7e66951185fbd39a83c359a4863d7998.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Example Applications of Rough Sets Theory – A Survey Christopher Chretien Laurentian University Sudbury, Ontario Canada October 2002
Example Applications of Rough Sets Theory – A Survey Christopher Chretien Laurentian University Sudbury, Ontario Canada October 2002
 Introduction l Research on the application of Rough Sets Theory l Discovering possible areas of application l Further understanding of Rough Sets Theory usage
Introduction l Research on the application of Rough Sets Theory l Discovering possible areas of application l Further understanding of Rough Sets Theory usage
 References l Lixiang Shen, Francis E. H. Tay, Liangsheng Qu and Yudi Shen (2000), Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory , Computers in Industry, vol. 43, Issue 1, 1 August 2000, pp. 61 -72. , URL: www. geocities. com/roughset/Fault_diagnosis_using_rough_sets_theory. pdf l Israel E. Chen-Jimenez, Andrew Kornecki, Janusz Zalewski, Software Safety Analysis Using Rough Sets, URL: http: //www-ece. engr. ucf. edu/~jza/classes/6885/rough. ps l Francis E. H. Tay and Lixiang Shen (2002), Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model , European Journal of Operational Research 141, pp. 643 -661, URL: http: //www. geocities. com/roughset/EJOR. pdf l Pawan Lingras (2001), Unsupervised Rough Set Classification Using GAs Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 16, 215– 228, found on: Cite. Seer, URL: http: //citeseer. nj. nec. com/cs l Rapp, S. , Jessen, M. and Dogil, G. (1994). Using Rough Sets Theory to Predict German Word Stress. in: Nebel, B. and Dreschler-Fischer, L. (Eds. ) KI-94: Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence 861, Springer-Verlag, URL: www. ims. uni-stuttgart. de/~rapp/ki 94 full. ps
