d2e6542864a900dd206687a45ba141eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47

Experience IBM Flash. System™ as an Application Accelerator what’s new, model 840 Detlef Helmbrecht European Storage Competence Center – Mainz – Germany © 2014 IBM Corporation

Agenda § Introduction to Flash Technology § New features of Model 840 § New GUI and CLI § Encryption § GA Restrictions § Q&A © 2014 IBM Corporation
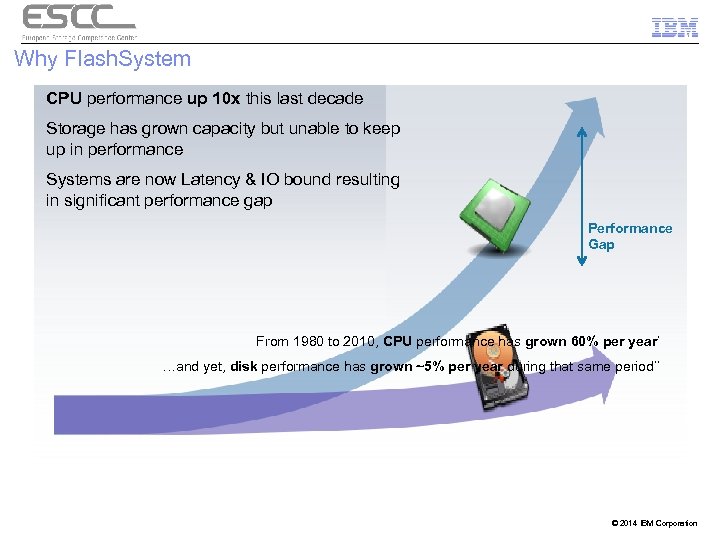
Why Flash. System CPU performance up 10 x this last decade Storage has grown capacity but unable to keep up in performance Systems are now Latency & IO bound resulting in significant performance gap Performance Gap From 1980 to 2010, CPU performance has grown 60% per year* …and yet, disk performance has grown ~5% per year during that same period** © 2014 IBM Corporation
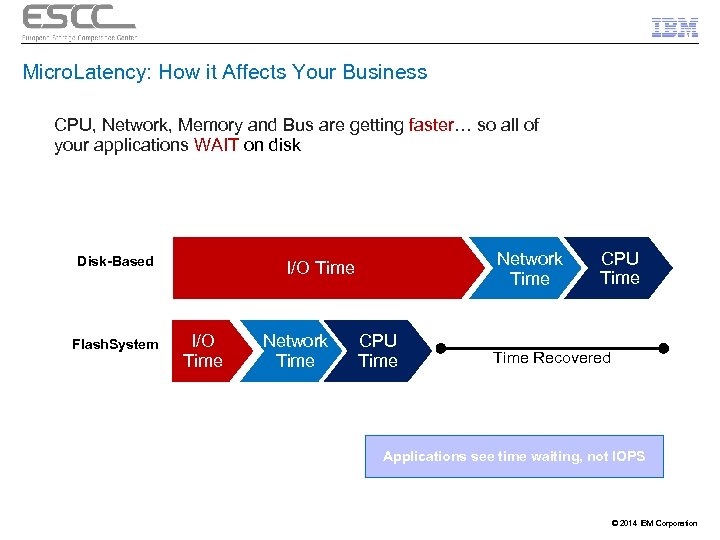
Micro. Latency: How it Affects Your Business CPU, Network, Memory and Bus are getting faster… so all of your applications WAIT on disk Disk-Based Flash. System Network Time I/O Time Network Time CPU Time Recovered Applications see time waiting, not IOPS © 2014 IBM Corporation
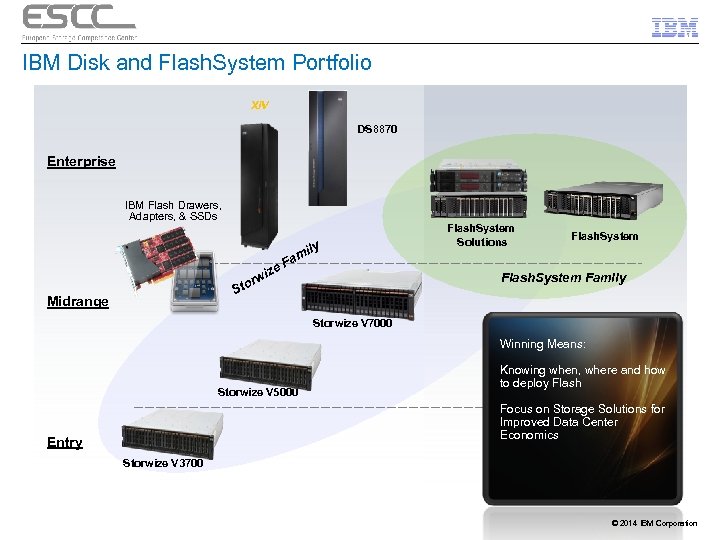
IBM Disk and Flash. System Portfolio XIV DS 8870 Enterprise IBM Flash Drawers, Adapters, & SSDs ly mi Flash. System Solutions Flash. System a F ize Flash. System Family rw Sto Midrange Storwize V 7000 Winning Means: Storwize V 5000 Knowing when, where and how to deploy Flash Focus on Storage Solutions for Improved Data Center Economics Entry Storwize V 3700 © 2014 IBM Corporation
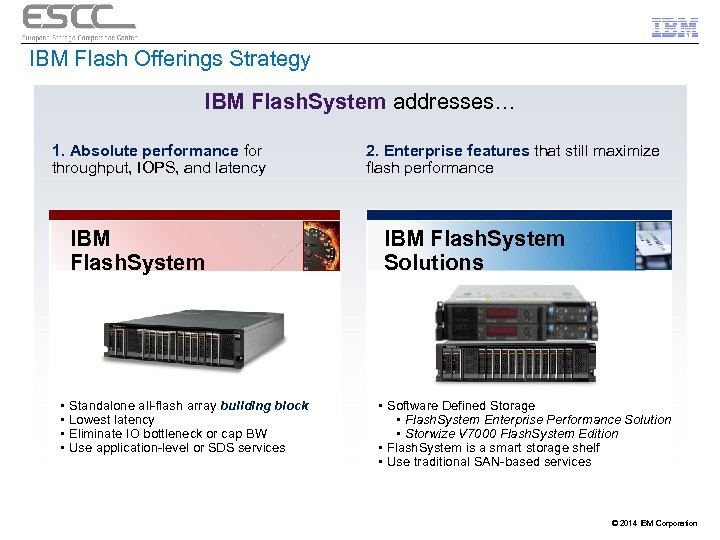
IBM Flash Offerings Strategy IBM Flash. System addresses… 1. Absolute performance for throughput, IOPS, and latency IBM Flash. System • • Standalone all-flash array building block Lowest latency Eliminate IO bottleneck or cap BW Use application-level or SDS services 2. Enterprise features that still maximize flash performance IBM Flash. System Solutions • Software Defined Storage • Flash. System Enterprise Performance Solution • Storwize V 7000 Flash. System Edition • Flash. System is a smart storage shelf • Use traditional SAN-based services © 2014 IBM Corporation
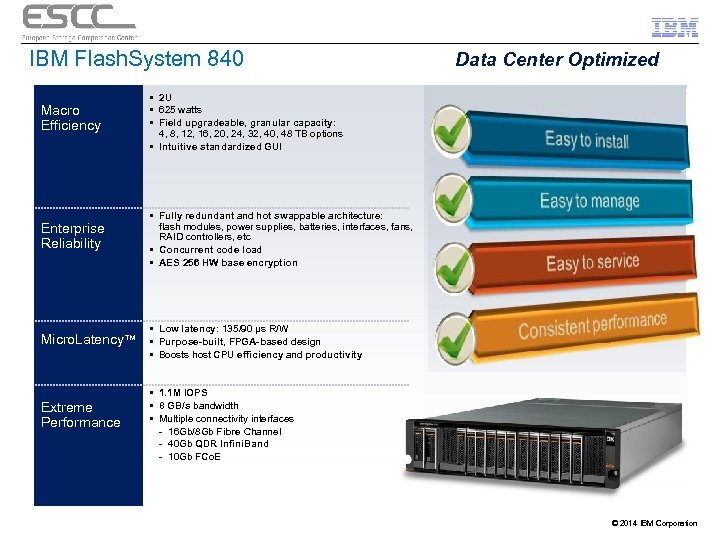
IBM Flash. System 840 Macro Efficiency • 2 U • 625 watts • Field upgradeable, granular capacity: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 32, 40, 48 TB options • Intuitive standardized GUI Enterprise Reliability • Fully redundant and hot swappable architecture: flash modules, power supplies, batteries, interfaces, fans, RAID controllers, etc • Concurrent code load • AES 256 HW base encryption Micro. Latency™ Data Center Optimized • Low latency: 135/90 µs R/W • Purpose-built, FPGA-based design • Boosts host CPU efficiency and productivity Extreme Performance • 1. 1 M IOPS • 8 GB/s bandwidth • Multiple connectivity interfaces - 16 Gb/8 Gb Fibre Channel - 40 Gb QDR Infini. Band - 10 Gb FCo. E © 2014 IBM Corporation
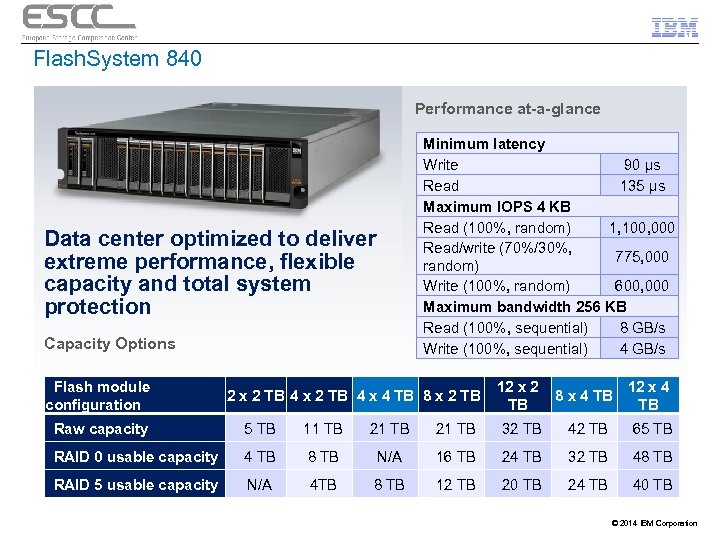
