5b75ad713f1657c9d8b26c2ee2c00a49.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Exam III Physics 101: Lecture 18 Elasticity and Oscillations Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 1
Exam III Physics 101: Lecture 18 Elasticity and Oscillations Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 1
 Example: hose A garden hose w/ inner diameter 2 cm, carries water at 2. 0 m/s. To spray your friend, you place your thumb over the nozzle giving an effective opening diameter of 0. 5 cm. What is the speed of the water exiting the hose? What is the pressure difference between inside the hose and outside? Continuity Equation Bernoulli Equation Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 2
Example: hose A garden hose w/ inner diameter 2 cm, carries water at 2. 0 m/s. To spray your friend, you place your thumb over the nozzle giving an effective opening diameter of 0. 5 cm. What is the speed of the water exiting the hose? What is the pressure difference between inside the hose and outside? Continuity Equation Bernoulli Equation Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 2
 Example: Lift a House Calculate the net lift on a 15 m x 15 m house when a 30 m/s wind (1. 29 kg/m 3) blows over the top. Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 3 48
Example: Lift a House Calculate the net lift on a 15 m x 15 m house when a 30 m/s wind (1. 29 kg/m 3) blows over the top. Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 3 48
 Overview l Springs (review) è Restoring force proportional to displacement è = -k x F è = ½ k x 2 U l Today è Young’s Modulus è Simple Harmonic Motion è Springs Revisited Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 4 05
Overview l Springs (review) è Restoring force proportional to displacement è = -k x F è = ½ k x 2 U l Today è Young’s Modulus è Simple Harmonic Motion è Springs Revisited Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 4 05
 Simple Harmonic Motion l Vibrations è Vocal cords when singing/speaking è String/rubber band l Simple Harmonic Motion è Restoring force proportional to displacement è Springs F = -kx Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 5 11
Simple Harmonic Motion l Vibrations è Vocal cords when singing/speaking è String/rubber band l Simple Harmonic Motion è Restoring force proportional to displacement è Springs F = -kx Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 5 11
