5f4bd42f4e3a4b6325d4c393fa04e24c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 EXPERIENCE WITH IN-HOUSE ASSAY: VALIDATION OF AN INHOUSE NAT ASSAY FOR THE DETECTION OF DIFFERENT GENOTYPES OF v. B 19 Marta José, Instituto Grifols S. A. , Barcelona, SPAIN So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
EXPERIENCE WITH IN-HOUSE ASSAY: VALIDATION OF AN INHOUSE NAT ASSAY FOR THE DETECTION OF DIFFERENT GENOTYPES OF v. B 19 Marta José, Instituto Grifols S. A. , Barcelona, SPAIN So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD DESIGN • Automatic DNA extraction using the Bio. Robot 9604 (QIAGEN). • Subsequent amplification by PCR of a conserved sequence of VP 1 capsid structural protein region. • Detection by means of a specific capture probe in a liquid medium and colorimetric reaction (ELISA-DIG Detection, Roche). • The internal control (from the extraction) is a plasmid which is amplified with the same primers as v. B 19 without competition, and detected with a different probe. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD DESIGN • Automatic DNA extraction using the Bio. Robot 9604 (QIAGEN). • Subsequent amplification by PCR of a conserved sequence of VP 1 capsid structural protein region. • Detection by means of a specific capture probe in a liquid medium and colorimetric reaction (ELISA-DIG Detection, Roche). • The internal control (from the extraction) is a plasmid which is amplified with the same primers as v. B 19 without competition, and detected with a different probe. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD DESIGN and VALIDATION • The method is designed to work in the exponential phase of the PCR reaction in order to use the same procedure as qualitative or quantitative assays. • The method is validated according to current guidelines for the following parameters: detection limit, quantitation limit, linearity, range, accuracy, precision, specificity and robustness. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD DESIGN and VALIDATION • The method is designed to work in the exponential phase of the PCR reaction in order to use the same procedure as qualitative or quantitative assays. • The method is validated according to current guidelines for the following parameters: detection limit, quantitation limit, linearity, range, accuracy, precision, specificity and robustness. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
