edd464c47150205f08965bd62c1f20f7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Experience with Affymetrix microarrays in kidney transplantation Gunilla Einecke University of Alberta Edmonton, Canada
Experience with Affymetrix microarrays in kidney transplantation Gunilla Einecke University of Alberta Edmonton, Canada
 Our Study Microarray analysis of kidney transplants • Establish additional diagnostic criteria for disease processes • Better understand mechanisms that lead to organ damage • Develop monitoring tools
Our Study Microarray analysis of kidney transplants • Establish additional diagnostic criteria for disease processes • Better understand mechanisms that lead to organ damage • Develop monitoring tools
 Models • Mouse kidney transplant model that simulates the human disease process • Human kidney transplant biopsies
Models • Mouse kidney transplant model that simulates the human disease process • Human kidney transplant biopsies
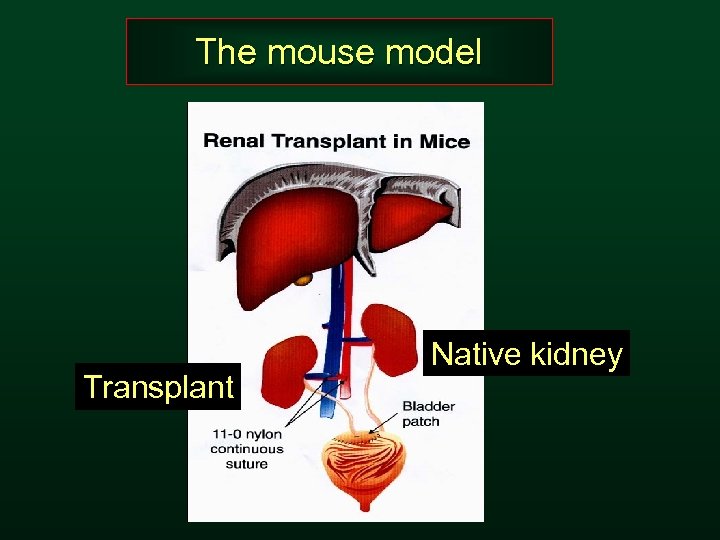 The mouse model Transplant Native kidney
The mouse model Transplant Native kidney
 Mouse model Kidney Transplants (Time course) • • • Normal CBA kidneys Isografts (CBA/CBA) at days (3, 4, ) 5, 7, 21 Allografts (CBA/B 6) at days (3, 4, ) 5, 7, 14, 21, 42 Cell cultures • • • Mixed lymphocyte culture (day 4) Cloned CTL Cultured macrophage lineage (RAW 264. 7 cells)
Mouse model Kidney Transplants (Time course) • • • Normal CBA kidneys Isografts (CBA/CBA) at days (3, 4, ) 5, 7, 21 Allografts (CBA/B 6) at days (3, 4, ) 5, 7, 14, 21, 42 Cell cultures • • • Mixed lymphocyte culture (day 4) Cloned CTL Cultured macrophage lineage (RAW 264. 7 cells)
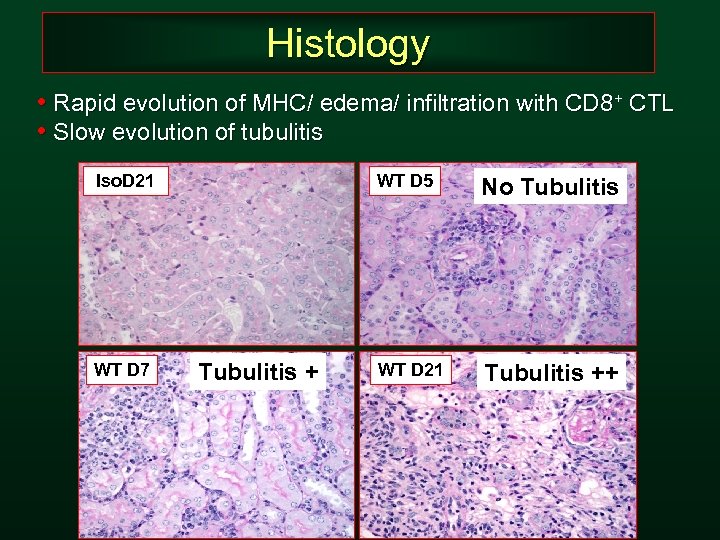 Histology • Rapid evolution of MHC/ edema/ infiltration with CD 8+ CTL • Slow evolution of tubulitis Iso. D 21 WT D 7 WT D 5 Tubulitis + No Tubulitis WT D 21 Tubulitis ++
Histology • Rapid evolution of MHC/ edema/ infiltration with CD 8+ CTL • Slow evolution of tubulitis Iso. D 21 WT D 7 WT D 5 Tubulitis + No Tubulitis WT D 21 Tubulitis ++
 Database of human kidney transplant biopsies • • Normal donor kidneys (n = 8) Well-functioning transplants without rejection (n = 10) Kidneys undergoing acute rejection (n = 7) Transplants with renal dysfunction without rejection (n = 4) • Affymetrix HG-U 95 Av 2 Gene. Chip Flechner SM, Kurian SM, Head SR, Sharp SM, Whisenant TC, Zhang J, Chismar JD, Horvath S, Mondala T, Gilmartin T, Cook DJ, Kay SA, Walker JR, Salomon DR: Kidney transplant rejection and tissue injury by gene profiling of biopsies and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Am J Transplant 2004 Sep; 4(9): 1475 -89
