f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Explanation-based constraint programming Narendra Jussien ナレンドラ・ジュシエン École des Mines de Nantes 助教授 AFPC 理事長 e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 1/48

Outline n n n context part 1 : explanations some definitions part 2 : using explanations part 3 : computation and implementations general overview and current work e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 2/48

Context and origin Dynamic constraint problems e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 3/48

Context Dynamic problems n Application domains l l l n Evolving problem structure l l n Online planning, mission planning Interactive / distributed solving Debugging, analysis Adding/removing constraints Before / While / After solving Key points l l e-constraints Avoiding re-computation (or being as efficient as possible) Avoiding radical changes between consecutive solutions FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 9/48

Part 1 explanations e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 10/48

Ph. D thesis (97) Dynamic problems n Main difficulties l Incremental constraint removal – How undoing past effects with no from scratch recomputation? l Avoiding « thrashing » phenomena – Avoiding already explored situations l Handling over-constrained problems – What if too many constraints are added? n A unique tool: event explanations l e-constraints Subset of constraints whose conjunction leads to a given event: value removal, contradiction, constraint addition, etc. FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 11/48
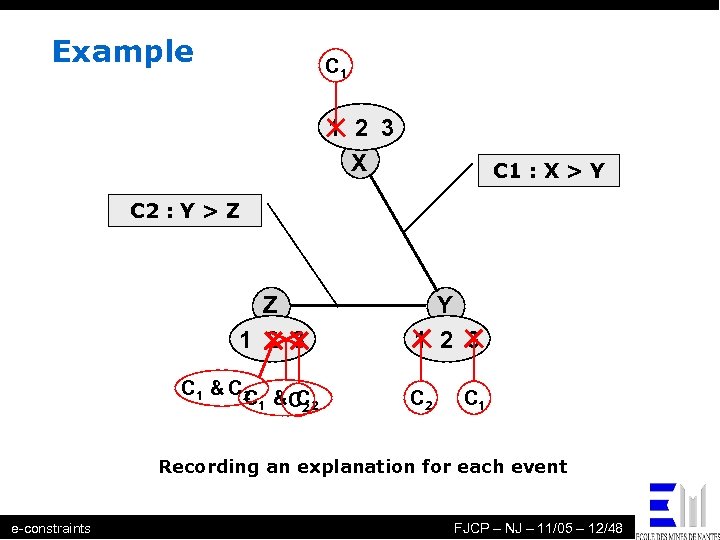
Example C 1 1 2 3 X C 1 : X > Y C 2 : Y > Z Z 1 2 3 C 1 & C 2 & C C 1 C 2 2 Y 1 2 3 C 2 C 1 Recording an explanation for each event e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 12/48

Beware! n Explanations vs. (A)TMS l l n (A)TMS = set(s) of hypothesis justifying some reasoning Explanations = (A)TMS “light” Explanations vs. nogoods l l Nogood : globally inconsistent partial assignment Explanation = “justified” nogood – Set of constraints justifying inconstencies n Explanations vs. “explanations” [Ilog version ] l Ilog = locally inconsistent set of constraints – also called “conflict sets” l e-constraints here = globally inconsistent set of constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 13/48

Ph. D thesis conclusions Explanations are interesting n Overcoming difficulties l Direct access to past effects of a constraint – Events justified by any explanation containing the given constraint l Avoiding “thrashing” – Explanations as a compact and generic information about situations to be avoided l Handling over-constrained problems – Focusing on constraints really responsible for the contradiction – Using incremental removal e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 14/48

Part 2 Using explanations Solving dynamic problems Analyzing and debugging constraints Defining new solving techniques e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 15/48

