fc68207ea84614f4f8b40fb725347e8b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66
 Every Major Human Disease Directly Involves Glycans! Gerald W. Hart, Ph. D. De. Lamar Professor & Director Department of Biological Chemistry Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine 725 N. Wolfe St. , Baltimore, MD 21205 -2185 Email: gwhart@jhmi. edu April 6, 2017
Every Major Human Disease Directly Involves Glycans! Gerald W. Hart, Ph. D. De. Lamar Professor & Director Department of Biological Chemistry Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine 725 N. Wolfe St. , Baltimore, MD 21205 -2185 Email: gwhart@jhmi. edu April 6, 2017
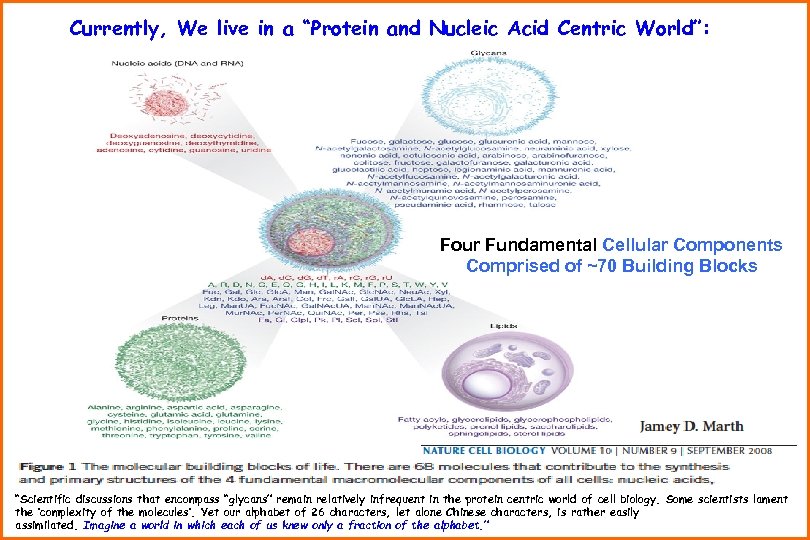 Currently, We live in a “Protein and Nucleic Acid Centric World”: Four Fundamental Cellular Components Comprised of ~70 Building Blocks “Scientific discussions that encompass “glycans” remain relatively infrequent in the protein centric world of cell biology. Some scientists lament the ‘complexity of the molecules’. Yet our alphabet of 26 characters, let alone Chinese characters, is rather easily assimilated. Imagine a world in which each of us knew only a fraction of the alphabet. ”
Currently, We live in a “Protein and Nucleic Acid Centric World”: Four Fundamental Cellular Components Comprised of ~70 Building Blocks “Scientific discussions that encompass “glycans” remain relatively infrequent in the protein centric world of cell biology. Some scientists lament the ‘complexity of the molecules’. Yet our alphabet of 26 characters, let alone Chinese characters, is rather easily assimilated. Imagine a world in which each of us knew only a fraction of the alphabet. ”
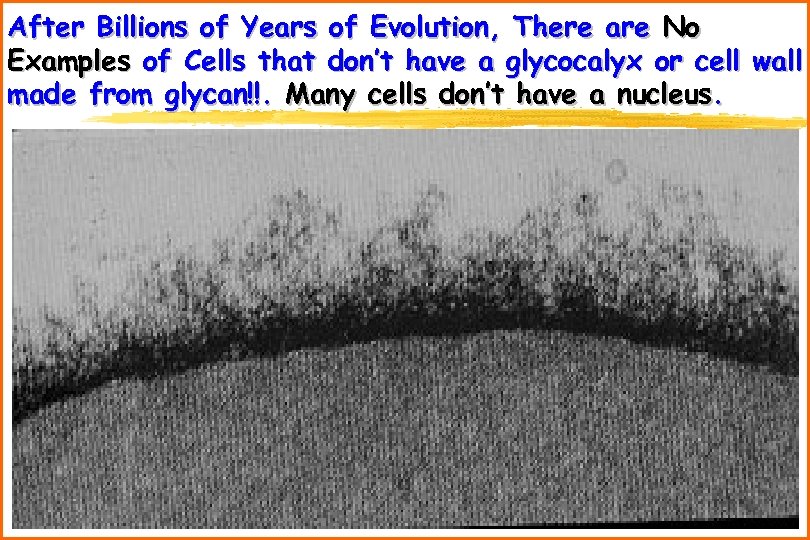 After Billions of Years of Evolution, There are No Examples of Cells that don’t have a glycocalyx or cell wall made from glycan!!. Many cells don’t have a nucleus.
After Billions of Years of Evolution, There are No Examples of Cells that don’t have a glycocalyx or cell wall made from glycan!!. Many cells don’t have a nucleus.
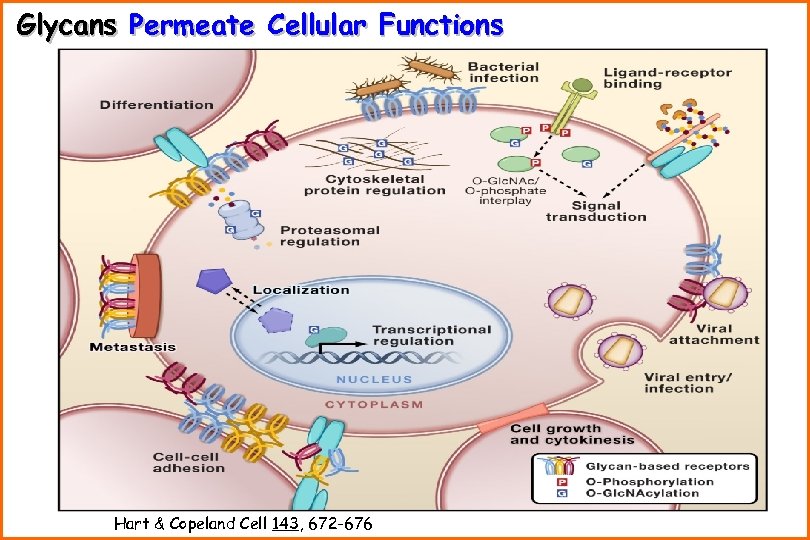 Glycans Permeate Cellular Functions Hart & Copeland Cell 143, 672 -676
Glycans Permeate Cellular Functions Hart & Copeland Cell 143, 672 -676
 NAS Report – Future of Glycosciences - Findings NIH, DOE, FDA, NSF, NIST Health - Glycans are directly involved in the etiology of every major disease. • Knowledge about glycoscience is needed to realize the goals of personalized medicine and to take advantage of the substantial investments in human genome and proteome research and its impact on human health. • Glycans are increasingly important in pharmaceutical development. Sustainability on this Planet Materials Science • Plant cell wall glycan construction and deconstruction, is important to develop nonpetroleum-based sustainable new materials. • Glycan-based materials have wide-ranging uses in areas such as fine chemicals and feedstocks, polymeric materials, and nanomaterials. Energy • Plant cell walls, made mostly of glycans, represent the planet’s dominant source of biological carbon sequestration, or biomass, and a potentially sustainable source of energy. • Overcoming the recalcitrance of plant cell walls to be converted into liquid fuels and other energy sources will be important to achieving a sustainable energy revolution. Complete Report: https: //download. nap. edu/catalog. php? record_id=13446 5
NAS Report – Future of Glycosciences - Findings NIH, DOE, FDA, NSF, NIST Health - Glycans are directly involved in the etiology of every major disease. • Knowledge about glycoscience is needed to realize the goals of personalized medicine and to take advantage of the substantial investments in human genome and proteome research and its impact on human health. • Glycans are increasingly important in pharmaceutical development. Sustainability on this Planet Materials Science • Plant cell wall glycan construction and deconstruction, is important to develop nonpetroleum-based sustainable new materials. • Glycan-based materials have wide-ranging uses in areas such as fine chemicals and feedstocks, polymeric materials, and nanomaterials. Energy • Plant cell walls, made mostly of glycans, represent the planet’s dominant source of biological carbon sequestration, or biomass, and a potentially sustainable source of energy. • Overcoming the recalcitrance of plant cell walls to be converted into liquid fuels and other energy sources will be important to achieving a sustainable energy revolution. Complete Report: https: //download. nap. edu/catalog. php? record_id=13446 5
 Glycans Are Involved in Every Human Disease! u Inflammation, which underlies cellular damage associated with most diseases, is regulated by glycans. u Glycans play an essential role in the regulation of the immune system u Glycans play a direct role in cancer progression and as biomarkers for early detection of cancer u Glycans play a key role in infectious disease and in vaccine development. u Both Intracellular and extracellular glycans underlie molecular mechanisms leading to chronic disease, such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. u Glycans play a critical role in the bioactivity and pharmacokinetics of drugs. u Glycans play a multi-faceted role in cardiovascular disease. u Genetic diseases of glycosylation and inborn errors of glycan metabolism illustrate the critical roles of glycans in human development.
