096dbd46fddb936fbad78fb541266af8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 83

Executive Briefing October 16, 2001 1 1

w Deputy State Auditor, MIS & IT Audit, Commonwealth of Massachusetts w Adjunct faculty at Bentley College w Member of Cobi. T Steering Committee w Served as member of Y 2 K Coordinating Council, Commonwealth of Massachusetts w 1994 -1995 International President of ISACA/F w Served as member of Governor’s Commission on Computer Crime, Governor’s Commission on Computer Technology and Law, and Governor’s Task Force on ECommerce w e-mail: john. beveridge@sao. state. ma. us 2

w How does responsible managment keep the ship on course? w How do we achieve satisfactory results for our clients and stake-holders? w How do we adapt in a timely manner to “best practices” for our organization’s environment? 3

When we spend a lot of money and what we have built doesn’t work, or is difficult to maintain, or is not accepted, or appears vulnerable, People have a lot to say 4

Stakeholders apply pressure Shareholders and Executive Lower cost, higher profitability and increased market share Customers and Staff More functionality at lower cost and greater ease of use Society Greater accountability for executives in private and public sector 5

What are the customers saying ? E-business Factors u Guarantee of delivery u Customer service u Ease of use u Increased dependence u Security 6

What signals are regulators giving? Federal Reserve u Focus on Operational Risk within which security and IT are very significant u All major risk issues have been caused by breakdowns in 3 Internal control 3 Oversight 3 Information Technology 7

Most Pressing Concerns about Information Technology w Security w Availability w Integrity and Effectiveness w Cost 8

th 11 September has Impacted us all in a Whole Lot of Ways Personal w Economic w Security w Risk w 9
Indicators? Measures? Scales? 10

The Answer Lies In: w Having clear understandings of the strategic value of technology w Bringing that strategic value to reality w Having appropriate frameworks of control w Employing the fundamentals of IT goverance w Building mechanisms to provide adequate assurance that IT governance objectives are addressed 11

Cobi. T’s Control Objectives and Management Guidelines are valuable IT governance tools that help in the understanding and management of risks and benefits associated with information integrity, security and availability and the management of related IT. 12

l Authoritative, up-to-date set of generally accepted IT control objectives and control practices for day-to-day use by business managers and auditors. l Structured and organized to provide a powerful control model 13
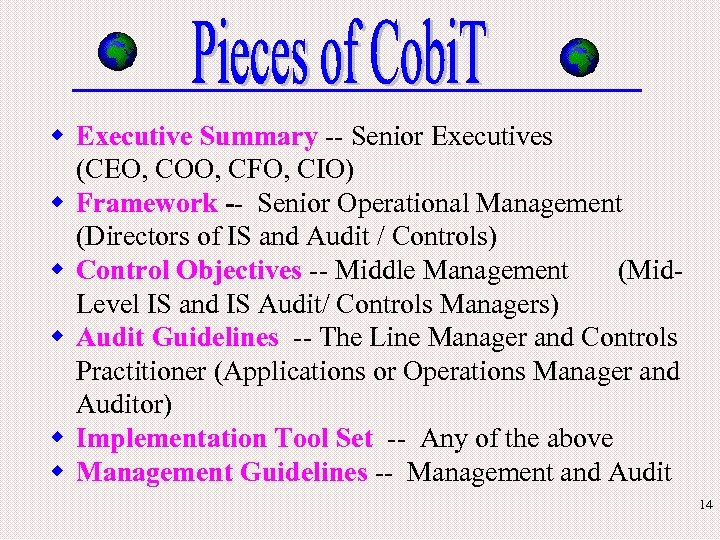
w Executive Summary -- Senior Executives (CEO, COO, CFO, CIO) w Framework -- Senior Operational Management (Directors of IS and Audit / Controls) w Control Objectives -- Middle Management (Mid. Level IS and IS Audit/ Controls Managers) w Audit Guidelines -- The Line Manager and Controls Practitioner (Applications or Operations Manager and Auditor) w Implementation Tool Set -- Any of the above w Management Guidelines -- Management and Audit 14

COBIT w. Management Guidelines Includes: – Critical Success Factors – Key Performance Indicators – Key Goal Indicators – Maturity models 15

w Right information, to only the right party, at the right time. w Information that is relevant, reliable and secure. w Information provided by systems that have integrity by a well-managed and properly controlled IT environment. 16

