cfff1f81da7ab5d586d50b9e68a5cda6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Exact Constraint Design Using Tolerance Analysis Methods Danny Smith Brigham Young University 15 June 2001 Special Acknowledgements to: ADCATS Research NSF Grant DMI 0084880 ADCATS 2001
Exact Constraint Design Using Tolerance Analysis Methods Danny Smith Brigham Young University 15 June 2001 Special Acknowledgements to: ADCATS Research NSF Grant DMI 0084880 ADCATS 2001
 Presentation Outline w Background n n Constraint Analysis and Screw Theory Tolerance Analysis w Variation-based Constraint Analysis of Assemblies (VCAA) Method w Case Studies w Conclusion ADCATS 2001
Presentation Outline w Background n n Constraint Analysis and Screw Theory Tolerance Analysis w Variation-based Constraint Analysis of Assemblies (VCAA) Method w Case Studies w Conclusion ADCATS 2001
 Why Analyze for Constraints? w Key Definitions: n n Degrees of Freedom Exact-constraint Overconstraint Underconstraint ADCATS 2001
Why Analyze for Constraints? w Key Definitions: n n Degrees of Freedom Exact-constraint Overconstraint Underconstraint ADCATS 2001
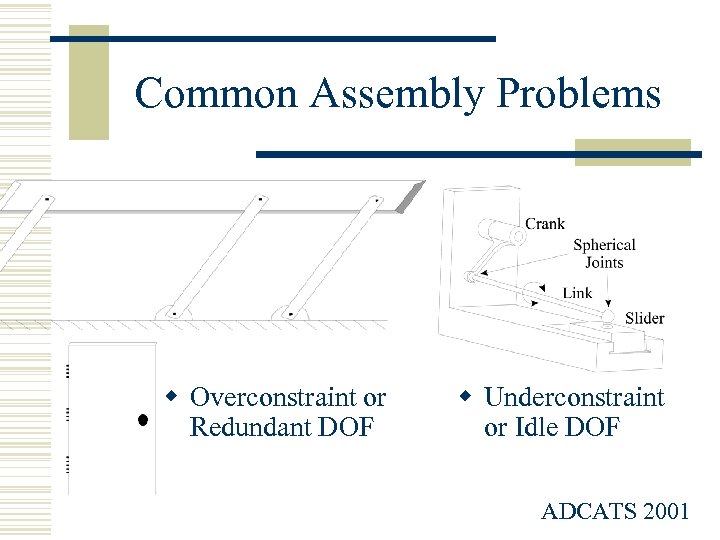 Common Assembly Problems w Overconstraint or Redundant DOF w Underconstraint or Idle DOF ADCATS 2001
Common Assembly Problems w Overconstraint or Redundant DOF w Underconstraint or Idle DOF ADCATS 2001
![Current Constraint Methods w Kinematic Constraint Pattern Analysis n [Blanding 1999] w Geometric Constraint Current Constraint Methods w Kinematic Constraint Pattern Analysis n [Blanding 1999] w Geometric Constraint](https://present5.com/presentation/cfff1f81da7ab5d586d50b9e68a5cda6/image-5.jpg) Current Constraint Methods w Kinematic Constraint Pattern Analysis n [Blanding 1999] w Geometric Constraint Solving n [Hoffmann and Vermeer 1995] w Screw Theory-Based Constraint Analysis n [Adams 1998], [Konkar 1993], and [Adams and Whitney 2001] ADCATS 2001
Current Constraint Methods w Kinematic Constraint Pattern Analysis n [Blanding 1999] w Geometric Constraint Solving n [Hoffmann and Vermeer 1995] w Screw Theory-Based Constraint Analysis n [Adams 1998], [Konkar 1993], and [Adams and Whitney 2001] ADCATS 2001
![Screws – Twists and Wrenches Twist Wrench Please see [Adams and Whitney 2001] for Screws – Twists and Wrenches Twist Wrench Please see [Adams and Whitney 2001] for](https://present5.com/presentation/cfff1f81da7ab5d586d50b9e68a5cda6/image-6.jpg) Screws – Twists and Wrenches Twist Wrench Please see [Adams and Whitney 2001] for details ADCATS 2001
Screws – Twists and Wrenches Twist Wrench Please see [Adams and Whitney 2001] for details ADCATS 2001
