64f5ca936ef2b6e79bf922df7e59ff9c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

f Fermilab Financial Management and SRF Planning Rich Stanek

Outline f Fermilab • Financial Management – Budgeting and Tracking System • SRF Plan and Cost Estimate – Historical and future costs • • Impact of ARRA Funds Labor Resources Schedules Summary • NOTE: Please keep in mind the distinction between SRF (the technology) and SRF (B&R code) May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 2

Financial Management f Fermilab • Work at FNAL is planned and budgeted via an internal set of Project and Task Numbers – ILC, SRF & 3. 9 GHz share common Project # (Project 18) – HINS, Project X, FNPL and ARRA have distinct Project # – All data is available via the Lab’s accounting system • Task Numbers point to elements of the Lab WBS – Also reference the ILC ART work packages where appropriate • Lab WBS relates to the DOE B&R codes • Creates a system that can be parsed and reported in various combinations – Task Leaders understand the importance of working to budget and capturing costs in the appropriate Task Number – Allows us to understand what a facility costs to build/operate and how to estimate future similar work May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 3

Facility/Component Leaders f Fermilab • For cavities and cryomodules everything focuses through Champion & Carter (TD SRF Dept. Leaders) • For dressed cavity & system testing everything focuses through Nagaitsev (AD Assoc. Division Head) and Leibfritz – Since these individuals have line responsibility for resources, things get done efficiently (scheduling, job assignments…) • Each SRF facility has defined leadership May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 4
