b00f894e0bbf90a02635adef10fdfc81.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Exploring Middle East Conflict Israel & Palestine
Exploring Middle East Conflict Israel & Palestine

 General Overview n. A decades old conflict between two religious-national groups Palestinians Israelis Arab Muslim Jewish
General Overview n. A decades old conflict between two religious-national groups Palestinians Israelis Arab Muslim Jewish
 Fundamentals n The cornerstone of the conflict is related to land, in particular, who claims modern day Israel – both sides have claims
Fundamentals n The cornerstone of the conflict is related to land, in particular, who claims modern day Israel – both sides have claims
 Causes of War sides claim jurisdiction over the land n The land has significant religious implications for two of the world’s largest religions n Both Islam & Judaism
Causes of War sides claim jurisdiction over the land n The land has significant religious implications for two of the world’s largest religions n Both Islam & Judaism
 A Shifting Land n For centuries the “Holy Land” – known as Palestine - fell under the rule of various empires. n Slowly, Arab groups consolidated control The Ottoman Empire I did this thing on the Ottoman Empire. Like, what was this? A whole empire based on putting your feet up? “ – Jerry Seinfeld
A Shifting Land n For centuries the “Holy Land” – known as Palestine - fell under the rule of various empires. n Slowly, Arab groups consolidated control The Ottoman Empire I did this thing on the Ottoman Empire. Like, what was this? A whole empire based on putting your feet up? “ – Jerry Seinfeld
 Anti-Semitism n By the turn of the century, Anti-Semitism was a global problem n To resist, new political movements emerged to advocate for Jewish rights
Anti-Semitism n By the turn of the century, Anti-Semitism was a global problem n To resist, new political movements emerged to advocate for Jewish rights
 Significant Terms Zionism - Nationalist movement founded by the Jewish journalist Theodor Herzl. Ø He argued that the best way of avoiding anti. Semitism in Europe was to create an independent Jewish state in Palestine. Ø By 1905 thousands of Jews were moving to Palestine Ø
Significant Terms Zionism - Nationalist movement founded by the Jewish journalist Theodor Herzl. Ø He argued that the best way of avoiding anti. Semitism in Europe was to create an independent Jewish state in Palestine. Ø By 1905 thousands of Jews were moving to Palestine Ø
 Colonial Implications: The Role of Britain n As WWI came to an end Palestine was under British control n The British made promises to several groups regarding the future of the land: A) Arabs B) Jews C) French
Colonial Implications: The Role of Britain n As WWI came to an end Palestine was under British control n The British made promises to several groups regarding the future of the land: A) Arabs B) Jews C) French
 The Balfour Declaration n Page 357 in your text book
The Balfour Declaration n Page 357 in your text book
 Balfour Implications n Jewish immigration to Palestine rapidly increases
Balfour Implications n Jewish immigration to Palestine rapidly increases
 Balfour Becomes BMP n British Mandate for Palestine n Official policy of support for Jewish land claims in Palestine n At this point only the Brits are largely supporting Zionism
Balfour Becomes BMP n British Mandate for Palestine n Official policy of support for Jewish land claims in Palestine n At this point only the Brits are largely supporting Zionism
 The Holocaust n 6 million European Jews killed n Worldwide anti-Semitism n Guilt spreads globally
The Holocaust n 6 million European Jews killed n Worldwide anti-Semitism n Guilt spreads globally
 Post WW 2 Developments n The tragic events of WW 2 (The Holocaust) resulted in a global awareness of the Zionist Movement n U. S President Harry Truman & PM Churchill lobbied heavy support for the Zionist cause
Post WW 2 Developments n The tragic events of WW 2 (The Holocaust) resulted in a global awareness of the Zionist Movement n U. S President Harry Truman & PM Churchill lobbied heavy support for the Zionist cause
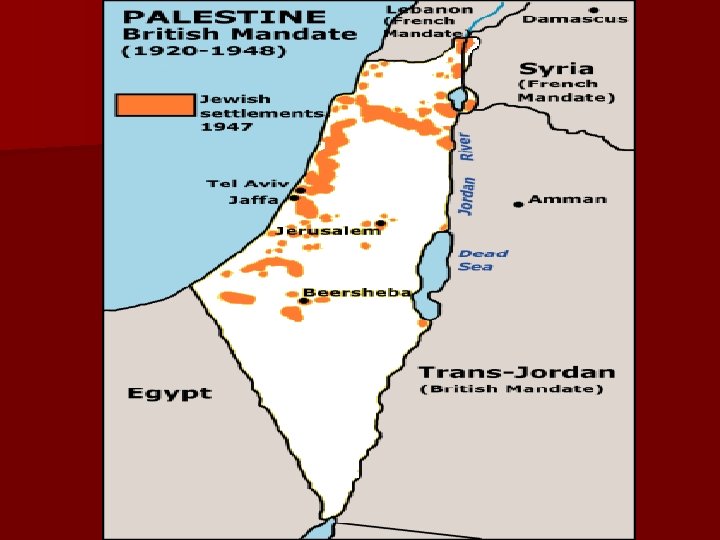
 n Starting in 1947, explain how Israel became a formalized state. What was the reaction from neighboring Arab states?