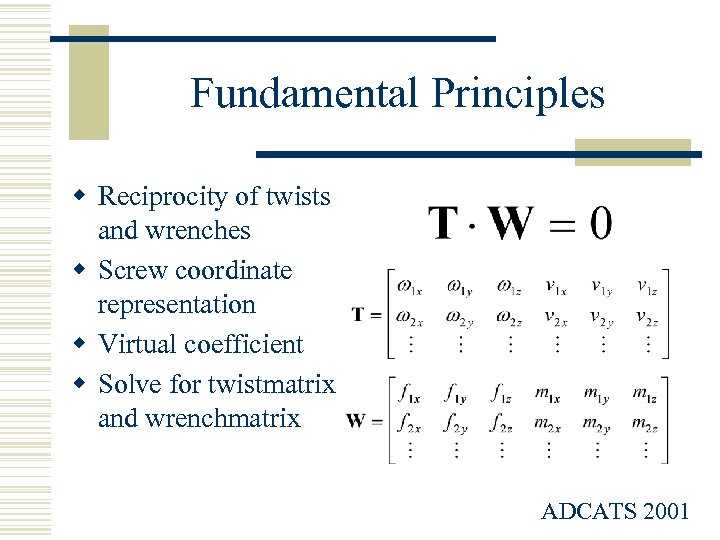 Fundamental Principles w Reciprocity of twists and wrenches w Screw coordinate representation w Virtual coefficient w Solve for twistmatrix and wrenchmatrix ADCATS 2001
Fundamental Principles w Reciprocity of twists and wrenches w Screw coordinate representation w Virtual coefficient w Solve for twistmatrix and wrenchmatrix ADCATS 2001
 Screw Theory Steps 1. Locate mating features on assembly using transformation matrices. 2. Form Twist matrices for each mating feature 3. Use screw algorithms and linear algebra to solve for Resultant Twist and Resultant Wrench matrices Please see [Adams and Whitney 2001] for details ADCATS 2001
Screw Theory Steps 1. Locate mating features on assembly using transformation matrices. 2. Form Twist matrices for each mating feature 3. Use screw algorithms and linear algebra to solve for Resultant Twist and Resultant Wrench matrices Please see [Adams and Whitney 2001] for details ADCATS 2001
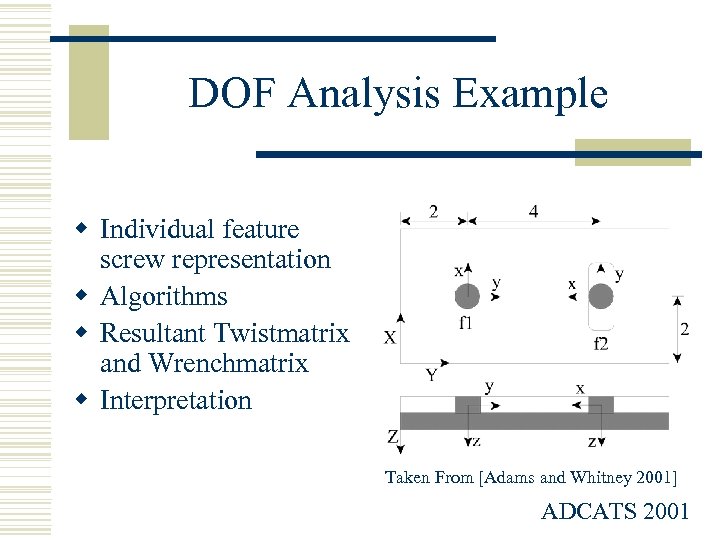 DOF Analysis Example w Individual feature screw representation w Algorithms w Resultant Twistmatrix and Wrenchmatrix w Interpretation Taken From [Adams and Whitney 2001] ADCATS 2001
DOF Analysis Example w Individual feature screw representation w Algorithms w Resultant Twistmatrix and Wrenchmatrix w Interpretation Taken From [Adams and Whitney 2001] ADCATS 2001
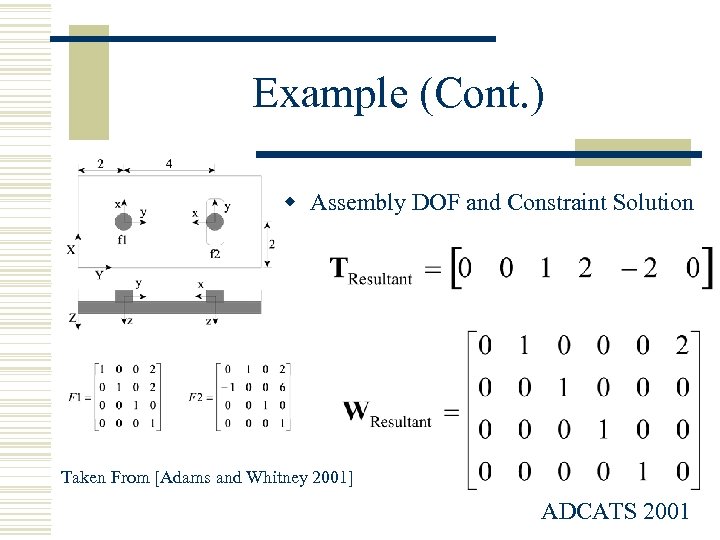 Example (Cont. ) w Assembly DOF and Constraint Solution Taken From [Adams and Whitney 2001] ADCATS 2001
Example (Cont. ) w Assembly DOF and Constraint Solution Taken From [Adams and Whitney 2001] ADCATS 2001
 Tolerance Analysis Background w Dimensional, Kinematic, and Geometric Variation w Direct Linearization Method (DLM) w Vector Loops w Global Coordinate Method (GCM) 1999] and Please see [Chase [Gao 1993] for complete details ADCATS 2001
Tolerance Analysis Background w Dimensional, Kinematic, and Geometric Variation w Direct Linearization Method (DLM) w Vector Loops w Global Coordinate Method (GCM) 1999] and Please see [Chase [Gao 1993] for complete details ADCATS 2001
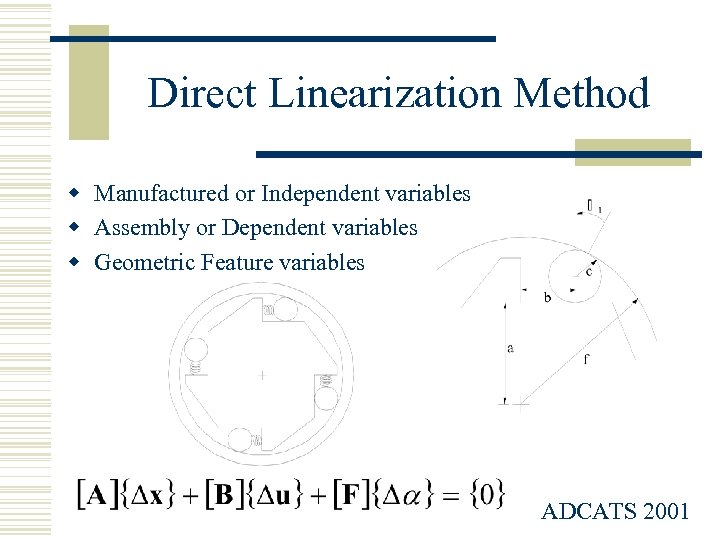 Direct Linearization Method w Manufactured or Independent variables w Assembly or Dependent variables w Geometric Feature variables ADCATS 2001
Direct Linearization Method w Manufactured or Independent variables w Assembly or Dependent variables w Geometric Feature variables ADCATS 2001
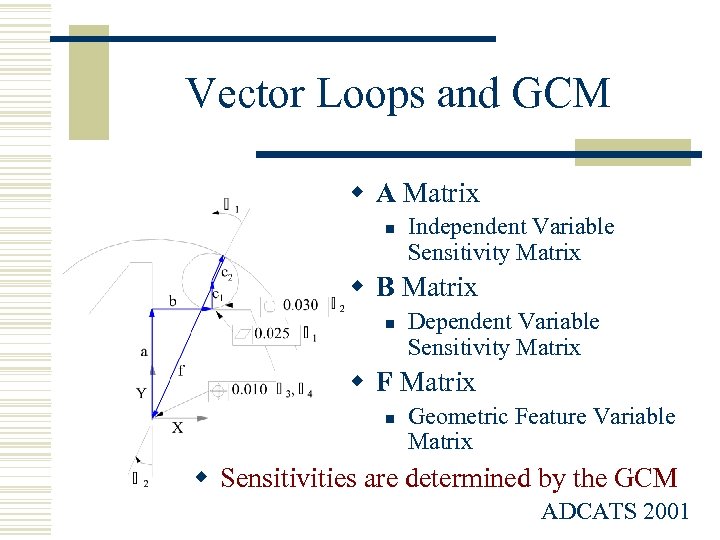 Vector Loops and GCM w A Matrix n Independent Variable Sensitivity Matrix w B Matrix n Dependent Variable Sensitivity Matrix w F Matrix n Geometric Feature Variable Matrix w Sensitivities are determined by the GCM ADCATS 2001