Flash. System 840 Performance at-a-glance Data center optimized to deliver extreme performance, flexible capacity and total system protection Capacity Options Flash module configuration Minimum latency Write 90 µs Read 135 µs Maximum IOPS 4 KB Read (100%, random) 1, 100, 000 Read/write (70%/30%, 775, 000 random) Write (100%, random) 600, 000 Maximum bandwidth 256 KB Read (100%, sequential) 8 GB/s Write (100%, sequential) 4 GB/s 2 x 2 TB 4 x 4 TB 8 x 2 TB 12 x 2 12 x 4 8 x 4 TB TB TB Raw capacity 5 TB 11 TB 21 TB 32 TB 42 TB 65 TB RAID 0 usable capacity 4 TB 8 TB N/A 16 TB 24 TB 32 TB 48 TB RAID 5 usable capacity N/A 4 TB 8 TB 12 TB 20 TB 24 TB 40 TB © 2014 IBM Corporation
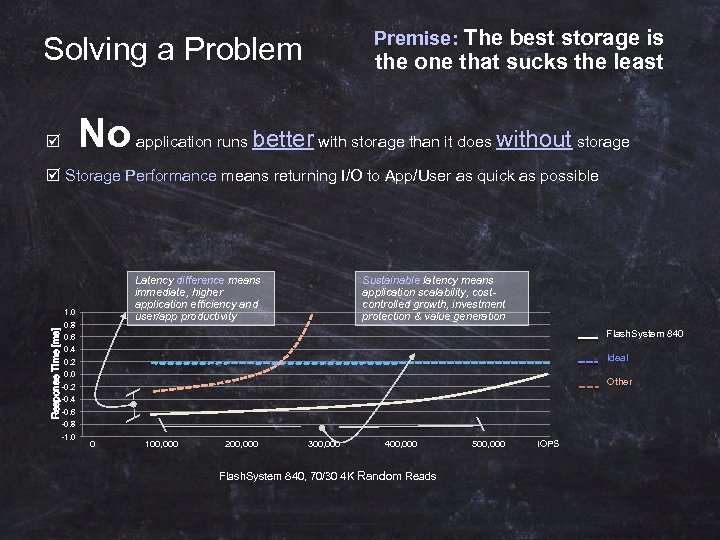
Premise: The best storage is Solving a Problem No the one that sucks the least application runs better with storage than it does without storage Storage Performance means returning I/O to App/User as quick as possible Latency difference means immediate, higher application efficiency and user/app productivity 0. 8 Flash. System 840 0. 6 0. 4 Ideal 0. 2 0. 0 -0. 2 l l Response Time [ms] 1. 0 Sustainable latency means application scalability, costcontrolled growth, investment protection & value generation -0. 4 -0. 6 -0. 8 -1. 0 0 Other l l 100, 000 200, 000 300, 000 400, 000 500, 000 IOPS Flash. System 840, 70/30 4 K Random Reads © 2014 IBM Corporation
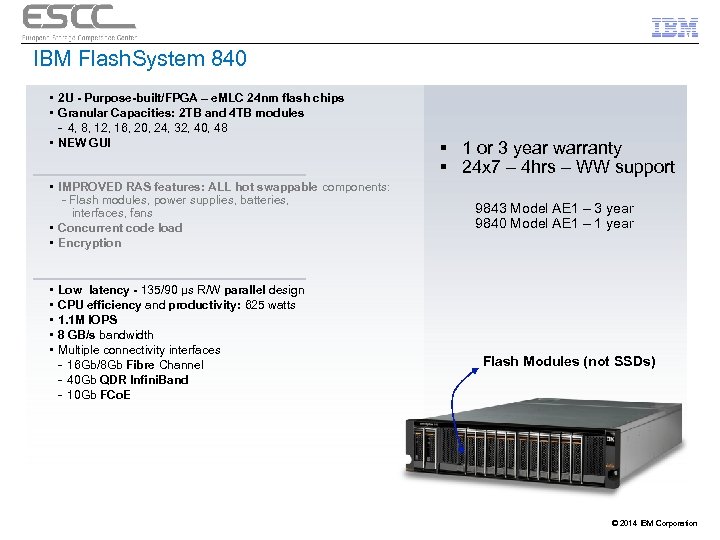
IBM Flash. System 840 • 2 U - Purpose-built/FPGA – e. MLC 24 nm flash chips • Granular Capacities: 2 TB and 4 TB modules - 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 32, 40, 48 • NEW GUI • IMPROVED RAS features: ALL hot swappable components: - Flash modules, power supplies, batteries, interfaces, fans • Concurrent code load • Encryption • • • Low latency - 135/90 µs R/W parallel design CPU efficiency and productivity: 625 watts 1. 1 M IOPS 8 GB/s bandwidth Multiple connectivity interfaces - 16 Gb/8 Gb Fibre Channel - 40 Gb QDR Infini. Band - 10 Gb FCo. E § 1 or 3 year warranty § 24 x 7 – 4 hrs – WW support 9843 Model AE 1 – 3 year 9840 Model AE 1 – 1 year Flash Modules (not SSDs) © 2014 IBM Corporation
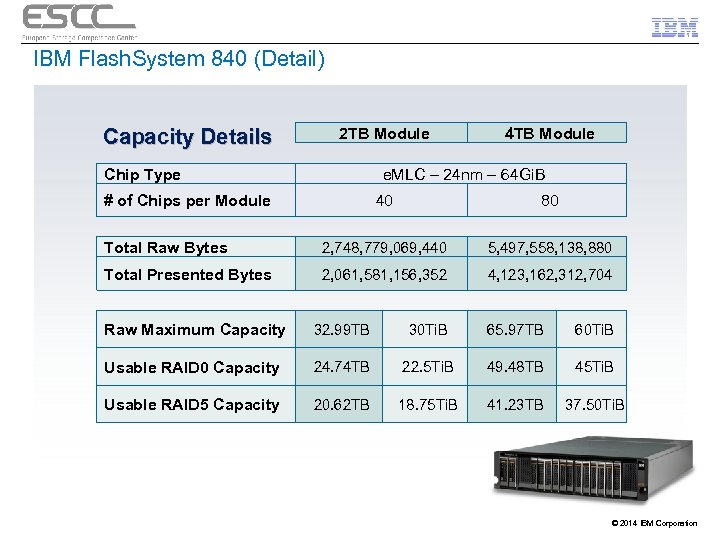
IBM Flash. System 840 (Detail) Capacity Details 2 TB Module Chip Type 4 TB Module e. MLC – 24 nm – 64 Gi. B # of Chips per Module 40 80 Total Raw Bytes 2, 748, 779, 069, 440 5, 497, 558, 138, 880 Total Presented Bytes 2, 061, 581, 156, 352 4, 123, 162, 312, 704 Raw Maximum Capacity 32. 99 TB 30 Ti. B 65. 97 TB 60 Ti. B Usable RAID 0 Capacity 24. 74 TB 22. 5 Ti. B 49. 48 TB 45 Ti. B Usable RAID 5 Capacity 20. 62 TB 18. 75 Ti. B 41. 23 TB 37. 50 Ti. B © 2014 IBM Corporation

IBM Flash. System 840 Capacity & Performance Configuration Guidelines • • • Cannot Mix 2 TB with 4 TB modules provide HIGHER capacity and scalability options Module type has little effect on Read performance Write performance continues to be based primarily on number of chips & flash controllers • More chips and flash controllers = more Write Bandwidth • Only significant in “write-heavy” environments • Only significant in “sustained” write environments Capacity upgrades are not yet available online, unless virtualized © 2014 IBM Corporation
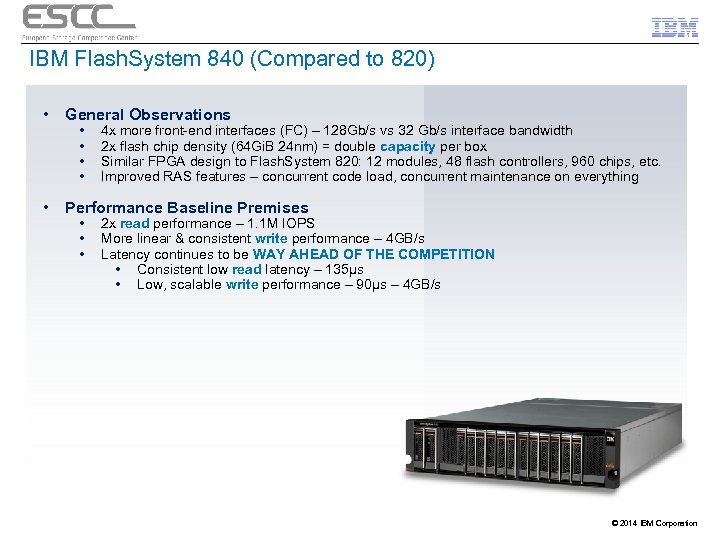
