5e3235963686106fbcd491477a6e5dcd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 EXTERNAL ANALYSIS (INDUSTRY AND COMPETITION) Payne (3) “Analysis is the critical starting point of strategic thinking. ” Kenichi Ohmae 1
EXTERNAL ANALYSIS (INDUSTRY AND COMPETITION) Payne (3) “Analysis is the critical starting point of strategic thinking. ” Kenichi Ohmae 1
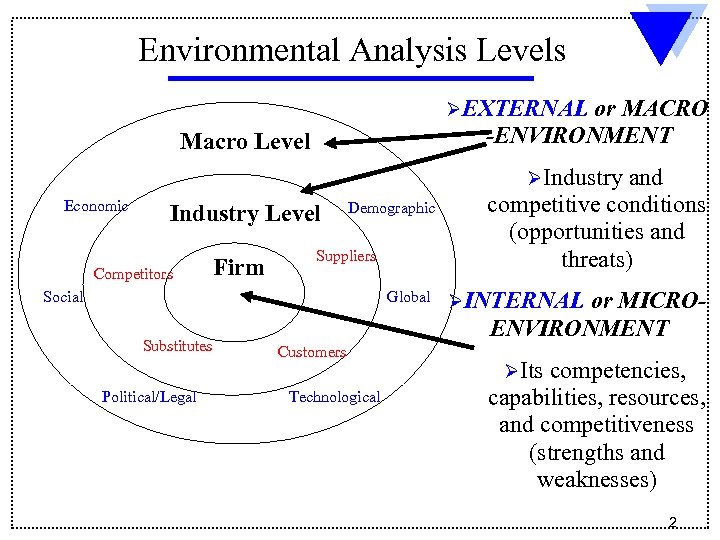 Environmental Analysis Levels ØEXTERNAL or MACRO -ENVIRONMENT Macro Level ØIndustry Economic Industry Level Competitors Social Substitutes Political/Legal Firm Demographic Suppliers Connect Global Customers Technological and competitive conditions (opportunities and threats) ØINTERNAL or MICROENVIRONMENT ØIts competencies, capabilities, resources, and competitiveness (strengths and weaknesses) 2
Environmental Analysis Levels ØEXTERNAL or MACRO -ENVIRONMENT Macro Level ØIndustry Economic Industry Level Competitors Social Substitutes Political/Legal Firm Demographic Suppliers Connect Global Customers Technological and competitive conditions (opportunities and threats) ØINTERNAL or MICROENVIRONMENT ØIts competencies, capabilities, resources, and competitiveness (strengths and weaknesses) 2
 Macro Environment (1) l Socio-cultural segment l l l l Women in the workplace Workforce diversity Attitudes about quality of worklife Concerns about environment Shifts in work and career preferences Shifts in product and service preferences Political/Legal Segment l l l Antitrust laws Taxation laws Deregulation philosophies Labor training laws Educational philosophies and policies 3
Macro Environment (1) l Socio-cultural segment l l l l Women in the workplace Workforce diversity Attitudes about quality of worklife Concerns about environment Shifts in work and career preferences Shifts in product and service preferences Political/Legal Segment l l l Antitrust laws Taxation laws Deregulation philosophies Labor training laws Educational philosophies and policies 3
 Macro Environment (2) l Economic segment l l l l Inflation rates Interest rates Trade deficits or surpluses Budget deficits or surpluses Personal savings rate Business savings rates Gross domestic product Technological Segment Product innovations Applications of knowledge Focus of private and government-supported R&D expenditures l New communication technologies l l l 4
Macro Environment (2) l Economic segment l l l l Inflation rates Interest rates Trade deficits or surpluses Budget deficits or surpluses Personal savings rate Business savings rates Gross domestic product Technological Segment Product innovations Applications of knowledge Focus of private and government-supported R&D expenditures l New communication technologies l l l 4
 Macro Environment (3) l Global Segment l l l Important political events Critical global markets Newly industrialize countries Different cultural and institutional attributes Demographic l l l Population size Age structure Geographic distribution Ethnic mix Income distribution 5
Macro Environment (3) l Global Segment l l l Important political events Critical global markets Newly industrialize countries Different cultural and institutional attributes Demographic l l l Population size Age structure Geographic distribution Ethnic mix Income distribution 5
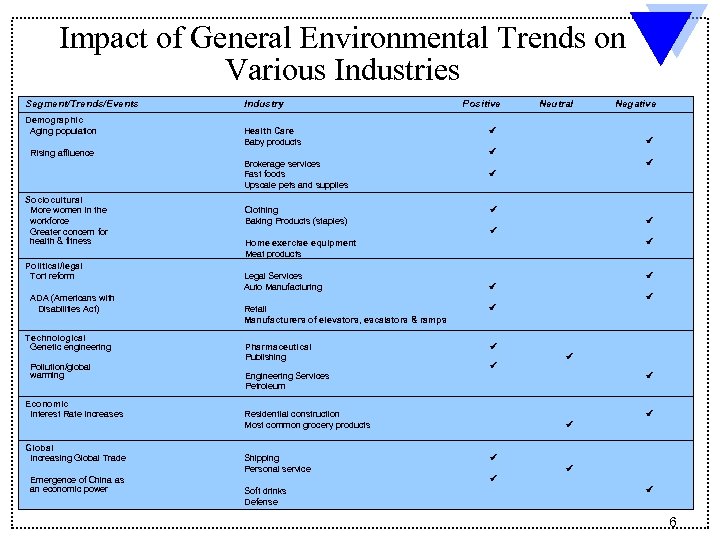 Impact of General Environmental Trends on Various Industries Segment/Trends/Events Demographic Aging population Industry Health Care Baby products Rising affluence Political/legal Tort reform ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) Technological Genetic engineering Pollution/global warming Economic Interest Rate Increases Global Increasing Global Trade Emergence of China as an economic power Neutral Negative Brokerage services Fast foods Upscale pets and supplies Sociocultural More women in the workforce Greater concern for health & fitness Positive Clothing Baking Products (staples) Home exercise equipment Meat products Legal Services Auto Manufacturing Retail Manufacturers of elevators, escalators & ramps Pharmaceutical Publishing Engineering Services Petroleum Residential construction Most common grocery products Shipping Personal service Soft drinks Defense 6
Impact of General Environmental Trends on Various Industries Segment/Trends/Events Demographic Aging population Industry Health Care Baby products Rising affluence Political/legal Tort reform ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) Technological Genetic engineering Pollution/global warming Economic Interest Rate Increases Global Increasing Global Trade Emergence of China as an economic power Neutral Negative Brokerage services Fast foods Upscale pets and supplies Sociocultural More women in the workforce Greater concern for health & fitness Positive Clothing Baking Products (staples) Home exercise equipment Meat products Legal Services Auto Manufacturing Retail Manufacturers of elevators, escalators & ramps Pharmaceutical Publishing Engineering Services Petroleum Residential construction Most common grocery products Shipping Personal service Soft drinks Defense 6