Vector Loops and GCM w A Matrix n Independent Variable Sensitivity Matrix w B Matrix n Dependent Variable Sensitivity Matrix w F Matrix n Geometric Feature Variable Matrix w Sensitivities are determined by the GCM ADCATS 2001
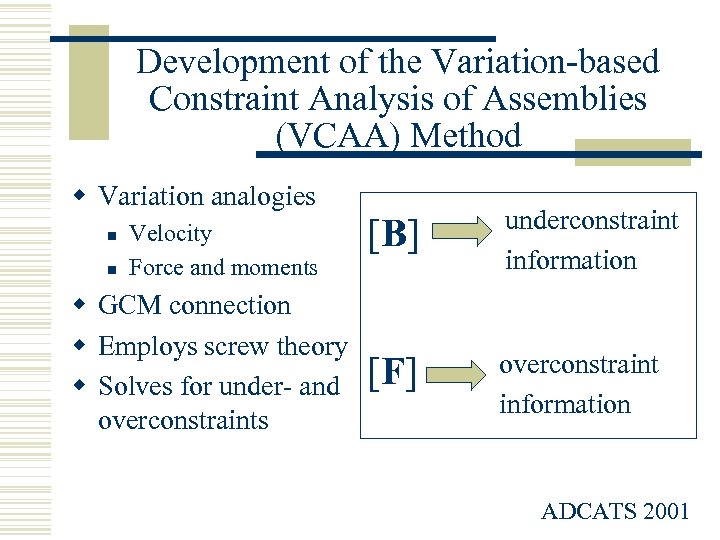 Development of the Variation-based Constraint Analysis of Assemblies (VCAA) Method w Variation analogies n n Velocity Force and moments w GCM connection w Employs screw theory w Solves for under- and overconstraints [B] underconstraint information [F] overconstraint information ADCATS 2001
Development of the Variation-based Constraint Analysis of Assemblies (VCAA) Method w Variation analogies n n Velocity Force and moments w GCM connection w Employs screw theory w Solves for under- and overconstraints [B] underconstraint information [F] overconstraint information ADCATS 2001
![VCAA for Underconstraints Tcolumn [B] DLM Tolerance Analysis Wintermediate-joint i Reciprocal Operation Transpose and VCAA for Underconstraints Tcolumn [B] DLM Tolerance Analysis Wintermediate-joint i Reciprocal Operation Transpose and](https://present5.com/presentation/cfff1f81da7ab5d586d50b9e68a5cda6/image-15.jpg) VCAA for Underconstraints Tcolumn [B] DLM Tolerance Analysis Wintermediate-joint i Reciprocal Operation Transpose and Switch Wintermediate-part j Union Matrices For Each Part Tjoint i Associate Dependent Variables to Joint Types TResultant-part j Reciprocal Operation ADCATS 2001
VCAA for Underconstraints Tcolumn [B] DLM Tolerance Analysis Wintermediate-joint i Reciprocal Operation Transpose and Switch Wintermediate-part j Union Matrices For Each Part Tjoint i Associate Dependent Variables to Joint Types TResultant-part j Reciprocal Operation ADCATS 2001
![VCAA for Overconstraints Wcolumn [F] DLM Tolerance Analysis Tintermediate-jointi Reciprocal Operation Transpose Associate Geometric VCAA for Overconstraints Wcolumn [F] DLM Tolerance Analysis Tintermediate-jointi Reciprocal Operation Transpose Associate Geometric](https://present5.com/presentation/cfff1f81da7ab5d586d50b9e68a5cda6/image-16.jpg) VCAA for Overconstraints Wcolumn [F] DLM Tolerance Analysis Tintermediate-jointi Reciprocal Operation Transpose Associate Geometric Feature Variables to Joint Types Tintermediate-part j or Tintermediate-loop k Union Matrices For Each Part or Loop Wjointi WResultant-partj or WResultant-loop k Reciprocal Operation ADCATS 2001
VCAA for Overconstraints Wcolumn [F] DLM Tolerance Analysis Tintermediate-jointi Reciprocal Operation Transpose Associate Geometric Feature Variables to Joint Types Tintermediate-part j or Tintermediate-loop k Union Matrices For Each Part or Loop Wjointi WResultant-partj or WResultant-loop k Reciprocal Operation ADCATS 2001
