e15df16c094fb5d826fc1747ad0d4215.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 EXPERIENCE WITH TECHNOLOGY NEEDS ASSESSMENT, DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION ANNEX I EXPERT GROUP SEMINAR ON WORKING TOGETHER TO RESPOND TO CLIMATE CHANGE 21 -22 MARCH 2005, OECD HEADQUARTERS, PARIS, FRANCE WILLIAM KOJO AGYEMANG-BONSU NATIONAL CLIMATE CHANGE COORDINATOR ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY, GHANA
EXPERIENCE WITH TECHNOLOGY NEEDS ASSESSMENT, DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION ANNEX I EXPERT GROUP SEMINAR ON WORKING TOGETHER TO RESPOND TO CLIMATE CHANGE 21 -22 MARCH 2005, OECD HEADQUARTERS, PARIS, FRANCE WILLIAM KOJO AGYEMANG-BONSU NATIONAL CLIMATE CHANGE COORDINATOR ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY, GHANA
 OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION w Elements of UNFCCC Technology Development and Transfer Framework w Ghana’s Technology Needs Assessment w CFL Example w Challenges w Conclusions
OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION w Elements of UNFCCC Technology Development and Transfer Framework w Ghana’s Technology Needs Assessment w CFL Example w Challenges w Conclusions
 Elements of UNFCCC Technology Development and Transfer Framework 1) Technology Needs Assessment n n 2) 3) 4) 5) Information needs Capacity building needs – institutional, human Assessment of enabling environment – systemic capacities, including barriers and actions to overcome them Financing Technology information Enabling Environment Capacity building Mechanisms for technology transfer – institutional and financing aspects
Elements of UNFCCC Technology Development and Transfer Framework 1) Technology Needs Assessment n n 2) 3) 4) 5) Information needs Capacity building needs – institutional, human Assessment of enabling environment – systemic capacities, including barriers and actions to overcome them Financing Technology information Enabling Environment Capacity building Mechanisms for technology transfer – institutional and financing aspects
 Ghana’s Technology Needs Assessment
Ghana’s Technology Needs Assessment
 Goals of the TNA w Contribute to global effort towards sustainable development and in particular the protection of the climate system. w Communicate to COP under UNFCCC and the global community Ghana’s climate change technology requirements. w Identify a portfolio of technology development and transfer programmes that have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to Ghana’s sustainable development