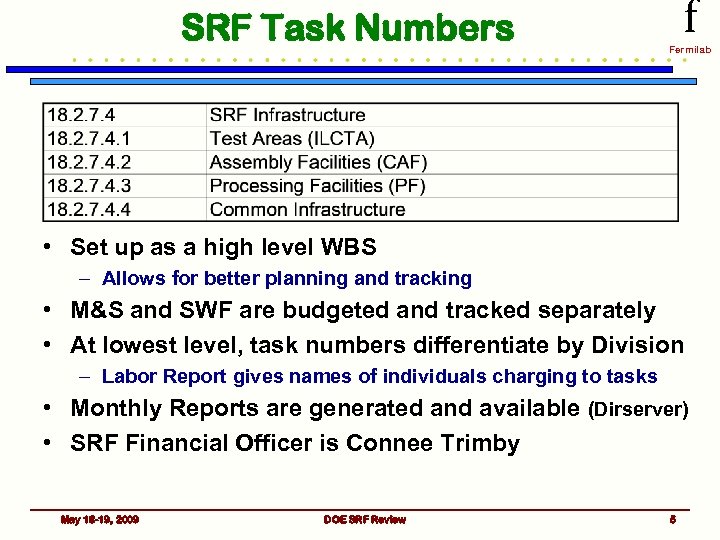
SRF Task Numbers f Fermilab • Set up as a high level WBS – Allows for better planning and tracking • M&S and SWF are budgeted and tracked separately • At lowest level, task numbers differentiate by Division – Labor Report gives names of individuals charging to tasks • Monthly Reports are generated and available (Dirserver) • SRF Financial Officer is Connee Trimby May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 5
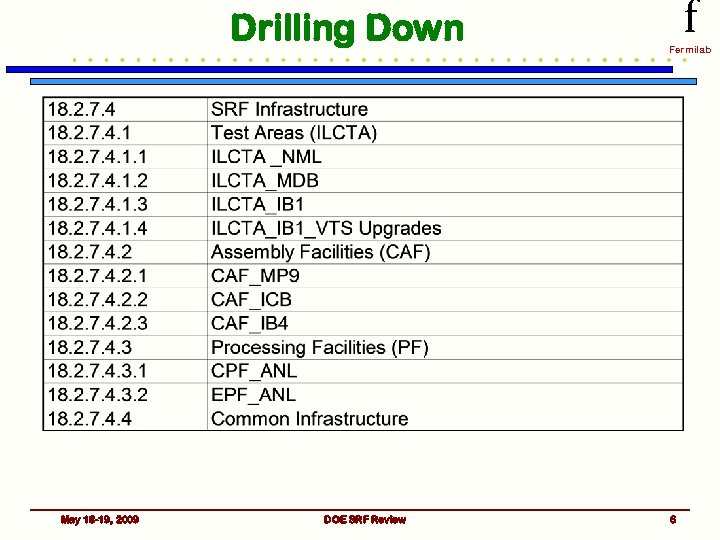
Drilling Down May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review f Fermilab 6
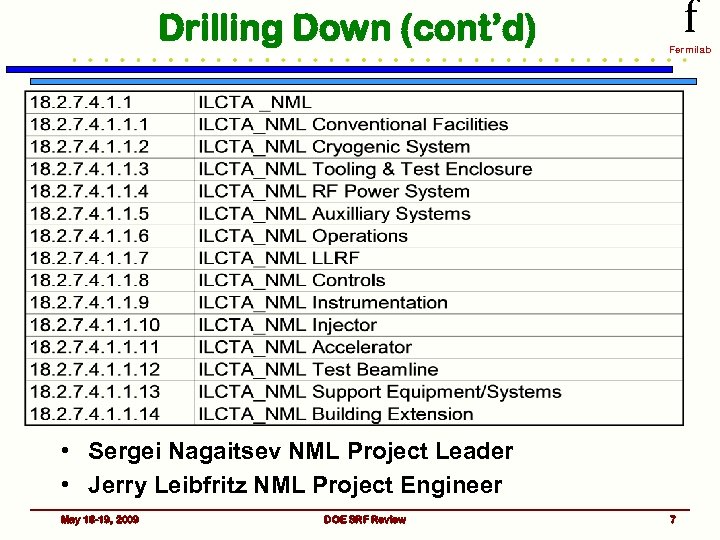
Drilling Down (cont’d) f Fermilab • Sergei Nagaitsev NML Project Leader • Jerry Leibfritz NML Project Engineer May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 7
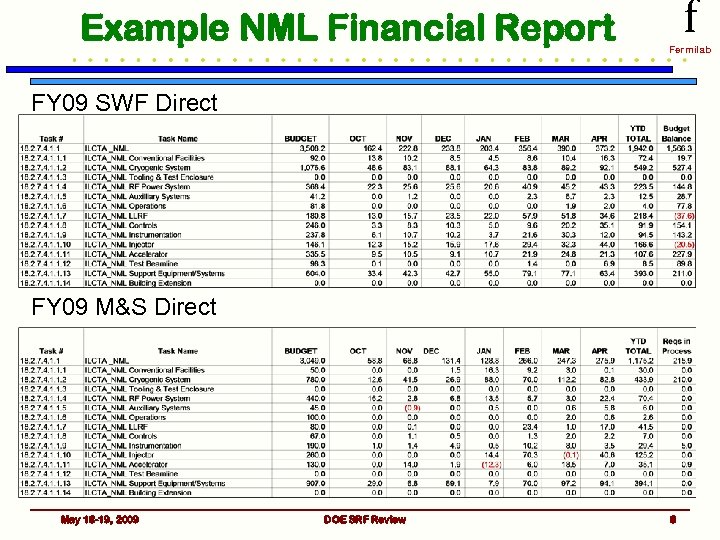
Example NML Financial Report f Fermilab FY 09 SWF Direct FY 09 M&S Direct May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 8
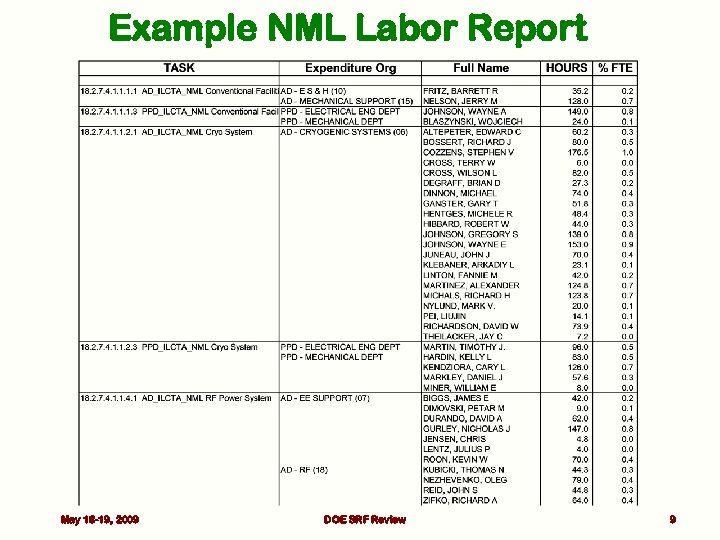
Example NML Labor Report May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 9
SRF Infrastructure Plan f Fermilab • The SRF Plan change based on – – R&D results Industrial capabilities and interests New information from actual usage of facilities Funding and OHEP guidance • Review the status and revisit the Plan (each year) – – Part of the funding cycle Are we still on track? Have conditions changed? Do we have better information? May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 10
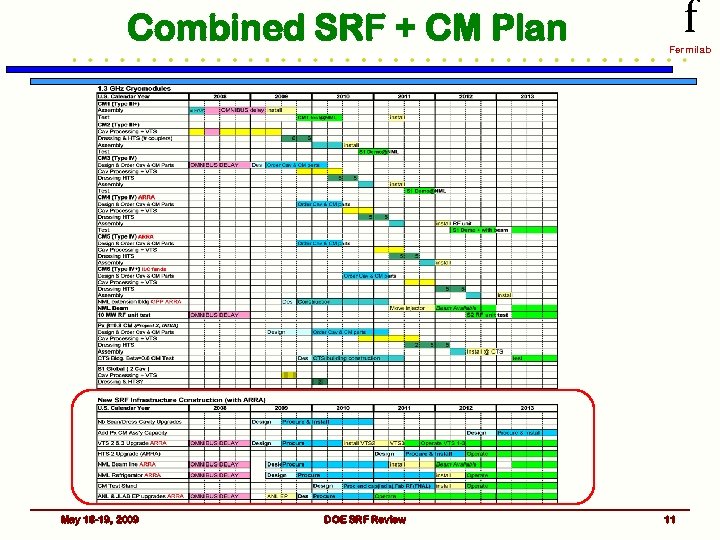
Combined SRF + CM Plan May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review f Fermilab 11

