bdf1e90cb010fbf61852500797f9042f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 99
 Extra Slides
Extra Slides
 Scientific Models and Inquiry • Models of atoms, periodic table, bonding, shape • Inquiry – Hot and cold packs – Well Wishes case study
Scientific Models and Inquiry • Models of atoms, periodic table, bonding, shape • Inquiry – Hot and cold packs – Well Wishes case study
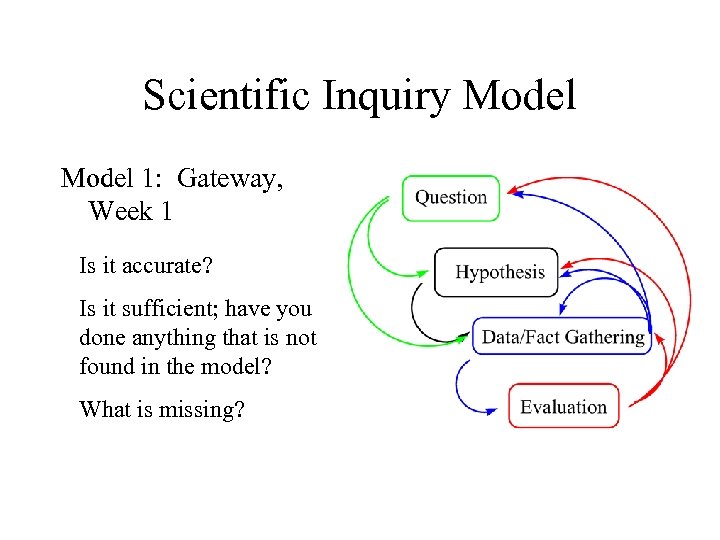 Scientific Inquiry Model 1: Gateway, Week 1 Is it accurate? Is it sufficient; have you done anything that is not found in the model? What is missing?
Scientific Inquiry Model 1: Gateway, Week 1 Is it accurate? Is it sufficient; have you done anything that is not found in the model? What is missing?
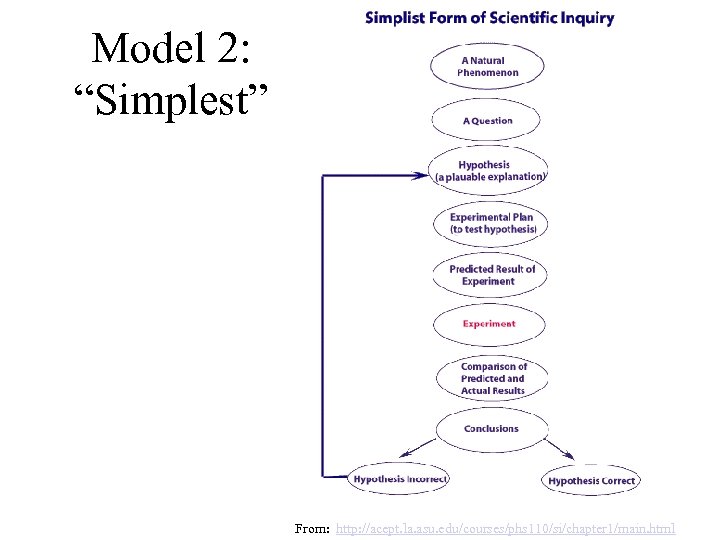 Model 2: “Simplest” From: http: //acept. la. asu. edu/courses/phs 110/si/chapter 1/main. html
Model 2: “Simplest” From: http: //acept. la. asu. edu/courses/phs 110/si/chapter 1/main. html
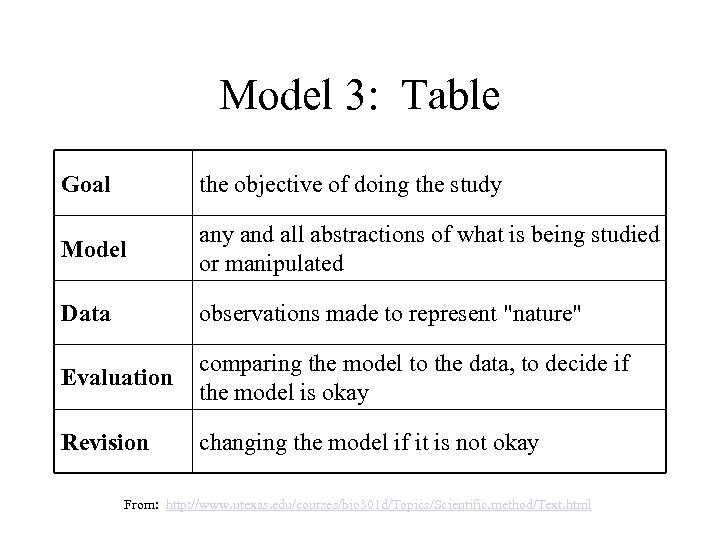 Model 3: Table Goal the objective of doing the study Model any and all abstractions of what is being studied or manipulated Data observations made to represent "nature" Evaluation comparing the model to the data, to decide if the model is okay Revision changing the model if it is not okay From: http: //www. utexas. edu/courses/bio 301 d/Topics/Scientific. method/Text. html
Model 3: Table Goal the objective of doing the study Model any and all abstractions of what is being studied or manipulated Data observations made to represent "nature" Evaluation comparing the model to the data, to decide if the model is okay Revision changing the model if it is not okay From: http: //www. utexas. edu/courses/bio 301 d/Topics/Scientific. method/Text. html
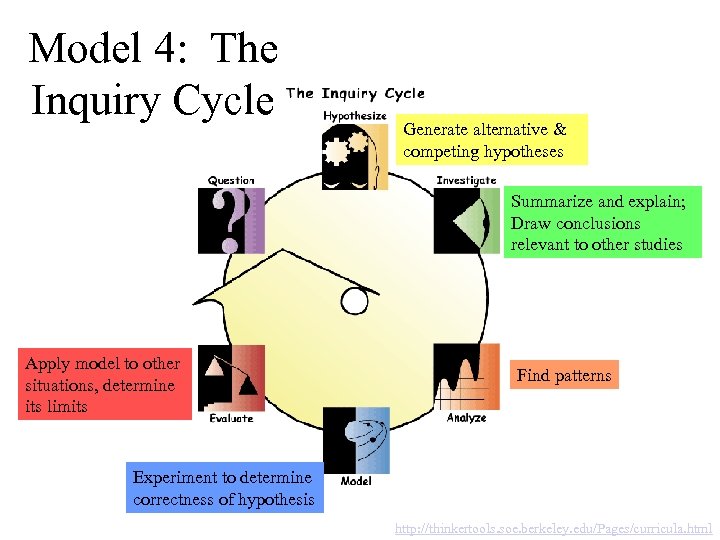 Model 4: The Inquiry Cycle Generate alternative & competing hypotheses Summarize and explain; Draw conclusions relevant to other studies Apply model to other situations, determine its limits Find patterns Experiment to determine correctness of hypothesis http: //thinkertools. soe. berkeley. edu/Pages/curricula. html
Model 4: The Inquiry Cycle Generate alternative & competing hypotheses Summarize and explain; Draw conclusions relevant to other studies Apply model to other situations, determine its limits Find patterns Experiment to determine correctness of hypothesis http: //thinkertools. soe. berkeley. edu/Pages/curricula. html
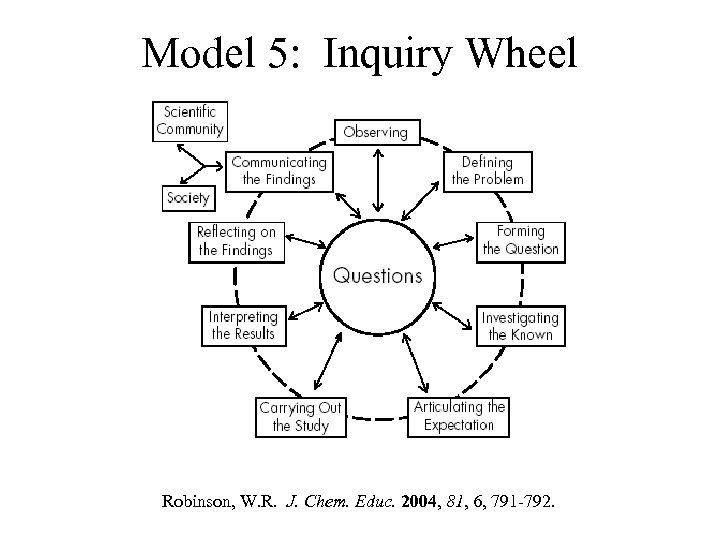 Model 5: Inquiry Wheel Robinson, W. R. J. Chem. Educ. 2004, 81, 6, 791 -792.
Model 5: Inquiry Wheel Robinson, W. R. J. Chem. Educ. 2004, 81, 6, 791 -792.
 Comparing models • • • What are similarities? Differences? Which model is most useful? Which is most comprehensive? Which do you like the best? What are the key “must haves”?
Comparing models • • • What are similarities? Differences? Which model is most useful? Which is most comprehensive? Which do you like the best? What are the key “must haves”?
 Communication of Inquiry Lab Report Research Paper Inquiry Models Introduction/background/questions/hypothesis Experimental/method/procedure Results/data Discussion/evaluation Conclusion/communication If you don’t report your work where other scientist can use it, have you completed the scientific process? ?
Communication of Inquiry Lab Report Research Paper Inquiry Models Introduction/background/questions/hypothesis Experimental/method/procedure Results/data Discussion/evaluation Conclusion/communication If you don’t report your work where other scientist can use it, have you completed the scientific process? ?
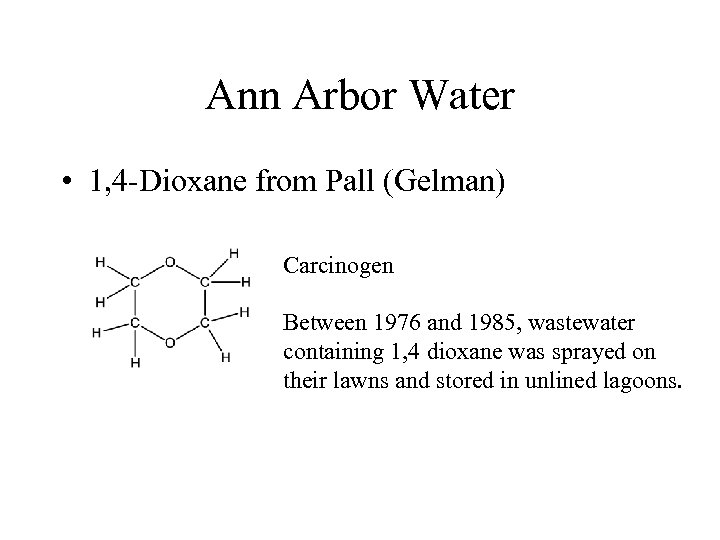 Ann Arbor Water • 1, 4 -Dioxane from Pall (Gelman) Carcinogen Between 1976 and 1985, wastewater containing 1, 4 dioxane was sprayed on their lawns and stored in unlined lagoons.
Ann Arbor Water • 1, 4 -Dioxane from Pall (Gelman) Carcinogen Between 1976 and 1985, wastewater containing 1, 4 dioxane was sprayed on their lawns and stored in unlined lagoons.
