8d5d997a32150182e3da4ac2fada6711.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Experiences in Deploying Machines Registration and Integrated Linux Firewall with Traffic Shaper for Large Campus Network Kasom Koth-arsa 1, Surasak Sanguanpong 2, Pirawat Watanpongse 2, Surachai Chitpinityon 3 , Chalermpol Chatampan 3 }Kasom. K, Surasak. S, Pirawat. W, Surachai. Ch, cpccpc}@ku. ac. th Computer Center, Faculty of Engineering of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering 3 Office of Computer Services 1 Engineering 2 Department Kasetsart University APAN, Xi’an, Network Security, 29 th August 2007 This work is partially supported by Commission of Higher Education (CHE), Uni. NET, Thailand 1
Experiences in Deploying Machines Registration and Integrated Linux Firewall with Traffic Shaper for Large Campus Network Kasom Koth-arsa 1, Surasak Sanguanpong 2, Pirawat Watanpongse 2, Surachai Chitpinityon 3 , Chalermpol Chatampan 3 }Kasom. K, Surasak. S, Pirawat. W, Surachai. Ch, cpccpc}@ku. ac. th Computer Center, Faculty of Engineering of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering 3 Office of Computer Services 1 Engineering 2 Department Kasetsart University APAN, Xi’an, Network Security, 29 th August 2007 This work is partially supported by Commission of Higher Education (CHE), Uni. NET, Thailand 1
 Kasetsart University n n Established in 1943 A. D. 7 campuses with ~43, 000 students, ~9600 academic and supported staffs 2
Kasetsart University n n Established in 1943 A. D. 7 campuses with ~43, 000 students, ~9600 academic and supported staffs 2