Database of human kidney transplant biopsies • • Normal donor kidneys (n = 8) Well-functioning transplants without rejection (n = 10) Kidneys undergoing acute rejection (n = 7) Transplants with renal dysfunction without rejection (n = 4) • Affymetrix HG-U 95 Av 2 Gene. Chip Flechner SM, Kurian SM, Head SR, Sharp SM, Whisenant TC, Zhang J, Chismar JD, Horvath S, Mondala T, Gilmartin T, Cook DJ, Kay SA, Walker JR, Salomon DR: Kidney transplant rejection and tissue injury by gene profiling of biopsies and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Am J Transplant 2004 Sep; 4(9): 1475 -89
 Human kidney transplant biopsies from Edmonton • Nephrectomy samples (n = 3) • Implant biopsies (n=4) • Biopsies for cause (n=33) • Affymetrix HG-U 133 2. 0 Plus Gene. Chip
Human kidney transplant biopsies from Edmonton • Nephrectomy samples (n = 3) • Implant biopsies (n=4) • Biopsies for cause (n=33) • Affymetrix HG-U 133 2. 0 Plus Gene. Chip
 The key elements in rejection observed in the graft • Effector T cell infiltration activation • Macrophage infiltration/activation • Late clonal B cell/plasma cells • IFN-g effects: local and systemic • Chemokines • Interstitial remodeling effects • Epithelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation • Decreased expression of kidney genes
The key elements in rejection observed in the graft • Effector T cell infiltration activation • Macrophage infiltration/activation • Late clonal B cell/plasma cells • IFN-g effects: local and systemic • Chemokines • Interstitial remodeling effects • Epithelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation • Decreased expression of kidney genes
 The key elements in rejection observed in the graft • Effector T cell infiltration activation • Macrophage infiltration/activation • Late clonal B cell/plasma cells • IFN-g effects: local and systemic • Chemokines • Interstitial remodeling effects • Epithelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation • Decreased expression of kidney genes