IT Governance Objectives w IT is aligned with the business enabling the entity to maximize benefit w IT resources are safeguarded and used in a responsible and ethical manner w IT-related risks are addressed through appropriate controls and managed to minimize risk and exposure 17

w Need for better operational control w While technology makes new business processes possible, it may come with reduced control w Demand for increased effectiveness, efficiency and security w Strategic importance of technology w The need to hold officers and senior management accountable and strengthen governance 18

§ Addresses key attributes of information produced by IT. § Provides a working control model for IT- related control objectives § Links recommended control practices for IT to business and control objectives. § Assists in evaluating appropriateness of controls 19

Cobi. T is an Authoritative Source w Built on a sound framework of control and IT-related control practices. w Aligned with de jure and de facto standards and regulations. w Has undergone expert review and exposure process, now in its 3 rd edition 20

Cobi. T Sources Professional standards for internal control and auditing (COSO, IFAC, AICPA, IIA, etc) Technical standards (ISO, EDIFACT, etc. ) Codes of Conduct Qualification criteria for IT systems and processes (ISO 9000, ITSEC, TCSEC, etc. ) Industry practices and requirements from industry forums (ESF, I 4) Emerging industry-specific requirements from banking, e-com, IT manufacturing. 21

Based on a Strong Foundation and Sound Principles of Internal Control 22

What is Internal Control? How it is defined impacts its design, exercise, and evaluation. 23

Control (as defined by COBIT) The policies, procedures, practices and organizational structures designed to provide reasonable assurance that business objectives will be achieved and that undesired events will be prevented or detected and corrected. w Source: COBIT Control Objectives, p. 12. 24

IT Control Objective A statement of desired result or purpose to be achieved by implementing control procedures in a particular IT activity 25

Internal Controls are framed by what is to be attained (control objectives) and the means to attain those goals (the controls). 26

Cobi. T Incorporates Key Internal Control Requirements ð Systemization ð Documentation ð Standards, defined expectations ð Measurement ð Appropriate risk assessment 27

Cobi. T Incorporates Key Internal Control Requirements ð Well-defined operational and control objectives ð Appropriate controls ð Competent and trustworthy people ð Monitoring & evaluation 28
Cobi. T Framework § Built on an understanding of the: Ø relationship of controls to control objectives, Ø importance of focusing on the relationship of control objectives to business objectives and business processes, Ø value of managed processes and resources tied to strategic initiatives. 29
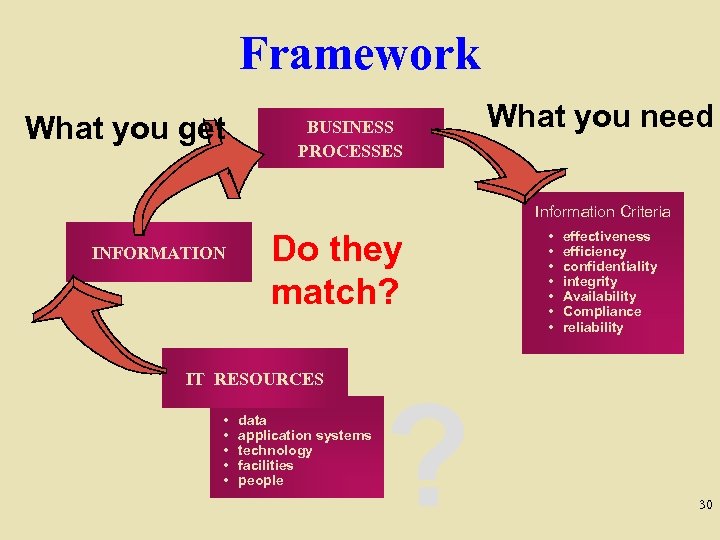
Framework What you get BUSINESS PROCESSES What you need Information Criteria INFORMATION Do they match? IT RESOURCES • • • data application systems technology facilities people ? • • effectiveness efficiency confidentiality integrity Availability Compliance reliability 30

Framework’s Three Components q “Business Requirements” for Information q IT Resources q IT Processes 31

Information Criteria -- The 1 st Component w Effectiveness w Efficiency w Confidentiality w Integrity w Availability w Compliance w Reliability of Information 32