 Case Studies of VCAA w Case 1 - One-way Clutch Assembly in 2 -D w Case 2 - Stacked Blocks Assembly in 2 -D w Case 3 - Crank Slider Assembly in 3 -D ADCATS 2001
Case Studies of VCAA w Case 1 - One-way Clutch Assembly in 2 -D w Case 2 - Stacked Blocks Assembly in 2 -D w Case 3 - Crank Slider Assembly in 3 -D ADCATS 2001
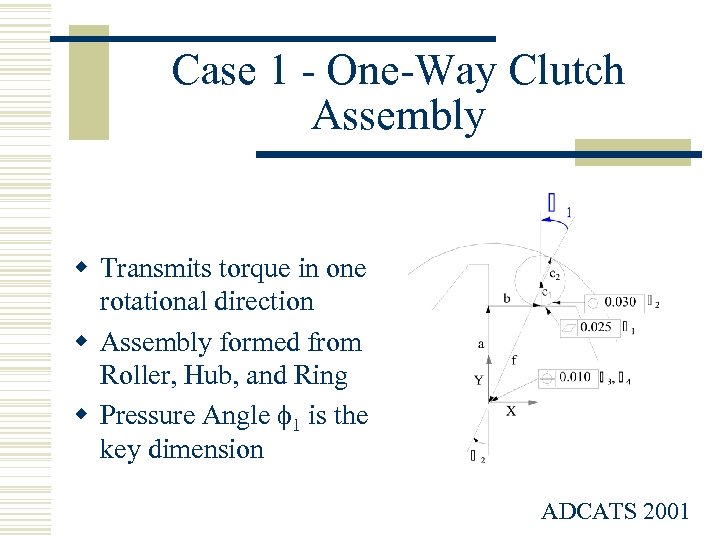 Case 1 - One-Way Clutch Assembly w Transmits torque in one rotational direction w Assembly formed from Roller, Hub, and Ring w Pressure Angle 1 is the key dimension ADCATS 2001
Case 1 - One-Way Clutch Assembly w Transmits torque in one rotational direction w Assembly formed from Roller, Hub, and Ring w Pressure Angle 1 is the key dimension ADCATS 2001
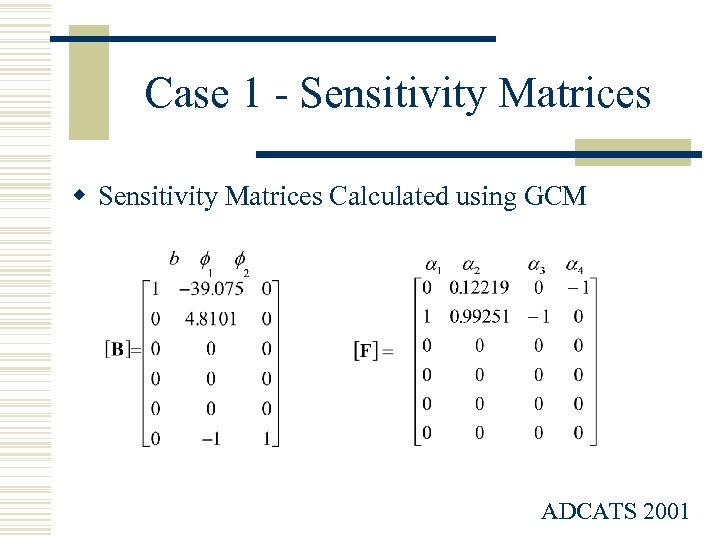 Case 1 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
Case 1 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
![Case 1 - Underconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Twists for each joint from [B] Case 1 - Underconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Twists for each joint from [B]](https://present5.com/presentation/cfff1f81da7ab5d586d50b9e68a5cda6/image-20.jpg) Case 1 - Underconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Twists for each joint from [B] w Perform intermediate steps n See [Adams 1998] w Evaluate Resultant Twist for each part to identify underconstraint information ADCATS 2001
Case 1 - Underconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Twists for each joint from [B] w Perform intermediate steps n See [Adams 1998] w Evaluate Resultant Twist for each part to identify underconstraint information ADCATS 2001
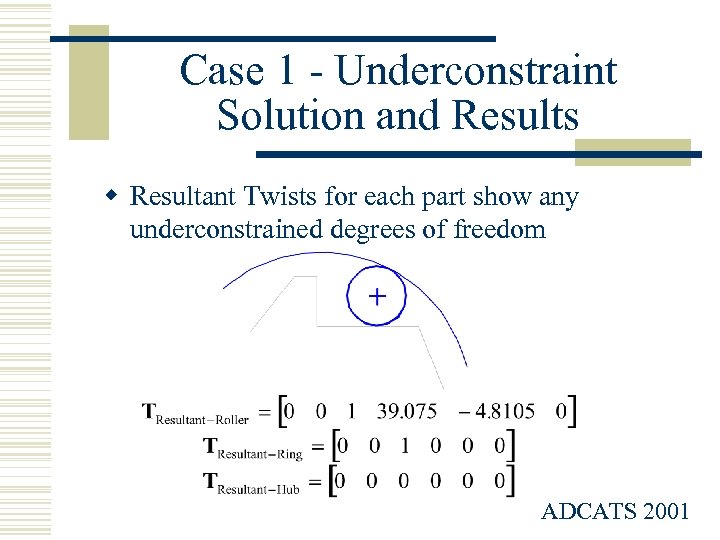 Case 1 - Underconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Twists for each part show any underconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
Case 1 - Underconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Twists for each part show any underconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
![Case 1 - Overconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Wrenches for each joint from [F] Case 1 - Overconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Wrenches for each joint from [F]](https://present5.com/presentation/cfff1f81da7ab5d586d50b9e68a5cda6/image-22.jpg) Case 1 - Overconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Wrenches for each joint from [F] w Perform intermediate steps n See [Adams 1998] w Evaluate Resultant Wrench for each part to identify overconstraint information ADCATS 2001