SRF Infrastructure Plan f Fermilab • FY 08 Omnibus delayed our plan (financially) and affected our work force (still recovering personnel) • Nevertheless very measurable progress on facilities • Plan based on $25 M/yr (SRF B&R) for FY 10 through FY 13 plus the ARRA funds ($52. 67 M total) May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 12

SRF Infrastructure Plan (in words) f Fermilab CAF • Cavity fab. & dressing upg. by end 2010, CM capacity upg. in 2013 – Second line higher throughput VTS • Install & commission VTS 2 & 3 by mid-2011 – Larger diameter higher throughput Upgrade PF @ ANL/TJNL – Complete capacity doubling by end 2011 higher throughput HTS • Install & commission HTS 2 by mid-2012 – Double-wide (located with CTS) higher throughput NML • Install & test CM 1 in NML by end of 2009 • Beam available in 2012 • New Cryo Plant operational by 2012 CTS • CM Test Stand operational by end of 2012/early 2013 May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 13
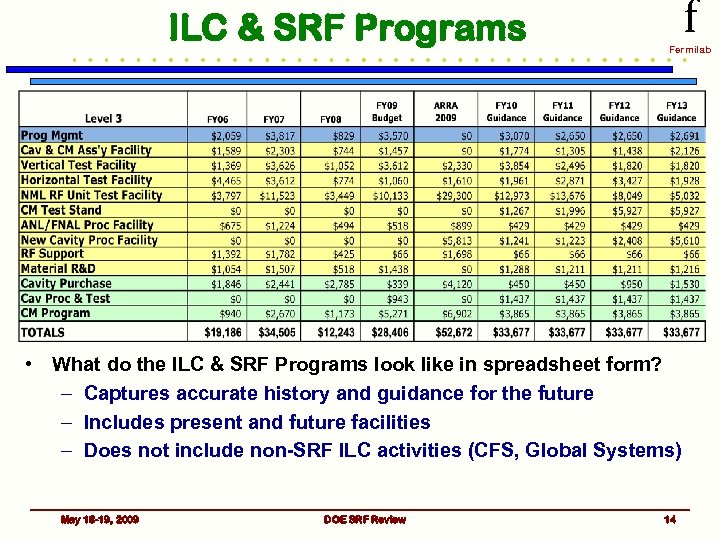
ILC & SRF Programs f Fermilab • What do the ILC & SRF Programs look like in spreadsheet form? – Captures accurate history and guidance for the future – Includes present and future facilities – Does not include non-SRF ILC activities (CFS, Global Systems) May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 14
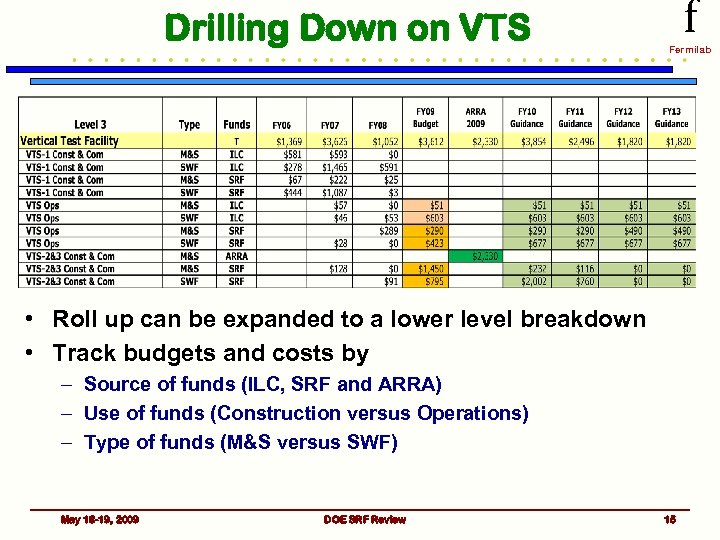
Drilling Down on VTS f Fermilab • Roll up can be expanded to a lower level breakdown • Track budgets and costs by – Source of funds (ILC, SRF and ARRA) – Use of funds (Construction versus Operations) – Type of funds (M&S versus SWF) May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 15
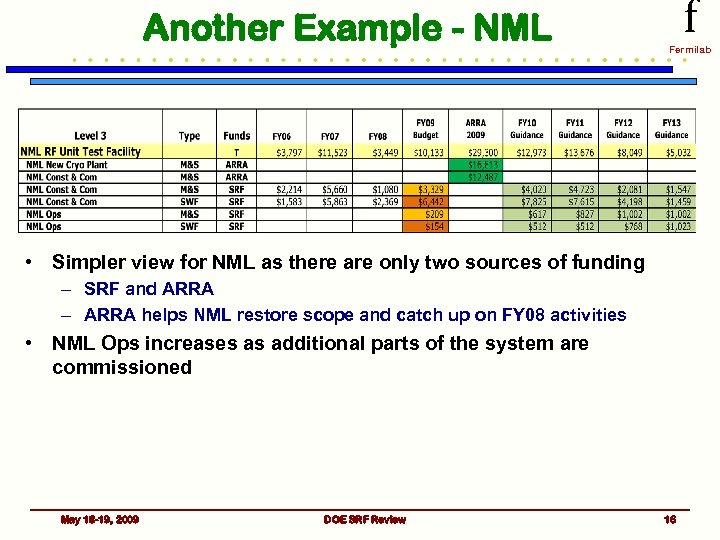
Another Example - NML f Fermilab • Simpler view for NML as there are only two sources of funding – SRF and ARRA – ARRA helps NML restore scope and catch up on FY 08 activities • NML Ops increases as additional parts of the system are commissioned May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 16