 Nontri. Net Quick Facts University Network - Nontri. Net n 41, 992 MAC addresses (As of 2007/08/28) n 8, 852 Clients (Personal, Wired) JGN Internet TIEN 2 45 Mbps 155 Mbps 630 Mbps n 3, 269 Clients (Service, Wired) Thai. SARN Uni. Net n 29, 342 Clients (Wireless) 1 Gbps (backup) n 495 Servers Bangkhen n 34 misc. devices 2 Mbps 34 Mbps n 10 Gig. E n Avg. In/out Traffic n 550/490 Mbps 34 Mbps Supan Buri Sri. Racha 34 Mbps Sakon. Nakhon Kampaengsaen 3
Nontri. Net Quick Facts University Network - Nontri. Net n 41, 992 MAC addresses (As of 2007/08/28) n 8, 852 Clients (Personal, Wired) JGN Internet TIEN 2 45 Mbps 155 Mbps 630 Mbps n 3, 269 Clients (Service, Wired) Thai. SARN Uni. Net n 29, 342 Clients (Wireless) 1 Gbps (backup) n 495 Servers Bangkhen n 34 misc. devices 2 Mbps 34 Mbps n 10 Gig. E n Avg. In/out Traffic n 550/490 Mbps 34 Mbps Supan Buri Sri. Racha 34 Mbps Sakon. Nakhon Kampaengsaen 3
 Obstacles & Opportunities n Large number of hosts n n Hard to keep track Non-productive bandwidth usage n P 2 P file sharing Qo. S issues n Security issues n 4
Obstacles & Opportunities n Large number of hosts n n Hard to keep track Non-productive bandwidth usage n P 2 P file sharing Qo. S issues n Security issues n 4
 Special Requirements Fully-integrated information database n Low cost n Customizable n Extensible n Scalable n 5
Special Requirements Fully-integrated information database n Low cost n Customizable n Extensible n Scalable n 5
 Our Designed Features Web-based Machines Registration n Linux Firewall & Traffic Shaper extension n 6
Our Designed Features Web-based Machines Registration n Linux Firewall & Traffic Shaper extension n 6
 SMART (Simple Machine Address Registration Tool) Mandatory Web-based Machines Registration n Registration Enforcement Agent: The Overlord n Centralized Database: Command Center n Distributed Data Entry: the Interface n 7
