 Exam n n n Short answer questions Diagram interpretation Some multiple choice Material from discussion sections will be included Lab material will not be covered (although diagrams may be used) Powerpoint presentations at http: //www. geology. wisc. edu/~laurel/204/
Exam n n n Short answer questions Diagram interpretation Some multiple choice Material from discussion sections will be included Lab material will not be covered (although diagrams may be used) Powerpoint presentations at http: //www. geology. wisc. edu/~laurel/204/
 TECTONIC BASINS The sedimentary record of tectonic processes
TECTONIC BASINS The sedimentary record of tectonic processes
 CONVERGENT SETTINGS n n n Thrust belt typically propagates into foreland basin, moving depocenter in the direction of thrust motion Piggyback Basin: basins that are on the hanging wall of a thrust fault and move with the hanging wall. Sediments evolve from fine-grained turbidites to shallow water continental seds over time
CONVERGENT SETTINGS n n n Thrust belt typically propagates into foreland basin, moving depocenter in the direction of thrust motion Piggyback Basin: basins that are on the hanging wall of a thrust fault and move with the hanging wall. Sediments evolve from fine-grained turbidites to shallow water continental seds over time
 Foreland basins can accumulate exceptionally thick (~10 km) stratigraphic successions
Foreland basins can accumulate exceptionally thick (~10 km) stratigraphic successions
 Homewood et al. (1986)
Homewood et al. (1986)
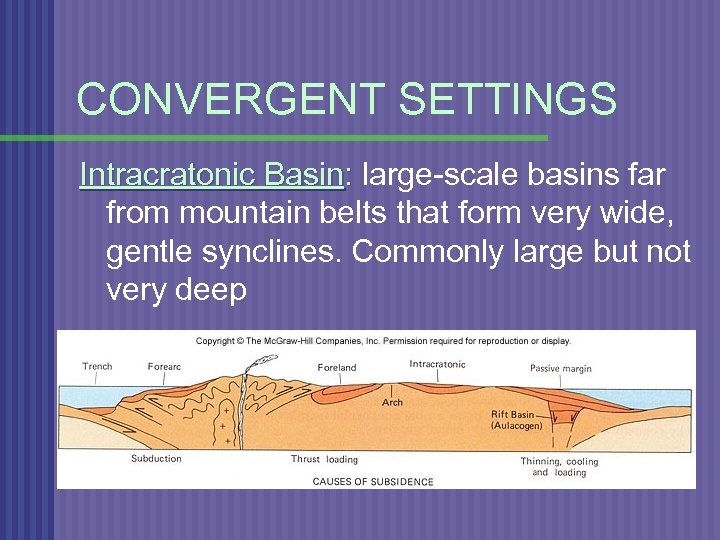 CONVERGENT SETTINGS Intracratonic Basin: large-scale basins far from mountain belts that form very wide, gentle synclines. Commonly large but not very deep
CONVERGENT SETTINGS Intracratonic Basin: large-scale basins far from mountain belts that form very wide, gentle synclines. Commonly large but not very deep
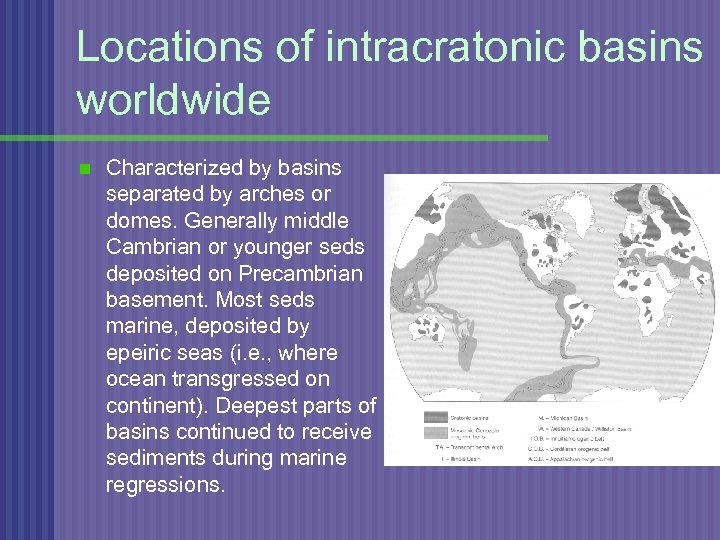 Locations of intracratonic basins worldwide n Characterized by basins separated by arches or domes. Generally middle Cambrian or younger seds deposited on Precambrian basement. Most seds marine, deposited by epeiric seas (i. e. , where ocean transgressed on continent). Deepest parts of basins continued to receive sediments during marine regressions.