Explanations for dynamic problems Theoretical aspects Practical applications e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 16/48
![Explanations for dynamic problems Theoretical aspects n [FLAIRS’ 03] Relation between explanations and theoretical Explanations for dynamic problems Theoretical aspects n [FLAIRS’ 03] Relation between explanations and theoretical](https://present5.com/presentation/f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12/image-12.jpg)
Explanations for dynamic problems Theoretical aspects n [FLAIRS’ 03] Relation between explanations and theoretical models for solving constraint problems l Proof-tree – Relation between explanations and propagation rules l Explanation = constraints appearing in a “logical” chain of rules n A formal viewpoint for constraint removal l Undoing past effects of a given constraint – Formal definition of the set of events to be undone l Constraint re-propagation – Formal characterization of constraints (rules) to be re-propagated n Interests l Simplified proofs for dynamic constraint removal algorithms – AC|DC, Dn. AC 4, Dn. AC 6, … l e-constraints A unique definition for both formal and operational aspects FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 17/48

Explanations for dynamic problems Applications n Dynamic scheduling problems l Shop scheduling problems – The RIO system l Renewable resources scheduling problems [PATAT’ 02] – Dynamic RCPSP : Abdallah Elkhyari’s Ph. D thesis (2003) n Timetabling problems (EMN) l l Week-scheduling taking into account individual student’s choices, teacher’s constraints, incompatibilities Automated solving and simulation – From one week to less than one minute for solving the problem – Simulation tool for the planner l e-constraints Student work [PATAT’ 04] FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 18/48
Explanations for dynamic problems Difficulties n Tools for analysis and simulation l l l n Providing information to the user ? How using explanation to help understanding the situation ? What simulation tools ? Explanations for global constraints e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 19/48

Explanations for analysis, debugging, and simulation Providing information to the user e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 20/48

Analysis / Debugging / Simulation Using explanations n Explaining contradictions l n Explaining why the expected solution is not present l n Explanation for value removals New simulation tools for constraints addition/removal : reusing past work ? l n Look at the explanation Recording past explanations (only “relevant” ones) Explaining “no response”: where is the bottleneck ? l Analyzing the explanation network – Dynamic links between constraints (through propagation) e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 21/48
Analysis / Debugging / Simulation User interaction n The user’s point of view l n The solver’s point of view l l n High level of abstraction, problem-related concepts Low level constraints: X 250 > Y 240 + 4 Problem-related concepts invisible The explanation’s point of view l e-constraints Currently: low level constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 22/48
![Analysis / Debugging / Simulation User interaction [WS ICLP’ 01] Conference projection Talks Integrity Analysis / Debugging / Simulation User interaction [WS ICLP’ 01] Conference projection Talks Integrity](https://present5.com/presentation/f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12/image-18.jpg)
Analysis / Debugging / Simulation User interaction [WS ICLP’ 01] Conference projection Talks Integrity Not day 4 MP e-constraints Options AM MP 4 No simult. MP MA FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 23/48
![Analysis / Debugging / Simulation Vizualizing explanations n n n [FLAIRS’ 04, SOFTVIS’ 05] Analysis / Debugging / Simulation Vizualizing explanations n n n [FLAIRS’ 04, SOFTVIS’ 05]](https://present5.com/presentation/f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12/image-19.jpg)
Analysis / Debugging / Simulation Vizualizing explanations n n n [FLAIRS’ 04, SOFTVIS’ 05] Establishing links between variables and constraints through exp Dynamic vs. static structure of the problem Matrix representation e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 24/48