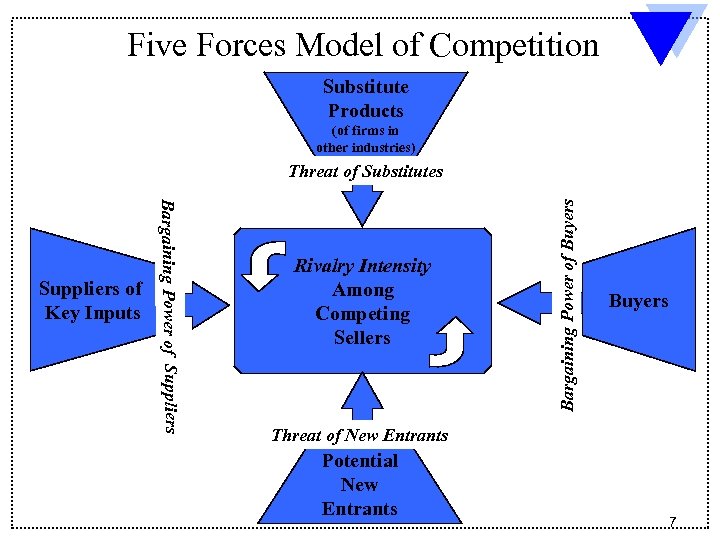 Five Forces Model of Competition Substitute Products (of firms in other industries) Bargaining Power of Suppliers of Key Inputs Rivalry Intensity Among Competing Sellers Bargaining Power of Buyers Threat of Substitutes Buyers Threat of New Entrants Potential New Entrants 7
Five Forces Model of Competition Substitute Products (of firms in other industries) Bargaining Power of Suppliers of Key Inputs Rivalry Intensity Among Competing Sellers Bargaining Power of Buyers Threat of Substitutes Buyers Threat of New Entrants Potential New Entrants 7
 Analyzing the Five Competitive Forces: How to Do It l Assess strength of each competitive force (Strong? Moderate? Weak? ) Ø Ø Ø Rivalry among competitors Substitute products Potential entry Bargaining power of suppliers Bargaining power of buyers Explain how each force acts to create competitive pressure l Decide whether overall competition is brutal, fierce, strong, normal/moderate, or weak l 8
Analyzing the Five Competitive Forces: How to Do It l Assess strength of each competitive force (Strong? Moderate? Weak? ) Ø Ø Ø Rivalry among competitors Substitute products Potential entry Bargaining power of suppliers Bargaining power of buyers Explain how each force acts to create competitive pressure l Decide whether overall competition is brutal, fierce, strong, normal/moderate, or weak l 8
 Rivalry Among Competing Sellers Usually the most powerful of the five forces l Check which weapons of competitive rivalry are most actively used by rivals in jockeying for position l Ø Ø Ø Ø Price Quality Performance features offered Customer service Warranties/guarantees Advertising/promotions Dealer networks Product innovation 9
Rivalry Among Competing Sellers Usually the most powerful of the five forces l Check which weapons of competitive rivalry are most actively used by rivals in jockeying for position l Ø Ø Ø Ø Price Quality Performance features offered Customer service Warranties/guarantees Advertising/promotions Dealer networks Product innovation 9
 What Causes Rivalry to Be Stronger? l l l l Lots of firms, more equal in size and capability Slow market growth Industry conditions tempt some firms to go on the offensive to boost volume and market share Customers have low costs in switching brands One or more firms initiates moves to bolster their standing at expense of rivals A successful strategic move carries a big payoff Costs more to get out of business than to stay in Firms have diverse strategies, corporate priorities, resources, and countries of origin 10
What Causes Rivalry to Be Stronger? l l l l Lots of firms, more equal in size and capability Slow market growth Industry conditions tempt some firms to go on the offensive to boost volume and market share Customers have low costs in switching brands One or more firms initiates moves to bolster their standing at expense of rivals A successful strategic move carries a big payoff Costs more to get out of business than to stay in Firms have diverse strategies, corporate priorities, resources, and countries of origin 10
 Competitive Force of Threat of New Entry l Seriousness of threat depends primarily on: Ø Ø l Barriers to entry Reaction of existing firms to entry Barriers exist when: Ø Newcomers confront obstacles Ø Economic factors put potential entrant at a disadvantage relative to incumbent firms 11
Competitive Force of Threat of New Entry l Seriousness of threat depends primarily on: Ø Ø l Barriers to entry Reaction of existing firms to entry Barriers exist when: Ø Newcomers confront obstacles Ø Economic factors put potential entrant at a disadvantage relative to incumbent firms 11
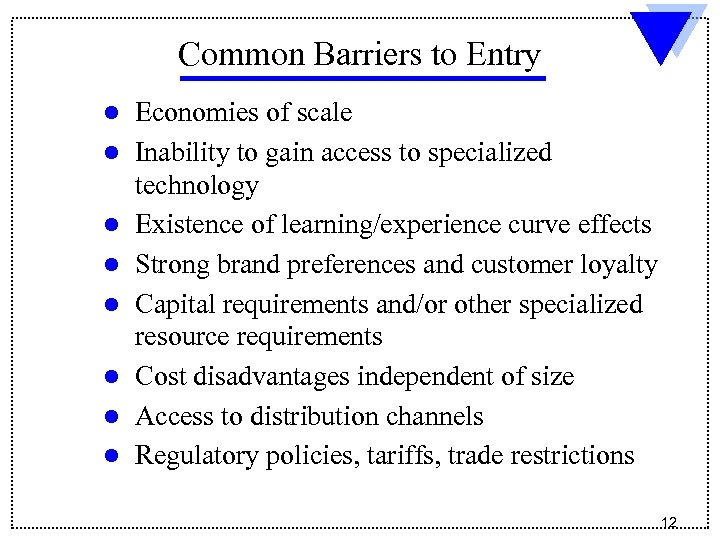 Common Barriers to Entry l l l l Economies of scale Inability to gain access to specialized technology Existence of learning/experience curve effects Strong brand preferences and customer loyalty Capital requirements and/or other specialized resource requirements Cost disadvantages independent of size Access to distribution channels Regulatory policies, tariffs, trade restrictions 12
Common Barriers to Entry l l l l Economies of scale Inability to gain access to specialized technology Existence of learning/experience curve effects Strong brand preferences and customer loyalty Capital requirements and/or other specialized resource requirements Cost disadvantages independent of size Access to distribution channels Regulatory policies, tariffs, trade restrictions 12
 How to Tell Whether Substitute Products Are a Strong Force l Sales of substitutes are growing rapidly l Producers of substitutes are planning to add new capacity l Substitutes’ profits are up The competitive threat of substitutes is stronger when they are: Readily available Attractively priced Believed to have comparable or better performance features Ø Customer switching costs are low Ø Ø Ø 13
How to Tell Whether Substitute Products Are a Strong Force l Sales of substitutes are growing rapidly l Producers of substitutes are planning to add new capacity l Substitutes’ profits are up The competitive threat of substitutes is stronger when they are: Readily available Attractively priced Believed to have comparable or better performance features Ø Customer switching costs are low Ø Ø Ø 13