Glycans Are Involved in Every Human Disease! u Inflammation, which underlies cellular damage associated with most diseases, is regulated by glycans. u Glycans play an essential role in the regulation of the immune system u Glycans play a direct role in cancer progression and as biomarkers for early detection of cancer u Glycans play a key role in infectious disease and in vaccine development. u Both Intracellular and extracellular glycans underlie molecular mechanisms leading to chronic disease, such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. u Glycans play a critical role in the bioactivity and pharmacokinetics of drugs. u Glycans play a multi-faceted role in cardiovascular disease. u Genetic diseases of glycosylation and inborn errors of glycan metabolism illustrate the critical roles of glycans in human development.
 Inflammation, which underlies cellular damage associated with most diseases, including infectious disease and metabolic disease, is regulated by glycans.
Inflammation, which underlies cellular damage associated with most diseases, including infectious disease and metabolic disease, is regulated by glycans.
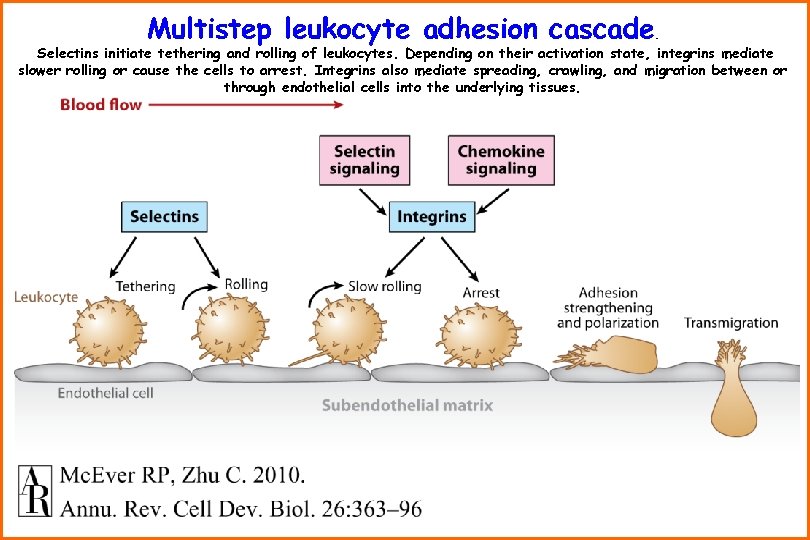 Multistep leukocyte adhesion cascade . Selectins initiate tethering and rolling of leukocytes. Depending on their activation state, integrins mediate slower rolling or cause the cells to arrest. Integrins also mediate spreading, crawling, and migration between or through endothelial cells into the underlying tissues.
Multistep leukocyte adhesion cascade . Selectins initiate tethering and rolling of leukocytes. Depending on their activation state, integrins mediate slower rolling or cause the cells to arrest. Integrins also mediate spreading, crawling, and migration between or through endothelial cells into the underlying tissues.
 Selectins Bind Glycans on Leukocytes to Slow Them Down!
Selectins Bind Glycans on Leukocytes to Slow Them Down!
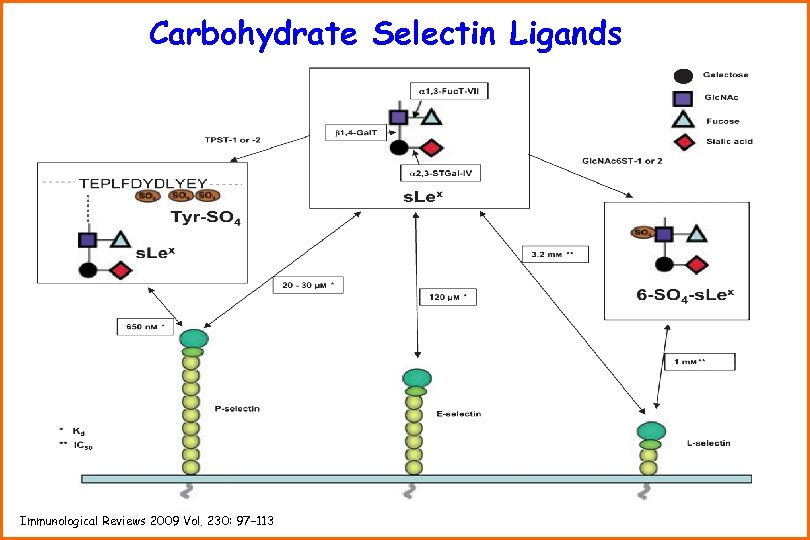 Carbohydrate Selectin Ligands Immunological Reviews 2009 Vol. 230: 97– 113
Carbohydrate Selectin Ligands Immunological Reviews 2009 Vol. 230: 97– 113
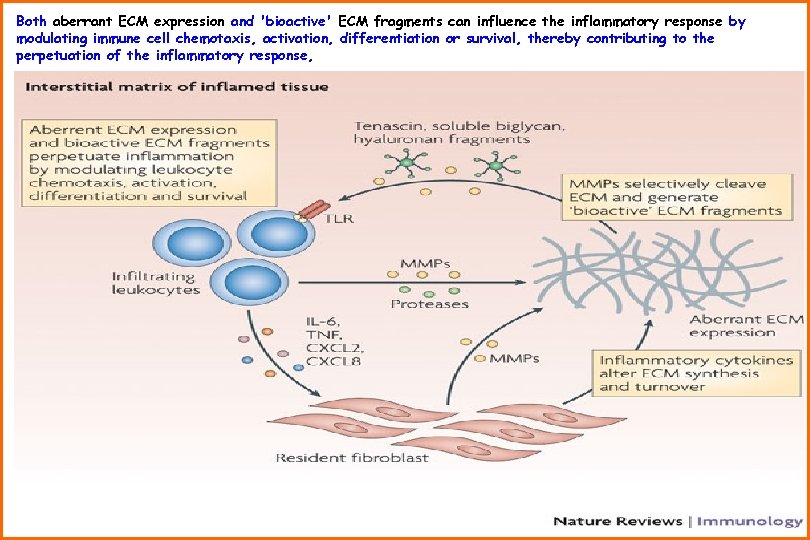 Both aberrant ECM expression and 'bioactive' ECM fragments can influence the inflammatory response by modulating immune cell chemotaxis, activation, differentiation or survival, thereby contributing to the perpetuation of the inflammatory response,
Both aberrant ECM expression and 'bioactive' ECM fragments can influence the inflammatory response by modulating immune cell chemotaxis, activation, differentiation or survival, thereby contributing to the perpetuation of the inflammatory response,
 Glycans play an essential role in the regulation of the immune system, both innate and humoral. In KO Mice for glycosyltransferase, viable animals nearly all have severe immune defects.
