ee85dd5c06e259302416256cb209cac0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Exclusion and the Golden Door: U. S. Immigration Policy Jonathan T. Lyons Political Science Capstone Fall 2007
Exclusion and the Golden Door: U. S. Immigration Policy Jonathan T. Lyons Political Science Capstone Fall 2007
 Overview • Policy History from 1790 -Present • How stereotypes and xenophobia influenced policy development • Current Status of Immigration
Overview • Policy History from 1790 -Present • How stereotypes and xenophobia influenced policy development • Current Status of Immigration
 First Immigration Legislation • Act of March 26 th, 1790 – Set residency requirement for citizenship at 2 years • Act of January 29 th, 1795 – Requirement amended to 5 years • Federalists vs. Jeffersonians
First Immigration Legislation • Act of March 26 th, 1790 – Set residency requirement for citizenship at 2 years • Act of January 29 th, 1795 – Requirement amended to 5 years • Federalists vs. Jeffersonians
 Alien and Sedition Acts (1798) • Naturalization Act • Alien and Alien Enemy Acts • Sedition Act. Infringement on Free Speech John Adams
Alien and Sedition Acts (1798) • Naturalization Act • Alien and Alien Enemy Acts • Sedition Act. Infringement on Free Speech John Adams
 Open-Door Era (1790 -1882) • Federalist acts expired with Thomas Jefferson Presidency • After the founding of the U. S. immigration is encouraged • 1819 - “An act regulating passenger ships and vessels” – Began recording the number of immigrants entering the United States Thomas Jefferson
Open-Door Era (1790 -1882) • Federalist acts expired with Thomas Jefferson Presidency • After the founding of the U. S. immigration is encouraged • 1819 - “An act regulating passenger ships and vessels” – Began recording the number of immigrants entering the United States Thomas Jefferson
 Open-Door Era • 1821 -1830: 143, 439 immigrants arrive • President John Tyler encourages immigration in his message to the 22 nd Congress in 1841 • “We hold out the to the people of other countries an invitation to come and settle among us”
Open-Door Era • 1821 -1830: 143, 439 immigrants arrive • President John Tyler encourages immigration in his message to the 22 nd Congress in 1841 • “We hold out the to the people of other countries an invitation to come and settle among us”
 Opposition to Early Immigration • The Irish Potato Famine (1845 -1851) and crop failures in Germany resulted in heavy Irish/German immigration • Irish immigrants are almost exclusively Catholic, German immigrants have large Catholic segment • Nativist sentiments emerged in northern cities such as Boston and New York
Opposition to Early Immigration • The Irish Potato Famine (1845 -1851) and crop failures in Germany resulted in heavy Irish/German immigration • Irish immigrants are almost exclusively Catholic, German immigrants have large Catholic segment • Nativist sentiments emerged in northern cities such as Boston and New York