 Competitive Force of Substitute Products Concept Substitutes matter when customers are attracted to the products or services of firms in other industries Examples v Eyeglasses vs. Contact Lens v MD vs. DPM vs. DC v Plastic vs. Glass vs. Metal 14
Competitive Force of Substitute Products Concept Substitutes matter when customers are attracted to the products or services of firms in other industries Examples v Eyeglasses vs. Contact Lens v MD vs. DPM vs. DC v Plastic vs. Glass vs. Metal 14
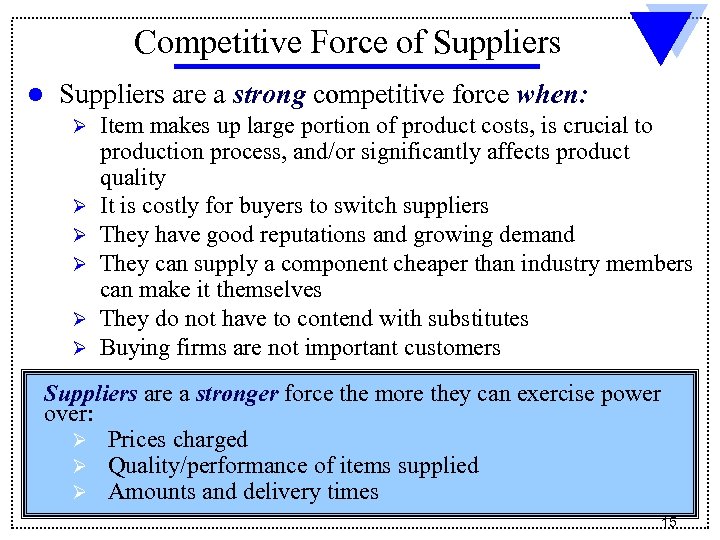 Competitive Force of Suppliers l Suppliers are a strong competitive force when: Ø Ø Ø Item makes up large portion of product costs, is crucial to production process, and/or significantly affects product quality It is costly for buyers to switch suppliers They have good reputations and growing demand They can supply a component cheaper than industry members can make it themselves They do not have to contend with substitutes Buying firms are not important customers Suppliers are a stronger force the more they can exercise power over: Ø Prices charged Ø Quality/performance of items supplied Ø Amounts and delivery times 15
Competitive Force of Suppliers l Suppliers are a strong competitive force when: Ø Ø Ø Item makes up large portion of product costs, is crucial to production process, and/or significantly affects product quality It is costly for buyers to switch suppliers They have good reputations and growing demand They can supply a component cheaper than industry members can make it themselves They do not have to contend with substitutes Buying firms are not important customers Suppliers are a stronger force the more they can exercise power over: Ø Prices charged Ø Quality/performance of items supplied Ø Amounts and delivery times 15
 Competitive Force of Buyers l Buyers are a strong competitive force when: Ø Ø Ø Ø They are large and purchase a sizable percentage of industry’s product They buy in volume quantities They can integrate backward Industry’s product is standardized Their costs in switching to substitutes or other brands are low They can purchase from several sellers Product purchased does not save buyer money Buyers are a stronger competitive force the more they have leverage to bargain over: Ø Price or Quality or Service Ø Other terms and conditions of sale 16
Competitive Force of Buyers l Buyers are a strong competitive force when: Ø Ø Ø Ø They are large and purchase a sizable percentage of industry’s product They buy in volume quantities They can integrate backward Industry’s product is standardized Their costs in switching to substitutes or other brands are low They can purchase from several sellers Product purchased does not save buyer money Buyers are a stronger competitive force the more they have leverage to bargain over: Ø Price or Quality or Service Ø Other terms and conditions of sale 16
 Strategic Implications of the Five Forces l Competitive environment is unattractive when: Ø Ø l Rivalry is strong Entry barriers are low Competition from substitutes is strong Suppliers and customers have considerable bargaining power Competitive environment is ideal when: Ø Ø Rivalry is moderate Entry barriers are high Good substitutes do not exist Suppliers and customers are in a weak bargaining position Objective is to craft a strategy that will: Insulate firm from competitive forces Ø Influence competitive pressures in ways that favor firm Ø Build a sustainable competitive advantage 17 Ø
Strategic Implications of the Five Forces l Competitive environment is unattractive when: Ø Ø l Rivalry is strong Entry barriers are low Competition from substitutes is strong Suppliers and customers have considerable bargaining power Competitive environment is ideal when: Ø Ø Rivalry is moderate Entry barriers are high Good substitutes do not exist Suppliers and customers are in a weak bargaining position Objective is to craft a strategy that will: Insulate firm from competitive forces Ø Influence competitive pressures in ways that favor firm Ø Build a sustainable competitive advantage 17 Ø
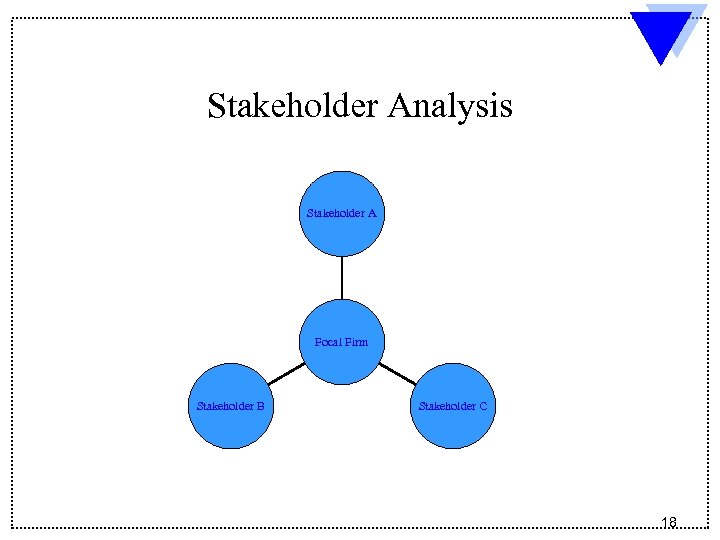 Stakeholder Analysis Stakeholder A Focal Firm Stakeholder B Stakeholder C 18
Stakeholder Analysis Stakeholder A Focal Firm Stakeholder B Stakeholder C 18
 Who are Stakeholders? l Identifying stakeholders is one way of sizing up the internal and external constituents that influence the firm. ü ü l Stakeholders are individuals and groups who can affect and are affected by a firm’s strategic outcomes and who have enforceable claims on its performance Stakeholders include individuals, groups, and other organizations who have an interest in the actions of an organization and who have the ability to influence it Stakeholders may be categorized as internal, interface and external. 19
Who are Stakeholders? l Identifying stakeholders is one way of sizing up the internal and external constituents that influence the firm. ü ü l Stakeholders are individuals and groups who can affect and are affected by a firm’s strategic outcomes and who have enforceable claims on its performance Stakeholders include individuals, groups, and other organizations who have an interest in the actions of an organization and who have the ability to influence it Stakeholders may be categorized as internal, interface and external. 19