Glycans play an essential role in the regulation of the immune system, both innate and humoral. In KO Mice for glycosyltransferase, viable animals nearly all have severe immune defects.
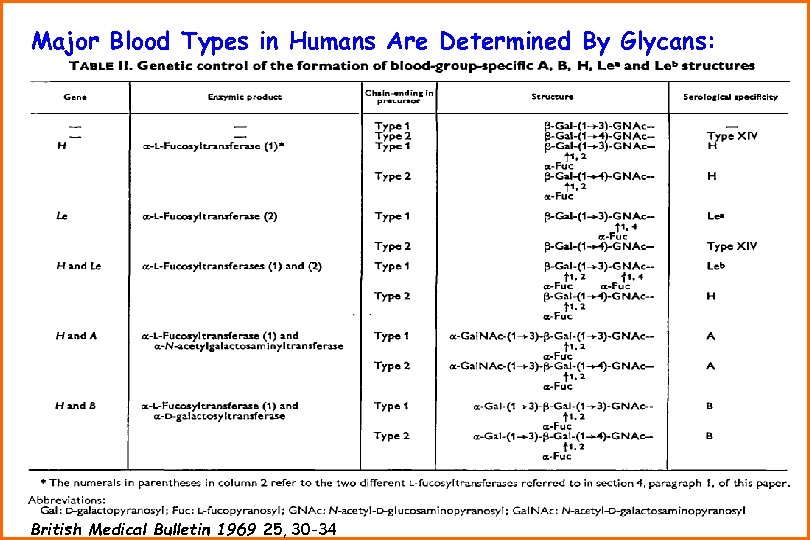 Major Blood Types in Humans Are Determined By Glycans: British Medical Bulletin 1969 25, 30 -34
Major Blood Types in Humans Are Determined By Glycans: British Medical Bulletin 1969 25, 30 -34
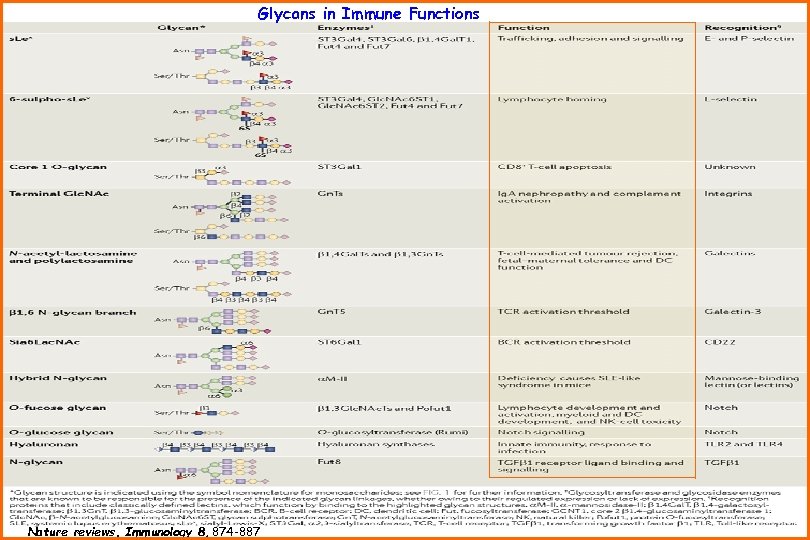 Glycans in Immune Functions Nature reviews. Immunology 8, 874 -887
Glycans in Immune Functions Nature reviews. Immunology 8, 874 -887
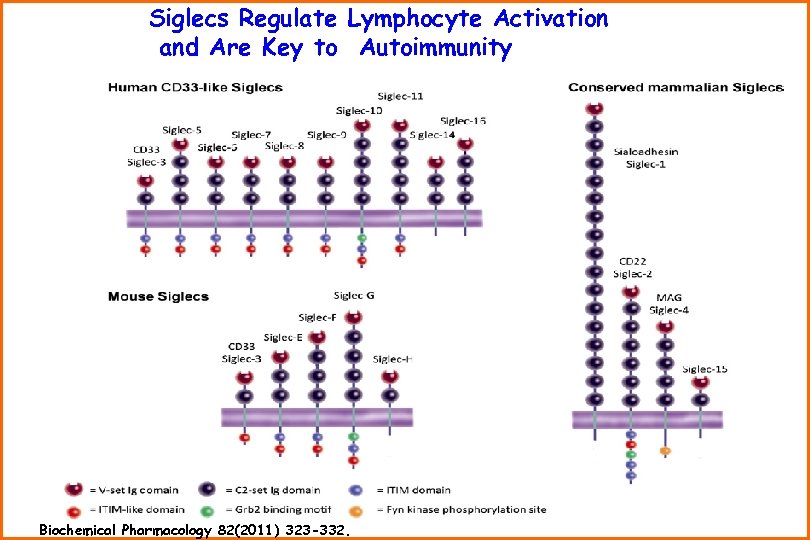 Siglecs Regulate Lymphocyte Activation and Are Key to Autoimmunity Biochemical Pharmacology 82(2011) 323 -332.
Siglecs Regulate Lymphocyte Activation and Are Key to Autoimmunity Biochemical Pharmacology 82(2011) 323 -332.
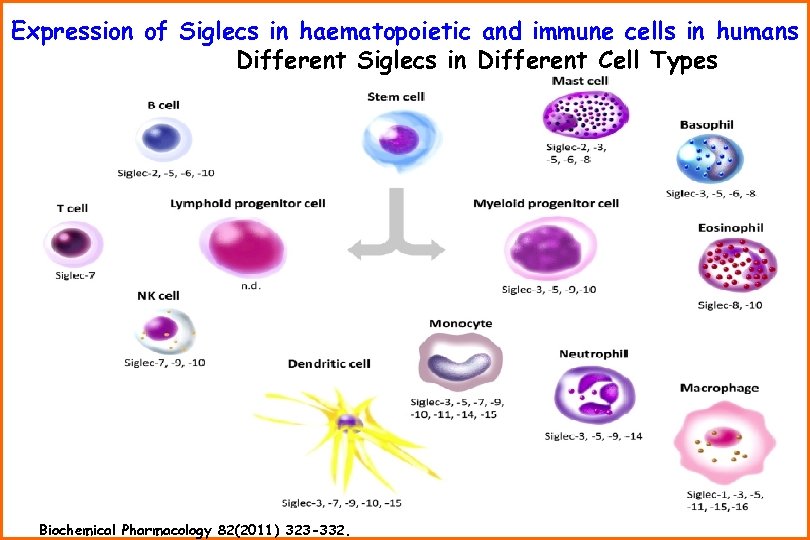 Expression of Siglecs in haematopoietic and immune cells in humans Different Siglecs in Different Cell Types Biochemical Pharmacology 82(2011) 323 -332.
