 Experimental Psychology PSY 433 Chapter 9 Conditioning and Learning
Experimental Psychology PSY 433 Chapter 9 Conditioning and Learning
 Willow the Reading Dog n http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=S_Lhwu. N 1 c 1 U n http: //thestarryeye. typepad. com/pets/2009/10/youtube-video-willow-a-dog-that-can-read. html
Willow the Reading Dog n http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=S_Lhwu. N 1 c 1 U n http: //thestarryeye. typepad. com/pets/2009/10/youtube-video-willow-a-dog-that-can-read. html
 Learning n A relatively permanent change in behavior or knowledge as a result of experience n Conditioning means learning. n Classical (respondent) conditioning -- learn an association between two stimuli n Instrumental (operant) conditioning -- learn an association between a behavior and a particular outcome.
Learning n A relatively permanent change in behavior or knowledge as a result of experience n Conditioning means learning. n Classical (respondent) conditioning -- learn an association between two stimuli n Instrumental (operant) conditioning -- learn an association between a behavior and a particular outcome.
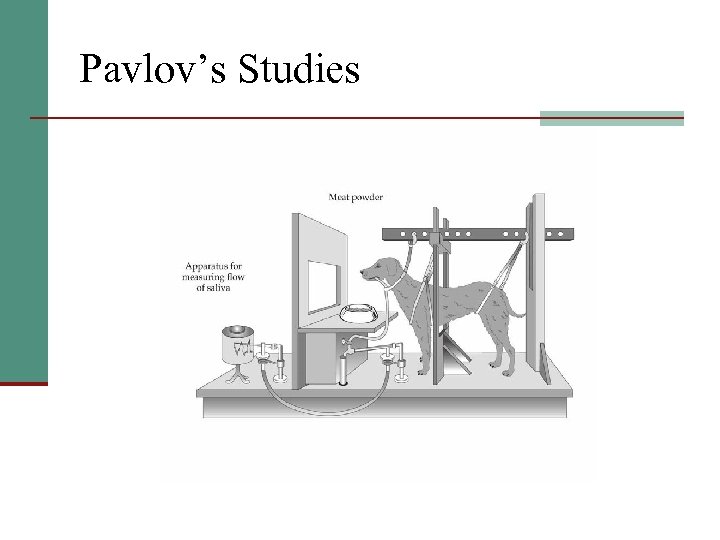 Pavlov’s Studies
Pavlov’s Studies
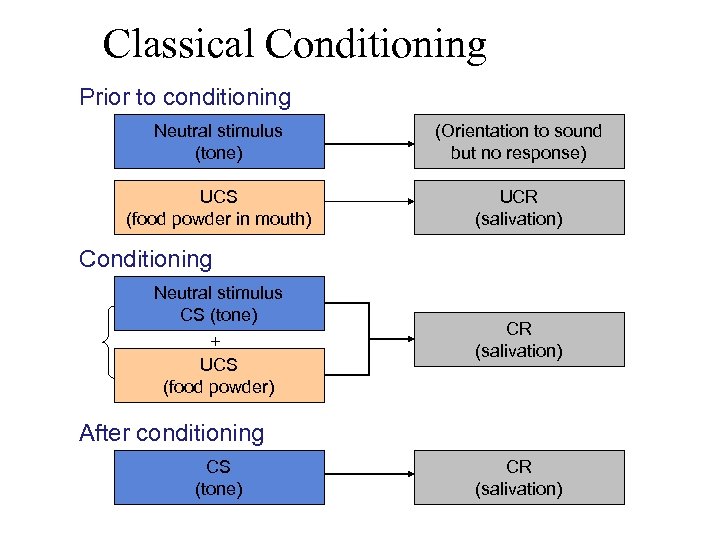 Classical Conditioning Prior to conditioning Neutral stimulus (tone) (Orientation to sound but no response) UCS (food powder in mouth) UCR (salivation) Conditioning Neutral stimulus CS (tone) + UCS (food powder) CR (salivation) After conditioning CS (tone) CR (salivation)
Classical Conditioning Prior to conditioning Neutral stimulus (tone) (Orientation to sound but no response) UCS (food powder in mouth) UCR (salivation) Conditioning Neutral stimulus CS (tone) + UCS (food powder) CR (salivation) After conditioning CS (tone) CR (salivation)
 Classical Conditioning Examples n Dog learns to associate food with the sight of a dog food can. n Patient learns to associate the sight of the dentist’s office with the pain of dental work (drill). n Standing in front of the refrigerator until you feel hungry for something. n Hot dogs at the ballpark, popcorn at the movies. n Phobias – fear of flying.