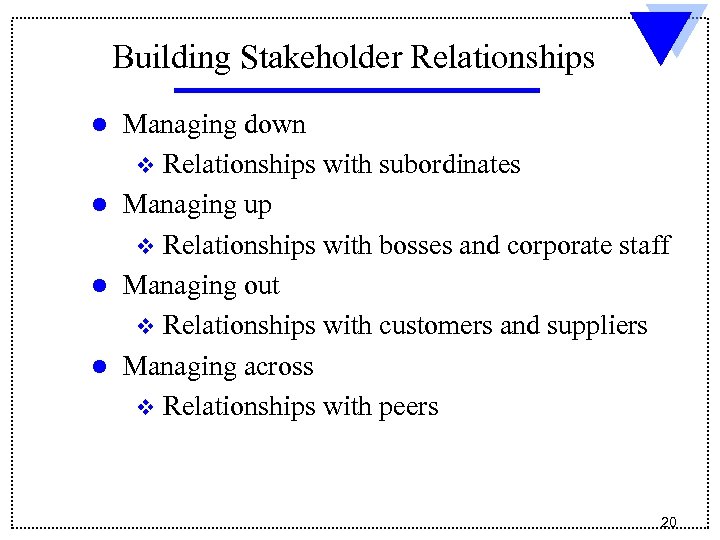 Building Stakeholder Relationships l l Managing down v Relationships with subordinates Managing up v Relationships with bosses and corporate staff Managing out v Relationships with customers and suppliers Managing across v Relationships with peers 20
Building Stakeholder Relationships l l Managing down v Relationships with subordinates Managing up v Relationships with bosses and corporate staff Managing out v Relationships with customers and suppliers Managing across v Relationships with peers 20
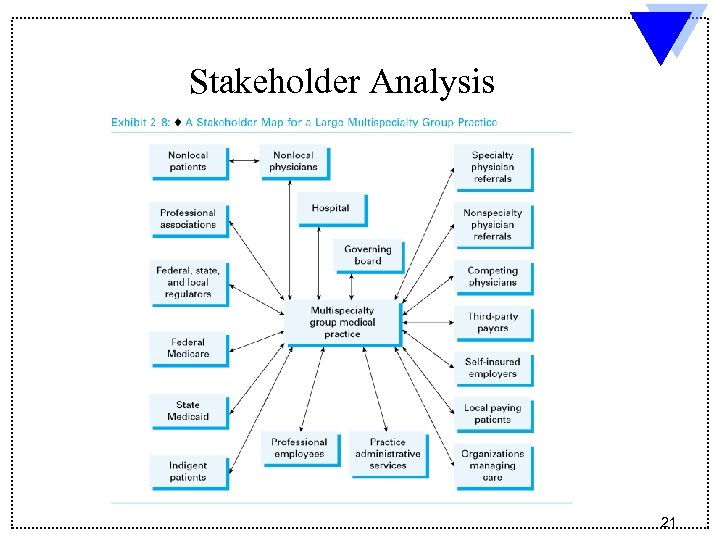 Stakeholder Analysis 21
Stakeholder Analysis 21
 Examples of Stakeholder Groups u. Internal stakeholders – Management – Professionals – Support Personnel u. Interface stakeholders – Shareholders – Board of Directors – Medical Staff u. External stakeholders – Suppliers – Competitors – Government Agencies –Patients 22
Examples of Stakeholder Groups u. Internal stakeholders – Management – Professionals – Support Personnel u. Interface stakeholders – Shareholders – Board of Directors – Medical Staff u. External stakeholders – Suppliers – Competitors – Government Agencies –Patients 22
 Relationships with Stakeholders l l l Organizations have dependency relationships with stakeholders Firms are not equally dependent on all stakeholders and not every stakeholder has the same level of influence An effective organization strategy requires consensus from a plurality of key stakeholders about what it should be doing and how these things should be done 23
Relationships with Stakeholders l l l Organizations have dependency relationships with stakeholders Firms are not equally dependent on all stakeholders and not every stakeholder has the same level of influence An effective organization strategy requires consensus from a plurality of key stakeholders about what it should be doing and how these things should be done 23
 Key Success Factors l KSFs or CSFs are competitive elements that most affect every strategic group member’s ability to prosper in the marketplace: Specific strategy elements Ø Product attributes Ø Resources or Competencies Ø Competitive capabilities Ø l KSFs spell difference between: Profit and loss Ø Competitive success or failure Ø Ask: For our organization to be successful, we MUST be especially good at ______? 24
Key Success Factors l KSFs or CSFs are competitive elements that most affect every strategic group member’s ability to prosper in the marketplace: Specific strategy elements Ø Product attributes Ø Resources or Competencies Ø Competitive capabilities Ø l KSFs spell difference between: Profit and loss Ø Competitive success or failure Ø Ask: For our organization to be successful, we MUST be especially good at ______? 24
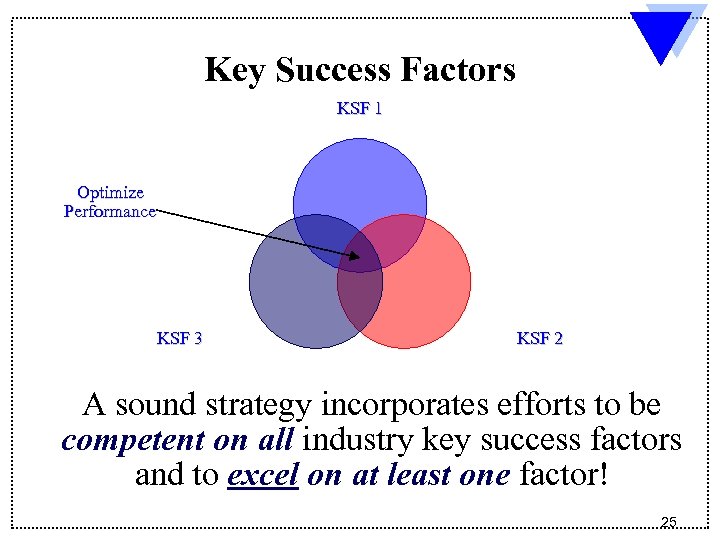 Key Success Factors KSF 1 Optimize Performance KSF 3 KSF 2 A sound strategy incorporates efforts to be competent on all industry key success factors and to excel on at least one factor! 25
Key Success Factors KSF 1 Optimize Performance KSF 3 KSF 2 A sound strategy incorporates efforts to be competent on all industry key success factors and to excel on at least one factor! 25
 Identifying Key Success Factors l l Answers to three questions pinpoint KSFs Ø On what basis do customers choose between competing brands or offerings of sellers? Ø What must a seller/provider do to be competitively successful -- what resources and competitive capabilities does it need? Ø What does it take for sellers/providers to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage? KSFs consist of the 3 - 5 really major determinants of financial and competitive success in a strategic group. (Recall our discussion on developing objectives? ) 26
Identifying Key Success Factors l l Answers to three questions pinpoint KSFs Ø On what basis do customers choose between competing brands or offerings of sellers? Ø What must a seller/provider do to be competitively successful -- what resources and competitive capabilities does it need? Ø What does it take for sellers/providers to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage? KSFs consist of the 3 - 5 really major determinants of financial and competitive success in a strategic group. (Recall our discussion on developing objectives? ) 26
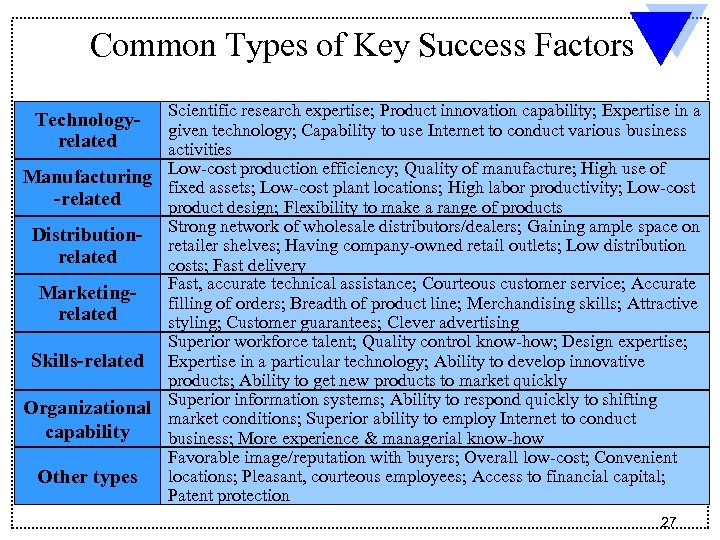 Common Types of Key Success Factors Scientific research expertise; Product innovation capability; Expertise in a given technology; Capability to use Internet to conduct various business activities Manufacturing Low-cost production efficiency; Quality of manufacture; High use of fixed assets; Low-cost plant locations; High labor productivity; Low-cost -related product design; Flexibility to make a range of products Distribution- Strong network of wholesale distributors/dealers; Gaining ample space on retailer shelves; Having company-owned retail outlets; Low distribution related costs; Fast delivery Fast, accurate technical assistance; Courteous customer service; Accurate Marketingfilling of orders; Breadth of product line; Merchandising skills; Attractive related styling; Customer guarantees; Clever advertising Superior workforce talent; Quality control know-how; Design expertise; Skills-related Expertise in a particular technology; Ability to develop innovative products; Ability to get new products to market quickly Organizational Superior information systems; Ability to respond quickly to shifting market conditions; Superior ability to employ Internet to conduct capability business; More experience & managerial know-how Favorable image/reputation with buyers; Overall low-cost; Convenient Other types locations; Pleasant, courteous employees; Access to financial capital; Patent protection Technologyrelated 27
