 Extraction Methods Static Headspace (HS) Dynamic Headspace Spray-and-Trap (ST) SPME Membrane Inlet Purge-and-Trap
Extraction Methods Static Headspace (HS) Dynamic Headspace Spray-and-Trap (ST) SPME Membrane Inlet Purge-and-Trap
 Purge-and-Trap Method Advantage : More sensitive than HS Drawback : 1. Foaming and slowness of the purging step 2. Large sample volume and long purging time (10~30 min)
Purge-and-Trap Method Advantage : More sensitive than HS Drawback : 1. Foaming and slowness of the purging step 2. Large sample volume and long purging time (10~30 min)
 Experimental Aim To construct an automated ST-GC system for on-line determination of dissolved VOCs in water.
Experimental Aim To construct an automated ST-GC system for on-line determination of dissolved VOCs in water.
 Micro-sorbent Trap Carboxen 1000 Carboxen 1003 1/16”
Micro-sorbent Trap Carboxen 1000 Carboxen 1003 1/16”
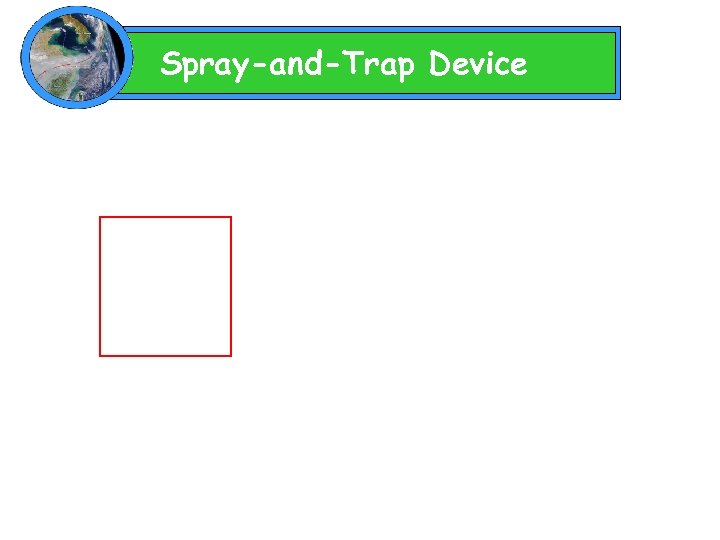 Spray-and-Trap Device
Spray-and-Trap Device
 Cleaning
Cleaning
 Sampling
Sampling
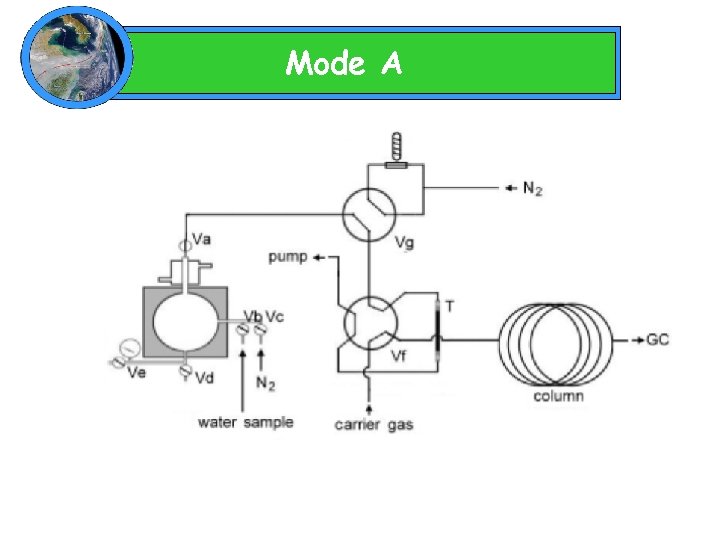 Mode A
Mode A
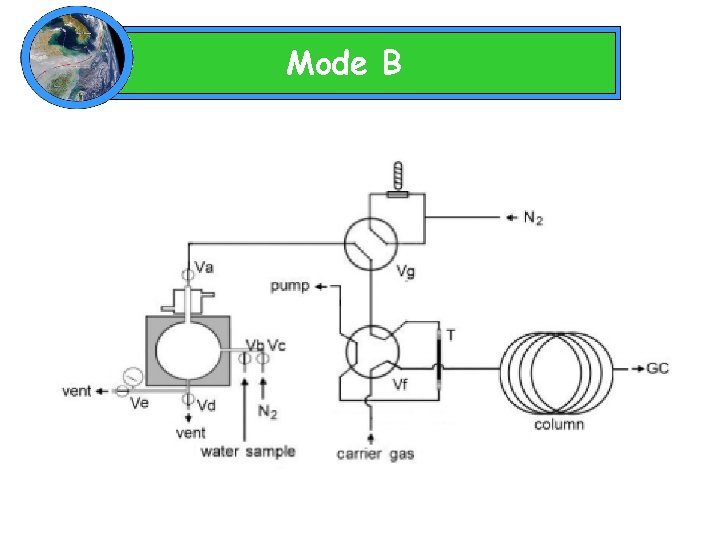 Mode B
Mode B
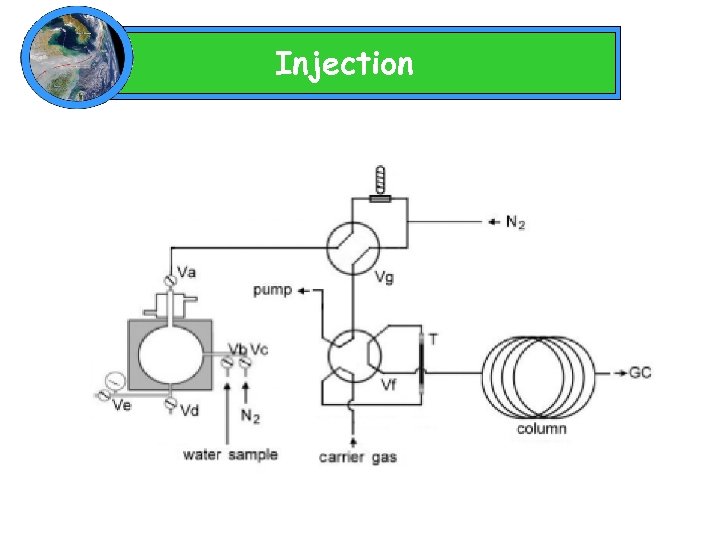 Injection
Injection
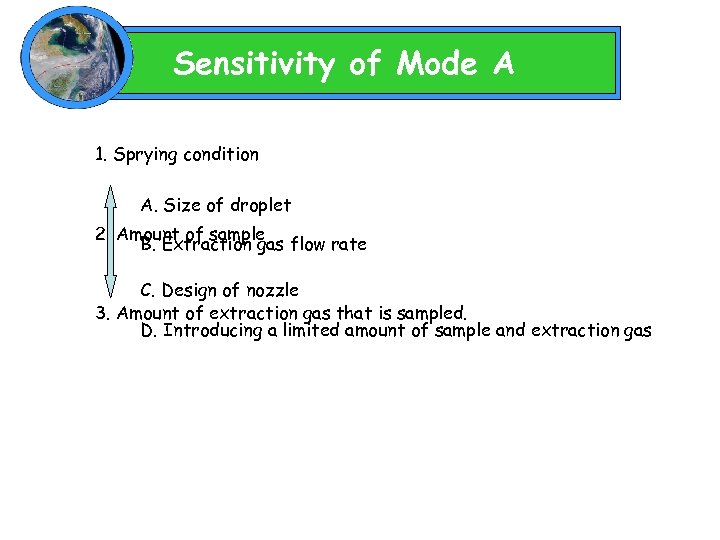 Sensitivity of Mode A 1. Sprying condition A. Size of droplet 2. Amount of sample B. Extraction gas flow rate C. Design of nozzle 3. Amount of extraction gas that is sampled. D. Introducing a limited amount of sample and extraction gas