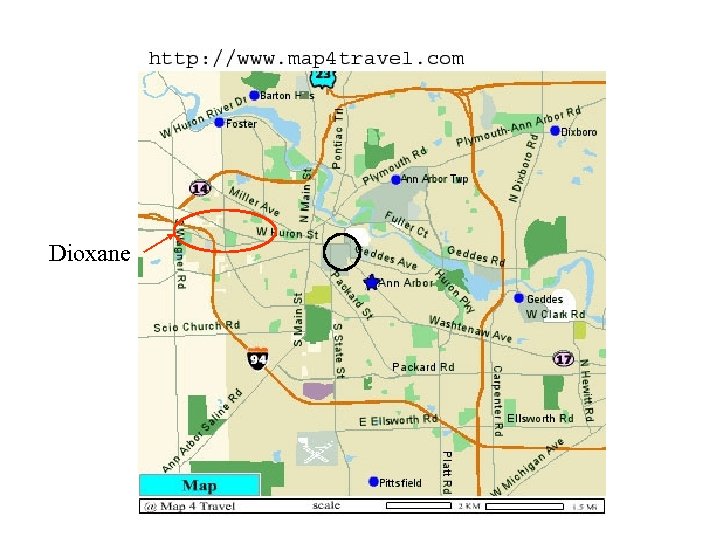 Dioxane
Dioxane
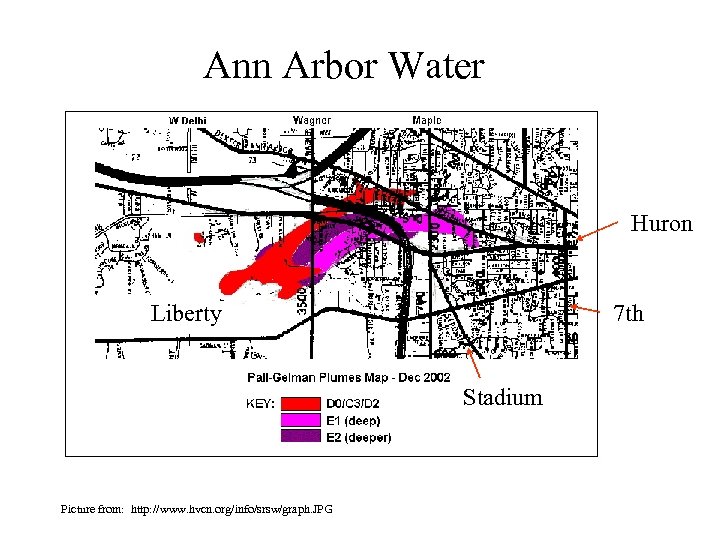 Ann Arbor Water Huron Liberty 7 th Stadium Picture from: http: //www. hvcn. org/info/srsw/graph. JPG
Ann Arbor Water Huron Liberty 7 th Stadium Picture from: http: //www. hvcn. org/info/srsw/graph. JPG
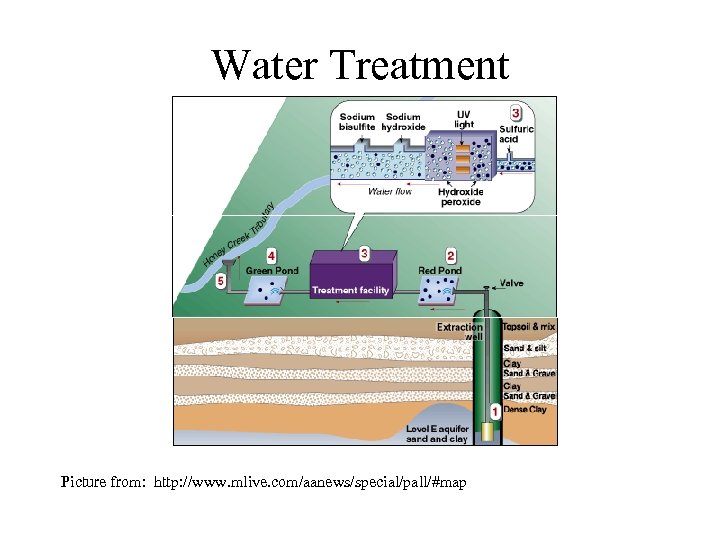 Water Treatment Picture from: http: //www. mlive. com/aanews/special/pall/#map
Water Treatment Picture from: http: //www. mlive. com/aanews/special/pall/#map
 Algae Blooms
Algae Blooms
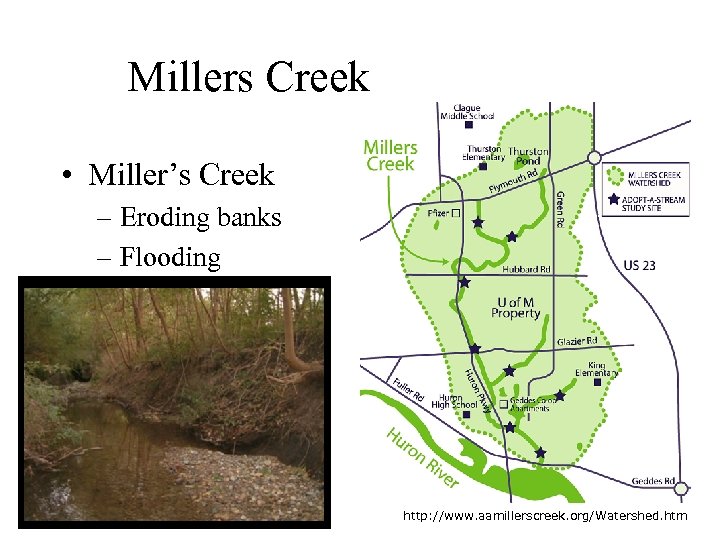 Millers Creek • Miller’s Creek – Eroding banks – Flooding http: //www. aamillerscreek. org/Watershed. htm
Millers Creek • Miller’s Creek – Eroding banks – Flooding http: //www. aamillerscreek. org/Watershed. htm
 A Finishing Thermochemistry: Heat and Phase Change • Why do we cool down when we sweat?
A Finishing Thermochemistry: Heat and Phase Change • Why do we cool down when we sweat?
 Silicon-Based Life Space slugs – Star Wars Is silicon-based life likely to be more stable or less stable than carbon-based life? J. Chem. Ed. 1988, 65, 414.
Silicon-Based Life Space slugs – Star Wars Is silicon-based life likely to be more stable or less stable than carbon-based life? J. Chem. Ed. 1988, 65, 414.
 Stability of Silicon vs Carbon • Consider decomposition of alkanes and silanes to the elements (no oxygen in space for that slug to worry about). • Consider combustion of silanes and alkanes (will those silicon-based life forms make it on earth? ).
Stability of Silicon vs Carbon • Consider decomposition of alkanes and silanes to the elements (no oxygen in space for that slug to worry about). • Consider combustion of silanes and alkanes (will those silicon-based life forms make it on earth? ).
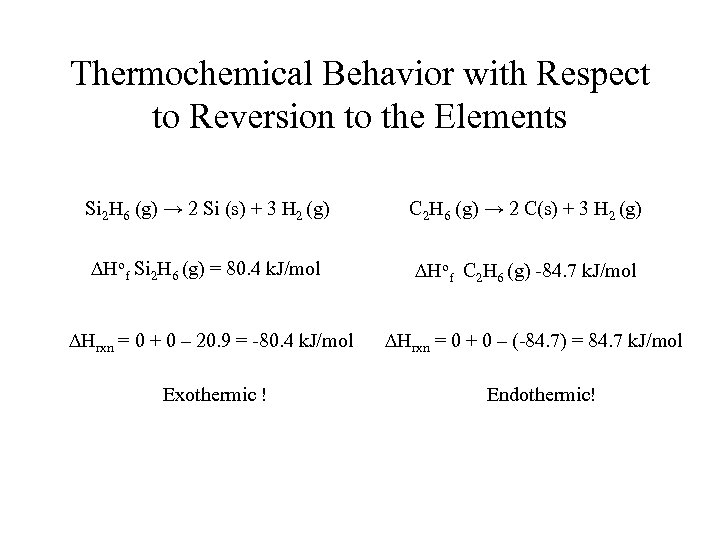 Thermochemical Behavior with Respect to Reversion to the Elements Si 2 H 6 (g) → 2 Si (s) + 3 H 2 (g) C 2 H 6 (g) → 2 C(s) + 3 H 2 (g) DHof Si 2 H 6 (g) = 80. 4 k. J/mol DHof C 2 H 6 (g) -84. 7 k. J/mol DHrxn = 0 + 0 – 20. 9 = -80. 4 k. J/mol Exothermic ! DHrxn = 0 + 0 – (-84. 7) = 84. 7 k. J/mol Endothermic!
Thermochemical Behavior with Respect to Reversion to the Elements Si 2 H 6 (g) → 2 Si (s) + 3 H 2 (g) C 2 H 6 (g) → 2 C(s) + 3 H 2 (g) DHof Si 2 H 6 (g) = 80. 4 k. J/mol DHof C 2 H 6 (g) -84. 7 k. J/mol DHrxn = 0 + 0 – 20. 9 = -80. 4 k. J/mol Exothermic ! DHrxn = 0 + 0 – (-84. 7) = 84. 7 k. J/mol Endothermic!
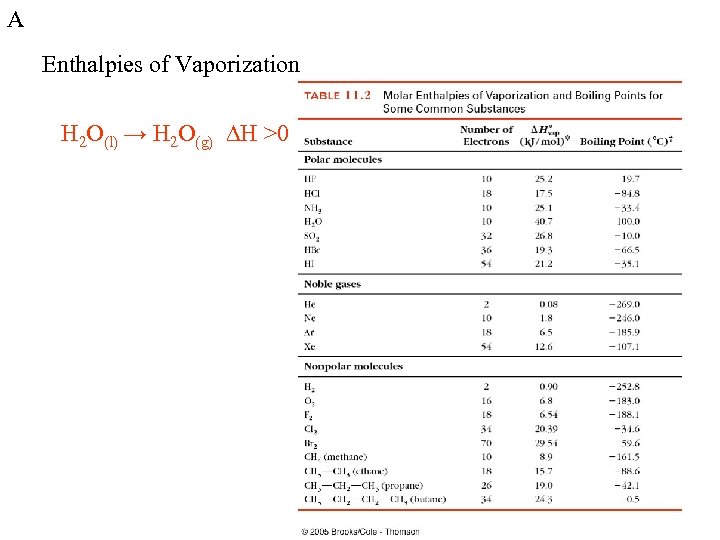 A Enthalpies of Vaporization H 2 O(l) → H 2 O(g) DH >0
A Enthalpies of Vaporization H 2 O(l) → H 2 O(g) DH >0
 Thermochemical Behavior with Respect to Combustion 7/2 O 2 (g) + Si 2 H 6 (g) → 2 Si. O 2 (s) + 3 H 2 O (g) DHf = Si 2 H 6 (g) = -80. 4 k. J/mol Si. O 2 (s) = -911 k. J/mol H 2 O(g) = -242 k. J/mol CO 2 (g) = -394 k. J/mol C 2 H 6 (g) = -85 k. J/mol DHrxn = [2(-911) + 3(-242)] – [1(-80. 4)] = -2468 k. J Exothermic ! 7/2 O 2 (g) + C 2 H 6 (g) → 2 CO 2 (s) + 3 H 2 O (g) DHrxn = [2(-394) + 3(-242)] –[1 (-85)] = -1429 k. J Exothermic!
Thermochemical Behavior with Respect to Combustion 7/2 O 2 (g) + Si 2 H 6 (g) → 2 Si. O 2 (s) + 3 H 2 O (g) DHf = Si 2 H 6 (g) = -80. 4 k. J/mol Si. O 2 (s) = -911 k. J/mol H 2 O(g) = -242 k. J/mol CO 2 (g) = -394 k. J/mol C 2 H 6 (g) = -85 k. J/mol DHrxn = [2(-911) + 3(-242)] – [1(-80. 4)] = -2468 k. J Exothermic ! 7/2 O 2 (g) + C 2 H 6 (g) → 2 CO 2 (s) + 3 H 2 O (g) DHrxn = [2(-394) + 3(-242)] –[1 (-85)] = -1429 k. J Exothermic!
 Silicon-Based Life Space slugs – Star Wars Is silicon-based life likely to be more stable or less stable than carbon-based life? Thermochemical considerations indicate that silicon-based life would tend to decompose exothermically! Our space slug unlikely to survive.
Silicon-Based Life Space slugs – Star Wars Is silicon-based life likely to be more stable or less stable than carbon-based life? Thermochemical considerations indicate that silicon-based life would tend to decompose exothermically! Our space slug unlikely to survive.