Expression of Siglecs in haematopoietic and immune cells in humans Different Siglecs in Different Cell Types Biochemical Pharmacology 82(2011) 323 -332.
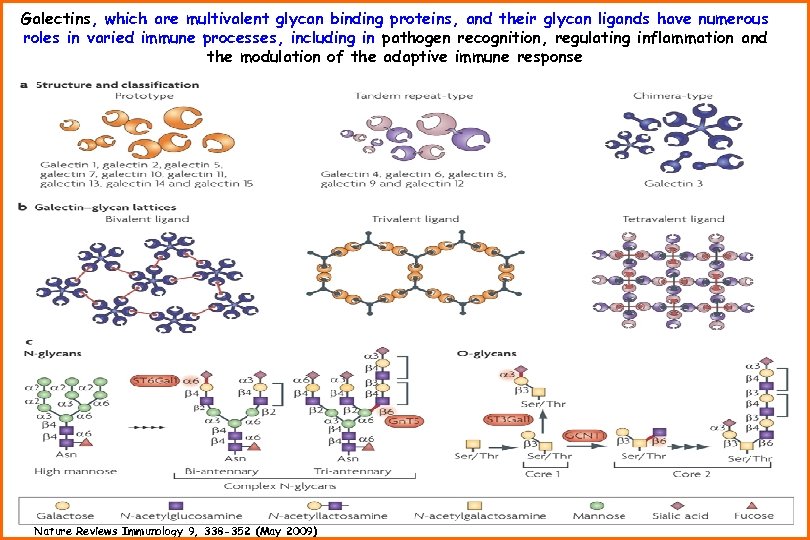 Galectins, which are multivalent glycan binding proteins, and their glycan ligands have numerous roles in varied immune processes, including in pathogen recognition, regulating inflammation and the modulation of the adaptive immune response Nature Reviews Immunology 9, 338 -352 (May 2009)
Galectins, which are multivalent glycan binding proteins, and their glycan ligands have numerous roles in varied immune processes, including in pathogen recognition, regulating inflammation and the modulation of the adaptive immune response Nature Reviews Immunology 9, 338 -352 (May 2009)
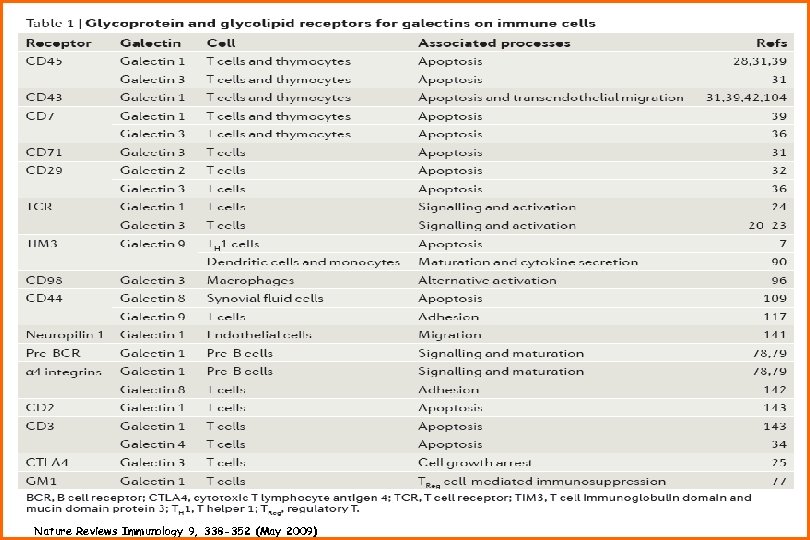 Nature Reviews Immunology 9, 338 -352 (May 2009)
Nature Reviews Immunology 9, 338 -352 (May 2009)
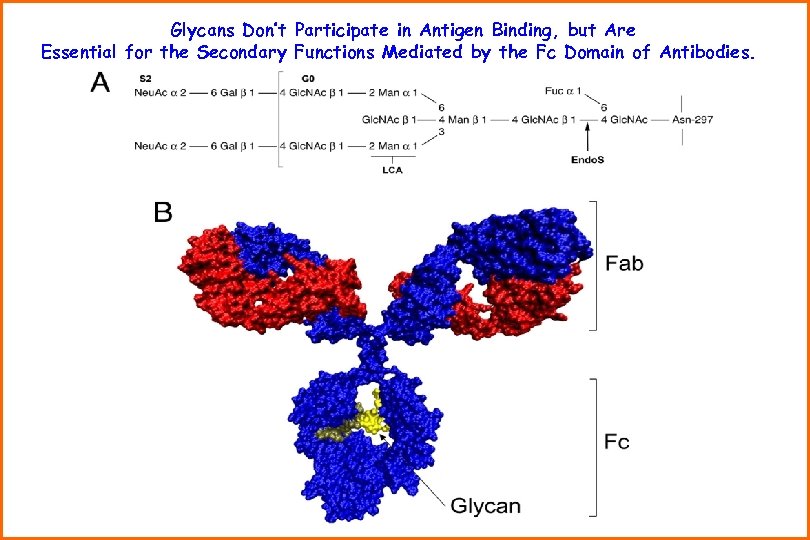 Glycans Don’t Participate in Antigen Binding, but Are Essential for the Secondary Functions Mediated by the Fc Domain of Antibodies.
Glycans Don’t Participate in Antigen Binding, but Are Essential for the Secondary Functions Mediated by the Fc Domain of Antibodies.