Case 1 - Overconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Wrenches for each joint from [F] w Perform intermediate steps n See [Adams 1998] w Evaluate Resultant Wrench for each part to identify overconstraint information ADCATS 2001
 Case 1 - Overconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Wrench for each set shows any overconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
Case 1 - Overconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Wrench for each set shows any overconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
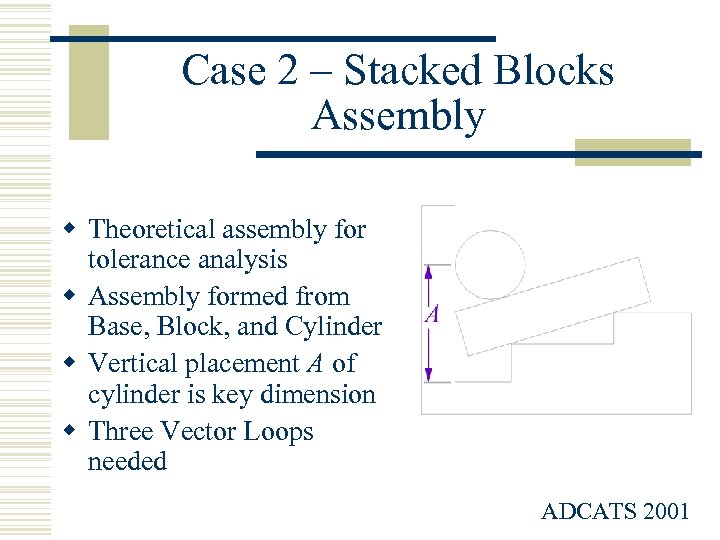 Case 2 – Stacked Blocks Assembly w Theoretical assembly for tolerance analysis w Assembly formed from Base, Block, and Cylinder w Vertical placement A of cylinder is key dimension w Three Vector Loops needed ADCATS 2001
Case 2 – Stacked Blocks Assembly w Theoretical assembly for tolerance analysis w Assembly formed from Base, Block, and Cylinder w Vertical placement A of cylinder is key dimension w Three Vector Loops needed ADCATS 2001
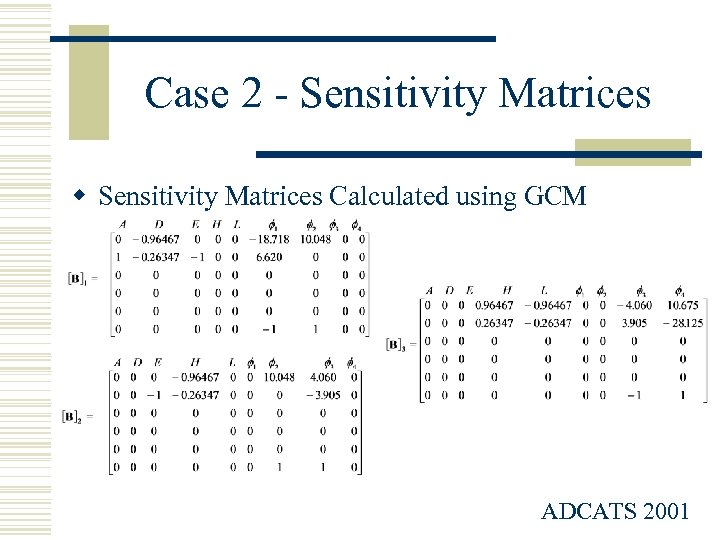 Case 2 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
Case 2 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
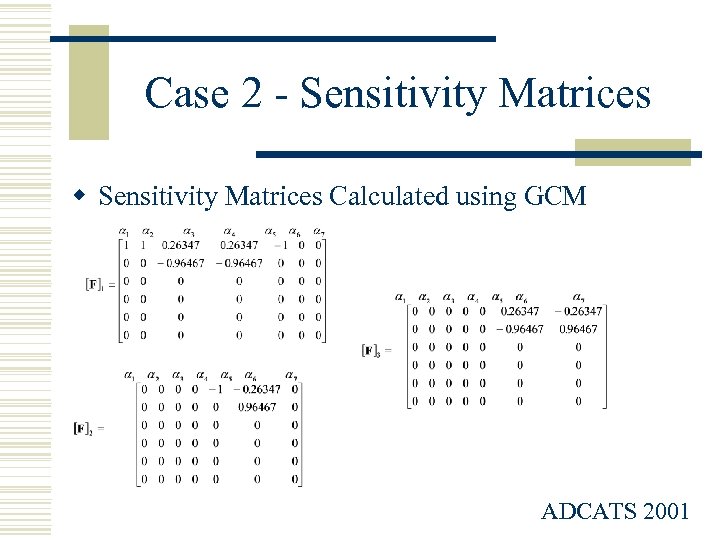 Case 2 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
Case 2 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
![Case 2 - Underconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Twists for each joint from [B] Case 2 - Underconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Twists for each joint from [B]](https://present5.com/presentation/cfff1f81da7ab5d586d50b9e68a5cda6/image-27.jpg) Case 2 - Underconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Twists for each joint from [B] w Perform intermediate steps n See [Adams 1998] w Evaluate Resultant Twist for each part to identify underconstraint information ADCATS 2001
Case 2 - Underconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Twists for each joint from [B] w Perform intermediate steps n See [Adams 1998] w Evaluate Resultant Twist for each part to identify underconstraint information ADCATS 2001
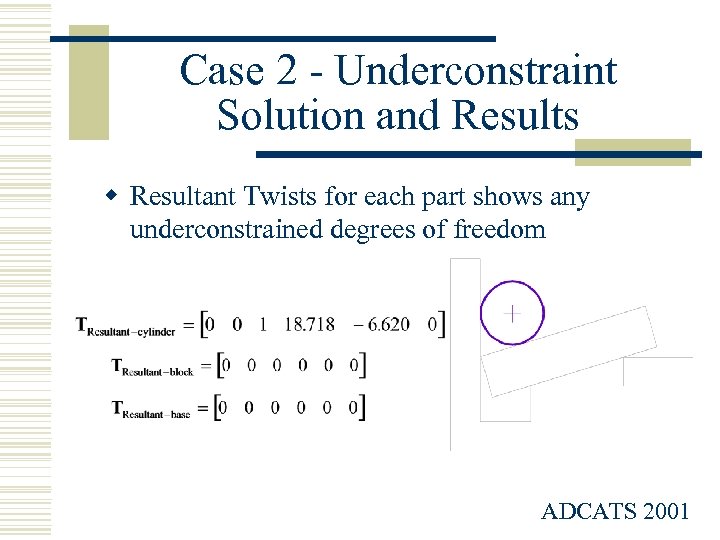 Case 2 - Underconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Twists for each part shows any underconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
Case 2 - Underconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Twists for each part shows any underconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
