d9d45cff434896ed55aaefe747a2a1b6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 EXPOSITORY, FUNCTIONAL, AND PERSUASIVE TEXT
EXPOSITORY, FUNCTIONAL, AND PERSUASIVE TEXT
 EXPOSITORY TEXT (REVIEW) Expository text = Non-fiction text What is expository text? § A non-fiction text that explains something. § For example an event in history, a discovery in science, how to solve a math problem, day-to-day procedures. The main purpose of expository text is to inform or describe What is non-fiction? § Non-fiction means not fake. It is factual.
EXPOSITORY TEXT (REVIEW) Expository text = Non-fiction text What is expository text? § A non-fiction text that explains something. § For example an event in history, a discovery in science, how to solve a math problem, day-to-day procedures. The main purpose of expository text is to inform or describe What is non-fiction? § Non-fiction means not fake. It is factual.
 TYPES OF EXPOSITORY TEXT Description- main idea and detail Sequence of Events- series of events that leads up to one conclusion. What else do we call sequence of events? § Chronological Order- time order of events § Logical order- most efficient order of events Compare/Contrast- describes how two or more events, places, characters, or other ideas are similar and or different in several ways
TYPES OF EXPOSITORY TEXT Description- main idea and detail Sequence of Events- series of events that leads up to one conclusion. What else do we call sequence of events? § Chronological Order- time order of events § Logical order- most efficient order of events Compare/Contrast- describes how two or more events, places, characters, or other ideas are similar and or different in several ways
 TYPES OF EXPOSITORY TEXT Cause/Effect-involves several reasons why an event occurred, or several effects from a cause, and of course, single cause/effects situation. Problem/Solution- authors use this technique to identify the problem, give possible solutions with possible results and finally, the solution that was chosen. Classification- I want you to come up with a definition. Analogy- identify the relation between two ordered pairs § Example~ hand: palm : : foot: _____ § Answer~ hand: palm : : foot: sole
TYPES OF EXPOSITORY TEXT Cause/Effect-involves several reasons why an event occurred, or several effects from a cause, and of course, single cause/effects situation. Problem/Solution- authors use this technique to identify the problem, give possible solutions with possible results and finally, the solution that was chosen. Classification- I want you to come up with a definition. Analogy- identify the relation between two ordered pairs § Example~ hand: palm : : foot: _____ § Answer~ hand: palm : : foot: sole
 FUNCTIONAL TEXT What is functional text? § Text you see and use everyday Give Examples of informational text that we see and use everyday.
FUNCTIONAL TEXT What is functional text? § Text you see and use everyday Give Examples of informational text that we see and use everyday.