References l Lixiang Shen, Francis E. H. Tay, Liangsheng Qu and Yudi Shen (2000), Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory , Computers in Industry, vol. 43, Issue 1, 1 August 2000, pp. 61 -72. , URL: www. geocities. com/roughset/Fault_diagnosis_using_rough_sets_theory. pdf l Israel E. Chen-Jimenez, Andrew Kornecki, Janusz Zalewski, Software Safety Analysis Using Rough Sets, URL: http: //www-ece. engr. ucf. edu/~jza/classes/6885/rough. ps l Francis E. H. Tay and Lixiang Shen (2002), Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model , European Journal of Operational Research 141, pp. 643 -661, URL: http: //www. geocities. com/roughset/EJOR. pdf l Pawan Lingras (2001), Unsupervised Rough Set Classification Using GAs Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 16, 215– 228, found on: Cite. Seer, URL: http: //citeseer. nj. nec. com/cs l Rapp, S. , Jessen, M. and Dogil, G. (1994). Using Rough Sets Theory to Predict German Word Stress. in: Nebel, B. and Dreschler-Fischer, L. (Eds. ) KI-94: Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence 861, Springer-Verlag, URL: www. ims. uni-stuttgart. de/~rapp/ki 94 full. ps
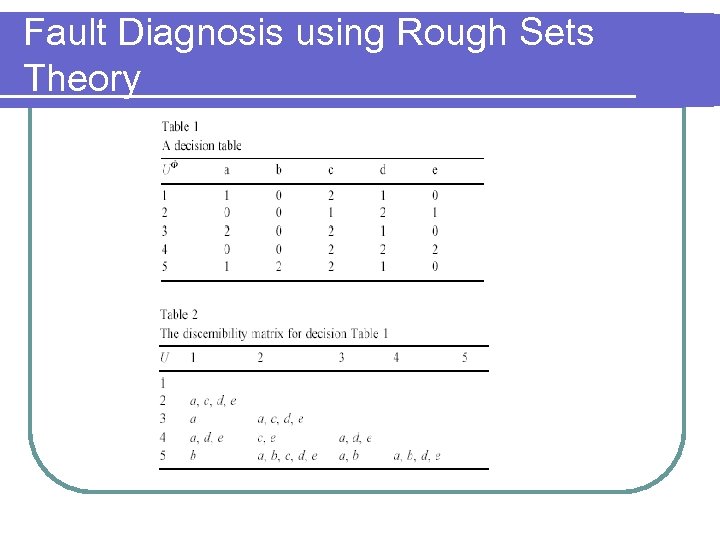
 Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory l Diagnosis of a valve fault for a multicylinder diesel engine l Rough Sets Theory is used to analyze the decision table composed of attributes extracted from the vibration signals
Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory l Diagnosis of a valve fault for a multicylinder diesel engine l Rough Sets Theory is used to analyze the decision table composed of attributes extracted from the vibration signals
 Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory l 4 states are studied among the signal characteristics Normal state l Intake valve clearance is too small l Intake valve clearance is too large l Exhaust valve clearance is too large l
Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory l 4 states are studied among the signal characteristics Normal state l Intake valve clearance is too small l Intake valve clearance is too large l Exhaust valve clearance is too large l
 Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory l 3 sampling points selected to collect vibration signals 1 st cylinder head l 2 nd cylinder head l centre of the piston stroke on the surface of the cylinder block l
Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory l 3 sampling points selected to collect vibration signals 1 st cylinder head l 2 nd cylinder head l centre of the piston stroke on the surface of the cylinder block l
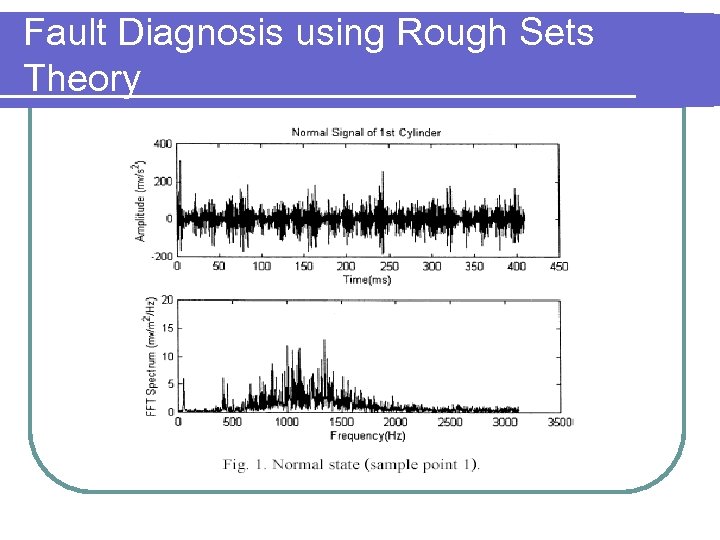 Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory
Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory
 Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory
Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory
 Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory
Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory
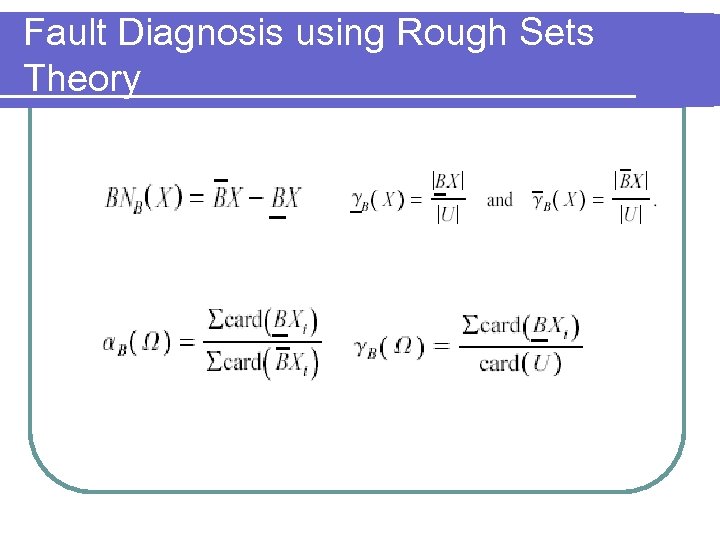
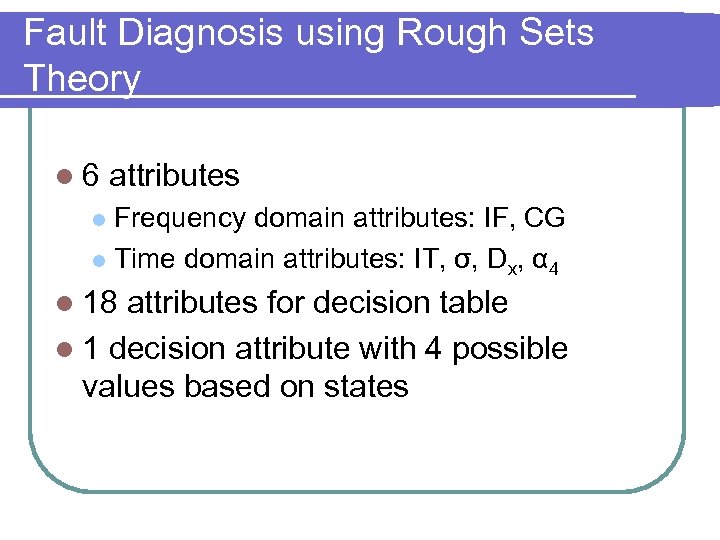 Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory l 6 attributes Frequency domain attributes: IF, CG l Time domain attributes: IT, σ, Dx, α 4 l l 18 attributes for decision table l 1 decision attribute with 4 possible values based on states
Fault Diagnosis using Rough Sets Theory l 6 attributes Frequency domain attributes: IF, CG l Time domain attributes: IT, σ, Dx, α 4 l l 18 attributes for decision table l 1 decision attribute with 4 possible values based on states
 Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets l Investigates the safety aspects of computer software in safety-critical applications l Assessment of software safety using qualitative evaluations
Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets l Investigates the safety aspects of computer software in safety-critical applications l Assessment of software safety using qualitative evaluations
 Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets l Use of checklists to collect data on software quality l Waterfall model Project Planning l Specification of requirements l Design l Implementation and integration l Verification and validation l Operation and maintenance l
Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets l Use of checklists to collect data on software quality l Waterfall model Project Planning l Specification of requirements l Design l Implementation and integration l Verification and validation l Operation and maintenance l
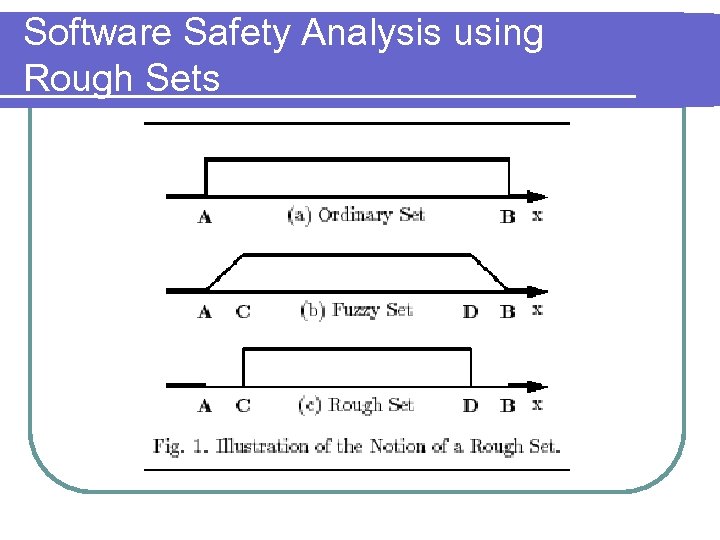 Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets
Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets
 Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets
Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets
 Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets l 8 student teams developing safetyrelated software Device control over the internet l Elevator controller l Air traffic control system l System satellite control system l
Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets l 8 student teams developing safetyrelated software Device control over the internet l Elevator controller l Air traffic control system l System satellite control system l
 Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets l 150 questions about the first 5 phases of the waterfall model l Overall safety level for 6 of the 8 projects was around 60%
Software Safety Analysis using Rough Sets l 150 questions about the first 5 phases of the waterfall model l Overall safety level for 6 of the 8 projects was around 60%
 Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model l Applications of Rough Sets model in economic and financial prediction l Emphasis on main areas of business failure prediction, database marketing and financial investment
Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model l Applications of Rough Sets model in economic and financial prediction l Emphasis on main areas of business failure prediction, database marketing and financial investment
 Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model l Business l failure prediction ETEVA l Database Marketing l Financial Investment l TSE
Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model l Business l failure prediction ETEVA l Database Marketing l Financial Investment l TSE
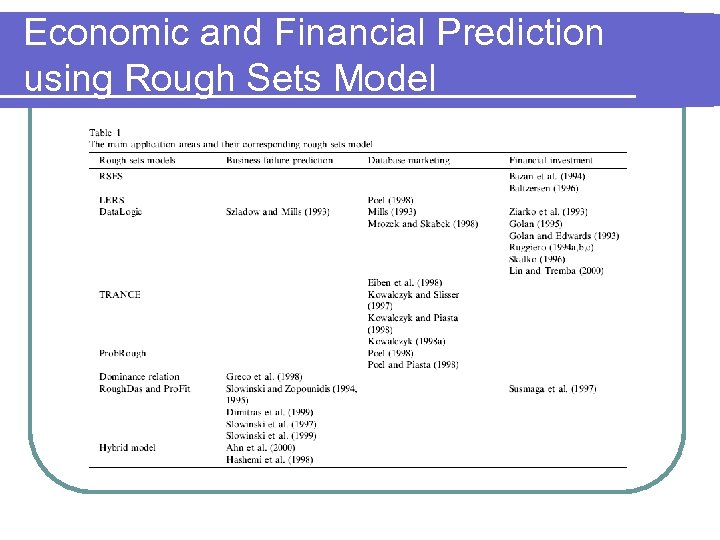 Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model
Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model
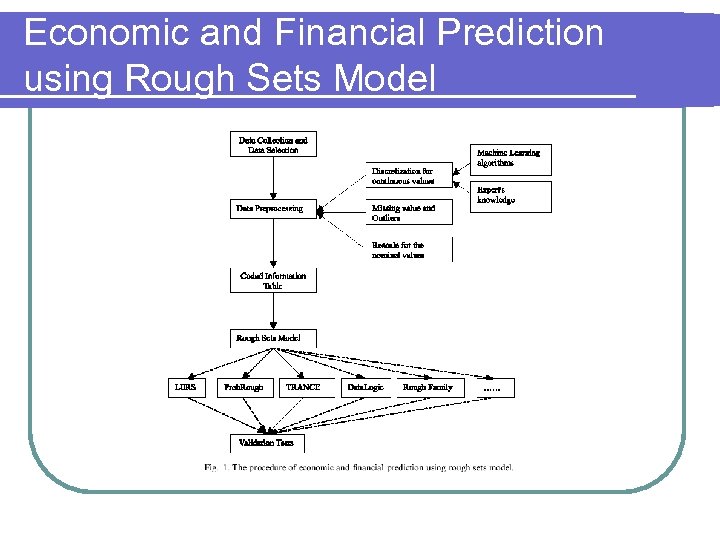 Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model
Economic and Financial Prediction using Rough Sets Model
 Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l Prediction of German word stress by extracting symbolic rules from sample data l Symbolic rules are induced with a machine learning approach based on Rough Sets Theory
Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l Prediction of German word stress by extracting symbolic rules from sample data l Symbolic rules are induced with a machine learning approach based on Rough Sets Theory
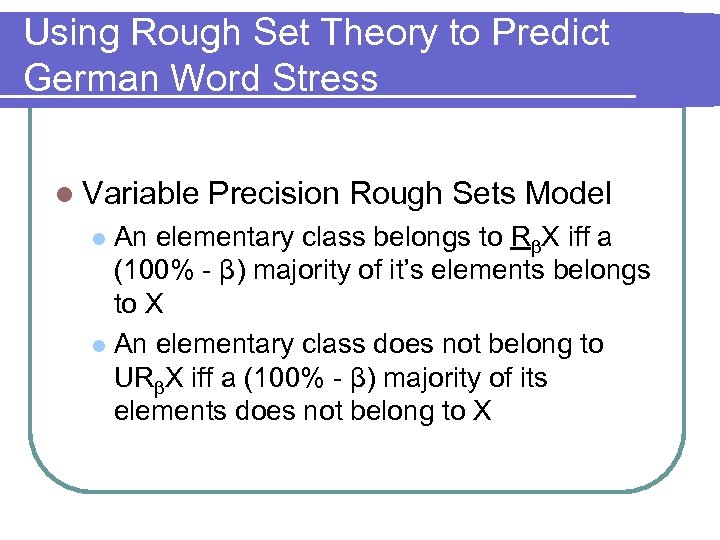 Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l Variable Precision Rough Sets Model An elementary class belongs to RβX iff a (100% - β) majority of it’s elements belongs to X l An elementary class does not belong to URβX iff a (100% - β) majority of its elements does not belong to X l
Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l Variable Precision Rough Sets Model An elementary class belongs to RβX iff a (100% - β) majority of it’s elements belongs to X l An elementary class does not belong to URβX iff a (100% - β) majority of its elements does not belong to X l
 Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l Corpus Monomorphemic words l At least 2 non-schwa syllables l Nouns l 242 words l
Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l Corpus Monomorphemic words l At least 2 non-schwa syllables l Nouns l 242 words l
 Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l Attributes: Typ, Onset, Hoeche, Laenge, Spannung, Coda l 36 attributes in total l Attributes aligned ‘from right to left’ l Decision attribute with possible values of final, penult and antepenult
Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l Attributes: Typ, Onset, Hoeche, Laenge, Spannung, Coda l 36 attributes in total l Attributes aligned ‘from right to left’ l Decision attribute with possible values of final, penult and antepenult
 Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l 1 st l Stress assignment operates from right to left l 2 nd l experiment Estimate predictive accuracy l 3 rd l experiment Remove length information
Using Rough Set Theory to Predict German Word Stress l 1 st l Stress assignment operates from right to left l 2 nd l experiment Estimate predictive accuracy l 3 rd l experiment Remove length information
 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Rough Set classification using Genetic Algorithms l Highway classification based on predominant usage
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Rough Set classification using Genetic Algorithms l Highway classification based on predominant usage
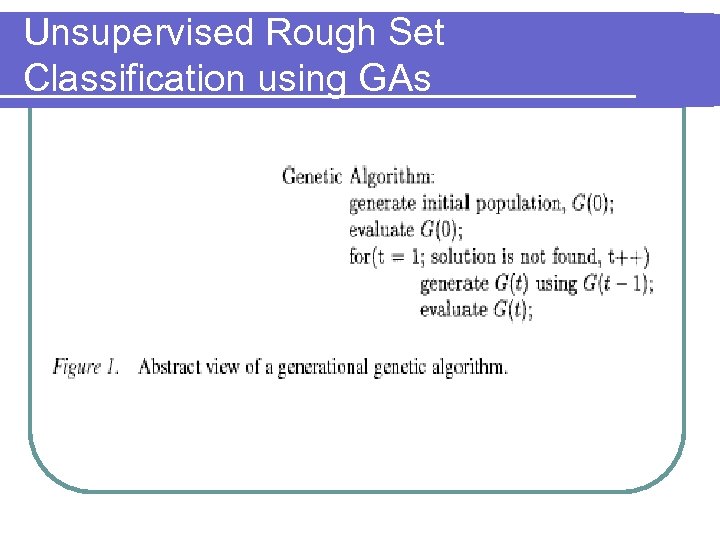
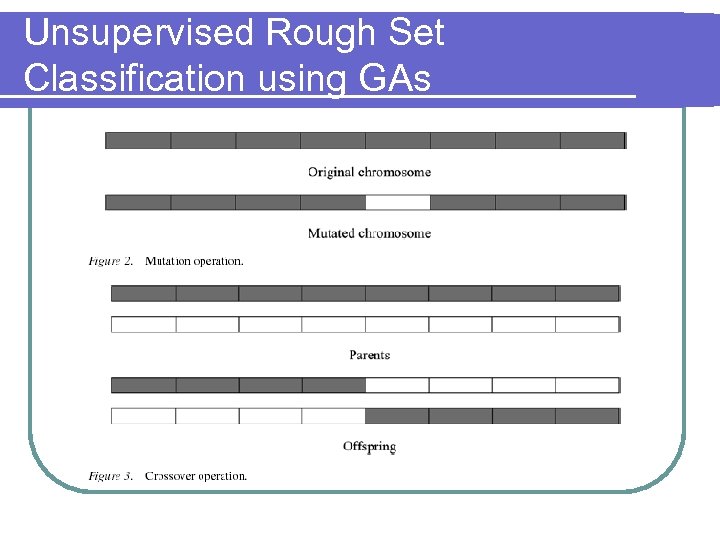
 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Applications of GAs Job shop scheduling l Training neural nets l Image feature extraction l Image feature identification l
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Applications of GAs Job shop scheduling l Training neural nets l Image feature extraction l Image feature identification l
 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs
 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs
 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs
 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs
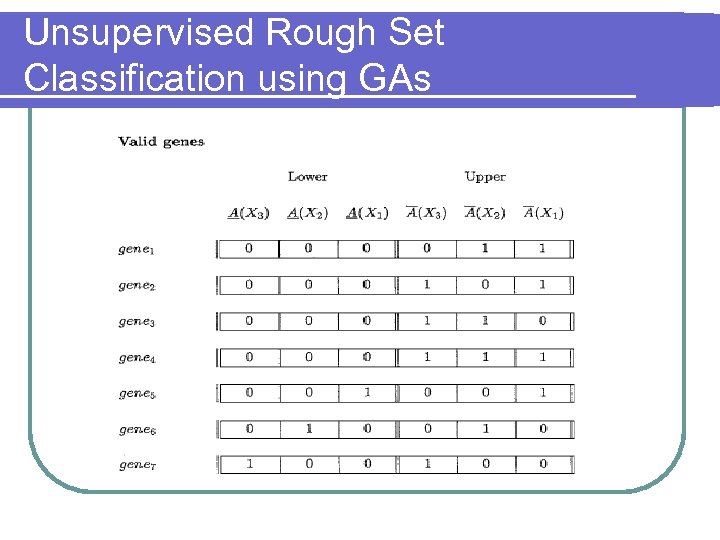
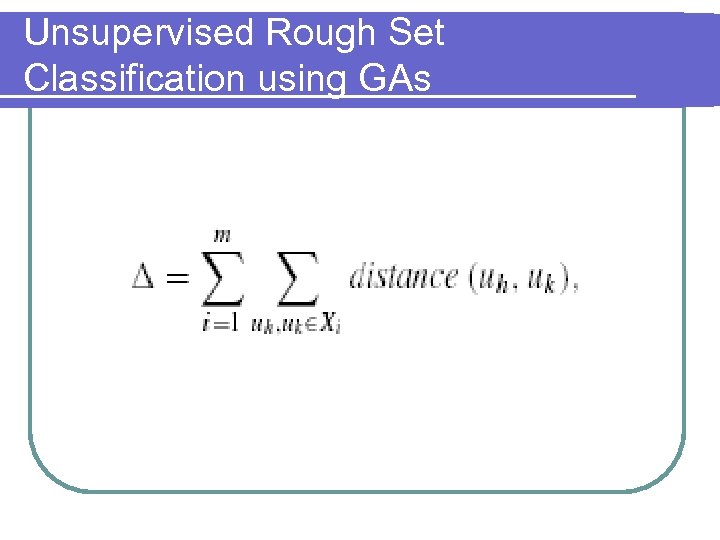
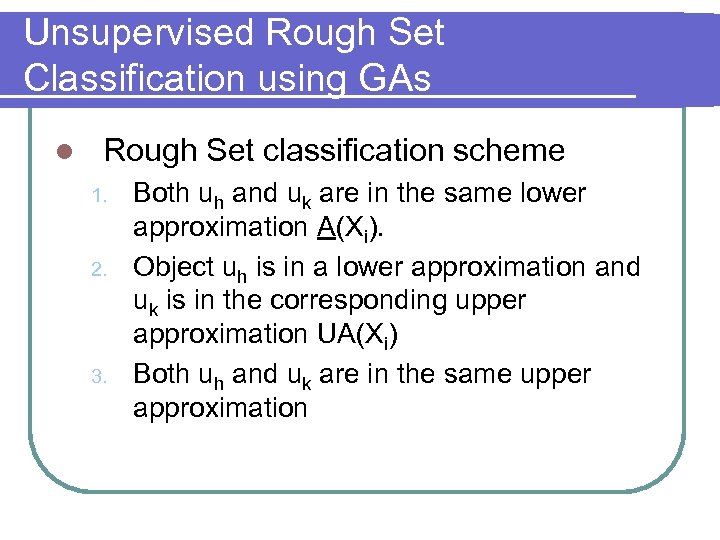 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Rough Set classification scheme 1. 2. 3. Both uh and uk are in the same lower approximation A(Xi). Object uh is in a lower approximation and uk is in the corresponding upper approximation UA(Xi) Both uh and uk are in the same upper approximation