Goals of the TNA w Contribute to global effort towards sustainable development and in particular the protection of the climate system. w Communicate to COP under UNFCCC and the global community Ghana’s climate change technology requirements. w Identify a portfolio of technology development and transfer programmes that have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to Ghana’s sustainable development
 Immediate Objectives w Identify, analyze and prioritize technologies that can form the basis for a portfolio of ESTs projects and programmes w Identify human, institutional and systemic capacity needs that ensure the smooth development, transfer and acquisition of ESTs w Enlist interest and commitment from key stakeholders and forge partnerships to support investment or barrier removal actions for purposes of enhancing the commercialization (or otherwise), and the diffusion of high priority technologies
Immediate Objectives w Identify, analyze and prioritize technologies that can form the basis for a portfolio of ESTs projects and programmes w Identify human, institutional and systemic capacity needs that ensure the smooth development, transfer and acquisition of ESTs w Enlist interest and commitment from key stakeholders and forge partnerships to support investment or barrier removal actions for purposes of enhancing the commercialization (or otherwise), and the diffusion of high priority technologies
 Stakeholders w w w w Government Quasi-Government Business Associations Financial Institutions NGOs Research/Academia Development Partners
Stakeholders w w w w Government Quasi-Government Business Associations Financial Institutions NGOs Research/Academia Development Partners
 Resources for Ghana’s Needs Assessment w Major funding from UNDP/GEF w Technical support provided by NREL with funds from CTI/USDOE
Resources for Ghana’s Needs Assessment w Major funding from UNDP/GEF w Technical support provided by NREL with funds from CTI/USDOE
 Overview of Ghana’s Approach to Needs Assessment w w w Development of background documentation Stakeholder identification (national/international) Organization of scoping meeting/stakeholder consultations Establishment of Technology selection criteria Choosing sectors/sub-sectors for assessment Establishment of core/expert teams Prioritizations of technologies Holding donor consultations In-depth analysis Preparation of needs assessment report Development of technology transfer implementation plan Publication of TNA final report