Infrastructure/Facility Plan f Fermilab • Funding sources – SRF – ARRA – ILC Includes Construction and Operations • Cost estimates for the new infrastructure done by Task Leaders using data from actual purchases, vendor quotes, engineering estimates and scaling from similar tasks – Cost estimates have additional back up information May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 17
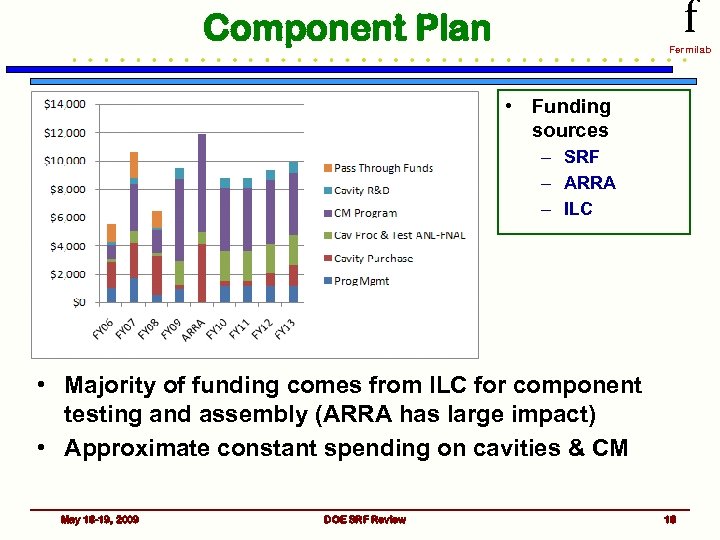
f Component Plan Fermilab • Funding sources – SRF – ARRA – ILC • Majority of funding comes from ILC for component testing and assembly (ARRA has large impact) • Approximate constant spending on cavities & CM May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 18
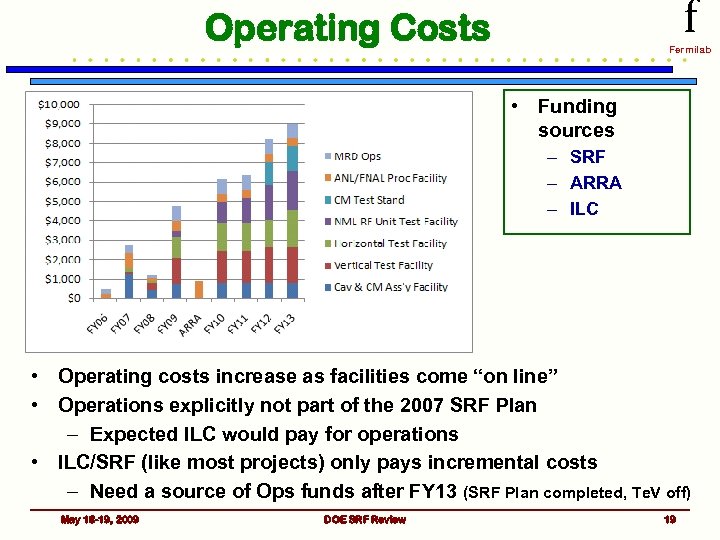
f Operating Costs Fermilab • Funding sources – SRF – ARRA – ILC • Operating costs increase as facilities come “on line” • Operations explicitly not part of the 2007 SRF Plan – Expected ILC would pay for operations • ILC/SRF (like most projects) only pays incremental costs – Need a source of Ops funds after FY 13 (SRF Plan completed, Te. V off) May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 19
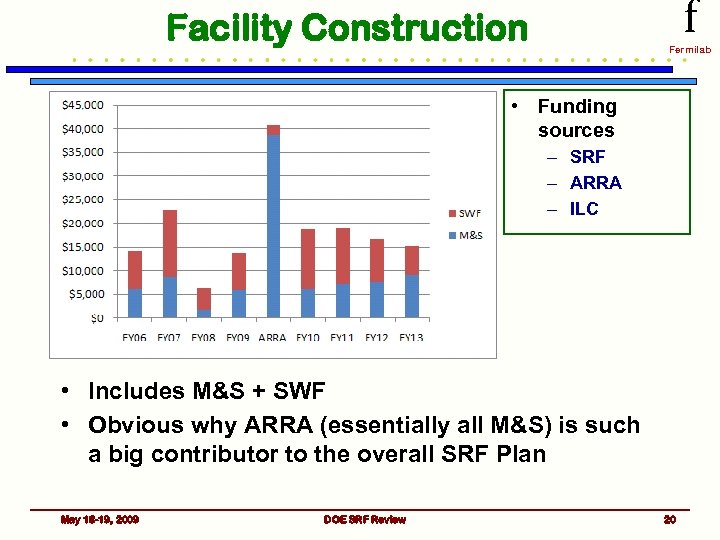
f Facility Construction Fermilab • Funding sources – SRF – ARRA – ILC • Includes M&S + SWF • Obvious why ARRA (essentially all M&S) is such a big contributor to the overall SRF Plan May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 20
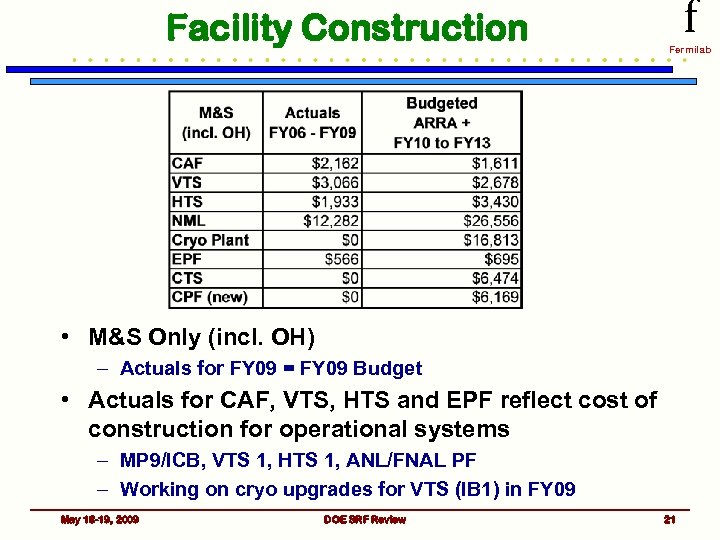
Facility Construction f Fermilab • M&S Only (incl. OH) – Actuals for FY 09 = FY 09 Budget • Actuals for CAF, VTS, HTS and EPF reflect cost of construction for operational systems – MP 9/ICB, VTS 1, HTS 1, ANL/FNAL PF – Working on cryo upgrades for VTS (IB 1) in FY 09 May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 21

Impact of ARRA on SRF f Fermilab • American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) presents an opportunity to – Accelerate parts of the current SRF Program – Restore elements thought to be financially unachievable – Begin to incorporate U. S. industrialization • ARRA has goals and conditions that match up well with our SRF Plan – – Get money into U. S. industry to stimulate the economy Create or save jobs Choose procurements that can be obligated quickly Target actions towards high tech applications • This has a longer lasting stimulus effect • SRF part of ARRA is targeted towards U. S. Industry May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 22