Common Types of Key Success Factors Scientific research expertise; Product innovation capability; Expertise in a given technology; Capability to use Internet to conduct various business activities Manufacturing Low-cost production efficiency; Quality of manufacture; High use of fixed assets; Low-cost plant locations; High labor productivity; Low-cost -related product design; Flexibility to make a range of products Distribution- Strong network of wholesale distributors/dealers; Gaining ample space on retailer shelves; Having company-owned retail outlets; Low distribution related costs; Fast delivery Fast, accurate technical assistance; Courteous customer service; Accurate Marketingfilling of orders; Breadth of product line; Merchandising skills; Attractive related styling; Customer guarantees; Clever advertising Superior workforce talent; Quality control know-how; Design expertise; Skills-related Expertise in a particular technology; Ability to develop innovative products; Ability to get new products to market quickly Organizational Superior information systems; Ability to respond quickly to shifting market conditions; Superior ability to employ Internet to conduct capability business; More experience & managerial know-how Favorable image/reputation with buyers; Overall low-cost; Convenient Other types locations; Pleasant, courteous employees; Access to financial capital; Patent protection Technologyrelated 27
 Example: KSFs for the Refractive Eye Surgery Industry l High numbers of procedures, which is a component of price, experience, and service. l Low rate of complications and high rate of success (20/20) l Positive word-of-mouth and reputation 28
Example: KSFs for the Refractive Eye Surgery Industry l High numbers of procedures, which is a component of price, experience, and service. l Low rate of complications and high rate of success (20/20) l Positive word-of-mouth and reputation 28
 Example: KSFs for Beer Industry l Utilization of brewing capacity -- to keep manufacturing costs low l Strong network of wholesale distributors -to gain access to retail outlets l Clever advertising -- to induce beer drinkers to buy a particular brand 29
Example: KSFs for Beer Industry l Utilization of brewing capacity -- to keep manufacturing costs low l Strong network of wholesale distributors -to gain access to retail outlets l Clever advertising -- to induce beer drinkers to buy a particular brand 29
 Strategic Group Mapping l One technique for revealing the different competitive positions of industry rivals is strategic group mapping l A strategic group consists of those rivals with similar competitive approaches in an industry 30
Strategic Group Mapping l One technique for revealing the different competitive positions of industry rivals is strategic group mapping l A strategic group consists of those rivals with similar competitive approaches in an industry 30
 Strategic Group Mapping l Firms in same strategic group have two or more competitive characteristics in common. . . Ø Sell in same price/quality range Cover same geographic areas Ø Be vertically integrated to same degree Ø Have comparable product line breadth Ø Emphasize same types of distribution channels Ø Offer buyers similar services Ø Use identical technological approaches Ø 31
Strategic Group Mapping l Firms in same strategic group have two or more competitive characteristics in common. . . Ø Sell in same price/quality range Cover same geographic areas Ø Be vertically integrated to same degree Ø Have comparable product line breadth Ø Emphasize same types of distribution channels Ø Offer buyers similar services Ø Use identical technological approaches Ø 31
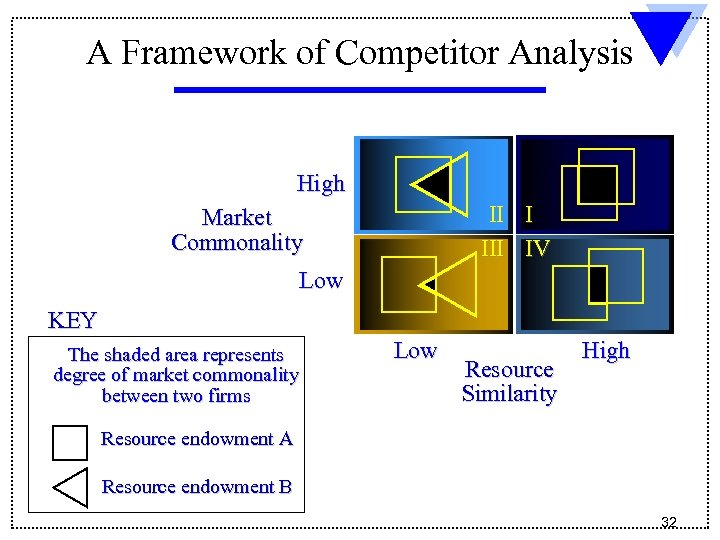 A Framework of Competitor Analysis High II I III IV Market Commonality Low KEY The shaded area represents degree of market commonality between two firms Low Resource Similarity High Resource endowment A Resource endowment B 32
A Framework of Competitor Analysis High II I III IV Market Commonality Low KEY The shaded area represents degree of market commonality between two firms Low Resource Similarity High Resource endowment A Resource endowment B 32
 Market Commonality l Market Commonality is concerned with Ø Ø l Most industries’ markets are somewhat related in terms of Ø Ø l the number of markets with which a firm and a competitor are jointly involved the degree of importance of the individual markets to each competitor technologies core competencies Multi-market competition Ø Firms competing in several markets 33