Overview of Ghana’s Approach to Needs Assessment w w w Development of background documentation Stakeholder identification (national/international) Organization of scoping meeting/stakeholder consultations Establishment of Technology selection criteria Choosing sectors/sub-sectors for assessment Establishment of core/expert teams Prioritizations of technologies Holding donor consultations In-depth analysis Preparation of needs assessment report Development of technology transfer implementation plan Publication of TNA final report
 Technology Priorities Setting Selection Criteria q q Development benefits Market Potential Contribution Towards Mitigating Climate Change Additional Attributes
Technology Priorities Setting Selection Criteria q q Development benefits Market Potential Contribution Towards Mitigating Climate Change Additional Attributes
 Selection Criteria q Development benefits Job creation Ø Wealth creation for the poor Ø Capacity building Ø Use of local resources Ø Contribution to GDP growth Ø Good effect on balance of trade Ø Health Improvement Ø Skills development Ø
Selection Criteria q Development benefits Job creation Ø Wealth creation for the poor Ø Capacity building Ø Use of local resources Ø Contribution to GDP growth Ø Good effect on balance of trade Ø Health Improvement Ø Skills development Ø
 Selection Criteria q Market Potential Ø Level of initial capital outlay Ø Affordability Ø Investment sustainability Ø Low maintenance – durability Ø Commercial availability and Ø Replicability
Selection Criteria q Market Potential Ø Level of initial capital outlay Ø Affordability Ø Investment sustainability Ø Low maintenance – durability Ø Commercial availability and Ø Replicability
 Selection Criteria q Contribution Towards Mitigating Climate Change Ø Ø Ø No or low GHG emissions Low potential for “leakage” Enhance sinks and waste recovery
Selection Criteria q Contribution Towards Mitigating Climate Change Ø Ø Ø No or low GHG emissions Low potential for “leakage” Enhance sinks and waste recovery
 Selection Criteria q Additional Attributes Ø Ø Ø Able to meet other social need(s) and are socially acceptable Promote international trade in the context of north-south and south-south cooperation Promote sub-regional cooperation with respect to optimization in use of resources for development
Selection Criteria q Additional Attributes Ø Ø Ø Able to meet other social need(s) and are socially acceptable Promote international trade in the context of north-south and south-south cooperation Promote sub-regional cooperation with respect to optimization in use of resources for development