Explanations and new solving techniques e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 25/48
![Explanations and new solving techniques Foundations [ILPS’ 97] [mac -dbt (pb: Problem) : void Explanations and new solving techniques Foundations [ILPS’ 97] [mac -dbt (pb: Problem) : void](https://present5.com/presentation/f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12/image-21.jpg)
Explanations and new solving techniques Foundations [ILPS’ 97] [mac -dbt (pb: Problem) : void -> while Un. Instantiated. Vars not empty ( try ( variable choice, enumerate(pb), value choice propagate(pb) ) catch contradiction ( backtrack(pb) ) )] Analyzing failure causes (explanations) Replace backtracking with repair e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 26/48
![Explanations and new solving techniques New algorithms n MAC-DBT l l l [CP’ 00] Explanations and new solving techniques New algorithms n MAC-DBT l l l [CP’ 00]](https://present5.com/presentation/f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12/image-22.jpg)
Explanations and new solving techniques New algorithms n MAC-DBT l l l [CP’ 00] Combining constraint propagation and dynamic backtracking [Ginsberg, 93] Important improvements for structured problems Improved stability 13 2 n 8 3 1 4 6 14 5 9 7 10 12 11 Dynamic Domain Splitting l l e-constraints [ECAI’ 98] MAC-DBT applied to numeric CSP First algorithm for solving dynamic numeric CSP FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 27/48
![Explanations and new solving techniques New algorithms n Decision-repair l [AIJ’ 02] An original Explanations and new solving techniques New algorithms n Decision-repair l [AIJ’ 02] An original](https://present5.com/presentation/f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12/image-23.jpg)
Explanations and new solving techniques New algorithms n Decision-repair l [AIJ’ 02] An original combination – Local search (on decisions) – Constraint propagation (partial assignments) l Application: open-shop scheduling – Highly competitive compared to ad-hoc techniques l Taillard and Brucker’s instances – Open instances solved for the first time l Guéret and Prins’s hard instances – Important stability improvement e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 28/48
![Explanations and new solving techniques A general framework [MIC’ 03] PLM ( V, C, Explanations and new solving techniques A general framework [MIC’ 03] PLM ( V, C,](https://present5.com/presentation/f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12/image-24.jpg)
Explanations and new solving techniques A general framework [MIC’ 03] PLM ( V, C, CD ) Pb : = ( V, C, CD ) repeat Pb : = filter(Pb) switch check(Pb) one solution : return Pb no solution : Pb : = forget(repair(record(Pb))) otherwise : Pb : = extend(Pb) endswitch until termination n n Propagate, Learn, Move (exploration) Complete (SB, CBJ, MAC-DBT, etc. ) and incomplete instances (decision-repair, tabu, etc. ) e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 29/48

Explanations and new solving techniques Challenges n Problems l l n Combinations l l n First applications: open-shop, RCPSP, timetabling Testing other (structured) problems Other PLM instances New values for the components Software tools l l Providing tools to combine components A first answer: Pa. LM – part of the choco constraint solver l http: //choco. sf. net e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 30/48
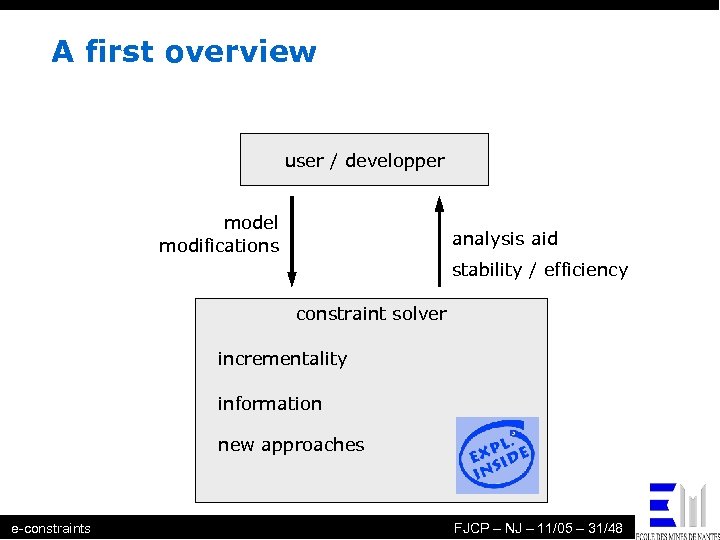
A first overview user / developper yes analysis aid no infinite / efficiency stability waiting model modifications constraint solver incrementality information new approaches e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 31/48

Part 3 Computation and implementations Computing explanations Spreading the news e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 32/48
![Computing explanations Different techniques n a posteriori computation [Junker, 01] l l l n Computing explanations Different techniques n a posteriori computation [Junker, 01] l l l n](https://present5.com/presentation/f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12/image-28.jpg)
Computing explanations Different techniques n a posteriori computation [Junker, 01] l l l n a priori computation [Sqalli, 96; Amilhastre, 02] l l l n Minimal explanation Significant time overhead Information about the resolution is lost Problem pre-compilation Instantaneous response times All possible requests need to be foreseen on the fly computation l e-constraints Pragmatic approach FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 33/48