Classical Conditioning Examples n Dog learns to associate food with the sight of a dog food can. n Patient learns to associate the sight of the dentist’s office with the pain of dental work (drill). n Standing in front of the refrigerator until you feel hungry for something. n Hot dogs at the ballpark, popcorn at the movies. n Phobias – fear of flying.
 Operant Conditioning n Operant conditioning – consequences of a behavior determine whether it will be repeated in the future. Thorndike’s S-R learning. n Also called instrumental conditioning. n n Skinner box – an animal is rewarded each time it makes a specific response.
Operant Conditioning n Operant conditioning – consequences of a behavior determine whether it will be repeated in the future. Thorndike’s S-R learning. n Also called instrumental conditioning. n n Skinner box – an animal is rewarded each time it makes a specific response.
 Positive reinforcement adds a good thing Negative reinforcement removes bad thing Increases Reinforcement + Behavior Consequences Punishment Reduces Punishment adds a bad thing Response cost removes good thing
Positive reinforcement adds a good thing Negative reinforcement removes bad thing Increases Reinforcement + Behavior Consequences Punishment Reduces Punishment adds a bad thing Response cost removes good thing
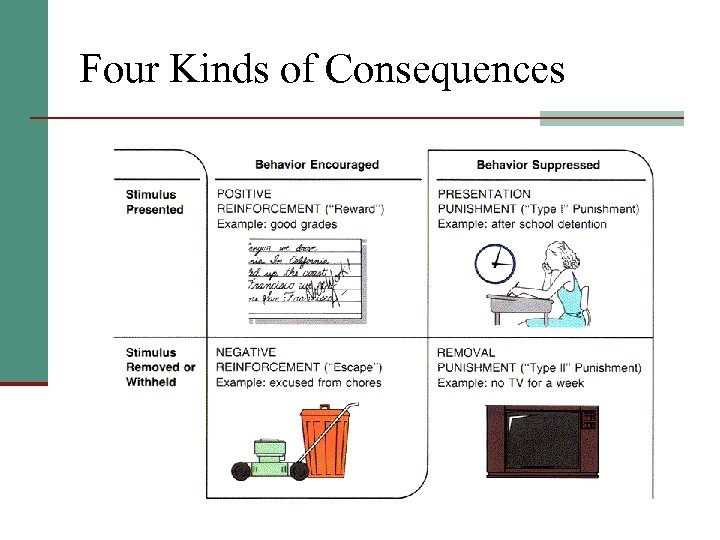 Four Kinds of Consequences
Four Kinds of Consequences
 Creative Punishment
Creative Punishment
 More Terminology n Discriminative stimulus – signals the opportunity to perform a behavior and get a reward. Traffic light tells us when to go. n “Open” sign tells us when we can buy coffee. n n Extinction – after learning, reward is withheld and the behavior gradually stops occurring. n Null contingency – no relationship between reward or punishment and behavior exists.
More Terminology n Discriminative stimulus – signals the opportunity to perform a behavior and get a reward. Traffic light tells us when to go. n “Open” sign tells us when we can buy coffee. n n Extinction – after learning, reward is withheld and the behavior gradually stops occurring. n Null contingency – no relationship between reward or punishment and behavior exists.
 DVs in Learning Experiments n Response rate – number of responses as a function of time. n Response amplitude -- amount of saliva. n Response latency -- time to accomplish a response. n Time to complete a maze n Resistance to extinction -- how long it takes a response to go away once it stops being rewarded.
DVs in Learning Experiments n Response rate – number of responses as a function of time. n Response amplitude -- amount of saliva. n Response latency -- time to accomplish a response. n Time to complete a maze n Resistance to extinction -- how long it takes a response to go away once it stops being rewarded.
 IVs in Learning Experiments n Magnitude of reinforcement (size of reward). n Delay prior to reinforcement. n Amount of deprivation (motivation to obtain the reward). n Intensity of the CS and UCS in classical conditioning.
IVs in Learning Experiments n Magnitude of reinforcement (size of reward). n Delay prior to reinforcement. n Amount of deprivation (motivation to obtain the reward). n Intensity of the CS and UCS in classical conditioning.