The key elements in rejection observed in the graft • Effector T cell infiltration activation • Macrophage infiltration/activation • Late clonal B cell/plasma cells • IFN-g effects: local and systemic • Chemokines • Interstitial remodeling effects • Epithelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation • Decreased expression of kidney genes
 CTL associated transcripts (CATs)
CTL associated transcripts (CATs)
 Defining CTL associated transcripts Definition: • absent in normal kidney • high expression in cultured lymphocytes (d 4 MLR and cloned cultured CTL) n = 287 transcripts
Defining CTL associated transcripts Definition: • absent in normal kidney • high expression in cultured lymphocytes (d 4 MLR and cloned cultured CTL) n = 287 transcripts
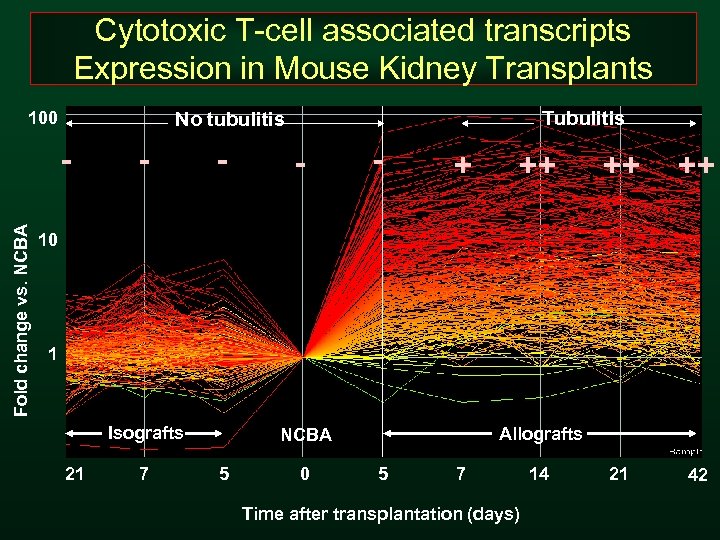 Cytotoxic T-cell associated transcripts Expression in Mouse Kidney Transplants Fold change vs. NCBA Tubulitis No tubulitis 100 - - + ++ ++ ++ 21 42 10 1 Isografts 21 7 Allografts NCBA 5 0 5 7 Time after transplantation (days) 14
Cytotoxic T-cell associated transcripts Expression in Mouse Kidney Transplants Fold change vs. NCBA Tubulitis No tubulitis 100 - - + ++ ++ ++ 21 42 10 1 Isografts 21 7 Allografts NCBA 5 0 5 7 Time after transplantation (days) 14
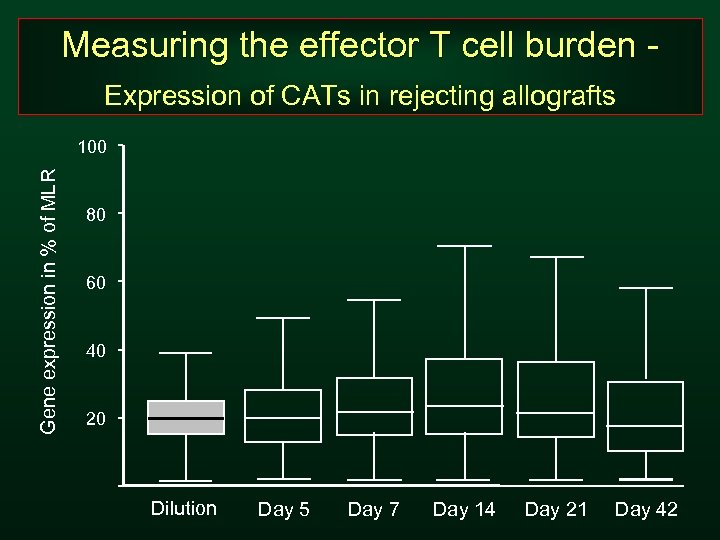 Measuring the effector T cell burden Expression of CATs in rejecting allografts Gene expression in % of MLR 100 80 60 40 20 Dilution Day 5 Day 7 Day 14 Day 21 Day 42
Measuring the effector T cell burden Expression of CATs in rejecting allografts Gene expression in % of MLR 100 80 60 40 20 Dilution Day 5 Day 7 Day 14 Day 21 Day 42
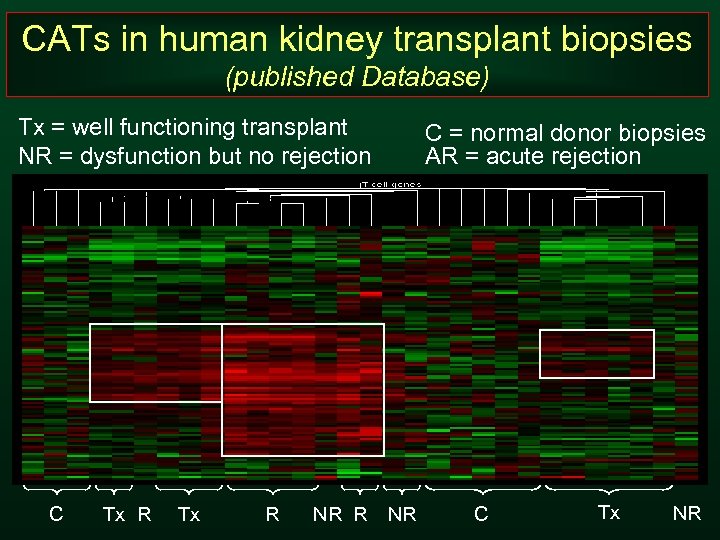 CATs in human kidney transplant biopsies (published Database) Tx = well functioning transplant NR = dysfunction but no rejection C Tx R NR R C = normal donor biopsies AR = acute rejection NR C Tx NR
CATs in human kidney transplant biopsies (published Database) Tx = well functioning transplant NR = dysfunction but no rejection C Tx R NR R C = normal donor biopsies AR = acute rejection NR C Tx NR
 Refining the CATs • Transcripts with increased expression (≥ 2 fold) in allografts D 5 • Not increased by r. IFN-g n = 168
Refining the CATs • Transcripts with increased expression (≥ 2 fold) in allografts D 5 • Not increased by r. IFN-g n = 168