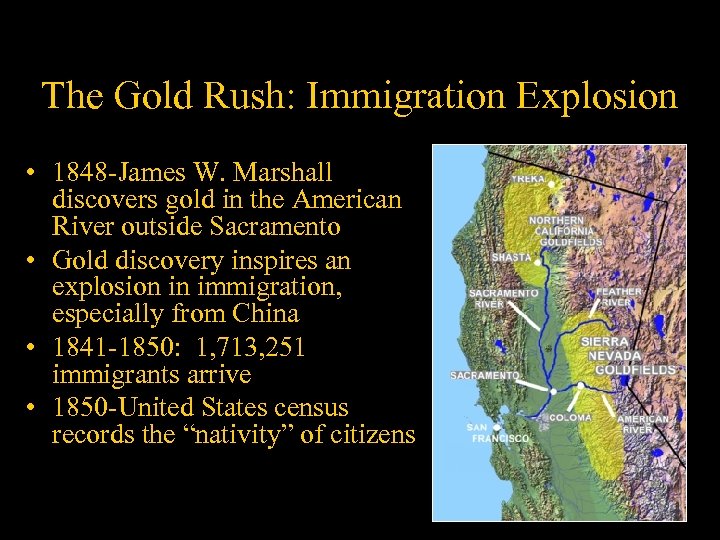 The Gold Rush: Immigration Explosion • 1848 -James W. Marshall discovers gold in the American River outside Sacramento • Gold discovery inspires an explosion in immigration, especially from China • 1841 -1850: 1, 713, 251 immigrants arrive • 1850 -United States census records the “nativity” of citizens
The Gold Rush: Immigration Explosion • 1848 -James W. Marshall discovers gold in the American River outside Sacramento • Gold discovery inspires an explosion in immigration, especially from China • 1841 -1850: 1, 713, 251 immigrants arrive • 1850 -United States census records the “nativity” of citizens
 Know-Nothing Movement (American Party) • Began as the Order of the Star Spangled Banner – Members had to be nativeborn white Protestants – Their oath: “to resist the insidious policy of the Church of Rome…by placing in all offices native -born Protestant citizens” Know-Nothing Party Flag
Know-Nothing Movement (American Party) • Began as the Order of the Star Spangled Banner – Members had to be nativeborn white Protestants – Their oath: “to resist the insidious policy of the Church of Rome…by placing in all offices native -born Protestant citizens” Know-Nothing Party Flag
 Open-Door Era • 1851 -1870: 4, 913, 039 immigrants arrive • 1862 -Homestead Act • 1863 -Central Pacific and Union Pacific hire Chinese and Irish laborers respectively to construct first transcontinental railroad – Completed at Promontory Summit, Utah on May 10 th, 1869
Open-Door Era • 1851 -1870: 4, 913, 039 immigrants arrive • 1862 -Homestead Act • 1863 -Central Pacific and Union Pacific hire Chinese and Irish laborers respectively to construct first transcontinental railroad – Completed at Promontory Summit, Utah on May 10 th, 1869
 Chinese Exclusion Act • Signed May 6 th, 1882 • Reaction to rapid expansion of Chinese immigration • First act directed at a nationality • Beginning of “Door-Ajar” Era
Chinese Exclusion Act • Signed May 6 th, 1882 • Reaction to rapid expansion of Chinese immigration • First act directed at a nationality • Beginning of “Door-Ajar” Era
 Door-Ajar Era • January 1 st, 1892 -Ellis Island opens • May 1892 -Geary Act – Extends exclusion of Chinese 10 additional years – Required all Chinese to obtain a certificate of residence within one year – Excluded Chinese from being witnesses
Door-Ajar Era • January 1 st, 1892 -Ellis Island opens • May 1892 -Geary Act – Extends exclusion of Chinese 10 additional years – Required all Chinese to obtain a certificate of residence within one year – Excluded Chinese from being witnesses
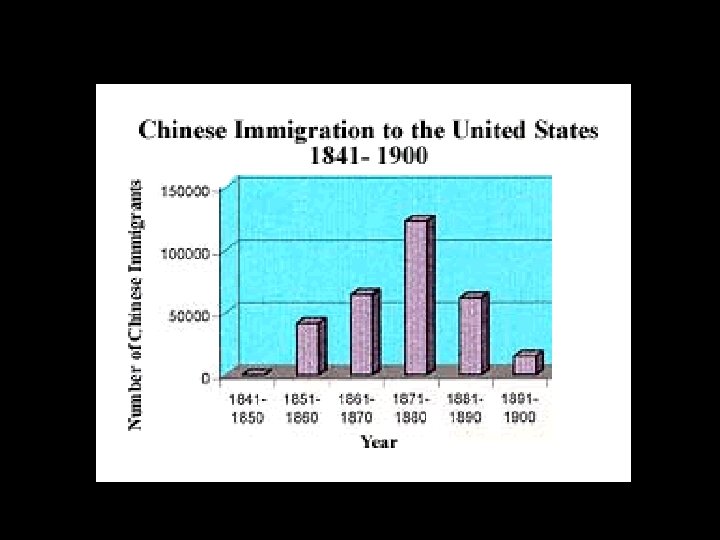
 Door-Ajar Era • 1904 -Chinese Exclusion Act extended indefinitely • Immigration Act of February 20 th, 1907 • Created the Dillingham Commission – Distinguished between “old” and “new” immigrants – Conclusions led to the establishment of Quota Acts • Immigration Act of 1917 -Asiatic Barred Zone