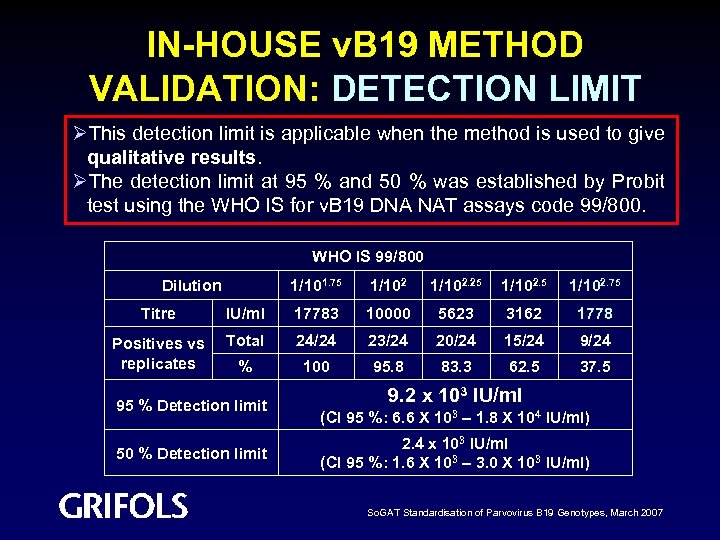 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: DETECTION LIMIT ØThis detection limit is applicable when the method is used to give qualitative results. ØThe detection limit at 95 % and 50 % was established by Probit test using the WHO IS for v. B 19 DNA NAT assays code 99/800. WHO IS 99/800 Dilution 1/101. 75 1/102. 25 1/102. 75 Titre IU/ml 17783 10000 5623 3162 1778 Positives vs replicates Total 24/24 23/24 20/24 15/24 9/24 % 100 95. 8 83. 3 62. 5 37. 5 95 % Detection limit 50 % Detection limit 9. 2 x 103 IU/ml (CI 95 %: 6. 6 X 103 – 1. 8 X 104 IU/ml) 2. 4 x 103 IU/ml (CI 95 %: 1. 6 X 103 – 3. 0 X 103 IU/ml) So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: DETECTION LIMIT ØThis detection limit is applicable when the method is used to give qualitative results. ØThe detection limit at 95 % and 50 % was established by Probit test using the WHO IS for v. B 19 DNA NAT assays code 99/800. WHO IS 99/800 Dilution 1/101. 75 1/102. 25 1/102. 75 Titre IU/ml 17783 10000 5623 3162 1778 Positives vs replicates Total 24/24 23/24 20/24 15/24 9/24 % 100 95. 8 83. 3 62. 5 37. 5 95 % Detection limit 50 % Detection limit 9. 2 x 103 IU/ml (CI 95 %: 6. 6 X 103 – 1. 8 X 104 IU/ml) 2. 4 x 103 IU/ml (CI 95 %: 1. 6 X 103 – 3. 0 X 103 IU/ml) So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
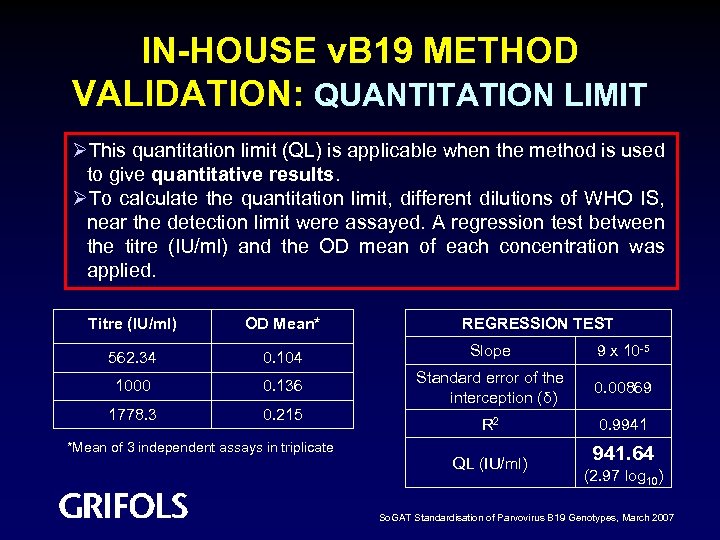 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: QUANTITATION LIMIT ØThis quantitation limit (QL) is applicable when the method is used to give quantitative results. ØTo calculate the quantitation limit, different dilutions of WHO IS, near the detection limit were assayed. A regression test between the titre (IU/ml) and the OD mean of each concentration was applied. REGRESSION TEST Titre (IU/ml) OD Mean* 562. 34 0. 104 Slope 9 x 10 -5 1000 0. 136 0. 00869 1778. 3 0. 215 Standard error of the interception (δ) R 2 0. 9941 QL (IU/ml) 941. 64 *Mean of 3 independent assays in triplicate (2. 97 log 10) So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: QUANTITATION LIMIT ØThis quantitation limit (QL) is applicable when the method is used to give quantitative results. ØTo calculate the quantitation limit, different dilutions of WHO IS, near the detection limit were assayed. A regression test between the titre (IU/ml) and the OD mean of each concentration was applied. REGRESSION TEST Titre (IU/ml) OD Mean* 562. 