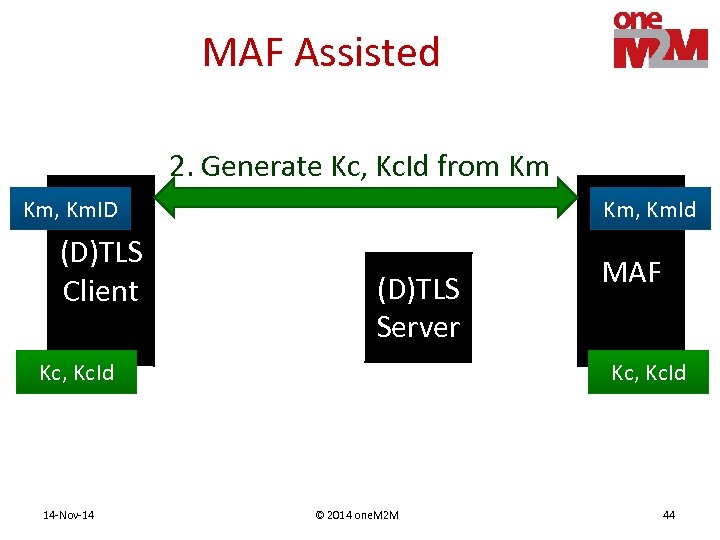 MAF Assisted 2. Generate Kc, Kc. Id from Km Km, Km. ID (D)TLS Client Km, Km. Id (D)TLS Server Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 MAF Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 44
MAF Assisted 2. Generate Kc, Kc. Id from Km Km, Km. ID (D)TLS Client Km, Km. Id (D)TLS Server Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 MAF Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 44
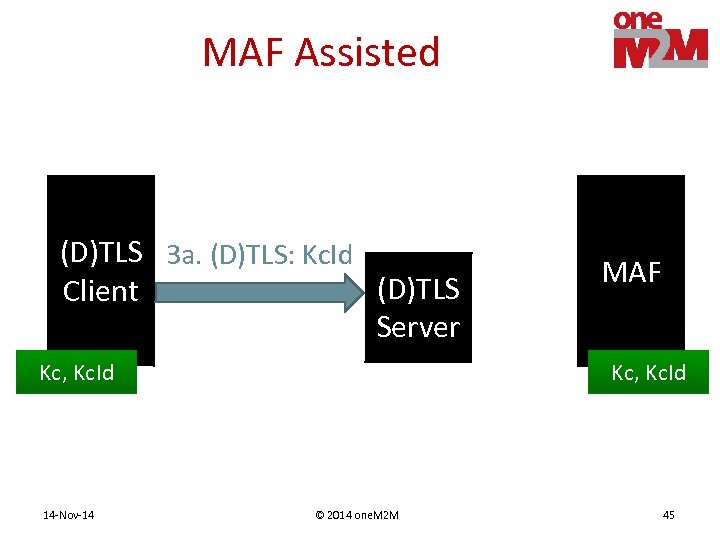 MAF Assisted (D)TLS 3 a. (D)TLS: Kc. Id (D)TLS Client Server Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 MAF Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 45
MAF Assisted (D)TLS 3 a. (D)TLS: Kc. Id (D)TLS Client Server Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 MAF Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 45
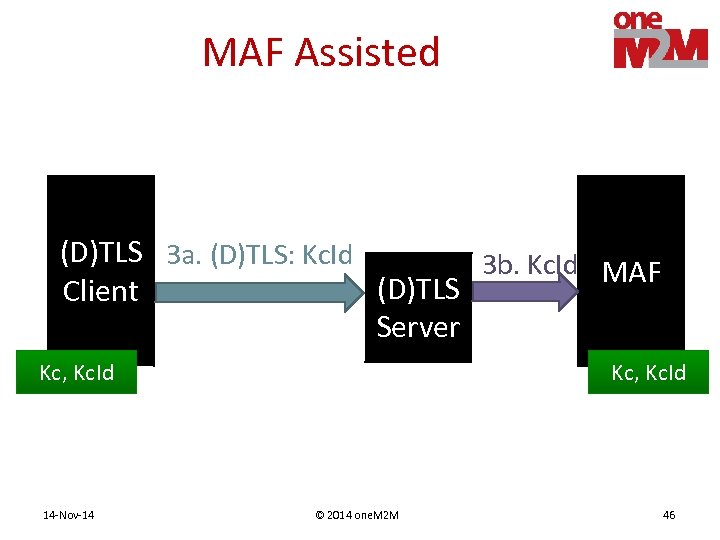 MAF Assisted (D)TLS 3 a. (D)TLS: Kc. Id 3 b. Kc. Id MAF (D)TLS Client Server Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 46
MAF Assisted (D)TLS 3 a. (D)TLS: Kc. Id 3 b. Kc. Id MAF (D)TLS Client Server Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 46