![Case 2 - Overconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Wrenches for each joint from [F] Case 2 - Overconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Wrenches for each joint from [F]](https://present5.com/presentation/cfff1f81da7ab5d586d50b9e68a5cda6/image-29.jpg) Case 2 - Overconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Wrenches for each joint from [F] w Perform intermediate steps n See [Adams 1998] w Evaluate Resultant Wrench for each part to identify overconstraint information ADCATS 2001
Case 2 - Overconstraint Analysis w Form Joint Wrenches for each joint from [F] w Perform intermediate steps n See [Adams 1998] w Evaluate Resultant Wrench for each part to identify overconstraint information ADCATS 2001
 Case 2 - Overconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Wrench for each set show any overconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
Case 2 - Overconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Wrench for each set show any overconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
 Case 3 – Crank Slider Assembly w Assembly formed from Base, Crank, Link, and Slider w Slider Position U is the key dimension w One Vector Loop needed ADCATS 2001
Case 3 – Crank Slider Assembly w Assembly formed from Base, Crank, Link, and Slider w Slider Position U is the key dimension w One Vector Loop needed ADCATS 2001
 Case 3 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
Case 3 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
 Case 3 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
Case 3 - Sensitivity Matrices w Sensitivity Matrices Calculated using GCM ADCATS 2001
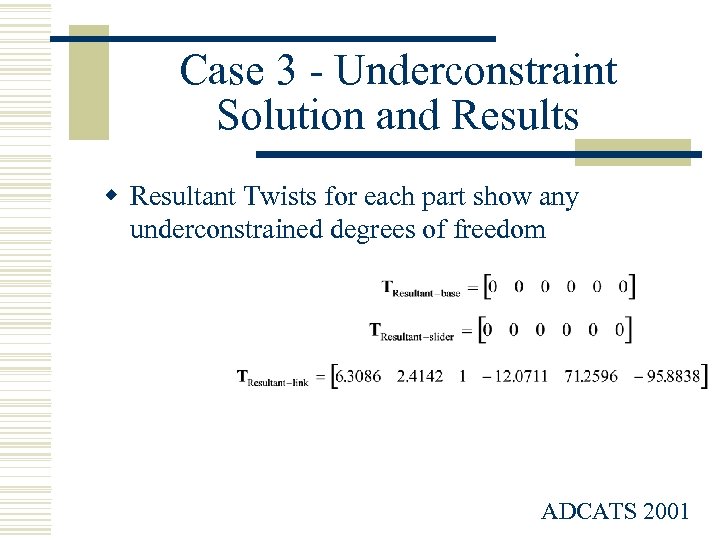 Case 3 - Underconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Twists for each part show any underconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
Case 3 - Underconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Twists for each part show any underconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
 Case 3 - Overconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Wrench for each set shows any overconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
Case 3 - Overconstraint Solution and Results w Resultant Wrench for each set shows any overconstrained degrees of freedom ADCATS 2001
 Conclusions w VCAA Method connects Constraint Analysis and Tolerance Analysis w Based on Screw Theory and the Global Coordinate Method w The VCAA Method can extract twist and wrench matrices directly from the vector model w Can perform a constraint analysis and a tolerance analysis simultaneously ADCATS 2001
Conclusions w VCAA Method connects Constraint Analysis and Tolerance Analysis w Based on Screw Theory and the Global Coordinate Method w The VCAA Method can extract twist and wrench matrices directly from the vector model w Can perform a constraint analysis and a tolerance analysis simultaneously ADCATS 2001