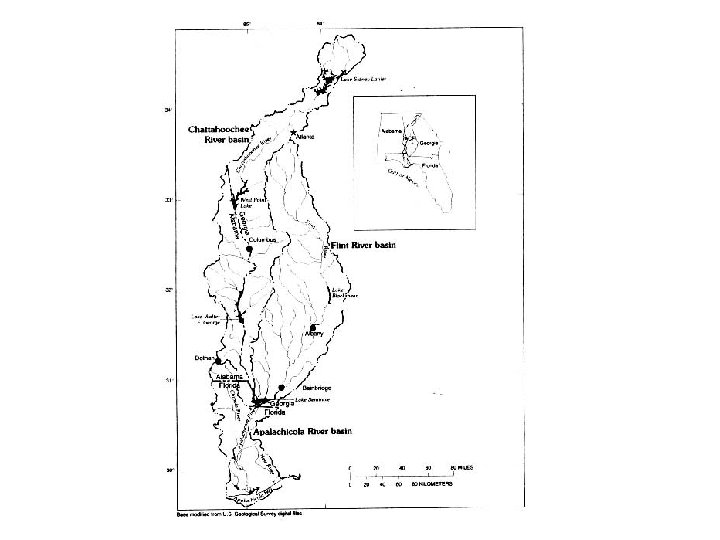
 Water Rights • Tri-state water war: between Georgia, Alabama and Florida. • The City of Atlanta: permit from Corps of Engineers to create reservoirs on the Chattahoochee, Flint, and Coosa Rivers • Retain an additional 529 million gallons of water per day • Stored in Lake Sidney Lanier, Atlanta's major source of drinking water. • Atlanta's long-term plan included an increase in withdrawals of 50% from the Chattahoochee and Flint by the year 2010.
Water Rights • Tri-state water war: between Georgia, Alabama and Florida. • The City of Atlanta: permit from Corps of Engineers to create reservoirs on the Chattahoochee, Flint, and Coosa Rivers • Retain an additional 529 million gallons of water per day • Stored in Lake Sidney Lanier, Atlanta's major source of drinking water. • Atlanta's long-term plan included an increase in withdrawals of 50% from the Chattahoochee and Flint by the year 2010.
 Problems • A 200. g sample of Al is heated in a flame and then immersed in 500. m. L of water in an insulated container. The initial temperature of the water was 22. 0 o. C. After the Al and water reach thermal equilibrium, the temperature of both was 33. 6 o. C. What was the temperature of the Al just before it was plunged into the water. • (Al 0. 902 J/go. C)
Problems • A 200. g sample of Al is heated in a flame and then immersed in 500. m. L of water in an insulated container. The initial temperature of the water was 22. 0 o. C. After the Al and water reach thermal equilibrium, the temperature of both was 33. 6 o. C. What was the temperature of the Al just before it was plunged into the water. • (Al 0. 902 J/go. C)
 Practice with Units The MCL for arsenic is 0. 01 mg/L. What is that in ppm, ppb, M (moles/L)?
Practice with Units The MCL for arsenic is 0. 01 mg/L. What is that in ppm, ppb, M (moles/L)?
 Problem 17) Specifications for lactated Ringer’s solution, used for IV injections, are as follows: For each 100 m. L of solution: 285 -315 mg Na+ 14. 1 -17. 3 mg K+ 4. 9 -6. 0 mg Ca+2 368 -408 mg Cl 231 -261 mg C 3 H 5 O 4 Specify the amounts of Na. Cl, KCl, Ca. Cl 2 • 2 H 2 O, and Na. C 3 H 5 O 3 needed to prepare 100 m. L of lactated Ringer’s solution.
Problem 17) Specifications for lactated Ringer’s solution, used for IV injections, are as follows: For each 100 m. L of solution: 285 -315 mg Na+ 14. 1 -17. 3 mg K+ 4. 9 -6. 0 mg Ca+2 368 -408 mg Cl 231 -261 mg C 3 H 5 O 4 Specify the amounts of Na. Cl, KCl, Ca. Cl 2 • 2 H 2 O, and Na. C 3 H 5 O 3 needed to prepare 100 m. L of lactated Ringer’s solution.
 The Polyprotics (Multiples) http: //www. okinawa. usmc. mil/Public%20 Affairs%20 Info/Archive%20 News%20 Pages/2003/030131 -twins. html http: //www. emory. edu/EMORY_MAGAZINE/spring 97/triplets. htmlhttp: //www. emory. edu/EMORY_MAGAZ INE/spring 97/triplets. html
The Polyprotics (Multiples) http: //www. okinawa. usmc. mil/Public%20 Affairs%20 Info/Archive%20 News%20 Pages/2003/030131 -twins. html http: //www. emory. edu/EMORY_MAGAZINE/spring 97/triplets. htmlhttp: //www. emory. edu/EMORY_MAGAZ INE/spring 97/triplets. html
 H 3 PO 4 • How many acidic protons? • How many ions in solution? • Calculate the concentrations of all of the ions in a 0. 1 M solution of phosphoric acid. – How many ICE tables will it take?
H 3 PO 4 • How many acidic protons? • How many ions in solution? • Calculate the concentrations of all of the ions in a 0. 1 M solution of phosphoric acid. – How many ICE tables will it take?
 Triprotic Acid • Phosphoric acid has three acidic protons: • Ka 1 = 6. 9 x 10 -3 • Ka 2 = 6. 2 x 10 -8 • Ka 3 = 4. 8 x 10 -13 • What trend do you observe in the Ka's and what is the chemical explanation for that trend?
