bc680bbdf9255bcfc569cb08c815b2d2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96
 Existing ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector: Whether the Protocols and Mechanisms for Quality Assurance from Knowledge Dissemination Agencies Exist and are Adequate? “Seva Ratna” M. Moni Deputy Director General (Agricultural Informatics Division & DISNIC Programme Division) National Informatics Centre Department of Information Technology (Government of India) E-mail: moni@hub. nic. in & Vice-President, AFITA, Tokyo (Japan) Vice-President, IAITA, Gandhinagar (Gujarat) Executive Member, INSAIT, UAS, Dharwad (Karnataka) Secretary General, Bhoovigyan Vikas Foundation (An Earth Care Foundation) , New Delhi 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
Existing ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector: Whether the Protocols and Mechanisms for Quality Assurance from Knowledge Dissemination Agencies Exist and are Adequate? “Seva Ratna” M. Moni Deputy Director General (Agricultural Informatics Division & DISNIC Programme Division) National Informatics Centre Department of Information Technology (Government of India) E-mail: moni@hub. nic. in & Vice-President, AFITA, Tokyo (Japan) Vice-President, IAITA, Gandhinagar (Gujarat) Executive Member, INSAIT, UAS, Dharwad (Karnataka) Secretary General, Bhoovigyan Vikas Foundation (An Earth Care Foundation) , New Delhi 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
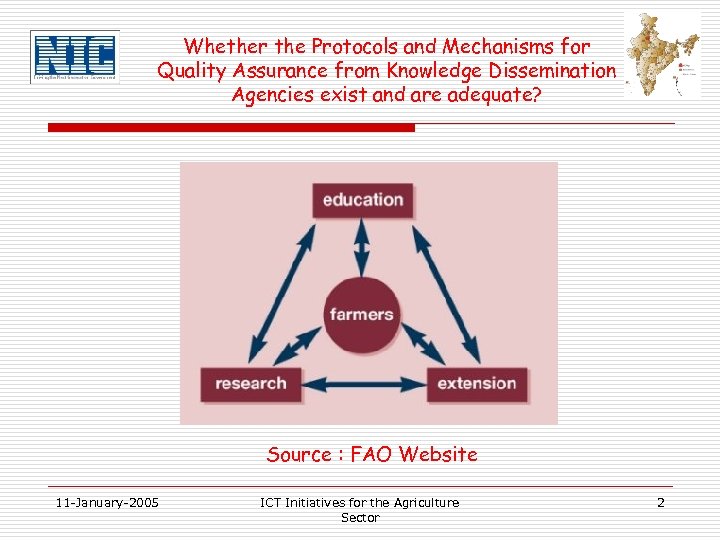 Whether the Protocols and Mechanisms for Quality Assurance from Knowledge Dissemination Agencies exist and are adequate? Source : FAO Website 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 2
Whether the Protocols and Mechanisms for Quality Assurance from Knowledge Dissemination Agencies exist and are adequate? Source : FAO Website 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 2
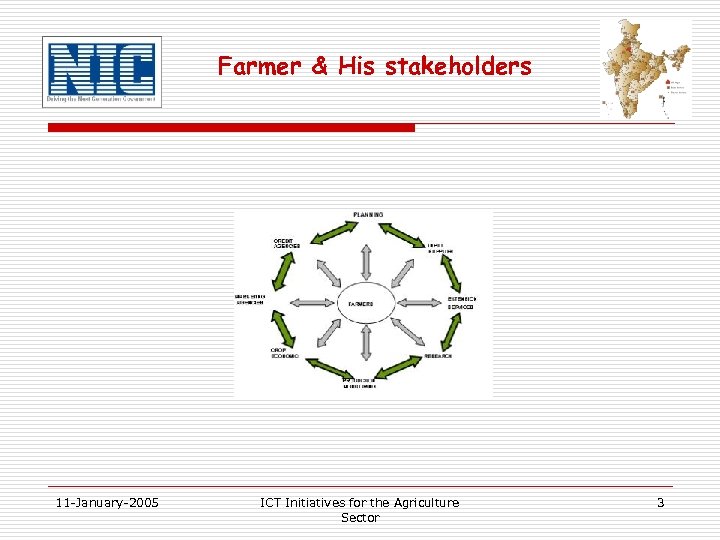 Farmer & His stakeholders 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 3
Farmer & His stakeholders 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 3
 National Agricultural Policy - 2000 Fusion of Frontier Technologies • Information & Communication Technology • Biotechnology • GIS & Remote Sensing Technology • Pre-Post harvest Technology • Energy saving Technology • Technology for Environment Protection 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 4
National Agricultural Policy - 2000 Fusion of Frontier Technologies • Information & Communication Technology • Biotechnology • GIS & Remote Sensing Technology • Pre-Post harvest Technology • Energy saving Technology • Technology for Environment Protection 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 4
 Focus : People Felt Needs Reaching the Unreached : Public Services ·From Digital Divide to Digital Opportunities for sustainable development and economic growth. · Fostering agricultural growth, poverty reduction and sustainable resources use. · Water, Energy, Education, Health, Agriculture & Rural Development, Biodiversity : Sustainable Development & Earth Care Policies · “Sustainable Societies in Viable Rural Space” : A Cluster of Villages is a viable rural space · Globalisation, Liberalisation and Privatisation · 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 5
Focus : People Felt Needs Reaching the Unreached : Public Services ·From Digital Divide to Digital Opportunities for sustainable development and economic growth. · Fostering agricultural growth, poverty reduction and sustainable resources use. · Water, Energy, Education, Health, Agriculture & Rural Development, Biodiversity : Sustainable Development & Earth Care Policies · “Sustainable Societies in Viable Rural Space” : A Cluster of Villages is a viable rural space · Globalisation, Liberalisation and Privatisation · 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 5
 Infusion of ICT in Agricultural Sector - A Challenge in the new Millenium • A Powerful Engine to reduce Marginalisation and Vulnerability of small farmers in India • Reaching the Unreached (i. e. Resource. Poor-Farmers) • Agricultural Knowledge & Information System - Integration of People & Institutions 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 6
Infusion of ICT in Agricultural Sector - A Challenge in the new Millenium • A Powerful Engine to reduce Marginalisation and Vulnerability of small farmers in India • Reaching the Unreached (i. e. Resource. Poor-Farmers) • Agricultural Knowledge & Information System - Integration of People & Institutions 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 6
 Theme of the Indian Science Congress 2004 “Science and Society in the 21 st century—Quest for Excellence”. Essentials : Quality Management System in every aspects of Research, Education, Training and Extension for sustainable development Session: Information and Communication Sciences & Technology -----Theme: IT in Public Service Vision: “USE I. T. ” & “I. C. T” Mission: “should use it” like Water and Electricity ------- Topic: Information needs of Indian Public & The NICNET 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 7
Theme of the Indian Science Congress 2004 “Science and Society in the 21 st century—Quest for Excellence”. Essentials : Quality Management System in every aspects of Research, Education, Training and Extension for sustainable development Session: Information and Communication Sciences & Technology -----Theme: IT in Public Service Vision: “USE I. T. ” & “I. C. T” Mission: “should use it” like Water and Electricity ------- Topic: Information needs of Indian Public & The NICNET 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 7
 Theme of the Indian Science Congress 2002 * Food Security * Nutrition Security * Environmental Security 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 8
Theme of the Indian Science Congress 2002 * Food Security * Nutrition Security * Environmental Security 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 8
 Food Security Population growing at the rate of 1. 8% annually Food Requirements in 2030 : • 260– 264 million tonnes of food grains · 130 -152 Mt. of milk · 151 -193 Mt. of vegetables · 84 -106 Mt. of fruits · 10 -14 Mt. of meat · 4 -5 Mt. of eggs · 10 -14 Mt. of fish and · 12 Mt. of edible oil to provide adequate nutrition to a population of 1. 3 billion people. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 9
Food Security Population growing at the rate of 1. 8% annually Food Requirements in 2030 : • 260– 264 million tonnes of food grains · 130 -152 Mt. of milk · 151 -193 Mt. of vegetables · 84 -106 Mt. of fruits · 10 -14 Mt. of meat · 4 -5 Mt. of eggs · 10 -14 Mt. of fish and · 12 Mt. of edible oil to provide adequate nutrition to a population of 1. 3 billion people. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 9
 To achieve the desired objective, there is need for · · 11 -January-2005 a paradigm shift from commodity centered to ecologically sustainable farming system; a renewed thrust to implement effectively various technological options generated by the scientists representing different disciplines. ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 10
To achieve the desired objective, there is need for · · 11 -January-2005 a paradigm shift from commodity centered to ecologically sustainable farming system; a renewed thrust to implement effectively various technological options generated by the scientists representing different disciplines. ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 10
 Plenary Sessions of the Congress 2002 • Improving Productivity and Alleviating Poverty, • Post Harvest Processing and Value-Addition, • Managing Resources for Increased Farm Sustainability, • Complementing New Technologies with Traditional Knowledge, • Nutritional Needs for Human Health, • Livestock for Nutrition and Financial Well Being, • Environmental and Agricultural Development and • Public Policies for Food, Nutrition and Environmental Security. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 11
Plenary Sessions of the Congress 2002 • Improving Productivity and Alleviating Poverty, • Post Harvest Processing and Value-Addition, • Managing Resources for Increased Farm Sustainability, • Complementing New Technologies with Traditional Knowledge, • Nutritional Needs for Human Health, • Livestock for Nutrition and Financial Well Being, • Environmental and Agricultural Development and • Public Policies for Food, Nutrition and Environmental Security. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 11
 G. B. Singh, 2000 : "Green Revolution in India - Gains and Pains", 21 st Indian Geography Congress, Nagpur (India), January 2 -4, 2000. The future growth in agriculture must, therefore, come from : X new technologies which are not only "cost effective" but also "in conformity" with the natural climatic regime of the country; X technologies relevant to rain-fed areas specifically; X continued genetic improvements for better seeds and yields; X data improvements for better research, better results, and sustainable planning; X bridging the gap between knowledge and practice; and X judicious land use resource surveys, efficient management practices and sustainable use of natural resources. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 12
G. B. Singh, 2000 : "Green Revolution in India - Gains and Pains", 21 st Indian Geography Congress, Nagpur (India), January 2 -4, 2000. The future growth in agriculture must, therefore, come from : X new technologies which are not only "cost effective" but also "in conformity" with the natural climatic regime of the country; X technologies relevant to rain-fed areas specifically; X continued genetic improvements for better seeds and yields; X data improvements for better research, better results, and sustainable planning; X bridging the gap between knowledge and practice; and X judicious land use resource surveys, efficient management practices and sustainable use of natural resources. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 12