 Question A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i. e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i. e. zero displacement) 3. The acceleration of the mass is constant +A x t -A Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 6 17
Question A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i. e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i. e. zero displacement) 3. The acceleration of the mass is constant +A x t -A Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 6 17
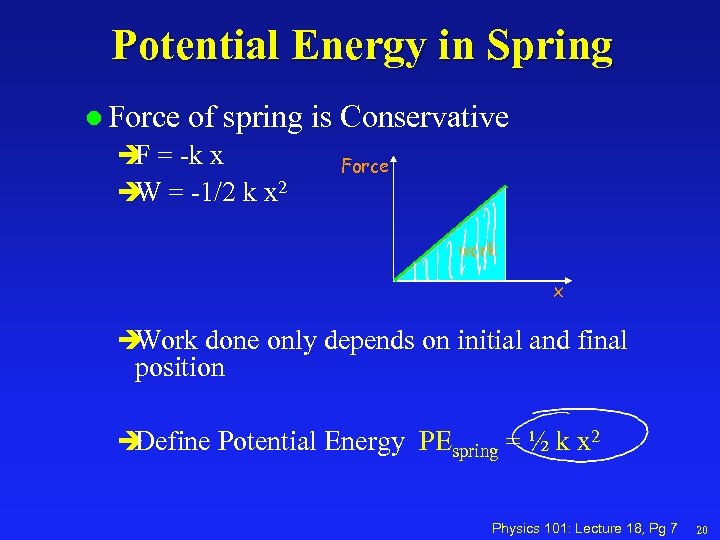 Potential Energy in Spring l Force of spring is Conservative è = -k x F è = -1/2 k x 2 W Force work x è Work done only depends on initial and final position è Define Potential Energy PEspring = ½ k x 2 Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 7 20
Potential Energy in Spring l Force of spring is Conservative è = -k x F è = -1/2 k x 2 W Force work x è Work done only depends on initial and final position è Define Potential Energy PEspring = ½ k x 2 Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 7 20
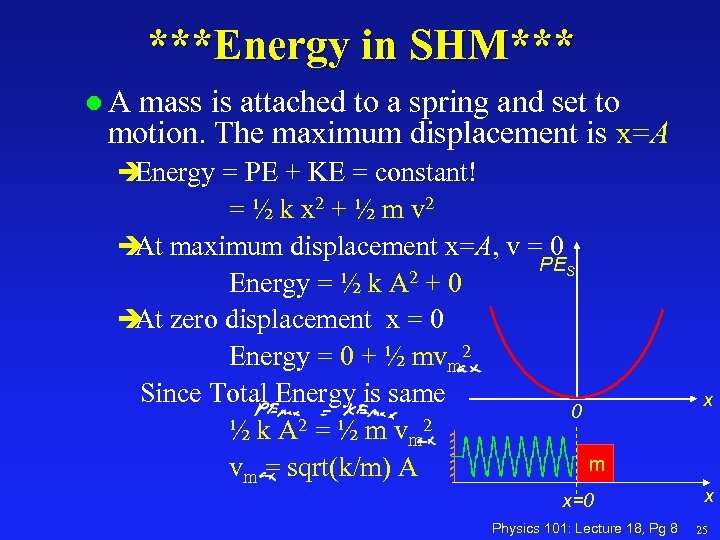 ***Energy in SHM*** l. A mass is attached to a spring and set to motion. The maximum displacement is x=A è Energy = PE + KE = constant! = ½ k x 2 + ½ m v 2 è maximum displacement x=A, v = 0 At PES 2+0 Energy = ½ k A è zero displacement x = 0 At Energy = 0 + ½ mvm 2 Since Total Energy is same 0 2=½mv 2 ½k. A m m vm = sqrt(k/m) A x=0 Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 8 x x 25
***Energy in SHM*** l. A mass is attached to a spring and set to motion. The maximum displacement is x=A è Energy = PE + KE = constant! = ½ k x 2 + ½ m v 2 è maximum displacement x=A, v = 0 At PES 2+0 Energy = ½ k A è zero displacement x = 0 At Energy = 0 + ½ mvm 2 Since Total Energy is same 0 2=½mv 2 ½k. A m m vm = sqrt(k/m) A x=0 Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 8 x x 25
 Question A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i. e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i. e. zero displacement) 3. The speed of the mass is constant +A x t -A Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 9 29
Question A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i. e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i. e. zero displacement) 3. The speed of the mass is constant +A x t -A Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 9 29
 Question l A spring oscillates back and forth on a frictionless horizontal surface. A camera takes pictures of the position every 1/10 th of a second. Which plot best shows the positions of the mass. 1 End. Point Equilibrium End. Point 2 3 Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 10 38