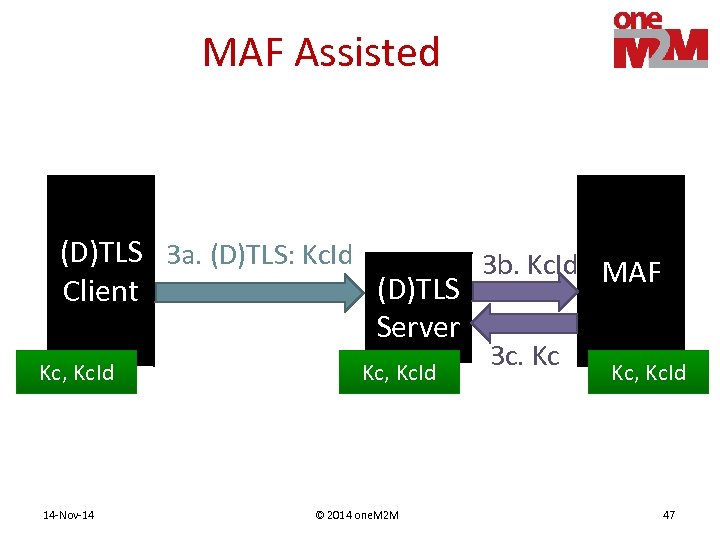 MAF Assisted (D)TLS 3 a. (D)TLS: Kc. Id 3 b. Kc. Id MAF (D)TLS Client Server Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 3 c. Kc Kc, Kc. Id 47
MAF Assisted (D)TLS 3 a. (D)TLS: Kc. Id 3 b. Kc. Id MAF (D)TLS Client Server Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 3 c. Kc Kc, Kc. Id 47
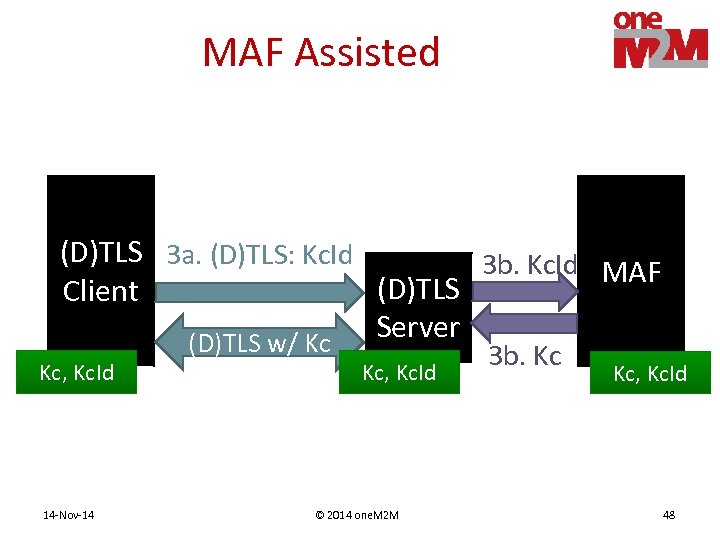 MAF Assisted (D)TLS 3 a. (D)TLS: Kc. Id 3 b. Kc. Id MAF (D)TLS Client Server (D)TLS w/ Kc Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 3 b. Kc Kc, Kc. Id 48
MAF Assisted (D)TLS 3 a. (D)TLS: Kc. Id 3 b. Kc. Id MAF (D)TLS Client Server (D)TLS w/ Kc Kc, Kc. Id 14 -Nov-14 Kc, Kc. Id © 2014 one. M 2 M 3 b. Kc Kc, Kc. Id 48
 Remote Provisioning PArticipants • Process provisions a shared key to two entities • M 2 M Enrolment Function (MEF) – Assists remote provisioning – Operated by 3 rd Party or M 2 M Service Provider • Enrolee – Entity requesting to be provisioned • Enrolment Target – Other entity that will ends up with the shared key 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 49