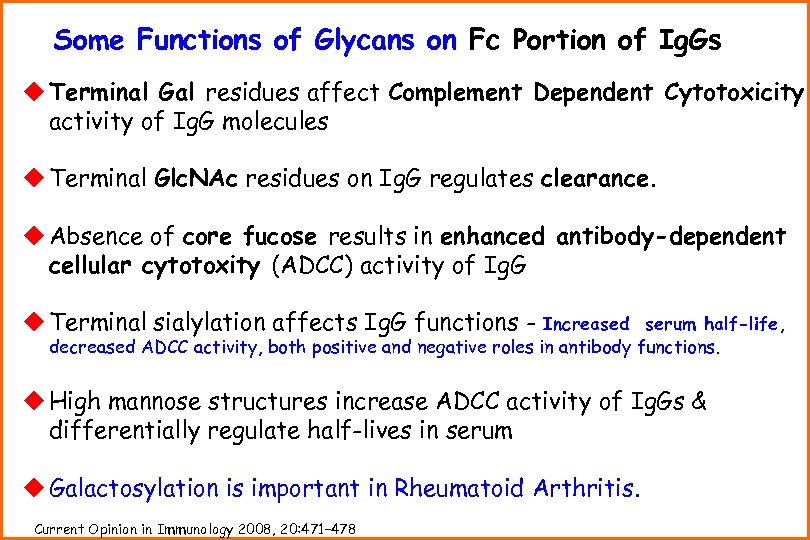 Some Functions of Glycans on Fc Portion of Ig. Gs u Terminal Gal residues affect Complement Dependent Cytotoxicity activity of Ig. G molecules u Terminal Glc. NAc residues on Ig. G regulates clearance. u Absence of core fucose results in enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxity (ADCC) activity of Ig. G u Terminal sialylation affects Ig. G functions - Increased serum half-life, decreased ADCC activity, both positive and negative roles in antibody functions. u High mannose structures increase ADCC activity of Ig. Gs & differentially regulate half-lives in serum u Galactosylation is important in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Current Opinion in Immunology 2008, 20: 471– 478
Some Functions of Glycans on Fc Portion of Ig. Gs u Terminal Gal residues affect Complement Dependent Cytotoxicity activity of Ig. G molecules u Terminal Glc. NAc residues on Ig. G regulates clearance. u Absence of core fucose results in enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxity (ADCC) activity of Ig. G u Terminal sialylation affects Ig. G functions - Increased serum half-life, decreased ADCC activity, both positive and negative roles in antibody functions. u High mannose structures increase ADCC activity of Ig. Gs & differentially regulate half-lives in serum u Galactosylation is important in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Current Opinion in Immunology 2008, 20: 471– 478
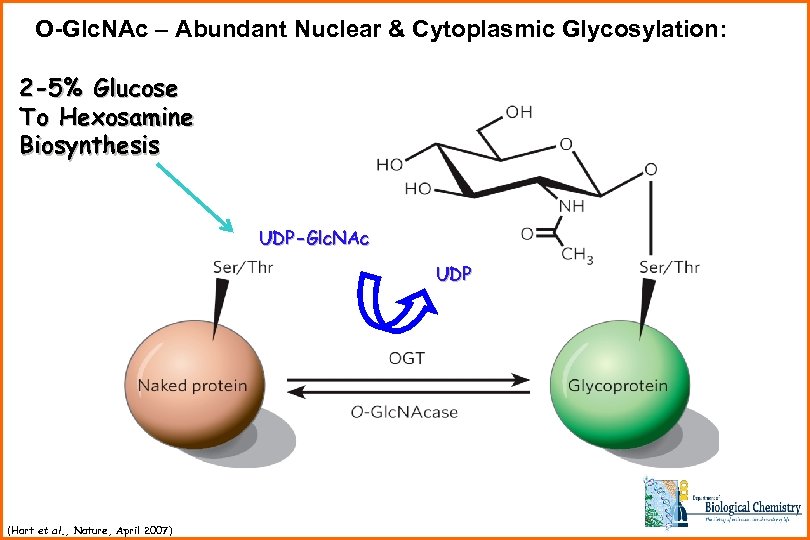 O-Glc. NAc – Abundant Nuclear & Cytoplasmic Glycosylation: 2 -5% Glucose To Hexosamine Biosynthesis UDP-Glc. NAc UDP (Hart et al. , Nature, April 2007)
O-Glc. NAc – Abundant Nuclear & Cytoplasmic Glycosylation: 2 -5% Glucose To Hexosamine Biosynthesis UDP-Glc. NAc UDP (Hart et al. , Nature, April 2007)
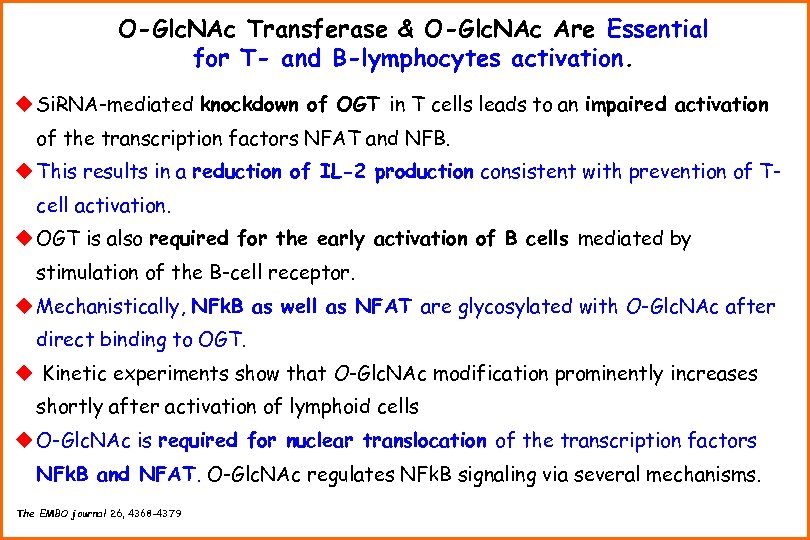 O-Glc. NAc Transferase & O-Glc. NAc Are Essential for T- and B-lymphocytes activation. u Si. RNA-mediated knockdown of OGT in T cells leads to an impaired activation of the transcription factors NFAT and NFB. u This results in a reduction of IL-2 production consistent with prevention of Tcell activation. u OGT is also required for the early activation of B cells mediated by stimulation of the B-cell receptor. u Mechanistically, NFk. B as well as NFAT are glycosylated with O-Glc. NAc after direct binding to OGT. u Kinetic experiments show that O-Glc. NAc modification prominently increases shortly after activation of lymphoid cells u O-Glc. NAc is required for nuclear translocation of the transcription factors NFk. B and NFAT. O-Glc. NAc regulates NFk. B signaling via several mechanisms. The EMBO journal 26, 4368 -4379
O-Glc. NAc Transferase & O-Glc. NAc Are Essential for T- and B-lymphocytes activation. u Si. RNA-mediated knockdown of OGT in T cells leads to an impaired activation of the transcription factors NFAT and NFB. u This results in a reduction of IL-2 production consistent with prevention of Tcell activation. u OGT is also required for the early activation of B cells mediated by stimulation of the B-cell receptor. u Mechanistically, NFk. B as well as NFAT are glycosylated with O-Glc. NAc after direct binding to OGT. u Kinetic experiments show that O-Glc. NAc modification prominently increases shortly after activation of lymphoid cells u O-Glc. NAc is required for nuclear translocation of the transcription factors NFk. B and NFAT. O-Glc. NAc regulates NFk. B signaling via several mechanisms. The EMBO journal 26, 4368 -4379