Locations of intracratonic basins worldwide n Characterized by basins separated by arches or domes. Generally middle Cambrian or younger seds deposited on Precambrian basement. Most seds marine, deposited by epeiric seas (i. e. , where ocean transgressed on continent). Deepest parts of basins continued to receive sediments during marine regressions.
 TRANSFORM SETTINGS Strike-slip fault = a fault on which the movement is parallel to fault’s strike n Basins form where irregularities in fault system cause depocenters to form locally n Distinctive in that they are not regional in extent n Fill with material sourced locally and from plate that is ‘passing by’ n
TRANSFORM SETTINGS Strike-slip fault = a fault on which the movement is parallel to fault’s strike n Basins form where irregularities in fault system cause depocenters to form locally n Distinctive in that they are not regional in extent n Fill with material sourced locally and from plate that is ‘passing by’ n
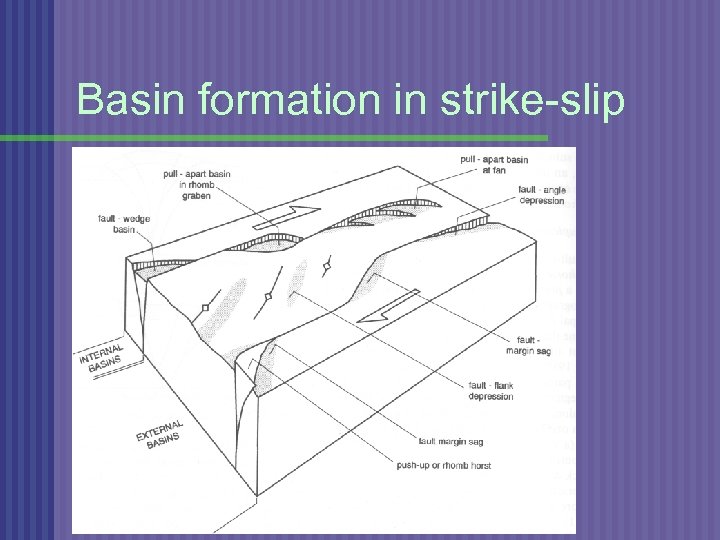 Basin formation in strike-slip
Basin formation in strike-slip
 TRANSFORM SETTINGS n n Pull-apart basins - caused by releasing step or dilational jog in fault system Strike-slip basins form in transtensional regimes and are usually relatively small but also deep; they are commonly filled with coarse facies (e. g. , alluvial fans) adjacent to lacustrine or marine deposits n Examples: Salton Sea, California; Ridge basin, California; Dead Sea, Israel
TRANSFORM SETTINGS n n Pull-apart basins - caused by releasing step or dilational jog in fault system Strike-slip basins form in transtensional regimes and are usually relatively small but also deep; they are commonly filled with coarse facies (e. g. , alluvial fans) adjacent to lacustrine or marine deposits n Examples: Salton Sea, California; Ridge basin, California; Dead Sea, Israel
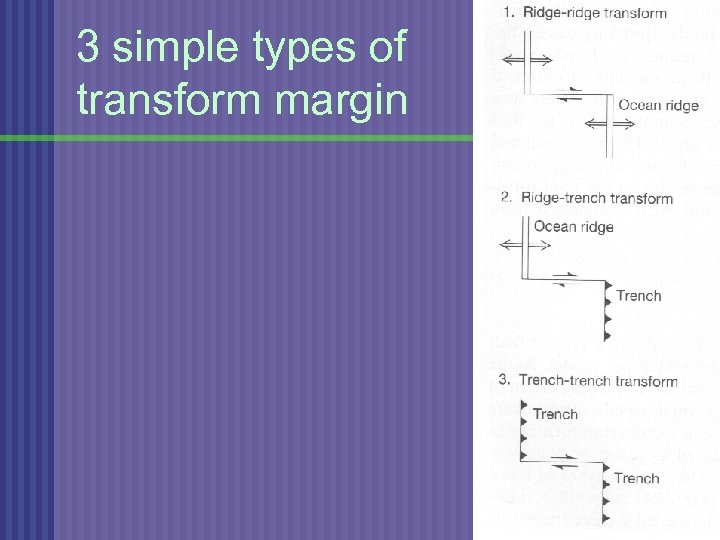 3 simple types of transform margin