IBM Flash. System 840 (Compared to 820) • General Observations • Performance Baseline Premises • • 4 x more front-end interfaces (FC) – 128 Gb/s vs 32 Gb/s interface bandwidth 2 x flash chip density (64 Gi. B 24 nm) = double capacity per box Similar FPGA design to Flash. System 820: 12 modules, 48 flash controllers, 960 chips, etc. Improved RAS features – concurrent code load, concurrent maintenance on everything 2 x read performance – 1. 1 M IOPS More linear & consistent write performance – 4 GB/s Latency continues to be WAY AHEAD OF THE COMPETITION • Consistent low read latency – 135µs • Low, scalable write performance – 90µs – 4 GB/s © 2014 IBM Corporation
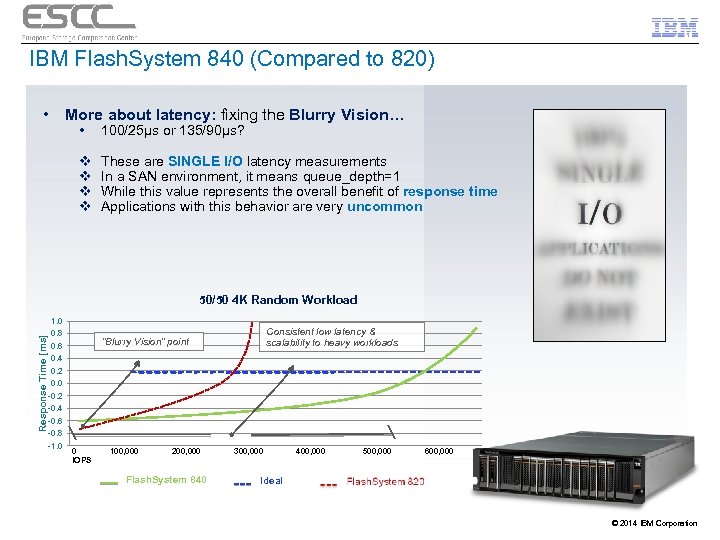
IBM Flash. System 840 (Compared to 820) • More about latency: fixing the Blurry Vision… • 100/25µs or 135/90µs? v v These are SINGLE I/O latency measurements In a SAN environment, it means queue_depth=1 While this value represents the overall benefit of response time Applications with this behavior are very uncommon 50/50 4 K Random Workload Response Time [ms] 1. 0 0. 8 Consistent low latency & scalability to heavy workloads “Blurry Vision” point 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0. 0 -0. 2 -0. 4 -0. 6 -0. 8 -1. 0 l l 0 IOPS 100, 000 200, 000 Flash. System 840 300, 000 400, 000 500, 000 600, 000 Ideal © 2014 IBM Corporation
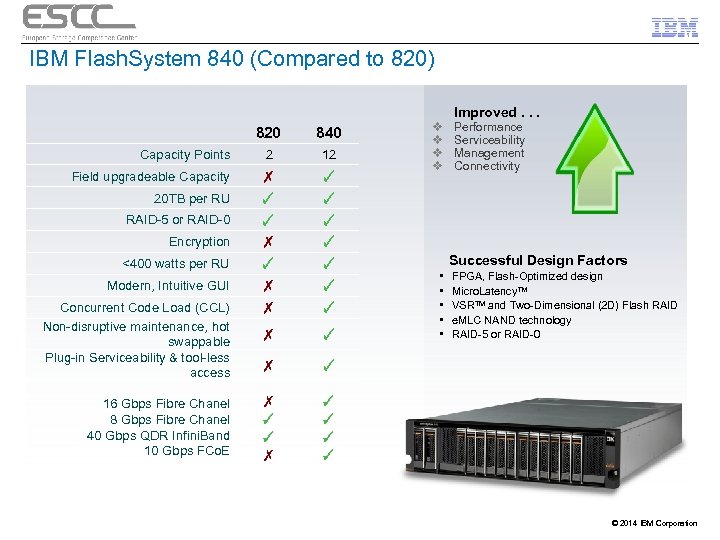
IBM Flash. System 840 (Compared to 820) 820 840 Capacity Points 2 12 Field upgradeable Capacity ✗ ✓ ✓ ✗ ✗ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✗ Improved. . . Performance Serviceability Management Connectivity ✓ ✗ ✓ ✓ ✗ v v ✓ ✓ 20 TB per RU RAID-5 or RAID-0 Encryption <400 watts per RU Modern, Intuitive GUI Concurrent Code Load (CCL) Non-disruptive maintenance, hot swappable Plug-in Serviceability & tool-less access 16 Gbps Fibre Chanel 8 Gbps Fibre Chanel 40 Gbps QDR Infini. Band 10 Gbps FCo. E Successful Design Factors • FPGA, Flash-Optimized design • Micro. Latency™ • VSRTM and Two-Dimensional (2 D) Flash RAID • e. MLC NAND technology • RAID-5 or RAID-0 © 2014 IBM Corporation
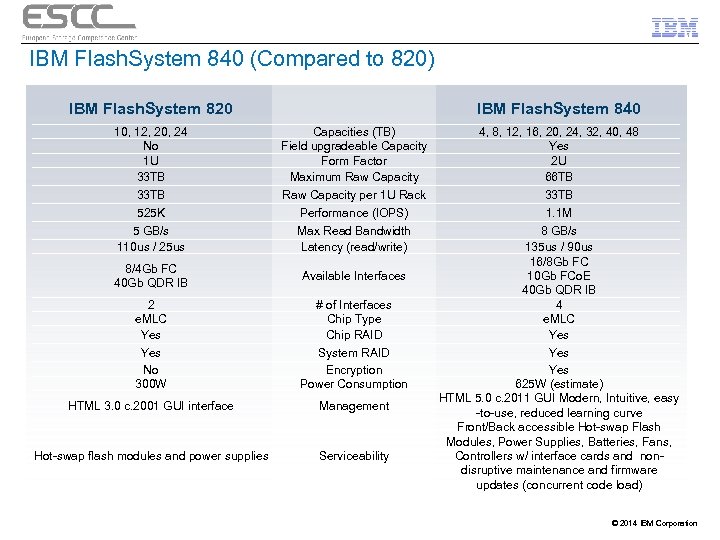
IBM Flash. System 840 (Compared to 820) IBM Flash. System 820 IBM Flash. System 840 10, 12, 20, 24 No 1 U 33 TB 525 K 5 GB/s 110 us / 25 us Capacities (TB) Field upgradeable Capacity Form Factor Maximum Raw Capacity per 1 U Rack Performance (IOPS) Max Read Bandwidth Latency (read/write) 8/4 Gb FC 40 Gb QDR IB Available Interfaces 2 e. MLC Yes No 300 W # of Interfaces Chip Type Chip RAID System RAID Encryption Power Consumption HTML 3. 0 c. 2001 GUI interface Management Hot-swap flash modules and power supplies Serviceability 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 32, 40, 48 Yes 2 U 66 TB 33 TB 1. 1 M 8 GB/s 135 us / 90 us 16/8 Gb FC 10 Gb FCo. E 40 Gb QDR IB 4 e. MLC Yes Yes 625 W (estimate) HTML 5. 0 c. 2011 GUI Modern, Intuitive, easy -to-use, reduced learning curve Front/Back accessible Hot-swap Flash Modules, Power Supplies, Batteries, Fans, Controllers w/ interface cards and nondisruptive maintenance and firmware updates (concurrent code load) © 2014 IBM Corporation

IBM Flash. System 840 The GUI that revolutionized storage, now available in Flash. System 840 © 2014 IBM Corporation