IT Resources -- The 2 nd Component w Data w Application Systems w Technology w Facilities w People 33
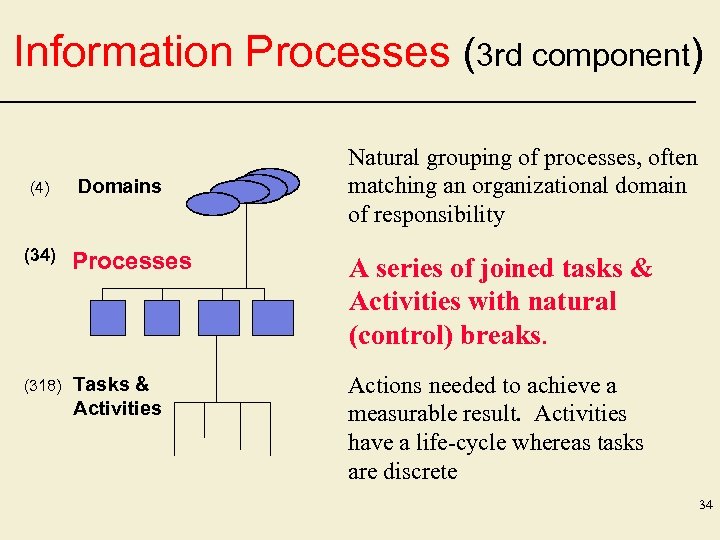
Information Processes (3 rd component) (4) Domains Natural grouping of processes, often matching an organizational domain of responsibility (34) Processes A series of joined tasks & Activities with natural (control) breaks. (318) Tasks & Activities Actions needed to achieve a measurable result. Activities have a life-cycle whereas tasks are discrete 34
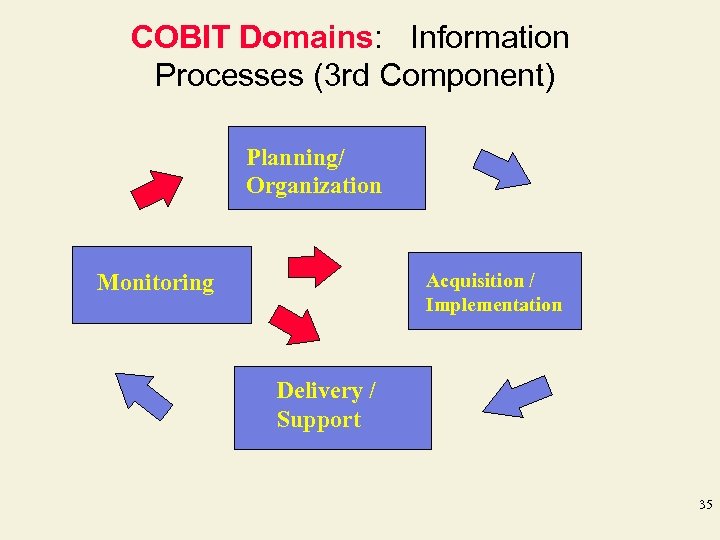
COBIT Domains: Information Processes (3 rd Component) Planning/ Organization Monitoring Acquisition / Implementation Delivery / Support 35
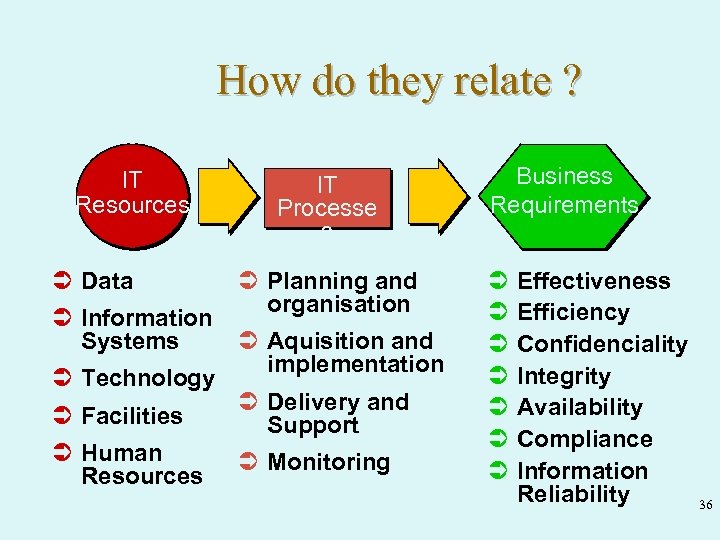
How do they relate ? IT Resources Ü Data Ü Information Systems Ü Technology IT Processe s Ü Planning and organisation Ü Aquisition and implementation Ü Facilities Ü Delivery and Support Ü Human Resources Ü Monitoring Business Requirements Ü Ü Ü Ü Effectiveness Efficiency Confidenciality Integrity Availability Compliance Information Reliability 36

