6184639e03917e5763759b5d04fc2bcb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Expected Value. Random variables Def. A random variable, X, is a numerical measure of the outcomes of an experiment

Example: Experiment- Two cards randomly selected Let X be the number of diamonds selected ¡

Events can be described in terms of random variables Example: ¡ is the event that exactly one diamond is selected ¡ is the event that at most one diamond is selected ¡

Probabilities of events can be stated as probabilities of the corresponding values of X
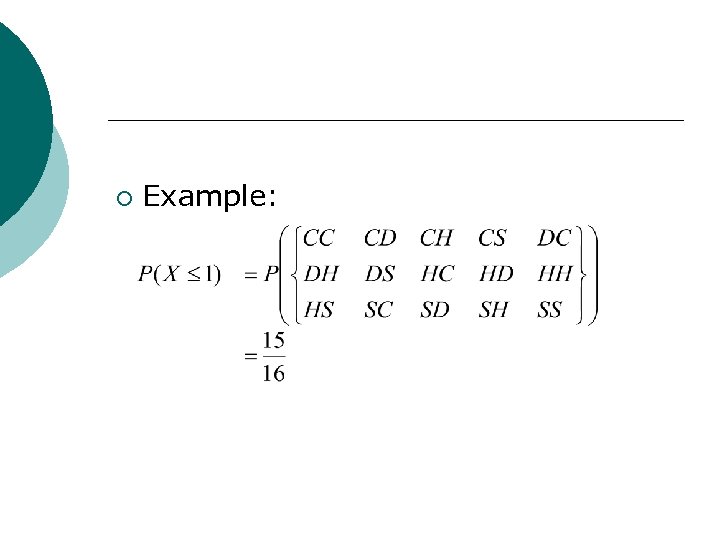
¡ Example:

In general, is the probability that X takes on the value x is the probability that X takes on a value that is less than or equal to x
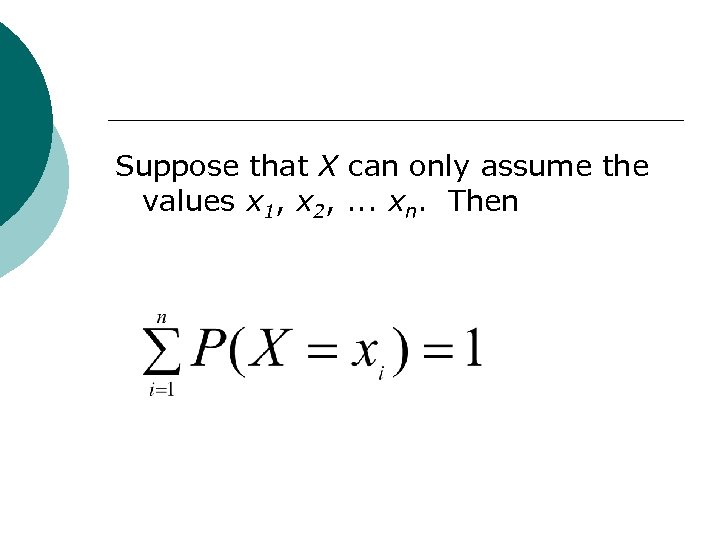
Suppose that X can only assume the values x 1, x 2, . . . xn. Then
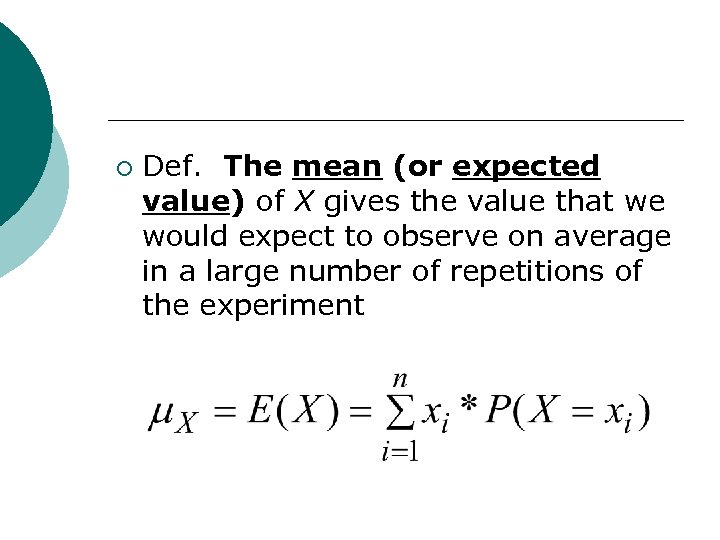
¡ Def. The mean (or expected value) of X gives the value that we would expect to observe on average in a large number of repetitions of the experiment
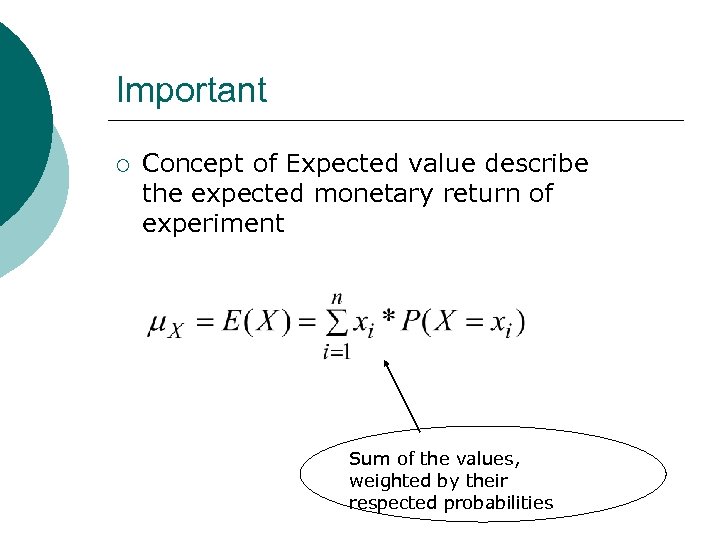
Important ¡ Concept of Expected value describe the expected monetary return of experiment Sum of the values, weighted by their respected probabilities