Question l A spring oscillates back and forth on a frictionless horizontal surface. A camera takes pictures of the position every 1/10 th of a second. Which plot best shows the positions of the mass. 1 End. Point Equilibrium End. Point 2 3 Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 10 38
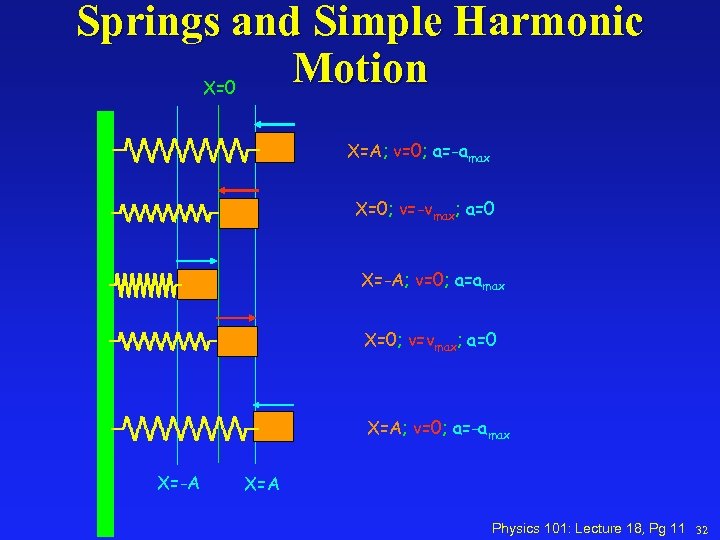 Springs and Simple Harmonic Motion X=0 X=A; v=0; a=-amax X=0; v=-vmax; a=0 X=-A; v=0; a=amax X=0; v=vmax; a=0 X=A; v=0; a=-amax X=-A X=A Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 11 32
Springs and Simple Harmonic Motion X=0 X=A; v=0; a=-amax X=0; v=-vmax; a=0 X=-A; v=0; a=amax X=0; v=vmax; a=0 X=A; v=0; a=-amax X=-A X=A Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 11 32
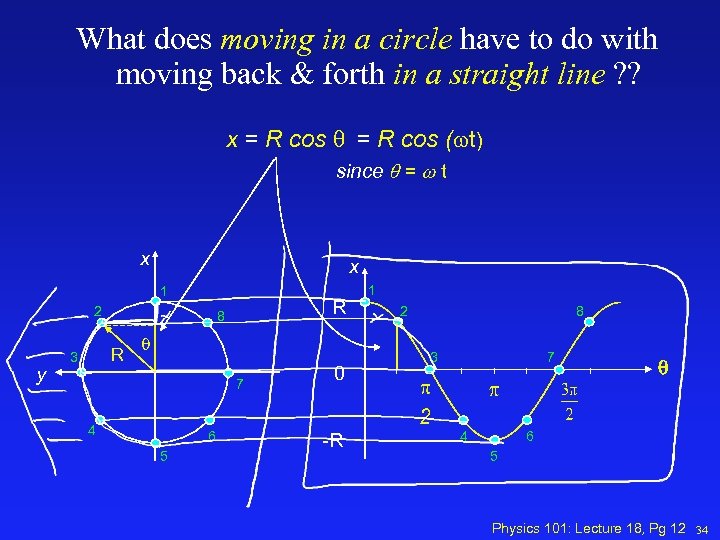 What does moving in a circle have to do with moving back & forth in a straight line ? ? x = R cos q = R cos ( t) since q = w t x x 1 2 y R 3 R 8 q 7 4 6 5 0 -R 1 2 8 7 3 4 6 5 Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 12 34
What does moving in a circle have to do with moving back & forth in a straight line ? ? x = R cos q = R cos ( t) since q = w t x x 1 2 y R 3 R 8 q 7 4 6 5 0 -R 1 2 8 7 3 4 6 5 Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 12 34
 SHM and Circles Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 13
SHM and Circles Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 13
![Simple Harmonic Motion: x(t) = [A]cos( t) v(t) = -[A ]sin( t) a(t) = Simple Harmonic Motion: x(t) = [A]cos( t) v(t) = -[A ]sin( t) a(t) =](https://present5.com/presentation/5b75ad713f1657c9d8b26c2ee2c00a49/image-14.jpg) Simple Harmonic Motion: x(t) = [A]cos( t) v(t) = -[A ]sin( t) a(t) = -[A 2]cos( t) x(t) = [A]sin( t) OR v(t) = [A ]cos( t) a(t) = -[A 2]sin( t) xmax = A Period = T (seconds per cycle) vmax = A Frequency = f = 1/T (cycles per second) amax = A 2 Angular frequency = = 2 f = 2 /T For spring: 2 = k/m Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 14 36
Simple Harmonic Motion: x(t) = [A]cos( t) v(t) = -[A ]sin( t) a(t) = -[A 2]cos( t) x(t) = [A]sin( t) OR v(t) = [A ]cos( t) a(t) = -[A 2]sin( t) xmax = A Period = T (seconds per cycle) vmax = A Frequency = f = 1/T (cycles per second) amax = A 2 Angular frequency = = 2 f = 2 /T For spring: 2 = k/m Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 14 36