 Contents of the Needs Assessment Report w w w Executive Summary Technology Transfer Implementation Plan – Indepth Analysis National Environmental Context Technology Priorities Review of Legislative and Institutional Framework Conclusions and Recommendations
Contents of the Needs Assessment Report w w w Executive Summary Technology Transfer Implementation Plan – Indepth Analysis National Environmental Context Technology Priorities Review of Legislative and Institutional Framework Conclusions and Recommendations
 Technology Implementation Plan – In-depth Analysis w w w Background of Technology - information Barriers to the development and transfer Suggested Actions to Remove Barriers Ø Ghana Actions v v Ø Existing programmes and policies Additional actions Actions expected from International Community
Technology Implementation Plan – In-depth Analysis w w w Background of Technology - information Barriers to the development and transfer Suggested Actions to Remove Barriers Ø Ghana Actions v v Ø Existing programmes and policies Additional actions Actions expected from International Community
 Technology Implementation Plan – In-depth Analysis w Expected results of technology transfer • • • w List of stakeholders • • w w Development, Economic and Social Benefits Market Penetration and sustainability GHG reduction and other environmental benefits National International (Informed by TT Clear website, CTI personal communication and website) Capacity needs Recommendations for the creation of enabling environment and general conclusions
Technology Implementation Plan – In-depth Analysis w Expected results of technology transfer • • • w List of stakeholders • • w w Development, Economic and Social Benefits Market Penetration and sustainability GHG reduction and other environmental benefits National International (Informed by TT Clear website, CTI personal communication and website) Capacity needs Recommendations for the creation of enabling environment and general conclusions
 Top Priority Technologies w Energy efficient lighting using compact fluorescent lamps w Industrial energy efficiency improvements – demand side management including power factor improvement and boiler efficiency enhancement w Methane gas capture from landfills w Use of bio-fuels (jatropha)
