0ac2de35377e7c04e598ce55dd1d4a73.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 F 5 -Chapter 4 Limiting factor analysis Lecturer: Ji Weili 2018/3/17 1
F 5 -Chapter 4 Limiting factor analysis Lecturer: Ji Weili 2018/3/17 1
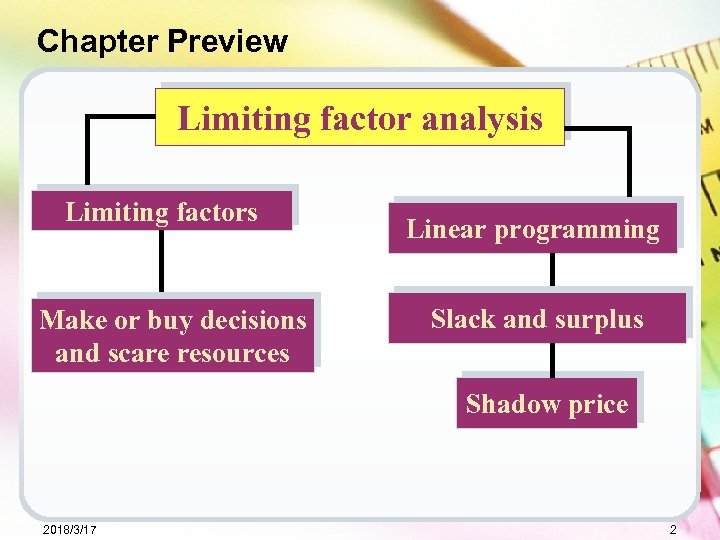 Chapter Preview Limiting factor analysis Limiting factors Make or buy decisions and scare resources Linear programming Slack and surplus Shadow price 2018/3/17 2
Chapter Preview Limiting factor analysis Limiting factors Make or buy decisions and scare resources Linear programming Slack and surplus Shadow price 2018/3/17 2
 Overview 1 2 2018/3/17 A revision of linear programming technique. Some new concepts: slack, surplus, shadow price or dual price 3
Overview 1 2 2018/3/17 A revision of linear programming technique. Some new concepts: slack, surplus, shadow price or dual price 3
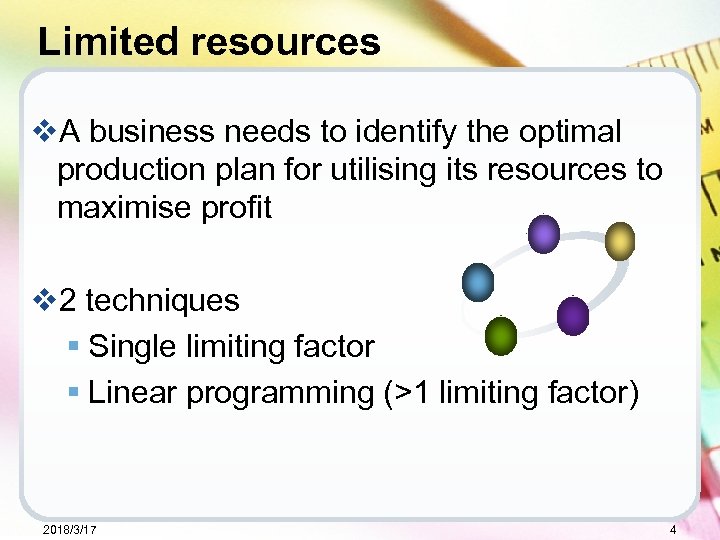 Limited resources v. A business needs to identify the optimal production plan for utilising its resources to maximise profit v 2 techniques § Single limiting factor § Linear programming (>1 limiting factor) 2018/3/17 4
Limited resources v. A business needs to identify the optimal production plan for utilising its resources to maximise profit v 2 techniques § Single limiting factor § Linear programming (>1 limiting factor) 2018/3/17 4
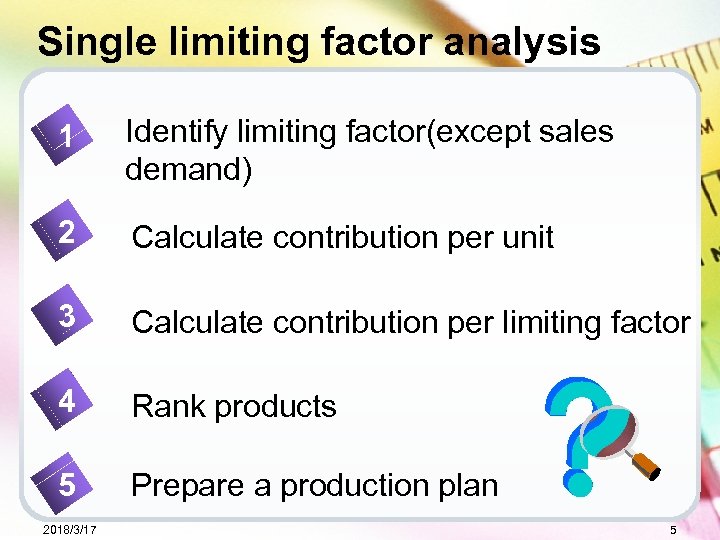 Single limiting factor analysis 1 Identify limiting factor(except sales demand) 2 Calculate contribution per unit 3 Calculate contribution per limiting factor 4 Rank products 5 Prepare a production plan 2018/3/17 5
Single limiting factor analysis 1 Identify limiting factor(except sales demand) 2 Calculate contribution per unit 3 Calculate contribution per limiting factor 4 Rank products 5 Prepare a production plan 2018/3/17 5
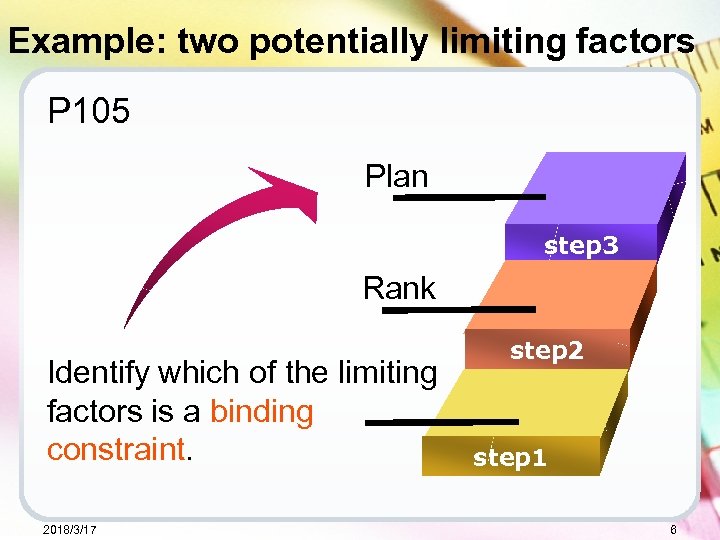 Example: two potentially limiting factors P 105 Plan 4 step 3 Rank Identify which of the limiting factors is a binding constraint. 2018/3/17 step 2 step 1 6
