64d121cbe6eb62cdfe41af7ca0f24e6e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Expectation and Reality in Digital Publishing: Some Australian Perspectives Xuemei Tian School of Business Information Technology ELPUB 2007 Conference – Vienna, Austria – June 2007
Introduction • Background • Methodology • Digital publishing – definition and characteristics • Ongoing supply chain • Development of technologies • Business models • Initial findings
Background • The publishing industry represents a highly significant manufacturing and distribution component of the content industry, which creates, transfers and stores knowledge. • The publishing industry has changed dramatically. Main changes include: – – Changes in publishing markets Increases in online business and digital content formats Changes to distribution channels and supply chains Increases in outsourcing, sub-contracting

Background • Business Challenges in Publishing – Rapid development of technologies – A turbulent business environment – The growth of global concentrates – Intense competition including that from new entrants and Open Access publishers – Stakeholders’ demands to improve financial performance – More sophisticated customers’ requirements – Changing customer relationships – Content is king
Background • To cope with the changes, publishers have been forced to: – Re-evaluate their resources and capabilities – Re-design business strategies – Re-engineer their business processes • The development and emergence of new supply chains • Seek new business models

Methodology • Focus groups – Focus groups have been employed as forums for industry feedback and as monitoring mechanisms, providing analyses and recommendations, based on knowledge ascertained as the research progresses. • Interviews – Ten formal interviews were conducted with major players within Australia’s publishing industry. • Survey – A national online survey of Australian publishers was completed • Case study – A series of eight case studies was conducted
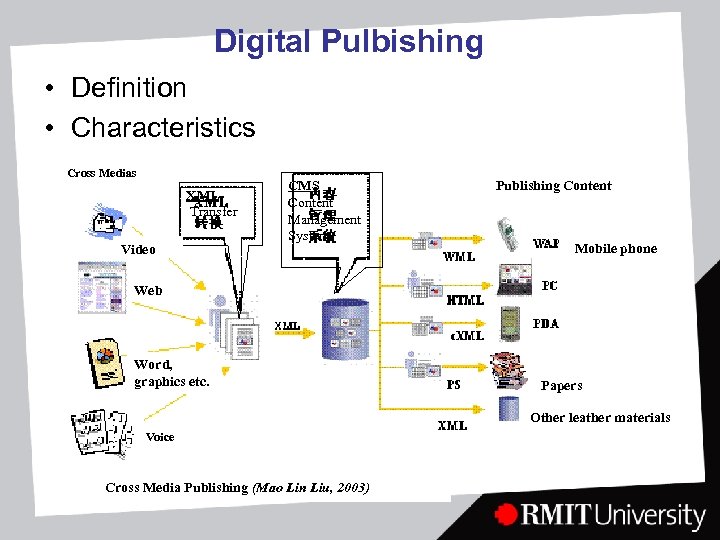
Digital Pulbishing • Definition • Characteristics Cross Medias XML Transfer Video CMS Content Management System Publishing Content Mobile phone Web Word, graphics etc. Papers Other leather materials Voice Cross Media Publishing (Mao Lin Liu, 2003)
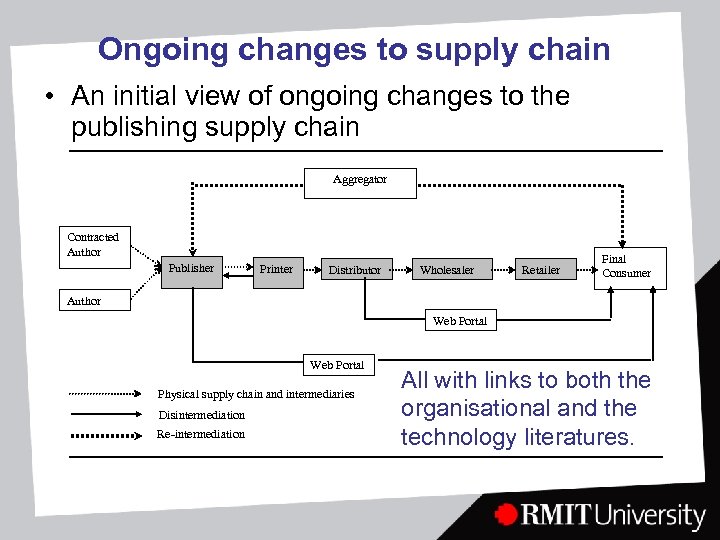
Ongoing changes to supply chain • An initial view of ongoing changes to the publishing supply chain Aggregator Contracted Author Publisher Printer Distributor Wholesaler Retailer Final Consumer Author Web Portal Physical supply chain and intermediaries Disintermediation Re-intermediation All with links to both the organisational and the technology literatures.