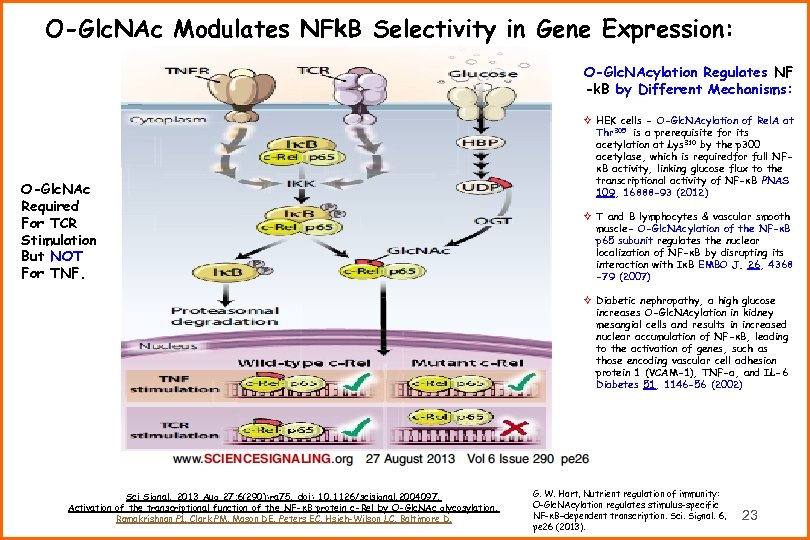 O-Glc. NAc Modulates NFk. B Selectivity in Gene Expression: O-Glc. NAcylation Regulates NF -k. B by Different Mechanisms: O-Glc. NAc Required For TCR Stimulation But NOT For TNF. Sci Signal. 2013 Aug 27; 6(290): ra 75. doi: 10. 1126/scisignal. 2004097. Activation of the transcriptional function of the NF-κB protein c-Rel by O-Glc. NAc glycosylation. Ramakrishnan P 1, Clark PM, Mason DE, Peters EC, Hsieh-Wilson LC, Baltimore D. ² HEK cells - O-Glc. NAcylation of Rel. A at Thr 305 is a prerequisite for its acetylation at Lys 310 by the p 300 acetylase, which is requiredfor full NFκB activity, linking glucose flux to the transcriptional activity of NF-κB PNAS 109, 16888 -93 (2012) ² T and B lymphocytes & vascular smooth muscle- O-Glc. NAcylation of the NF-κB p 65 subunit regulates the nuclear localization of NF-κB by disrupting its interaction with IκB EMBO J. 26, 4368 -79 (2007) ² Diabetic nephropathy, a high glucose increases O-Glc. NAcylation in kidney mesangial cells and results in increased nuclear accumulation of NF-κB, leading to the activation of genes, such as those encoding vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM-1), TNF-α, and IL-6 Diabetes 51, 1146 -56 (2002) G. W. Hart, Nutrient regulation of immunity: O-Glc. NAcylation regulates stimulus-specific NF-κB–dependent transcription. Sci. Signal. 6, pe 26 (2013). 23
O-Glc. NAc Modulates NFk. B Selectivity in Gene Expression: O-Glc. NAcylation Regulates NF -k. B by Different Mechanisms: O-Glc. NAc Required For TCR Stimulation But NOT For TNF. Sci Signal. 2013 Aug 27; 6(290): ra 75. doi: 10. 1126/scisignal. 2004097. Activation of the transcriptional function of the NF-κB protein c-Rel by O-Glc. NAc glycosylation. Ramakrishnan P 1, Clark PM, Mason DE, Peters EC, Hsieh-Wilson LC, Baltimore D. ² HEK cells - O-Glc. NAcylation of Rel. A at Thr 305 is a prerequisite for its acetylation at Lys 310 by the p 300 acetylase, which is requiredfor full NFκB activity, linking glucose flux to the transcriptional activity of NF-κB PNAS 109, 16888 -93 (2012) ² T and B lymphocytes & vascular smooth muscle- O-Glc. NAcylation of the NF-κB p 65 subunit regulates the nuclear localization of NF-κB by disrupting its interaction with IκB EMBO J. 26, 4368 -79 (2007) ² Diabetic nephropathy, a high glucose increases O-Glc. NAcylation in kidney mesangial cells and results in increased nuclear accumulation of NF-κB, leading to the activation of genes, such as those encoding vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM-1), TNF-α, and IL-6 Diabetes 51, 1146 -56 (2002) G. W. Hart, Nutrient regulation of immunity: O-Glc. NAcylation regulates stimulus-specific NF-κB–dependent transcription. Sci. Signal. 6, pe 26 (2013). 23
 Glycans play a direct role in cancer progression and as biomarkers for early detection of cancer