Remote Provisioning PArticipants • Process provisions a shared key to two entities • M 2 M Enrolment Function (MEF) – Assists remote provisioning – Operated by 3 rd Party or M 2 M Service Provider • Enrolee – Entity requesting to be provisioned • Enrolment Target – Other entity that will ends up with the shared key 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 49
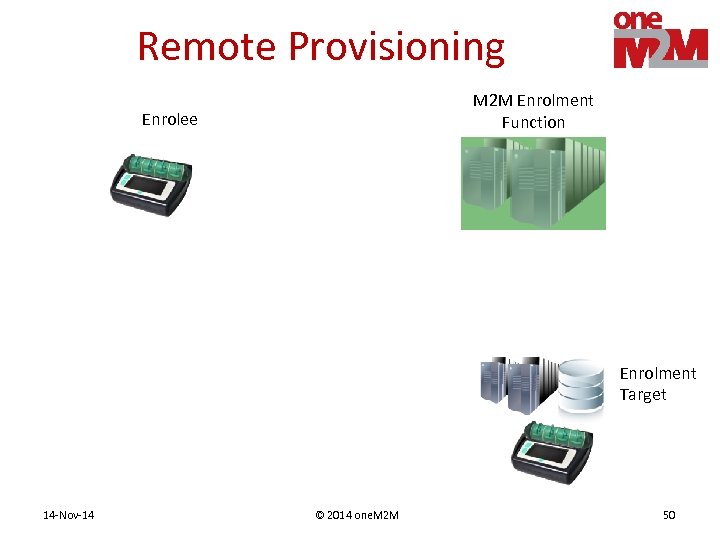 Remote Provisioning M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 50
Remote Provisioning M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 50
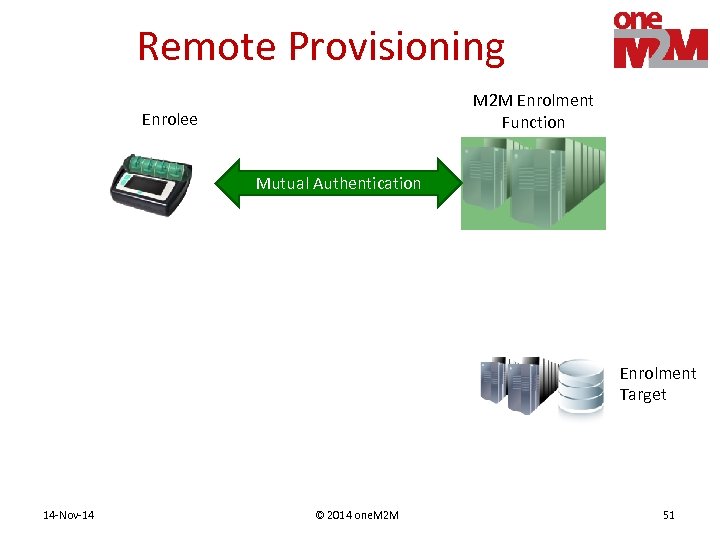 Remote Provisioning M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Mutual Authentication Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 51
Remote Provisioning M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Mutual Authentication Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 51
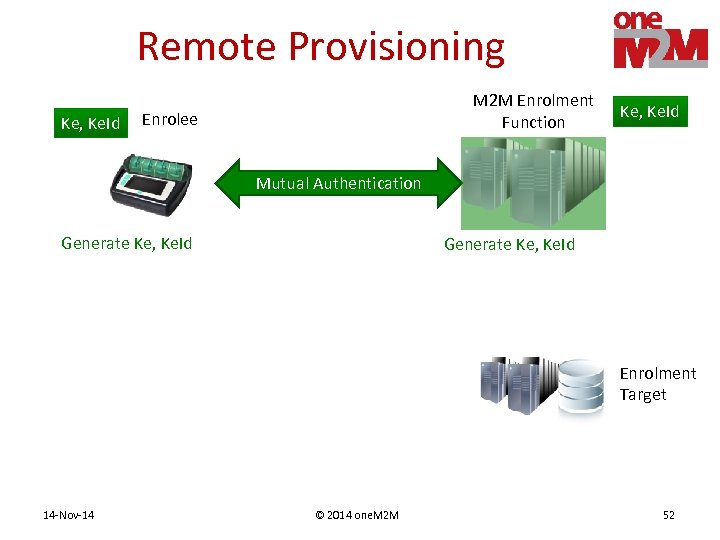 Remote Provisioning Ke, Ke. Id M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Ke, Ke. Id Mutual Authentication Generate Ke, Ke. Id Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 52
Remote Provisioning Ke, Ke. Id M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Ke, Ke. Id Mutual Authentication Generate Ke, Ke. Id Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 52