IBM Flash. System 840 • 2 U - Purpose-built/FPGA – e. MLC 24 nm flash chips • Granular Capacities: 2 TB and 4 TB modules - 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 32, 40, 48 • NEW GUI • IMPROVED RAS features: ALL hot swappable components: - Flash modules, power supplies, batteries, interfaces, fans • Concurrent code load • Encryption • • • v Encryption • Optional, licensable feature • AES-XTS 256 -bit data-at-rest • Local management • Module-level implementation (Self-Encrypted Flash Controller) • Zero impact on performance Low latency - 135/90 µs R/W parallel design CPU efficiency and productivity: 625 watts 1. 1 M IOPS 8 GB/s bandwidth Multiple connectivity interfaces - 16 Gb/8 Gb Fibre Channel - 40 Gb QDR Infini. Band - 10 Gb FCo. E © 2014 IBM Corporation
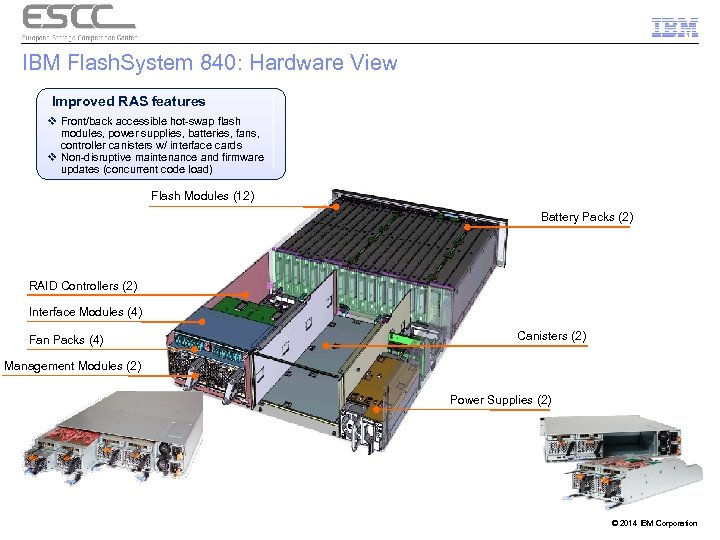
IBM Flash. System 840: Hardware View Improved RAS features v Front/back accessible hot-swap flash modules, power supplies, batteries, fans, controller canisters w/ interface cards v Non-disruptive maintenance and firmware updates (concurrent code load) Flash Modules (12) Battery Packs (2) RAID Controllers (2) Interface Modules (4) Fan Packs (4) Canisters (2) Management Modules (2) Power Supplies (2) © 2014 IBM Corporation
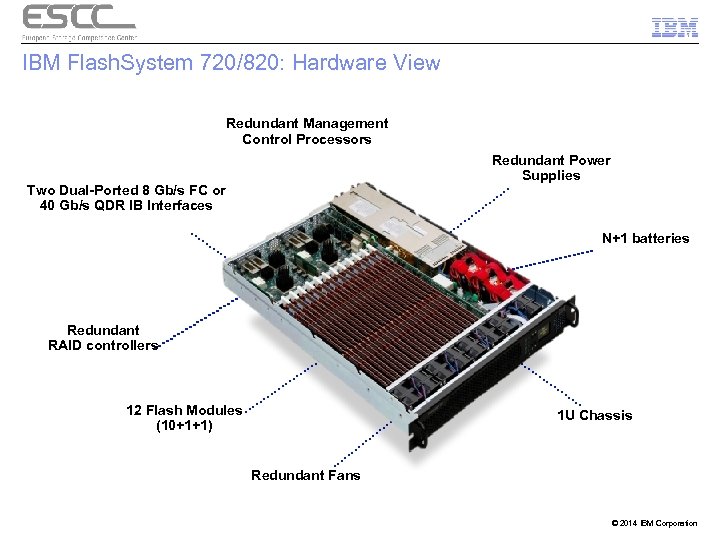
IBM Flash. System 720/820: Hardware View Redundant Management Control Processors Redundant Power Supplies Two Dual-Ported 8 Gb/s FC or 40 Gb/s QDR IB Interfaces N+1 batteries Redundant RAID controllers 12 Flash Modules (10+1+1) 1 U Chassis Redundant Fans © 2014 IBM Corporation
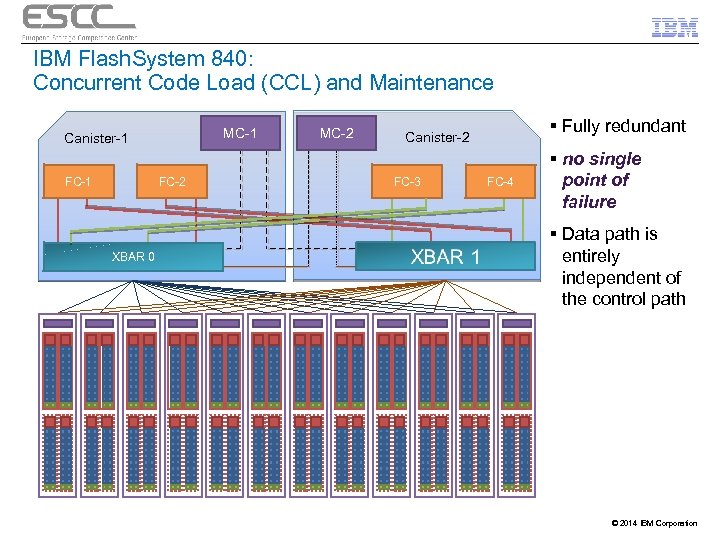
IBM Flash. System 840: Concurrent Code Load (CCL) and Maintenance MC-1 Canister-1 FC-2 XBAR 0 MC-2 § Fully redundant Canister-2 FC-3 FC-4 § no single point of failure § Data path is entirely independent of the control path © 2014 IBM Corporation
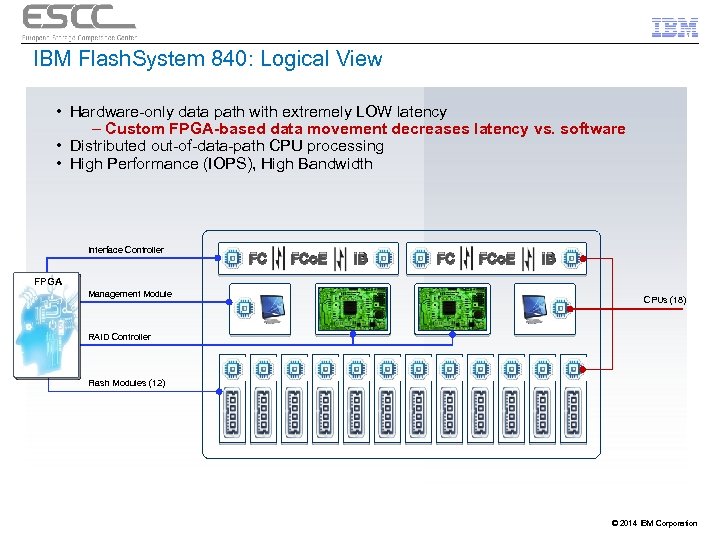
IBM Flash. System 840: Logical View • Hardware-only data path with extremely LOW latency – Custom FPGA-based data movement decreases latency vs. software • Distributed out-of-data-path CPU processing • High Performance (IOPS), High Bandwidth Interface Controller FC FCo. E IB FPGA Management Module CPUs (18) RAID Controller Flash Modules (12) © 2014 IBM Corporation
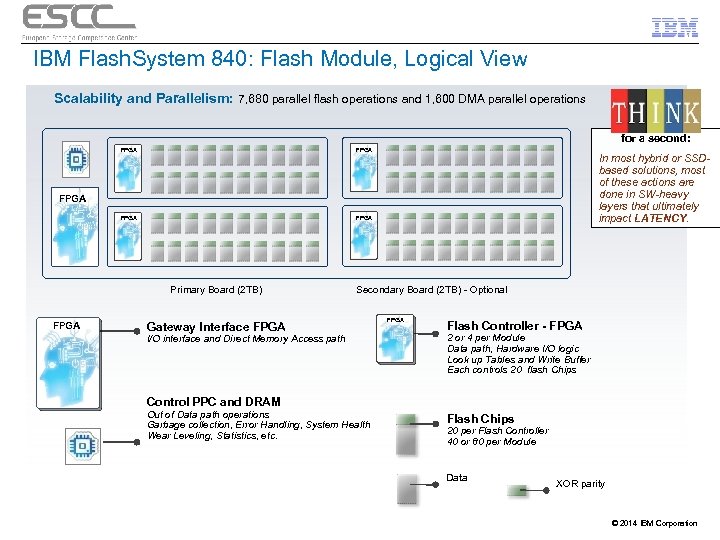
IBM Flash. System 840: Flash Module, Logical View Scalability and Parallelism: 7, 680 parallel flash operations and 1, 600 DMA parallel operations for a second: FPGA In most hybrid or SSDbased solutions, most of these actions are done in SW-heavy layers that ultimately impact LATENCY. FPGA Primary Board (2 TB) FPGA Secondary Board (2 TB) - Optional Gateway Interface FPGA I/O interface and Direct Memory Access path FPGA Flash Controller - FPGA 2 or 4 per Module Data path, Hardware I/O logic Look up Tables and Write Buffer Each controls 20 flash Chips Control PPC and DRAM Out of Data path operations Garbage collection, Error Handling, System Health Wear Leveling, Statistics, etc. Flash Chips 20 per Flash Controller 40 or 80 per Module Data XOR parity © 2014 IBM Corporation
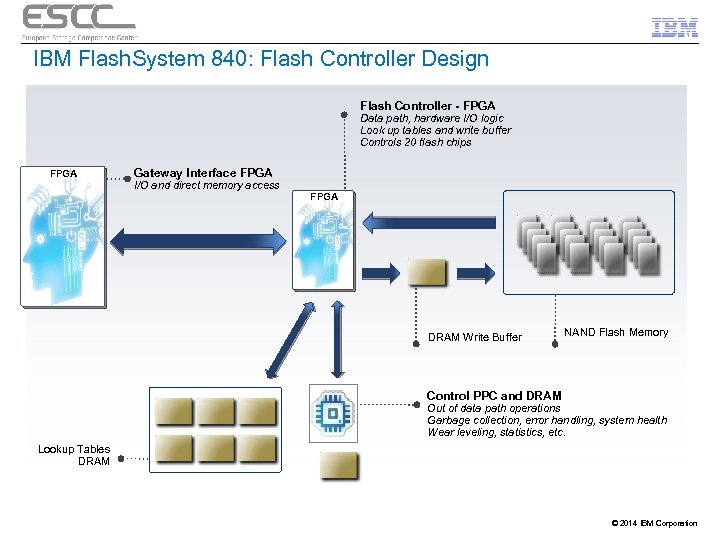
IBM Flash. System 840: Flash Controller Design Flash Controller - FPGA Data path, hardware I/O logic Look up tables and write buffer Controls 20 flash chips FPGA Gateway Interface FPGA I/O and direct memory access FPGA DRAM Write Buffer NAND Flash Memory Control PPC and DRAM Out of data path operations Garbage collection, error handling, system health Wear leveling, statistics, etc. Lookup Tables DRAM © 2014 IBM Corporation
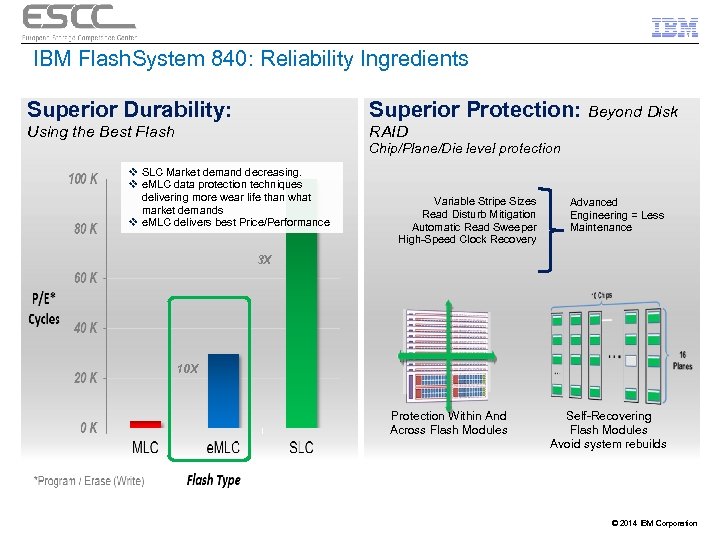