 Productivity Paradigms • Industrial Revolution • Agricultural Revolution • Green Revolution • White Revolution • Yellow Revolution • Blue Revolution • Rainbow Revolution • Information Technology Revolution • Bio-Technology Revolution 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 13
Productivity Paradigms • Industrial Revolution • Agricultural Revolution • Green Revolution • White Revolution • Yellow Revolution • Blue Revolution • Rainbow Revolution • Information Technology Revolution • Bio-Technology Revolution 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 13
 Objectives • Protocols & Mechanisms for Quality Assurance • Knowledge Dissemination Agencies • Adequacy • ICT Initiatives 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
Objectives • Protocols & Mechanisms for Quality Assurance • Knowledge Dissemination Agencies • Adequacy • ICT Initiatives 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
 Knowledge Dissemination Agencies • 600 District Administrations with Agricultural officers upto Village level jurisdiction • 89 ICAR Institutions • 33 Agricultural Universities • ~ 215 Agricultural Colleges • 12000 Students pass out every year • 280 Krishi Vigyan Kendras • Fertiliser Companies (IFFCO. KRIBHCO, GCFL etc) • i. KISAN in Andhra Pradesh, Parrys in Tamilnadu and Mahendra & Mahendra in Tamilnadu 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
Knowledge Dissemination Agencies • 600 District Administrations with Agricultural officers upto Village level jurisdiction • 89 ICAR Institutions • 33 Agricultural Universities • ~ 215 Agricultural Colleges • 12000 Students pass out every year • 280 Krishi Vigyan Kendras • Fertiliser Companies (IFFCO. KRIBHCO, GCFL etc) • i. KISAN in Andhra Pradesh, Parrys in Tamilnadu and Mahendra & Mahendra in Tamilnadu 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
 Adequacy • Not Adequate – Perception • Extension Reforms under consideration • Mc. Kinsey Report says that “Digital inclusion” can usher in an additional 1% GDP contribution • A Way Forward? 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
Adequacy • Not Adequate – Perception • Extension Reforms under consideration • Mc. Kinsey Report says that “Digital inclusion” can usher in an additional 1% GDP contribution • A Way Forward? 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
 V Informatics and Productivity – A Complementarity Relationship AGRISNET – Agricultural Informatics & Communication Gateway to reach V into Rural India – A pipeline Project since 1995 V AGMARKNET, DACNET, ARISNET, COOPNET, Seed. NET, HORTNET, PPIN, APHNET, FISHNET, LISNET, AFPINET, ARINET, NDMNET, VISTARNET V Ag. RIS – Agricultural Resources Information System : A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Development V Agricultural Extension : An Agricultural Knowledge & Information System V 11 -January-2005 Dial 1551 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 17
V Informatics and Productivity – A Complementarity Relationship AGRISNET – Agricultural Informatics & Communication Gateway to reach V into Rural India – A pipeline Project since 1995 V AGMARKNET, DACNET, ARISNET, COOPNET, Seed. NET, HORTNET, PPIN, APHNET, FISHNET, LISNET, AFPINET, ARINET, NDMNET, VISTARNET V Ag. RIS – Agricultural Resources Information System : A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Development V Agricultural Extension : An Agricultural Knowledge & Information System V 11 -January-2005 Dial 1551 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 17
 V Emergence of an e-Farmer Agricultural Knowledge & Information System using Geomatics V Technology Development of Specialised Agricultural Extension XML (Ae. XML) V V V NIC’ VISTARNET will use Ae. XML and Geomatics Technology To Achieve “Knowledge Society in Agriculture”, at least “ an agriculture information centre in each village” is required. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 18
V Emergence of an e-Farmer Agricultural Knowledge & Information System using Geomatics V Technology Development of Specialised Agricultural Extension XML (Ae. XML) V V V NIC’ VISTARNET will use Ae. XML and Geomatics Technology To Achieve “Knowledge Society in Agriculture”, at least “ an agriculture information centre in each village” is required. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 18
 ICT accelerates globalisation and make access to knowledge and information much easier for the people to attain “rural prosperity” in respect of: · Creation of technologies (- IPR Divide), · Diffusion of recent Innovation (- Digital Divide), · Diffusion of old Innovation (- Extension Divide), · Diffusion of human development skills - Educational skills). ( Ref: UNDP’s Human Development Report 2001 – Technology Achievement Index 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 19
ICT accelerates globalisation and make access to knowledge and information much easier for the people to attain “rural prosperity” in respect of: · Creation of technologies (- IPR Divide), · Diffusion of recent Innovation (- Digital Divide), · Diffusion of old Innovation (- Extension Divide), · Diffusion of human development skills - Educational skills). ( Ref: UNDP’s Human Development Report 2001 – Technology Achievement Index 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 19
 Localisation · One of the major problems of using ICT for rural prosperity is language barrier i. e. “localization”. · Over the years, the Government of India, its institutions and collaborators have striven towards enabling the Internet to support “multiple” Indian scripts and languages. · 13 Language Resources Centres for 18 Indian languages · A “national policy on localisation” is anvil. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 20
Localisation · One of the major problems of using ICT for rural prosperity is language barrier i. e. “localization”. · Over the years, the Government of India, its institutions and collaborators have striven towards enabling the Internet to support “multiple” Indian scripts and languages. · 13 Language Resources Centres for 18 Indian languages · A “national policy on localisation” is anvil. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 20
 People Needs · People’s needs - A bottom up approach · The "I want that and I want it now" effect. · India's basic development goals are to eradicate poverty and accelerate human development. · Food Security and Nutrient Security. · Agricultural Market led extension Reforms. · Different people have different needs Micro-level Planning, Grass-root level planning, District Planning, Decentralised Planning, Regional Planning, National Planning • Macro Rational, Micro Irrational; Micro rational, Macro irrational • “One Size fits All” - e. g. Green Revolution Pains and Gains 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 21
People Needs · People’s needs - A bottom up approach · The "I want that and I want it now" effect. · India's basic development goals are to eradicate poverty and accelerate human development. · Food Security and Nutrient Security. · Agricultural Market led extension Reforms. · Different people have different needs Micro-level Planning, Grass-root level planning, District Planning, Decentralised Planning, Regional Planning, National Planning • Macro Rational, Micro Irrational; Micro rational, Macro irrational • “One Size fits All” - e. g. Green Revolution Pains and Gains 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 21
 People Needs : The way forward - “Information Systems as an Investment and not Expenditure” 'Local government is about meeting people's needs, ' Sustainable development and Sustainable Lifestyles. · Change social problems into opportunities. · Libraries : the life-force for learning · Convert people needs into 21 st century services. · Bringing ICT closer to people needs. (i. e. the new wave of ICT, the related infrastructures and applications and services, will address today's key societal challenges. ) · ICT Diffusion and Fusion of Technologies for economic growth and sustainable development. · Making every citizen and business benefit from ICT. · · 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 22
People Needs : The way forward - “Information Systems as an Investment and not Expenditure” 'Local government is about meeting people's needs, ' Sustainable development and Sustainable Lifestyles. · Change social problems into opportunities. · Libraries : the life-force for learning · Convert people needs into 21 st century services. · Bringing ICT closer to people needs. (i. e. the new wave of ICT, the related infrastructures and applications and services, will address today's key societal challenges. ) · ICT Diffusion and Fusion of Technologies for economic growth and sustainable development. · Making every citizen and business benefit from ICT. · · 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 22
 Impact of ICT Diffusion on Economic Growth & Sustainable Development • The diffusion of ICT throughout all industries is, therefore, far more important than the production of ICT industries per se. • Various study results strongly support that the “payoff” effect of ICT on economic growth can be achieved only through a robust National Information Infrastructure (NII) that supports ICT adoption and application. • ICT diffusion derives economic force from the complementary development of a knowledge-intensive society. (Eunice Wang (1999) : ICT and Economic Development in Taiwan : Analysis of the Evidence, Telecommunications Policy, 23(3, 4), April/May 1999, pp 235 -243) • In the present “crucial decade” of this millenium, a high rate of investment in Information Technology capital and a supportive environment are expected to achieve “digital economy”. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 23