n Starting in 1947, explain how Israel became a formalized state. What was the reaction from neighboring Arab states?
 May 1948 n With support from England & USA, Israel declares itself the official Jewish homeland n Israel is now recognized Jewish homeland n Arab citizens revolt and civil war erupts (1948) n Jews still maintain a minority of the population
May 1948 n With support from England & USA, Israel declares itself the official Jewish homeland n Israel is now recognized Jewish homeland n Arab citizens revolt and civil war erupts (1948) n Jews still maintain a minority of the population
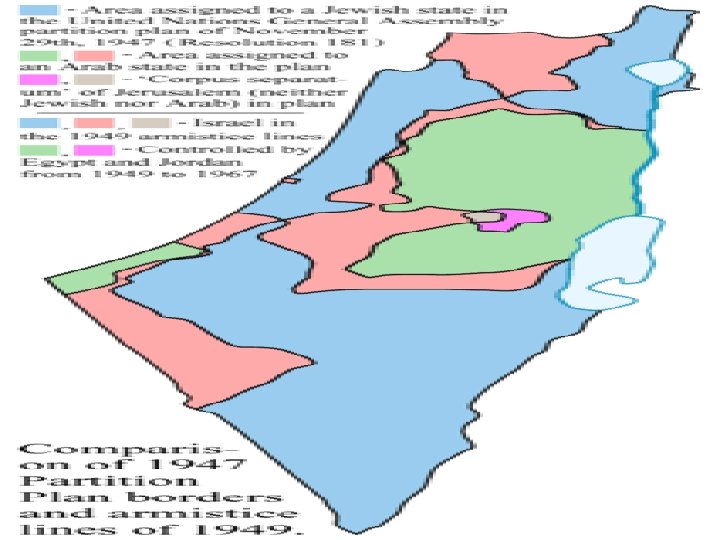
 Arab Response n Almost immediately, the armies of Egypt, Lebanon, Syria & Iraq mobilize n Amazingly, Israel defends its newly claimed territory.
Arab Response n Almost immediately, the armies of Egypt, Lebanon, Syria & Iraq mobilize n Amazingly, Israel defends its newly claimed territory.