Triprotic Acid • Phosphoric acid has three acidic protons: • Ka 1 = 6. 9 x 10 -3 • Ka 2 = 6. 2 x 10 -8 • Ka 3 = 4. 8 x 10 -13 • What trend do you observe in the Ka's and what is the chemical explanation for that trend?
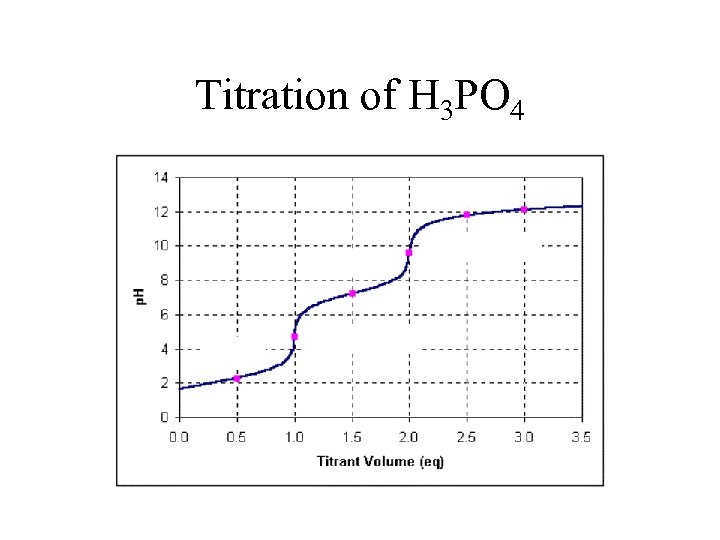 Titration of H 3 PO 4
Titration of H 3 PO 4
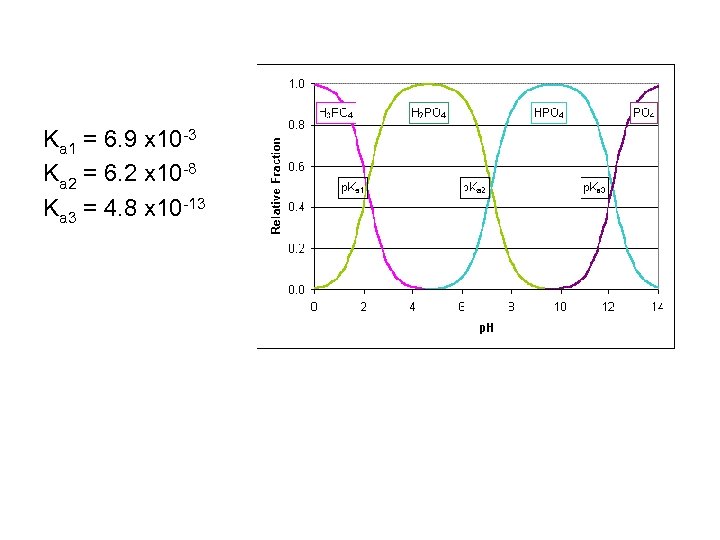 Ka 1 = 6. 9 x 10 -3 Ka 2 = 6. 2 x 10 -8 Ka 3 = 4. 8 x 10 -13
Ka 1 = 6. 9 x 10 -3 Ka 2 = 6. 2 x 10 -8 Ka 3 = 4. 8 x 10 -13
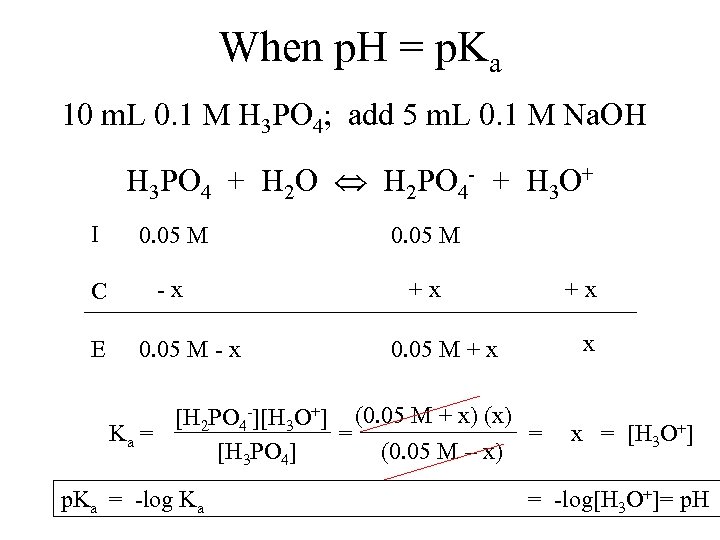 When p. H = p. Ka 10 m. L 0. 1 M H 3 PO 4; add 5 m. L 0. 1 M Na. OH H 3 PO 4 + H 2 O H 2 PO 4 - + H 3 O+ I 0. 05 M C - x + x E 0. 05 M - x 0. 05 M + x [H 2 PO 4 -][H 3 O+] (0. 05 M + x) (x) Ka = = = [H 3 PO 4] (0. 05 M – x) + x x x = [H 3 O+] p. Ka = -log Ka = -log[H 3 O+]= p. H
When p. H = p. Ka 10 m. L 0. 1 M H 3 PO 4; add 5 m. L 0. 1 M Na. OH H 3 PO 4 + H 2 O H 2 PO 4 - + H 3 O+ I 0. 05 M C - x + x E 0. 05 M - x 0. 05 M + x [H 2 PO 4 -][H 3 O+] (0. 05 M + x) (x) Ka = = = [H 3 PO 4] (0. 05 M – x) + x x x = [H 3 O+] p. Ka = -log Ka = -log[H 3 O+]= p. H
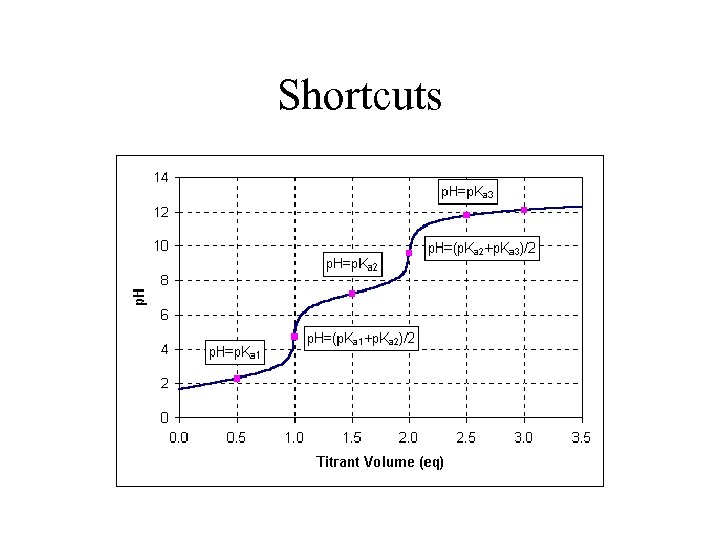 Shortcuts
Shortcuts
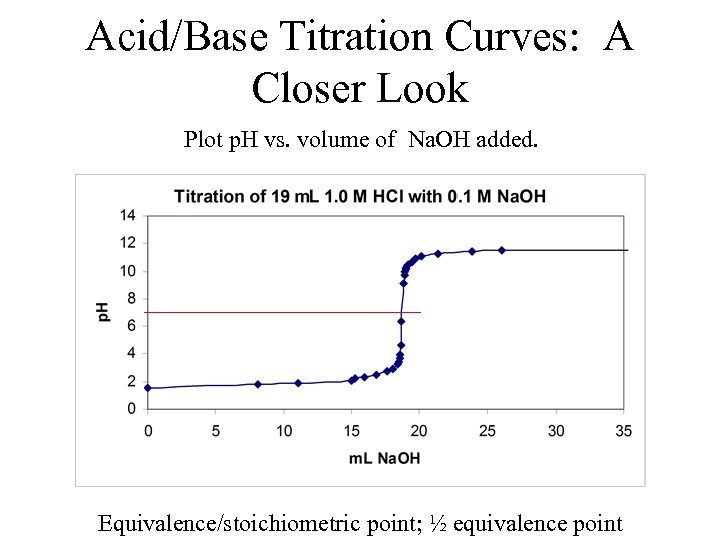 Acid/Base Titration Curves: A Closer Look Plot p. H vs. volume of Na. OH added. Equivalence/stoichiometric point; ½ equivalence point
Acid/Base Titration Curves: A Closer Look Plot p. H vs. volume of Na. OH added. Equivalence/stoichiometric point; ½ equivalence point
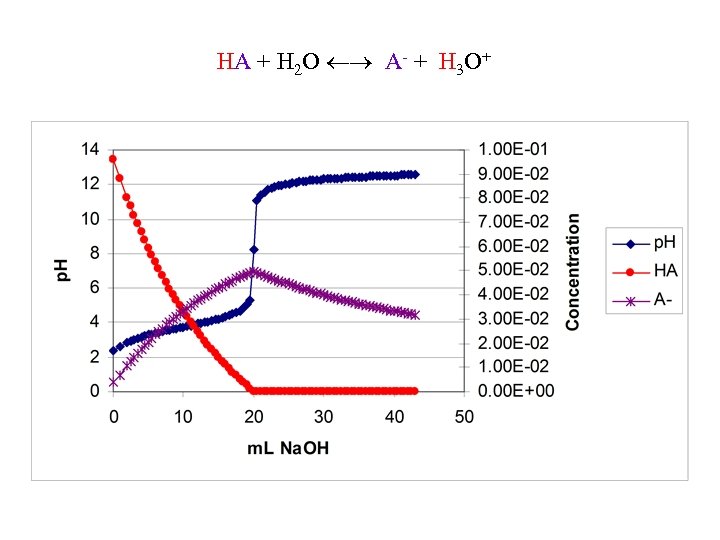 HA + H 2 O A- + H 3 O+
HA + H 2 O A- + H 3 O+
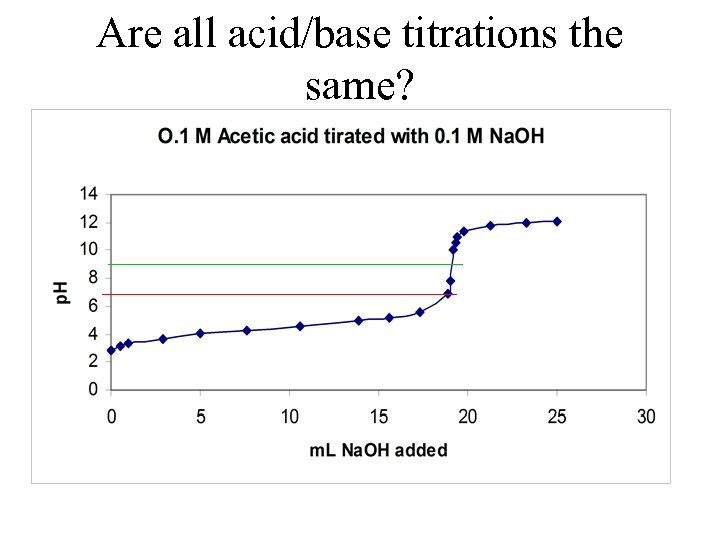 Are all acid/base titrations the same?
Are all acid/base titrations the same?
 Titrating Base with Acid A weak base (NH 3) + HCl p. H at Starting line: What governs the reaction until the equivalence point is reached? What’s going on at the stoichiometric point? What happens after the stoichiometric point?
Titrating Base with Acid A weak base (NH 3) + HCl p. H at Starting line: What governs the reaction until the equivalence point is reached? What’s going on at the stoichiometric point? What happens after the stoichiometric point?
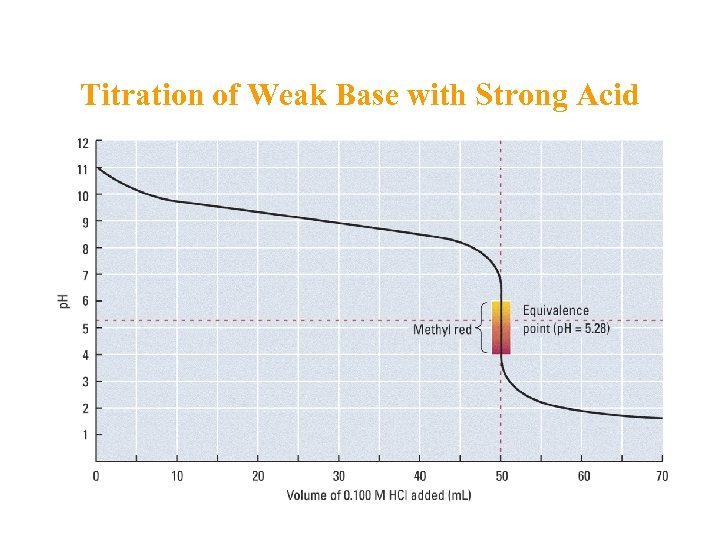 Titration of Weak Base with Strong Acid
Titration of Weak Base with Strong Acid
 Buffers http: //www. fws. gov/r 5 crc/Habitat/Riparianbuffers. html
Buffers http: //www. fws. gov/r 5 crc/Habitat/Riparianbuffers. html
 Acidosis – Acidosis is caused by an accumulation of acid or a significant loss of bicarbonate – Kidney and lungs control your body’s p. H • Lungs can’t remove CO 2 (an acid) • Kidney not able to regulate bicarbonate; ingestion of too much acid • Generation of lactic acid upon breakdown of glucose….
Acidosis – Acidosis is caused by an accumulation of acid or a significant loss of bicarbonate – Kidney and lungs control your body’s p. H • Lungs can’t remove CO 2 (an acid) • Kidney not able to regulate bicarbonate; ingestion of too much acid • Generation of lactic acid upon breakdown of glucose….
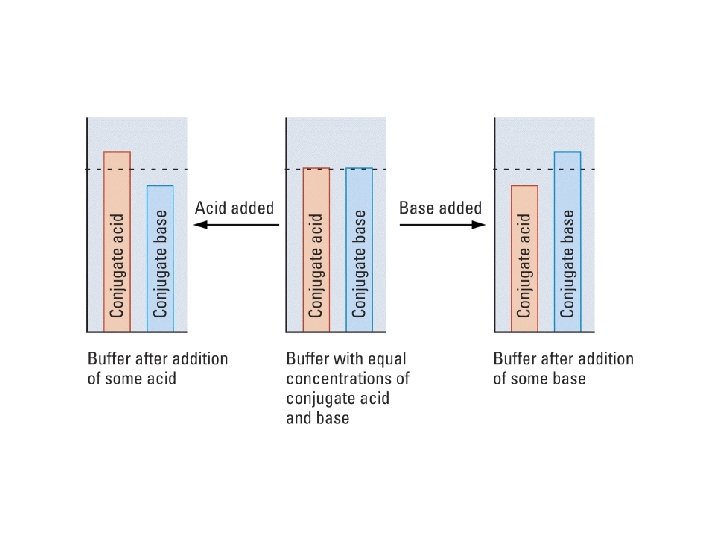
 Buffers • Acid/base equilibria at work! • If we need an equilibrium, can strong acids/bases work as buffers? • Seeing a buffer in action…human buffer simulation HA + H 2 O H 3 O+ + A- When more acid is added to this solution H 3 O+ + A- → H 2 O + HA When more base is added, OH- + HA → H 2 O + A-
Buffers • Acid/base equilibria at work! • If we need an equilibrium, can strong acids/bases work as buffers? • Seeing a buffer in action…human buffer simulation HA + H 2 O H 3 O+ + A- When more acid is added to this solution H 3 O+ + A- → H 2 O + HA When more base is added, OH- + HA → H 2 O + A-
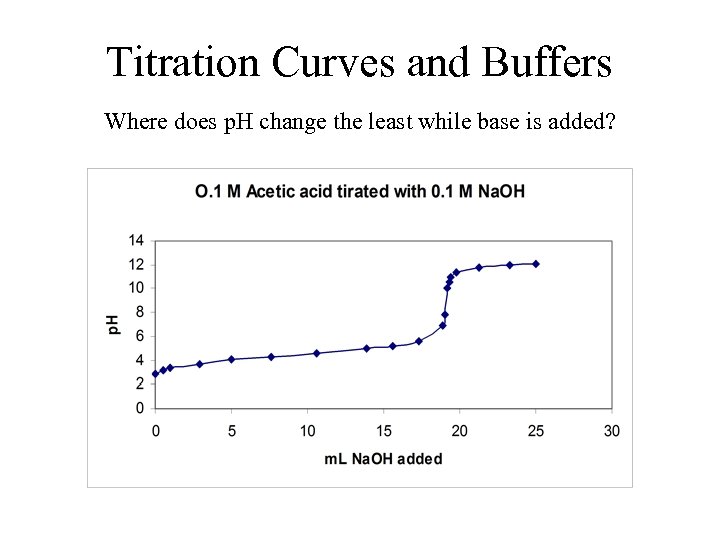 Titration Curves and Buffers Where does p. H change the least while base is added?
Titration Curves and Buffers Where does p. H change the least while base is added?
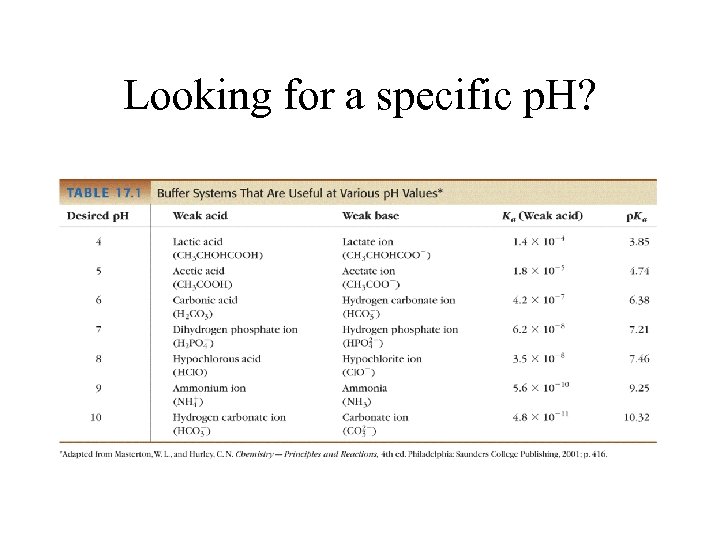 Looking for a specific p. H?
Looking for a specific p. H?
