9344e58389f54b0e42e6d91093baa6a2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Evidence-Based Practices in Psychiatric Rehabilitation Bob Drake October, 2010

Financial Support to PRC ¨ Grants from NIDA, NIDRR, NIMH, RWJF, SAMHSA ¨ Contracts from Guilford Press, Hazelden Press, Mac. Arthur Foundation, Oxford Press, New York Office of Mental Health, Research Foundation for Mental Health ¨ Gifts from Johnson & Johnson Corporate Contributions, Segal Foundation, Thomson Foundation, Vail Foundation, West Foundation

OVERVIEW ¨ Definition ¨ Update on evidence-based practices ¨ Common themes ¨ Dissemination and implementation

History of Mental Health in U. S. ¨ Cottage industry ¨ Little attention to outcomes ¨ Ineffective and harmful interventions persist for years ¨ Effective interventions rarely used

Evidence-based Medicine ¨ The combination of science, client values/preference, and clinical expertise ¨ In mental health care, this means combining science and recovery ideology

Evidence-Based Practices ¨ Standardized interventions ¨ Controlled research ¨ More than 1 research group ¨ Objective outcome measures ¨ Meaningful outcomes

Evidence-Based Rehabilitation Practices Robert Wood Johnson Foundation 1998 ¨ Assertive Community Treatment ¨ Supported Employment ¨ Family Psychoeducation ¨ Illness Management and Recovery ¨ Integrated Treatment for Co- occurring Disorders

Assertive Community Treatment (ACT) ¨ Community-based team ¨ Low caseload ¨ Multidisciplinary ¨ Outreach ¨ Direct service provision ¨ 24 hours/7 days
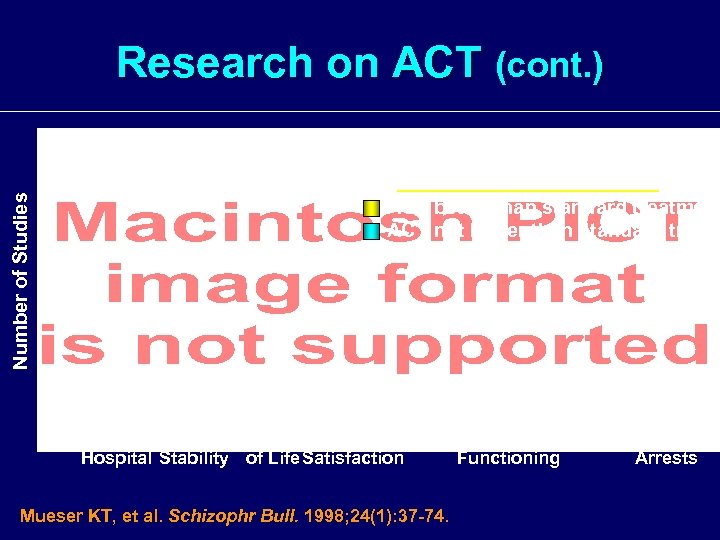
Number of Studies Research on ACT (cont. ) 25 Randomized Controlled Trials ACT better than standard treatment ACT not better than standard treatm Time in Housing Quality Client Symptoms Social Vocational Jail/ Hospital Stability of Life Satisfaction Functioning Arrests Mueser KT, et al. Schizophr Bull. 1998; 24(1): 37 -74.
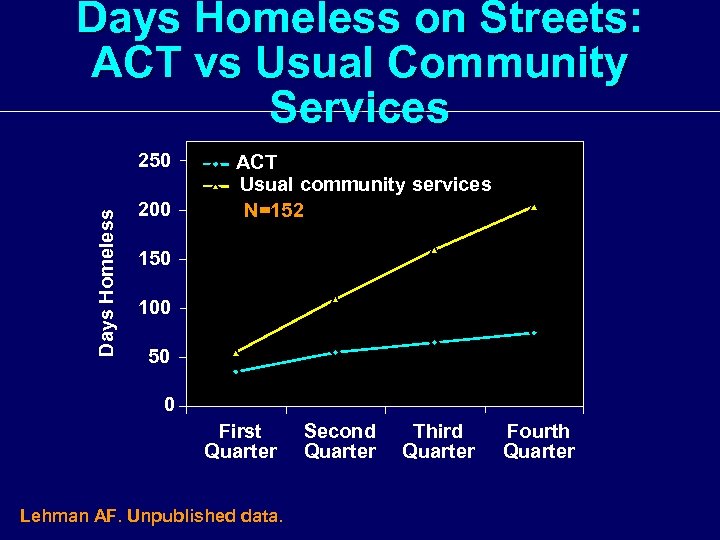
Days Homeless on Streets: ACT vs Usual Community Services Days Homeless 250 200 ACT Usual community services N=152 150 100 50 0 First Quarter Lehman AF. Unpublished data. Second Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter

Current ACT Issues 1. Hospital system changes 2. Quality of usual services 3. Forensic ACT 4. Other expansions and components 5. Transitions

Supported Employment ¨ Focus on competitive work ¨ Rapid job search ¨ De-emphasis on prevocational training and assessment ¨ Attention to client preferences ¨ Follow-along supports as needed

Supported Employment RCTs
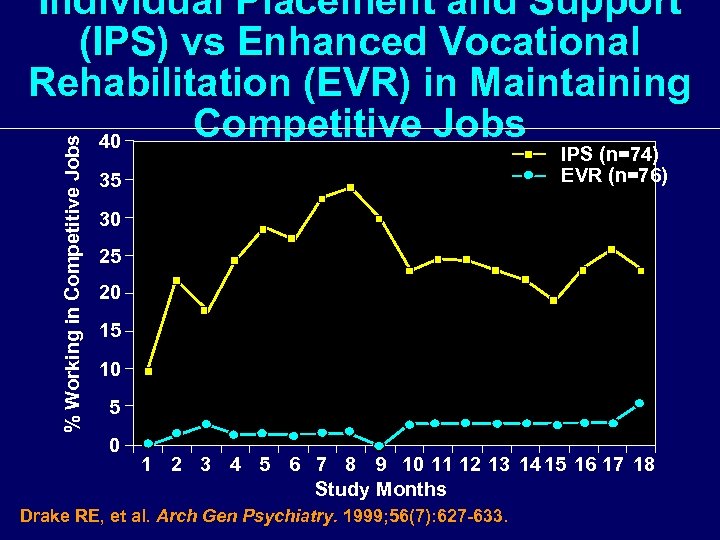
% Working in Competitive Jobs Individual Placement and Support (IPS) vs Enhanced Vocational Rehabilitation (EVR) in Maintaining Competitive Jobs 40 IPS (n=74) EVR (n=76) 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Study Months Drake RE, et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999; 56(7): 627 -633.

Current SE Issues 1. Financing 2. Cognitive strategies 3. Effective specialists 4. Disability reform

Family Psychoeducation ¨ Provided by professionals ¨ Long-term (over 6 months) ¨ Single and multiple family group formats ¨ Focus on education, stress reduction, coping, and other support ¨ Oriented toward future, not past

% Cumulative Relapse Rate Effects of Family Intervention on 2 -Year Relapse Rates (12 Studies) Standard Care (n=203) Single Family Multiple Family Single and Multiple Treatment Group Treatment Family Group (n=231) (n=266) Treatment (n=243) Mueser KT, Glynn SM. Behavioral Family Therapy for Psychiatric Disorders; 1999. Montero I, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2001; 27(4): 661 -670.

Current FPE Issues 1. Effectiveness failure 2. Family-to-family and alternatives

Illness Management Training ¨ Helping people learn to manage their own illnesses ¨ Relapse prevention ¨ Minimize the effects of residual symptoms

Research on Illness Management Components ¨ Psychoeducation increases knowledge and awareness ¨ Behavioral tailoring increases effective use of medications ¨ Warning sign recognition reduces relapses ¨ Cognitive-behavioral treatment reduces residual symptoms
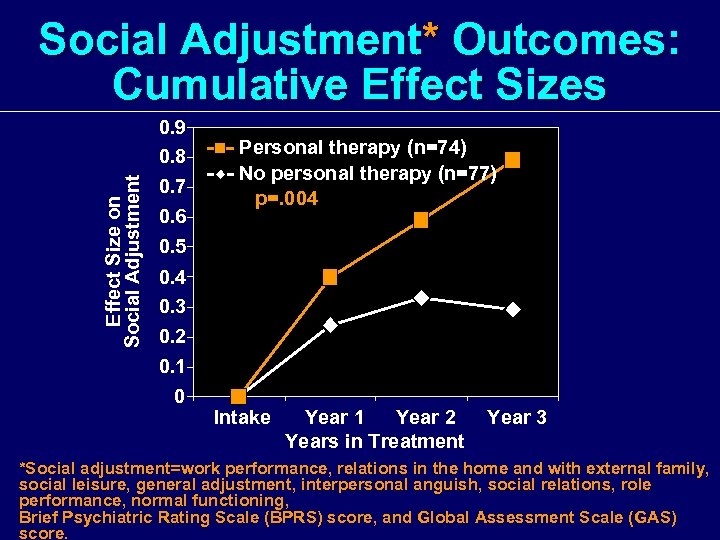
Effect Size on Social Adjustment* Outcomes: Cumulative Effect Sizes 0. 9 0. 8 0. 7 0. 6 0. 5 0. 4 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 Personal therapy (n=74) No personal therapy (n=77) p=. 004 Intake Year 1 Year 2 Years in Treatment Year 3 *Social adjustment=work performance, relations in the home and with external family, social leisure, general adjustment, interpersonal anguish, social relations, role performance, normal functioning, Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) score, and Global Assessment Scale (GAS) score.