Elements of ARRA SRF Plan f Fermilab • ARRA planning assumed ILC and SRF B&R lines continue to be funded per OHEP Guidance May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 23

Cryogenics - NML Test Facility f Fermilab • Procure Cryo Plant for Test Areas (NML & CTS) – 300 W @ 2 K – Use fixed price contracts as much as possible • Limited vendor list still expect U. S. competition • Cryo Plant allows for better operation of test systems – – Meets the required RF Unit Rep Rate (heat load) More reliable Maintains correct shield temperatures Provides more efficient and cost effective operation May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 24
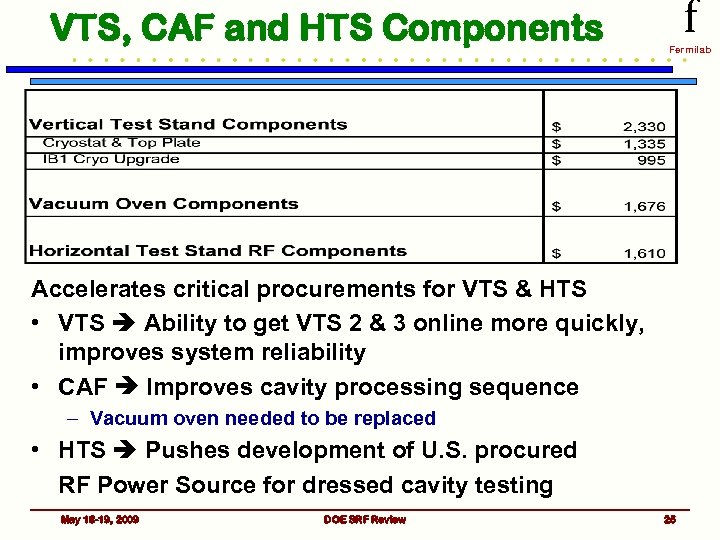
VTS, CAF and HTS Components f Fermilab Accelerates critical procurements for VTS & HTS • VTS Ability to get VTS 2 & 3 online more quickly, improves system reliability • CAF Improves cavity processing sequence – Vacuum oven needed to be replaced • HTS Pushes development of U. S. procured RF Power Source for dressed cavity testing May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 25
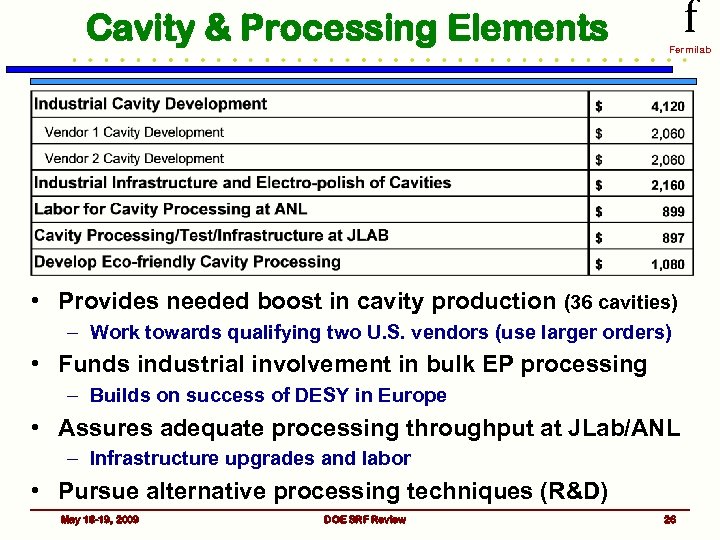
Cavity & Processing Elements f Fermilab • Provides needed boost in cavity production (36 cavities) – Work towards qualifying two U. S. vendors (use larger orders) • Funds industrial involvement in bulk EP processing – Builds on success of DESY in Europe • Assures adequate processing throughput at JLab/ANL – Infrastructure upgrades and labor • Pursue alternative processing techniques (R&D) May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 26