Example: two potentially limiting factors P 105 Plan 4 step 3 Rank Identify which of the limiting factors is a binding constraint. 2018/3/17 step 2 step 1 6
 Make or buy decisions and scarce resources Make or buy? Combining internal and external production Decision rule---minimise costs Example: 2. 1. 1 P 107 2018/3/17 7
Make or buy decisions and scarce resources Make or buy? Combining internal and external production Decision rule---minimise costs Example: 2. 1. 1 P 107 2018/3/17 7
 Linear programming steps 1 Define variables P 110 – let x = number of the Super produced – let y = number of the Deluxe produced – let p = contribution per month 2018/3/17 8
Linear programming steps 1 Define variables P 110 – let x = number of the Super produced – let y = number of the Deluxe produced – let p = contribution per month 2018/3/17 8
 Linear programming steps Establish constraints § subject to: • Machine hour 5 x + 1. 5 y 400 • Government restrictionsx + y 150 • Non-negativity x, y > 0 2 3 Formulate objective function § Max p =100 x + 200 y 2018/3/17 9
Linear programming steps Establish constraints § subject to: • Machine hour 5 x + 1. 5 y 400 • Government restrictionsx + y 150 • Non-negativity x, y > 0 2 3 Formulate objective function § Max p =100 x + 200 y 2018/3/17 9
 Linear programming steps 4 Plot constraints on graph § Find co-ordinates • Machine hour 5 x + 1. 5 y= 400 • when x=0, y=267 • y=0, x=80 • Government restrictions x + y=150 When • Non-negativity 2018/3/17 10 x=0, y=150 y=0, x= 150 x, y > 0 10
Linear programming steps 4 Plot constraints on graph § Find co-ordinates • Machine hour 5 x + 1. 5 y= 400 • when x=0, y=267 • y=0, x=80 • Government restrictions x + y=150 When • Non-negativity 2018/3/17 10 x=0, y=150 y=0, x= 150 x, y > 0 10
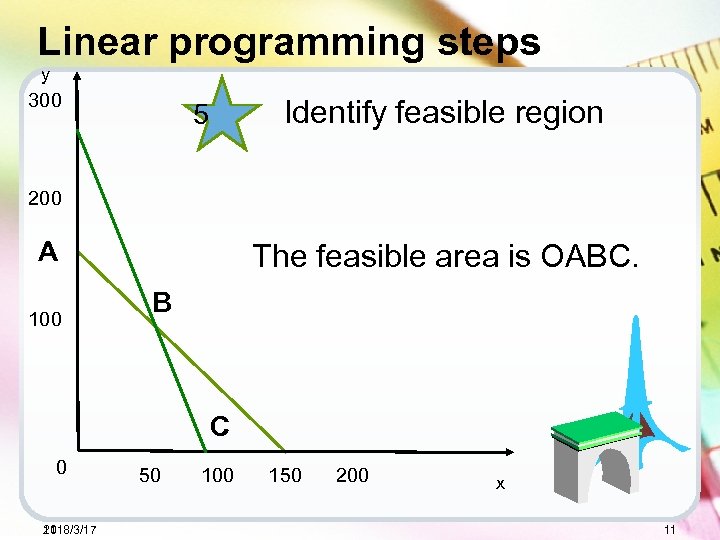 Linear programming steps y 300 Identify feasible region 5 200 A 100 The feasible area is OABC. B C 0 2018/3/17 11 50 100 150 200 x 11