Market Commonality l Market Commonality is concerned with Ø Ø l Most industries’ markets are somewhat related in terms of Ø Ø l the number of markets with which a firm and a competitor are jointly involved the degree of importance of the individual markets to each competitor technologies core competencies Multi-market competition Ø Firms competing in several markets 33
 Resource Similarity l Resource similarity Ø l Firms with similar types and amounts of resources are likely to Ø Ø l the extent to which the firm’s tangible and intangible resources are comparable to a competitor’s in terms of both type and amount have similar strengths and weaknesses use similar broad strategies Assessing resource similarity can be difficult if critical resources are intangible rather than tangible 34
Resource Similarity l Resource similarity Ø l Firms with similar types and amounts of resources are likely to Ø Ø l the extent to which the firm’s tangible and intangible resources are comparable to a competitor’s in terms of both type and amount have similar strengths and weaknesses use similar broad strategies Assessing resource similarity can be difficult if critical resources are intangible rather than tangible 34
 Procedure: Constructing a Strategic Group Map STEP 1: Identify competitive characteristics that differentiate firms in an industry from one another STEP 2: Plot firms on a two-variable map using pairs of these differentiating characteristics STEP 3: Assign firms that fall in about the same strategy space to same strategic group STEP 4: Draw circles around each group, making circles proportional to size of group’s respective share of total industry sales 35
Procedure: Constructing a Strategic Group Map STEP 1: Identify competitive characteristics that differentiate firms in an industry from one another STEP 2: Plot firms on a two-variable map using pairs of these differentiating characteristics STEP 3: Assign firms that fall in about the same strategy space to same strategic group STEP 4: Draw circles around each group, making circles proportional to size of group’s respective share of total industry sales 35
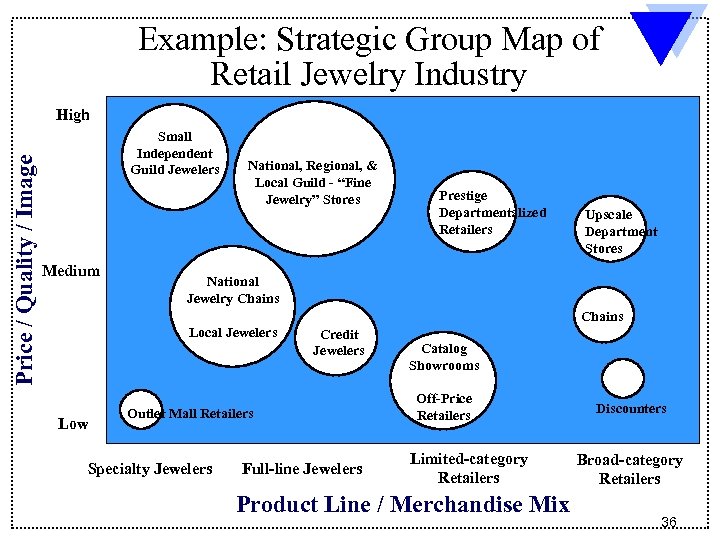 Example: Strategic Group Map of Retail Jewelry Industry Price / Quality / Image High Small Independent Guild Jewelers Medium National, Regional, & Local Guild - “Fine Jewelry” Stores Prestige Departmentalized Retailers Upscale Department Stores National Jewelry Chains Local Jewelers Low Credit Jewelers Outlet Mall Retailers Specialty Jewelers Full-line Jewelers Catalog Showrooms Off-Price Retailers Limited-category Retailers Product Line / Merchandise Mix Discounters Broad-category Retailers 36
Example: Strategic Group Map of Retail Jewelry Industry Price / Quality / Image High Small Independent Guild Jewelers Medium National, Regional, & Local Guild - “Fine Jewelry” Stores Prestige Departmentalized Retailers Upscale Department Stores National Jewelry Chains Local Jewelers Low Credit Jewelers Outlet Mall Retailers Specialty Jewelers Full-line Jewelers Catalog Showrooms Off-Price Retailers Limited-category Retailers Product Line / Merchandise Mix Discounters Broad-category Retailers 36
 Guidelines: Strategic Group Maps l l l Variables selected as axes should not be highly correlated Variables chosen as axes should expose big differences in how rivals compete Variables do not have to be either quantitative or continuous Drawing sizes of circles proportional to combined sales of firms in each strategic group allows map to reflect relative sizes of each strategic group If more than two good competitive variables can be used, several maps can be drawn 37
Guidelines: Strategic Group Maps l l l Variables selected as axes should not be highly correlated Variables chosen as axes should expose big differences in how rivals compete Variables do not have to be either quantitative or continuous Drawing sizes of circles proportional to combined sales of firms in each strategic group allows map to reflect relative sizes of each strategic group If more than two good competitive variables can be used, several maps can be drawn 37
 Interpreting Strategic Group Maps (i. e. , Implications of the Strategic Groups Concept) l Driving forces and competitive pressures often favor some strategic groups and hurt others – such recognition may be the key to developing a competitive advantage. l Profit potential of different strategic groups varies due to strengths and weaknesses in each group’s market position. Important niches may be identified that are not currently being filled by competitors. l The closer strategic groups are on map, the stronger the competitive rivalry among member firms tends to be (“Organizations most like yours are the most dangerous. ”) 38
Interpreting Strategic Group Maps (i. e. , Implications of the Strategic Groups Concept) l Driving forces and competitive pressures often favor some strategic groups and hurt others – such recognition may be the key to developing a competitive advantage. l Profit potential of different strategic groups varies due to strengths and weaknesses in each group’s market position. Important niches may be identified that are not currently being filled by competitors. l The closer strategic groups are on map, the stronger the competitive rivalry among member firms tends to be (“Organizations most like yours are the most dangerous. ”) 38