Computing explanations A pragmatic approach n Using the “embedded” knowledge l n An explicit trace of the behavior of the solver No minimality guaranteed l Hypothesis – efficient/quick solver = “good” explanations n Overhead due to computation and storage l e-constraints Usage overcomes this overhead FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 34/48

Computing explanations A real difficulty: global constraints n “Design patterns” of CP l An efficient solution for a recurrent sub-problem – Generalized differences: all. Different – Renewable resources: cumulative – Regulation constraints: stretch n Main interests – Modeling – Stability / efficiency e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 35/48
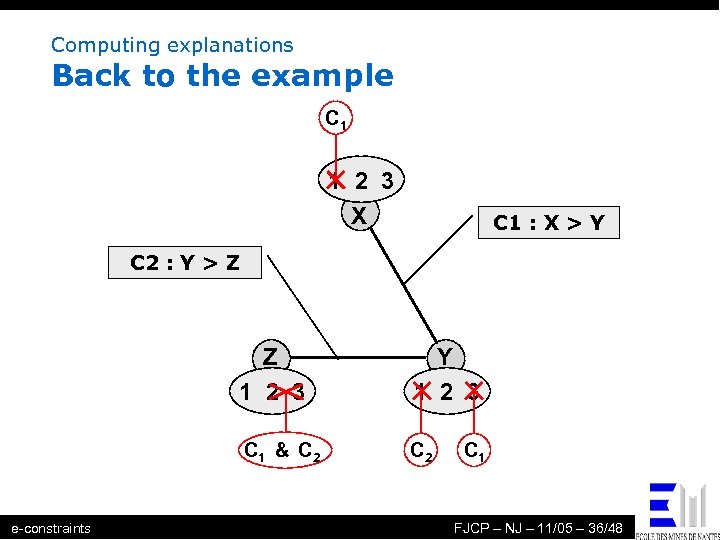
Computing explanations Back to the example C 1 1 2 3 X C 1 : X > Y C 2 : Y > Z Z 1 2 3 C 1 & C 2 e-constraints Y 1 2 3 C 2 C 1 FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 36/48
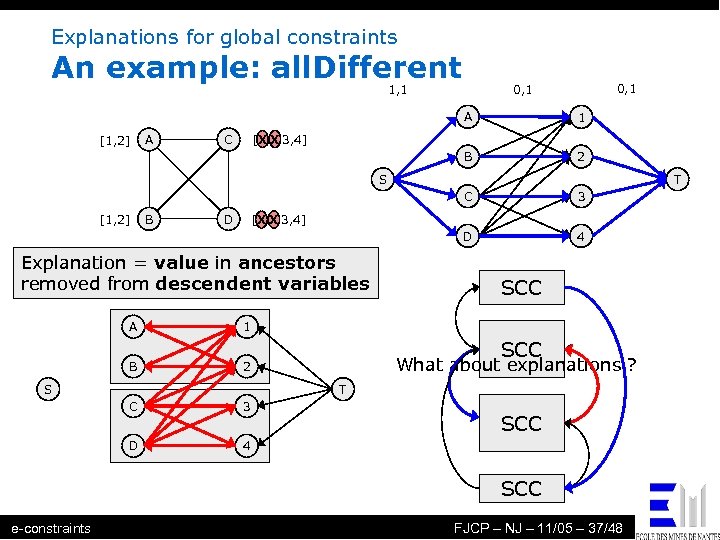
Explanations for global constraints An example: all. Different 1, 1 0, 1 A B [1, 2] A 1 2 [1, 2, 3, 4] XX C S T C D [1, 2] B D 3 4 [1, 2, 3, 4] XX Explanation = value in ancestors removed from descendent variables A 1 B 2 SCC S SCC What about explanations ? T C 3 D 4 SCC e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 37/48