Door-Ajar Era • 1904 -Chinese Exclusion Act extended indefinitely • Immigration Act of February 20 th, 1907 • Created the Dillingham Commission – Distinguished between “old” and “new” immigrants – Conclusions led to the establishment of Quota Acts • Immigration Act of 1917 -Asiatic Barred Zone
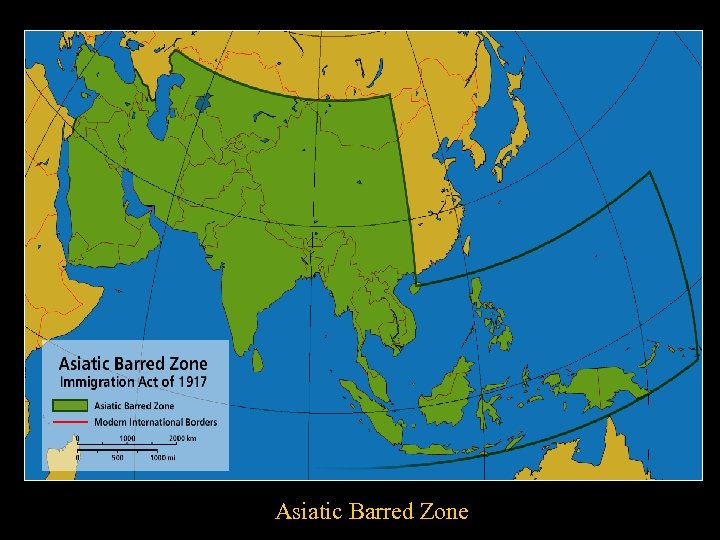 Asiatic Barred Zone
Asiatic Barred Zone
 Quota System • Began with Emergency Quota Act of 1921 • Immigrants could only constitute 3% of their country’s existing population in the U. S. according to 1910 census data • 357, 000 per year • President Calvin Coolidge: “America is for Americans” Calvin Coolidge
Quota System • Began with Emergency Quota Act of 1921 • Immigrants could only constitute 3% of their country’s existing population in the U. S. according to 1910 census data • 357, 000 per year • President Calvin Coolidge: “America is for Americans” Calvin Coolidge
 Quota System • Albert Johnson-chairman of House of Representatives C. I. N. • Johnson-Reed Immigration Act of 1924 – Changed quota to 2% of resident nationalities – Reduced annual total immigration to 150, 000 – Shifted back to 1890 census as benchmark
Quota System • Albert Johnson-chairman of House of Representatives C. I. N. • Johnson-Reed Immigration Act of 1924 – Changed quota to 2% of resident nationalities – Reduced annual total immigration to 150, 000 – Shifted back to 1890 census as benchmark
 National Origins System • Created in the Johnson-Reed Act but delayed until 1929 • Eugenics-driven policy • “Encouraged” immigration of “old” Northwestern Europeans and discouraged “new” immigration from Southeastern Europe
National Origins System • Created in the Johnson-Reed Act but delayed until 1929 • Eugenics-driven policy • “Encouraged” immigration of “old” Northwestern Europeans and discouraged “new” immigration from Southeastern Europe
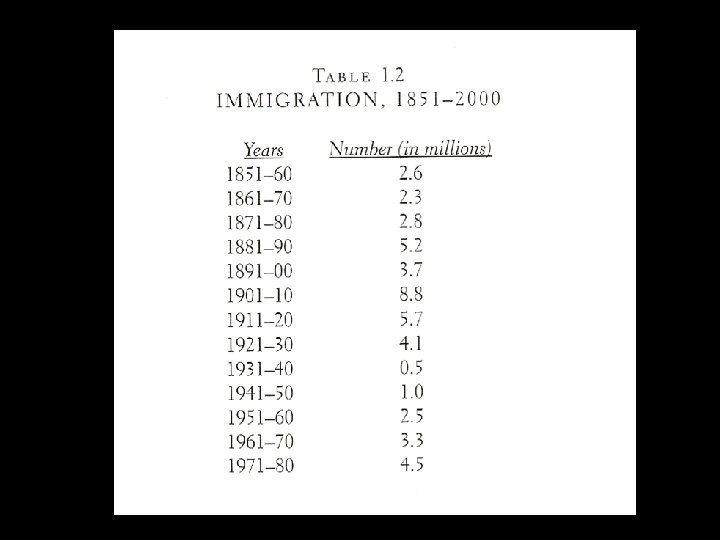
 Immigration During Quota System • National Origins made no specifications against immigrants from Western Hemisphere • Coolidge saw limits on this type of immigration as counterproductive • Mexicans welcomed during labor shortage of World War I, then deported during Great Depression
Immigration During Quota System • National Origins made no specifications against immigrants from Western Hemisphere • Coolidge saw limits on this type of immigration as counterproductive • Mexicans welcomed during labor shortage of World War I, then deported during Great Depression
 Bracero Program • 1942 -Agreement between Mexico and U. S. – Contracted over 4. 5 million Mexican nationals for work on U. S. farms – “Mojados” undocumented Mexican laborers
Bracero Program • 1942 -Agreement between Mexico and U. S. – Contracted over 4. 5 million Mexican nationals for work on U. S. farms – “Mojados” undocumented Mexican laborers