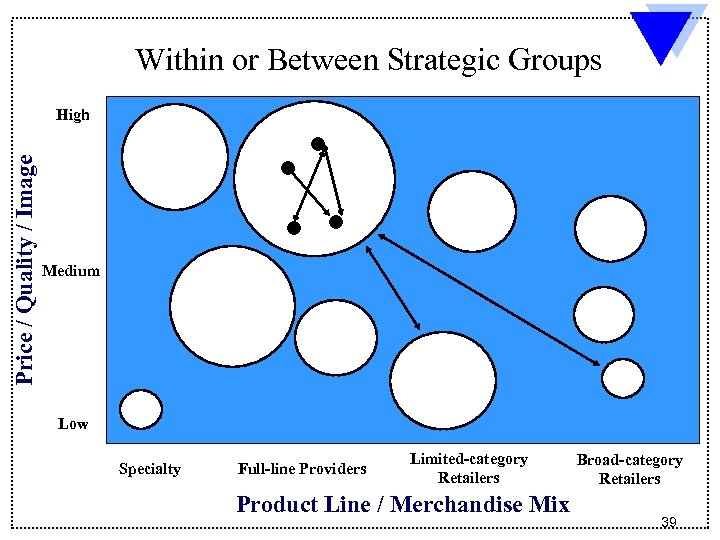 Within or Between Strategic Groups Price / Quality / Image High Medium Low Specialty Full-line Providers Limited-category Retailers Product Line / Merchandise Mix Broad-category Retailers 39
Within or Between Strategic Groups Price / Quality / Image High Medium Low Specialty Full-line Providers Limited-category Retailers Product Line / Merchandise Mix Broad-category Retailers 39
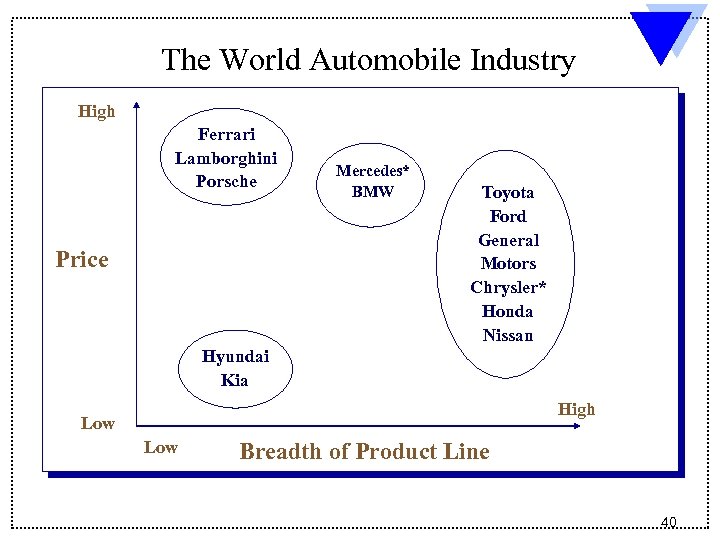 The World Automobile Industry High Ferrari Lamborghini Porsche Price Mercedes* BMW Toyota Ford General Motors Chrysler* Honda Nissan Hyundai Kia High Low Breadth of Product Line 40
The World Automobile Industry High Ferrari Lamborghini Porsche Price Mercedes* BMW Toyota Ford General Motors Chrysler* Honda Nissan Hyundai Kia High Low Breadth of Product Line 40
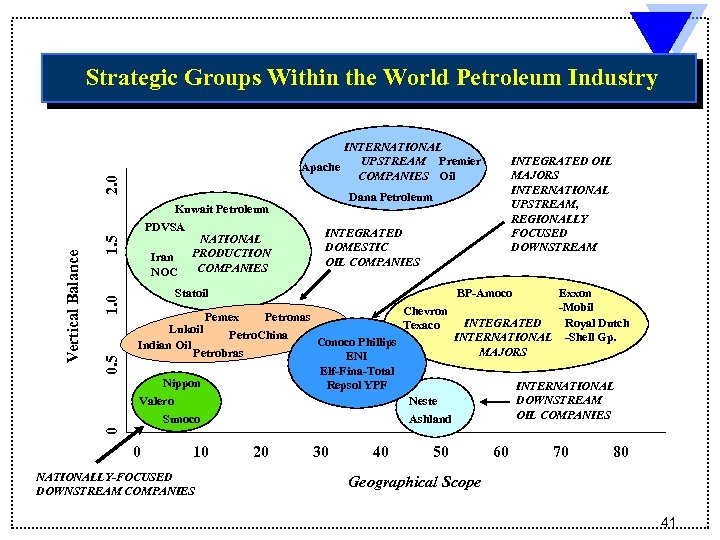 Strategic Groups Within the World Petroleum Industry 0. 5 1. 0 1. 5 Kuwait Petroleum PDVSA NATIONAL Iran PRODUCTION COMPANIES NOC INTEGRATED OIL MAJORS INTERNATIONAL UPSTREAM, REGIONALLY FOCUSED DOWNSTREAM Dana Petroleum INTEGRATED DOMESTIC OIL COMPANIES Statoil BP-Amoco Exxon -Mobil Chevron Pemex Petronas INTEGRATED Royal Dutch Texaco Lukoil Petro. China INTERNATIONAL -Shell Gp. Conoco Phillips Indian Oil Phillips MAJORS Petrobras ENI Elf-Fina-Total ENI Nippon Repsol YPF INTERNATIONAL Repsol DOWNSTREAM Valero Neste OIL COMPANIES Ashland Sunoco 0 Vertical Balance 2. 0 INTERNATIONAL UPSTREAM Premier Apache COMPANIES Oil 0 10 NATIONALLY-FOCUSED DOWNSTREAM COMPANIES 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Geographical Scope 41
Strategic Groups Within the World Petroleum Industry 0. 5 1. 0 1. 5 Kuwait Petroleum PDVSA NATIONAL Iran PRODUCTION COMPANIES NOC INTEGRATED OIL MAJORS INTERNATIONAL UPSTREAM, REGIONALLY FOCUSED DOWNSTREAM Dana Petroleum INTEGRATED DOMESTIC OIL COMPANIES Statoil BP-Amoco Exxon -Mobil Chevron Pemex Petronas INTEGRATED Royal Dutch Texaco Lukoil Petro. China INTERNATIONAL -Shell Gp. Conoco Phillips Indian Oil Phillips MAJORS Petrobras ENI Elf-Fina-Total ENI Nippon Repsol YPF INTERNATIONAL Repsol DOWNSTREAM Valero Neste OIL COMPANIES Ashland Sunoco 0 Vertical Balance 2. 0 INTERNATIONAL UPSTREAM Premier Apache COMPANIES Oil 0 10 NATIONALLY-FOCUSED DOWNSTREAM COMPANIES 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Geographical Scope 41
 Competitor Analysis and Strength Assessment l Successful strategists take great pains in scouting competitors Ø Ø Ø Understanding their strategies Watching their actions Evaluating their vulnerability to driving forces and competitive pressures Sizing up their resource strengths and weaknesses and their capabilities Trying to anticipate rivals’ next moves 42
Competitor Analysis and Strength Assessment l Successful strategists take great pains in scouting competitors Ø Ø Ø Understanding their strategies Watching their actions Evaluating their vulnerability to driving forces and competitive pressures Sizing up their resource strengths and weaknesses and their capabilities Trying to anticipate rivals’ next moves 42
 Predicting Strategic Moves of Rivals l A firm’s own best strategic moves are affected by: Current strategies of competitors Ø Actions competitors are likely to take next Ø l Predicting rivals’ next moves involves: Ø Analyzing their current competitive positions Ø Examining public pronouncements about what it will take to be successful in industry Ø Gathering information from grapevine about current activities and potential changes Ø Studying past actions and leadership Ø Determining who has flexibility to make major strategic changes and who is locked into pursuing same basic strategy 43
Predicting Strategic Moves of Rivals l A firm’s own best strategic moves are affected by: Current strategies of competitors Ø Actions competitors are likely to take next Ø l Predicting rivals’ next moves involves: Ø Analyzing their current competitive positions Ø Examining public pronouncements about what it will take to be successful in industry Ø Gathering information from grapevine about current activities and potential changes Ø Studying past actions and leadership Ø Determining who has flexibility to make major strategic changes and who is locked into pursuing same basic strategy 43
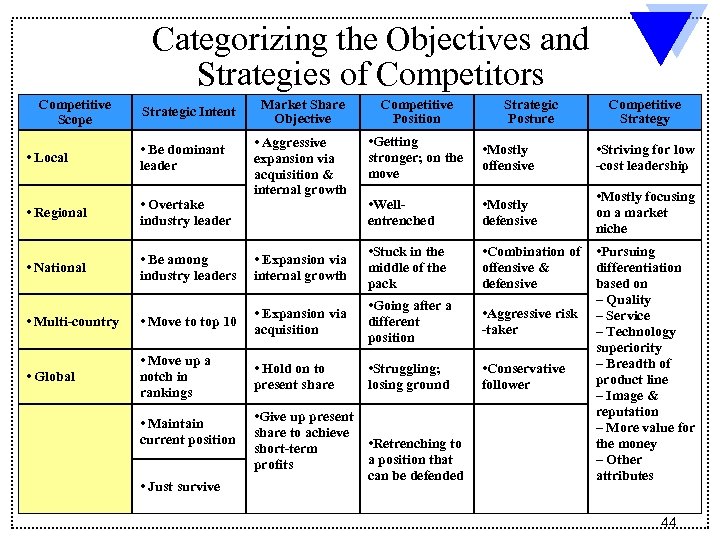 Categorizing the Objectives and Strategies of Competitors Competitive Scope Strategic Intent Market Share Objective Competitive Position Strategic Posture • Aggressive expansion via acquisition & internal growth • Getting stronger; on the move • Mostly offensive • Striving for low -cost leadership • Wellentrenched • Mostly defensive • Mostly focusing on a market niche • Local • Be dominant leader • Regional • Overtake industry leader • National • Be among industry leaders • Expansion via internal growth • Stuck in the middle of the pack • Combination of offensive & defensive • Multi-country • Move to top 10 • Expansion via acquisition • Going after a different position • Aggressive risk -taker • Global • Move up a notch in rankings • Hold on to present share • Struggling; losing ground • Conservative follower • Maintain current position • Just survive • Give up present share to achieve • Retrenching to short-term a position that profits can be defended Competitive Strategy • Pursuing differentiation based on – Quality – Service – Technology superiority – Breadth of product line – Image & reputation – More value for the money – Other attributes 44