Developments of Publishing Technology • Current use of e-commerce in Australia – Asia Pacific’s B 2 B e-commerce is forecasted to grow rapidly at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 59% percent (IDC, 2004). – Australia’s e-commerce is estimated to be worth $11. 3 billion dollars annually (Australian Government Information Management Office, 2005). – Australia is among the leading nations in terms of measures of Internet infrastructure, penetration and activity. Australia is ranked second in the Asia Pacific region in terms of e-commerce infrastructure (e. Marketer, 2005). – However, in comparison with other countries, small and mediumsized enterprises (SMEs) have been relatively slow in adopting ecommerce (The Age, 2002; NOIE, 2002; Sensis, 2005).

Development in Publishing Technology • Longevity of existing technologies: Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) • Disruptive technologies: Internet and Web • Disintermediation: Technology predicted to remove players from the value chain. • Online/Web/Digital: Current trend including Re-intermediation. • Future technology: Semantic Web
Business models • Definition: this project adhered to Weill and Vitales’s (2001) approach to business models. A description of the roles and relationships among a firm’s customers, allies and suppliers identifies the major flows of product, information and money and also the major benefits to participants. • Survey results: subscription-based and content creation models maintain popularity, particularly in the context of niche markets. • Three Business models: an educational book publisher’s current and future models, and a trade book publisher’s future model.
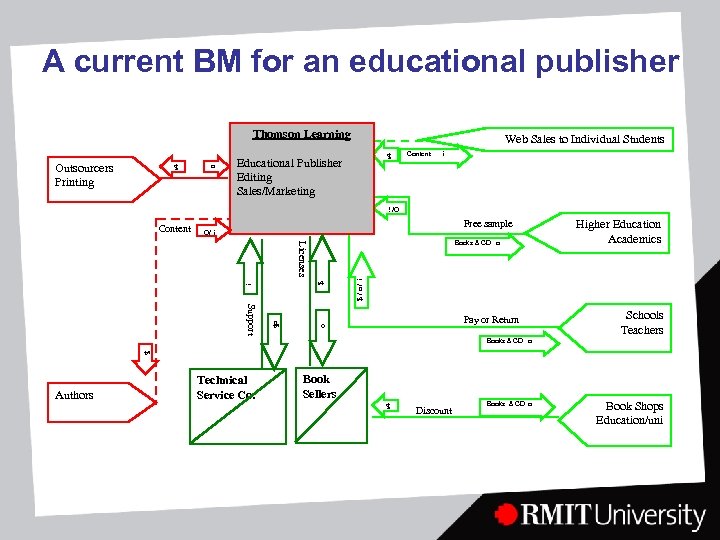
A current BM for an educational publisher Thomson Learning o $ Outsourcers Printing Web Sales to Individual Students Educational Publisher Editing Sales/Marketing Content i $ O/ i Content Free sample O/ i $/o/ i i $ Licenses Books & CD o Higher Education Academics o o$ Support Pay or Return Schools Teachers Books & CD o $ Book Sellers $ Authors Technical Service Co. Discount Books & CD o Book Shops Education/uni
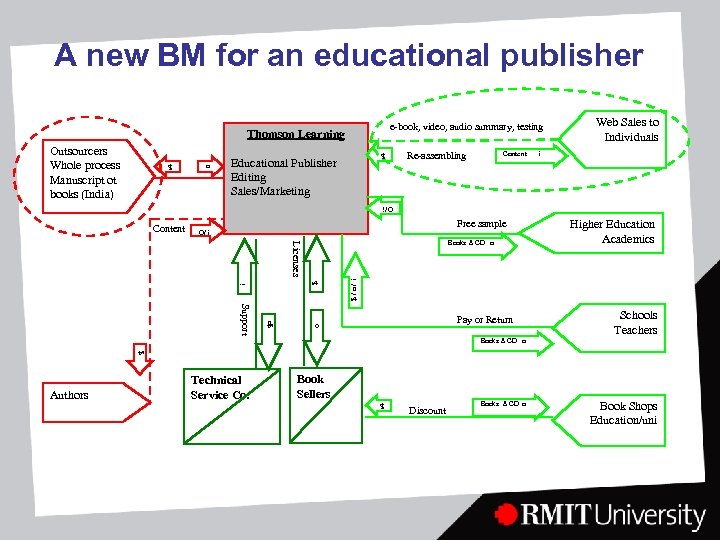