3 simple types of transform margin
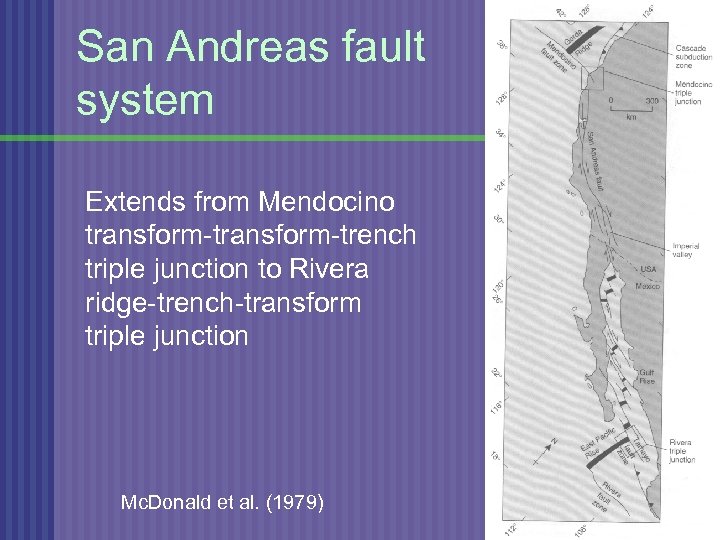 San Andreas fault system Extends from Mendocino transform-trench triple junction to Rivera ridge-trench-transform triple junction Mc. Donald et al. (1979)
San Andreas fault system Extends from Mendocino transform-trench triple junction to Rivera ridge-trench-transform triple junction Mc. Donald et al. (1979)
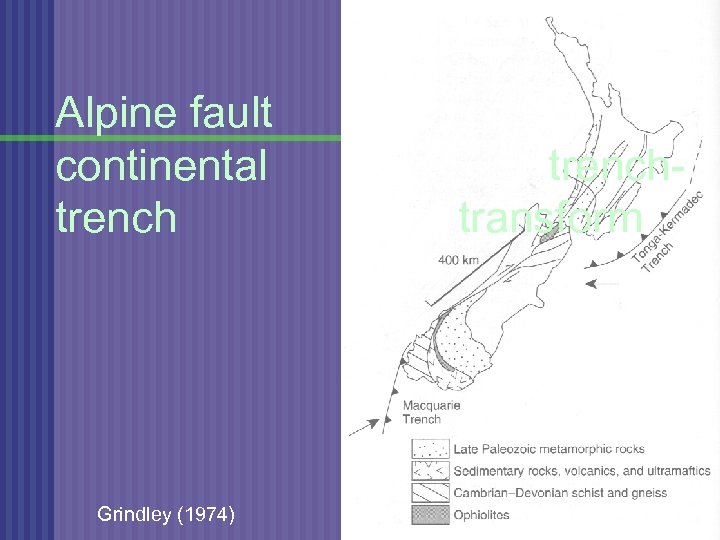 Alpine fault continental trench Grindley (1974) trenchtransform
Alpine fault continental trench Grindley (1974) trenchtransform
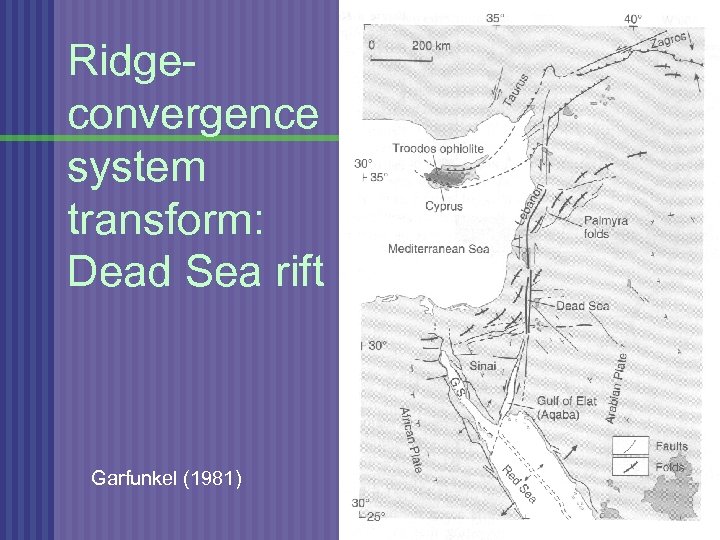 Ridgeconvergence system transform: Dead Sea rift Garfunkel (1981)
Ridgeconvergence system transform: Dead Sea rift Garfunkel (1981)
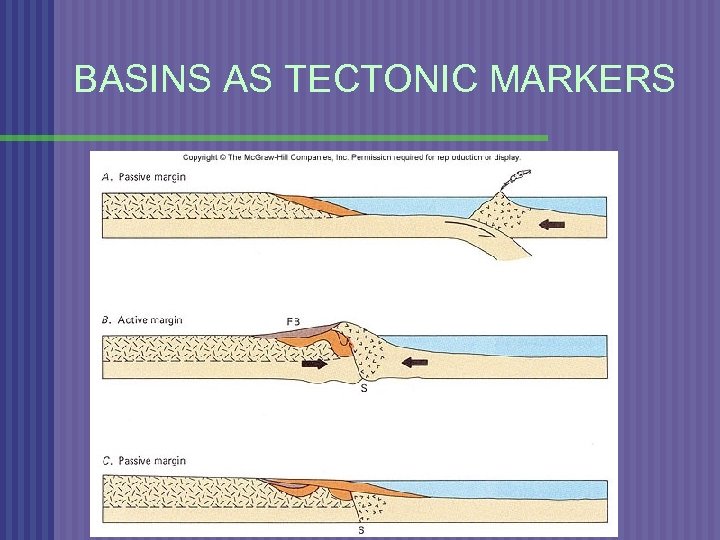 BASINS AS TECTONIC MARKERS
BASINS AS TECTONIC MARKERS