Top Priority Technologies w Energy efficient lighting using compact fluorescent lamps w Industrial energy efficiency improvements – demand side management including power factor improvement and boiler efficiency enhancement w Methane gas capture from landfills w Use of bio-fuels (jatropha)
 CFL EXAMPLE
CFL EXAMPLE
 Background w Power shortages w Drought and low hydro availability w Electricity rate reform n ~100% retail rate increases in 2002 w Lighting end use significant n n One third of energy share Coincident with peak w CFL promotion as key part of response
Background w Power shortages w Drought and low hydro availability w Electricity rate reform n ~100% retail rate increases in 2002 w Lighting end use significant n n One third of energy share Coincident with peak w CFL promotion as key part of response
 Goals w Transform the Ghanaian lighting market from incandescent lamps to CFL w Reduce the risk of a power crisis w Mitigate the impact of electricity price hikes, on electricity consumers w Reduce power demand need for added generation
Goals w Transform the Ghanaian lighting market from incandescent lamps to CFL w Reduce the risk of a power crisis w Mitigate the impact of electricity price hikes, on electricity consumers w Reduce power demand need for added generation
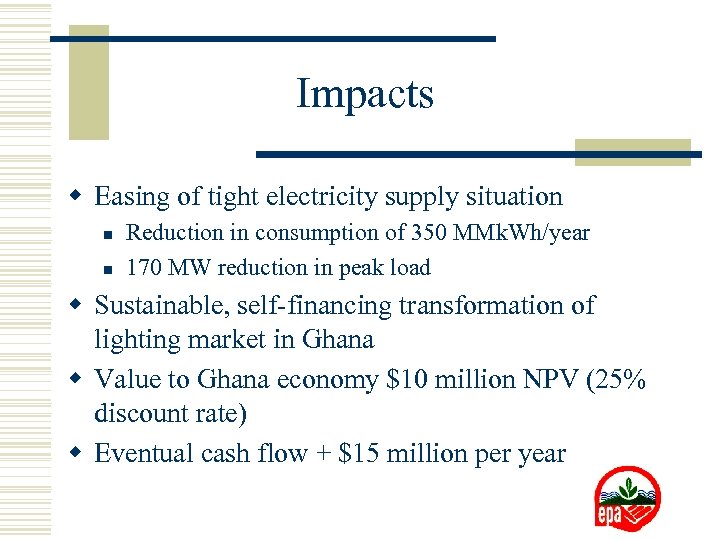 Impacts w Easing of tight electricity supply situation n n Reduction in consumption of 350 MMk. Wh/year 170 MW reduction in peak load w Sustainable, self-financing transformation of lighting market in Ghana w Value to Ghana economy $10 million NPV (25% discount rate) w Eventual cash flow + $15 million per year
Impacts w Easing of tight electricity supply situation n n Reduction in consumption of 350 MMk. Wh/year 170 MW reduction in peak load w Sustainable, self-financing transformation of lighting market in Ghana w Value to Ghana economy $10 million NPV (25% discount rate) w Eventual cash flow + $15 million per year
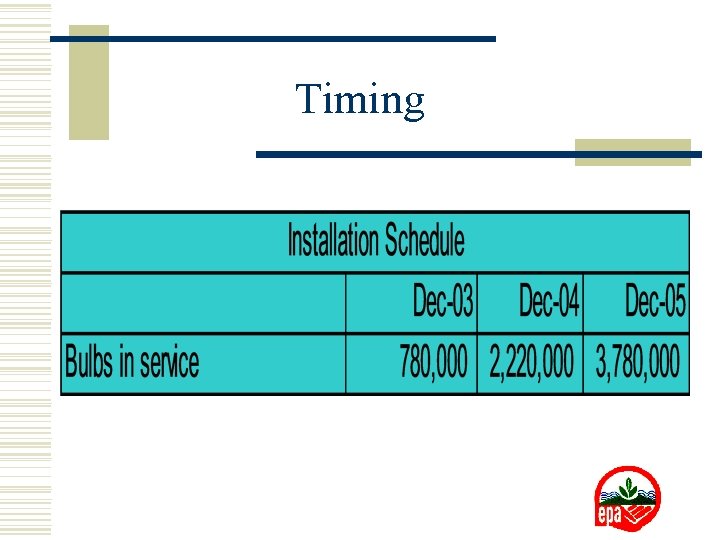 Timing
Timing
 Organization w Initiative of Ghana Energy Foundation w Integrated into Ghana’s Technology Transfer Needs Assessment under the UNFCCC n n n Ghana EPA lead organization VRA, ECG, Energy Commission, broad representation of other Ghana stakeholders Technical support from NREL on behalf of Climate Technology Initiative w Ministry of Energy formed Committee on CFL Promotion
Organization w Initiative of Ghana Energy Foundation w Integrated into Ghana’s Technology Transfer Needs Assessment under the UNFCCC n n n Ghana EPA lead organization VRA, ECG, Energy Commission, broad representation of other Ghana stakeholders Technical support from NREL on behalf of Climate Technology Initiative w Ministry of Energy formed Committee on CFL Promotion