Sensitivity of Mode A 1. Sprying condition A. Size of droplet 2. Amount of sample B. Extraction gas flow rate C. Design of nozzle 3. Amount of extraction gas that is sampled. D. Introducing a limited amount of sample and extraction gas
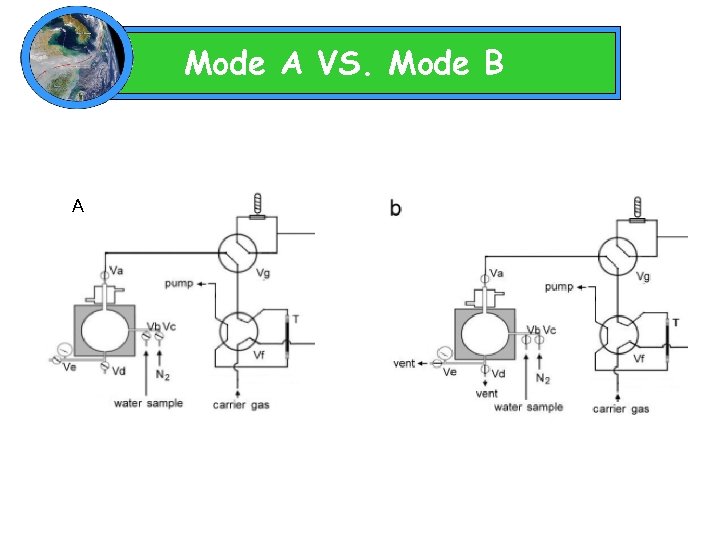 Mode A VS. Mode B A
Mode A VS. Mode B A
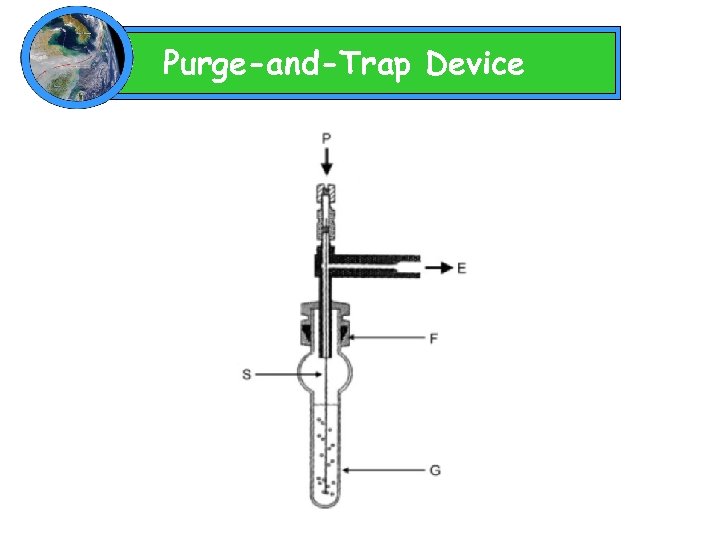 Purge-and-Trap Device
Purge-and-Trap Device
 Analytical conditions for ST and PT
Analytical conditions for ST and PT
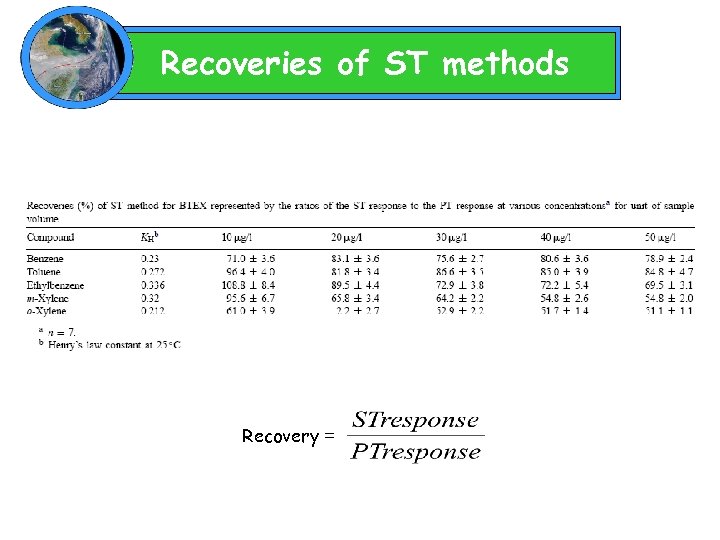 Recoveries of ST methods Recovery =
Recoveries of ST methods Recovery =
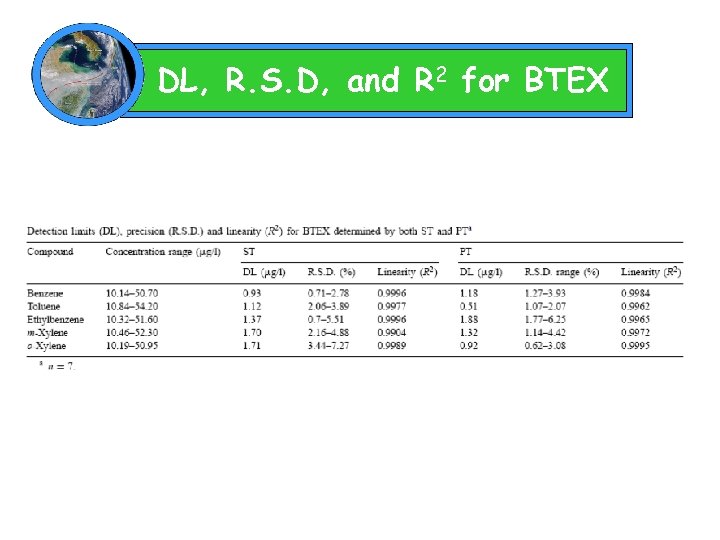 DL, R. S. D, and R 2 for BTEX
DL, R. S. D, and R 2 for BTEX
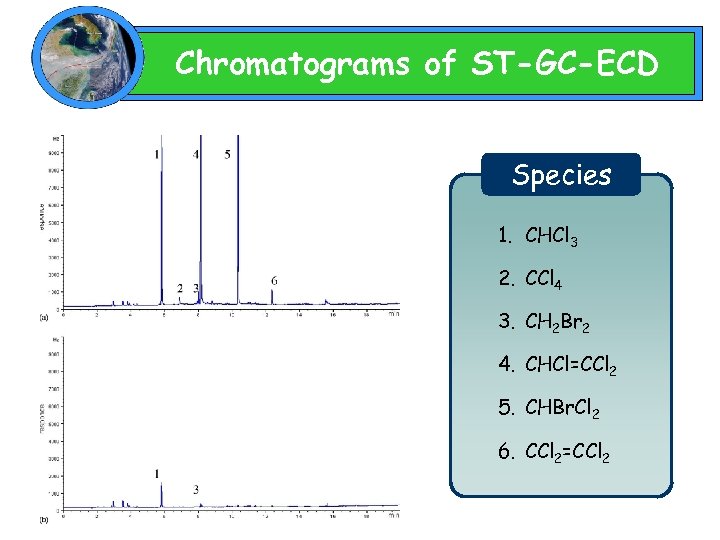 Chromatograms of ST-GC-ECD Species 1. CHCl 3 2. CCl 4 3. CH 2 Br 2 4. CHCl=CCl 2 5. CHBr. Cl 2 6. CCl 2=CCl 2
Chromatograms of ST-GC-ECD Species 1. CHCl 3 2. CCl 4 3. CH 2 Br 2 4. CHCl=CCl 2 5. CHBr. Cl 2 6. CCl 2=CCl 2
 Conclusion An automated spray-and-trap device was built in the laboratory. The studied ST method was validated in comparison with classic PT: recoveries precision, and linearity. The ST method shows a fast response to abrupt changes in sample quality, which makes it suitable for on-site monitoring of a water body.
Conclusion An automated spray-and-trap device was built in the laboratory. The studied ST method was validated in comparison with classic PT: recoveries precision, and linearity. The ST method shows a fast response to abrupt changes in sample quality, which makes it suitable for on-site monitoring of a water body.