 Example A 3 kg mass is attached to a spring (k=24 N/m). It is stretched 5 cm. At time t=0 it is released and oscillates. Which equation describes the position as a function of time x(t) = A) 5 sin( t) B) 5 cos( t) C) 24 sin( t) D) 24 cos( t) E) -24 cos( t) Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 15 39
Example A 3 kg mass is attached to a spring (k=24 N/m). It is stretched 5 cm. At time t=0 it is released and oscillates. Which equation describes the position as a function of time x(t) = A) 5 sin( t) B) 5 cos( t) C) 24 sin( t) D) 24 cos( t) E) -24 cos( t) Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 15 39
 Example A 3 kg mass is attached to a spring (k=24 N/m). It is stretched 5 cm. At time t=0 it is released and oscillates. What is the total energy of the block spring system? Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 16 43
Example A 3 kg mass is attached to a spring (k=24 N/m). It is stretched 5 cm. At time t=0 it is released and oscillates. What is the total energy of the block spring system? Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 16 43
 Example A 3 kg mass is attached to a spring (k=24 N/m). It is stretched 5 cm. At time t=0 it is released and oscillates. What is the maximum speed of the block? Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 17 46
Example A 3 kg mass is attached to a spring (k=24 N/m). It is stretched 5 cm. At time t=0 it is released and oscillates. What is the maximum speed of the block? Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 17 46
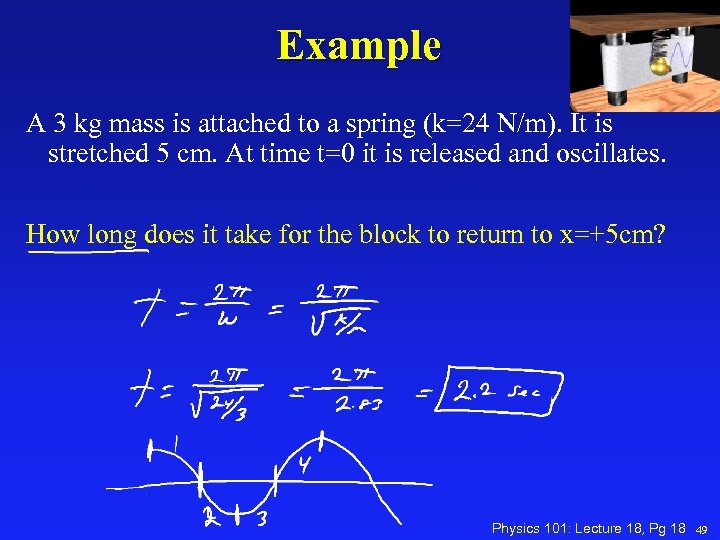 Example A 3 kg mass is attached to a spring (k=24 N/m). It is stretched 5 cm. At time t=0 it is released and oscillates. How long does it take for the block to return to x=+5 cm? Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 18 49
Example A 3 kg mass is attached to a spring (k=24 N/m). It is stretched 5 cm. At time t=0 it is released and oscillates. How long does it take for the block to return to x=+5 cm? Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 18 49
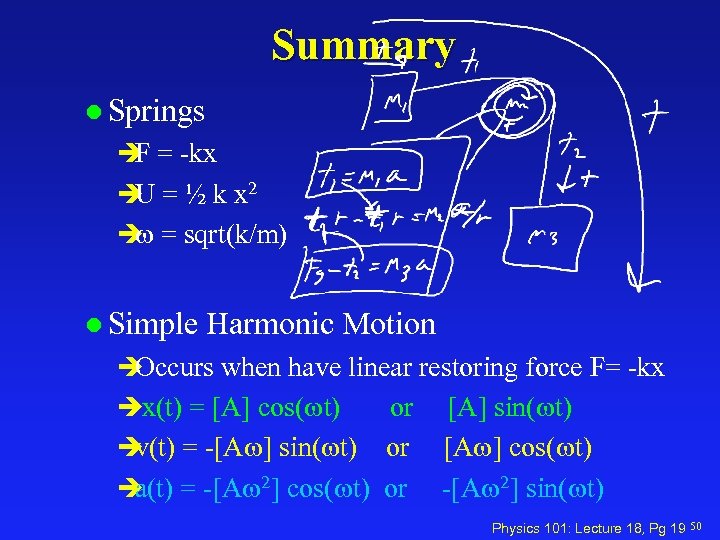 Summary l Springs è = -kx F è = ½ k x 2 U è = sqrt(k/m) l Simple Harmonic Motion è Occurs when have linear restoring force F= -kx èx(t) = [A] cos( t) or è = -[A ] sin( t) or v(t) è = -[A 2] cos( t) or a(t) [A] sin( t) [A ] cos( t) -[A 2] sin( t) Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 19 50
Summary l Springs è = -kx F è = ½ k x 2 U è = sqrt(k/m) l Simple Harmonic Motion è Occurs when have linear restoring force F= -kx èx(t) = [A] cos( t) or è = -[A ] sin( t) or v(t) è = -[A 2] cos( t) or a(t) [A] sin( t) [A ] cos( t) -[A 2] sin( t) Physics 101: Lecture 18, Pg 19 50