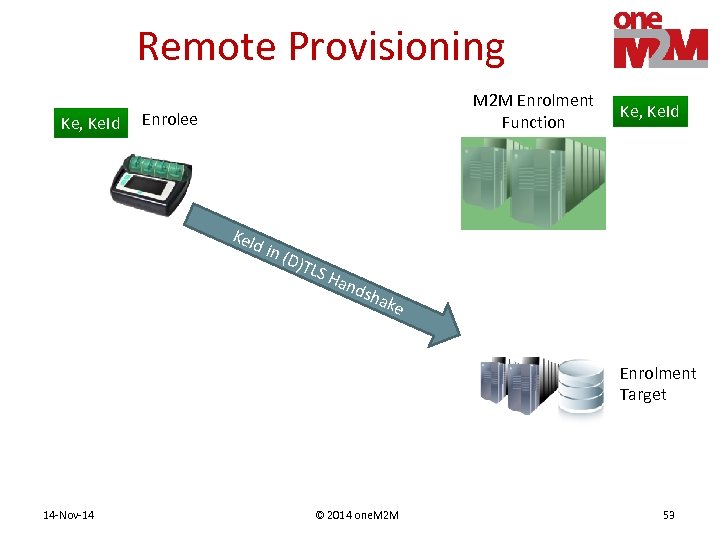 Remote Provisioning Ke, Ke. Id M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Ke. I d in (D)T LS H and s Ke, Ke. Id hak e Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 53
Remote Provisioning Ke, Ke. Id M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Ke. I d in (D)T LS H and s Ke, Ke. Id hak e Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 53
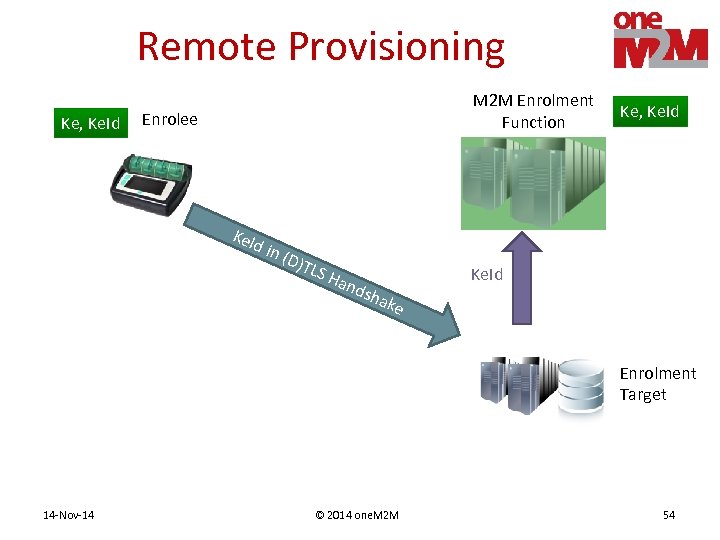 Remote Provisioning Ke, Ke. Id M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Ke. I d in (D)T LS H and s Ke, Ke. Id hak e Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 54
Remote Provisioning Ke, Ke. Id M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Ke. I d in (D)T LS H and s Ke, Ke. Id hak e Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 54
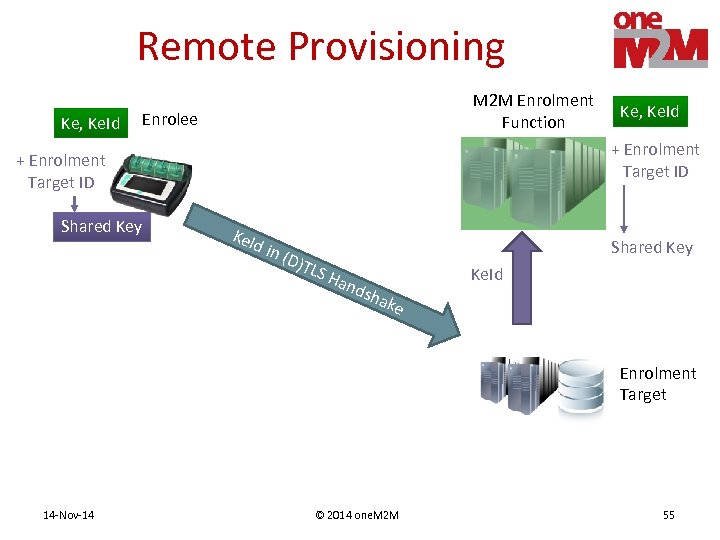 Remote Provisioning Ke, Ke. Id M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee + Enrolment Target ID Shared Key Ke, Ke. Id Ke. I d in Shared Key (D)T LS H and s Ke. Id hak e Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 55