IBM Flash. System 840: Reliability Ingredients Superior Durability: Superior Protection: Beyond Disk Using the Best Flash RAID Chip/Plane/Die level protection v SLC Market demand decreasing. v e. MLC data protection techniques delivering more wear life than what market demands v e. MLC delivers best Price/Performance Variable Stripe Sizes Read Disturb Mitigation Automatic Read Sweeper High-Speed Clock Recovery Advanced Engineering = Less Maintenance 3 X 10 X Protection Within And Across Flash Modules Self-Recovering Flash Modules Avoid system rebuilds © 2014 IBM Corporation

IBM Flash. System 840 Built-in Encryption Protecting business’s most valuable asset § Industry standard AES-XTS required by most leading compliance regulations such as HIPAA and FIPS § Local key management § All performance measurements published at GA and later include the affect of encryption, even if it is not enabled – we encrypt with a default key © 2014 IBM Corporation

Basic encryption concepts: § Symmetric vs. Asymmetric cryptography § Symmetric (e. g. Triple-DES, AES): uses a single secret key for both encryption and decryption – Allows for very fast and efficient encryption & decryption – Ideal for high speed bulk encryption – Having a single “secret” key creates a key distribution problem § Asymmetric (e. g. D-H, RSA, ECC): uses a public/private key pair – uses one key to wrap, or sign – uses the other key to unwrap, or check signature – the concepts that underpin the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) § Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) – Symmetric block encryption specification established by US Government’s NIST in 2001, encrypts 16 -byte blocks of data. – XTS-AES-256 • XTS effectively encrypts every block of data differently • 256 is the length, in bits © 2014 IBM Corporation
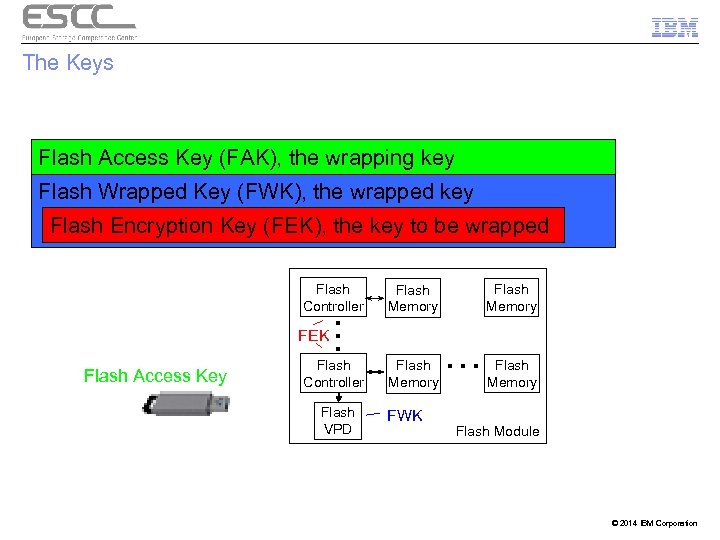
The Keys Flash Access Key (FAK), the wrapping key Flash Wrapped Key (FWK), the wrapped key Flash Encryption Key (FEK), the key to be wrapped Flash Controller … FEK Flash Access Key Flash Controller Flash VPD Flash Memory FWK … Flash Memory Flash Module © 2014 IBM Corporation
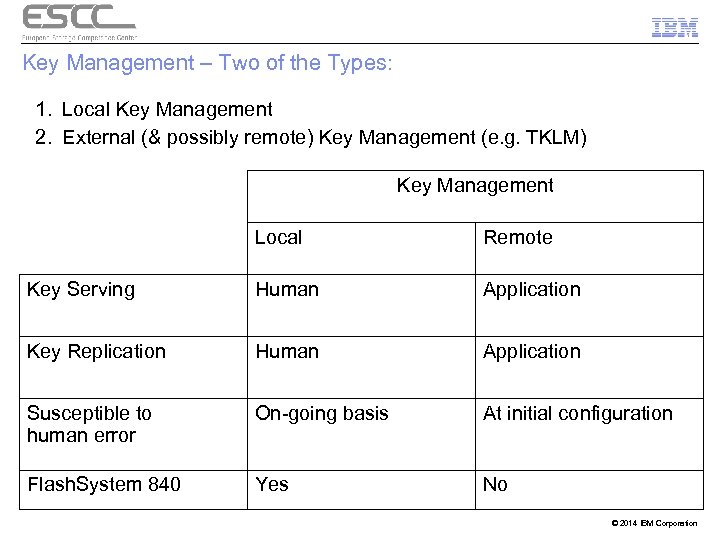
Key Management – Two of the Types: 1. Local Key Management 2. External (& possibly remote) Key Management (e. g. TKLM) Key Management Local Remote Key Serving Human Application Key Replication Human Application Susceptible to human error On-going basis At initial configuration Flash. System 840 Yes No © 2014 IBM Corporation
Flash. System 840 Streamline Management § Modern design § Icon-based navigation, informative graphics, and visualizations § Reduce complexity § Improve efficiency and productivity § Unified, cross-platform design © 2014 IBM Corporation
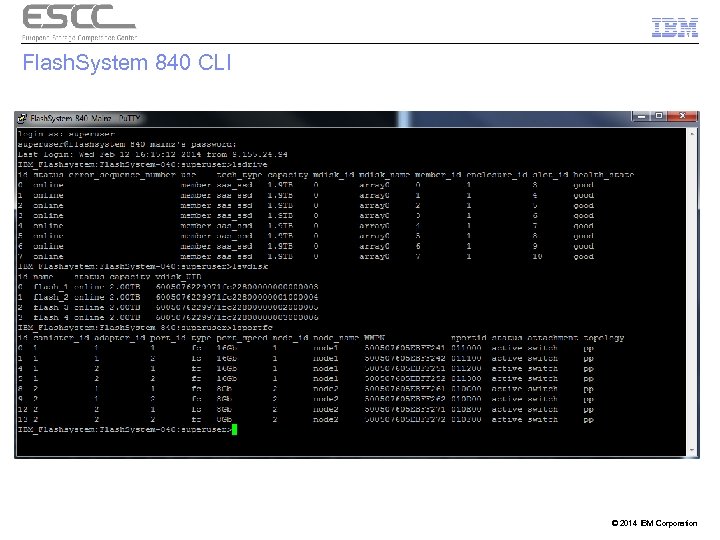
Flash. System 840 CLI © 2014 IBM Corporation

Easily integrated into any environment • 8 Gb or 16 Gb Fibre Channel • 10 Gb Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCo. E) • 40 Gb Infini. Band © 2014 IBM Corporation

IBM Flash. System Solutions Flash. System Enterprise Performance Solution & Storwize V 7000 Flash. System Edition Flash. System Enterprise Performance Solution Storwize V 7000 Flash. System Edition © 2014 IBM Corporation
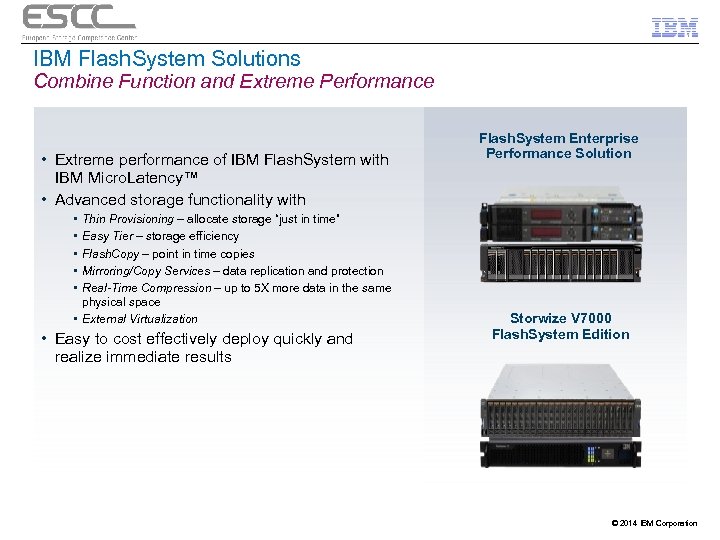