A new BM for an educational publisher e-book, video, audio summary, testing Thomson Learning o $ Outsourcers Whole process Manuscript ot books (India) Educational Publisher Editing Sales/Marketing Re-assembling Content Web Sales to Individuals i $ O/ i Content Free sample O/ i $/o/ i i $ Licenses Books & CD o Higher Education Academics o o$ Support Pay or Return Schools Teachers Books & CD o $ Book Sellers $ Authors Technical Service Co. Discount Books & CD o Book Shops Education/uni
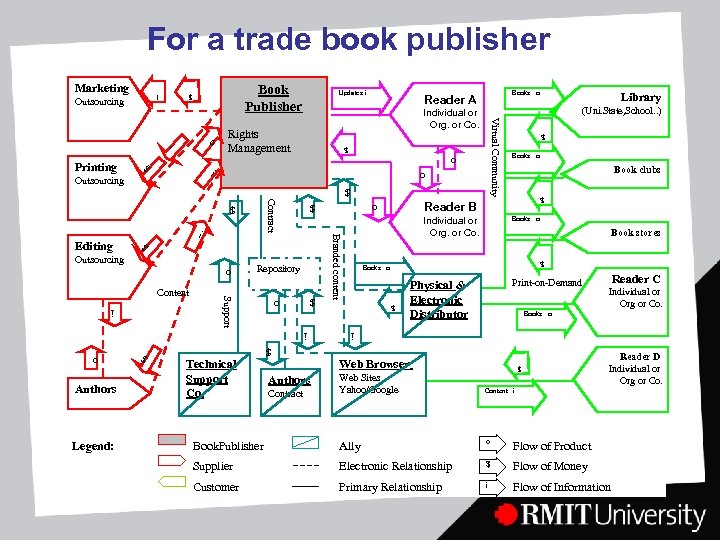
For a trade book publisher o $ i o $ $ i i Legend: $ Authors Technical Support Co. $ o Authors Contract Book stores Books o Print-on-Demand Physical & Electronic Distributor Reader C Individual or Org or Co. Books o Web Browser Web Sites Yahoo/Google $ o Books o i $ Support Content Repository $ $ o o Outsourcing Reader B Individual or Org. or Co. Branded content Editing Book clubs $ Contract i $ Books o $ i Outsourcing Rights Management Library (Uni. State, School. . ) Individual or Org. or Co. $ Printing Books o Reader A Virtual Community o Updates i $ I Outsourcing Book Publisher $ Marketing Reader D Individual or Org or Co. Content i Book. Publisher Ally o Flow of Product Supplier Electronic Relationship $ Flow of Money Customer Primary Relationship i Flow of Information

Project progress and initial findings • The Australian publishing industry has adopted a somewhat conservative approach to the challenges and opportunities presented by digital publishing. • The majority of publishers believe however, that in the foreseeable future, there could be major changes in the industry. • As publishing businesses have varying objectives, the pace of change from traditional to digital publishing will also vary, depending on their market and client base, as well as the take-up of technology. • It seems clear however, that any reluctance on the part of publishers to embrace technological change could prove detrimental to their future.

Project progress and initial findings • Currently, book publishing models appear to be very familiar (i. e. largely traditional) with adding on digital elements. • In the next decade book publishing models may appear as a different profile.

The future business models of publishing • How do YOU think future publishing business models will change?
64d121cbe6eb62cdfe41af7ca0f24e6e.ppt