 Bibliography w Adams, Jeffrey D. Feature Based Analysis of Selective Limited Motion in Assemblies. Master of Science Thesis, Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1998. w Adams, Jeffrey D. ; Whitney, Daniel E. “Application of Screw Theory to Constraint Analysis of Mechanical Assemblies Joined by Features. ” In Journal of Mechanical Design: Transactions of the ASME, Vol. 123, pp. 26 -32, March 2001. w Blanding, Douglass L. Exact Constraint: Machine Design Using Kinematic Principles. New York: ASME Press, 1999. w Chase, Kenneth W. Dimensioning & Tolerancing Handbook, ed. Paul J. Drake, Jr. , New York: Mc. Graw Hill, “Multi_Dimensional Tolerance Analysis. ”, 1999. ADCATS 2001
Bibliography w Adams, Jeffrey D. Feature Based Analysis of Selective Limited Motion in Assemblies. Master of Science Thesis, Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1998. w Adams, Jeffrey D. ; Whitney, Daniel E. “Application of Screw Theory to Constraint Analysis of Mechanical Assemblies Joined by Features. ” In Journal of Mechanical Design: Transactions of the ASME, Vol. 123, pp. 26 -32, March 2001. w Blanding, Douglass L. Exact Constraint: Machine Design Using Kinematic Principles. New York: ASME Press, 1999. w Chase, Kenneth W. Dimensioning & Tolerancing Handbook, ed. Paul J. Drake, Jr. , New York: Mc. Graw Hill, “Multi_Dimensional Tolerance Analysis. ”, 1999. ADCATS 2001
 Bibliography (cont. ) w Chase, Kenneth W. ; Gao, Jinsong; Magelby, Spencer; Sorensen, Carl. “Including Geometric Feature Variations in Tolerance Analysis of Mechanical Assemblies. ” In IIE (Institute of Industrial Engineers) Transactions, Chapman & Hall Ltd. , pp. 795_807, 10 Oct 1996. w Gao, Jinsong; Chase, Kenneth; Magleby, Spencer. “Generalized 3 -D Tolerance Analysis of Mechanical Assemblies with Small Kinematic Adjustments. ” In IIE (Institute of Industrial Engineers) Transactions, Chapman & Hall Ltd, pp. 367_377, 4 April 1998. w Gao, Jinsong; Chase, Kenneth; Magleby, Spencer. “Global Coordinate Method for Determining Sensitivity in Assembly Tolerance Analysis” in Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Conference and Exposition, Anaheim, California, 1998 ADCATS 2001
Bibliography (cont. ) w Chase, Kenneth W. ; Gao, Jinsong; Magelby, Spencer; Sorensen, Carl. “Including Geometric Feature Variations in Tolerance Analysis of Mechanical Assemblies. ” In IIE (Institute of Industrial Engineers) Transactions, Chapman & Hall Ltd. , pp. 795_807, 10 Oct 1996. w Gao, Jinsong; Chase, Kenneth; Magleby, Spencer. “Generalized 3 -D Tolerance Analysis of Mechanical Assemblies with Small Kinematic Adjustments. ” In IIE (Institute of Industrial Engineers) Transactions, Chapman & Hall Ltd, pp. 367_377, 4 April 1998. w Gao, Jinsong; Chase, Kenneth; Magleby, Spencer. “Global Coordinate Method for Determining Sensitivity in Assembly Tolerance Analysis” in Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Conference and Exposition, Anaheim, California, 1998 ADCATS 2001