Remote Provisioning Ke, Ke. Id M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee + Enrolment Target ID Shared Key Ke, Ke. Id Ke. I d in Shared Key (D)T LS H and s Ke. Id hak e Enrolment Target 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 55
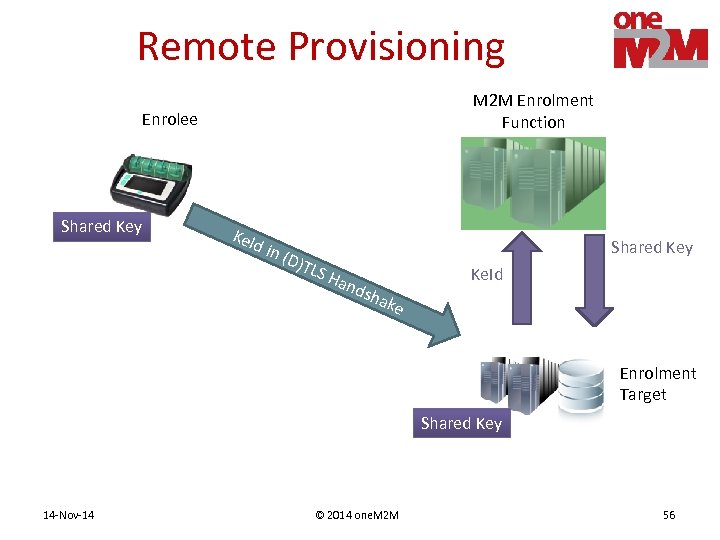 Remote Provisioning M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Shared Key Ke. I d in Shared Key (D)T LS H and s Ke. Id hak e Enrolment Target Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 56
Remote Provisioning M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Shared Key Ke. I d in Shared Key (D)T LS H and s Ke. Id hak e Enrolment Target Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 56
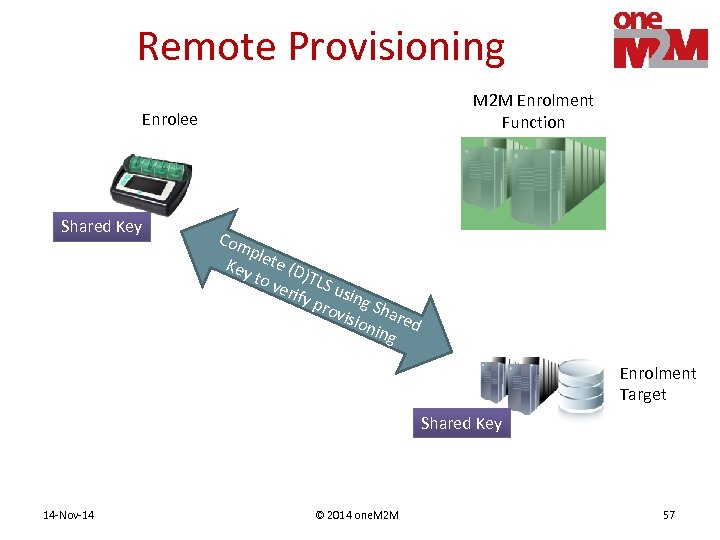 Remote Provisioning M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Shared Key Com pl Key ete (D to v )TLS erif u y pr sing S ovis har e ion ing d Enrolment Target Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 57
Remote Provisioning M 2 M Enrolment Function Enrolee Shared Key Com pl Key ete (D to v )TLS erif u y pr sing S ovis har e ion ing d Enrolment Target Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 © 2014 one. M 2 M 57