![Henderson-Hasselbalch Rules Buffers HA + H 2 O H 3 O+ + A- [A-][H Henderson-Hasselbalch Rules Buffers HA + H 2 O H 3 O+ + A- [A-][H](https://present5.com/presentation/bdf1e90cb010fbf61852500797f9042f/image-48.jpg) Henderson-Hasselbalch Rules Buffers HA + H 2 O H 3 O+ + A- [A-][H 3 O+] Ka = [HA] [A-][H 3 O+] log. Ka = log [HA] = log[H 3 O+] + log ([A-]) [HA] -log. Ka = - log[H 3 O+] - log ([A-]) [HA] p. Ka = p. H - log ([A-]) [HA] p. H = p. Ka + log ([A-]) [HA]
Henderson-Hasselbalch Rules Buffers HA + H 2 O H 3 O+ + A- [A-][H 3 O+] Ka = [HA] [A-][H 3 O+] log. Ka = log [HA] = log[H 3 O+] + log ([A-]) [HA] -log. Ka = - log[H 3 O+] - log ([A-]) [HA] p. Ka = p. H - log ([A-]) [HA] p. H = p. Ka + log ([A-]) [HA]
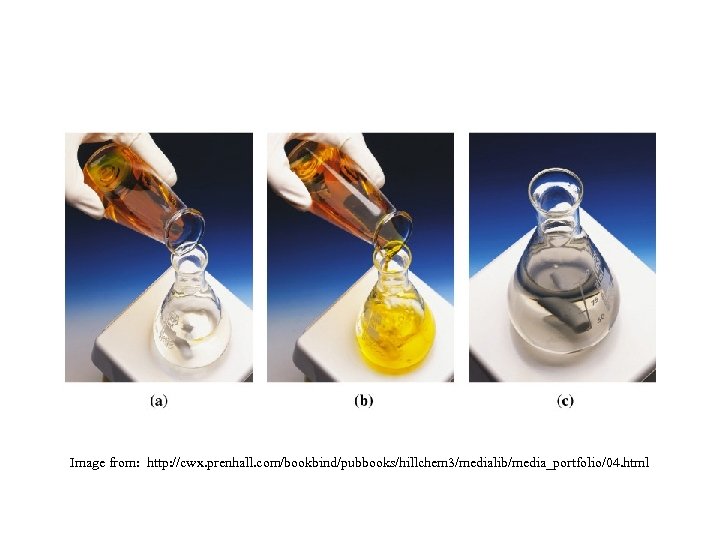 Image from: http: //cwx. prenhall. com/bookbind/pubbooks/hillchem 3/medialib/media_portfolio/04. html
Image from: http: //cwx. prenhall. com/bookbind/pubbooks/hillchem 3/medialib/media_portfolio/04. html
 Question 4 You are given three different aqueous solutions and told that they each contain either Na. OH, Na 2 CO 3, or Na. HCO 3. You do some experiments and gather the following data: Sample A: Phenolphthalein is colorless in the solution. Methyl orange is orange. Sample B: The sample was titrated with HCl until the pink color of phenolphthalein disappeared, then methyl orange was added to the solution. The solution became a pink color. Sample C: Two equal volumes of the sample were titrated with standardized HCl. Using phenolphthalein as the indicator, it took 15. 00 m. L of acid to reach the equivalence point; using methyl orange as the indicator required 30. 00 m. L of HCl to achieve neutralization. [Methyl orange changes colors from p. H 3. 01 (red) to p. H 4. 4 (orange) Phenolphthalein changes color from p. H 8 (clear) to p. H 9 (pink)]
Question 4 You are given three different aqueous solutions and told that they each contain either Na. OH, Na 2 CO 3, or Na. HCO 3. You do some experiments and gather the following data: Sample A: Phenolphthalein is colorless in the solution. Methyl orange is orange. Sample B: The sample was titrated with HCl until the pink color of phenolphthalein disappeared, then methyl orange was added to the solution. The solution became a pink color. Sample C: Two equal volumes of the sample were titrated with standardized HCl. Using phenolphthalein as the indicator, it took 15. 00 m. L of acid to reach the equivalence point; using methyl orange as the indicator required 30. 00 m. L of HCl to achieve neutralization. [Methyl orange changes colors from p. H 3. 01 (red) to p. H 4. 4 (orange) Phenolphthalein changes color from p. H 8 (clear) to p. H 9 (pink)]
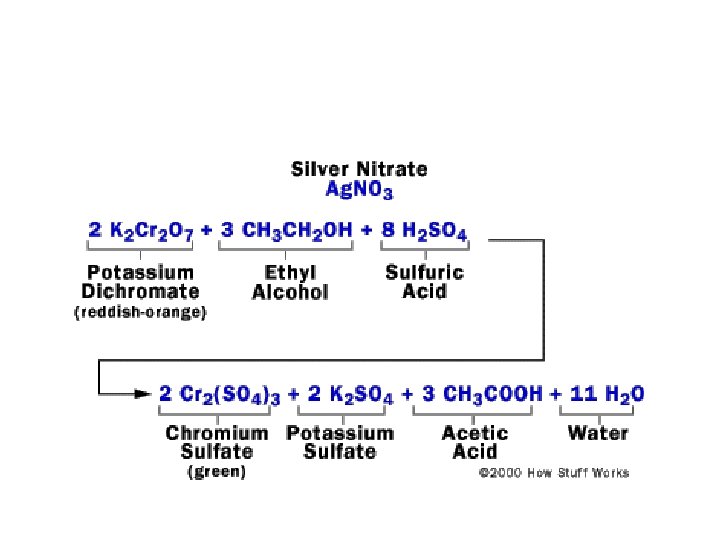
 (a) Orange K 2 Cr 2 O 7(aq) is about to be added to colorless ethanol (CH 3 CH 2 OH(aq)) that has been acidified with H 2 SO 4. (b) The ethanol solution becomes colored due to the Cr 2 O 7 -2(aq). (c) After the reaction, the solution becomes a pale violet color, signifying that the Cr 2 O 7 -2(aq) is gone and that Cr+3 is now present (along with CH 3 COOH)
(a) Orange K 2 Cr 2 O 7(aq) is about to be added to colorless ethanol (CH 3 CH 2 OH(aq)) that has been acidified with H 2 SO 4. (b) The ethanol solution becomes colored due to the Cr 2 O 7 -2(aq). (c) After the reaction, the solution becomes a pale violet color, signifying that the Cr 2 O 7 -2(aq) is gone and that Cr+3 is now present (along with CH 3 COOH)
 Fuel Cells • H 2 + ½ O 2 H 2 O • http: //science. howstuffworks. com/fuel-cell 1. htm • A fuel cell converts the chemicals hydrogen and oxygen into water, and in the process it produces electricity. • Combustion engines like the turbine and the gasoline engine burn fuels and use the pressure created by the expansion of the gases to do mechanical work. Batteries converted chemical energy back into electrical energy when needed. Fuel cells should do both tasks more efficiently.
Fuel Cells • H 2 + ½ O 2 H 2 O • http: //science. howstuffworks. com/fuel-cell 1. htm • A fuel cell converts the chemicals hydrogen and oxygen into water, and in the process it produces electricity. • Combustion engines like the turbine and the gasoline engine burn fuels and use the pressure created by the expansion of the gases to do mechanical work. Batteries converted chemical energy back into electrical energy when needed. Fuel cells should do both tasks more efficiently.
 • the pressurized hydrogen gas (H 2) entering the fuel cell on the anode side. This gas is forced through the catalyst by the pressure. When an H 2 molecule comes in contact with the platinum on the catalyst, it splits into two H+ ions and two electrons (e-). The electrons are conducted through the anode, where they make their way through the external circuit (doing useful work such as turning a motor) and return to the cathode side of the fuel cell. • Meanwhile, on the cathode side of the fuel cell, oxygen gas (O 2) is being forced through
• the pressurized hydrogen gas (H 2) entering the fuel cell on the anode side. This gas is forced through the catalyst by the pressure. When an H 2 molecule comes in contact with the platinum on the catalyst, it splits into two H+ ions and two electrons (e-). The electrons are conducted through the anode, where they make their way through the external circuit (doing useful work such as turning a motor) and return to the cathode side of the fuel cell. • Meanwhile, on the cathode side of the fuel cell, oxygen gas (O 2) is being forced through
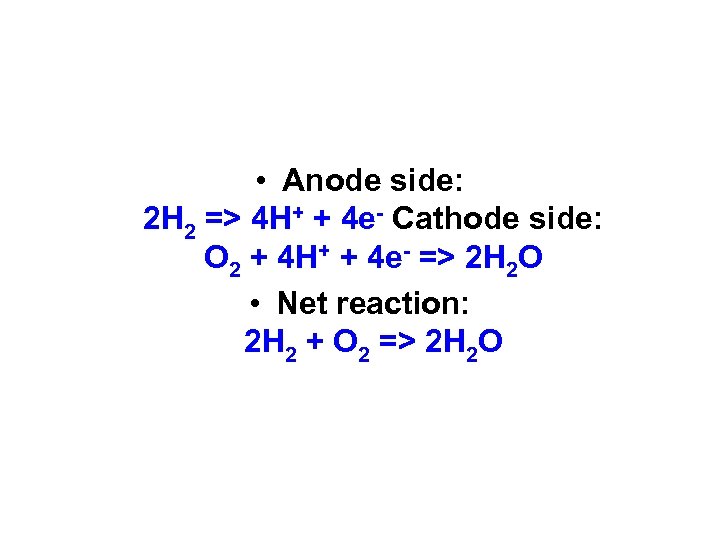 • Anode side: 2 H 2 => 4 H+ + 4 e- Cathode side: O 2 + 4 H+ + 4 e- => 2 H 2 O • Net reaction: 2 H 2 + O 2 => 2 H 2 O
• Anode side: 2 H 2 => 4 H+ + 4 e- Cathode side: O 2 + 4 H+ + 4 e- => 2 H 2 O • Net reaction: 2 H 2 + O 2 => 2 H 2 O
 • The electrolyte is the proton exchange membrane. This specially treated material, which looks something like ordinary kitchen plastic wrap, only conducts positively charged ions. The membrane blocks electrons. • The catalyst is a special material that facilitates the reaction of oxygen and hydrogen. It is usually made of platinum powder very thinly coated onto carbon paper or cloth. The catalyst is rough and porous so that the maximum surface area of the platinum can be exposed to the hydrogen or
• The electrolyte is the proton exchange membrane. This specially treated material, which looks something like ordinary kitchen plastic wrap, only conducts positively charged ions. The membrane blocks electrons. • The catalyst is a special material that facilitates the reaction of oxygen and hydrogen. It is usually made of platinum powder very thinly coated onto carbon paper or cloth. The catalyst is rough and porous so that the maximum surface area of the platinum can be exposed to the hydrogen or
 Problems • H 2 source. Hydrogen is difficult to store and distribute, so it would be much more convenient if fuel cells could use fuels that are more readily available. This problem is addressed by a device called a reformer. A reformer turns hydrocarbon or alcohol fuels into hydrogen, which is then fed to the fuel cell. Unfortunately, reformers are not perfect. They generate heat and produce other gases besides hydrogen. They use various devices to try to clean up the hydrogen, but even so, the hydrogen that comes out of them is not
Problems • H 2 source. Hydrogen is difficult to store and distribute, so it would be much more convenient if fuel cells could use fuels that are more readily available. This problem is addressed by a device called a reformer. A reformer turns hydrocarbon or alcohol fuels into hydrogen, which is then fed to the fuel cell. Unfortunately, reformers are not perfect. They generate heat and produce other gases besides hydrogen. They use various devices to try to clean up the hydrogen, but even so, the hydrogen that comes out of them is not
 • How stuff works compares efficiencies • Biodiesel
• How stuff works compares efficiencies • Biodiesel