Linear programming steps y 300 Identify feasible region 5 200 A 100 The feasible area is OABC. B C 0 2018/3/17 11 50 100 150 200 x 11
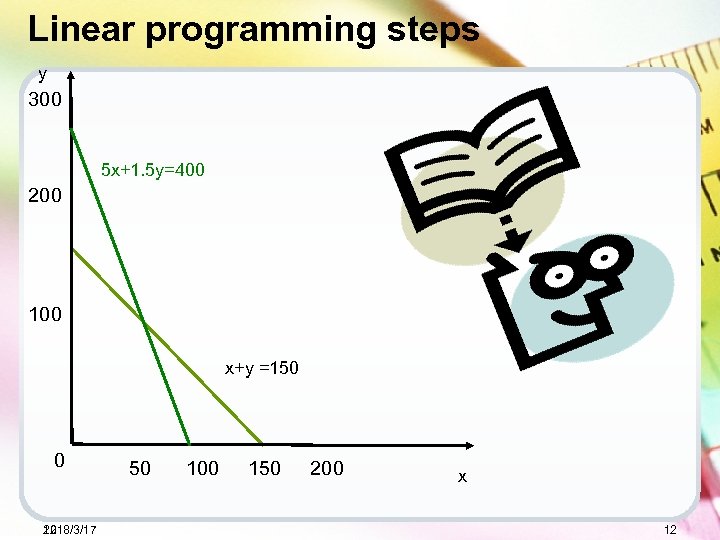 Linear programming steps y 300 5 x+1. 5 y=400 200 100 x+y =150 0 2018/3/17 12 50 100 150 200 x 12
Linear programming steps y 300 5 x+1. 5 y=400 200 100 x+y =150 0 2018/3/17 12 50 100 150 200 x 12
 Linear programming steps Plot objective function and identify optimal point 6 p =100 x + 200 y Pick any value for p • Say p= 10000 – When x=0, y=50 – When y=0, x=100 2018/3/17 13 13
Linear programming steps Plot objective function and identify optimal point 6 p =100 x + 200 y Pick any value for p • Say p= 10000 – When x=0, y=50 – When y=0, x=100 2018/3/17 13 13
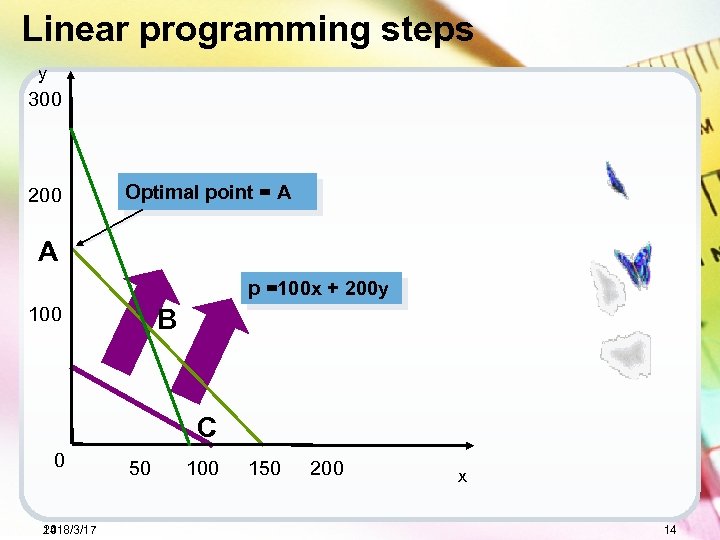 Linear programming steps y 300 200 Optimal point = A A p =100 x + 200 y 100 B C 0 2018/3/17 14 50 100 150 200 x 14
Linear programming steps y 300 200 Optimal point = A A p =100 x + 200 y 100 B C 0 2018/3/17 14 50 100 150 200 x 14
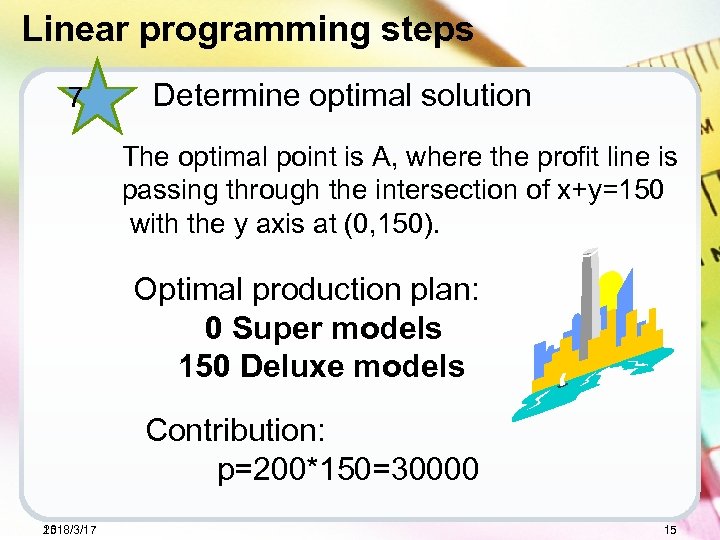 Linear programming steps 7 Determine optimal solution The optimal point is A, where the profit line is passing through the intersection of x+y=150 with the y axis at (0, 150). Optimal production plan: 0 Super models 150 Deluxe models Contribution: p=200*150=30000 2018/3/17 15 15
Linear programming steps 7 Determine optimal solution The optimal point is A, where the profit line is passing through the intersection of x+y=150 with the y axis at (0, 150). Optimal production plan: 0 Super models 150 Deluxe models Contribution: p=200*150=30000 2018/3/17 15 15
 Linear programming Please note the format of your answers. Two methods to find the best Let me see! solution—graphing or using simultaneous equations. Attention: You must draw the graph whatever. 16
Linear programming Please note the format of your answers. Two methods to find the best Let me see! solution—graphing or using simultaneous equations. Attention: You must draw the graph whatever. 16