 Arab/Israeli Wars Group 1 – War of Independence Group 2 – Suez Crisis Group 3 – 6 Day War Group 4 – Yom Kippur War Group 5 – 1 st Intifada
Arab/Israeli Wars Group 1 – War of Independence Group 2 – Suez Crisis Group 3 – 6 Day War Group 4 – Yom Kippur War Group 5 – 1 st Intifada
 Arab/Israeli Wars You mission: - Create a multi-media presentation that provides an overview of your conflict. Please limit your examination to 4 slides Slide 1 – Brief background on the conflict Slide 2 – Description of the actual conflict Slide 3 – Outcome of the conflict Slide 4 – Consequences of the outcome
Arab/Israeli Wars You mission: - Create a multi-media presentation that provides an overview of your conflict. Please limit your examination to 4 slides Slide 1 – Brief background on the conflict Slide 2 – Description of the actual conflict Slide 3 – Outcome of the conflict Slide 4 – Consequences of the outcome
 Themes of Conflict n IDF combat competency n Reduction of Arab land n Increased Western support n Terrorism – on both sides
Themes of Conflict n IDF combat competency n Reduction of Arab land n Increased Western support n Terrorism – on both sides
 The 6 Arab-Israeli Wars 2) The 1956 Suez Crisis Ø Egypt is under control of Gamal Nasser who seized power in a bloodless coup in 1954 Ø Nasser was a firm believer in Pan Arab Nationalism and a staunch opponent of the Zionist Movement
The 6 Arab-Israeli Wars 2) The 1956 Suez Crisis Ø Egypt is under control of Gamal Nasser who seized power in a bloodless coup in 1954 Ø Nasser was a firm believer in Pan Arab Nationalism and a staunch opponent of the Zionist Movement
 Nasser Ø Viewing western influence as detrimental to Arab interests, Nasser began a rapid program of nationalization Ø His most noted act of nationalization came when he seized control of the Suez Canal (a very important shipping lane)
Nasser Ø Viewing western influence as detrimental to Arab interests, Nasser began a rapid program of nationalization Ø His most noted act of nationalization came when he seized control of the Suez Canal (a very important shipping lane)
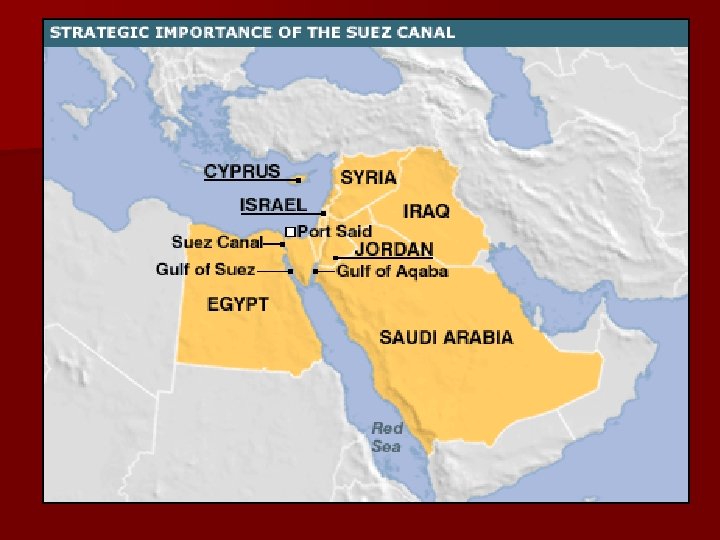