34 0. 104 Slope 9 x 10 -5 1000 0. 136 0. 00869 1778. 3 0. 215 Standard error of the interception (δ) R 2 0. 9941 QL (IU/ml) 941. 64 *Mean of 3 independent assays in triplicate (2. 97 log 10) So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
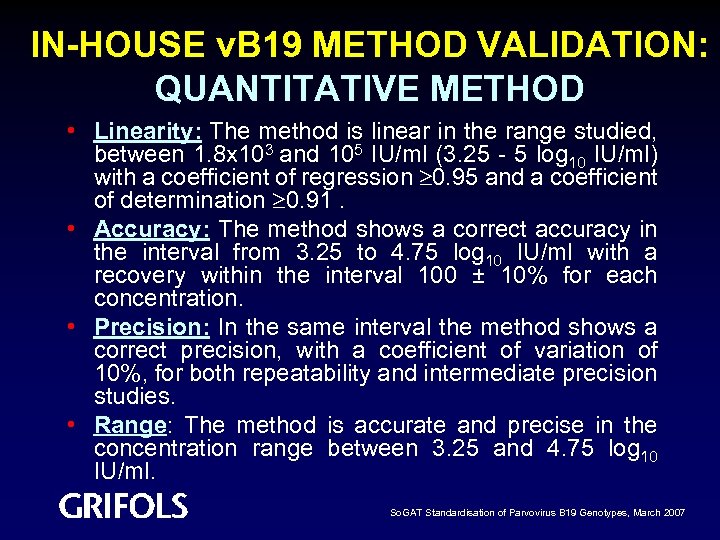 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: QUANTITATIVE METHOD • Linearity: The method is linear in the range studied, between 1. 8 x 103 and 105 IU/ml (3. 25 - 5 log 10 IU/ml) with a coefficient of regression 0. 95 and a coefficient of determination 0. 91. • Accuracy: The method shows a correct accuracy in the interval from 3. 25 to 4. 75 log 10 IU/ml with a recovery within the interval 100 ± 10% for each concentration. • Precision: In the same interval the method shows a correct precision, with a coefficient of variation of 10%, for both repeatability and intermediate precision studies. • Range: The method is accurate and precise in the concentration range between 3. 25 and 4. 75 log 10 IU/ml. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: QUANTITATIVE METHOD • Linearity: The method is linear in the range studied, between 1. 8 x 103 and 105 IU/ml (3. 25 - 5 log 10 IU/ml) with a coefficient of regression 0. 95 and a coefficient of determination 0. 91. • Accuracy: The method shows a correct accuracy in the interval from 3. 25 to 4. 75 log 10 IU/ml with a recovery within the interval 100 ± 10% for each concentration. • Precision: In the same interval the method shows a correct precision, with a coefficient of variation of 10%, for both repeatability and intermediate precision studies. • Range: The method is accurate and precise in the concentration range between 3. 25 and 4. 75 log 10 IU/ml. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