f Cryomodule Components Fermilab • Order cryomodule components from U. S. industry (2) – Up to now Zanon (Italy) • Supports value engineering – Looking to improve the design and fabrication methods • In conjunction with ongoing ILC procurements, ARRA funds provide an adequate stream of cryomodule parts May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 27
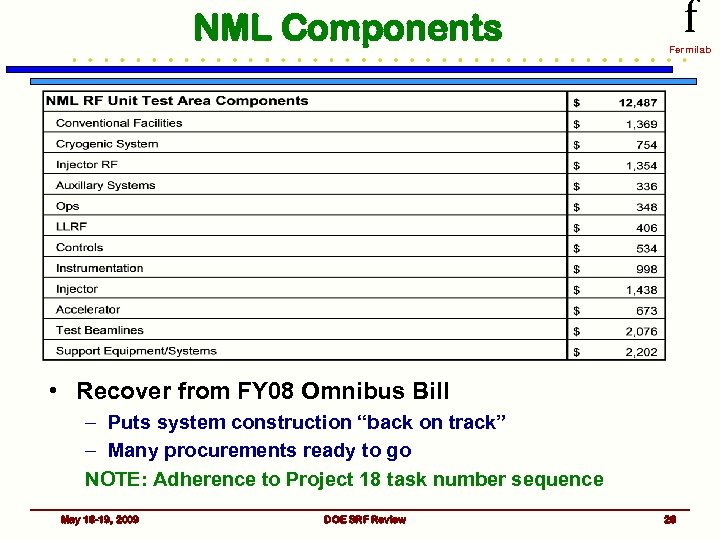
NML Components f Fermilab • Recover from FY 08 Omnibus Bill – Puts system construction “back on track” – Many procurements ready to go NOTE: Adherence to Project 18 task number sequence May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 28
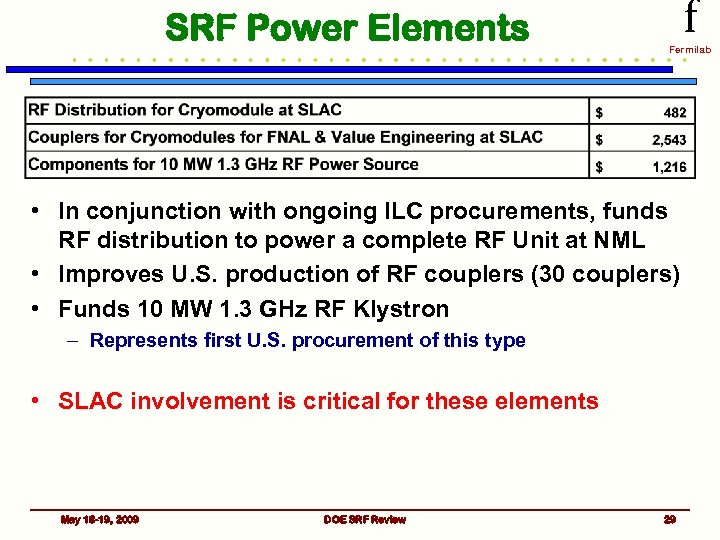
SRF Power Elements f Fermilab • In conjunction with ongoing ILC procurements, funds RF distribution to power a complete RF Unit at NML • Improves U. S. production of RF couplers (30 couplers) • Funds 10 MW 1. 3 GHz RF Klystron – Represents first U. S. procurement of this type • SLAC involvement is critical for these elements May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 29
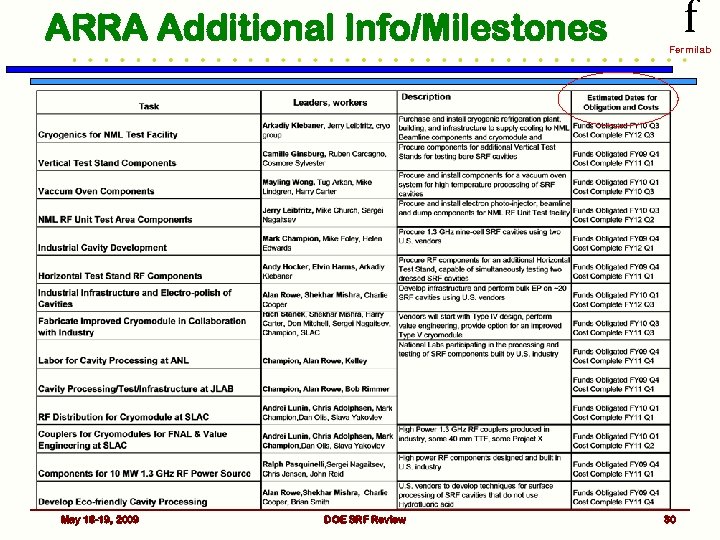
ARRA Additional Info/Milestones May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review f Fermilab 30

Labor Resources f Fermilab • Labor resources are limited – In FY 09, have SWF budget for ~89 FTE (combined ILC + SRF) • Currently have ~70 FTE working on these tasks – Current FY 09 SRF labor ~ half of FY 08 Q 1 FTE • Finishing 3. 9 GHz will help • Need to add more people to the effort to stay on schedule • Supplement internal staff with contract employees – Works well for general purpose needs – In some cases, using contract employees is difficult especially when experience is essential – Cryogenic engineers – RF engineers – High vacuum technicians • Also adding consultant help – H Padamsee, P Kelley… May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 31
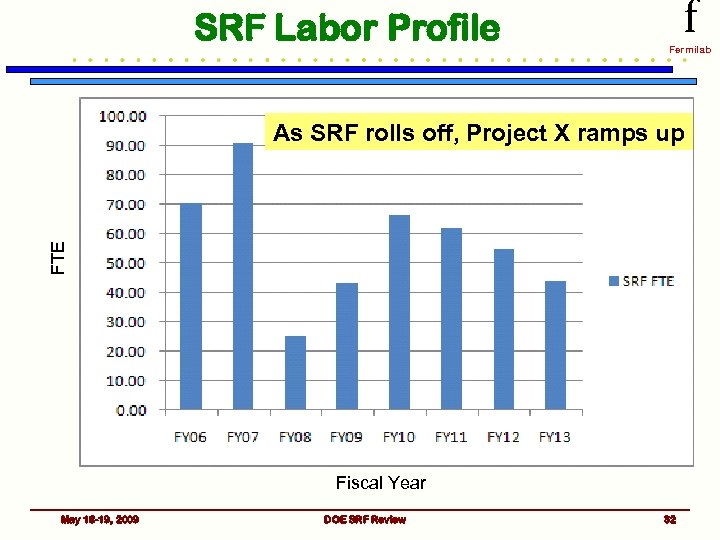
SRF Labor Profile f Fermilab FTE As SRF rolls off, Project X ramps up Fiscal Year May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 32
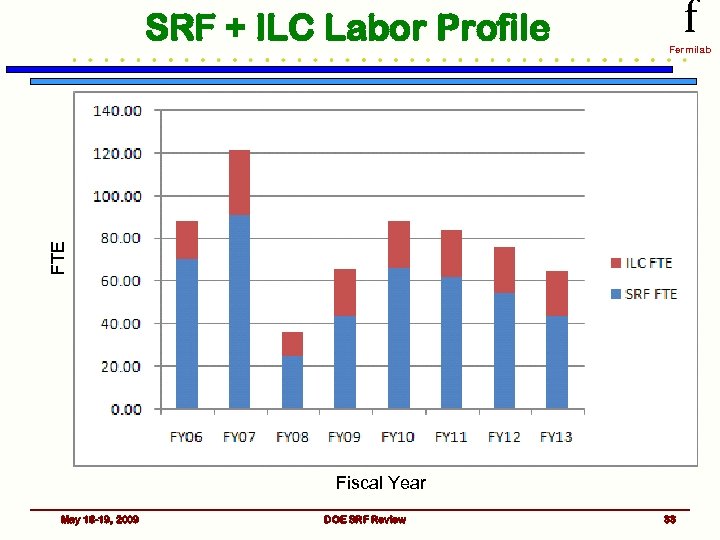
f Fermilab FTE SRF + ILC Labor Profile Fiscal Year May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 33