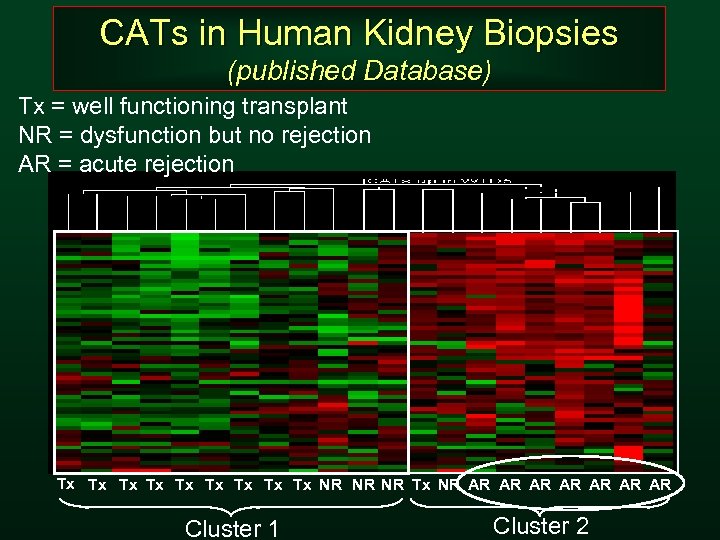 CATs in Human Kidney Biopsies (published Database) Tx = well functioning transplant NR = dysfunction but no rejection AR = acute rejection Tx Tx Tx NR NR NR Tx NR AR AR Cluster 1 Cluster 2
CATs in Human Kidney Biopsies (published Database) Tx = well functioning transplant NR = dysfunction but no rejection AR = acute rejection Tx Tx Tx NR NR NR Tx NR AR AR Cluster 1 Cluster 2
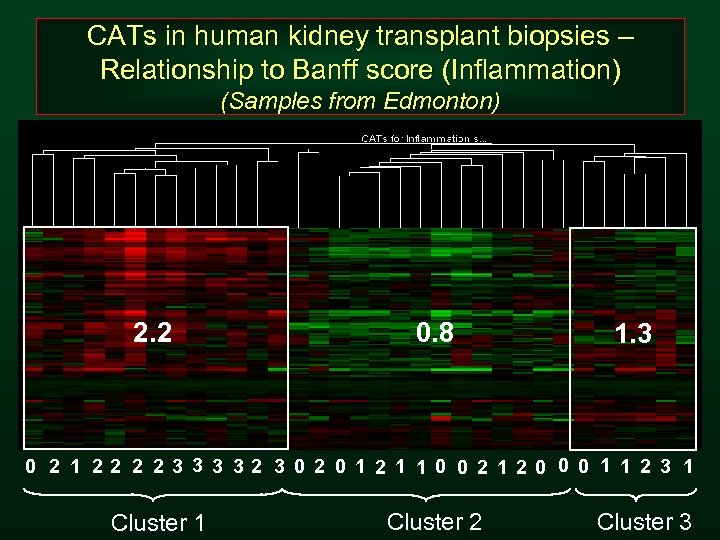 CATs in human kidney transplant biopsies – Relationship to Banff score (Inflammation) (Samples from Edmonton) 2. 2 0. 8 1. 3 0 2 1 22 2 2 3 32 3 0 2 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 2 120 0 0 1 1 2 3 1 Cluster 2 Cluster 3
CATs in human kidney transplant biopsies – Relationship to Banff score (Inflammation) (Samples from Edmonton) 2. 2 0. 8 1. 3 0 2 1 22 2 2 3 32 3 0 2 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 2 120 0 0 1 1 2 3 1 Cluster 2 Cluster 3
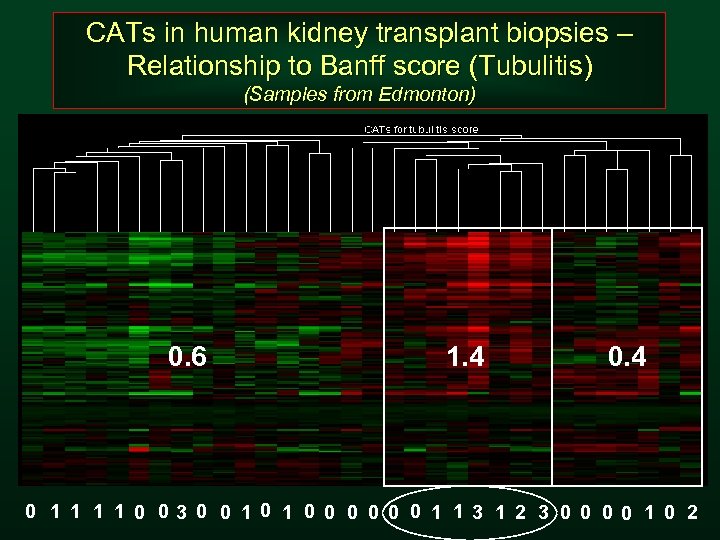 CATs in human kidney transplant biopsies – Relationship to Banff score (Tubulitis) (Samples from Edmonton) 0. 6 1. 4 0 1 1 0 03 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 3 1 2 3 0 0 1 0 2
CATs in human kidney transplant biopsies – Relationship to Banff score (Tubulitis) (Samples from Edmonton) 0. 6 1. 4 0 1 1 0 03 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 3 1 2 3 0 0 1 0 2
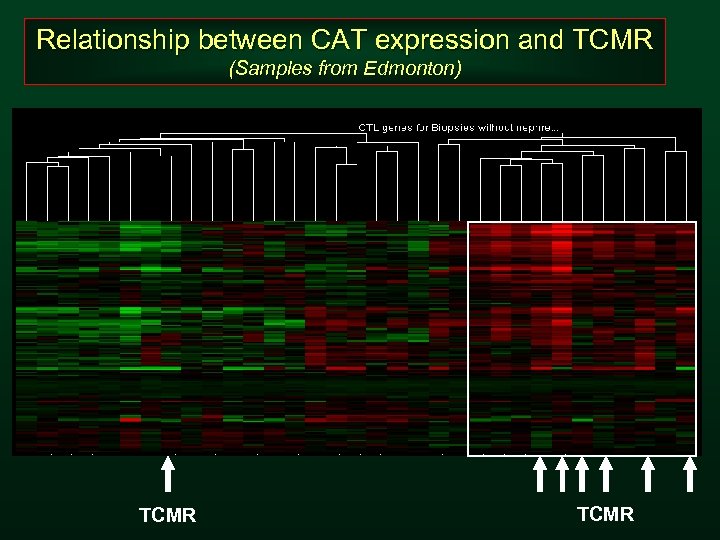 Relationship between CAT expression and TCMR (Samples from Edmonton) TCMR
Relationship between CAT expression and TCMR (Samples from Edmonton) TCMR
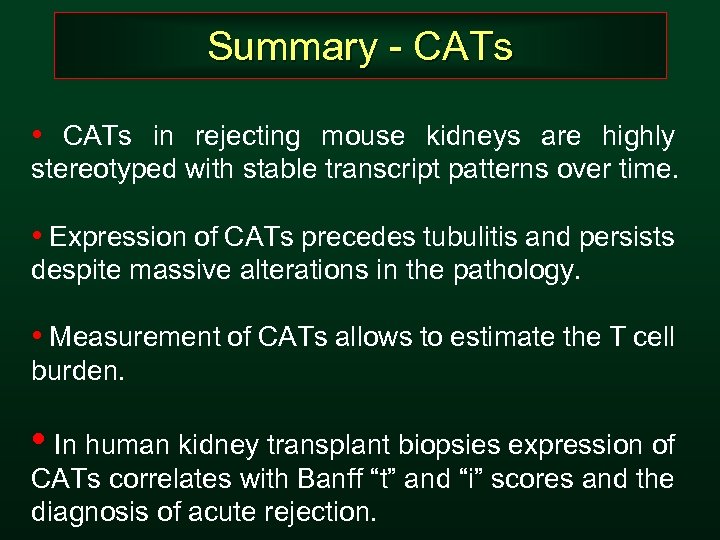 Summary - CATs • CATs in rejecting mouse kidneys are highly stereotyped with stable transcript patterns over time. • Expression of CATs precedes tubulitis and persists despite massive alterations in the pathology. • Measurement of CATs allows to estimate the T cell burden. • In human kidney transplant biopsies expression of CATs correlates with Banff “t” and “i” scores and the diagnosis of acute rejection.
Summary - CATs • CATs in rejecting mouse kidneys are highly stereotyped with stable transcript patterns over time. • Expression of CATs precedes tubulitis and persists despite massive alterations in the pathology. • Measurement of CATs allows to estimate the T cell burden. • In human kidney transplant biopsies expression of CATs correlates with Banff “t” and “i” scores and the diagnosis of acute rejection.