IBM Flash. System Solutions Combine Function and Extreme Performance • Extreme performance of IBM Flash. System with IBM Micro. Latency™ • Advanced storage functionality with Flash. System Enterprise Performance Solution • • • Thin Provisioning – allocate storage “just in time” Easy Tier – storage efficiency Flash. Copy – point in time copies Mirroring/Copy Services – data replication and protection Real-Time Compression – up to 5 X more data in the same physical space • External Virtualization • Easy to cost effectively deploy quickly and realize immediate results Storwize V 7000 Flash. System Edition © 2014 IBM Corporation
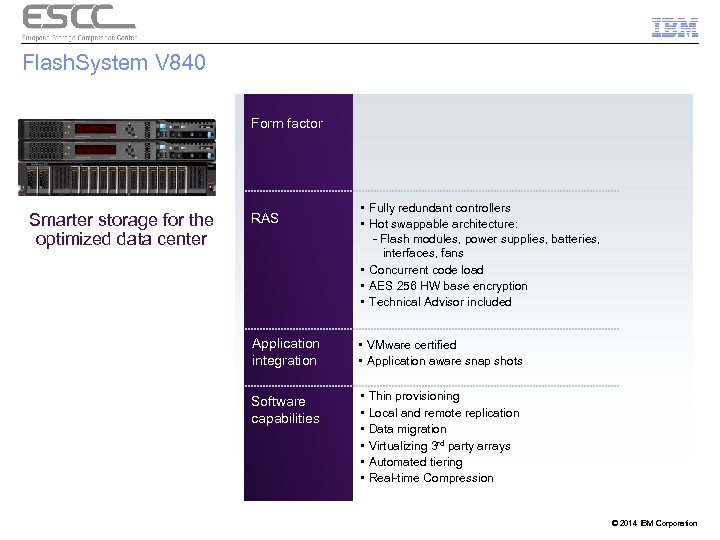
Flash. System V 840 Form factor Smarter storage for the optimized data center RAS • Fully redundant controllers • Hot swappable architecture: - Flash modules, power supplies, batteries, interfaces, fans • Concurrent code load • AES 256 HW base encryption • Technical Advisor included Application integration • VMware certified • Application aware snap shots Software capabilities • • • Thin provisioning Local and remote replication Data migration Virtualizing 3 rd party arrays Automated tiering Real-time Compression © 2014 IBM Corporation
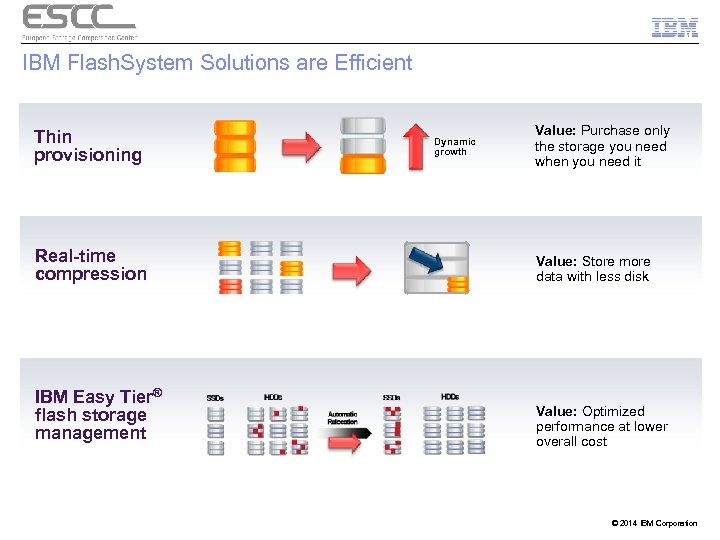
IBM Flash. System Solutions are Efficient Thin provisioning Dynamic growth Value: Purchase only the storage you need when you need it Real-time compression Value: Store more data with less disk IBM Easy Tier® flash storage management Value: Optimized performance at lower overall cost © 2014 IBM Corporation
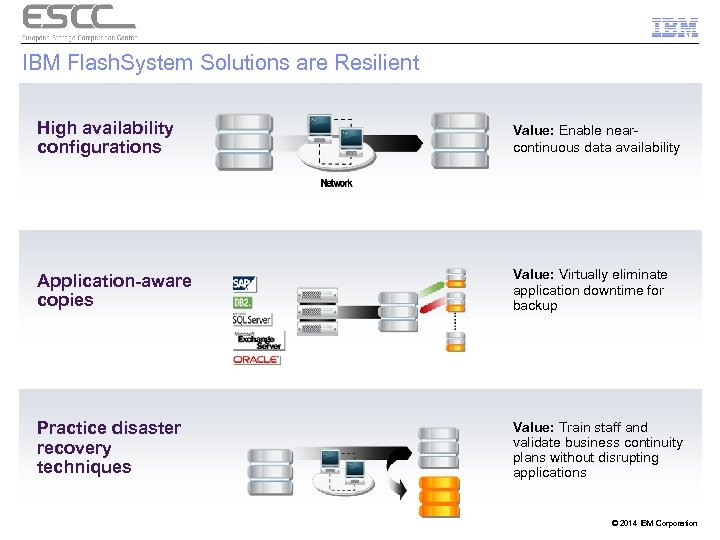
IBM Flash. System Solutions are Resilient High availability configurations Value: Enable nearcontinuous data availability Application-aware copies Value: Virtually eliminate application downtime for backup Practice disaster recovery techniques Value: Train staff and validate business continuity plans without disrupting applications © 2014 IBM Corporation
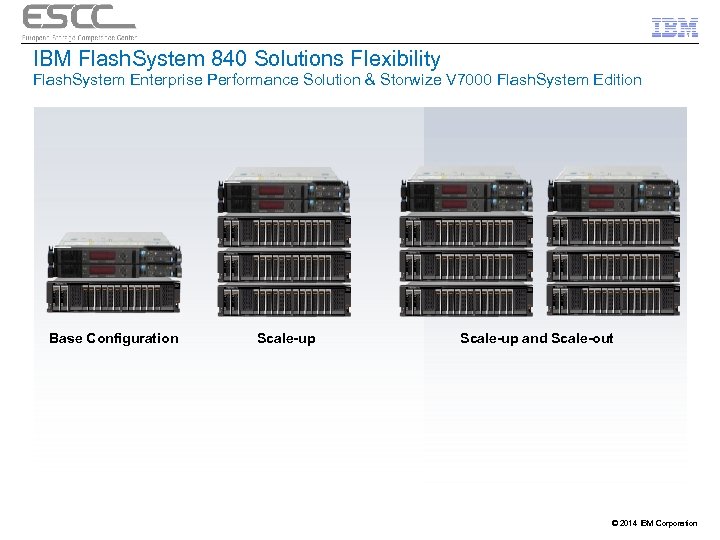
IBM Flash. System 840 Solutions Flexibility Flash. System Enterprise Performance Solution & Storwize V 7000 Flash. System Edition Base Configuration Scale-up and Scale-out © 2014 IBM Corporation
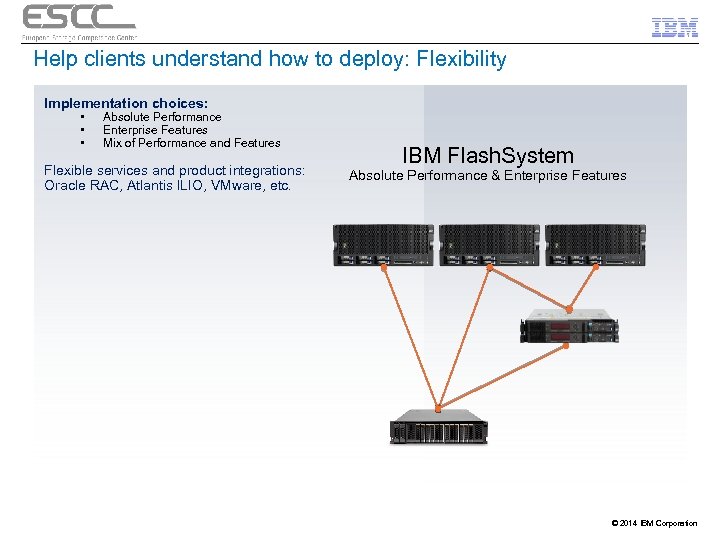
Help clients understand how to deploy: Flexibility Implementation choices: • • • Absolute Performance Enterprise Features Mix of Performance and Features Flexible services and product integrations: Oracle RAC, Atlantis ILIO, VMware, etc. IBM Flash. System Absolute Performance & Enterprise Features © 2014 IBM Corporation
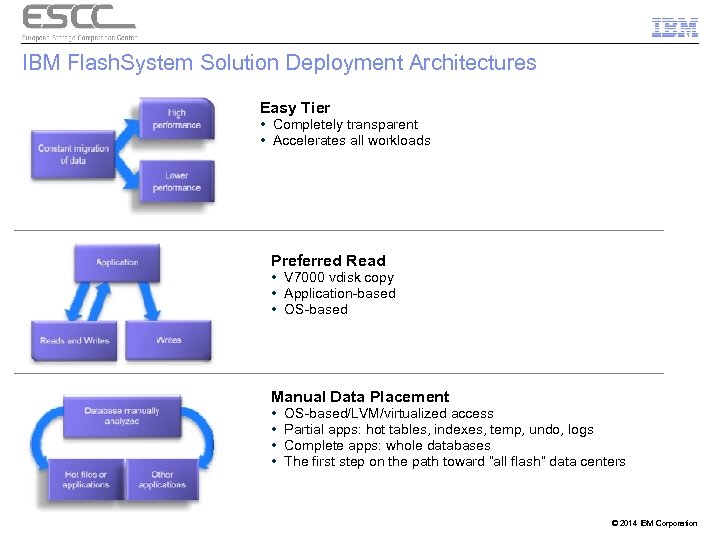
IBM Flash. System Solution Deployment Architectures Easy Tier • Completely transparent • Accelerates all workloads Preferred Read • V 7000 vdisk copy • Application-based • OS-based Manual Data Placement • • OS-based/LVM/virtualized access Partial apps: hot tables, indexes, temp, undo, logs Complete apps: whole databases The first step on the path toward “all flash” data centers © 2014 IBM Corporation