SMART (Simple Machine Address Registration Tool) Mandatory Web-based Machines Registration n Registration Enforcement Agent: The Overlord n Centralized Database: Command Center n Distributed Data Entry: the Interface n 7
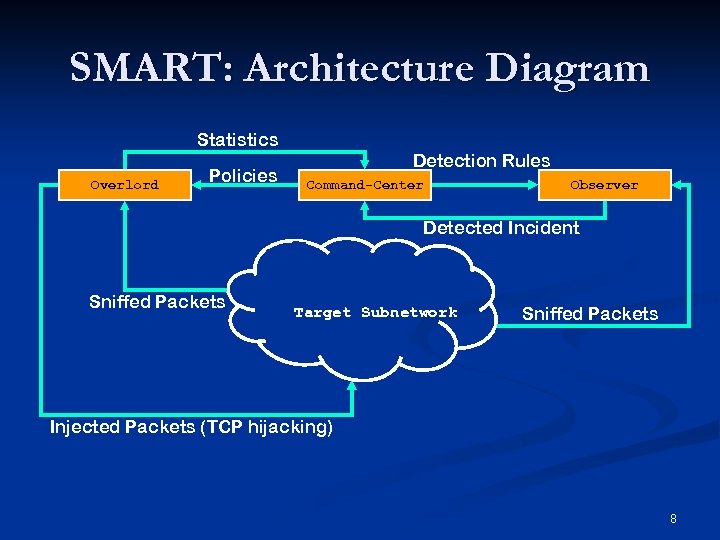 SMART: Architecture Diagram Statistics Overlord Policies Detection Rules Command-Center Observer Detected Incident Sniffed Packets Target Subnetwork Sniffed Packets Injected Packets (TCP hijacking) 8
SMART: Architecture Diagram Statistics Overlord Policies Detection Rules Command-Center Observer Detected Incident Sniffed Packets Target Subnetwork Sniffed Packets Injected Packets (TCP hijacking) 8
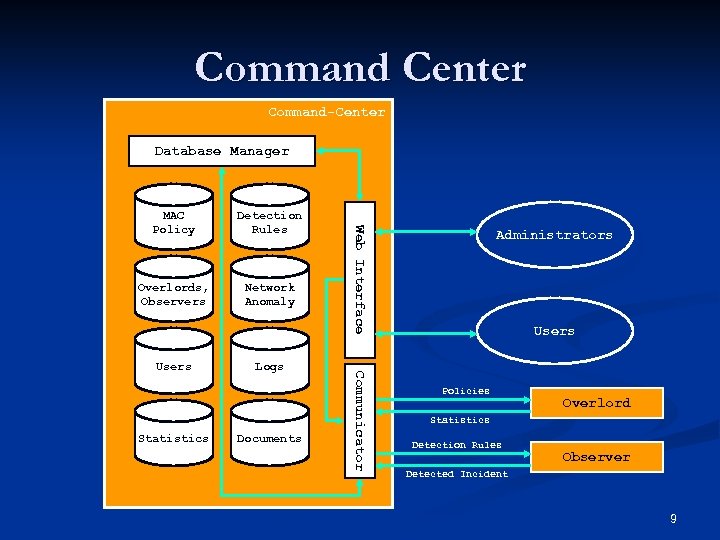 Command Center Command-Center Database Manager Detection Rules Overlords, Observers Network Anomaly Statistics Logs Documents Communicator Users Web Interface MAC Policy Administrators Users Policies Overlord Statistics Detection Rules Observer Detected Incident 9
Command Center Command-Center Database Manager Detection Rules Overlords, Observers Network Anomaly Statistics Logs Documents Communicator Users Web Interface MAC Policy Administrators Users Policies Overlord Statistics Detection Rules Observer Detected Incident 9
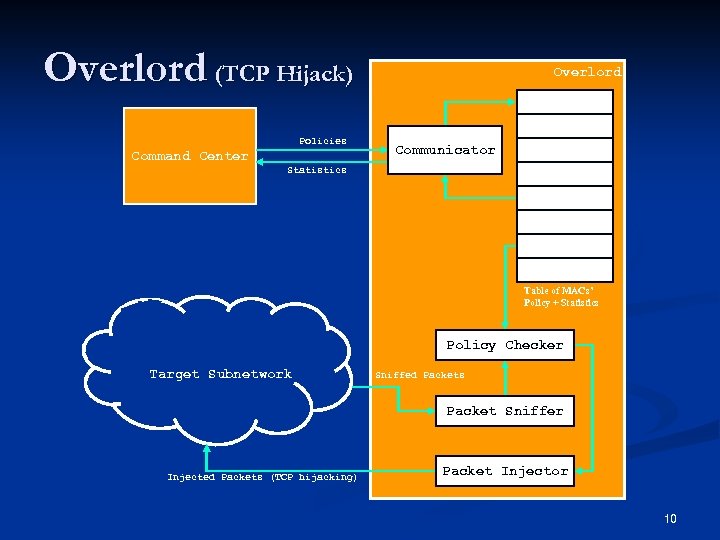 Overlord (TCP Hijack) Policies Command Center Overlord Communicator Statistics Table of MACs’ Policy + Statistics Policy Checker Target Subnetwork Sniffed Packets Packet Sniffer Injected Packets (TCP hijacking) Packet Injector 10
Overlord (TCP Hijack) Policies Command Center Overlord Communicator Statistics Table of MACs’ Policy + Statistics Policy Checker Target Subnetwork Sniffed Packets Packet Sniffer Injected Packets (TCP hijacking) Packet Injector 10