Current IMR Issues 1. More research 2. Training 3. Hard outcomes 4. Simplification

Integrated Dual Disorders Treatment ¨ Mental health and substance abuse treatments combined by 1 team • Assertive • Stage-wise • Individualized • Comprehensive • Long-term
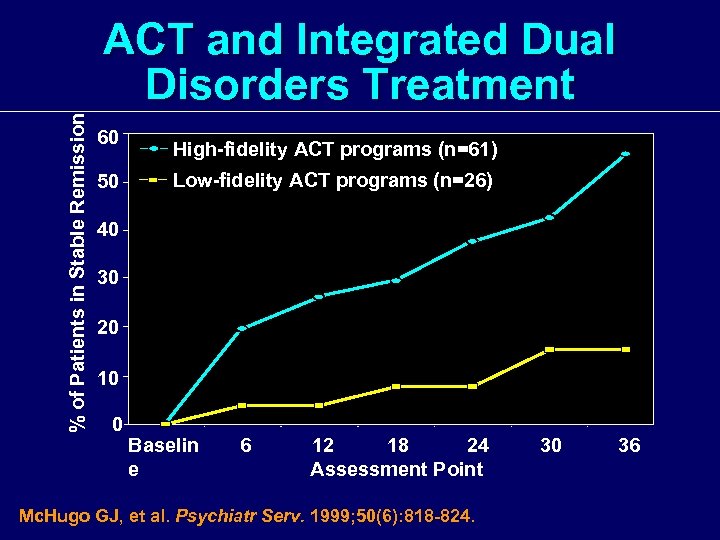
% of Patients in Stable Remission ACT and Integrated Dual Disorders Treatment 60 50 High-fidelity ACT programs (n=61) Low-fidelity ACT programs (n=26) 40 30 20 10 0 Baselin e 6 12 18 24 Assessment Point Mc. Hugo GJ, et al. Psychiatr Serv. 1999; 50(6): 818 -824. 30 36

Current IDDT Issues 1. Standardization 2. Group and residential interventions 3. Supported employment 4. Staging 5. Simplification

Common Features of Evidence. Based Rehabilitation Practices ¨ Shared decision making and choice ¨ Individualization ¨ Skills and supports in the community ¨ Adult roles ¨ Quality of life

Additional Rehabilitation Practices ¨ Social skills training ¨ Supported housing ¨ Supported education ¨ Integrated medical care ¨ Trauma interventions

Dissemination and Implementation ¨ Science to service gap ¨ No simple solution for complex systems ¨ Multiple strategies ¨ Phases of implementation ¨ All stakeholders ¨ Fidelity

National EBP Project ¨ Phase I: conduct reviews, prepare implementation packages (toolkits), and establish state technical assistance centers ¨ Phase II: field tests to refine procedures and resource materials ¨ Phase III: national demonstration


System Changes 1 ¨ Evidence-based medicine ¨ Address 3 components: science, consumer involvement, practitioner skills ¨ Align financing and structures with goals ¨ Integrate treatment and rehabilitation: mental health, substance abuse, vocational rehabilitation, general health, housing, selfhelp, family supports

System Changes 2 ¨ Improve data systems to focus on outcomes and fidelity ¨ Enhance self-management ¨ Electronic records and decision supports: education, assessment, outcomes, decision making ¨ Engineer micro-systems of care ¨ Learning collaboratives ¨ Distance learning

Current Concerns ¨ Fidelity and outcomes ¨ Access and acceptability ¨ Durability ¨ Multi-cultural services ¨ Flexibility ¨ Financing ¨ Organization

Conclusions ¨ Evidence-based rehabilitation interventions are available and will improve rapidly ¨ Implementation requires changes in organization and financing ¨ Flexible, individualized application requires flexible clinicians and organizations

Further Information ¨ Patti O’Brien ¨ Patti. O’Brien@Dartmouth. edu ¨ 603 -448 -0263 ¨ www. mentalhealth. samhsa. gov
9344e58389f54b0e42e6d91093baa6a2.ppt