Impact of ICT Diffusion on Economic Growth & Sustainable Development • The diffusion of ICT throughout all industries is, therefore, far more important than the production of ICT industries per se. • Various study results strongly support that the “payoff” effect of ICT on economic growth can be achieved only through a robust National Information Infrastructure (NII) that supports ICT adoption and application. • ICT diffusion derives economic force from the complementary development of a knowledge-intensive society. (Eunice Wang (1999) : ICT and Economic Development in Taiwan : Analysis of the Evidence, Telecommunications Policy, 23(3, 4), April/May 1999, pp 235 -243) • In the present “crucial decade” of this millenium, a high rate of investment in Information Technology capital and a supportive environment are expected to achieve “digital economy”. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 23
 An Information Technology aided age of “New Economy” - “Digital Economy” - is emerging and its rapid growth, however, depend on : • A higher rate of growth related to investment in Information systems & Applications; • A rise in Total Factor Productivity (TFP) growth due to information utilisation across the economy and resulting “spill-over” effects; • • An increase in factor utilisation; and A decline in the non-accelerating inflation rate and rate of unemployment (Moni. M : “New productivity Paradigms and Strategies in the e-age - Government Initiatives on IT-led Development in India”, presented at the International Conference on “Productivity in the e-age” organised by NPC and APO, November 22 -24, 2000, at New Delhi) 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 24
An Information Technology aided age of “New Economy” - “Digital Economy” - is emerging and its rapid growth, however, depend on : • A higher rate of growth related to investment in Information systems & Applications; • A rise in Total Factor Productivity (TFP) growth due to information utilisation across the economy and resulting “spill-over” effects; • • An increase in factor utilisation; and A decline in the non-accelerating inflation rate and rate of unemployment (Moni. M : “New productivity Paradigms and Strategies in the e-age - Government Initiatives on IT-led Development in India”, presented at the International Conference on “Productivity in the e-age” organised by NPC and APO, November 22 -24, 2000, at New Delhi) 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 24
 IT in Public Services: e-Governance & Convergence of core technologies ·e-Government (e-Service, e-democracy and e-Governance) · · Government to Government (G 2 G) ·Government to Business (G 2 B) · Government to Citizen (G 2 C) ·Government to Employees (G 2 E) Development of appropriate models for each location and each segment of society 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
IT in Public Services: e-Governance & Convergence of core technologies ·e-Government (e-Service, e-democracy and e-Governance) · · Government to Government (G 2 G) ·Government to Business (G 2 B) · Government to Citizen (G 2 C) ·Government to Employees (G 2 E) Development of appropriate models for each location and each segment of society 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
 Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • “Computerisation of Societal Systems” • “Using Internet Towards Doubling Per Capita Rural GDP in Ten Years”. • Rural development is a process of sustained growth of the rural economy (agriculture, industry, construction, transportation and commerce). • Industrial growth and Economic growth are dependent on production and productivity in agriculture. • Agricultural development, along with rural enterprise is therefore the cornerstone for promoting sustainable rural livelihoods • The development strategy should, inter alia, facilitate skill improvement, provide employment in rural areas, transfer of appropriate technology for industrialisation, and promote selfreliance among the people, and build-up a strong rural community base. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 26
Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • “Computerisation of Societal Systems” • “Using Internet Towards Doubling Per Capita Rural GDP in Ten Years”. • Rural development is a process of sustained growth of the rural economy (agriculture, industry, construction, transportation and commerce). • Industrial growth and Economic growth are dependent on production and productivity in agriculture. • Agricultural development, along with rural enterprise is therefore the cornerstone for promoting sustainable rural livelihoods • The development strategy should, inter alia, facilitate skill improvement, provide employment in rural areas, transfer of appropriate technology for industrialisation, and promote selfreliance among the people, and build-up a strong rural community base. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 26
 Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • Agriculture, including crop & animal husbandry, forestry & agroforestry, fisheries, and agro-industries, provide livelihoods to over 70% of the Indian Population. • Agriculture is decentralised but small scale manufacturing(Small & Marginal Farmers) units. • Multifunctionality of Agriculture and Land : An Economic Activity (producing goods) and A service to the Community (food security, rural employment, and environmental obligations such as soil conservation, sustainable natural resources management and biodiversity protection) • Multifunctional Agriculture – the bottom line for integrated rural development • An Agricultural Knowledge & Information System for rural empowerment & improved livelihoods (i. e. e-Farmer) is the need of the hour. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 27
Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • Agriculture, including crop & animal husbandry, forestry & agroforestry, fisheries, and agro-industries, provide livelihoods to over 70% of the Indian Population. • Agriculture is decentralised but small scale manufacturing(Small & Marginal Farmers) units. • Multifunctionality of Agriculture and Land : An Economic Activity (producing goods) and A service to the Community (food security, rural employment, and environmental obligations such as soil conservation, sustainable natural resources management and biodiversity protection) • Multifunctional Agriculture – the bottom line for integrated rural development • An Agricultural Knowledge & Information System for rural empowerment & improved livelihoods (i. e. e-Farmer) is the need of the hour. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 27
 Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • The locus of agricultural growth has since been shifted from production front to the processing and marketing front. • Rural cooperatives once again emerge as an alternative for making rural economy vibrant through agro and rural based industries. • The rural economy can be vibrant iff agro and rural industries are positioned and integrated with the national and global economy. • Rural towns are essential to farm households, as they offer “economies of agglomeration”. • Globalisation of Agriculture & Farmer’s Dependency Relation (i. e. locked into for buying and selling their produce) 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 28
Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • The locus of agricultural growth has since been shifted from production front to the processing and marketing front. • Rural cooperatives once again emerge as an alternative for making rural economy vibrant through agro and rural based industries. • The rural economy can be vibrant iff agro and rural industries are positioned and integrated with the national and global economy. • Rural towns are essential to farm households, as they offer “economies of agglomeration”. • Globalisation of Agriculture & Farmer’s Dependency Relation (i. e. locked into for buying and selling their produce) 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 28
 Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • A good agricultural production and step-up prices (farm prices) would put more money into the hands of the people living in the rural areas. • The Mc. Kinsey Analysis on intermediary economics (Fruits and Vegetables) shows that farm-gate price available to the farmers is only 25% of the retail price in Indian condition whereas the same is 70% in the case of DUTCH and the U. S. farmers, where more efficient marketing system is in place. • To benefit the farming communities from the new global market access opportunities, the internal agricultural marketing system of the country needs to be integrated and strengthened. • Various studies reveal that farmers, on an average, invariably higher price by selling their produce in the regulated markets compared to rural, village and unregulated wholesale markets. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 29
Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • A good agricultural production and step-up prices (farm prices) would put more money into the hands of the people living in the rural areas. • The Mc. Kinsey Analysis on intermediary economics (Fruits and Vegetables) shows that farm-gate price available to the farmers is only 25% of the retail price in Indian condition whereas the same is 70% in the case of DUTCH and the U. S. farmers, where more efficient marketing system is in place. • To benefit the farming communities from the new global market access opportunities, the internal agricultural marketing system of the country needs to be integrated and strengthened. • Various studies reveal that farmers, on an average, invariably higher price by selling their produce in the regulated markets compared to rural, village and unregulated wholesale markets. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 29
 Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • Investment in Agricultural Marketing System to make the agricultural sector vibrant and enable it to face the competition of international trade environment without affecting the livelihoods of those depend on farming. • ICTs in agricultural marketing will generate useful databases and information packages for expanding marketing opportunities, especially on-line information on-demand availability of different products, product specifications with regard to price, quality, pack size, packaging material, quantity and the time frame of supply. • Agri-Business, not the Agri-culture is the need of the hour. • Agri-Business is an orderly chain of firms supplying inputs to production of agriculture or processors of the output of production agricultural firms. • Agri-Business Opportunities in rural areas : Pathways to Rural Prosperity, negating the Hypothesis “the more farmers produce, the less they get” 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 30
Digital Inclusion to Foster Rural Enterprises • Investment in Agricultural Marketing System to make the agricultural sector vibrant and enable it to face the competition of international trade environment without affecting the livelihoods of those depend on farming. • ICTs in agricultural marketing will generate useful databases and information packages for expanding marketing opportunities, especially on-line information on-demand availability of different products, product specifications with regard to price, quality, pack size, packaging material, quantity and the time frame of supply. • Agri-Business, not the Agri-culture is the need of the hour. • Agri-Business is an orderly chain of firms supplying inputs to production of agriculture or processors of the output of production agricultural firms. • Agri-Business Opportunities in rural areas : Pathways to Rural Prosperity, negating the Hypothesis “the more farmers produce, the less they get” 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 30
 Digital Opportunities (Os & 1 s) for Fostering Agricultural Growth • Digital opportunities for fostering agricultural growth. • Our economic and industrial growths are dependent on production and productivity in agriculture. • Convergence of core technologies and e-Governance has become the tool for sustainable development and globalisation of economy. • Agriculture in India needs a "productivity and quality revolution", which can be brought out through the much-needed reforms: information access, extension services, credit, marketing, pricing, and rural infrastructure (water, roads, bridges, hospitals and schools), in addition to land reforms. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 31
Digital Opportunities (Os & 1 s) for Fostering Agricultural Growth • Digital opportunities for fostering agricultural growth. • Our economic and industrial growths are dependent on production and productivity in agriculture. • Convergence of core technologies and e-Governance has become the tool for sustainable development and globalisation of economy. • Agriculture in India needs a "productivity and quality revolution", which can be brought out through the much-needed reforms: information access, extension services, credit, marketing, pricing, and rural infrastructure (water, roads, bridges, hospitals and schools), in addition to land reforms. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 31
 Digital Opportunities To achieve knowledge society in agriculture, the following to happen: • An agriculture information centre in each village; • Interactive exchange of information for planning and day-to-day operations by farmers; • Availability of all the extension and advisory services on demand. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 32
Digital Opportunities To achieve knowledge society in agriculture, the following to happen: • An agriculture information centre in each village; • Interactive exchange of information for planning and day-to-day operations by farmers; • Availability of all the extension and advisory services on demand. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 32
 Digital Opportunities The vision 2020 Document of the Department of Agriculture & Cooperation (Government of India) envisages that the tools of ICT will : • provide networking of Agriculture Sector not only in the Country but also globally and the Centre and State Government Departments will have reservoir of databases; • bring farmers, researchers, scientists and administrators together by establishing "agriculture online" through exchange of ideas and information. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 33
Digital Opportunities The vision 2020 Document of the Department of Agriculture & Cooperation (Government of India) envisages that the tools of ICT will : • provide networking of Agriculture Sector not only in the Country but also globally and the Centre and State Government Departments will have reservoir of databases; • bring farmers, researchers, scientists and administrators together by establishing "agriculture online" through exchange of ideas and information. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 33
 Digital Opportunities The National Conference on Informatics for Sustainable Agricultural Development (ISDA) organised by the Ministry of Agriculture and National Informatics Centre (NIC), in May 1995, has given much-needed "roadmap" to usher in "ICT led agricultural development" in the Country. The National Agricultural Policy (2000) lays emphasis on the use of ICT for achieving a more rapid development of Agriculture. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 34
Digital Opportunities The National Conference on Informatics for Sustainable Agricultural Development (ISDA) organised by the Ministry of Agriculture and National Informatics Centre (NIC), in May 1995, has given much-needed "roadmap" to usher in "ICT led agricultural development" in the Country. The National Agricultural Policy (2000) lays emphasis on the use of ICT for achieving a more rapid development of Agriculture. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 34
 Digital Development in Rural Areas: A Journey started in 1985 with the establishment of NICNET in districts of India • DISNIC Programme – District Information System in 28 Sectors. • DISNIC-Agriculture, DISNIC-Industry, DISNIC-Health, DISNIC-PLAN, etc Agricultural Informatics & Communication ISDA-95 : Informatics for Sustainable Development in Agriculture A ROAD MAP for Agricultural Informatics & Communication • ISDA-95 recommended 3 -6 % of the Annual Budget Outlay for Agricultural informatics & communication • Vittal Committee (1998) recommended only 2 -3% for ICT Applications in Governments. • DACNET – an e. GOV 4 D Programme for the Department of Agriculture • AGMARKNET 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 35
Digital Development in Rural Areas: A Journey started in 1985 with the establishment of NICNET in districts of India • DISNIC Programme – District Information System in 28 Sectors. • DISNIC-Agriculture, DISNIC-Industry, DISNIC-Health, DISNIC-PLAN, etc Agricultural Informatics & Communication ISDA-95 : Informatics for Sustainable Development in Agriculture A ROAD MAP for Agricultural Informatics & Communication • ISDA-95 recommended 3 -6 % of the Annual Budget Outlay for Agricultural informatics & communication • Vittal Committee (1998) recommended only 2 -3% for ICT Applications in Governments. • DACNET – an e. GOV 4 D Programme for the Department of Agriculture • AGMARKNET 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 35
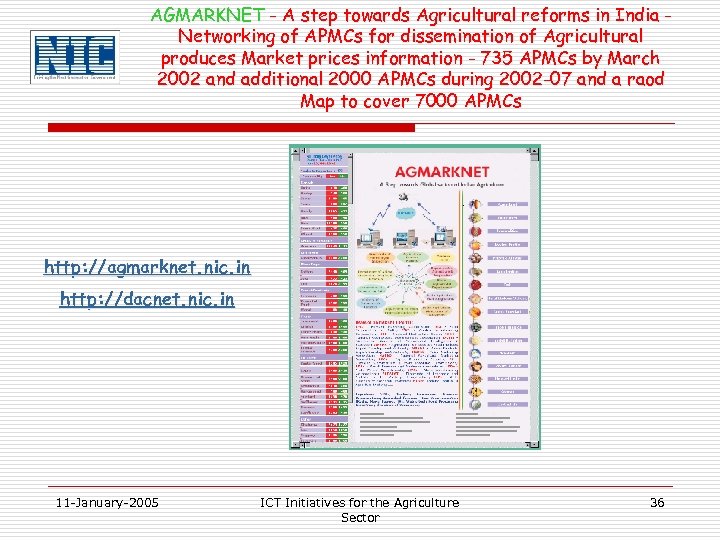 AGMARKNET - A step towards Agricultural reforms in India Networking of APMCs for dissemination of Agricultural produces Market prices information - 735 APMCs by March 2002 and additional 2000 APMCs during 2002 -07 and a raod Map to cover 7000 APMCs http: //agmarknet. nic. in http: //dacnet. nic. in 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 36
AGMARKNET - A step towards Agricultural reforms in India Networking of APMCs for dissemination of Agricultural produces Market prices information - 735 APMCs by March 2002 and additional 2000 APMCs during 2002 -07 and a raod Map to cover 7000 APMCs http: //agmarknet. nic. in http: //dacnet. nic. in 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 36
 AGMARKNET – A Powerful ICT Initiative for Rural Empowerment, a Warehousing of “data-fordevelopment” & a “free-trade-zone” on Internet • AGMARKNET - A step towards Agricultural reforms in India Networking of APMCs for dissemination of Agricultural produces Market prices information - 735 APMCs by March 2002, and additional 2000 APMCs during 2002 -07; Road Map is to network 7000 APMCs and 32000 Rural Markets • Times of India (31 May 2002) – The AGMARKNET Venture is a heartening initiative from the much criticized and slow-to-react government, especially on the issue of easing infrastructure constraints on Agriculture. • Reaching the Unreached • “reduction of distress sale” • “right to information” • “base for production planning” • “base for marketing-led agricultural extension’ • “reduced marketing margins” • “vertical linkages in export crop markets that connect multinational traders to domestic traders” • An Unified Agricultural Marketing Price System for the Country. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 37