Categorizing the Objectives and Strategies of Competitors Competitive Scope Strategic Intent Market Share Objective Competitive Position Strategic Posture • Aggressive expansion via acquisition & internal growth • Getting stronger; on the move • Mostly offensive • Striving for low -cost leadership • Wellentrenched • Mostly defensive • Mostly focusing on a market niche • Local • Be dominant leader • Regional • Overtake industry leader • National • Be among industry leaders • Expansion via internal growth • Stuck in the middle of the pack • Combination of offensive & defensive • Multi-country • Move to top 10 • Expansion via acquisition • Going after a different position • Aggressive risk -taker • Global • Move up a notch in rankings • Hold on to present share • Struggling; losing ground • Conservative follower • Maintain current position • Just survive • Give up present share to achieve • Retrenching to short-term a position that profits can be defended Competitive Strategy • Pursuing differentiation based on – Quality – Service – Technology superiority – Breadth of product line – Image & reputation – More value for the money – Other attributes 44
 Assessing a Company’s Competitive Strength versus Key Rivals 1. List industry key success factors and other relevant measures of competitive strength 2. Rate firm and key rivals on each factor using rating scale of 1 - 10 (1 = weak; 10 = strong) 3. Decide whether to use a weighted or unweighted rating system 4. Sum individual ratings to get overall measure of competitive strength for each rival 5. Determine whether the firm enjoys a competitive advantage or suffers from competitive disadvantage 45
Assessing a Company’s Competitive Strength versus Key Rivals 1. List industry key success factors and other relevant measures of competitive strength 2. Rate firm and key rivals on each factor using rating scale of 1 - 10 (1 = weak; 10 = strong) 3. Decide whether to use a weighted or unweighted rating system 4. Sum individual ratings to get overall measure of competitive strength for each rival 5. Determine whether the firm enjoys a competitive advantage or suffers from competitive disadvantage 45
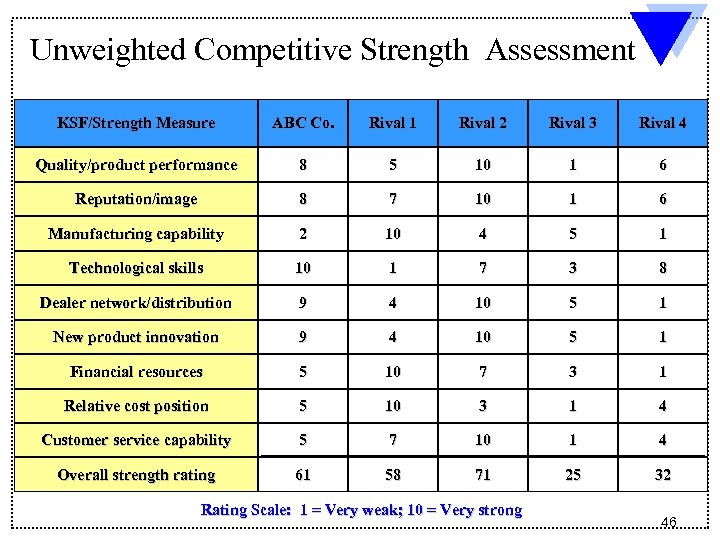 Unweighted Competitive Strength Assessment KSF/Strength Measure ABC Co. Rival 1 Rival 2 Rival 3 Rival 4 Quality/product performance 8 5 10 1 6 Reputation/image 8 7 10 1 6 Manufacturing capability 2 10 4 5 1 Technological skills 10 1 7 3 8 Dealer network/distribution 9 4 10 5 1 New product innovation 9 4 10 5 1 Financial resources 5 10 7 3 1 Relative cost position 5 10 3 1 4 Customer service capability 5 7 10 1 4 Overall strength rating 61 58 71 25 32 Rating Scale: 1 = Very weak; 10 = Very strong 46
Unweighted Competitive Strength Assessment KSF/Strength Measure ABC Co. Rival 1 Rival 2 Rival 3 Rival 4 Quality/product performance 8 5 10 1 6 Reputation/image 8 7 10 1 6 Manufacturing capability 2 10 4 5 1 Technological skills 10 1 7 3 8 Dealer network/distribution 9 4 10 5 1 New product innovation 9 4 10 5 1 Financial resources 5 10 7 3 1 Relative cost position 5 10 3 1 4 Customer service capability 5 7 10 1 4 Overall strength rating 61 58 71 25 32 Rating Scale: 1 = Very weak; 10 = Very strong 46
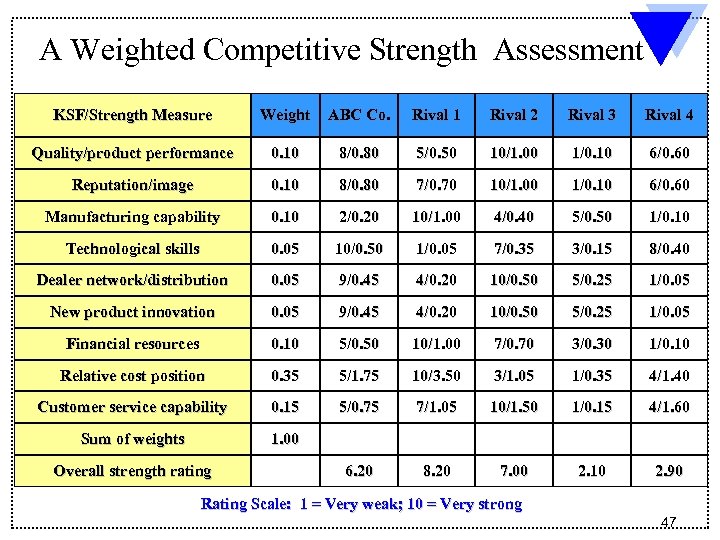 A Weighted Competitive Strength Assessment KSF/Strength Measure Weight ABC Co. Rival 1 Rival 2 Rival 3 Rival 4 Quality/product performance 0. 10 8/0. 80 5/0. 50 10/1. 00 1/0. 10 6/0. 60 Reputation/image 0. 10 8/0. 80 7/0. 70 10/1. 00 1/0. 10 6/0. 60 Manufacturing capability 0. 10 2/0. 20 10/1. 00 4/0. 40 5/0. 50 1/0. 10 Technological skills 0. 05 10/0. 50 1/0. 05 7/0. 35 3/0. 15 8/0. 40 Dealer network/distribution 0. 05 9/0. 45 4/0. 20 10/0. 50 5/0. 25 1/0. 05 New product innovation 0. 05 9/0. 45 4/0. 20 10/0. 50 5/0. 25 1/0. 05 Financial resources 0. 10 5/0. 50 10/1. 00 7/0. 70 3/0. 30 1/0. 10 Relative cost position 0. 35 5/1. 75 10/3. 50 3/1. 05 1/0. 35 4/1. 40 Customer service capability 0. 15 5/0. 75 7/1. 05 10/1. 50 1/0. 15 4/1. 60 Sum of weights 1. 00 6. 20 8. 20 7. 00 2. 10 2. 90 Overall strength rating Rating Scale: 1 = Very weak; 10 = Very strong 47
A Weighted Competitive Strength Assessment KSF/Strength Measure Weight ABC Co. Rival 1 Rival 2 Rival 3 Rival 4 Quality/product performance 0. 10 8/0. 80 5/0. 50 10/1. 00 1/0. 10 6/0. 60 Reputation/image 0. 10 8/0. 80 7/0. 70 10/1. 00 1/0. 10 6/0. 60 Manufacturing capability 0. 10 2/0. 20 10/1. 00 4/0. 40 5/0. 50 1/0. 10 Technological skills 0. 05 10/0. 50 1/0. 05 7/0. 35 3/0. 15 8/0. 40 Dealer network/distribution 0. 05 9/0. 45 4/0. 20 10/0. 50 5/0. 25 1/0. 05 New product innovation 0. 05 9/0. 45 4/0. 20 10/0. 50 5/0. 25 1/0. 05 Financial resources 0. 10 5/0. 50 10/1. 00 7/0. 70 3/0. 30 1/0. 10 Relative cost position 0. 35 5/1. 75 10/3. 50 3/1. 05 1/0. 35 4/1. 40 Customer service capability 0. 15 5/0. 75 7/1. 05 10/1. 50 1/0. 15 4/1. 60 Sum of weights 1. 00 6. 20 8. 20 7. 00 2. 10 2. 90 Overall strength rating Rating Scale: 1 = Very weak; 10 = Very strong 47