IT Resource Management Cobi. T underscores and demonstrates that IT resources need to be managed by naturally grouped processes to provide organizations with type and quality, and security of information required to achieve organizational objectives. 37
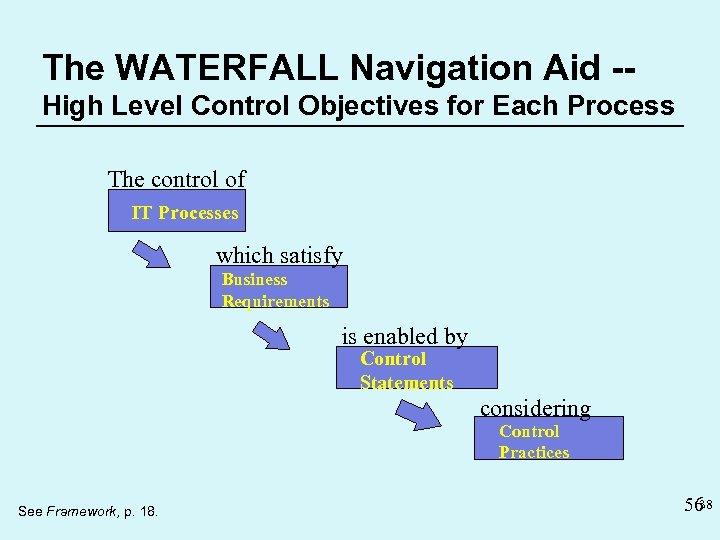
The WATERFALL Navigation Aid -High Level Control Objectives for Each Process The control of IT Processes which satisfy Business Requirements is enabled by Control Statements considering Control Practices See Framework, p. 18. 38 56

Cobi. T’s Control Objectives w Contains management control practices by high-level control objective within four categories, or domains, of the control objectives. w Contains statements of the desired results or purposes to be achieved by implementing specific control procedures within an IT activity. w Assists in establishing clear policy and good practices for IT control 39

Planning and Organization w Strategy and tactical plans for IT w Identify ways that IT can best contribute to the achievement of business objectives w Plan, communicate, and manage the realization of the strategic vision w Establish the IT organization, and w Set the stage for managing information and the technology infrastructure 40
Acquisition and Implementation Domain w IT solutions – – Identified Developed or acquired Implemented Integrated into the business processes w Change and maintain existing systems 41

Delivery and Support Domain w w Deliver required services Ensure security and continuity of services Set up support processes, including training Process data (including “application” controls) 42

Monitoring Domain w Regularly assess IT processes for – Quality – Appropriateness of controls – Compliance with control requirements w Addresses management oversight of organization’s control provisions w Provide for an audit function 43
Relation to Other Control Models Cobi. T is in alignment with other control models: – COSO – COCO – Cadbury – King 44

Reinforces Control Responsibilities w Management -- has primary responsibility for ensuring that controls are in place and in effect to provide reasonable assurance that operational and control objectives will be met. w Users -- exercise and monitor controls. w Audit -- evaluates, advises and provides statements of assurance regarding the adequacy of controls. 45

46

As a control model, Cobi. T should be tailored to agency, IT platform, and system standards Use Cobi. T as the Structure to which you link agency-specific operational and control requirements, policies, and standards 47

Using Cobi. T w w w w Organizational tool Management tool Good practices standard Strengthen third-party contracts Criteria for Evaluation Strengthen risk management Basis for improved management 48

Using Cobi. T in Evaluating IT Controls ð Selecting areas or control objectives for evaluation ð Determining type of evaluation ð Engagement/assessment planning ð Framing scope and evaluation objectives to Cobi. T ð Development of control assessment approach 49

Use of Cobi. T to Plan Control Evaluations w Assessing the control environment and identifying high risk processes w Conducting a high-level and detailed policy and procedures review w Performing a control review w Using Cobi. T-related matrices 50

Using Cobi. T Matrices to Focus on: w IT Functions – Their importance? – Level of performance? – Control documentation? w Responsible Parties of IT – Performed by? – Contracted services? – Primary responsible party? w Risk Assessment – Importance, level of risk, control documentation 51