AGMARKNET – A Powerful ICT Initiative for Rural Empowerment, a Warehousing of “data-fordevelopment” & a “free-trade-zone” on Internet • AGMARKNET - A step towards Agricultural reforms in India Networking of APMCs for dissemination of Agricultural produces Market prices information - 735 APMCs by March 2002, and additional 2000 APMCs during 2002 -07; Road Map is to network 7000 APMCs and 32000 Rural Markets • Times of India (31 May 2002) – The AGMARKNET Venture is a heartening initiative from the much criticized and slow-to-react government, especially on the issue of easing infrastructure constraints on Agriculture. • Reaching the Unreached • “reduction of distress sale” • “right to information” • “base for production planning” • “base for marketing-led agricultural extension’ • “reduced marketing margins” • “vertical linkages in export crop markets that connect multinational traders to domestic traders” • An Unified Agricultural Marketing Price System for the Country. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 37
 AGMARKNET – A Powerful ICT Initiative for Rural Empowerment, a Warehousing of “data-fordevelopment” & a “free-trade-zone” on Internet • AGMARKNET – A Sun-Shine Website for farmers to bargain better prices for their produce, and marching towards “an e-Commerce and e -Business Portal” in India. • • What was a “technology push” in 1990 s is taking the shape of “consumer pull” at grass-root level in India pull A Step Towards a Digital Inclusion for fostering Rural Enterprises http: //agmarknet. nic. in http: //www. eapf. net 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 38
AGMARKNET – A Powerful ICT Initiative for Rural Empowerment, a Warehousing of “data-fordevelopment” & a “free-trade-zone” on Internet • AGMARKNET – A Sun-Shine Website for farmers to bargain better prices for their produce, and marching towards “an e-Commerce and e -Business Portal” in India. • • What was a “technology push” in 1990 s is taking the shape of “consumer pull” at grass-root level in India pull A Step Towards a Digital Inclusion for fostering Rural Enterprises http: //agmarknet. nic. in http: //www. eapf. net 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 38
 AGMARKNET - A major G 2 C & G 2 G Application … About AGMARKNET "It might be advantageous to have a network down to the mandi level to begin with. This can be progressively extended to villages and household level in due course of time". Sharad Joshi Founder, Shetkari Sanghatana Maharashtra & Former Chairman, High level Task Force on Agriculture (2000) Government of India 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 39
AGMARKNET - A major G 2 C & G 2 G Application … About AGMARKNET "It might be advantageous to have a network down to the mandi level to begin with. This can be progressively extended to villages and household level in due course of time". Sharad Joshi Founder, Shetkari Sanghatana Maharashtra & Former Chairman, High level Task Force on Agriculture (2000) Government of India 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 39
 AGMARKNET - "Website to help farmers bargain better” Source : Ashish Kotamkar, Asia Pacific Network Information Centre Times News network, Friday May 31, 2002 IT’S a well-known fact that Indian farmers rarely know the actual price and stock level of his produce at the mandis where they come to sell it. A long chain, vested interests and sheer spread of the markets not only makes it difficult for them to take decisions regarding produce mix, but also deprives them of whatever little bargaining power they may have had. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 40
AGMARKNET - "Website to help farmers bargain better” Source : Ashish Kotamkar, Asia Pacific Network Information Centre Times News network, Friday May 31, 2002 IT’S a well-known fact that Indian farmers rarely know the actual price and stock level of his produce at the mandis where they come to sell it. A long chain, vested interests and sheer spread of the markets not only makes it difficult for them to take decisions regarding produce mix, but also deprives them of whatever little bargaining power they may have had. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 40
 AGMARKNET -"Website to help farmers bargain better" It’s possible to check out at this site the delivery positions and prices of various commodities and vegetables at practically every mandi in India. The AGMARKNET venture is a heartening initiative from the much criticised and slow-to-react government, especially on the issue of easing the infrastructural constraints on agriculture. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 41
AGMARKNET -"Website to help farmers bargain better" It’s possible to check out at this site the delivery positions and prices of various commodities and vegetables at practically every mandi in India. The AGMARKNET venture is a heartening initiative from the much criticised and slow-to-react government, especially on the issue of easing the infrastructural constraints on agriculture. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 41
 Seen in this light, the AGMARKNET’s proposed aim to create a ‘nationwide network for speedy collection and dissemination of market information’, could potentially reduce prices paid to intermediaries and bring benefits to a wide cross section of farmers and consumers. The Challenge, if the full potential of such ventures have utilised, is to take IT to rural India in a big way. Ruralmural@indiatimes. com 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 42
Seen in this light, the AGMARKNET’s proposed aim to create a ‘nationwide network for speedy collection and dissemination of market information’, could potentially reduce prices paid to intermediaries and bring benefits to a wide cross section of farmers and consumers. The Challenge, if the full potential of such ventures have utilised, is to take IT to rural India in a big way. Ruralmural@indiatimes. com 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 42
 Current Objectives • E-commerce program • Web – enrichment to facilitate ICT for Market extension • Progressive networking of 7000 wholesale market • Information generation and dissemination • Training and education, online exchange of information among markets and other users. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 43
Current Objectives • E-commerce program • Web – enrichment to facilitate ICT for Market extension • Progressive networking of 7000 wholesale market • Information generation and dissemination • Training and education, online exchange of information among markets and other users. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 43
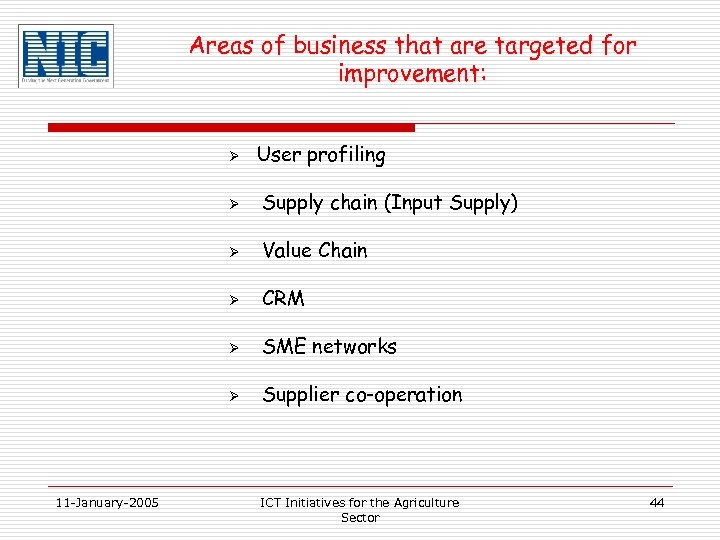 Areas of business that are targeted for improvement: Ø User profiling Ø Ø Value Chain Ø CRM Ø SME networks Ø 11 -January-2005 Supply chain (Input Supply) Supplier co-operation ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 44
Areas of business that are targeted for improvement: Ø User profiling Ø Ø Value Chain Ø CRM Ø SME networks Ø 11 -January-2005 Supply chain (Input Supply) Supplier co-operation ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 44
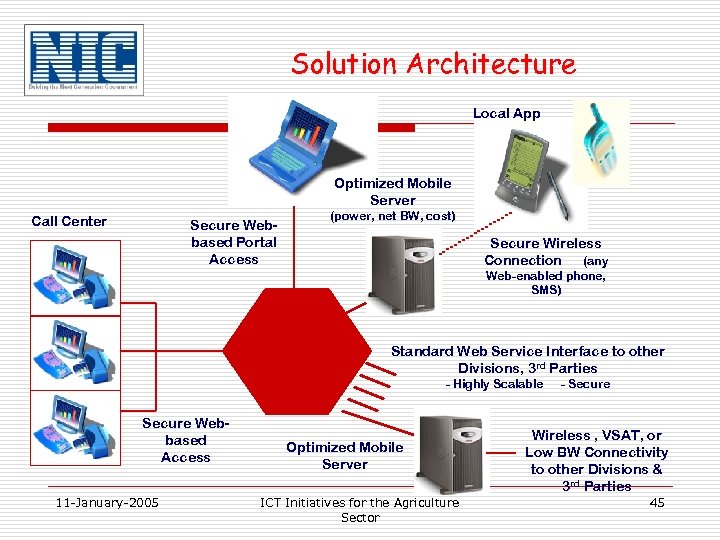 Solution Architecture Local App Optimized Mobile Server Call Center Secure Webbased Portal Access (power, net BW, cost) Secure Wireless Connection (any Web-enabled phone, SMS) Standard Web Service Interface to other Divisions, 3 rd Parties - Highly Scalable Secure Webbased Access 11 -January-2005 Optimized Mobile Server ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector - Secure Wireless , VSAT, or Low BW Connectivity to other Divisions & 3 rd Parties 45
Solution Architecture Local App Optimized Mobile Server Call Center Secure Webbased Portal Access (power, net BW, cost) Secure Wireless Connection (any Web-enabled phone, SMS) Standard Web Service Interface to other Divisions, 3 rd Parties - Highly Scalable Secure Webbased Access 11 -January-2005 Optimized Mobile Server ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector - Secure Wireless , VSAT, or Low BW Connectivity to other Divisions & 3 rd Parties 45
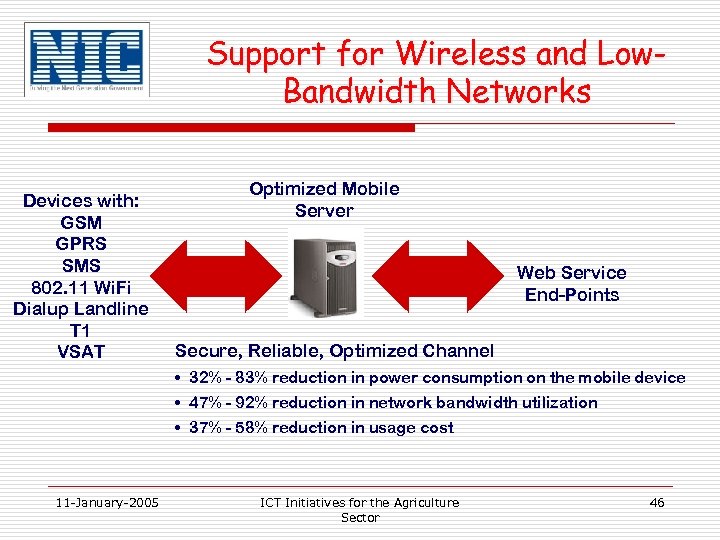 Support for Wireless and Low. Bandwidth Networks Devices with: GSM GPRS SMS 802. 11 Wi. Fi Dialup Landline T 1 VSAT Optimized Mobile Server Web Service End-Points Secure, Reliable, Optimized Channel • 32% - 83% reduction in power consumption on the mobile device • 47% - 92% reduction in network bandwidth utilization • 37% - 58% reduction in usage cost 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 46
Support for Wireless and Low. Bandwidth Networks Devices with: GSM GPRS SMS 802. 11 Wi. Fi Dialup Landline T 1 VSAT Optimized Mobile Server Web Service End-Points Secure, Reliable, Optimized Channel • 32% - 83% reduction in power consumption on the mobile device • 47% - 92% reduction in network bandwidth utilization • 37% - 58% reduction in usage cost 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 46
 Enhancement of the existing portal (Web-based system) that will enable networked agricultural organization (private and public) to: • • • Build relationships and alliances faster Re-engineer and integrate their processes Develop more and better value-added products and services Share knowledge and experiences Enhance innovation Promote Web-based business trading 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 47