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Rough Set classification scheme 1. 2. 3. Both uh and uk are in the same lower approximation A(Xi). Object uh is in a lower approximation and uk is in the corresponding upper approximation UA(Xi) Both uh and uk are in the same upper approximation
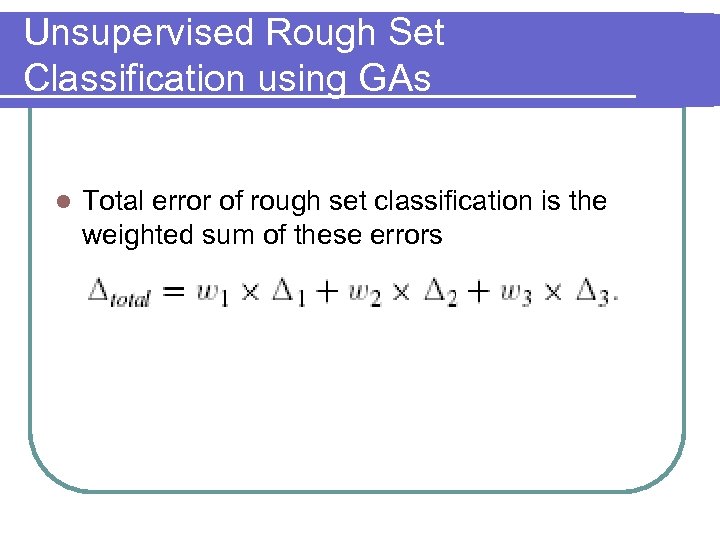 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Total error of rough set classification is the weighted sum of these errors
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Total error of rough set classification is the weighted sum of these errors
 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Rough classification of highways PTC sites l Roads classified on the basis of trip purposes and trip length characteristics l Classes: commuter, business, long distance and recreational highways l Traffic patterns: hourly, daily, monthly l
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Rough classification of highways PTC sites l Roads classified on the basis of trip purposes and trip length characteristics l Classes: commuter, business, long distance and recreational highways l Traffic patterns: hourly, daily, monthly l
 Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Experiment 264 monthly traffic patterns on Alberta highways (1987 -1991) l Rough genome consisted of 264 genes l Classes: commuter/business, long distance, recreational l
Unsupervised Rough Set Classification using GAs l Experiment 264 monthly traffic patterns on Alberta highways (1987 -1991) l Rough genome consisted of 264 genes l Classes: commuter/business, long distance, recreational l
 Conclusion l Triggering a better understanding of Rough Sets Theory l Opening eyes to different fields of application
Conclusion l Triggering a better understanding of Rough Sets Theory l Opening eyes to different fields of application