Cobi. T Helps Identify Key Risks to the Organization è è è Unaware of the risks Poor understanding of CSFs Absence of KPIs No “scorecard” or basis of measurement Absence of monitoring and evaluation Weak IT control environment 52

Cobi. T helps senior management, business process owners, and IT gain increased benefit from independent examiners 53

Audit Insight: Overview of Audit Planning w Auditee selection (may be Cobi. T driven) w Entrance Conference and on-site preaudit information gathering (Cobi. T) w Develop proposed scope and audit objectives (Cobi. T-framed) w Finalize audit work program (Cobi. Tframed) w Engagement conference (reference Cobi. T as criteria) and audit (Cobi. T as review criteria) 54

Audit Planning: w Who are they? (type of agency, enabling legislation) w What do they do? (mission, business objectives) w How do they plan to do it? (strategy/plan) w How do they do it? (functions, processes) w With what resources? (IT, operational resources, management & staff, raw materials, etc. ) w By what rules? (policies, standards, legal and regulatory requirements) w Under what risks? (risk analysis) 55

Audit Planning: w Who does it? (internal & external players, their roles and responsibilities) w Who knows what is done? (reporting lines, designated points of accountability) w How do they known it is done right? (measurement registers, assurance mechanisms, evaluations, score cards, etc. ) w Where are they? (centralized or distributed) 56

Audit Guidelines w They are evaluation guidelines. w Generic guideline identifies various tasks to be performed in assessing ANY control objective within a process. This generic guideline extracted all repetitive tasks into one -- to be performed for all control objectives. w 34 others are specific process-oriented task suggestions to provide management assurance that a control objective is being addressed. 57

The IT process is therefore audited by: Obtaining an understanding of business requirements, related risks, and relevant control measures Evaluating the appropriateness of stated controls Assessing compliance by testing whether the stated controls are working as prescribed, consistently and continuously. Substantiating the risk of the control objective not being met by using analytical techniques and/or consulting alternative sources. 58

Organization & Management Review è Clarity and appropriateness of responsibility definitions è assignment of responsibilities è points of accountability è reporting mechanisms for actions taken and activities performed è Efforts to monitor and evaluate adequacy of exercise of responsibilities 59

Using Cobit to Address Third-Party Providers of IT-Related Services è Are desired processes are in place? è Have we established accountability è Do we agree on the levels of control? è Do the service contracts adequately identify deliverables and responsibilities? è Is there ongoing monitoring and evaluation of providers and partners? 60

Using the Management Guidelines 61
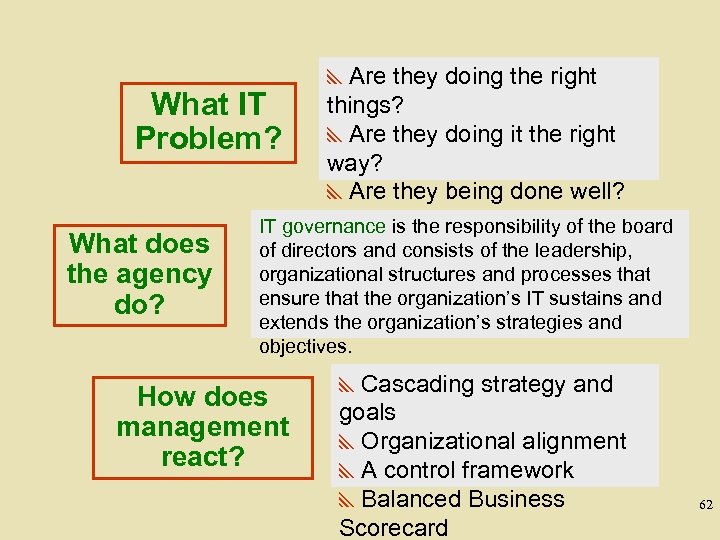
What IT Problem? What does the agency do? y. Are they doing the right things? y. Are they doing it the right way? y. Are they being done well? y. Are we getting benefits? IT governance is the responsibility of the board of directors and consists of the leadership, organizational structures and processes that ensure that the organization’s IT sustains and extends the organization’s strategies and objectives. How does management react? y. Cascading strategy and goals y. Organizational alignment y. A control framework y. Balanced Business Scorecard 62
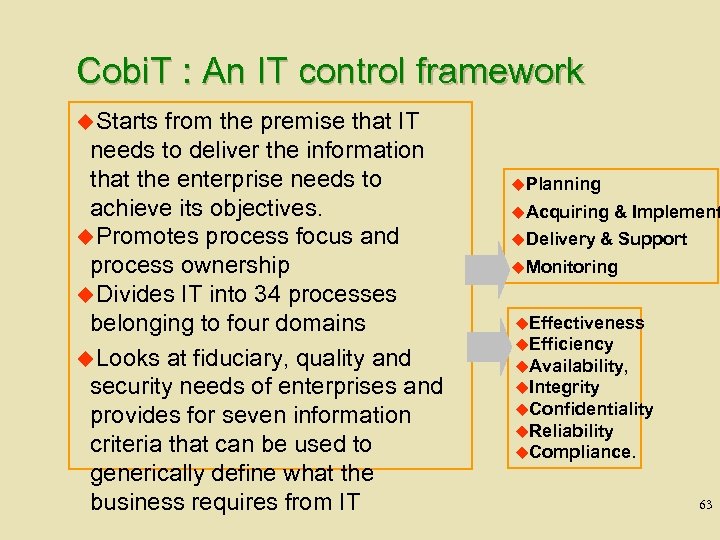
Cobi. T : An IT control framework u. Starts from the premise that IT needs to deliver the information that the enterprise needs to achieve its objectives. u. Promotes process focus and process ownership u. Divides IT into 34 processes belonging to four domains u. Looks at fiduciary, quality and security needs of enterprises and provides for seven information criteria that can be used to generically define what the business requires from IT u. Planning u. Acquiring u. Delivery & Implement & Support u. Monitoring u. Effectiveness u. Efficiency u. Availability, u. Integrity u. Confidentiality u. Reliability u. Compliance. 63