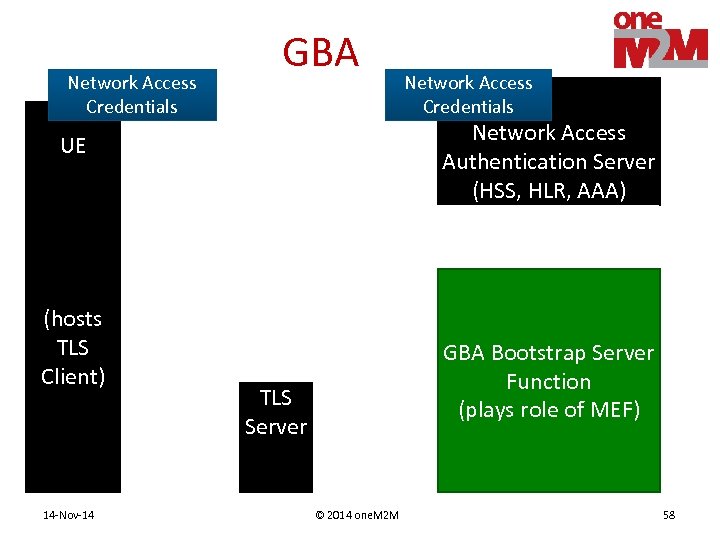 Network Access Credentials GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE (hosts TLS Client) 14 -Nov-14 Network Access Credentials GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 58
Network Access Credentials GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE (hosts TLS Client) 14 -Nov-14 Network Access Credentials GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 58
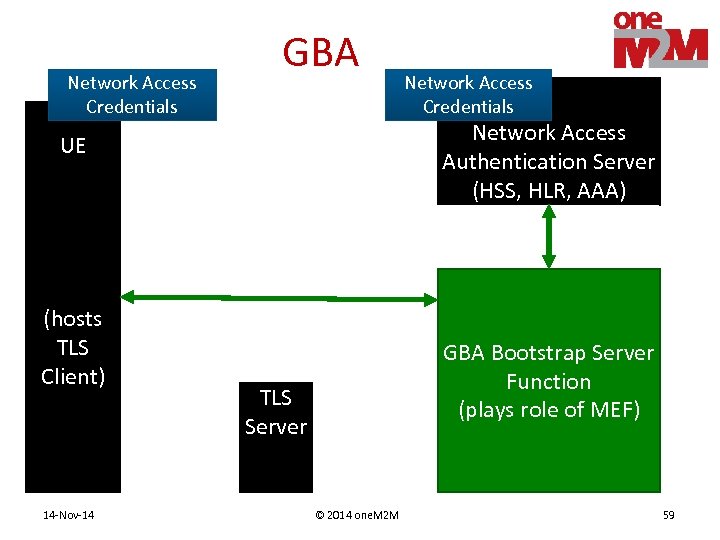 Network Access Credentials GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE (hosts TLS Client) 14 -Nov-14 Network Access Credentials GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 59
Network Access Credentials GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE (hosts TLS Client) 14 -Nov-14 Network Access Credentials GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 59
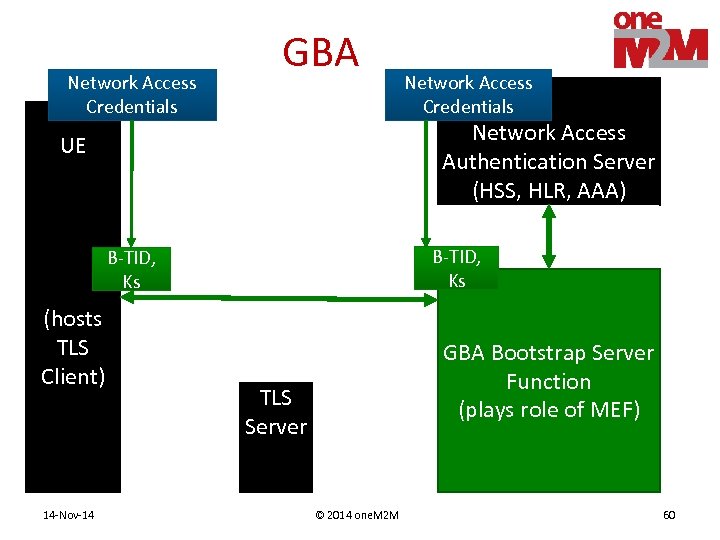 Network Access Credentials GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE B-TID, Ks (hosts TLS Client) 14 -Nov-14 Network Access Credentials GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 60
Network Access Credentials GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE B-TID, Ks (hosts TLS Client) 14 -Nov-14 Network Access Credentials GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 60