 Response A tri-lateral force of England, France & Israel invades Egypt in an attempt to take back the Suez Canal
Response A tri-lateral force of England, France & Israel invades Egypt in an attempt to take back the Suez Canal
 Canada’s Role n F. A Minister Pearson urges restraint n Proposes a Peacekeeping force n United Nations Emergency Force was deployed to the Sinai Peninsula n Remain there until 1967
Canada’s Role n F. A Minister Pearson urges restraint n Proposes a Peacekeeping force n United Nations Emergency Force was deployed to the Sinai Peninsula n Remain there until 1967
 3 rd Arab Israeli War – 6 Day War Ø May 1967, Egypt expels the UNEF from the Sinai Ø Unilaterally closes the Straits of Tiran and amasses troops on the Sinai – Jordan & Syria follow suit Ø Egypt and Jordan enter into a collective defense agreement
3 rd Arab Israeli War – 6 Day War Ø May 1967, Egypt expels the UNEF from the Sinai Ø Unilaterally closes the Straits of Tiran and amasses troops on the Sinai – Jordan & Syria follow suit Ø Egypt and Jordan enter into a collective defense agreement
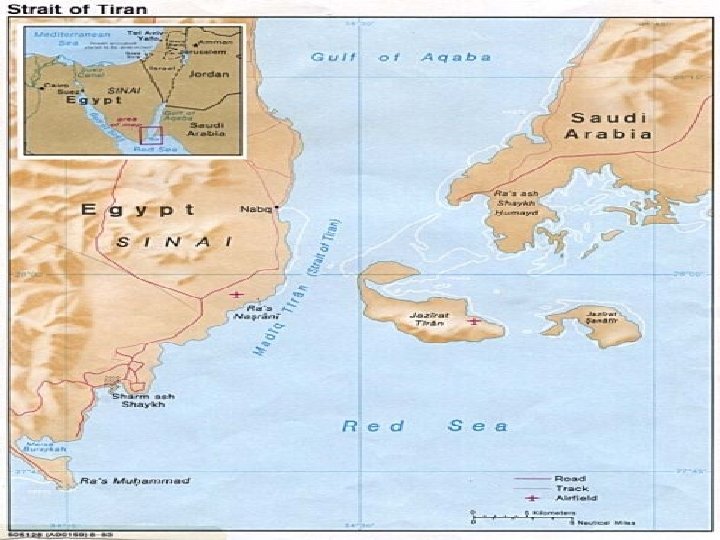 continued
continued
 Israel Reaction Ø Before the advances of Egypt and Jordan, Israel launches a pre-emptive strike against the Egyptian air force – completely destroying it Ø Israel’s intelligence service – MOSSAD – is used heavily for intel
Israel Reaction Ø Before the advances of Egypt and Jordan, Israel launches a pre-emptive strike against the Egyptian air force – completely destroying it Ø Israel’s intelligence service – MOSSAD – is used heavily for intel
 War at Jerusalem Ø Arab forces invade Jerusalem but are quickly pushed back
War at Jerusalem Ø Arab forces invade Jerusalem but are quickly pushed back
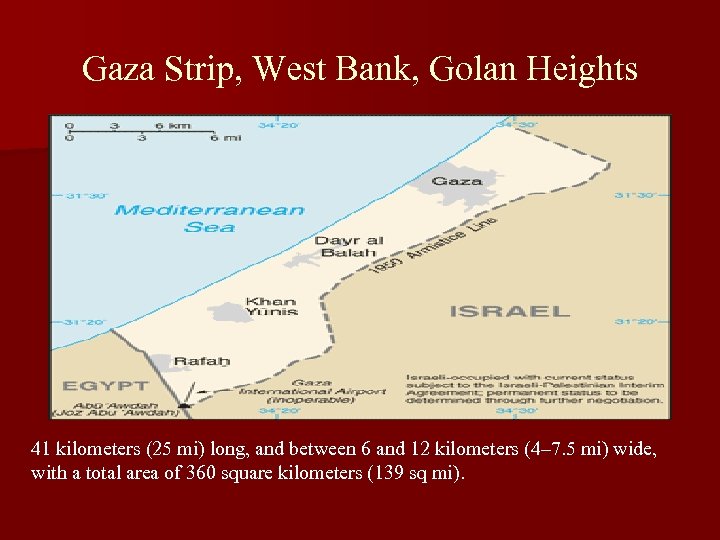 Gaza Strip, West Bank, Golan Heights 41 kilometers (25 mi) long, and between 6 and 12 kilometers (4– 7. 5 mi) wide, with a total area of 360 square kilometers (139 sq mi).
Gaza Strip, West Bank, Golan Heights 41 kilometers (25 mi) long, and between 6 and 12 kilometers (4– 7. 5 mi) wide, with a total area of 360 square kilometers (139 sq mi).