Why governance? l “Due diligence” IT is strategic to the business l IT is critical to the business l Expectations and reality don’t match l IT involves huge investments and large risks l 64

IT is strategic to most businesses If so, wouldn’t you want to know whether your information technology organization is: · Likely to achieve its objectives? · Resilient enough to learn and adapt? · Judiciously managing the risks it faces? · Appropriately recognizing opportunities and acting upon them? 65

Management Guidelines § § § Generic and action oriented For the purpose of • • • IT Control profiling - what’s important? Awareness - where’s the risk? Benchmarking - what do others do? Supporting decision making and follow up • • • Key performance indicators of IT processes Critical success factors of controls Control implementation choices 66

Management Guidelines Critical Success Factors l the most important things to do to increase the probability of success of the process l observable - usually measurable - characteristics of the organisation and process l are either strategic, technological, organizational or procedural in nature l focus on obtaining, maintaining and leveraging capability and skills l expressed in terms of the IT process, not necessarily the business 67

Management Guidelines Key Goal Indicators l l l describe the outcome of the process and are therefore a ‘lag’ indicator, i. e. , measurable after the fact Are an indicator of the success of the process but may also be expressed in terms of the business contribution if that contribution is specific to the IT process represent the process goal, i. e. , a measure of “what”, a target to achieve may also describe a measure of the impact of not reaching the process goal KGIs are IT oriented but are also business driven Are expressed in precise measurable terms wherever possible 68

Management Guidelines Key Performance Indicators l are a measure of “how well” the process is performing l predict the probability of success or failure in the future, i. e. KPIs are ‘LEAD’ indicators l are process oriented but IT driven l focus on the process and learning dimensions of the balanced scorecard l are expressed in precise measurable terms l should help in improving the IT process 69