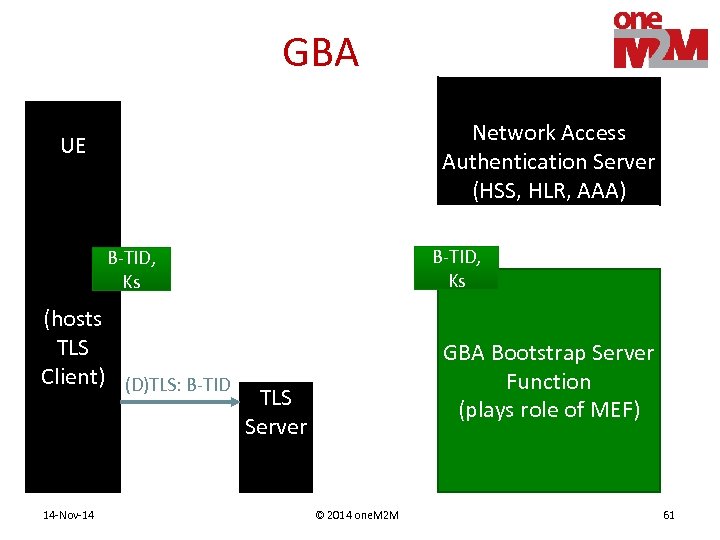 GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE B-TID, Ks (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID 14 -Nov-14 GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 61
GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE B-TID, Ks (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID 14 -Nov-14 GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Server © 2014 one. M 2 M 61
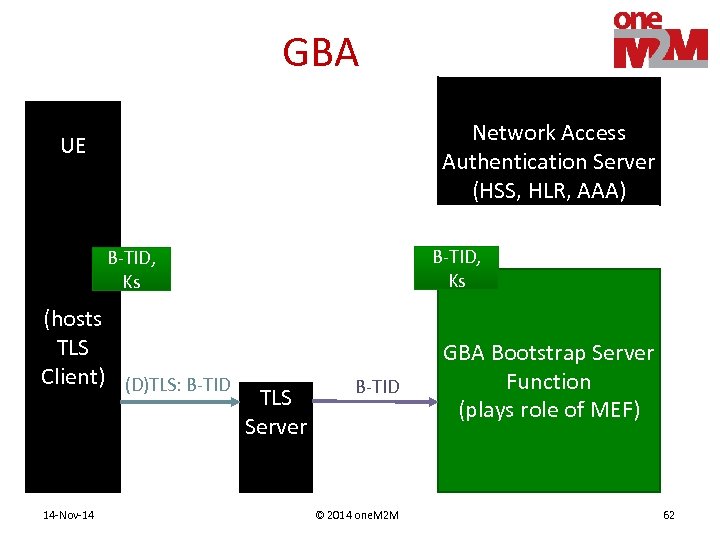 GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE B-TID, Ks (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID 14 -Nov-14 TLS Server B-TID © 2014 one. M 2 M GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) 62
GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE B-TID, Ks (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID 14 -Nov-14 TLS Server B-TID © 2014 one. M 2 M GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) 62