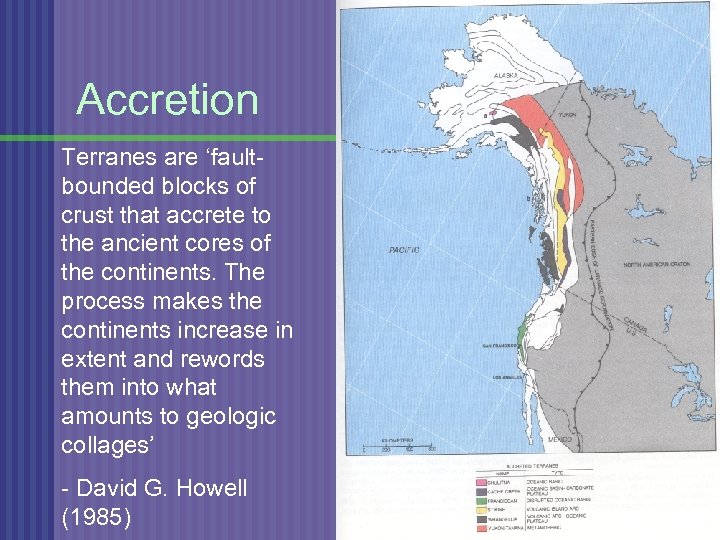 Accretion Terranes are ‘faultbounded blocks of crust that accrete to the ancient cores of the continents. The process makes the continents increase in extent and rewords them into what amounts to geologic collages’ - David G. Howell (1985)
Accretion Terranes are ‘faultbounded blocks of crust that accrete to the ancient cores of the continents. The process makes the continents increase in extent and rewords them into what amounts to geologic collages’ - David G. Howell (1985)
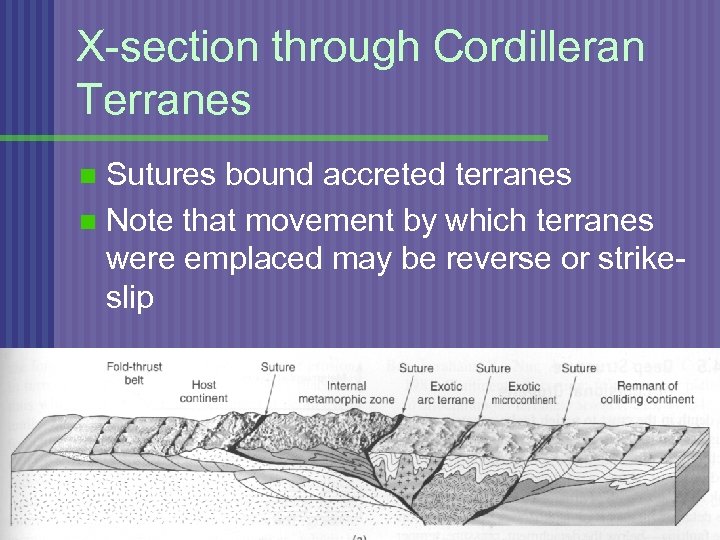 X-section through Cordilleran Terranes Sutures bound accreted terranes n Note that movement by which terranes were emplaced may be reverse or strikeslip n
X-section through Cordilleran Terranes Sutures bound accreted terranes n Note that movement by which terranes were emplaced may be reverse or strikeslip n
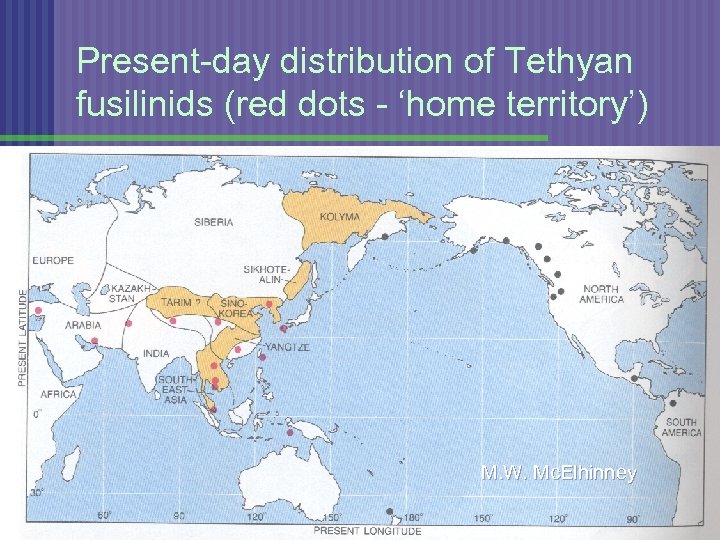 Present-day distribution of Tethyan fusilinids (red dots - ‘home territory’) M. W. Mc. Elhinney
Present-day distribution of Tethyan fusilinids (red dots - ‘home territory’) M. W. Mc. Elhinney