Maturity Models • • • Refer to business requirements and control capabilities at different levels Are scales that lend themselves to pragmatic comparison Are scales where the difference can be made measurable in an easy manner Are recognizable as a “profile” of the enterprise in relation to IT governance and control Assist in determining As-Is and To-Be positions relative to IT governance and control maturity Lend themselves to support gap analysis to determine what needs to be done to achieve a chosen level 70
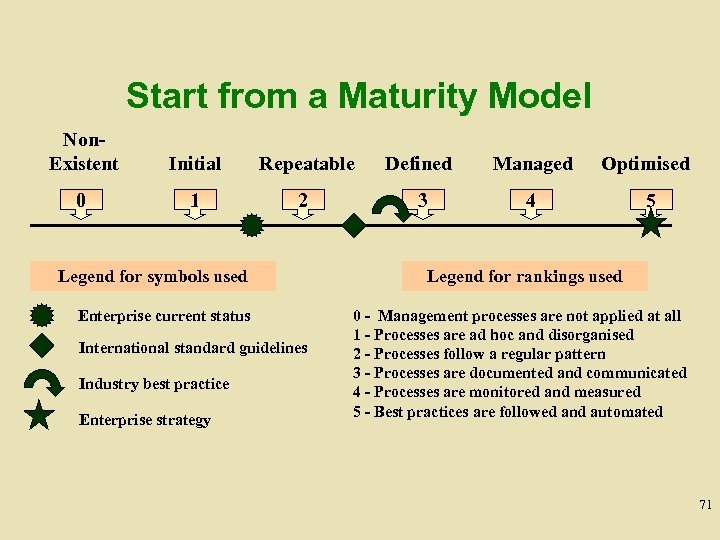
Start from a Maturity Model Non. Existent Initial Repeatable Defined Managed Optimised 0 1 2 3 4 5 Legend for symbols used Enterprise current status International standard guidelines Industry best practice Enterprise strategy Legend for rankings used 0 - Management processes are not applied at all 1 - Processes are ad hoc and disorganised 2 - Processes follow a regular pattern 3 - Processes are documented and communicated 4 - Processes are monitored and measured 5 - Best practices are followed and automated 71

What Management should do · Align IT strategy with business goals · Cascade strategy and goals down into the agency · Set up organizational structures that facilitate strategy implementation · Adopt a control and governance framework · Provide IT infrastructures that facilitate creation and sharing of business information · Embed responsibilities for risk management in the organization · Focus on important IT processes and core IT competencies 72 · Measure performance (Balanced Business

Cobi. T Recognizes w IT is an integral part of the organization w IT governance is an integral part of corporate governance w Focus on control objectives can strengthen appropriateness and use of internal controls w Measurement is crucial to internal control w Monitoring and evaluation are integral to a system of internal control 73

Benefits of Cobi. T w Supports IT governance objectives. w Helps ensure that IT processes are defined and assigned. w Helps to focus on control objectives. w Leads to more cost-effective IT services. w Helps management to better utilize internal and external auditors w Provides benchmarks for best practices for IT management and IT control 74
Benefits of Cobi. T w Helps ensure the organization complies with applicable rules, regulations and contractual obligations. w Opportunity for complementary adoption of COSO and Cobi. T (or other control models). w Authoritative nature of Cobit encompassing adoption of well-recognized and established standards for IT control. 75

Benefits of Cobi. T w Strengthens assessment, understanding and exercise of appropriate internal controls. w Provides a good framework for risk assessment and risk management. w Improves communication among management, business process owners, users and auditors regarding IT governance, and between internal and external audit. w Helps auditors and control professionals to be proactive business advisors. 76

Benefits of Cobi. T w Provides a framework for ensuring that outsourced IT functions are addressed in thirdparty contracts. w Helps to strengthen the relationship between IT Services and the user community through improved SLAs. w Supports management’s efforts to demonstrate due diligence with respect to IT-based operations. 77

Benefits of Cobi. T Helps to provide reasonable assurance that: – IT process objectives are understood – IT risks have been identified – Appropriate controls have been implemented – Appropriate monitoring and evaluation processes in effect – IT process objectives and can be achieved. 78
Cobi. T w Strengthens the understanding, design, implementation, exercise, and evaluation of internal control through improved focus on information criteria and IT-related control objectives w Strengthens management’s efforts to “ensure” and Audit’s efforts to provide “assurance” 79

A Tip regarding Cobi. T w Cobi. T is generic - adapt it to your organization in cooperation with the business-process owners! – – Determine focus (quality, security, fiduciary) Harmonize existing policies and procedures with Cobi. T Determine control responsibilities Identify key performance indicators and critical success factors 80

Another Tip or Two w Study it carefully -- it takes some time to understand - keep in mind that you are dealing with a control framework w Start with Cobi. T’s Control Objectives Framework and progress to the Management Guidelines. w Build the mechanisms to provide assurance that control objectives are being addressed and that controls are working as intended 81

Cobi. T For additional information: www. isaca. org www. ITgovernance. org or email or give me a call at (617) 727 -6200 ext 135 82

Go Forth and COBITize Thank You 83 83
096dbd46fddb936fbad78fb541266af8.ppt