 Bracero Program • Postwar economy was strong, due in part to Bracero labor • Mexican laborers filled void left by exclusion of Asian immigrants and National Origin Systems • 1954 - “Operation Wetback” enacted to stem the tide of undocumented laborers
Bracero Program • Postwar economy was strong, due in part to Bracero labor • Mexican laborers filled void left by exclusion of Asian immigrants and National Origin Systems • 1954 - “Operation Wetback” enacted to stem the tide of undocumented laborers
 Civil Rights Legislation • December 31, 1964 Bracero Program ends • Immigration Act of 1965 – Ended the quota system – First regulation of Western Hemisphere immigration – Set limit of 20, 000 visas per year on nations of Eastern Hemisphere Lyndon B. Johnson
Civil Rights Legislation • December 31, 1964 Bracero Program ends • Immigration Act of 1965 – Ended the quota system – First regulation of Western Hemisphere immigration – Set limit of 20, 000 visas per year on nations of Eastern Hemisphere Lyndon B. Johnson
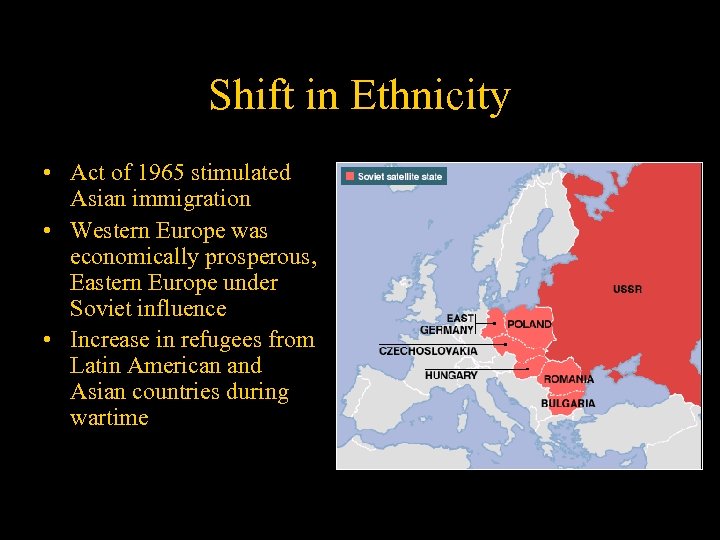 Shift in Ethnicity • Act of 1965 stimulated Asian immigration • Western Europe was economically prosperous, Eastern Europe under Soviet influence • Increase in refugees from Latin American and Asian countries during wartime
Shift in Ethnicity • Act of 1965 stimulated Asian immigration • Western Europe was economically prosperous, Eastern Europe under Soviet influence • Increase in refugees from Latin American and Asian countries during wartime
 Illegal Immigration • 1980 -number of legal immigrants entering annually reaches 500, 000 • 1986 -Immigration Reform and Control Act – Placed sanctions on employers who hired illegal immigrants – Offered amnesty, 2 million undocumented immigrants gained eventual citizenship
Illegal Immigration • 1980 -number of legal immigrants entering annually reaches 500, 000 • 1986 -Immigration Reform and Control Act – Placed sanctions on employers who hired illegal immigrants – Offered amnesty, 2 million undocumented immigrants gained eventual citizenship
 Proposition 187 • Passed by California in 1994 • Denied public benefits to illegal aliens • Immediately blocked and then overturned by Supreme Court in 1998 Gray Davis
Proposition 187 • Passed by California in 1994 • Denied public benefits to illegal aliens • Immediately blocked and then overturned by Supreme Court in 1998 Gray Davis
 Post 9/11 Immigration Policy • March 1, 2003 -INS transitions into U. S. C. I. S. • Department of Homeland Security • Creation of Immigration Customs and Enforcement
Post 9/11 Immigration Policy • March 1, 2003 -INS transitions into U. S. C. I. S. • Department of Homeland Security • Creation of Immigration Customs and Enforcement
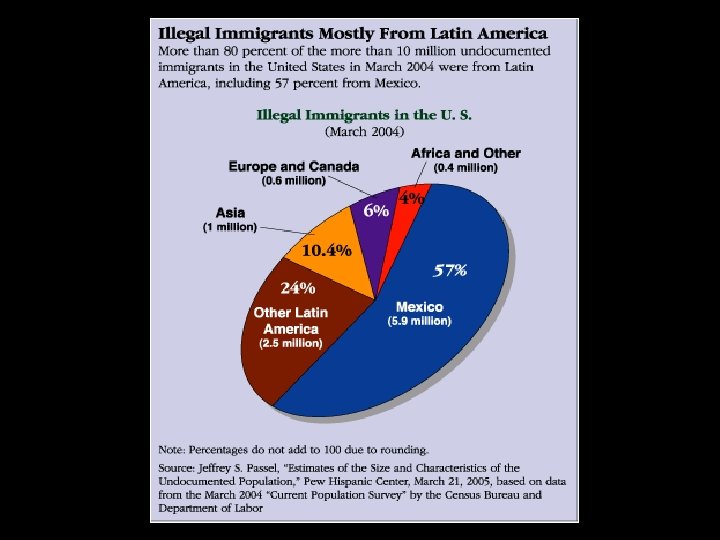