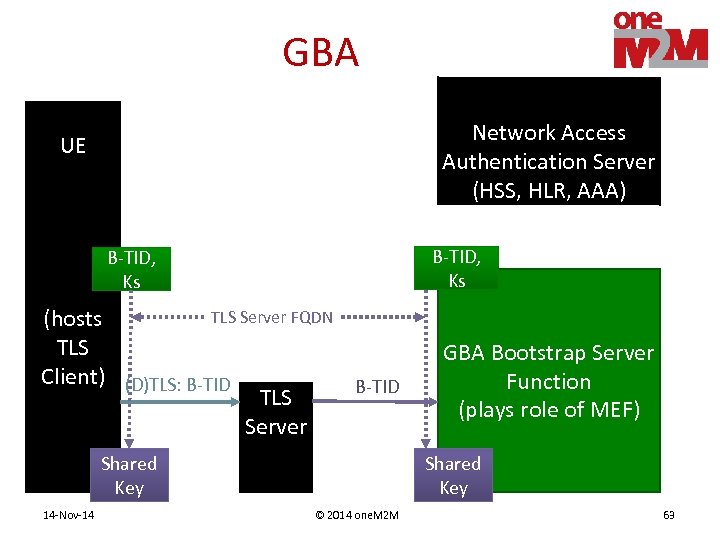 GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE B-TID, Ks TLS Server FQDN (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID TLS Server Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) Shared Key © 2014 one. M 2 M 63
GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE B-TID, Ks TLS Server FQDN (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID TLS Server Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) Shared Key © 2014 one. M 2 M 63
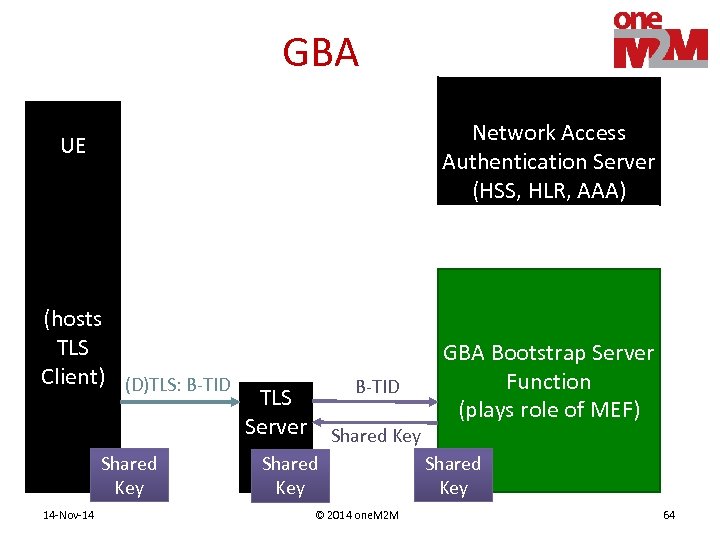 GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 B-TID TLS Server Shared Key © 2014 one. M 2 M GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) Shared Key 64
GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 B-TID TLS Server Shared Key © 2014 one. M 2 M GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) Shared Key 64
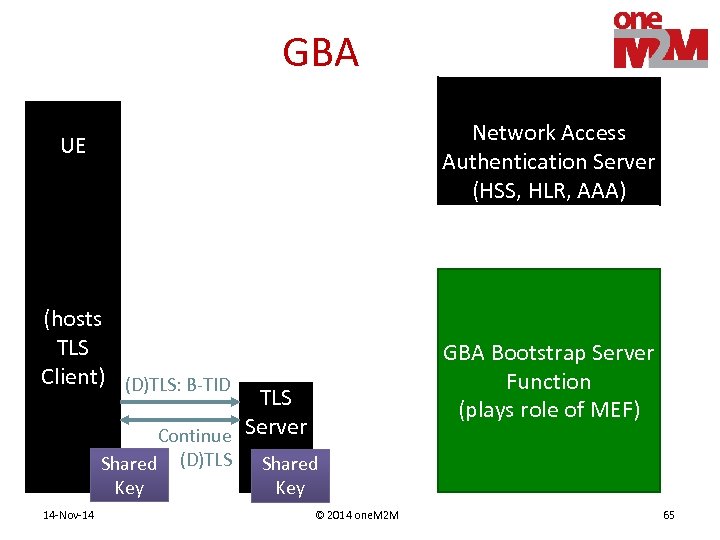 GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Continue Server Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 (D)TLS Shared Key © 2014 one. M 2 M 65
GBA Network Access Authentication Server (HSS, HLR, AAA) UE (hosts TLS Client) (D)TLS: B-TID GBA Bootstrap Server Function (plays role of MEF) TLS Continue Server Shared Key 14 -Nov-14 (D)TLS Shared Key © 2014 one. M 2 M 65