 Renal Genes
Renal Genes
 Defining Renal genes Definition: • Present in normal CBA kidney • Absent in cultured effector lymphocytes (MLR and CTL line) • Absent in cultured macrophage line (RAW 264. 7 cells) n = 1293
Defining Renal genes Definition: • Present in normal CBA kidney • Absent in cultured effector lymphocytes (MLR and CTL line) • Absent in cultured macrophage line (RAW 264. 7 cells) n = 1293
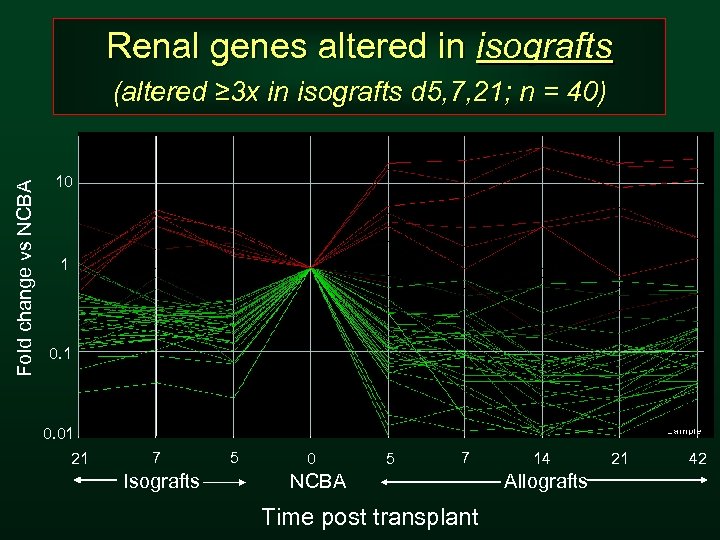 Renal genes altered in isografts Fold change vs NCBA (altered ≥ 3 x in isografts d 5, 7, 21; n = 40) 10 1 0. 01 21 7 Isografts 5 0 5 7 NCBA Time post transplant 14 Allografts 21 42
Renal genes altered in isografts Fold change vs NCBA (altered ≥ 3 x in isografts d 5, 7, 21; n = 40) 10 1 0. 01 21 7 Isografts 5 0 5 7 NCBA Time post transplant 14 Allografts 21 42
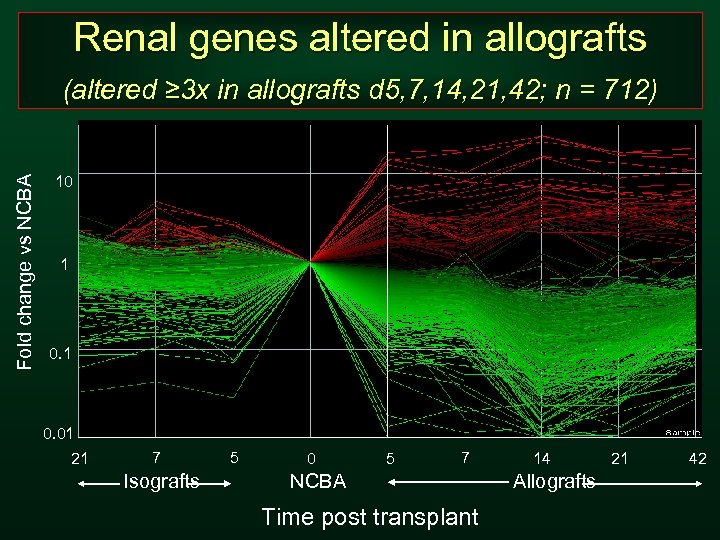 Renal genes altered in allografts Fold change vs NCBA (altered ≥ 3 x in allografts d 5, 7, 14, 21, 42; n = 712) 10 1 0. 01 21 7 Isografts 5 0 5 7 NCBA Time post transplant 14 Allografts 21 42
Renal genes altered in allografts Fold change vs NCBA (altered ≥ 3 x in allografts d 5, 7, 14, 21, 42; n = 712) 10 1 0. 01 21 7 Isografts 5 0 5 7 NCBA Time post transplant 14 Allografts 21 42
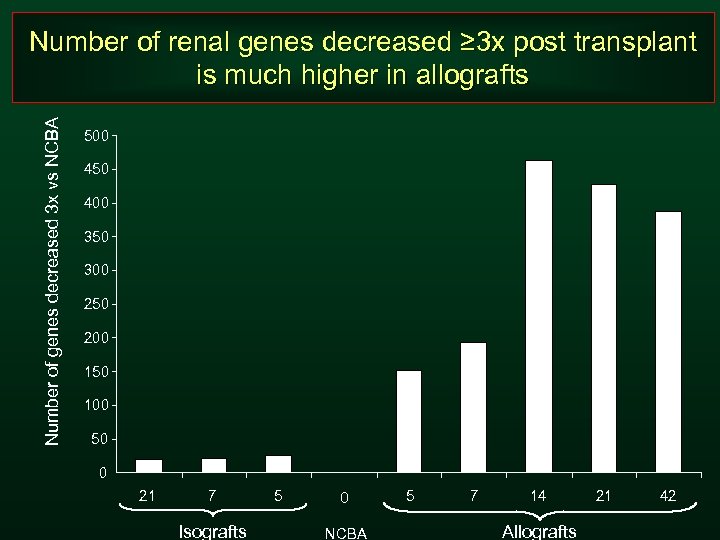 Number of genes decreased 3 x vs NCBA Number of renal genes decreased ≥ 3 x post transplant is much higher in allografts 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 21 7 Isografts 5 0 NCBA 5 7 14 Allografts 21 42
Number of genes decreased 3 x vs NCBA Number of renal genes decreased ≥ 3 x post transplant is much higher in allografts 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 21 7 Isografts 5 0 NCBA 5 7 14 Allografts 21 42
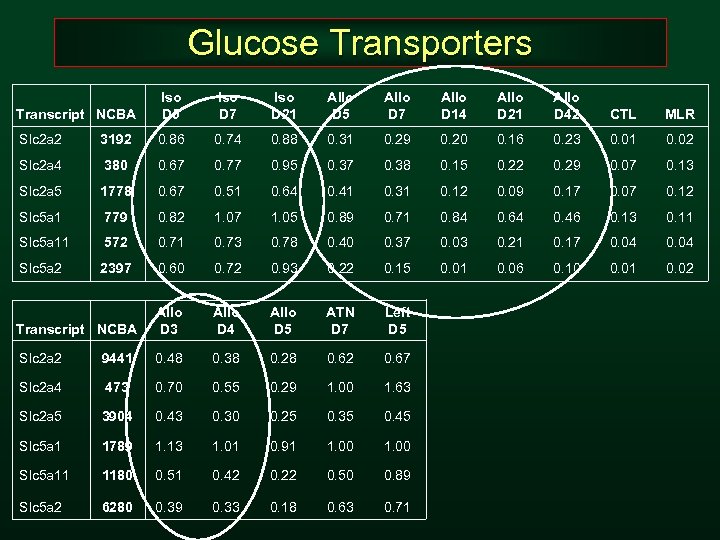 Glucose Transporters Transcript NCBA Iso D 5 Iso D 7 Iso D 21 Allo D 5 Allo D 7 Allo D 14 Allo D 21 Allo D 42 CTL MLR Slc 2 a 2 3192 0. 86 0. 74 0. 88 0. 31 0. 29 0. 20 0. 16 0. 23 0. 01 0. 02 Slc 2 a 4 380 0. 67 0. 77 0. 95 0. 37 0. 38 0. 15 0. 22 0. 29 0. 07 0. 13 Slc 2 a 5 1778 0. 67 0. 51 0. 64 0. 41 0. 31 0. 12 0. 09 0. 17 0. 07 0. 12 Slc 5 a 1 779 0. 82 1. 