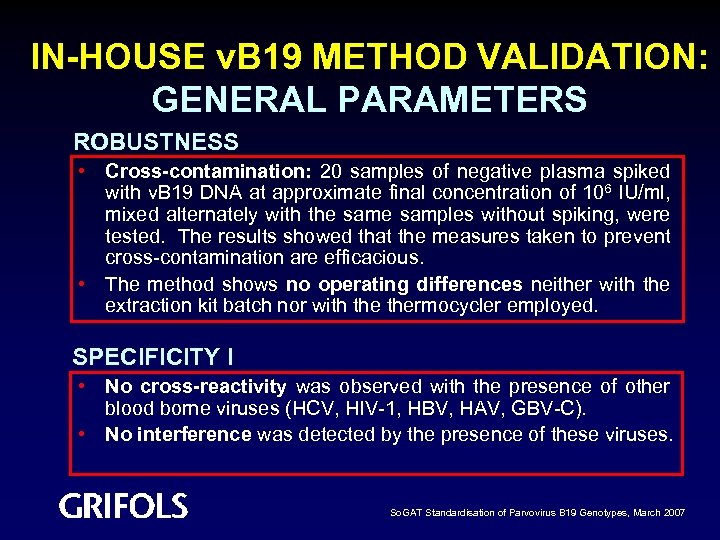 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: GENERAL PARAMETERS ROBUSTNESS • Cross-contamination: 20 samples of negative plasma spiked with v. B 19 DNA at approximate final concentration of 106 IU/ml, mixed alternately with the samples without spiking, were tested. The results showed that the measures taken to prevent cross-contamination are efficacious. • The method shows no operating differences neither with the extraction kit batch nor with thermocycler employed. SPECIFICITY I • No cross-reactivity was observed with the presence of other blood borne viruses (HCV, HIV-1, HBV, HAV, GBV-C). • No interference was detected by the presence of these viruses. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: GENERAL PARAMETERS ROBUSTNESS • Cross-contamination: 20 samples of negative plasma spiked with v. B 19 DNA at approximate final concentration of 106 IU/ml, mixed alternately with the samples without spiking, were tested. The results showed that the measures taken to prevent cross-contamination are efficacious. • The method shows no operating differences neither with the extraction kit batch nor with thermocycler employed. SPECIFICITY I • No cross-reactivity was observed with the presence of other blood borne viruses (HCV, HIV-1, HBV, HAV, GBV-C). • No interference was detected by the presence of these viruses. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
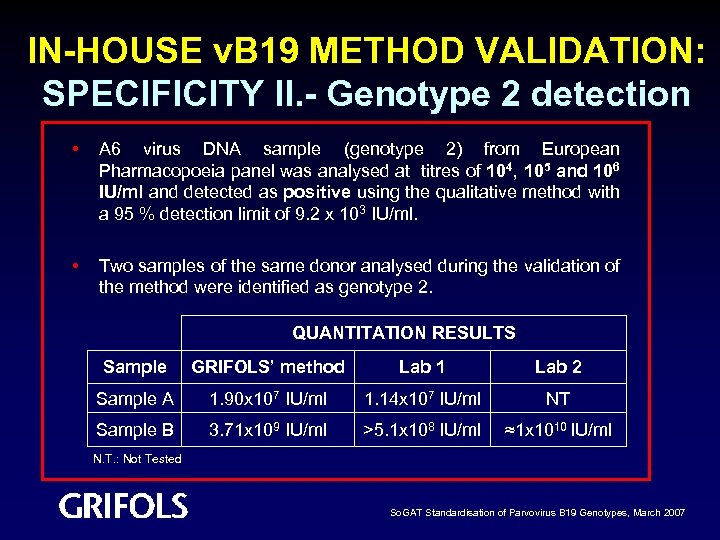 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: SPECIFICITY II. - Genotype 2 detection • A 6 virus DNA sample (genotype 2) from European Pharmacopoeia panel was analysed at titres of 104, 105 and 106 IU/ml and detected as positive using the qualitative method with a 95 % detection limit of 9. 2 x 103 IU/ml. • Two samples of the same donor analysed during the validation of the method were identified as genotype 2. QUANTITATION RESULTS Sample GRIFOLS’ method Lab 1 Lab 2 Sample A 1. 90 x 107 IU/ml 1. 14 x 107 IU/ml NT Sample B 3. 71 x 109 IU/ml >5. 1 x 108 IU/ml ≈1 x 1010 IU/ml N. T. : Not Tested So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: SPECIFICITY II. - Genotype 2 detection • A 6 virus DNA sample (genotype 2) from European Pharmacopoeia panel was analysed at titres of 104, 105 and 106 IU/ml and detected as positive using the qualitative method with a 95 % detection limit of 9. 2 x 103 IU/ml. • Two samples of the same donor analysed during the validation of the method were identified as genotype 2. QUANTITATION RESULTS Sample GRIFOLS’ method Lab 1 Lab 2 Sample A 1. 90 x 107 IU/ml 1. 14 x 107 IU/ml NT Sample B 3. 71 x 109 IU/ml >5. 1 x 108 IU/ml ≈1 x 1010 IU/ml N. T. : Not Tested So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