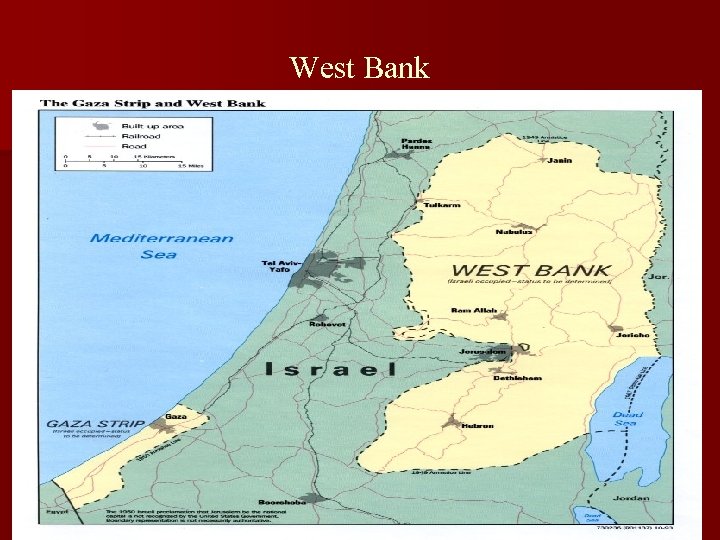 West Bank
West Bank
 Yom Kippur Ø October 1973 – Egypt & Syria once again invade Israel in an attempt to vindicate the disastrous 6 -Day-War Ø Yom Kippur is a Jewish religious observance Ø Israel, once again, defeats invading military and captures large portion of Golan Heights
Yom Kippur Ø October 1973 – Egypt & Syria once again invade Israel in an attempt to vindicate the disastrous 6 -Day-War Ø Yom Kippur is a Jewish religious observance Ø Israel, once again, defeats invading military and captures large portion of Golan Heights
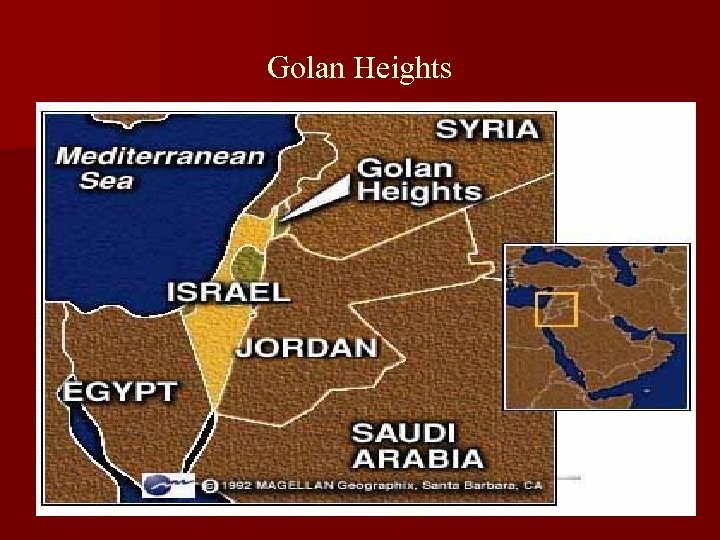 Golan Heights
Golan Heights
 Aftermath Ø Nuclear showdown b/t Superpowers ( Nixon vs. Brezhnev) – Anwar Sadat asks for Soviet help Ø Israel captures large portion of Golan Heights Ø New American President arrives on the scene:
Aftermath Ø Nuclear showdown b/t Superpowers ( Nixon vs. Brezhnev) – Anwar Sadat asks for Soviet help Ø Israel captures large portion of Golan Heights Ø New American President arrives on the scene:
 The Road Map Ø Carter hoped his legacy would be defined by an end to the Middle East Conflict Ø His efforts culminated in the Camp David Accords
The Road Map Ø Carter hoped his legacy would be defined by an end to the Middle East Conflict Ø His efforts culminated in the Camp David Accords
 Camp David Fails n Despite a series of promises made, neither side could agree on a path for peace n Core issue was forced resettlement of Palestinians
Camp David Fails n Despite a series of promises made, neither side could agree on a path for peace n Core issue was forced resettlement of Palestinians
 Intifada - Resistance Ø In the lead up to Yom Kippur the Jewish gov’t actively re-settled thousands of Arabs Ø Lead to the formation of the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) in 1967 Ø The PLO pushes for Intifada – uprising – all Palestinian people resist Israeli in any manner they can
Intifada - Resistance Ø In the lead up to Yom Kippur the Jewish gov’t actively re-settled thousands of Arabs Ø Lead to the formation of the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) in 1967 Ø The PLO pushes for Intifada – uprising – all Palestinian people resist Israeli in any manner they can

 How to Resist? As the 1970 s rolled into the 1980 s the PLO waged various resistance campaigns n Terrorism was a fixture n Black September & the Munich Olympics – 11 Israeli athletes killed n
How to Resist? As the 1970 s rolled into the 1980 s the PLO waged various resistance campaigns n Terrorism was a fixture n Black September & the Munich Olympics – 11 Israeli athletes killed n
 Role of Religion n n Muslim Arabs linked oppression in Palestine with the concept of Jihad (“Struggle or war”) Dawson Field Hijackings – 4 planes hijacked in Jordan Violence becomes a daily occurrence in Israel Religious mandate to fight against the infidel
Role of Religion n n Muslim Arabs linked oppression in Palestine with the concept of Jihad (“Struggle or war”) Dawson Field Hijackings – 4 planes hijacked in Jordan Violence becomes a daily occurrence in Israel Religious mandate to fight against the infidel
 The Net Tightens n n Israel significantly restricts the movements of Palestinians Gaza and the West Bank become military zones Documentation needed / search and seizure permissible Israel slowly creates additional settlements