07 1. 05 0. 89 0. 71 0. 84 0. 64 0. 46 0. 13 0. 11 Slc 5 a 11 572 0. 71 0. 73 0. 78 0. 40 0. 37 0. 03 0. 21 0. 17 0. 04 Slc 5 a 2 2397 0. 60 0. 72 0. 93 0. 22 0. 15 0. 01 0. 06 0. 10 0. 01 0. 02 Transcript NCBA Allo D 3 Allo D 4 Allo D 5 ATN D 7 Left D 5 Slc 2 a 2 9441 0. 48 0. 38 0. 28 0. 62 0. 67 Slc 2 a 4 473 0. 70 0. 55 0. 29 1. 00 1. 63 Slc 2 a 5 3904 0. 43 0. 30 0. 25 0. 35 0. 45 Slc 5 a 1 1789 1. 13 1. 01 0. 91 1. 00 Slc 5 a 11 1180 0. 51 0. 42 0. 22 0. 50 0. 89 Slc 5 a 2 6280 0. 39 0. 33 0. 18 0. 63 0. 71
Glucose Transporters Transcript NCBA Iso D 5 Iso D 7 Iso D 21 Allo D 5 Allo D 7 Allo D 14 Allo D 21 Allo D 42 CTL MLR Slc 2 a 2 3192 0. 86 0. 74 0. 88 0. 31 0. 29 0. 20 0. 16 0. 23 0. 01 0. 02 Slc 2 a 4 380 0. 67 0. 77 0. 95 0. 37 0. 38 0. 15 0. 22 0. 29 0. 07 0. 13 Slc 2 a 5 1778 0. 67 0. 51 0. 64 0. 41 0. 31 0. 12 0. 09 0. 17 0. 07 0. 12 Slc 5 a 1 779 0. 82 1. 07 1. 05 0. 89 0. 71 0. 84 0. 64 0. 46 0. 13 0. 11 Slc 5 a 11 572 0. 71 0. 73 0. 78 0. 40 0. 37 0. 03 0. 21 0. 17 0. 04 Slc 5 a 2 2397 0. 60 0. 72 0. 93 0. 22 0. 15 0. 01 0. 06 0. 10 0. 01 0. 02 Transcript NCBA Allo D 3 Allo D 4 Allo D 5 ATN D 7 Left D 5 Slc 2 a 2 9441 0. 48 0. 38 0. 28 0. 62 0. 67 Slc 2 a 4 473 0. 70 0. 55 0. 29 1. 00 1. 63 Slc 2 a 5 3904 0. 43 0. 30 0. 25 0. 35 0. 45 Slc 5 a 1 1789 1. 13 1. 01 0. 91 1. 00 Slc 5 a 11 1180 0. 51 0. 42 0. 22 0. 50 0. 89 Slc 5 a 2 6280 0. 39 0. 33 0. 18 0. 63 0. 71
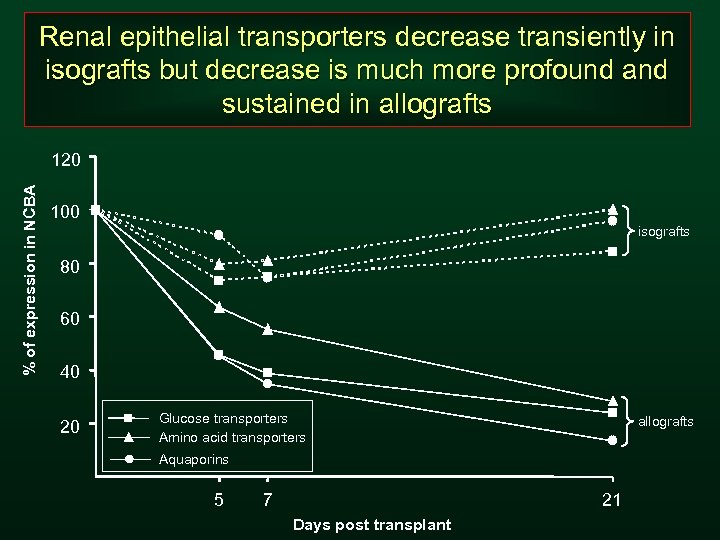 Renal epithelial transporters decrease transiently in isografts but decrease is much more profound and sustained in allografts % of expression in NCBA 120 100 isografts 80 60 40 20 Glucose transporters Amino acid transporters allografts Aquaporins 5 7 21 Days post transplant
Renal epithelial transporters decrease transiently in isografts but decrease is much more profound and sustained in allografts % of expression in NCBA 120 100 isografts 80 60 40 20 Glucose transporters Amino acid transporters allografts Aquaporins 5 7 21 Days post transplant
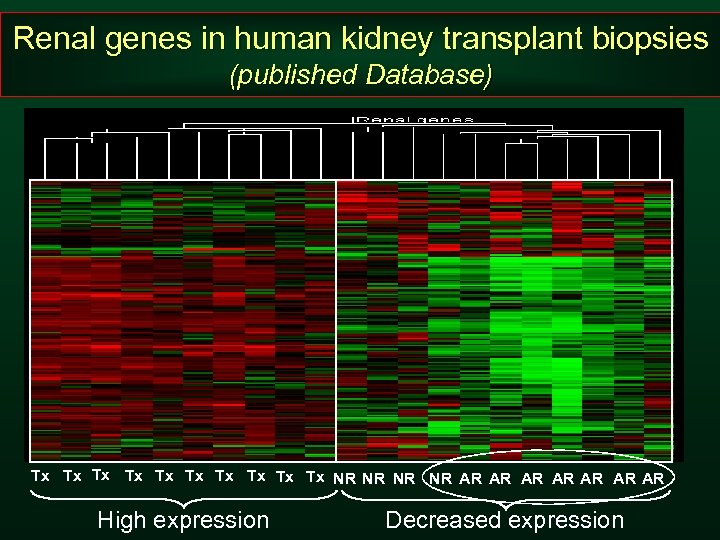 Renal genes in human kidney transplant biopsies (published Database) Tx Tx Tx NR NR AR AR High expression Decreased expression