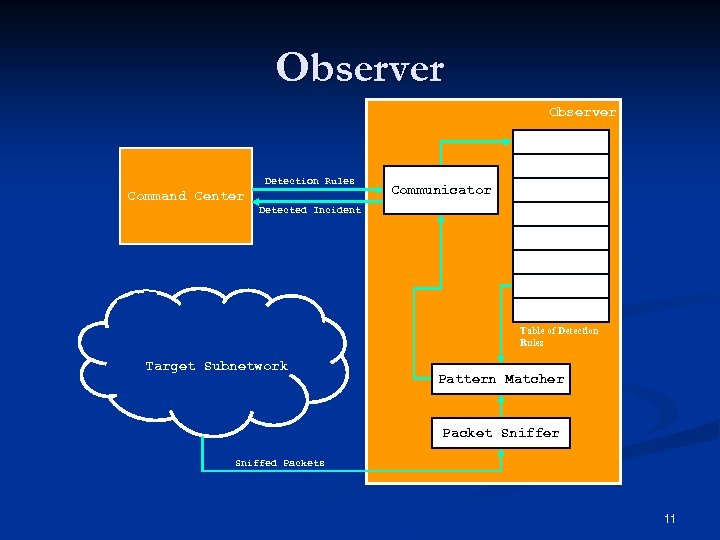 Observer Detection Rules Command Center Communicator Detected Incident Table of Detection Rules Target Subnetwork Pattern Matcher Packet Sniffer Sniffed Packets 11
Observer Detection Rules Command Center Communicator Detected Incident Table of Detection Rules Target Subnetwork Pattern Matcher Packet Sniffer Sniffed Packets 11
 Linux Firewall & Traffic Shaper Extension Intelligent Master Controller n User-friendly configuration interface n Automatic egress SYN-flood/P 2 P blocking n Per-host traffic shaping n 12
Linux Firewall & Traffic Shaper Extension Intelligent Master Controller n User-friendly configuration interface n Automatic egress SYN-flood/P 2 P blocking n Per-host traffic shaping n 12
 Mechanism Use Linux server as a bridge n Traffic classification through iptables n Traffic control through tc n Use IPP 2 P and our in-house daemon to identify P 2 P traffic n Use our in-house daemon to detect some problematic network pattern n 13
Mechanism Use Linux server as a bridge n Traffic classification through iptables n Traffic control through tc n Use IPP 2 P and our in-house daemon to identify P 2 P traffic n Use our in-house daemon to detect some problematic network pattern n 13
 Hardware n Dell Power Edge 2900 Xeon 5160 Dual core(3. 0 GHz) n 1 GB of RAM n 160 GB SATA hard disk n 2 x SUN 10 Gigabit Ethernet Controller PCI Express Card (SR module) n 14
Hardware n Dell Power Edge 2900 Xeon 5160 Dual core(3. 0 GHz) n 1 GB of RAM n 160 GB SATA hard disk n 2 x SUN 10 Gigabit Ethernet Controller PCI Express Card (SR module) n 14