The Net Tightens n n Israel significantly restricts the movements of Palestinians Gaza and the West Bank become military zones Documentation needed / search and seizure permissible Israel slowly creates additional settlements
 A Road with no Destination From Intafada 1 to Intafada 2 several attempts at peace are made n Deals focus on land for peace n 2 major road blocks 1) Palestinian terrorism 2) Israeli land grabs and restrictions
A Road with no Destination From Intafada 1 to Intafada 2 several attempts at peace are made n Deals focus on land for peace n 2 major road blocks 1) Palestinian terrorism 2) Israeli land grabs and restrictions
 Israel 2014 n The PLO has lost its influence and splintered Palestinian Authority Fatah Moderate Hamas More Radical
Israel 2014 n The PLO has lost its influence and splintered Palestinian Authority Fatah Moderate Hamas More Radical
 Restriction n Israel has erected Berlin-like walls around Gaza n Shelling is a regular occurrence (concern with population density)
Restriction n Israel has erected Berlin-like walls around Gaza n Shelling is a regular occurrence (concern with population density)
 2 State Solution Peace talks now focus on a 2 state plan n Palestine & Israel n No formalized plan – so far n
2 State Solution Peace talks now focus on a 2 state plan n Palestine & Israel n No formalized plan – so far n
 Canada n The Harper government is a staunch supporter of Israel n Condemns Hamas n Canada sends millions in aid to Israel every year – most spent on military
Canada n The Harper government is a staunch supporter of Israel n Condemns Hamas n Canada sends millions in aid to Israel every year – most spent on military
 The Road to Peace
The Road to Peace
 The Case for Israel 1937 Peel Commission
The Case for Israel 1937 Peel Commission
 UN Resolution 242 Land For Peace
UN Resolution 242 Land For Peace
 The Current State You Tell Me: What is the current state of the Israel/Palestine conflict? Summarize events from 2009 -2012
The Current State You Tell Me: What is the current state of the Israel/Palestine conflict? Summarize events from 2009 -2012
 No End in Sight Ø Continued loss of Palestinian territories – Military control Ø Siege of Gaza Ø Growth of Hamas and Hezbollah Ø Palestinian Authority Two State Solution
No End in Sight Ø Continued loss of Palestinian territories – Military control Ø Siege of Gaza Ø Growth of Hamas and Hezbollah Ø Palestinian Authority Two State Solution
 Mess-o-Potamia Name of the peace plan during the post Intafada era but pre-Obama A) Land for peace B) 2 state solution C) Guns for land
Mess-o-Potamia Name of the peace plan during the post Intafada era but pre-Obama A) Land for peace B) 2 state solution C) Guns for land
 n Nasser’s A) B) C) plan to combat Zionism Muslim Solidarity Pan Arab Nationalism Islamic Jihad
n Nasser’s A) B) C) plan to combat Zionism Muslim Solidarity Pan Arab Nationalism Islamic Jihad
 n Name A) B) C) of the failed 1993 peace deal Norway Agreement Potsdam Conference Oslo Accords
n Name A) B) C) of the failed 1993 peace deal Norway Agreement Potsdam Conference Oslo Accords
 n Group A) B) C) responsible for Munich Massacre Al Qaeda Black September Al Shahaab
n Group A) B) C) responsible for Munich Massacre Al Qaeda Black September Al Shahaab
 n Controlling Fatah B) PLM C) Hamas A) Gaza Strip government
n Controlling Fatah B) PLM C) Hamas A) Gaza Strip government
 n Who A) B) C) D) is to blame? Israel Palestine Combination of both USA and UK
n Who A) B) C) D) is to blame? Israel Palestine Combination of both USA and UK