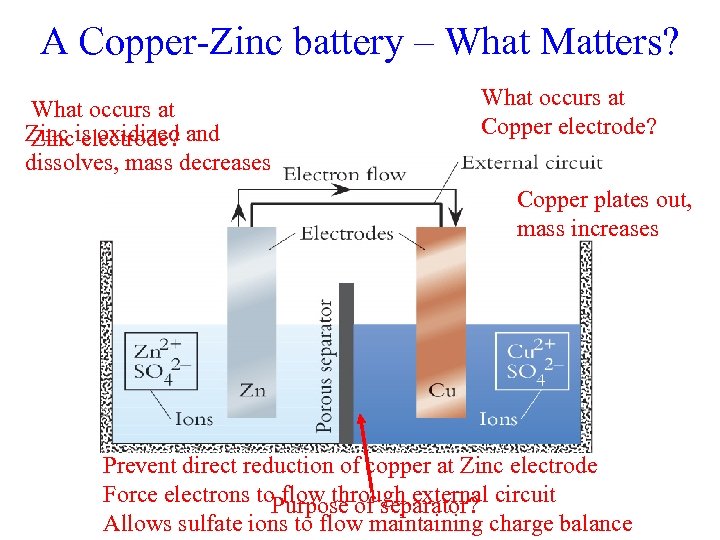 A Copper-Zinc battery – What Matters? What occurs at Zinc is oxidized and Zinc electrode? dissolves, mass decreases What occurs at Copper electrode? Copper plates out, mass increases Prevent direct reduction of copper at Zinc electrode Force electrons to flow through external circuit Purpose of separator? Allows sulfate ions to flow maintaining charge balance
A Copper-Zinc battery – What Matters? What occurs at Zinc is oxidized and Zinc electrode? dissolves, mass decreases What occurs at Copper electrode? Copper plates out, mass increases Prevent direct reduction of copper at Zinc electrode Force electrons to flow through external circuit Purpose of separator? Allows sulfate ions to flow maintaining charge balance
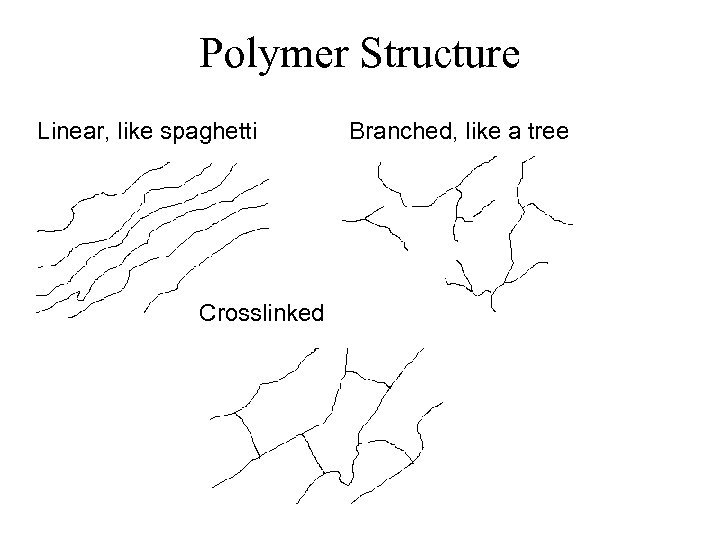 Polymer Structure Linear, like spaghetti Crosslinked Branched, like a tree
Polymer Structure Linear, like spaghetti Crosslinked Branched, like a tree
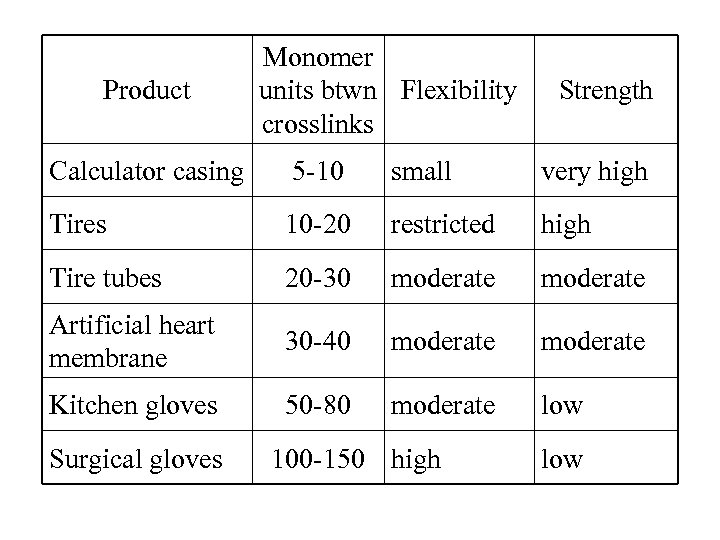 Product Monomer units btwn Flexibility crosslinks Strength Calculator casing 5 -10 small very high Tires 10 -20 restricted high Tire tubes 20 -30 moderate Artificial heart membrane 30 -40 moderate Kitchen gloves 50 -80 moderate low Surgical gloves 100 -150 high low
Product Monomer units btwn Flexibility crosslinks Strength Calculator casing 5 -10 small very high Tires 10 -20 restricted high Tire tubes 20 -30 moderate Artificial heart membrane 30 -40 moderate Kitchen gloves 50 -80 moderate low Surgical gloves 100 -150 high low
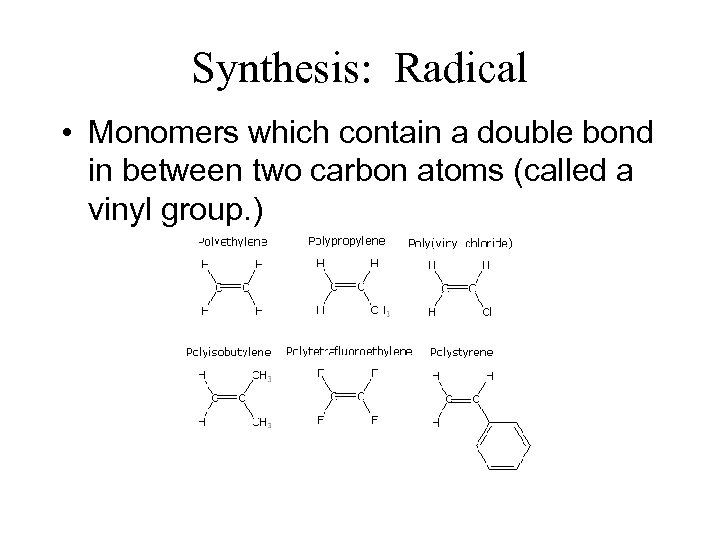 Synthesis: Radical • Monomers which contain a double bond in between two carbon atoms (called a vinyl group. )
Synthesis: Radical • Monomers which contain a double bond in between two carbon atoms (called a vinyl group. )
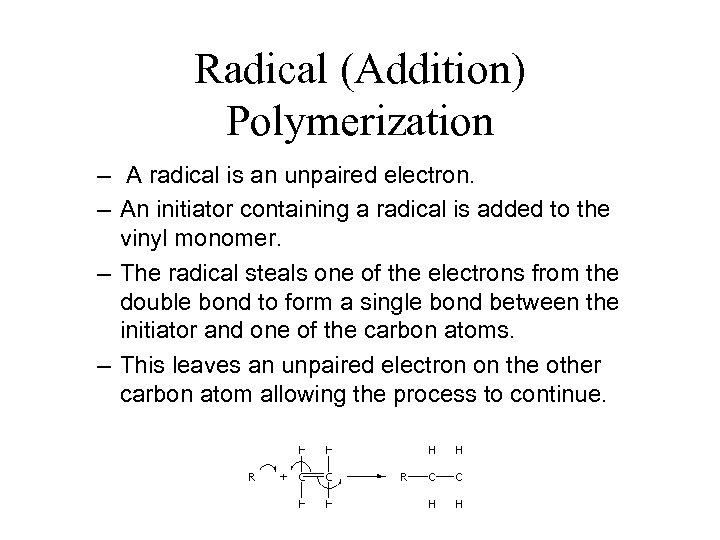 Radical (Addition) Polymerization – A radical is an unpaired electron. – An initiator containing a radical is added to the vinyl monomer. – The radical steals one of the electrons from the double bond to form a single bond between the initiator and one of the carbon atoms. – This leaves an unpaired electron on the other carbon atom allowing the process to continue.
Radical (Addition) Polymerization – A radical is an unpaired electron. – An initiator containing a radical is added to the vinyl monomer. – The radical steals one of the electrons from the double bond to form a single bond between the initiator and one of the carbon atoms. – This leaves an unpaired electron on the other carbon atom allowing the process to continue.
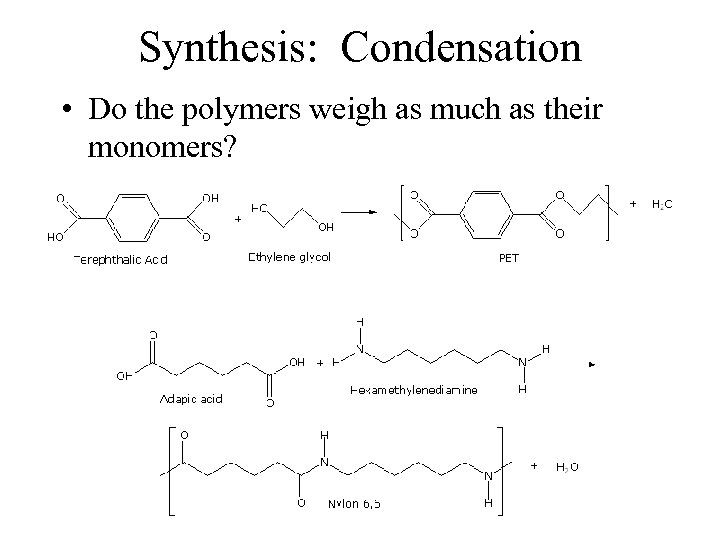 Synthesis: Condensation • Do the polymers weigh as much as their monomers?
Synthesis: Condensation • Do the polymers weigh as much as their monomers?
 Polymer Recycling • PET - Polyethylene Terephthalate is a transparent plastic with good gas barrier properties. It is also relatively cheap and strong. This makes it especially suitable for producing soft drink bottles • HDPE - High Density Polyethylene is another plastic commonly used for drink bottles. It is translucent and strong with a good resistance against chemicals. Pigments are used to add color to HDPE bottles. • PVC - Polyvinyl Chloride is frequently used for drainage pipes because of its superior chemical resistance. It also a good insulator and is used for cable jacketing. • LDPE - Low Density Polyethylene is a tough and highly flexible plastic that is used for producing plastic bags, cable jacketing and bottles. Other applications include products that can be heat sealed. Taken from: http: //www. visionengineer. com/env/plastic_recycling_symbols. shtml
Polymer Recycling • PET - Polyethylene Terephthalate is a transparent plastic with good gas barrier properties. It is also relatively cheap and strong. This makes it especially suitable for producing soft drink bottles • HDPE - High Density Polyethylene is another plastic commonly used for drink bottles. It is translucent and strong with a good resistance against chemicals. Pigments are used to add color to HDPE bottles. • PVC - Polyvinyl Chloride is frequently used for drainage pipes because of its superior chemical resistance. It also a good insulator and is used for cable jacketing. • LDPE - Low Density Polyethylene is a tough and highly flexible plastic that is used for producing plastic bags, cable jacketing and bottles. Other applications include products that can be heat sealed. Taken from: http: //www. visionengineer. com/env/plastic_recycling_symbols. shtml
 Recycling Continued • PP - Polypropylene is a strong and light plastic. It has a relatively high melting point and is used in products exposed to high temperatures. These include yogurt and ice cream containers that are filled while hot. • PS - Polystyrene is rather stiff and rigid. In this form, it is used in disposable cutlery and CD jewel cases. Packing foam is also produced by blowing air bubbles into PS while it is still setting. • Other - This designation is used for plastic products that do not fall into any of the other categories. Further sorting of these items is required at recycling centers. An example is melamine, which is often used in plastic plates an cups. Which kinds of polymers does Ann Arbor recycle? Taken from: http: //www. visionengineer. com/env/plastic_recycling_symbols. shtml
Recycling Continued • PP - Polypropylene is a strong and light plastic. It has a relatively high melting point and is used in products exposed to high temperatures. These include yogurt and ice cream containers that are filled while hot. • PS - Polystyrene is rather stiff and rigid. In this form, it is used in disposable cutlery and CD jewel cases. Packing foam is also produced by blowing air bubbles into PS while it is still setting. • Other - This designation is used for plastic products that do not fall into any of the other categories. Further sorting of these items is required at recycling centers. An example is melamine, which is often used in plastic plates an cups. Which kinds of polymers does Ann Arbor recycle? Taken from: http: //www. visionengineer. com/env/plastic_recycling_symbols. shtml
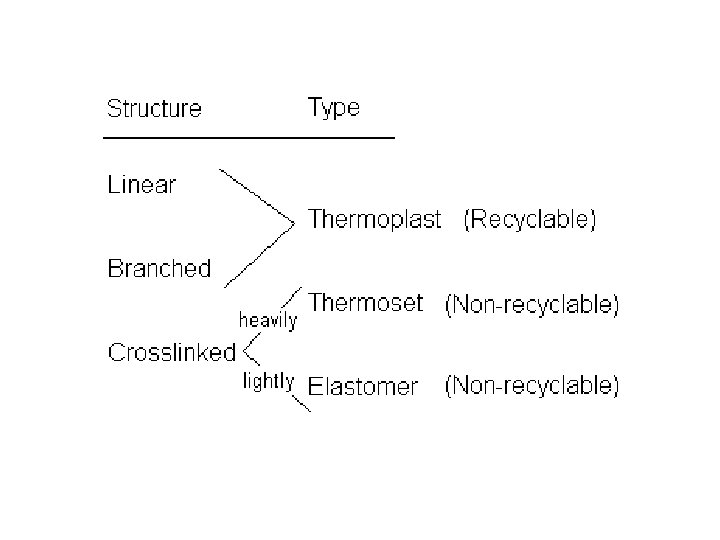
 How are Polymers Recycled? • One of the keys to recycling is the ability to melt a polymer and reform it. • Thermoplasts: Soften and melt when heated, and therefore can be reshaped. (Ex: the polyethylene used to make a pop bottle) • Thermosets: are harder, stiffer and more rigid than thermoplasts. They are processed at temperatures above their melting point. Once they are cooled and become hard they cannot be reshaped (hence thermo -"set"). . (Ex: epoxy, polyester, bakelite, and fiberglass. ) • Elastomers: are very stretchy, pliable materials, like anything made out of rubber (Ex: rubber bands or tires) From: www. risfc. org/ print. php? sid=452
How are Polymers Recycled? • One of the keys to recycling is the ability to melt a polymer and reform it. • Thermoplasts: Soften and melt when heated, and therefore can be reshaped. (Ex: the polyethylene used to make a pop bottle) • Thermosets: are harder, stiffer and more rigid than thermoplasts. They are processed at temperatures above their melting point. Once they are cooled and become hard they cannot be reshaped (hence thermo -"set"). . (Ex: epoxy, polyester, bakelite, and fiberglass. ) • Elastomers: are very stretchy, pliable materials, like anything made out of rubber (Ex: rubber bands or tires) From: www. risfc. org/ print. php? sid=452
 1998 MMR Vaccine linked to Autism • From: www-student. newn. cam. ac. uk/ nigma/site 6/sc. htm
1998 MMR Vaccine linked to Autism • From: www-student. newn. cam. ac. uk/ nigma/site 6/sc. htm
 Autism • Isolation (some born with it; sometimes it seems to develop) • Many experts argue that improved diagnosis and deeper awareness among professionals have led to more accurate and earlier identification of the problem. Others contend that the absolute number of cases is rising, not just medicine's ability to find them. In their view, something in the environment must be to blame.