 Delivery Modes w Installation by task force members n Initial emphasis on this mode w Retail sales by task force w Sales through employers w Sales through retail outlets
Delivery Modes w Installation by task force members n Initial emphasis on this mode w Retail sales by task force w Sales through employers w Sales through retail outlets
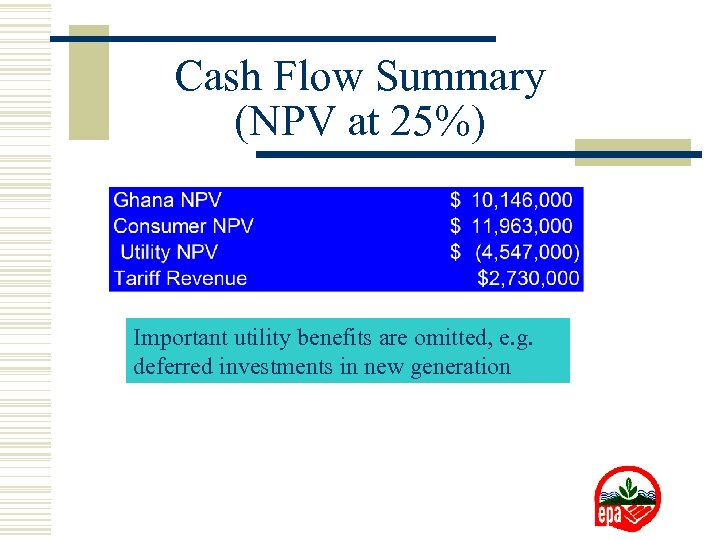 Cash Flow Summary (NPV at 25%) Important utility benefits are omitted, e. g. deferred investments in new generation
Cash Flow Summary (NPV at 25%) Important utility benefits are omitted, e. g. deferred investments in new generation
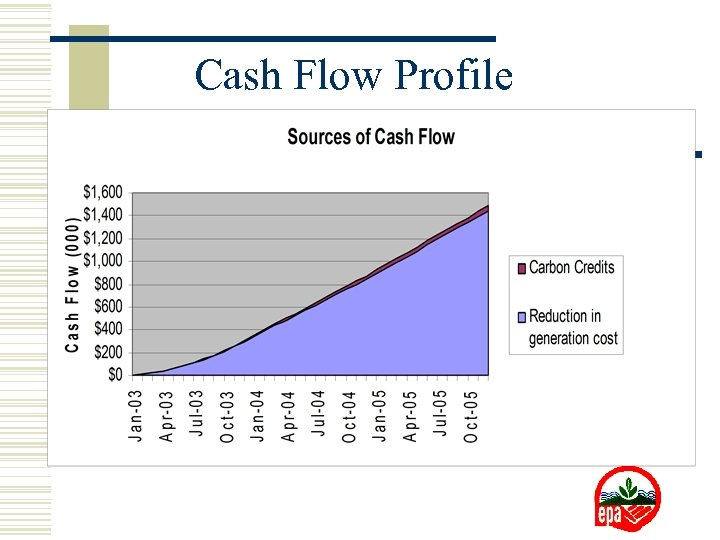 Cash Flow Profile
Cash Flow Profile
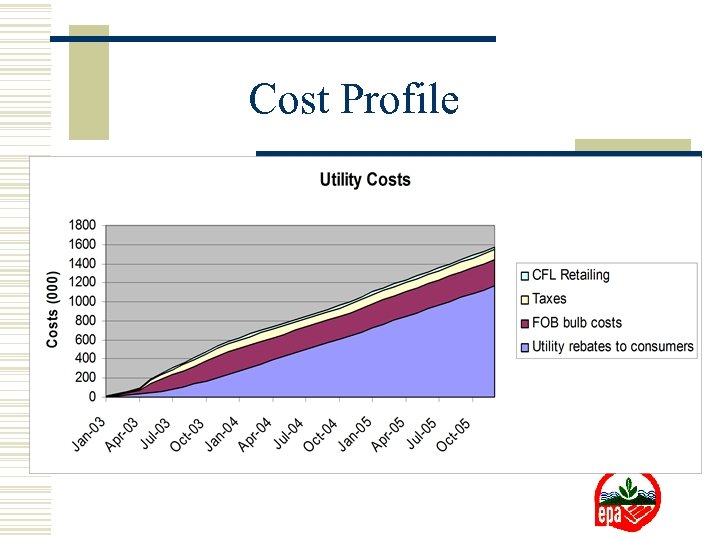 Cost Profile
Cost Profile
 Financing w CFL installation n n Self financing $250, 00 line of credit sought to cover initial purchases w Public Awareness and Outreach n $500, 000 Grant financing sought
Financing w CFL installation n n Self financing $250, 00 line of credit sought to cover initial purchases w Public Awareness and Outreach n $500, 000 Grant financing sought
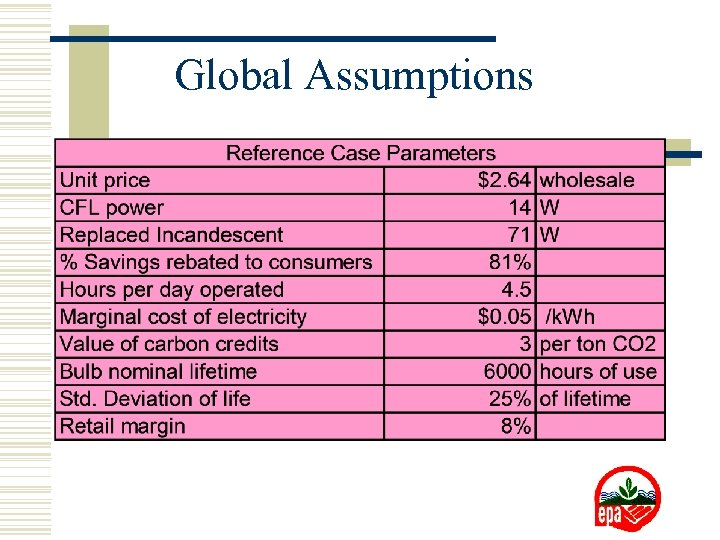 Global Assumptions
Global Assumptions
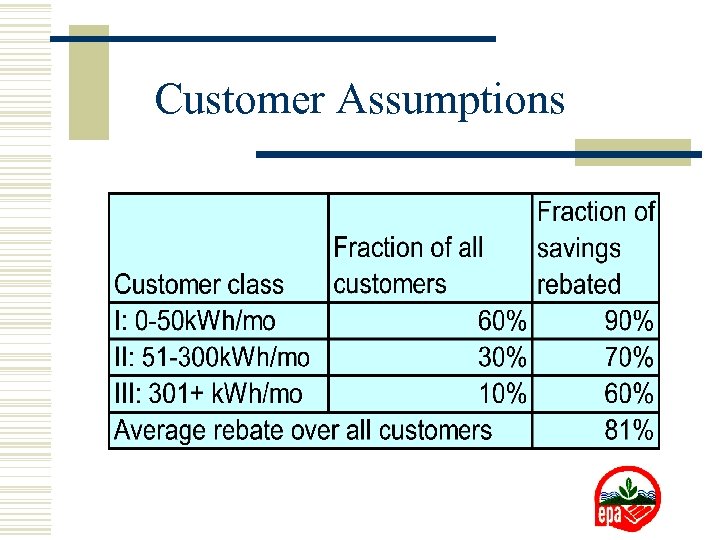 Customer Assumptions
Customer Assumptions
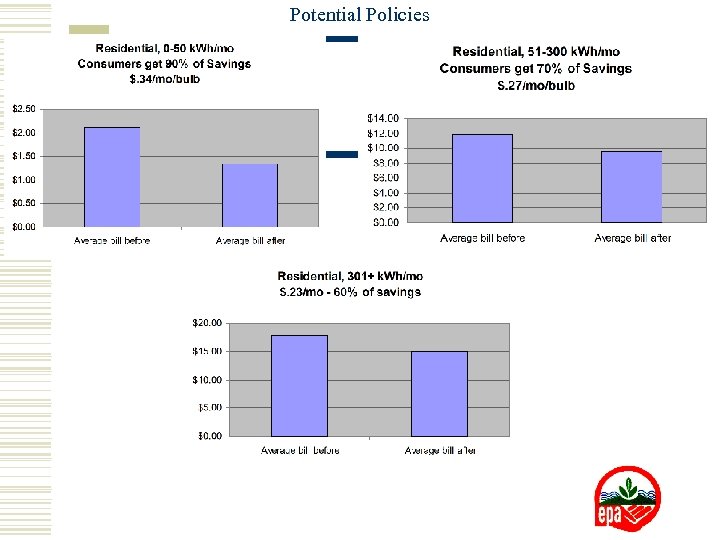 Potential Policies
Potential Policies
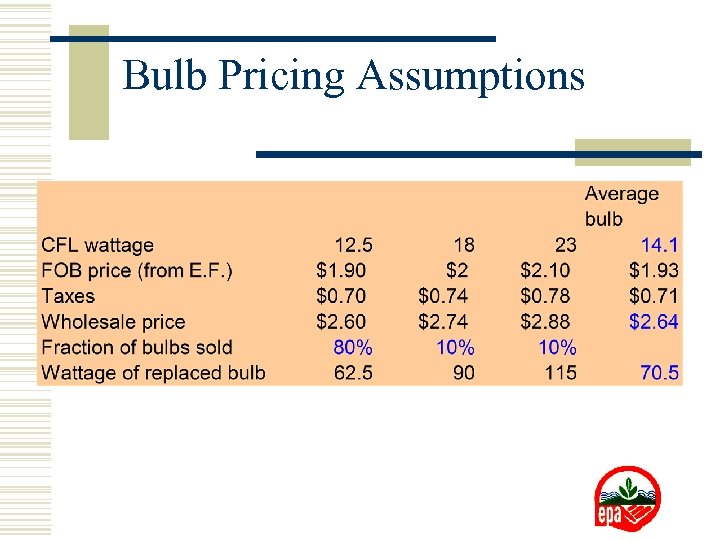 Bulb Pricing Assumptions
Bulb Pricing Assumptions
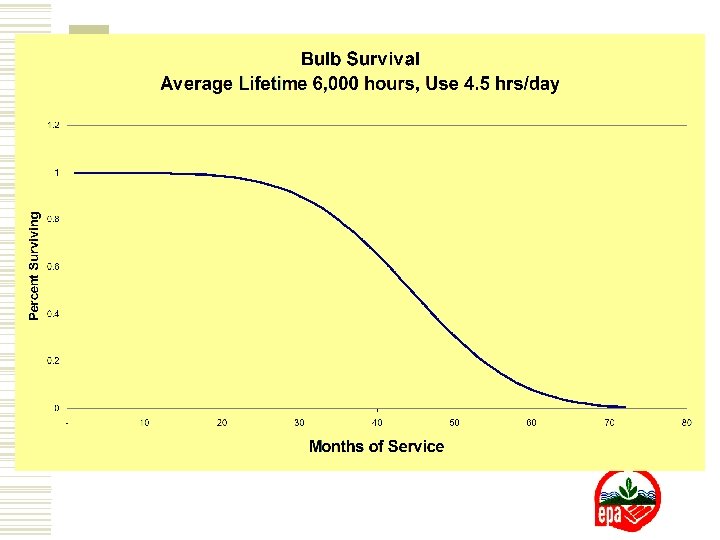
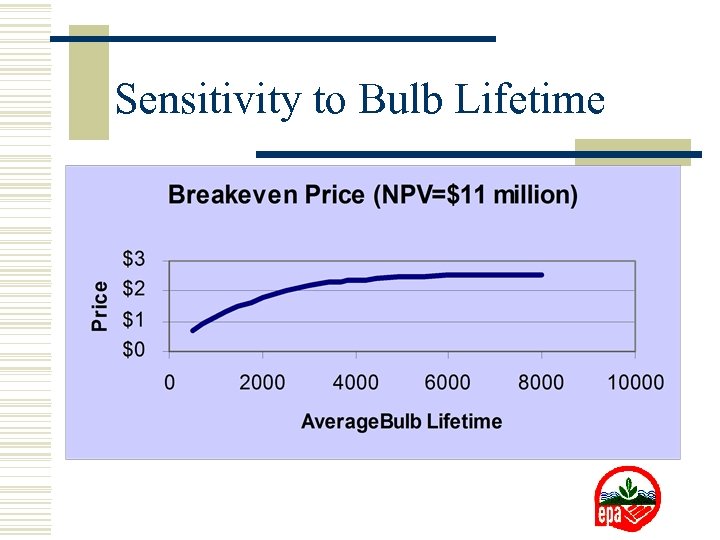 Sensitivity to Bulb Lifetime
Sensitivity to Bulb Lifetime
 CHALLENGES w Access to technology information w Development of bankable project portfolios w Developing implementation models and business plans – capacity, barrier removal strategies w Creation of the enabling environment for sustained technology development and transfer, including market transformation w Building of business partnerships and identification of technology transfer intermediaries
CHALLENGES w Access to technology information w Development of bankable project portfolios w Developing implementation models and business plans – capacity, barrier removal strategies w Creation of the enabling environment for sustained technology development and transfer, including market transformation w Building of business partnerships and identification of technology transfer intermediaries