Example (Exercise 13): An investment in Project A will result in a loss of $26, 000 with probability 0. 30, break even with probability 0. 50, or result in a profit of $68, 000 with probability 0. 20. An investment in Project B will result in a loss of $71, 000 with probability 0. 20, break even with probability 0. 65, or result in a profit of $143, 000 with probability 0. 15. Which investment is better? ¡
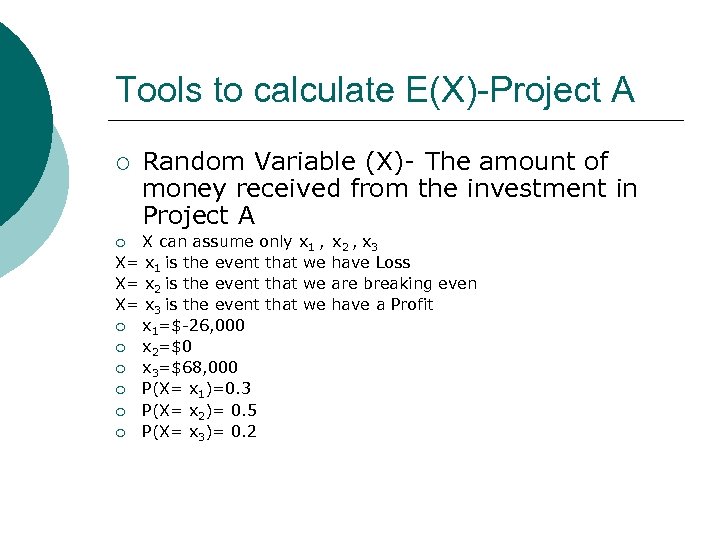
Tools to calculate E(X)-Project A ¡ Random Variable (X)- The amount of money received from the investment in Project A X can assume only x 1 , X= x 1 is the event that we X= x 2 is the event that we X= x 3 is the event that we ¡ x 1=$-26, 000 ¡ x 2=$0 ¡ x 3=$68, 000 ¡ P(X= x 1)=0. 3 ¡ P(X= x 2)= 0. 5 ¡ P(X= x 3)= 0. 2 ¡ x 2 , x 3 have Loss are breaking even have a Profit
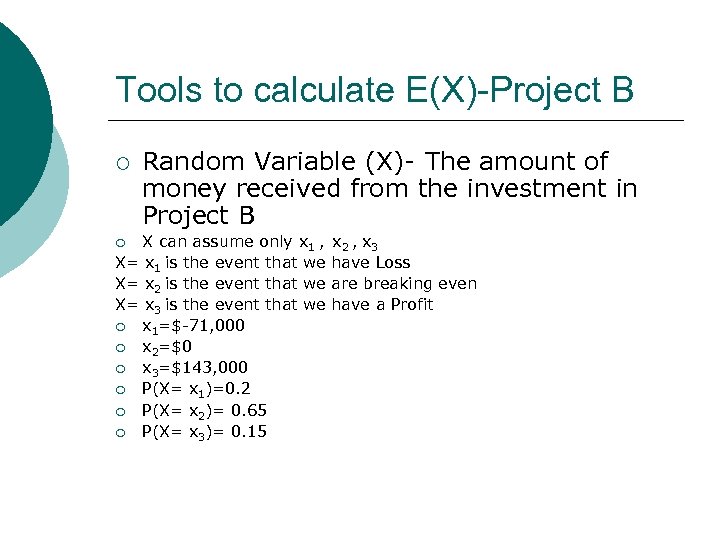
Tools to calculate E(X)-Project B ¡ Random Variable (X)- The amount of money received from the investment in Project B X can assume only x 1 , X= x 1 is the event that we X= x 2 is the event that we X= x 3 is the event that we ¡ x 1=$-71, 000 ¡ x 2=$0 ¡ x 3=$143, 000 ¡ P(X= x 1)=0. 2 ¡ P(X= x 2)= 0. 65 ¡ P(X= x 3)= 0. 15 ¡ x 2 , x 3 have Loss are breaking even have a Profit


Focus on the Project How can Expected value help us with the decision on whether or not to attempt a loan workout? ¡ Recall: Events S- An attempted workout is a Success F- An attempted workout is a Failure ¡

Tools to calculate E(X) Random Variable (X)- The amount of money Acadia receives from a future loan workout attempt ¡ X can assume only Full Value Default Value x 1=$ 4, 000 x 2=$ 250, 000 ¡

¡ Using Expected value formula The sheet Expected Value in the Excel file Loan Focus. xls performs the following computation for the expected value of X.

Decision? Recall ¡ Bank Forecloses a loan if Benefits of Foreclosure > Benefits of Workout ¡ Bank enters a Loan Workout if Expected Value Workout > Expected Value Foreclose

Since the expected value of a work out is $1, 991, 000 and the “expected value” of foreclosing is a guaranteed $2, 100, 000, it might seem that Acadia Bank should foreclose on John Sanders’ loan.
6184639e03917e5763759b5d04fc2bcb.ppt