Glycans play a direct role in cancer progression and as biomarkers for early detection of cancer
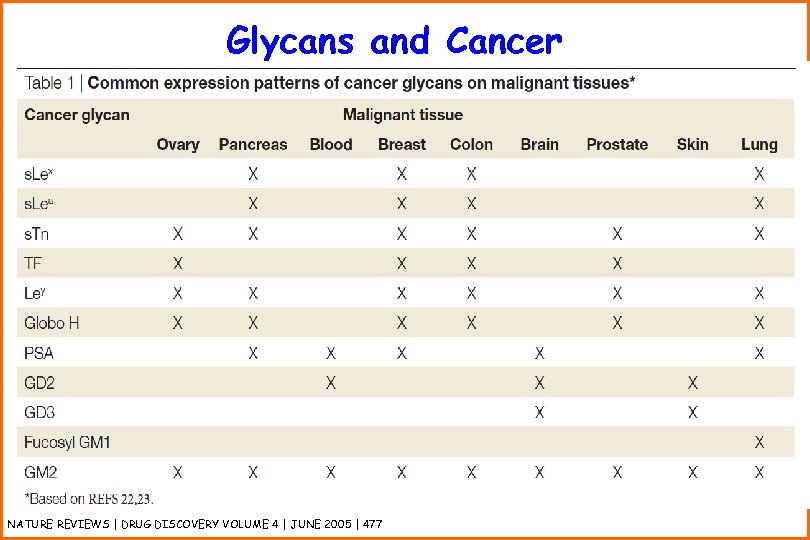 Glycans and Cancer NATURE REVIEWS | DRUG DISCOVERY VOLUME 4 | JUNE 2005 | 477
Glycans and Cancer NATURE REVIEWS | DRUG DISCOVERY VOLUME 4 | JUNE 2005 | 477
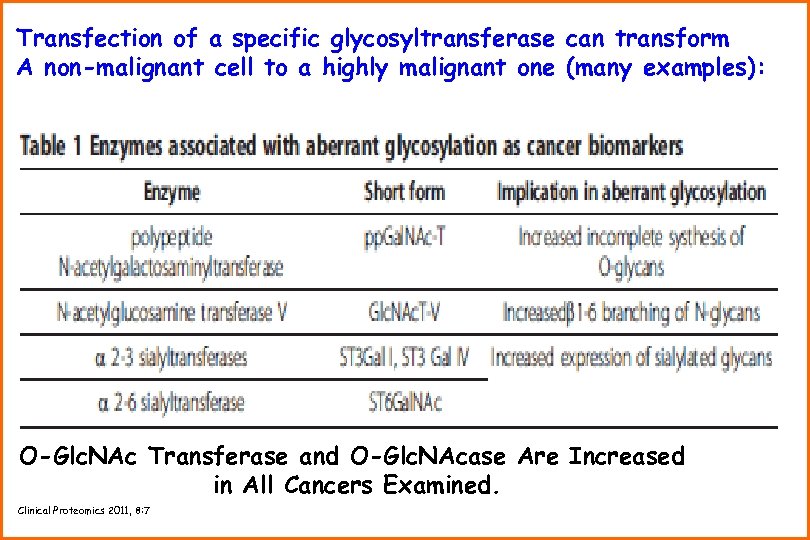 Transfection of a specific glycosyltransferase can transform A non-malignant cell to a highly malignant one (many examples): O-Glc. NAc Transferase and O-Glc. NAcase Are Increased in All Cancers Examined. Clinical Proteomics 2011, 8: 7
Transfection of a specific glycosyltransferase can transform A non-malignant cell to a highly malignant one (many examples): O-Glc. NAc Transferase and O-Glc. NAcase Are Increased in All Cancers Examined. Clinical Proteomics 2011, 8: 7
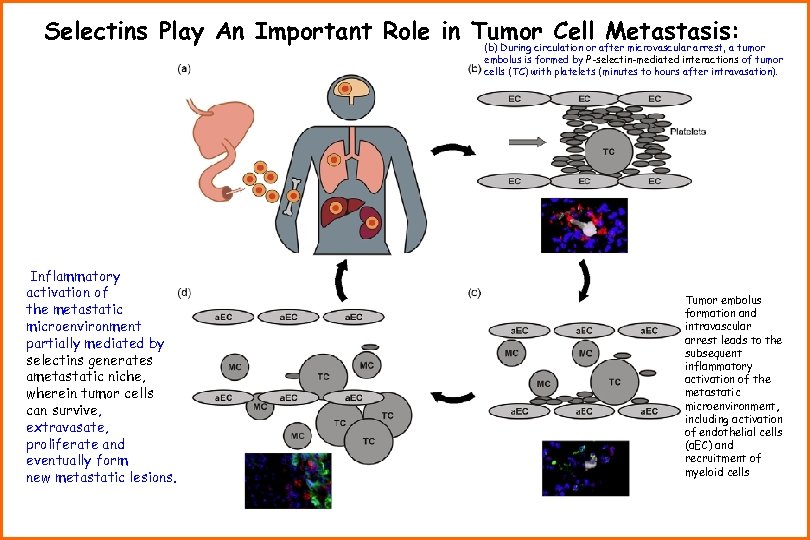 Selectins Play An Important Role in Tumor Cell Metastasis: (b) During circulation or after microvascular arrest, a tumor embolus is formed by P-selectin-mediated interactions of tumor cells (TC) with platelets (minutes to hours after intravasation). Inflammatory activation of the metastatic microenvironment partially mediated by selectins generates ametastatic niche, wherein tumor cells can survive, extravasate, proliferate and eventually form new metastatic lesions. Tumor embolus formation and intravascular arrest leads to the subsequent inflammatory activation of the metastatic microenvironment, including activation of endothelial cells (a. EC) and recruitment of myeloid cells
Selectins Play An Important Role in Tumor Cell Metastasis: (b) During circulation or after microvascular arrest, a tumor embolus is formed by P-selectin-mediated interactions of tumor cells (TC) with platelets (minutes to hours after intravasation). Inflammatory activation of the metastatic microenvironment partially mediated by selectins generates ametastatic niche, wherein tumor cells can survive, extravasate, proliferate and eventually form new metastatic lesions. Tumor embolus formation and intravascular arrest leads to the subsequent inflammatory activation of the metastatic microenvironment, including activation of endothelial cells (a. EC) and recruitment of myeloid cells
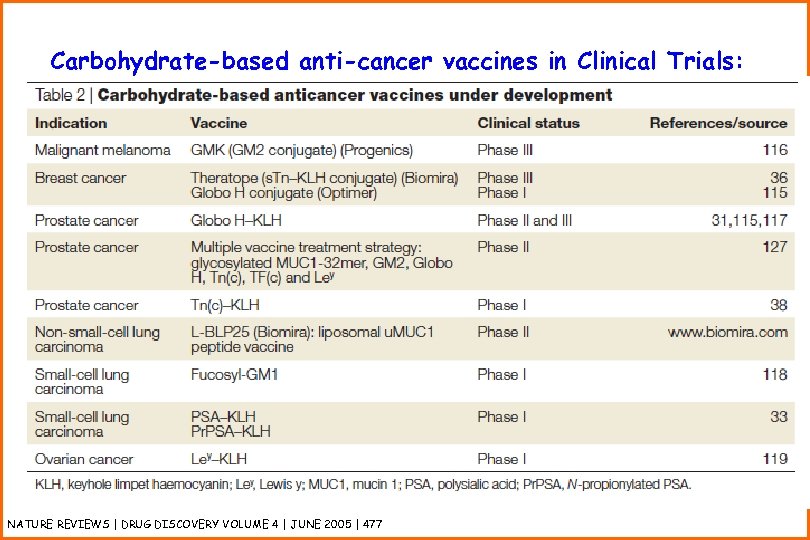 Carbohydrate-based anti-cancer vaccines in Clinical Trials: NATURE REVIEWS | DRUG DISCOVERY VOLUME 4 | JUNE 2005 | 477
Carbohydrate-based anti-cancer vaccines in Clinical Trials: NATURE REVIEWS | DRUG DISCOVERY VOLUME 4 | JUNE 2005 | 477
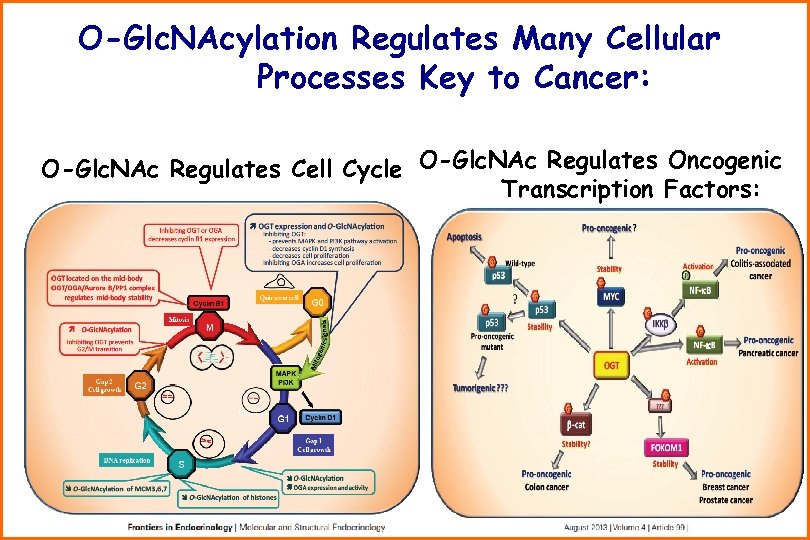 O-Glc. NAcylation Regulates Many Cellular Processes Key to Cancer: O-Glc. NAc Regulates Cell Cycle O-Glc. NAc Regulates Oncogenic Transcription Factors:
O-Glc. NAcylation Regulates Many Cellular Processes Key to Cancer: O-Glc. NAc Regulates Cell Cycle O-Glc. NAc Regulates Oncogenic Transcription Factors:
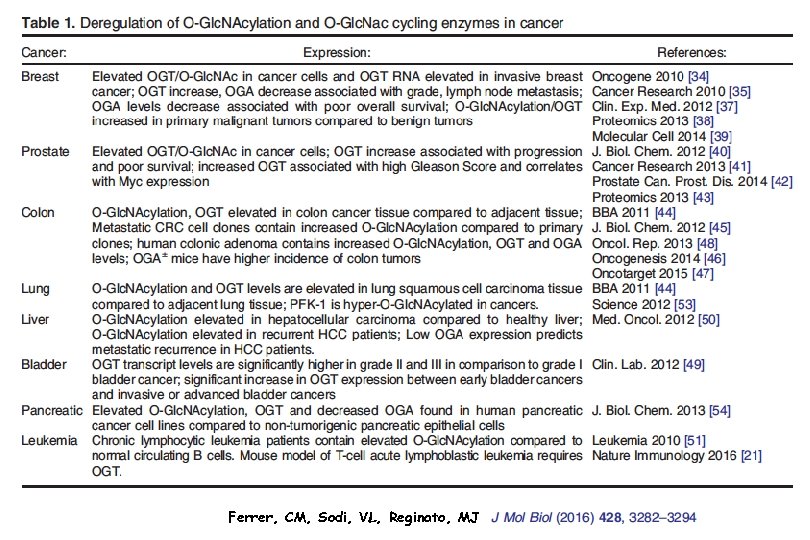 Ferrer, CM, Sodi, VL, Reginato, MJ 30
Ferrer, CM, Sodi, VL, Reginato, MJ 30
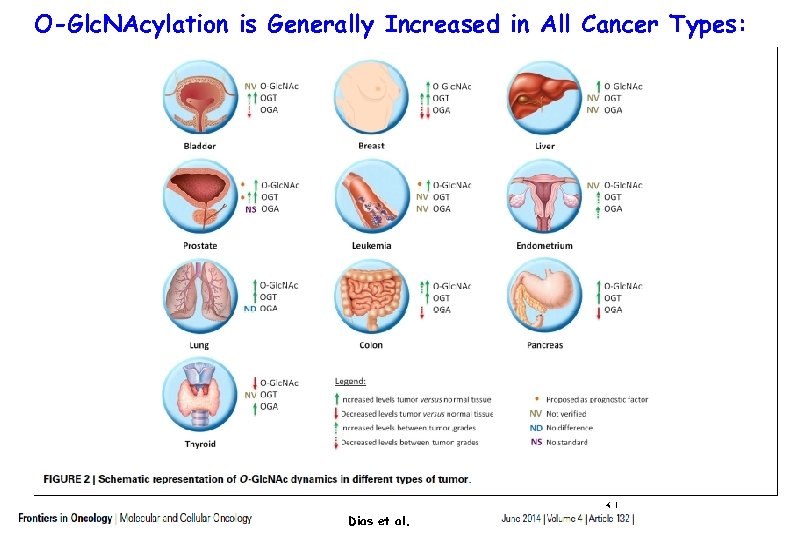 O-Glc. NAcylation is Generally Increased in All Cancer Types: Dias et al. 31
O-Glc. NAcylation is Generally Increased in All Cancer Types: Dias et al. 31