Technical Advisor Overview (Flash. System 840 & V 840) § The STG Technical Advisor (TA) enhances end-to-end support for client’s complex IT solutions. TA is an integrated approach for proactive, coordinated support to allow customers to maximize IT availability at an effective cost § The TA offering is built around three value propositions: – Proactive approach to ensure high availability for vital IT services – Client Advocate that manages problem resolution through the entire support process – Integrated Support for both hardware and software § History: – Global Program established successfully in 2008 for XIV storage array – Technical Advisors are located worldwide in close proximity to clients – TA’s are an integral part of the leading edge IBM Support Structure – Technical Advisor support is now being extended to include XIV, Protec. TIER, So. NAS and Flash. System 840 & V 840 46 Global Offering Development © 2014 IBM Corporation

New Features (One Page) § Up to twelve 4 TB (or 2 TB) flash modules in a small 2 U form factor. § Up to 1, 100, 000 IOPS, up to 8 GB/s bandwidth and latency as low as 90µs. § Hot swappable components replaced via front and rear of the unit – no need to disrupt the system in the rack. § New IBM SAN Volume Controller CLI and GUI for common management look and feel. § Connectivity – eight 16 Gb/s Fibre-channel ports – sixteen 8 Gb/s Fibre-channel ports – sixteen 10 Gb/s Fibre-channel over Ethernet ports – eight 40 Gb/s Infini. Band ports. § Encryption for data at rest. § Concurrent code loads providing no client application downtime. © 2014 IBM Corporation
Open points solved with SP 1 § Components not yet concurrently maintainable – batteries, – RAID canisters, – interface cards. – FCo. E – Infiniband § Revised support for IBM Flash. System 840 concurrent code load – http: //www-01. ibm. com/common/ssi/cgi-bin/ssialias? subtype=ca&infotype=an&appname=i. Source&supplier=897&letternum=ENUS 114 -024 © 2014 IBM Corporation

Q&A © 2014 IBM Corporation
Resources IBM Flash Storage: http: //www-03. ibm. com/systems/storage/flash/index. html Support Matrix (SSIC): http: //www-03. ibm. com/systems/support/storage/ssic/interoperability. wss Redbooks Flash. System: http: //www. redbooks. ibm. com/redbooks. nsf/searchsite? Search. View&query=Flash. System 840 Tour: http: //www-03. ibm. com/systems/data/flash/storage/flash/tour/840/index. html © 2014 IBM Corporation

Disclaimers § Copyright © 2013 by International Business Machines Corporation. § This publication is provided “AS IS. ” IBM product information is subject to change without notice. § No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form without written permission from IBM Corporation. Product data has been reviewed for accuracy as of the date of initial publication. Product data is subject to change without notice. § This document could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. IBM may make changes, improvements or alterations to the products, programs and services described in this document, including termination of such products, programs and services, at any time and without notice. Any statements regarding IBM’s future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only. The information contained in this document is current as of the initial date of publication only and is subject to change without notice. IBM shall have no responsibility to update such information. § Information concerning non-IBM products was obtained from the suppliers of those products, their published announcements or other publicly available sources. IBM has not tested those products