Enhancement of the existing portal (Web-based system) that will enable networked agricultural organization (private and public) to: • • • Build relationships and alliances faster Re-engineer and integrate their processes Develop more and better value-added products and services Share knowledge and experiences Enhance innovation Promote Web-based business trading 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 47
 DACNET : An e. GOV 4 D Infrastructure e. Gov 4 D – e-Governance for Development Information Exchange 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
DACNET : An e. GOV 4 D Infrastructure e. Gov 4 D – e-Governance for Development Information Exchange 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector
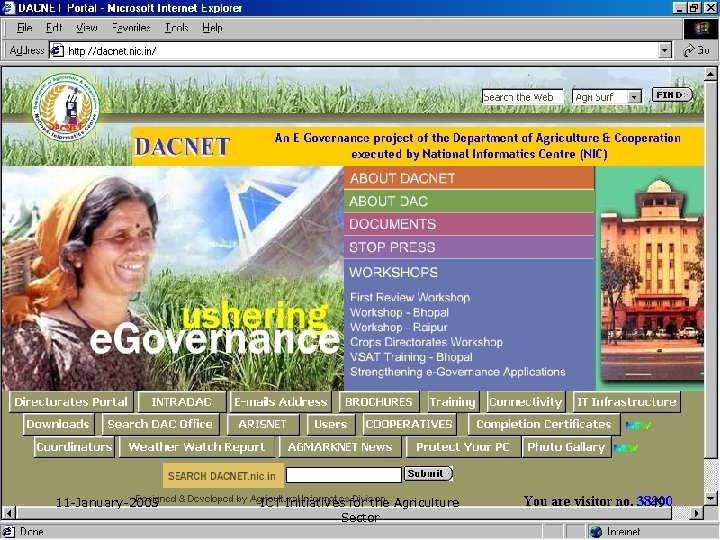 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 49
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 49
 Reaching the Rural Poor (“Un-Reached”) • How? • When? • With What? • By Whom? A location specific e-Government Model is what required to reach the Rural Poor. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 50
Reaching the Rural Poor (“Un-Reached”) • How? • When? • With What? • By Whom? A location specific e-Government Model is what required to reach the Rural Poor. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 50
 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture To analyse Information Needs of Agriculture Sector and existing delivery channels w. r. t the following issues: - • Whether mechanism for knowledge sharing on rights and access to information is adequate? • Whether the Protocols and Mechanisms for Quality Assurance from Knowledge Dissemination Agencies exist and are adequate? 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 51
ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture To analyse Information Needs of Agriculture Sector and existing delivery channels w. r. t the following issues: - • Whether mechanism for knowledge sharing on rights and access to information is adequate? • Whether the Protocols and Mechanisms for Quality Assurance from Knowledge Dissemination Agencies exist and are adequate? 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 51
 Models of e-Government (i. e. digital government) Good Governance and institutions are indispensable for sound agricultural and rural development in developing countries. Models of e-Government (i. e. digital government) are continuously evolving and improvising to harness the potential offered by the Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) and deal with new realities in the area of governance, through out the World. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 52
Models of e-Government (i. e. digital government) Good Governance and institutions are indispensable for sound agricultural and rural development in developing countries. Models of e-Government (i. e. digital government) are continuously evolving and improvising to harness the potential offered by the Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) and deal with new realities in the area of governance, through out the World. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 52
 Generic Models of e-Government (www. Digital governance. org)are relevant while discussing “design of an e-Government for Poor” • Broadcasting / Wider-Dissemination Model • Critical Flow Model • Comparative Analysis Model • E-Advocacy/ Lobbying and Pressure Group Model. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 53
Generic Models of e-Government (www. Digital governance. org)are relevant while discussing “design of an e-Government for Poor” • Broadcasting / Wider-Dissemination Model • Critical Flow Model • Comparative Analysis Model • E-Advocacy/ Lobbying and Pressure Group Model. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 53
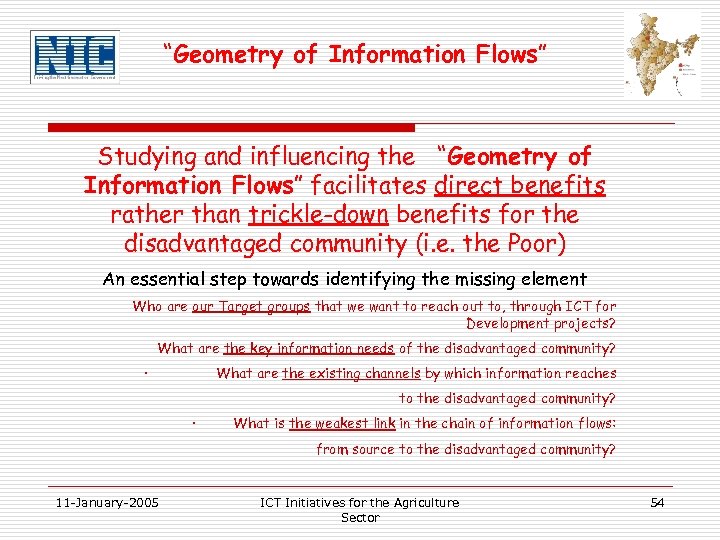 “Geometry of Information Flows” Studying and influencing the “Geometry of Information Flows” facilitates direct benefits rather than trickle-down benefits for the disadvantaged community (i. e. the Poor) An essential step towards identifying the missing element Who are our Target groups that we want to reach out to, through ICT for Development projects? What are the key information needs of the disadvantaged community? · What are the existing channels by which information reaches to the disadvantaged community? · What is the weakest link in the chain of information flows: from source to the disadvantaged community? 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 54
“Geometry of Information Flows” Studying and influencing the “Geometry of Information Flows” facilitates direct benefits rather than trickle-down benefits for the disadvantaged community (i. e. the Poor) An essential step towards identifying the missing element Who are our Target groups that we want to reach out to, through ICT for Development projects? What are the key information needs of the disadvantaged community? · What are the existing channels by which information reaches to the disadvantaged community? · What is the weakest link in the chain of information flows: from source to the disadvantaged community? 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 54
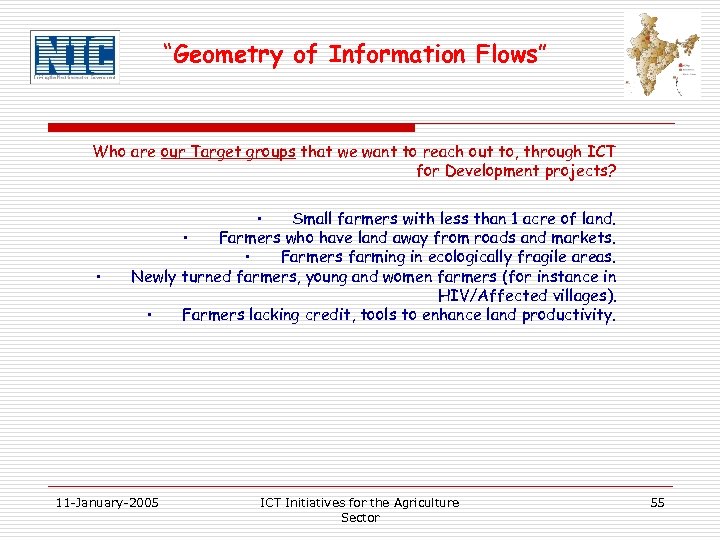 “Geometry of Information Flows” Who are our Target groups that we want to reach out to, through ICT for Development projects? • • Small farmers with less than 1 acre of land. • Farmers who have land away from roads and markets. • Farmers farming in ecologically fragile areas. Newly turned farmers, young and women farmers (for instance in HIV/Affected villages). • Farmers lacking credit, tools to enhance land productivity. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 55
“Geometry of Information Flows” Who are our Target groups that we want to reach out to, through ICT for Development projects? • • Small farmers with less than 1 acre of land. • Farmers who have land away from roads and markets. • Farmers farming in ecologically fragile areas. Newly turned farmers, young and women farmers (for instance in HIV/Affected villages). • Farmers lacking credit, tools to enhance land productivity. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 55
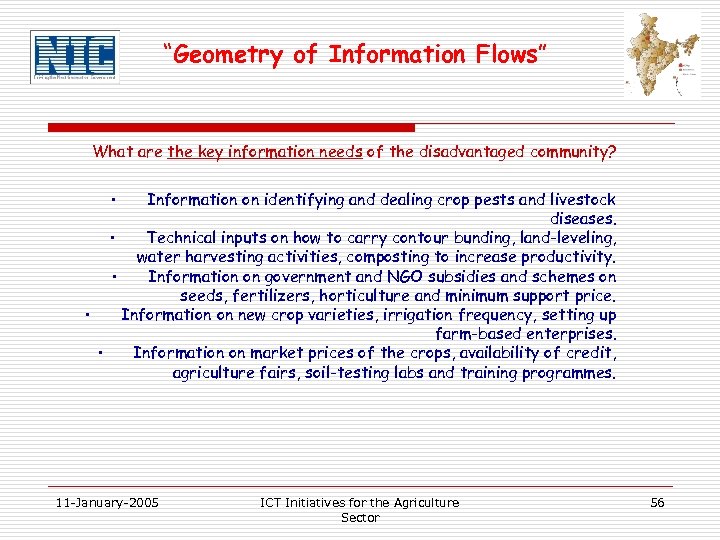 “Geometry of Information Flows” What are the key information needs of the disadvantaged community? • Information on identifying and dealing crop pests and livestock diseases. • Technical inputs on how to carry contour bunding, land-leveling, water harvesting activities, composting to increase productivity. • Information on government and NGO subsidies and schemes on seeds, fertilizers, horticulture and minimum support price. • Information on new crop varieties, irrigation frequency, setting up farm-based enterprises. • Information on market prices of the crops, availability of credit, agriculture fairs, soil-testing labs and training programmes. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 56
“Geometry of Information Flows” What are the key information needs of the disadvantaged community? • Information on identifying and dealing crop pests and livestock diseases. • Technical inputs on how to carry contour bunding, land-leveling, water harvesting activities, composting to increase productivity. • Information on government and NGO subsidies and schemes on seeds, fertilizers, horticulture and minimum support price. • Information on new crop varieties, irrigation frequency, setting up farm-based enterprises. • Information on market prices of the crops, availability of credit, agriculture fairs, soil-testing labs and training programmes. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 56
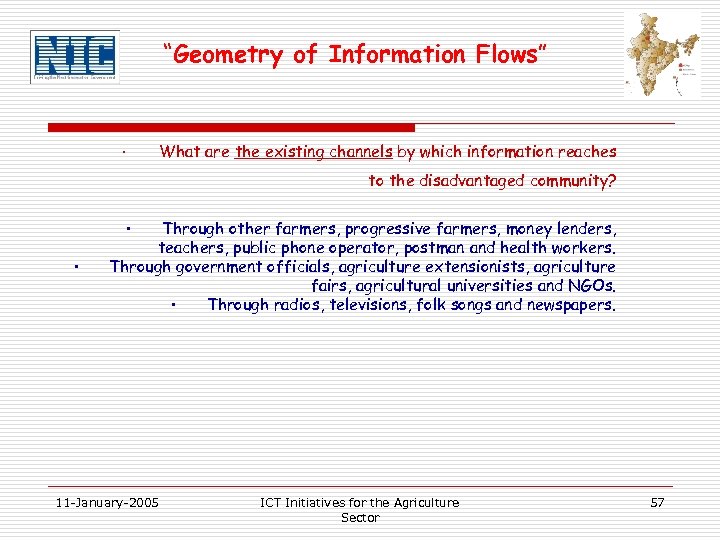 “Geometry of Information Flows” · What are the existing channels by which information reaches to the disadvantaged community? • • Through other farmers, progressive farmers, money lenders, teachers, public phone operator, postman and health workers. Through government officials, agriculture extensionists, agriculture fairs, agricultural universities and NGOs. • Through radios, televisions, folk songs and newspapers. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 57
“Geometry of Information Flows” · What are the existing channels by which information reaches to the disadvantaged community? • • Through other farmers, progressive farmers, money lenders, teachers, public phone operator, postman and health workers. Through government officials, agriculture extensionists, agriculture fairs, agricultural universities and NGOs. • Through radios, televisions, folk songs and newspapers. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 57
 “Geometry of Information Flows” · What is the weakest link in the chain of information flows: from source to the disadvantaged community? • • • Information may be available at local agricultural centres or in markets but these are not easily accessible by farmers. High levels of illiteracy prevent farmers to benefit from available information. • Agriculture extensionists are knowledgeable but do not visit farmlands away from roads or in remote areas. Agriculture extensionists and local agricultural centres do not have updated knowledge of new crop varieties, pest control and government schemes and subsidies. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 58
“Geometry of Information Flows” · What is the weakest link in the chain of information flows: from source to the disadvantaged community? • • • Information may be available at local agricultural centres or in markets but these are not easily accessible by farmers. High levels of illiteracy prevent farmers to benefit from available information. • Agriculture extensionists are knowledgeable but do not visit farmlands away from roads or in remote areas. Agriculture extensionists and local agricultural centres do not have updated knowledge of new crop varieties, pest control and government schemes and subsidies. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 58