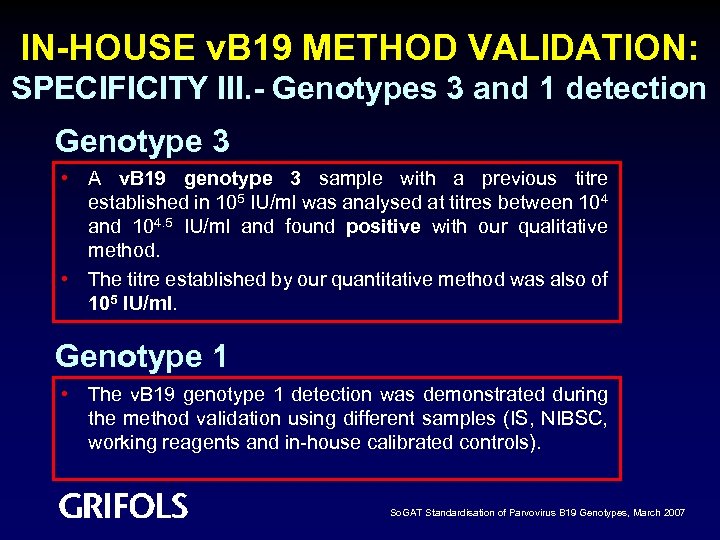 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: SPECIFICITY III. - Genotypes 3 and 1 detection Genotype 3 • A v. B 19 genotype 3 sample with a previous titre established in 105 IU/ml was analysed at titres between 104 and 104. 5 IU/ml and found positive with our qualitative method. • The titre established by our quantitative method was also of 105 IU/ml. Genotype 1 • The v. B 19 genotype 1 detection was demonstrated during the method validation using different samples (IS, NIBSC, working reagents and in-house calibrated controls). So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: SPECIFICITY III. - Genotypes 3 and 1 detection Genotype 3 • A v. B 19 genotype 3 sample with a previous titre established in 105 IU/ml was analysed at titres between 104 and 104. 5 IU/ml and found positive with our qualitative method. • The titre established by our quantitative method was also of 105 IU/ml. Genotype 1 • The v. B 19 genotype 1 detection was demonstrated during the method validation using different samples (IS, NIBSC, working reagents and in-house calibrated controls). So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
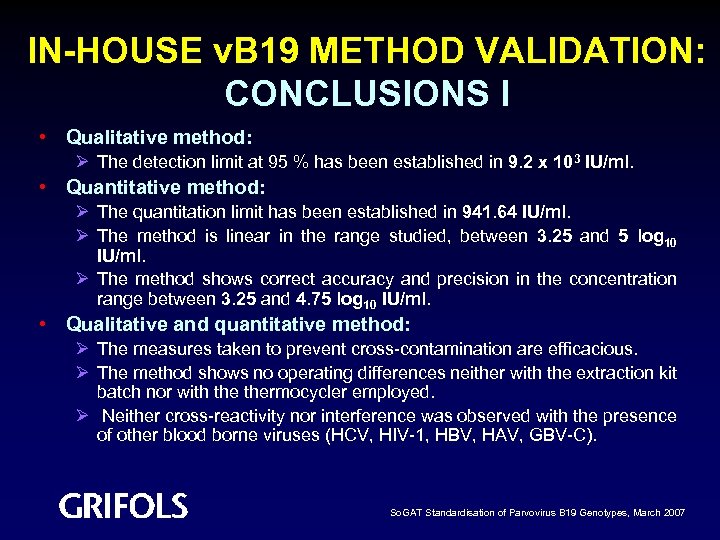 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: CONCLUSIONS I • Qualitative method: Ø The detection limit at 95 % has been established in 9. 2 x 103 IU/ml. • Quantitative method: Ø The quantitation limit has been established in 941. 64 IU/ml. Ø The method is linear in the range studied, between 3. 25 and 5 log 10 IU/ml. Ø The method shows correct accuracy and precision in the concentration range between 3. 25 and 4. 75 log 10 IU/ml. • Qualitative and quantitative method: Ø The measures taken to prevent cross-contamination are efficacious. Ø The method shows no operating differences neither with the extraction kit batch nor with thermocycler employed. Ø Neither cross-reactivity nor interference was observed with the presence of other blood borne viruses (HCV, HIV-1, HBV, HAV, GBV-C). So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: CONCLUSIONS I • Qualitative method: Ø The detection limit at 95 % has been established in 9. 