in connection with this publication and cannot confirm the accuracy of performance, compatibility or any other claims related to non-IBM products. § IBM makes no representations or warranties, expressed or implied, regarding non-IBM products and services, including those designated as Server. Proven. § IBM is not responsible for the performance or interoperability of any non-IBM products discussed herein. Performance data for IBM and non-IBM products and services contained in this document was derived under specific operating and environmental conditions. The actual results obtained by any party implementing such products or services will depend on a large number of factors specific to such party’s operating environment and may vary significantly. IBM makes no representation that these results can be expected or obtained in any implementation of any such products or services. © 2014 IBM Corporation

Disclaimers (continued) § MB, GB and TB equal 1, 000, 000 and 1, 000, 000 bytes, respectively, where referring to storage capacity. Actual storage capacity will vary based upon many factors and may be less than stated. Some numbers given for storage capacities give capacity in native mode followed by capacity using data compression technology. § THE INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED “AS-IS” WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED. IBM EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NONINFRINGEMENT. IBM products are warranted according to the terms and conditions of the agreements (e. g. , IBM Customer Agreement, Statement of Limited Warranty, International Program License Agreement, etc. ) under which they are provided. § References in this document to IBM products, programs or services does not imply that IBM intends to make such products, programs or services available in all countries in which IBM operates or does business. Consult your local IBM business contact for information on the product or services available in your area. Any reference to an IBM program or product in this document is not intended to state or imply that only that program may be used. Any functionally equivalent program or product that does not infringe IBM’s intellectual property rights may be used instead. It is the user’s responsibility to evaluate and verify the operation of any non-IBM product, program or service. § IBM's customer is responsible for ensuring its own compliance with legal requirements. It is the customer's sole responsibility to obtain advice of competent legal counsel as to the identification and interpretation of any relevant laws and regulatory requirements that may affect the customer's business and any actions the customer may need to take to comply with such laws. IBM does not provide legal advice or represent or warrant that its services or products will ensure that the customer is in compliance with any law. § The provision of the information contained herein is not intended to, and does not, grant any right or license under any IBM patents or copyrights. Inquiries regarding patent or copyright licenses should be made, in writing, to: IBM Director of Licensing IBM Corporation North Castle Drive Armonk, NY 10504 -1785 U. S. A. © 2014 IBM Corporation
d2e6542864a900dd206687a45ba141eb.ppt