 Immigration and Customs Enforcement • J. W. Barnes, Senior Special Agent • Current illegal population grossly underestimated • Border towns controlled, deserts are a revolving door • Only illegal immigrants deported easily are those with a criminal record
Immigration and Customs Enforcement • J. W. Barnes, Senior Special Agent • Current illegal population grossly underestimated • Border towns controlled, deserts are a revolving door • Only illegal immigrants deported easily are those with a criminal record
 Proposed Legislation • • • Amnesty Real ID Guest-Worker Program Project 28 June 28 th, 2007 -Senate votes to block massive reform of U. S. immigration policy
Proposed Legislation • • • Amnesty Real ID Guest-Worker Program Project 28 June 28 th, 2007 -Senate votes to block massive reform of U. S. immigration policy
 2008 Presidential Candidates
2008 Presidential Candidates
 Candidates Statements and Recent Voting • Clinton and Obama-both gave speeches using the phrase “out of the shadows” • In favor of C. I. R. A. of 2006 • Huckabee-voting record favors helping illegal aliens within U. S. • Romney-empowered MA police to arrest and deport illegal aliens
Candidates Statements and Recent Voting • Clinton and Obama-both gave speeches using the phrase “out of the shadows” • In favor of C. I. R. A. of 2006 • Huckabee-voting record favors helping illegal aliens within U. S. • Romney-empowered MA police to arrest and deport illegal aliens
 Conclusions • Stereotypes and anti-foreign sentiments influenced policy development • Current policy in need of overhaul • How will U. S. immigration policy further develop?
Conclusions • Stereotypes and anti-foreign sentiments influenced policy development • Current policy in need of overhaul • How will U. S. immigration policy further develop?
 Further Reading • Beasley, Vanessa B. , ed. 2006. Who Belongs in America? Presidents, Rhetoric, and Immigration. College Station, TX: Texas A&M University Press • Daniels, Roger. 2004. Guarding the Golden Door: American Immigration Policy and Immigrants Since 1882. New York, NY: Hill and Wang Publishing • Hutchinson, E. P. 1981. Legislative History of American Immigration Policy 1798 -1965. Philadelphia, PA: University of Pennsylvania Press • King, Desmond. 2000. Making Americans: Immigration, Race, and the Origins of the Diverse Democracy. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press
Further Reading • Beasley, Vanessa B. , ed. 2006. Who Belongs in America? Presidents, Rhetoric, and Immigration. College Station, TX: Texas A&M University Press • Daniels, Roger. 2004. Guarding the Golden Door: American Immigration Policy and Immigrants Since 1882. New York, NY: Hill and Wang Publishing • Hutchinson, E. P. 1981. Legislative History of American Immigration Policy 1798 -1965. Philadelphia, PA: University of Pennsylvania Press • King, Desmond. 2000. Making Americans: Immigration, Race, and the Origins of the Diverse Democracy. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press