 “e-Government for Poor”: Information, Communication and Poverty Reduction • One of the major problems of using ICT for poor is language barrier. • “Networking of People” and “Networking of Information” are essential. • Digital development in Rural Areas: A Journey started in 1985 with the establishment of NICNET in districts of India • Digital Development in Rural Areas: Government’s Initiatives and Agenda on Agricultural Informatics & Communication in India • An agriculture information centre in each village; • Interactive exchange of information for planning and day-to-day operations by farmers; • Availability of all the extension and advisory services on demand. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 59
“e-Government for Poor”: Information, Communication and Poverty Reduction • One of the major problems of using ICT for poor is language barrier. • “Networking of People” and “Networking of Information” are essential. • Digital development in Rural Areas: A Journey started in 1985 with the establishment of NICNET in districts of India • Digital Development in Rural Areas: Government’s Initiatives and Agenda on Agricultural Informatics & Communication in India • An agriculture information centre in each village; • Interactive exchange of information for planning and day-to-day operations by farmers; • Availability of all the extension and advisory services on demand. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 59
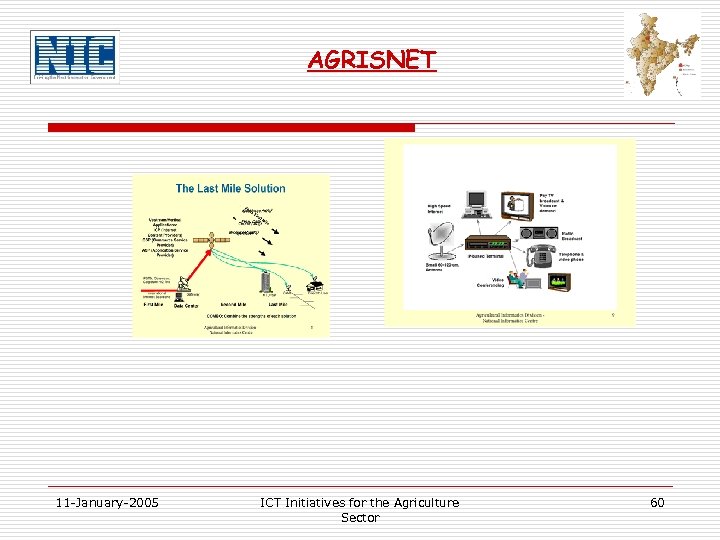 AGRISNET 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 60
AGRISNET 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 60
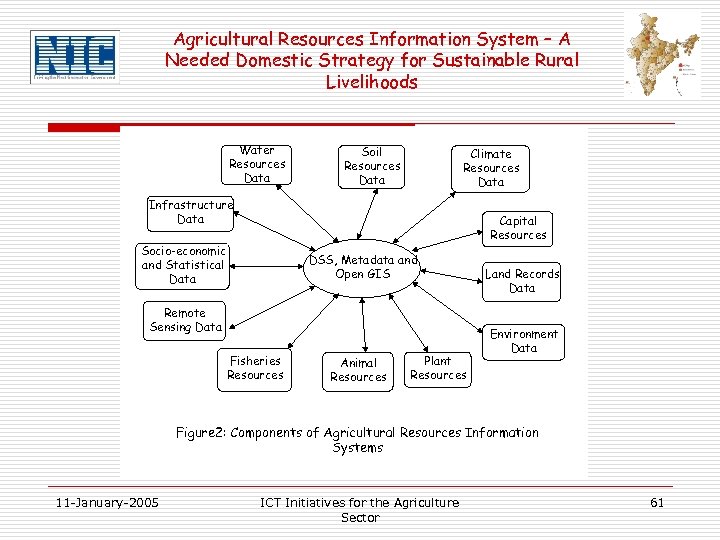 Agricultural Resources Information System – A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Livelihoods Water Resources Data Soil Resources Data Climate Resources Data Infrastructure Data Capital Resources Socio-economic and Statistical Data DSS, Metadata and Open GIS Remote Sensing Data Fisheries Resources Animal Resources Plant Resources Land Records Data Environment Data Figure 2: Components of Agricultural Resources Information Systems 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 61
Agricultural Resources Information System – A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Livelihoods Water Resources Data Soil Resources Data Climate Resources Data Infrastructure Data Capital Resources Socio-economic and Statistical Data DSS, Metadata and Open GIS Remote Sensing Data Fisheries Resources Animal Resources Plant Resources Land Records Data Environment Data Figure 2: Components of Agricultural Resources Information Systems 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 61
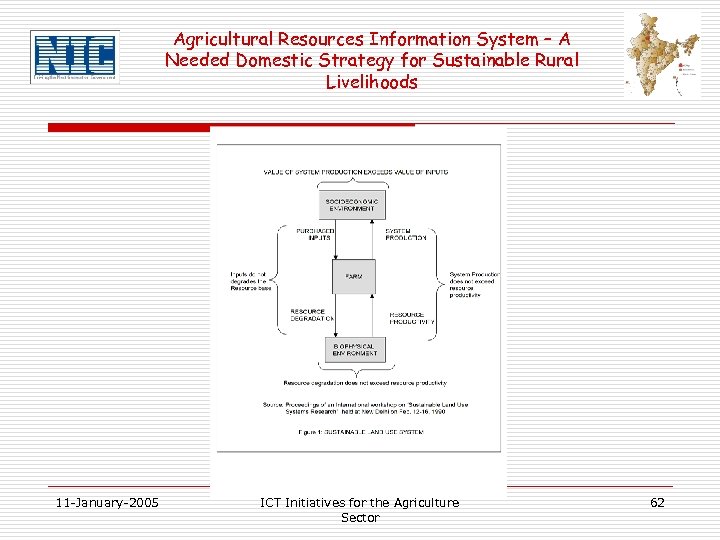 Agricultural Resources Information System – A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Livelihoods 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 62
Agricultural Resources Information System – A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Livelihoods 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 62
 Agricultural Resources Information System – A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Livelihoods Decision Technology System (DTS), built upon the Agricultural Resources Information System, is what required for undertaking: • Crop Suitability based on factor endowment • Land Suitability Assessment; • Land Productivity Assessment; • Population Supporting Capacity; • Land Evaluation and Land Use Planning; • Land Degradation Risk Assessment; • Quantification of Land Resources Constraints; • Land Management; • Agro-ecological Planning; 11 -January-2005 Characterization for ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector Research and 63
Agricultural Resources Information System – A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Livelihoods Decision Technology System (DTS), built upon the Agricultural Resources Information System, is what required for undertaking: • Crop Suitability based on factor endowment • Land Suitability Assessment; • Land Productivity Assessment; • Population Supporting Capacity; • Land Evaluation and Land Use Planning; • Land Degradation Risk Assessment; • Quantification of Land Resources Constraints; • Land Management; • Agro-ecological Planning; 11 -January-2005 Characterization for ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector Research and 63
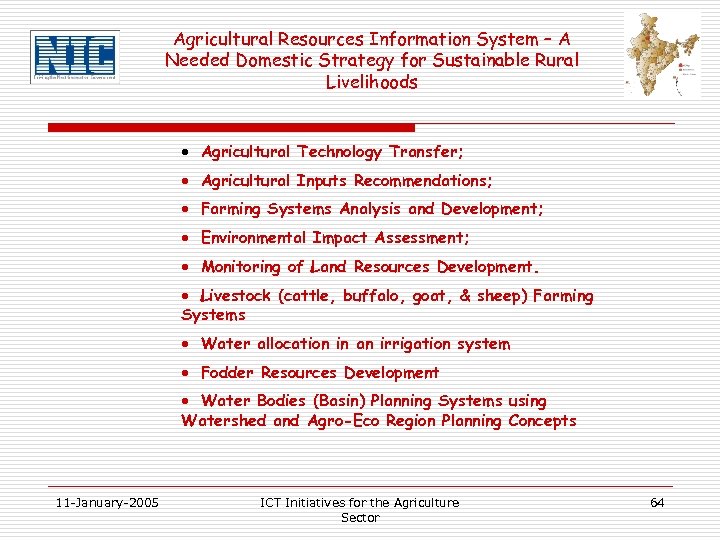 Agricultural Resources Information System – A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Livelihoods · Agricultural Technology Transfer; · Agricultural Inputs Recommendations; · Farming Systems Analysis and Development; · Environmental Impact Assessment; · Monitoring of Land Resources Development. · Livestock (cattle, buffalo, goat, & sheep) Farming Systems · Water allocation in an irrigation system · Fodder Resources Development · Water Bodies (Basin) Planning Systems using Watershed and Agro-Eco Region Planning Concepts 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 64
Agricultural Resources Information System – A Needed Domestic Strategy for Sustainable Rural Livelihoods · Agricultural Technology Transfer; · Agricultural Inputs Recommendations; · Farming Systems Analysis and Development; · Environmental Impact Assessment; · Monitoring of Land Resources Development. · Livestock (cattle, buffalo, goat, & sheep) Farming Systems · Water allocation in an irrigation system · Fodder Resources Development · Water Bodies (Basin) Planning Systems using Watershed and Agro-Eco Region Planning Concepts 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 64
 Pilot Demonstration Projects Typologies • A Tribal District · • A Hill District • A Dry-land District • A Socially backward District • A Green Revolution District • A Coastal district • A Dairy-farming District • A district dominated by cash crop district • A district in a mining/ industrial belt • A district dominated by forest economy • A district dominated by one or two urban centers • A district in arid-zone • A district, which is flood prone but having vast wasteland that could be used to generate forest cover. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 65
Pilot Demonstration Projects Typologies • A Tribal District · • A Hill District • A Dry-land District • A Socially backward District • A Green Revolution District • A Coastal district • A Dairy-farming District • A district dominated by cash crop district • A district in a mining/ industrial belt • A district dominated by forest economy • A district dominated by one or two urban centers • A district in arid-zone • A district, which is flood prone but having vast wasteland that could be used to generate forest cover. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 65
 Ag. RIS : An e-Governance Component of the “e-Government for the Poor” in India By 2012, Ag. RIS is expected to be implemented in all 600 Districts of India 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 66
Ag. RIS : An e-Governance Component of the “e-Government for the Poor” in India By 2012, Ag. RIS is expected to be implemented in all 600 Districts of India 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 66
 AGRISNET (A NICNET Based Agricultural Informatics & Communication Network to Usher in Digital Opportunities for Sustainable Agricultural Development in India) A Central Sector Scheme for Strengthening ICT Apparatus for Agriculture & Cooperation in States & UTs Department of Agriculture & Cooperation Ministry of Agriculture 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 67
AGRISNET (A NICNET Based Agricultural Informatics & Communication Network to Usher in Digital Opportunities for Sustainable Agricultural Development in India) A Central Sector Scheme for Strengthening ICT Apparatus for Agriculture & Cooperation in States & UTs Department of Agriculture & Cooperation Ministry of Agriculture 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 67
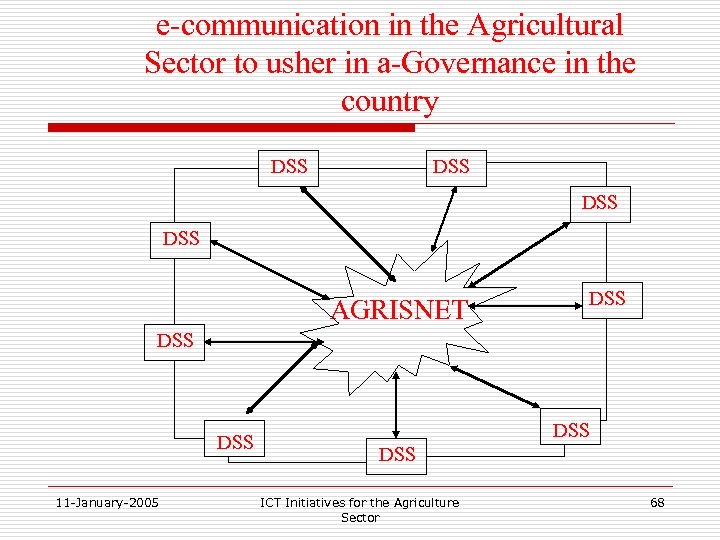 e-communication in the Agricultural Sector to usher in a-Governance in the country DSS DSS AGRISNET DSS DSS 11 -January-2005 DSS ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 68
e-communication in the Agricultural Sector to usher in a-Governance in the country DSS DSS AGRISNET DSS DSS 11 -January-2005 DSS ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 68
 AGRISNET, Ag. RIS : A Step towards establishing a location-specific e-Government model for the Poor in India 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 69
AGRISNET, Ag. RIS : A Step towards establishing a location-specific e-Government model for the Poor in India 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 69
 DACNET v This Scheme had its “spread effect” on the employees of the Directorates through its “IT empowerment” component and is being viewed as a “model framework” for realizing e-governance in other departments of the Ministry. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 70
DACNET v This Scheme had its “spread effect” on the employees of the Directorates through its “IT empowerment” component and is being viewed as a “model framework” for realizing e-governance in other departments of the Ministry. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 70
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 71
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 71
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 72
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 72
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 73