 Software Linux 2. 6. 18 -8. 1. 8. el 5 (Cent. OS’s stocked kernel) on Cent. OS 5 (64 bit) n bridge-utils n ebtables n iptables n IPP 2 P n Our in-house developed daemon for automatically adjust the shaping/blocking policy. n 15
Software Linux 2. 6. 18 -8. 1. 8. el 5 (Cent. OS’s stocked kernel) on Cent. OS 5 (64 bit) n bridge-utils n ebtables n iptables n IPP 2 P n Our in-house developed daemon for automatically adjust the shaping/blocking policy. n 15
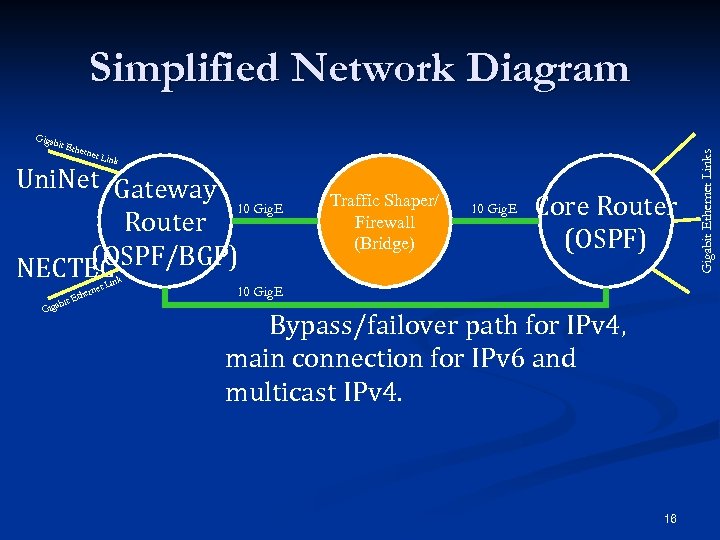 Giga bit E thern et Li nk Uni. Net Gateway 10 Gig. E Router (OSPF/BGP) NECTEC it ab Gig t erne Eth Link Traffic Shaper/ Firewall (Bridge) 10 Gig. E Core Router (OSPF) 10 Gig. E Bypass/failover path for IPv 4, main connection for IPv 6 and multicast IPv 4. 16 Gigabit Ethernet Links Simplified Network Diagram
Giga bit E thern et Li nk Uni. Net Gateway 10 Gig. E Router (OSPF/BGP) NECTEC it ab Gig t erne Eth Link Traffic Shaper/ Firewall (Bridge) 10 Gig. E Core Router (OSPF) 10 Gig. E Bypass/failover path for IPv 4, main connection for IPv 6 and multicast IPv 4. 16 Gigabit Ethernet Links Simplified Network Diagram
 How we shape the traffic Use iptables’ ‘MARK’ target to mark the class of traffic for every packets n Hierarchical Token Bucket (HTB) as packet shaper n Stochastic Fairness Queuing (SFQ) as queuing algorithm n 17
How we shape the traffic Use iptables’ ‘MARK’ target to mark the class of traffic for every packets n Hierarchical Token Bucket (HTB) as packet shaper n Stochastic Fairness Queuing (SFQ) as queuing algorithm n 17
 Traffic Classification Port-based n Content based (L 7) n n n using IPP 2 P through iptables Automatically adjust iptables’ rules using our daemon 18
Traffic Classification Port-based n Content based (L 7) n n n using IPP 2 P through iptables Automatically adjust iptables’ rules using our daemon 18