Labor Needs f Fermilab • Current Labor Force working on the just SRF part of the Program ~ 48 FTE (slightly increasing each month) • SRF Plan calls for ~ 57 FTE/yr (on average/based on 4 yrs) with a peak of ~ 67 FTE needed in FY 10 / ~ 63 FTE in FY 11 • With 3. 9 GHz winding down ~10 FTE free up • Must increase the work force (in certain disciplines) as well as redirect people to work on specific tasks – Cryogenic and mechanical engineering – RF engineering – Need to train additional techs for clean room environment and to work with chemical processing equipment • Utilize contract personnel • Continue to integrate new people into the Program as they become available May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 34
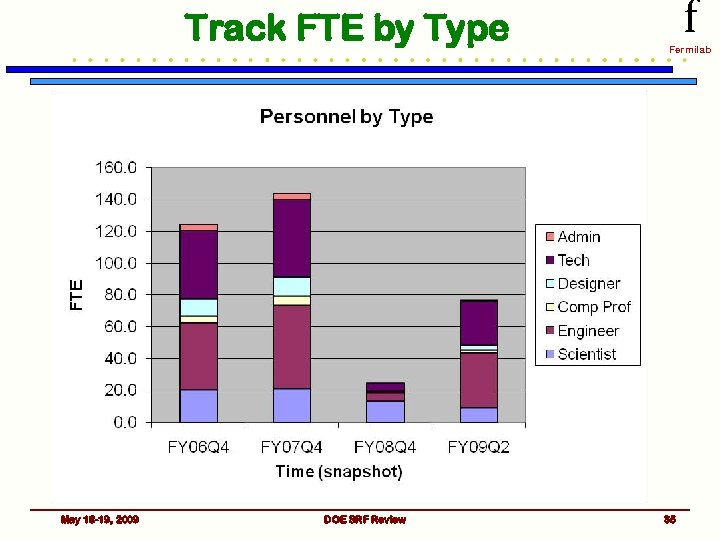
Track FTE by Type May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review f Fermilab 35

Other Labor Considerations f Fermilab • Labor planning is not just about total FTE but must take into account specific individuals shared by projects – In June 2008, looked at all individuals either working or planned for the various SRF related projects • Identified people who were oversubscribed • Worked towards setting priorities and rearranging assignments • Opportunities exist (at other institutions) to embed personnel and learn (JLab, Cornell, DESY…) – Want to take advantage of these opportunities – Some are already in place but looking for other candidates • Labor is a critical resource which must be managed May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 36

Labor Management Examples f Fermilab • Actively manage labor assignments – Appointed U. S. 1. 3 GHz Cavity Manager (Mark Champion) • Coordinates movement of cavities between facilities • Contact person for JLab, Cornell and ANL Processing – Bolstered ANL/FNAL PF by appointing Scientific Lead (Genfa Wu) to coordinate with Mike Kelly – Selected Allan Rowe to lead the engineering efforts for defining future cavity processing and coordinating industrial involvement – Added (or in process of adding) contract personnel • • May 18 -19, 2009 2 engineers 4 designers 2 techs for ANL/FNAL Facility 3 techs for cryo group DOE SRF Review 37

Schedules and Milestones f Fermilab • SRF Program Office manages individual elements of the Plan by setting scope of work, budget and high level milestones – Individual parts of the program have project schedules and more detailed lower level milestones • Technical progress on critical systems is monitored and reported weekly – via standing management & coordination meetings • All of this information is fed into our planning process results in our SRF Budget Plan May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 38
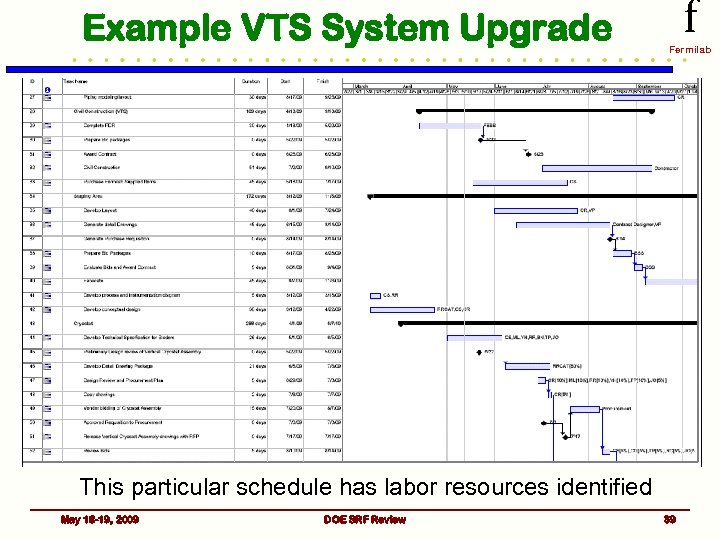
Example VTS System Upgrade f Fermilab This particular schedule has labor resources identified May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 39
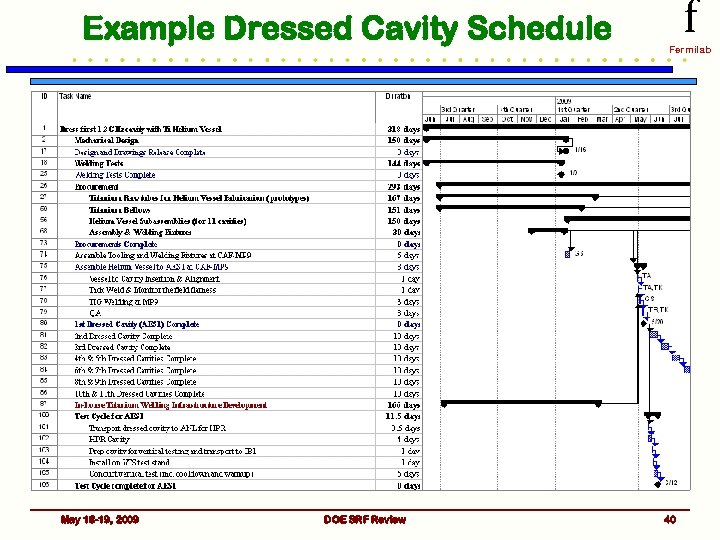
Example Dressed Cavity Schedule May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review f Fermilab 40