Autism • Isolation (some born with it; sometimes it seems to develop) • Many experts argue that improved diagnosis and deeper awareness among professionals have led to more accurate and earlier identification of the problem. Others contend that the absolute number of cases is rising, not just medicine's ability to find them. In their view, something in the environment must be to blame.
 MMR • Measles (1964) is a virus which causes a rash, cough, runny nose, eye irritation, and fever in most people, but can also lead to pneumonia, seizures, brain damage, and death in some 1 in 2500 cases. • Mumps (1967) virus causes fever, headache, and swollen glands, but can also lead to deafness, meningitis, swollen testicles or ovaries, and death in some cases. • Rubella, (1970) also known as the German Measles, is generally a mild disease, but can cause serious birth defects in the child of a woman who becomes infected while pregnant. http: //www. nlm. nih. gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002026. htm
MMR • Measles (1964) is a virus which causes a rash, cough, runny nose, eye irritation, and fever in most people, but can also lead to pneumonia, seizures, brain damage, and death in some 1 in 2500 cases. • Mumps (1967) virus causes fever, headache, and swollen glands, but can also lead to deafness, meningitis, swollen testicles or ovaries, and death in some cases. • Rubella, (1970) also known as the German Measles, is generally a mild disease, but can cause serious birth defects in the child of a woman who becomes infected while pregnant. http: //www. nlm. nih. gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002026. htm
 Measles in the US • Prior to licensure of the first measles vaccine in 1963, virtually every person in the U. S. got the measles by age 20. Since the vaccine became available, there has been a 99% reduction in the incidence of measles. However, measles is still being “imported” from other countries. The most recent outbreaks occurred in the U. S. between 1989 and 1991, resulting in 755, 000 cases and 123 reported deaths. • From: http: //www. immunizationinfo. org/vaccine. Info/vaccine_detail. cfv? id=8
Measles in the US • Prior to licensure of the first measles vaccine in 1963, virtually every person in the U. S. got the measles by age 20. Since the vaccine became available, there has been a 99% reduction in the incidence of measles. However, measles is still being “imported” from other countries. The most recent outbreaks occurred in the U. S. between 1989 and 1991, resulting in 755, 000 cases and 123 reported deaths. • From: http: //www. immunizationinfo. org/vaccine. Info/vaccine_detail. cfv? id=8
 The Triple Vaccine • Given ~ 15 months and then again at 4 -6 or 11 -13 years • Mild to moderate side effects: – – – fever (1 in 6 children) rash (1 in 20) swollen glands (rare) seizure (1 in 3, 000) Joint pain/stiffness (1 in 4, usually young women) low platelet count/bleeding (1 in 30, 000) • Severe adverse effects may include: – allergic reaction (less than 1 per million) – long-term seizure/brain damage/deafness (so rare that the association with the vaccine is questionable)
The Triple Vaccine • Given ~ 15 months and then again at 4 -6 or 11 -13 years • Mild to moderate side effects: – – – fever (1 in 6 children) rash (1 in 20) swollen glands (rare) seizure (1 in 3, 000) Joint pain/stiffness (1 in 4, usually young women) low platelet count/bleeding (1 in 30, 000) • Severe adverse effects may include: – allergic reaction (less than 1 per million) – long-term seizure/brain damage/deafness (so rare that the association with the vaccine is questionable)
 Vaccine Source • Product: M-M-R® II Manufacturer: Merck Year licensed: 1971 • (First used in US and Scandanavia 1972) • MMR is a live vaccine containing measles, mumps and rubella viruses that have been modified so they do not cause symptoms. It produces an immune response sufficient to protect children from the diseases.
Vaccine Source • Product: M-M-R® II Manufacturer: Merck Year licensed: 1971 • (First used in US and Scandanavia 1972) • MMR is a live vaccine containing measles, mumps and rubella viruses that have been modified so they do not cause symptoms. It produces an immune response sufficient to protect children from the diseases.
 • 1988 The MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) triple vaccine is introduced in the UK, a year after Britain had a measles outbreak which killed 17 children
• 1988 The MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) triple vaccine is introduced in the UK, a year after Britain had a measles outbreak which killed 17 children
 The Wakefield Study Ileal-lymphoid-nodular hyperplasia, non-specific colitis, and pervasive developmental disorder in children A J Wakefield, S H Murch, A Anthony, J Linnell, D M Casson, M Malik, M Berelowitz, A P Dhillon, M A Thomson, P Harvey, A Valentine, S E Davies, J A Walker-Smith The Lancet, Volume 351, Number 9103 28 February 1998 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Study Group, University Departments of Medicine and Histopathology (and the University Departments of Paediatric Gastroenterology Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Neurology (and Radiology (Royal Free Hospital and School of Medicine, London NW 3 2 QG, UK Correspondence to: Dr A J Wakefield
The Wakefield Study Ileal-lymphoid-nodular hyperplasia, non-specific colitis, and pervasive developmental disorder in children A J Wakefield, S H Murch, A Anthony, J Linnell, D M Casson, M Malik, M Berelowitz, A P Dhillon, M A Thomson, P Harvey, A Valentine, S E Davies, J A Walker-Smith The Lancet, Volume 351, Number 9103 28 February 1998 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Study Group, University Departments of Medicine and Histopathology (and the University Departments of Paediatric Gastroenterology Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Neurology (and Radiology (Royal Free Hospital and School of Medicine, London NW 3 2 QG, UK Correspondence to: Dr A J Wakefield
 Background • Evidence gastrointestinal disorders and autism are linked. • “Fudenberg 16 noted that for 15 of 20 autistic children, the first symptoms developed within a week of [MMR] vaccination. ” • “Gupta 17 commented on the striking association between measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination and the onset of behavioral symptoms in all the children that he had investigated for regressive autism. ”
Background • Evidence gastrointestinal disorders and autism are linked. • “Fudenberg 16 noted that for 15 of 20 autistic children, the first symptoms developed within a week of [MMR] vaccination. ” • “Gupta 17 commented on the striking association between measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination and the onset of behavioral symptoms in all the children that he had investigated for regressive autism. ”
![Methods 12 children (mean age 6 years [range 3 -10], 11 boys) were referred Methods 12 children (mean age 6 years [range 3 -10], 11 boys) were referred](https://present5.com/presentation/bdf1e90cb010fbf61852500797f9042f/image-78.jpg) Methods 12 children (mean age 6 years [range 3 -10], 11 boys) were referred to a pediatric gastroenterology unit with a history of normal development followed by loss of acquired skills, including language, together with diarrhea and abdominal pain. Children underwent gastroenterological, neurological, and developmental assessment and review of developmental records. Ileocolonoscopy and biopsy sampling, magnetic-resonance imaging (MRI), electroencephalography (EEG), and lumbar puncture were done under sedation. Barium follow-through radiography was done where possible. Biochemical, haematological, and immunological profiles were examined. Findings Onset of behavioural symptoms was associated, by the parents, with measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination in eight of the 12 children, with measles infection in one child, and otitis media in another. All 12 children had intestinal abnormalities, ranging from lymphoid nodular hyperplasia to aphthoid ulceration. Histology showed patchy chronic inflammation in the colon in 11 children and reactive ileal lymphoid hyperplasia in seven, but no granulomas. Behavioural disorders included autism (nine), disintegrative psychosis (one), and possible postviral or vaccinal encephalitis (two). There were no focal neurological abnormalities and MRI and EEG tests were normal. Abnormal laboratory results were significantly raised urinary methylmalonic acid compared with age-matched controls (p=0· 003), low hemoglobin in four children, and a low serum Ig. A in four children. Interpretation We identified associated gastrointestinal disease and developmental regression in a group of previously normal children, which was generally associated in time with possible environmental triggers.
Methods 12 children (mean age 6 years [range 3 -10], 11 boys) were referred to a pediatric gastroenterology unit with a history of normal development followed by loss of acquired skills, including language, together with diarrhea and abdominal pain. Children underwent gastroenterological, neurological, and developmental assessment and review of developmental records. Ileocolonoscopy and biopsy sampling, magnetic-resonance imaging (MRI), electroencephalography (EEG), and lumbar puncture were done under sedation. Barium follow-through radiography was done where possible. Biochemical, haematological, and immunological profiles were examined. Findings Onset of behavioural symptoms was associated, by the parents, with measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination in eight of the 12 children, with measles infection in one child, and otitis media in another. All 12 children had intestinal abnormalities, ranging from lymphoid nodular hyperplasia to aphthoid ulceration. Histology showed patchy chronic inflammation in the colon in 11 children and reactive ileal lymphoid hyperplasia in seven, but no granulomas. Behavioural disorders included autism (nine), disintegrative psychosis (one), and possible postviral or vaccinal encephalitis (two). There were no focal neurological abnormalities and MRI and EEG tests were normal. Abnormal laboratory results were significantly raised urinary methylmalonic acid compared with age-matched controls (p=0· 003), low hemoglobin in four children, and a low serum Ig. A in four children. Interpretation We identified associated gastrointestinal disease and developmental regression in a group of previously normal children, which was generally associated in time with possible environmental triggers.