 CHALLENGES w “Distressed” international political will to discuss the issue of technology development and transfer (compared to e. g. CDM) as reflected under UNFCCC w Lack clear direction for engaging the private sector to promote cooperation and effective partnership development w Inadequate and uncertainties in financing options – where (under UNFCCC and other donor sources), when, what and how?
CHALLENGES w “Distressed” international political will to discuss the issue of technology development and transfer (compared to e. g. CDM) as reflected under UNFCCC w Lack clear direction for engaging the private sector to promote cooperation and effective partnership development w Inadequate and uncertainties in financing options – where (under UNFCCC and other donor sources), when, what and how?
 CONCLUSIONS w Technology needs assessment is the critical niche w The weakest link of the technology development and transfer chain is the mechanism for technology transfer - including financing w Technology transfer is not a formula but an innovative process, involving learning by doing w Therefore there is the need for joint research and development through partnerships that will address the fear of loss of IPRs
CONCLUSIONS w Technology needs assessment is the critical niche w The weakest link of the technology development and transfer chain is the mechanism for technology transfer - including financing w Technology transfer is not a formula but an innovative process, involving learning by doing w Therefore there is the need for joint research and development through partnerships that will address the fear of loss of IPRs
 CONCLUSIONS w Opportunities for financing technology development and transfer arise from barrier identification and removal strategies identified during technology needs and needs assessment w Sustained partnership that is built on mutual trust and benefit sharing is crucial for technology transfer w There is need to work to reduce risk associated with needed technologies to make them marketable w Entrepreneurial skills development is required
CONCLUSIONS w Opportunities for financing technology development and transfer arise from barrier identification and removal strategies identified during technology needs and needs assessment w Sustained partnership that is built on mutual trust and benefit sharing is crucial for technology transfer w There is need to work to reduce risk associated with needed technologies to make them marketable w Entrepreneurial skills development is required