 Slack and surplus v. When maximum availability of a resource is not used, slack occurs. v. When more than a minimum requirement is used, surplus occurs. v. Slack is associated with ≤ constraints and surplus with ≥ constraints. 2018/3/17 17 17
Slack and surplus v. When maximum availability of a resource is not used, slack occurs. v. When more than a minimum requirement is used, surplus occurs. v. Slack is associated with ≤ constraints and surplus with ≥ constraints. 2018/3/17 17 17
 Limiting factors and shadow prices v. The shadow price or dual price is the extra contribution or profit that may be created by having one additional unit of the limiting factor at the original cost. v. Key points: 1)The shadow price represents the maximum premium above the basic rate that an organization should be willing to pay for one extra unit of a resource. 2018/3/17 18 18
Limiting factors and shadow prices v. The shadow price or dual price is the extra contribution or profit that may be created by having one additional unit of the limiting factor at the original cost. v. Key points: 1)The shadow price represents the maximum premium above the basic rate that an organization should be willing to pay for one extra unit of a resource. 2018/3/17 18 18
 Limiting factors and shadow prices 2)If a constraint is not binding at the optimal solution, the shadow price is zero. 3)Shadow prices are only valid for a small range. 4)Shadow prices provide a measure of the sensitivity of the effect of a unit change in a constraint. Example: calculating shadow prices P 1217. 3 2018/3/17 19 19
Limiting factors and shadow prices 2)If a constraint is not binding at the optimal solution, the shadow price is zero. 3)Shadow prices are only valid for a small range. 4)Shadow prices provide a measure of the sensitivity of the effect of a unit change in a constraint. Example: calculating shadow prices P 1217. 3 2018/3/17 19 19
 End of Chapter 4 2018/3/17 20
End of Chapter 4 2018/3/17 20