Explanations for global constraints Learning from the experience n When facing complex algorithms l l n Existing instrumented constraints l l n Theoretical study of the algorithm Production of an efficient algorithm for both propagation and explanation computation Unary resources: immediate selections and task intervals N-ary resources: histogram, core-times Flow–based constraints: all. Diff. , GCC, flow [UICS’ 03] Regulation-based constraints: stretch Automated generation l Using a catalog of explained properties e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 38/48

Implementations “Spreading the news” n n A contribution to the “constraints” technology Providing integrated tools l Several implementations – 94/97 : Relax(FD) – scheme, claire – 98/99 : DECorum – bibliothèque C++ library – 00/03 : Pa. LM V 1, V 2, V 3 –choco/claire library – 04 : JPa. LM–JChoco/Java package l There are users (event not from Nantes ) – Newcomers are welcome (cf. timetabling problem) – Forums (cf. www. e-constraints. net) n Providing external tools e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 39/48
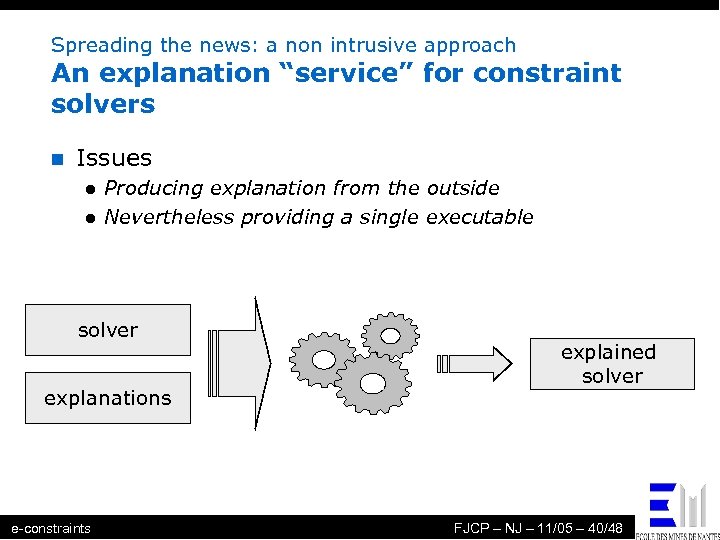
Spreading the news: a non intrusive approach An explanation “service” for constraint solvers n Issues l l Producing explanation from the outside Nevertheless providing a single executable solver explanations e-constraints explained solver FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 40/48
A non intrusive solution Aspect oriented programming n Aim l n Aspect oriented programming (AOP) l l n Expressing transverse functionalities as single modules (explanations, caching, billing, etc. ) A decomposition language (transverse) Code weaver Beyond explanations l Aspects for other solver services – Eg: local search l e-constraints An aspect-oriented language for CP FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 41/48

General overview and future (current) work Several point of views Future work e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 42/48

About “explanations” n From theory … l l l n … to practice l l l n Theoretical fundations for explanations A “practical” theory Several computation approaches studied Interaction tools New search techniques Implementations External impact l l l e-constraints Teaching / Spreading “constraints” A general trend: from the black box to the glass box Other research groups, other techniques FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 44/48

Several fields n Artificial Intelligence l l l n Operations research l l n Discrete and numeric CSP Combining propagation and intelligent backtracking Relations between local search and propagation Shop scheduling (Open-Shop) Resource scheduling (dynamic RCPSP) Timetabling problems Flow problems Software engineering l l l e-constraints Explanation-based solver implementation Constraints and AOP Tools for software development (PTIDEJ) [ASE 01] FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 45/48

Future work n Three main topics l Explanation and global constraints – Towards a “universal” system l New search techniques – Convice people that explanations are “essential” l CP and AOP – Towards real “programming” n New possibilities l Interfacing solvers – Constraints to solver knowledge sharing l Learning techniques for constraint solvers – Improving filtering using gathered information e-constraints FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 47/48
General perspectives n Dynamic problems l l l n Robustness and stability Specific extensions (scheduling, online systems) Practical validation Complex systems l l e-constraints Distributed, collaborative, uncertain environment Multi-objective techniques, probabilistic algorithms, etc. FJCP – NJ – 11/05 – 48/48
f7f2c8a5f197d7159640add61456dd12.ppt