Renal genes in human kidney transplant biopsies (published Database) Tx Tx Tx NR NR AR AR High expression Decreased expression
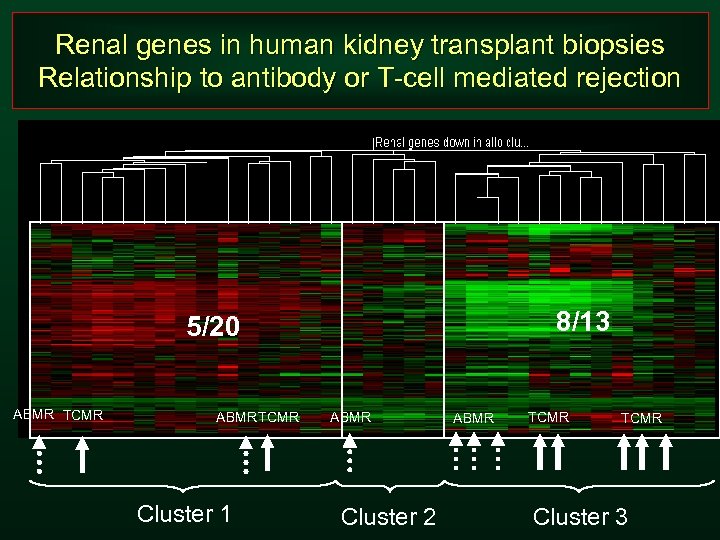 Renal genes in human kidney transplant biopsies Relationship to antibody or T-cell mediated rejection 8/13 5/20 ABMR TCMR Cluster 1 ABMR Cluster 2 ABMR TCMR Cluster 3
Renal genes in human kidney transplant biopsies Relationship to antibody or T-cell mediated rejection 8/13 5/20 ABMR TCMR Cluster 1 ABMR Cluster 2 ABMR TCMR Cluster 3
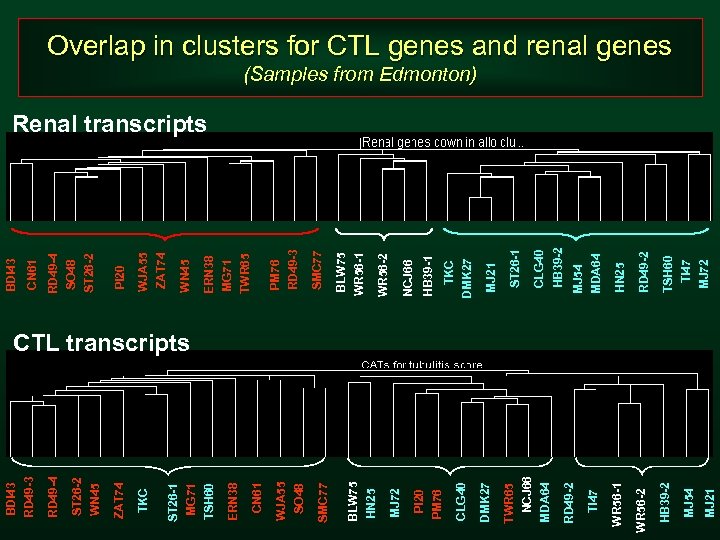 MJ 21 MJ 54 HB 39 -2 MJ 72 TSH 60 TI 47 RD 49 -2 WR 56 -2 MJ 54 MDA 64 HB 39 -2 CLG 40 ST 26 -1 MJ 21 TKC DMK 27 HB 39 -1 NCJ 66 WR 56 -2 BLW 75 WR 56 -1 SMC 77 PM 76 RD 49 -3 ERN 38 MG 71 TWR 65 WN 45 ZAT 74 WJA 55 PI 20 RD 49 -4 SO 48 ST 26 -2 CN 61 BDI 43 HN 25 CTL transcripts WR 56 -1 TI 47 RD 49 -2 NCJ 66 MDA 64 TWR 65 DMK 27 CLG 40 PI 20 PM 76 MJ 72 BLW 75 HN 25 SMC 77 WJA 55 SO 48 CN 61 ERN 38 ST 26 -1 MG 71 TSH 60 TKC ZAT 74 ST 26 -2 WN 45 RD 49 -4 BDI 43 RD 49 -3 Overlap in clusters for CTL genes and renal genes (Samples from Edmonton) Renal transcripts
MJ 21 MJ 54 HB 39 -2 MJ 72 TSH 60 TI 47 RD 49 -2 WR 56 -2 MJ 54 MDA 64 HB 39 -2 CLG 40 ST 26 -1 MJ 21 TKC DMK 27 HB 39 -1 NCJ 66 WR 56 -2 BLW 75 WR 56 -1 SMC 77 PM 76 RD 49 -3 ERN 38 MG 71 TWR 65 WN 45 ZAT 74 WJA 55 PI 20 RD 49 -4 SO 48 ST 26 -2 CN 61 BDI 43 HN 25 CTL transcripts WR 56 -1 TI 47 RD 49 -2 NCJ 66 MDA 64 TWR 65 DMK 27 CLG 40 PI 20 PM 76 MJ 72 BLW 75 HN 25 SMC 77 WJA 55 SO 48 CN 61 ERN 38 ST 26 -1 MG 71 TSH 60 TKC ZAT 74 ST 26 -2 WN 45 RD 49 -4 BDI 43 RD 49 -3 Overlap in clusters for CTL genes and renal genes (Samples from Edmonton) Renal transcripts
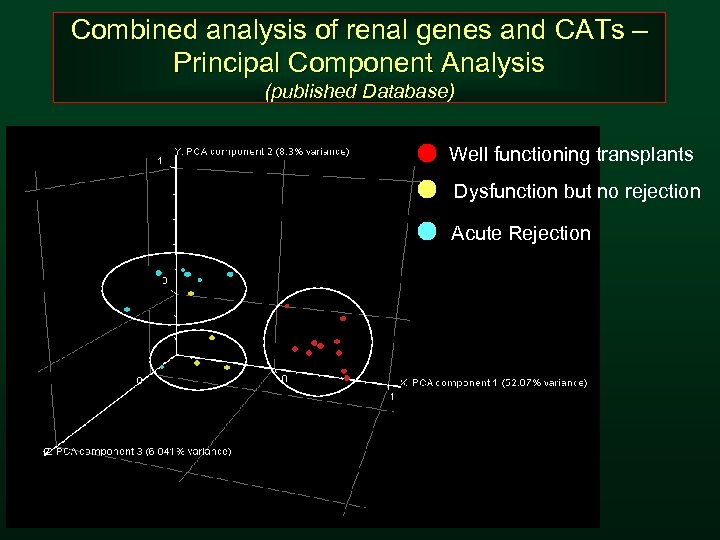 Combined analysis of renal genes and CATs – Principal Component Analysis (published Database) Well functioning transplants Dysfunction but no rejection Acute Rejection
Combined analysis of renal genes and CATs – Principal Component Analysis (published Database) Well functioning transplants Dysfunction but no rejection Acute Rejection