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 73
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 74
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 74
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 75
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 75
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 76
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 76
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 77
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 77
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 78
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 78
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 79
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 79
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 80
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 80
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 81
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 81
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 82
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 82
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 83
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 83
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 84
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 84
 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 85
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 85
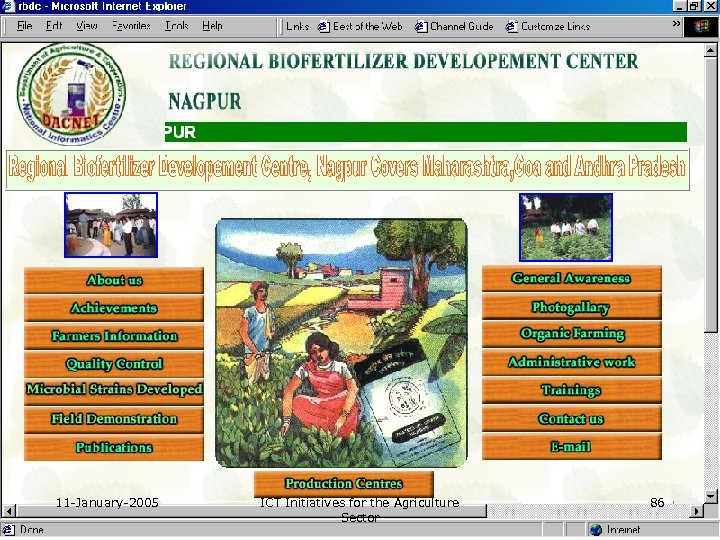 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 86
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 86
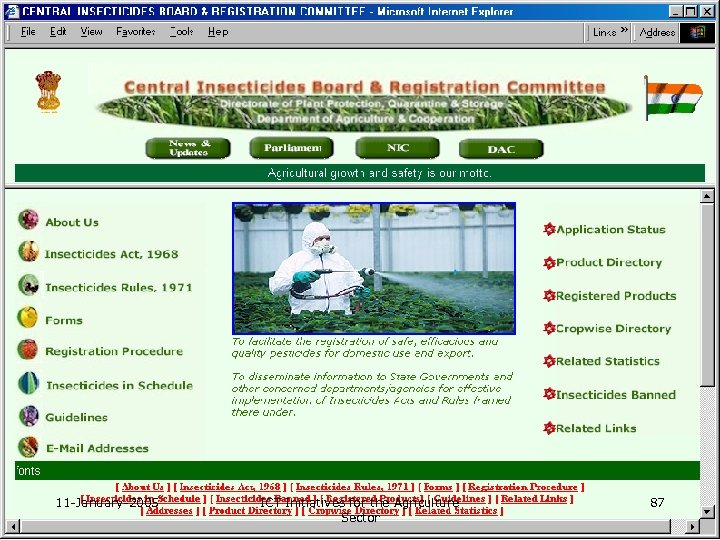 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 87
11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 87
 Digital Opportunities Ö A Positive Force for Agricultural Growth, Poverty Reduction and Sustainable Resource Use in India. Ö What was a “technology push” in 1990 s is beginning to take a shape of “consumer pull” at grass-root level in India. Ö India is endowed with regional diversities for its uneven “economic and agricultural development” Ö A journey ‘from digital divide to digital opportunities” for sustainable Agricultural development has thus begun in the beginning of the 21 st Century. Ö The challenge is to take ICT to rural India in a big way. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 88
Digital Opportunities Ö A Positive Force for Agricultural Growth, Poverty Reduction and Sustainable Resource Use in India. Ö What was a “technology push” in 1990 s is beginning to take a shape of “consumer pull” at grass-root level in India. Ö India is endowed with regional diversities for its uneven “economic and agricultural development” Ö A journey ‘from digital divide to digital opportunities” for sustainable Agricultural development has thus begun in the beginning of the 21 st Century. Ö The challenge is to take ICT to rural India in a big way. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 88
 RAP Publication 2002/03 Small-Holder Farmers in India : Food Security and Agricultural Policy In India, NIC of the Ministry of Information Technology through initiatives such as the DISNIC-AGRIS Project, and AGRISNET ( a NICNET based Agricultural informatics & Communication Network) - seeks to reach all agricultural districts and blocks through its massive “Gateway networks”. Through these networks, farmers will have opportunity to learn of and benefit from new and improved agricultural practicies, to have weather-forecast-based guidance for timely agricultural operations, to be alerted by satellite surveys of pests and diseases, and to access crop-output forecasting and marketing strategies for domestic and for export trade” Dr. R. B. Singh, Former Asst. Director General & FAO Regional Representative for Asia & Pacific 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 89
RAP Publication 2002/03 Small-Holder Farmers in India : Food Security and Agricultural Policy In India, NIC of the Ministry of Information Technology through initiatives such as the DISNIC-AGRIS Project, and AGRISNET ( a NICNET based Agricultural informatics & Communication Network) - seeks to reach all agricultural districts and blocks through its massive “Gateway networks”. Through these networks, farmers will have opportunity to learn of and benefit from new and improved agricultural practicies, to have weather-forecast-based guidance for timely agricultural operations, to be alerted by satellite surveys of pests and diseases, and to access crop-output forecasting and marketing strategies for domestic and for export trade” Dr. R. B. Singh, Former Asst. Director General & FAO Regional Representative for Asia & Pacific 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 89
 NIC’s Approach - An Integrated Approach The INTERNET Technology Agricultural Development & Backward Area Development Farm & Non-Farm Linkages 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 90
NIC’s Approach - An Integrated Approach The INTERNET Technology Agricultural Development & Backward Area Development Farm & Non-Farm Linkages 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 90
 Poverty. Net in India The Poverty. Net in India takes the form of the Government’s Digital Initiatives and Agenda (viz. , AGRISNET, Ag. RIS, AGMARKNET, DACNET, VISTARNET, APHNET, FISHNET, HORTNET, Seed. NET, PPIN, COOPNET, FERTNET, ARISNET, AFPINET, ARINET, NDMNET, etc), as a step towards "reaching" agricultural knowledge and technology to the rural Poor. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 91
Poverty. Net in India The Poverty. Net in India takes the form of the Government’s Digital Initiatives and Agenda (viz. , AGRISNET, Ag. RIS, AGMARKNET, DACNET, VISTARNET, APHNET, FISHNET, HORTNET, Seed. NET, PPIN, COOPNET, FERTNET, ARISNET, AFPINET, ARINET, NDMNET, etc), as a step towards "reaching" agricultural knowledge and technology to the rural Poor. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 91
 DISNIC Programme Revisited DISNIC : A District level Government Informatics Programme (1987) “DISNIC-PLAN : An Informatics Blueprint that covers Villages” – A Sponsored Project of the Planning Commission Sustainability of Natural Resources Endowment, Full Employment, Empowerment of Women, Production System Planning ICT for Social development ICT for Economic Development 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 92
DISNIC Programme Revisited DISNIC : A District level Government Informatics Programme (1987) “DISNIC-PLAN : An Informatics Blueprint that covers Villages” – A Sponsored Project of the Planning Commission Sustainability of Natural Resources Endowment, Full Employment, Empowerment of Women, Production System Planning ICT for Social development ICT for Economic Development 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 92
 Informatics Blueprint that Covers Villages • Regional Workshops at Pune, Panajim, Thiruvananthapuram, New Delhi • 28 Pilot Districts (One in each State) • One Block in each identified District • Many Central Governments have sent in their input parameters for inclusion • Many State Agricultural Universities and ICAR Institutes responded positively • As many number of Hypotheses facilitating sustainable investment at Village or cluster of villages, as possible. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 93
Informatics Blueprint that Covers Villages • Regional Workshops at Pune, Panajim, Thiruvananthapuram, New Delhi • 28 Pilot Districts (One in each State) • One Block in each identified District • Many Central Governments have sent in their input parameters for inclusion • Many State Agricultural Universities and ICAR Institutes responded positively • As many number of Hypotheses facilitating sustainable investment at Village or cluster of villages, as possible. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 93
 Rural Prosperity • Networking of about 1. 46 lakhs Cooperative Societies • Localisation for Content Generation : Digital Opportunities • e-Government for Poor • Induction of 25000 Students (13000 Students from about 215 Departments of Geography and 12000 Students from about 200 Colleges of Agriculture) for ICT enabled Agricultural Development through KVK • Agricultural Information Centre at Village level • Reaching the Unreached 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 94
Rural Prosperity • Networking of about 1. 46 lakhs Cooperative Societies • Localisation for Content Generation : Digital Opportunities • e-Government for Poor • Induction of 25000 Students (13000 Students from about 215 Departments of Geography and 12000 Students from about 200 Colleges of Agriculture) for ICT enabled Agricultural Development through KVK • Agricultural Information Centre at Village level • Reaching the Unreached 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 94
 I wish to conclude. . . I thank TASS and IARI for giving me an opportunity to share my experience on evolving strategy, since ISDA-1995 for “ICTs for Agriculture and Rural Development” which has emerged as a Powerful Engine for fostering agricultural growth, poverty reduction and sustainable resource use. A “New Deal” for “Rural India”. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 95
I wish to conclude. . . I thank TASS and IARI for giving me an opportunity to share my experience on evolving strategy, since ISDA-1995 for “ICTs for Agriculture and Rural Development” which has emerged as a Powerful Engine for fostering agricultural growth, poverty reduction and sustainable resource use. A “New Deal” for “Rural India”. 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 95
 Thanks 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 96
Thanks 11 -January-2005 ICT Initiatives for the Agriculture Sector 96