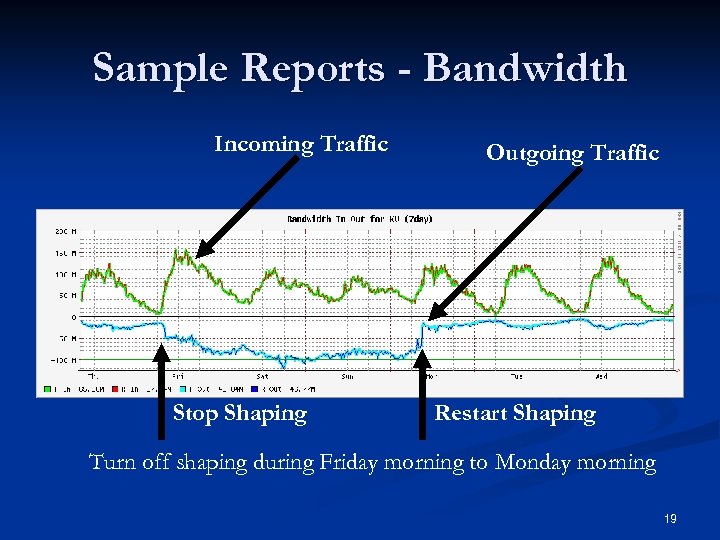 Sample Reports - Bandwidth Incoming Traffic Stop Shaping Outgoing Traffic Restart Shaping Turn off shaping during Friday morning to Monday morning 19
Sample Reports - Bandwidth Incoming Traffic Stop Shaping Outgoing Traffic Restart Shaping Turn off shaping during Friday morning to Monday morning 19
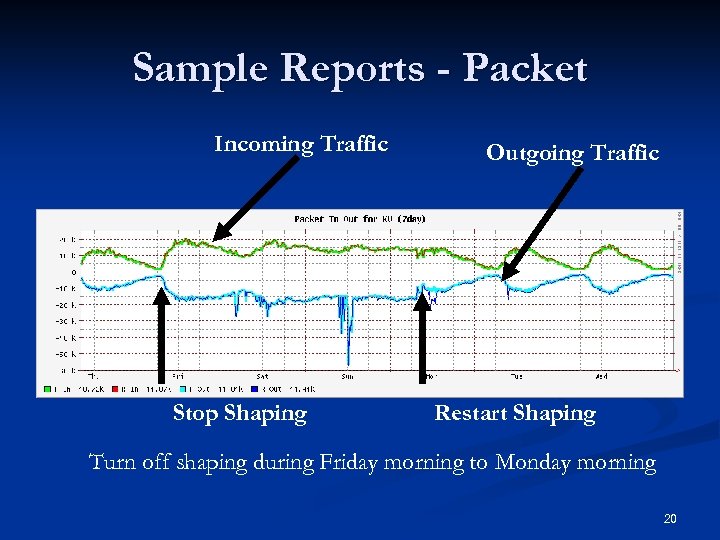 Sample Reports - Packet Incoming Traffic Stop Shaping Outgoing Traffic Restart Shaping Turn off shaping during Friday morning to Monday morning 20
Sample Reports - Packet Incoming Traffic Stop Shaping Outgoing Traffic Restart Shaping Turn off shaping during Friday morning to Monday morning 20
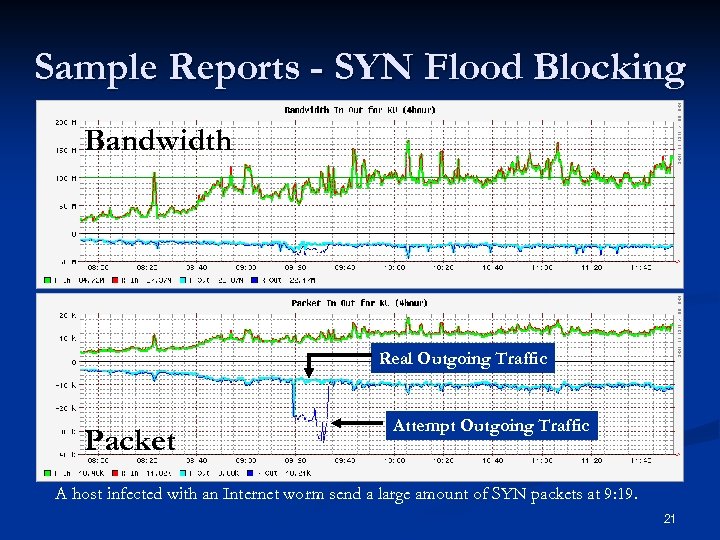 Sample Reports - SYN Flood Blocking Bandwidth Real Outgoing Traffic Packet Attempt Outgoing Traffic A host infected with an Internet worm send a large amount of SYN packets at 9: 19. 21
Sample Reports - SYN Flood Blocking Bandwidth Real Outgoing Traffic Packet Attempt Outgoing Traffic A host infected with an Internet worm send a large amount of SYN packets at 9: 19. 21
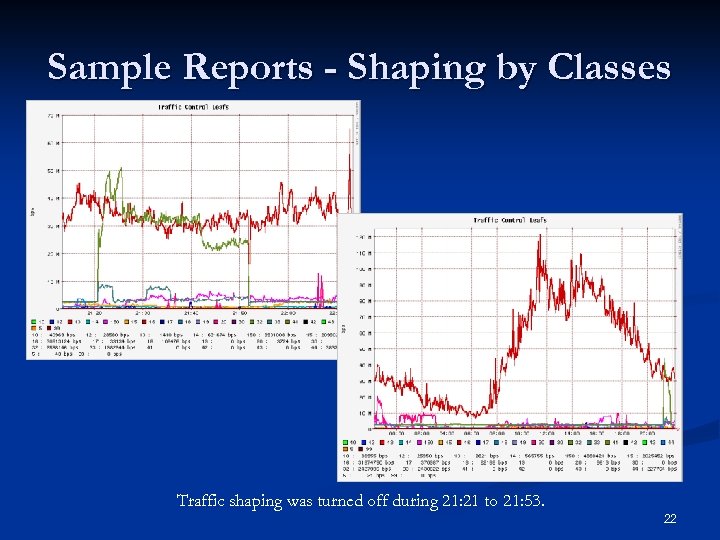 Sample Reports - Shaping by Classes Traffic shaping was turned off during 21: 21 to 21: 53. 22
Sample Reports - Shaping by Classes Traffic shaping was turned off during 21: 21 to 21: 53. 22
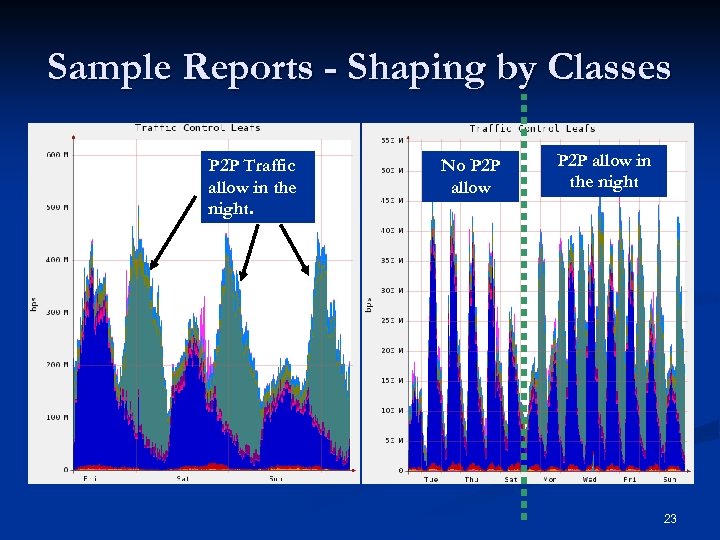 Sample Reports - Shaping by Classes P 2 P Traffic allow in the night. No P 2 P allow in the night 23
Sample Reports - Shaping by Classes P 2 P Traffic allow in the night. No P 2 P allow in the night 23
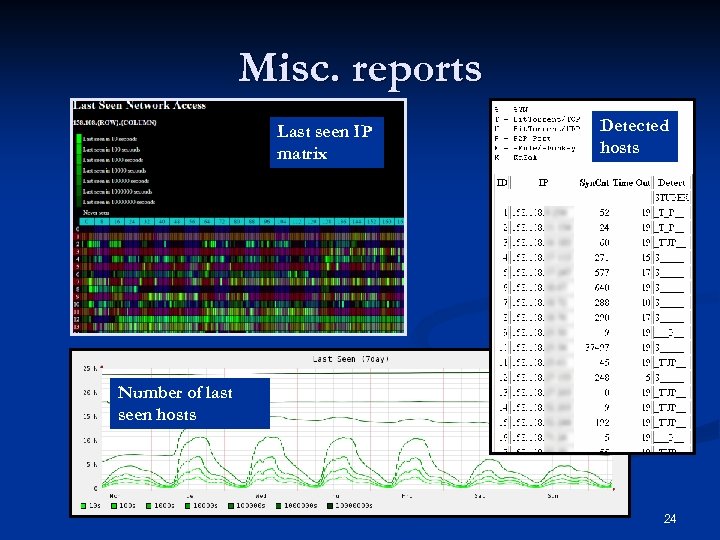 Misc. reports Last seen IP matrix Detected hosts Number of last seen hosts 24
Misc. reports Last seen IP matrix Detected hosts Number of last seen hosts 24