2 x 103 IU/ml. • Quantitative method: Ø The quantitation limit has been established in 941. 64 IU/ml. Ø The method is linear in the range studied, between 3. 25 and 5 log 10 IU/ml. Ø The method shows correct accuracy and precision in the concentration range between 3. 25 and 4. 75 log 10 IU/ml. • Qualitative and quantitative method: Ø The measures taken to prevent cross-contamination are efficacious. Ø The method shows no operating differences neither with the extraction kit batch nor with thermocycler employed. Ø Neither cross-reactivity nor interference was observed with the presence of other blood borne viruses (HCV, HIV-1, HBV, HAV, GBV-C). So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
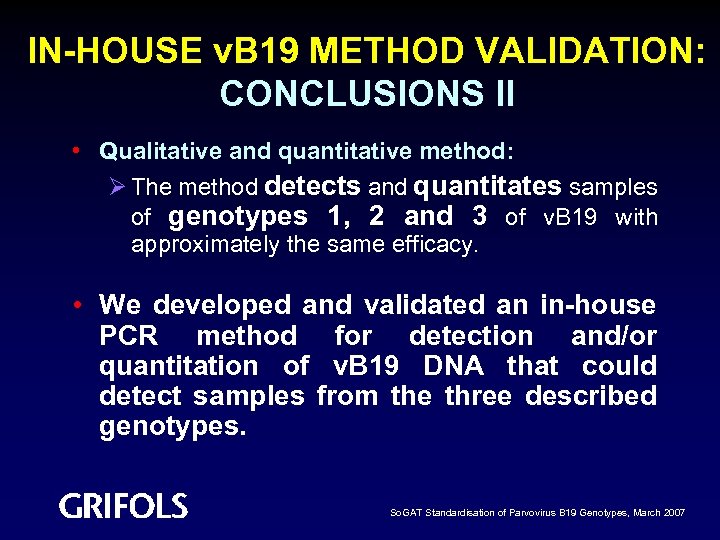 IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: CONCLUSIONS II • Qualitative and quantitative method: Ø The method detects and quantitates samples of genotypes 1, 2 and 3 of v. B 19 with approximately the same efficacy. • We developed and validated an in-house PCR method for detection and/or quantitation of v. B 19 DNA that could detect samples from the three described genotypes. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
IN-HOUSE v. B 19 METHOD VALIDATION: CONCLUSIONS II • Qualitative and quantitative method: Ø The method detects and quantitates samples of genotypes 1, 2 and 3 of v. B 19 with approximately the same efficacy. • We developed and validated an in-house PCR method for detection and/or quantitation of v. B 19 DNA that could detect samples from the three described genotypes. So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS INSTITUTO GRIFOLS: Araceli Maya Mireia Prat Dr. Rodrigo Gajardo Dr. Juan I. Jorquera NATIONAL BLOOD SERVICE CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY, UK: Dr. Daniel Candotti Dr. Jean Pierre Allain BIOMAT (GRIFOLS): SANQUIN, NETHERLANDS: Margarita Estrada Dr. Dolors Xairó Dr. Marco Koppelman So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS INSTITUTO GRIFOLS: Araceli Maya Mireia Prat Dr. Rodrigo Gajardo Dr. Juan I. Jorquera NATIONAL BLOOD SERVICE CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY, UK: Dr. Daniel Candotti Dr. Jean Pierre Allain BIOMAT (GRIFOLS): SANQUIN, NETHERLANDS: Margarita Estrada Dr. Dolors Xairó Dr. Marco Koppelman So. GAT Standardisation of Parvovirus B 19 Genotypes, March 2007