Example NML Detailed Milestones • Completed NML Milestones • • • • Refrigerator #1 Operational (8/07) Begin Civil Design of Build. Extension (8/07) Commission Refrig. #1 (Liquify Helium) (9/07) Move RF Systems to NML (5 MW & CC 2) (10/07) Install CM Support Girders (4/08) 1 st Cryomodule Delivery to NML (8/08) Delivery of 1 st Waveguide from SLAC(9/08) Commission Vacuum Pump & Frick(12/08) Cryo System Feedbox/Endcap Delivery(2/09) Delivery of Remaining WG from SLAC(2/09) Move CC 2 to NML (3/09) Install Cryo Feedbox/Endcaps (4/09) Commission 300 k. W RF into Load (5/09) May 18 -19, 2009 f Fermilab • Future NML Milestones • • • • Warm RF Tests of CC 2 (5/09) Commission Cryo Distribution Sys. (CC 2) (6/09) CM 1 Safety Documentation Complete (6/09) Prelim. GPP Design Complete (6/09) CC 2 Operational (6/09) 3 MW RF System Operational (7/09) Begin 1 st Cryomodule RF Tests (Warm) (7/09) CM 1 Ready for Cooldown (8/09) Cathode Equipment from INFN (8/09) INFN to Assemble Cathode at NML (8/09) Order Cryoplant (8/09) Begin Construction of Build. Extension (8/09) Cold RF Testing of CM 1 (9/09) Refrigerator #2 Operational (9/09) 2 nd Cryomodule Delivery to NML (2/10) DOE SRF Review 41

f End of FY 09: SRF Milestones Fermilab 1) Vertical Test Stand: VTS-1 operational and capable of testing single and nine cell 1. 3 GHz elliptical cavities or HINS 325 MHz SSR 1 spoke resonators at about two tests per scheduled month Done 2) Horizontal Test Stand: HTS-1 capable of testing 1. 3 GHz dressed cavities at 1. 8 K at a rate of one per month In Progress Awaiting arrival of first dressed 1. 3 GHz cavity May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 42

End of FY 09: SRF Milestones f Fermilab 3) ANL/FNAL EP facility: capable of Electro-polish, ultrasonic rinse, High Pressure Rinse of single or nine-cell cavities at a rate of 1 process per two weeks. Ultra clean water, cavity handling fixtures and clean room performance validated In Progress System validated for single-cells, continue to work on nine-cell commissioning 4) CAF: fixtures & clean rooms validated for assembly of CM and dressing of 1. 3 GHz cavities In Progress TIG welding of Ti validated for cavity dressing. CM 1 and 3. 9 GHz assembled 5) Tumbling machine: operational for single cells In Progress May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 43
End of FY 09: SRF Milestones f Fermilab 6) Optical inspection device: operational for single and nine cell cavities Done Control system improvements in progress 7) Automated Cavity tuner: DESY-KEK-FNAL collaboration 1 st of 4 machines near completion In Progress 8) NML Refrigeration: Single Te. V satellite based NML refrigerator operational and with large vacuum pump able to achieve 60 W at 1. 8 K In Progress 9) 3 MW 1. 3 GHz RF power source operational in NML In Progress May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 44

Summary f Fermilab • SRF Plan exists it has evolved since 2007 – Conditions, elements of the plan, and finances changed • SRF Plan is managed and controlled by a central Program Management Office (Kephart) – Set priorities, budgets and scope of work for facilities – Individual Task Leaders control their parts of the Plan • Monthly budget and obligation report + labor detail report cost • Detailed schedules and milestones track progress • ARRA funding provides a tremendous opportunity to – – Partially recover from the FY 08 SRF B&R shutdown Accelerate parts of the current SRF Plan Restore elements of SRF Plan (dropped for financial reasons) Include a start towards U. S. industrialization of SRF technology May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 45
Conclusion f Fermilab • SRF is one of the enabling technologies for future accelerator efforts • These future efforts will require additional R&D as well as proven fabrication & testing expertise for cavities and cryomodules SRF infrastructure – Fermilab has a plan to build these facilities • Incorporates & expands existing U. S. capabilities – Both in industry and at other National Labs • Reuses parts of our existing infrastructure • Fermilab is well positioned to continue to build the SRF Infrastructure capable of sustaining the U. S. efforts on programs such as Project X or ILC May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 46
64f5ca936ef2b6e79bf922df7e59ff9c.ppt