 Conclusions n Complete control of unregistered machines n Prevent unauthorized/unregistered net usage Automatic co-operate between registration and firewall/traffic shaping n Complete control of P 2 P traffics under desired policy (class, usage period, bandwidth, etc(. n Prevent our machines from becoming a source of SYN-flood attack n 25
Conclusions n Complete control of unregistered machines n Prevent unauthorized/unregistered net usage Automatic co-operate between registration and firewall/traffic shaping n Complete control of P 2 P traffics under desired policy (class, usage period, bandwidth, etc(. n Prevent our machines from becoming a source of SYN-flood attack n 25
 Conclusions (cont. ) Free up NOC officer’s time n Real-world, low-cost, high-efficiency implementation (currently online) n 26
Conclusions (cont. ) Free up NOC officer’s time n Real-world, low-cost, high-efficiency implementation (currently online) n 26
 References n n n The Official Bit. Torrent Home Page http: //www. bittorrent. org/ Kazaa http: //www. kazaa. com/ Netfilter/iptables project homepage http: //www. netfilter. org/ Official IPP 2 P homepage http: //www. ipp 2 p. org/ HTB home http: //luxik. cdi. cz/~devik/qos/htb/ SFQ queuing discipline http: //www. opalsoft. net/qos/DS-25. htm 27
References n n n The Official Bit. Torrent Home Page http: //www. bittorrent. org/ Kazaa http: //www. kazaa. com/ Netfilter/iptables project homepage http: //www. netfilter. org/ Official IPP 2 P homepage http: //www. ipp 2 p. org/ HTB home http: //luxik. cdi. cz/~devik/qos/htb/ SFQ queuing discipline http: //www. opalsoft. net/qos/DS-25. htm 27
 Questions? 28
Questions? 28
 Thank you 29
Thank you 29