 PERSUASIVE TEXT What is persuasive text? § Text that is designed to move or sway the reader/listener through the use of argument and/or entreaty, whether to change the reader's opinion or to rally support for a cause or belief. Examples of persuasive text seen daily? § Ads/Commercials § Editorials/Opinion pieces
PERSUASIVE TEXT What is persuasive text? § Text that is designed to move or sway the reader/listener through the use of argument and/or entreaty, whether to change the reader's opinion or to rally support for a cause or belief. Examples of persuasive text seen daily? § Ads/Commercials § Editorials/Opinion pieces
 RHETORIC What is rhetoric? § The art or study of using language effectively and persuasively. § Skill in using language effectively and persuasively. What does that mean to you? § Potential answer: using language that actually has the ability to make people change their opinion
RHETORIC What is rhetoric? § The art or study of using language effectively and persuasively. § Skill in using language effectively and persuasively. What does that mean to you? § Potential answer: using language that actually has the ability to make people change their opinion
 RHETORIC- ETHOS Ethos-Ethos is an ethical appeal or an argument from the author's credibility § I now want you to create a student friendly definition for ethos § Potential answer: the author's authority
RHETORIC- ETHOS Ethos-Ethos is an ethical appeal or an argument from the author's credibility § I now want you to create a student friendly definition for ethos § Potential answer: the author's authority
 RHETORIC- PATHOS Pathos- means of persuasion that elicits a strong emotional response from the audience. § I now want you to create a student friendly definition for pathos § Potential answer: emotional appeal in persuasive writing.
RHETORIC- PATHOS Pathos- means of persuasion that elicits a strong emotional response from the audience. § I now want you to create a student friendly definition for pathos § Potential answer: emotional appeal in persuasive writing.
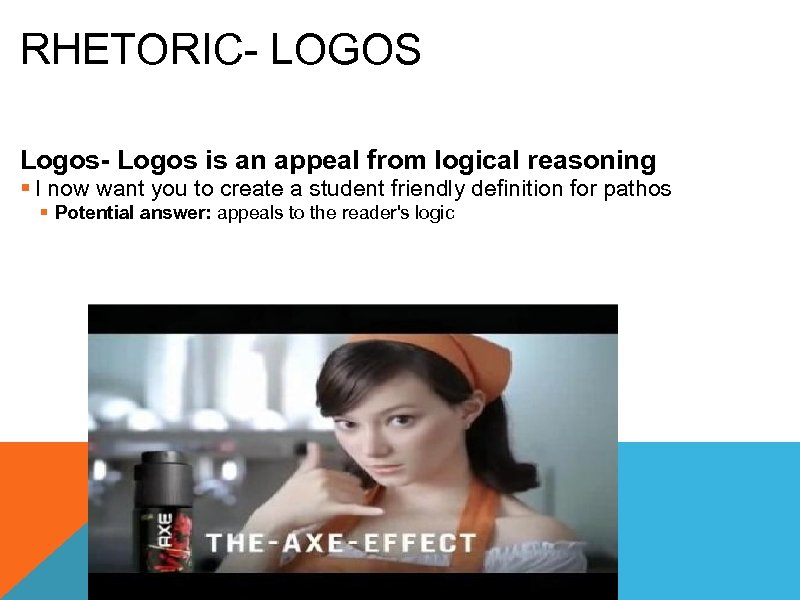 RHETORIC- LOGOS Logos- Logos is an appeal from logical reasoning § I now want you to create a student friendly definition for pathos § Potential answer: appeals to the reader's logic
RHETORIC- LOGOS Logos- Logos is an appeal from logical reasoning § I now want you to create a student friendly definition for pathos § Potential answer: appeals to the reader's logic
 LOGICAL FALLACIES What is a logical fallacy? Dictionary definition: A logical fallacy is, roughly speaking, an error of reasoning. When someone adopts a position, or tries to persuade someone else to adopt a position, based on a bad piece of reasoning, they commit a fallacy. That is fine and dandy, however, I think we can come up with something that works for us. § Work with your tables to create a student friendly definition for logical fallacies
LOGICAL FALLACIES What is a logical fallacy? Dictionary definition: A logical fallacy is, roughly speaking, an error of reasoning. When someone adopts a position, or tries to persuade someone else to adopt a position, based on a bad piece of reasoning, they commit a fallacy. That is fine and dandy, however, I think we can come up with something that works for us. § Work with your tables to create a student friendly definition for logical fallacies
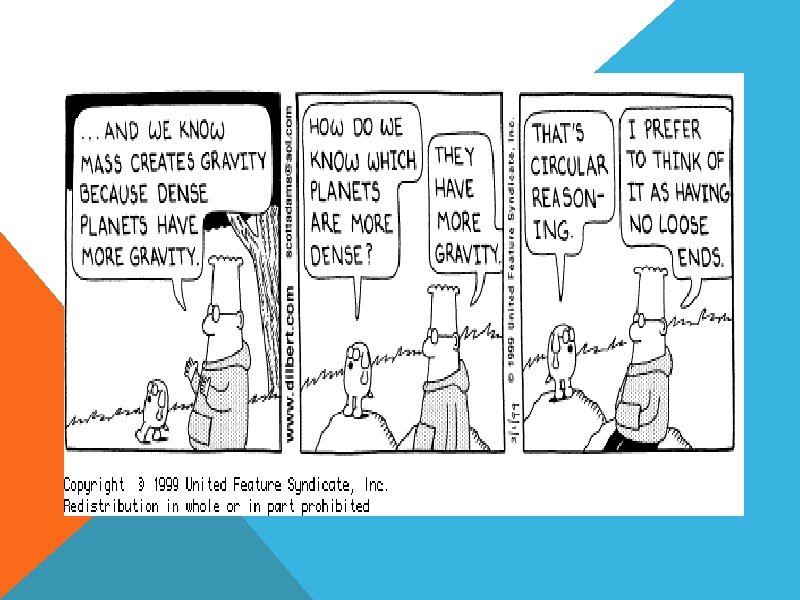
 LOGICAL FALLACIES~ CIRCULAR REASONING Falsely arguing that something is true by repeating the same statement in different words Example: "Only an untrustworthy person would run for office. The fact that politicians are untrustworthy is proof of this. "
LOGICAL FALLACIES~ CIRCULAR REASONING Falsely arguing that something is true by repeating the same statement in different words Example: "Only an untrustworthy person would run for office. The fact that politicians are untrustworthy is proof of this. "
 LOGICAL FALLACIES~ FALSE CAUSALITY An event or action influences another that is not reasonably related. Example: " We were robbed right after that family moved in, so they must be the culprits. "
LOGICAL FALLACIES~ FALSE CAUSALITY An event or action influences another that is not reasonably related. Example: " We were robbed right after that family moved in, so they must be the culprits. "
 LOGICAL FALLACIES~ OVERGENERALIZATION The stupid but common fallacy of incorrectly applying one or two examples to all cases Example: A teenager has causing trouble in the community lately: vandalizing the park and shoplifting. This proves that all teenagers are trouble-makers and should not be allowed out of their homes until they are twenty -five
LOGICAL FALLACIES~ OVERGENERALIZATION The stupid but common fallacy of incorrectly applying one or two examples to all cases Example: A teenager has causing trouble in the community lately: vandalizing the park and shoplifting. This proves that all teenagers are trouble-makers and should not be allowed out of their homes until they are twenty -five

 LOGICAL FALLACIES~ OVERSIMPLIFICATION The fallacy of deceiving an audience by giving simple answers or slogans in response to complex questions, especially when appealing to less educated or unsophisticated audiences. Example: "If the glove doesn’t fit, you must vote to acquit. " § This was used to acquit OJ Simpson of murder in 1995.
LOGICAL FALLACIES~ OVERSIMPLIFICATION The fallacy of deceiving an audience by giving simple answers or slogans in response to complex questions, especially when appealing to less educated or unsophisticated audiences. Example: "If the glove doesn’t fit, you must vote to acquit. " § This was used to acquit OJ Simpson of murder in 1995.

 LOGICAL FALLACIES~ SELFCONTRADICTION Advancing an argument that is self-contradictory, or that is based on mutually inconsistent premises Example: A used car salespersons says, "Hey, you can’t trust those other car salesmen. They’ll say anything to get you to buy a car from them. "
LOGICAL FALLACIES~ SELFCONTRADICTION Advancing an argument that is self-contradictory, or that is based on mutually inconsistent premises Example: A used car salespersons says, "Hey, you can’t trust those other car salesmen. They’ll say anything to get you to buy a car from them. "