 Results • 9 -10 of 12 children developed autism; parents noted behavioral change 24 h to 2 months after vaccine (15 -21 months old) • Some (3) autism diagnoses made by non-hospital physicians
Results • 9 -10 of 12 children developed autism; parents noted behavioral change 24 h to 2 months after vaccine (15 -21 months old) • Some (3) autism diagnoses made by non-hospital physicians
 Discussion • “Intestinal and behavioral pathologies may have occurred together by chance, reflecting a selection bias in a selfreferred group; however, the uniformity of the intestinal pathological changes and the fact that previous studies have found intestinal dysfunction in children with autisticspectrum disorders, suggests that the connection is real and reflects a unique disease process. ” • We did not prove an association between measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine and the syndrome described. ” • “If there is a causal link between measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine and this syndrome, a rising incidence might be anticipated after the introduction of this vaccine in the UK in 1988. Published evidence is inadequate to show whethere is a change in incidence 22 or a link with measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine. 23”
Discussion • “Intestinal and behavioral pathologies may have occurred together by chance, reflecting a selection bias in a selfreferred group; however, the uniformity of the intestinal pathological changes and the fact that previous studies have found intestinal dysfunction in children with autisticspectrum disorders, suggests that the connection is real and reflects a unique disease process. ” • We did not prove an association between measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine and the syndrome described. ” • “If there is a causal link between measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine and this syndrome, a rising incidence might be anticipated after the introduction of this vaccine in the UK in 1988. Published evidence is inadequate to show whethere is a change in incidence 22 or a link with measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine. 23”
 Conclusions “We have identified a chronic enterocolitis in children that may be related to neuropsychiatric dysfunction. In most cases, onset of symptoms was after measles, mumps, and rubella immunization. Further investigations are needed to examine this syndrome and its possible relation to this vaccine. ”
Conclusions “We have identified a chronic enterocolitis in children that may be related to neuropsychiatric dysfunction. In most cases, onset of symptoms was after measles, mumps, and rubella immunization. Further investigations are needed to examine this syndrome and its possible relation to this vaccine. ”
 Recommendations • Suspend MMR vaccination until further data is collected • Hypothesis: the ultimate culprit for the children's autism was measles virus in the vaccine
Recommendations • Suspend MMR vaccination until further data is collected • Hypothesis: the ultimate culprit for the children's autism was measles virus in the vaccine
 More Information • Other research in Ph. D dissertation from Wakefield’s lab: Results, no live measles, mumps, or rubella virus. “Conclusion. The results do not support previous data implicating persistent measles virus infection with the aetiology of IBD or autistic enteropathy. ” • Funded by funds from a group of parents filing a multibillion dollar lawsuit against the vaccine companies. • Most patients in the journal study were not routine admissions, but referred by the lawyers in the lawsuit. http: //briandeer. com/mmr/wakefield-post. htm
More Information • Other research in Ph. D dissertation from Wakefield’s lab: Results, no live measles, mumps, or rubella virus. “Conclusion. The results do not support previous data implicating persistent measles virus infection with the aetiology of IBD or autistic enteropathy. ” • Funded by funds from a group of parents filing a multibillion dollar lawsuit against the vaccine companies. • Most patients in the journal study were not routine admissions, but referred by the lawyers in the lawsuit. http: //briandeer. com/mmr/wakefield-post. htm
 Investigation Reveals • Wakefield filed a string of patents for vaccine and products that would only succeed if MMR vaccine went down • Ten of the 13 physicians involved in the original report have withdrawn their support • The Journal editor was a former colleague of Wakefield’s.
Investigation Reveals • Wakefield filed a string of patents for vaccine and products that would only succeed if MMR vaccine went down • Ten of the 13 physicians involved in the original report have withdrawn their support • The Journal editor was a former colleague of Wakefield’s.
 Since the Scare • The Institute of Medicine in Washington, part of the National Academy of Sciences, has compiled 14 large-scale studies in the United States, Canada and Europe that all exonerate the vaccine. Wakefield suggests each study has been flawed either because of its methodology or because its authors massaged the findings to get the answers they sought.
Since the Scare • The Institute of Medicine in Washington, part of the National Academy of Sciences, has compiled 14 large-scale studies in the United States, Canada and Europe that all exonerate the vaccine. Wakefield suggests each study has been flawed either because of its methodology or because its authors massaged the findings to get the answers they sought.
 One Study • Madsen, K. M. , et. al. , New England Journal of Medicine 2002, 347, 19, 1477 -1482. ) • Introduction: “Studies designed to evaluate the suggested link between MMR vaccination and autism do not support an association, but the evidence is weak and based on case-series, cross-sectional, and ecologic studies. ”
One Study • Madsen, K. M. , et. al. , New England Journal of Medicine 2002, 347, 19, 1477 -1482. ) • Introduction: “Studies designed to evaluate the suggested link between MMR vaccination and autism do not support an association, but the evidence is weak and based on case-series, cross-sectional, and ecologic studies. ”
 Case series http: //servers. medlib. hscbklyn. edu/ebm/2600. htm
Case series http: //servers. medlib. hscbklyn. edu/ebm/2600. htm
 Cross-sectional • Collects data all at one time and one time only from a variety of people, subjects, or phenomena. Provides a snapshot of the variables at one particular point in time in a cross-section of a population. • Data on many variables but increased error • Data from a large number of subjects • Data from dispersed subjects but increased cost with each location • Data on attitudes and behaviors • Cannot measure change or establish cause and effect • Good for exploratory research to generate hypothesis • No control of independent variable http: //www. csulb. edu/~msaintg/ppa 696/696 preex. htm#Cross-Sectional%20 Design
Cross-sectional • Collects data all at one time and one time only from a variety of people, subjects, or phenomena. Provides a snapshot of the variables at one particular point in time in a cross-section of a population. • Data on many variables but increased error • Data from a large number of subjects • Data from dispersed subjects but increased cost with each location • Data on attitudes and behaviors • Cannot measure change or establish cause and effect • Good for exploratory research to generate hypothesis • No control of independent variable http: //www. csulb. edu/~msaintg/ppa 696/696 preex. htm#Cross-Sectional%20 Design
 Ecologic • Looks at data on populations or groups of people for correlations (this group has high blood pressure and high cancer rates therefore there might be a link. ) Dales, L. ; Hammer, S. J. ; Smith, N. J. JAMA 2001, 285, 9, 11831185. Results Essentially no correlation was observed between the secular trend of early childhood MMR immunization rates in California and the secular trend in numbers of children with autism enrolled in California’s regional service center system. For the 1980 -1994 birth cohorts, a marked, sustained increase in autism case numbers was noted, from 44 cases per 100000 live births in the 1980 cohort to 208 cases per 100000 live births in the 1994 cohort (a 373% relative increase), but changes in early childhood MMR immunization coverage over the same time period were much smaller and of shorter duration. Immunization coverage by the age of 24 months increased from 72% to
Ecologic • Looks at data on populations or groups of people for correlations (this group has high blood pressure and high cancer rates therefore there might be a link. ) Dales, L. ; Hammer, S. J. ; Smith, N. J. JAMA 2001, 285, 9, 11831185. Results Essentially no correlation was observed between the secular trend of early childhood MMR immunization rates in California and the secular trend in numbers of children with autism enrolled in California’s regional service center system. For the 1980 -1994 birth cohorts, a marked, sustained increase in autism case numbers was noted, from 44 cases per 100000 live births in the 1980 cohort to 208 cases per 100000 live births in the 1994 cohort (a 373% relative increase), but changes in early childhood MMR immunization coverage over the same time period were much smaller and of shorter duration. Immunization coverage by the age of 24 months increased from 72% to
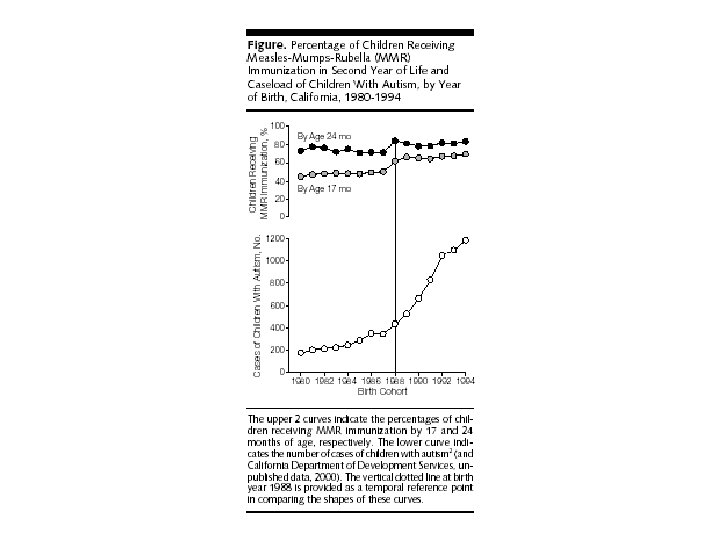
 Back to the NEJM study • Study includes all children born in Denmark 19911998 (440, 655 received MMR vaccination; 96, 648 did not) • Conclusions: No risk in vaccinated versus unvaccinated children (adjusted relative risk = 0. 92) • Increase in autism from 2 cases/10, 000 (1980 s) children to 10 cases/10, 000 children (1990 s)
Back to the NEJM study • Study includes all children born in Denmark 19911998 (440, 655 received MMR vaccination; 96, 648 did not) • Conclusions: No risk in vaccinated versus unvaccinated children (adjusted relative risk = 0. 92) • Increase in autism from 2 cases/10, 000 (1980 s) children to 10 cases/10, 000 children (1990 s)
 Strengths of Study • Exposure data collected independent of parent recall and before diagnosis of autism; • Autism reporting independent of recording of MMR vaccine • Controlled for cofounders (age, sex, calendar period, socioeconomic status, mother’s education, gestational age, and birth weight) • Checked validity of autism diagnosis high since only specialists in child and adolescent psychiatry are authorized to code diagnosis of autism in the Danish Psychiatric Central Register.
Strengths of Study • Exposure data collected independent of parent recall and before diagnosis of autism; • Autism reporting independent of recording of MMR vaccine • Controlled for cofounders (age, sex, calendar period, socioeconomic status, mother’s education, gestational age, and birth weight) • Checked validity of autism diagnosis high since only specialists in child and adolescent psychiatry are authorized to code diagnosis of autism in the Danish Psychiatric Central Register.
 Study Critiques • Family history of autism not recorded; may have chosen not to receive MMR vaccine. (But would have expected to see higher risks at beginning of study before scare. )
Study Critiques • Family history of autism not recorded; may have chosen not to receive MMR vaccine. (But would have expected to see higher risks at beginning of study before scare. )
 M Ethics Name a situation in science where an ethical decision must be made? What behaviors/practices in science would you consider unethical?
M Ethics Name a situation in science where an ethical decision must be made? What behaviors/practices in science would you consider unethical?
 M List all of the ethical issues in the case of Millikan? List all of the ethical issues in the case of Schön? How are the situations in the two cases similar? How are they different? Did Millikan behave ethically in reporting his data? Why or why not? Did Schön behave ethically in reporting his data? Why or why not?
M List all of the ethical issues in the case of Millikan? List all of the ethical issues in the case of Schön? How are the situations in the two cases similar? How are they different? Did Millikan behave ethically in reporting his data? Why or why not? Did Schön behave ethically in reporting his data? Why or why not?
 M If you were faced with a portion of your data that "didn't fit" your hypothesis what would your options be? What are the consequences of publishing incorrect data?
M If you were faced with a portion of your data that "didn't fit" your hypothesis what would your options be? What are the consequences of publishing incorrect data?
 M From 9/12: Masses of Handfuls of Pennies 42. 43 43. 53 47. 54 50. 075 67. 606 67. 874 100. 140 132. 73 170. 20
M From 9/12: Masses of Handfuls of Pennies 42. 43 43. 53 47. 54 50. 075 67. 606 67. 874 100. 140 132. 73 170. 20
 A Mark and Jerry List the ethical issues in this case What are the consequences of reporting the data? What are the consequences of NOT reporting the data? Does the fact that Jerry Elrod tells Mark that anything under 5% unfavorable results is insignificant relieve Mark of any further responsibility? f Mark wonders whether Jerry's 5% standard for I reporting data meets regulatory standards of acceptability, how might he go about finding out?
A Mark and Jerry List the ethical issues in this case What are the consequences of reporting the data? What are the consequences of NOT reporting the data? Does the fact that Jerry Elrod tells Mark that anything under 5% unfavorable results is insignificant relieve Mark of any further responsibility? f Mark wonders whether Jerry's 5% standard for I reporting data meets regulatory standards of acceptability, how might he go about finding out?
 A Under what conditions, if any, do you think it is ethical for scientists not to report all data in cases related to pollution?
A Under what conditions, if any, do you think it is ethical for scientists not to report all data in cases related to pollution?