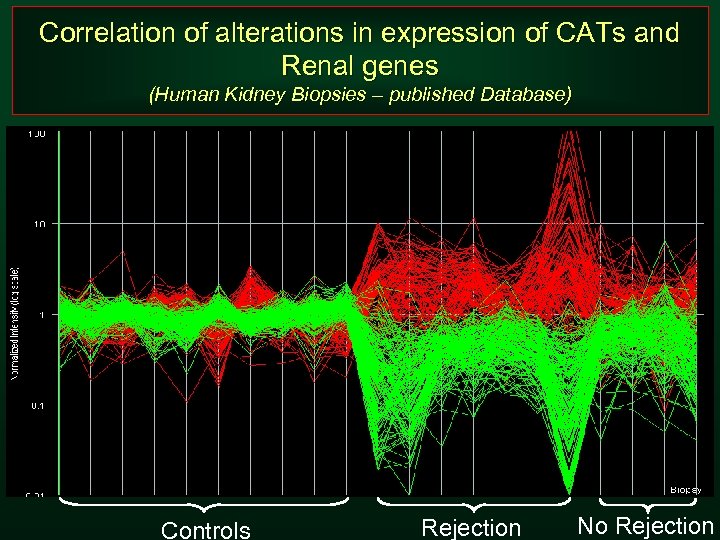 Correlation of alterations in expression of CATs and Renal genes (Human Kidney Biopsies – published Database) Controls Rejection No Rejection
Correlation of alterations in expression of CATs and Renal genes (Human Kidney Biopsies – published Database) Controls Rejection No Rejection
 Summary – Renal genes • Mouse isografts show some alterations in expression of renal genes. • In allografts, decreased expression of Renal genes is much more profound and sustained. • Decreased expression of many Renal genes occurs before tubulitis develops.
Summary – Renal genes • Mouse isografts show some alterations in expression of renal genes. • In allografts, decreased expression of Renal genes is much more profound and sustained. • Decreased expression of many Renal genes occurs before tubulitis develops.
 Conclusions • Pathogenesis-based transcript sets may be the basis for a secure and robust diagnosis of T cell mediated rejection but require further refinement • The combined analysis of several transcript sets plus further refinements may increase sensitivity and specificity.
Conclusions • Pathogenesis-based transcript sets may be the basis for a secure and robust diagnosis of T cell mediated rejection but require further refinement • The combined analysis of several transcript sets plus further refinements may increase sensitivity and specificity.
 Where to go from here • Further refine the sets of CTL associated transcripts and renal genes • Develop additional signatures Improve understanding of mechanisms of disease (targets for drug discovery) • Develop diagnostic and monitoring tools • Adaptation as end points for clinical trials • Application to other transplants • Application to other inflammatory processes
Where to go from here • Further refine the sets of CTL associated transcripts and renal genes • Develop additional signatures Improve understanding of mechanisms of disease (targets for drug discovery) • Develop diagnostic and monitoring tools • Adaptation as end points for clinical trials • Application to other transplants • Application to other inflammatory processes