 Bibliography (cont. ) w Gao, Jinsong. Nonlinear Tolerance Analysis of Mechanical Assemblies. A Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation, Provo, Utah: Brigham Young University, August 1993. w Hoffmann, Christoph; Vermeer, Pamela. Computing in Euclidean Geometry (2 nd Edition), ed. Du, Ding-Zhu; Hwang, Frank, Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd. , “Geometric Constraint Solving in U 2 and U 3. ”, pp. 266 -298, 1995. w Konkar, Ranjit. Incremental Kinematic Analysis and Symbolic Synthesis of Mechanisms. Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation, Palo Alto, California: Stanford University, June 1993. w Konkar, Ranjit; Cutkosky, M. “Incremental Kinematic Analysis of Mechanisms. ” In Journal of Mechanical Design, Vol. 117, pp. 589 -596, December 1995. ADCATS 2001
Bibliography (cont. ) w Gao, Jinsong. Nonlinear Tolerance Analysis of Mechanical Assemblies. A Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation, Provo, Utah: Brigham Young University, August 1993. w Hoffmann, Christoph; Vermeer, Pamela. Computing in Euclidean Geometry (2 nd Edition), ed. Du, Ding-Zhu; Hwang, Frank, Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd. , “Geometric Constraint Solving in U 2 and U 3. ”, pp. 266 -298, 1995. w Konkar, Ranjit. Incremental Kinematic Analysis and Symbolic Synthesis of Mechanisms. Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation, Palo Alto, California: Stanford University, June 1993. w Konkar, Ranjit; Cutkosky, M. “Incremental Kinematic Analysis of Mechanisms. ” In Journal of Mechanical Design, Vol. 117, pp. 589 -596, December 1995. ADCATS 2001
 Bibliography (cont. ) w Roth, Bernard. “Screws, Motors, and Wrenches that Cannot be Bought in a Hardware Store. ” In Robotics Research, Chapter 8, pp 679 -693, 1984. w Waldron, K. J. “The Constraint Analysis of Mechanisms. ” In The Journal of Mechanisms, Volume 1, pp 101 -114. Great Britain: Pergamon Press, 1966. ADCATS 2001
Bibliography (cont. ) w Roth, Bernard. “Screws, Motors, and Wrenches that Cannot be Bought in a Hardware Store. ” In Robotics Research, Chapter 8, pp 679 -693, 1984. w Waldron, K. J. “The Constraint Analysis of Mechanisms. ” In The Journal of Mechanisms, Volume 1, pp 101 -114. Great Britain: Pergamon Press, 1966. ADCATS 2001