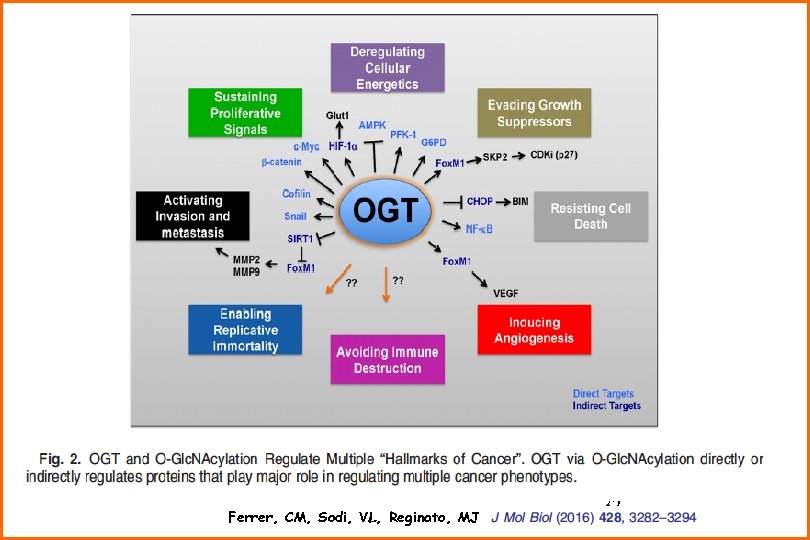 Ferrer, CM, Sodi, VL, Reginato, MJ 32
Ferrer, CM, Sodi, VL, Reginato, MJ 32
 Reviews On O-Glc. NAcylation and Cancer Р~85 papers 1: Ferrer CM, Sodi VL, Reginato MJ. O-Glc. NAcylation in Cancer Biology: Linking Metabolism and Signaling. J Mol Biol. 2016 Aug 14; 428(16): 3282 -94. 2: Taparra K, Tran PT, Zachara NE. Hijacking the Hexosamine Biosynthetic Pathway to Promote EMT-Mediated Neoplastic Phenotypes. Front Oncol. 2016 Apr 18; 6: 85. 3: Singh JP, Zhang K, Wu J, Yang X. O-Glc. NAc signaling in cancer metabolism and epigenetics. Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28; 356(2 Pt A): 244 -50. 4: Ma Z, Vosseller K. Cancer metabolism and elevated O-Glc. NAc in oncogenic signaling. J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 12; 289(50): 3445765. 5: Forma E, Jóźwiak P, Bryś M, Krześlak A. The potential role of O-Glc. NAc modification in cancer epigenetics. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2014 Sep; 19(3) 438 -60. 6: Li Z, Yi W. Regulation of cancer metabolism by O-Glc. NAcylation. Glycoconj J. 2014 Apr; 31(3): 185 -91. 7: Chaiyawat P, Netsirisawan P, Svasti J, Champattanachai V. Aberrant O-Glc. NAcylated Proteins: New Perspectives in Breast and Colorectal Cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Nov 11; 5: 193. 8: Jóźwiak P, Forma E, Bryś M, Krześlak A. O-Glc. NAcylation and Metabolic Reprograming in Cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Sep 9; 5: 145. 9: de Queiroz RM, Carvalho E, Dias WB. O-Glc. NAcylation: The Sweet Side of the Cancer. Front Oncol. 2014 Jun 3; 4: 132. 10: Ma Z, Vosseller K. O-Glc. NAc in cancer biology. Amino Acids. 2013 Oct; 45(4): 719 -33. 11: Slawson C, Copeland RJ, Hart GW. O-Glc. NAc signaling: a metabolic link between diabetes and cancer? Trends Biochem Sci. 2010 Oct; 35(10): 547 -55. 33 12: Chou TY, Hart GW. O-linked N-acetylglucosamine and cancer: messages from the glycosylation of c-Myc. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001; 491: 413 -8.
Reviews On O-Glc. NAcylation and Cancer Р~85 papers 1: Ferrer CM, Sodi VL, Reginato MJ. O-Glc. NAcylation in Cancer Biology: Linking Metabolism and Signaling. J Mol Biol. 2016 Aug 14; 428(16): 3282 -94. 2: Taparra K, Tran PT, Zachara NE. Hijacking the Hexosamine Biosynthetic Pathway to Promote EMT-Mediated Neoplastic Phenotypes. Front Oncol. 2016 Apr 18; 6: 85. 3: Singh JP, Zhang K, Wu J, Yang X. O-Glc. NAc signaling in cancer metabolism and epigenetics. Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28; 356(2 Pt A): 244 -50. 4: Ma Z, Vosseller K. Cancer metabolism and elevated O-Glc. NAc in oncogenic signaling. J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 12; 289(50): 3445765. 5: Forma E, Jóźwiak P, Bryś M, Krześlak A. The potential role of O-Glc. NAc modification in cancer epigenetics. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2014 Sep; 19(3) 438 -60. 6: Li Z, Yi W. Regulation of cancer metabolism by O-Glc. NAcylation. Glycoconj J. 2014 Apr; 31(3): 185 -91. 7: Chaiyawat P, Netsirisawan P, Svasti J, Champattanachai V. Aberrant O-Glc. NAcylated Proteins: New Perspectives in Breast and Colorectal Cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Nov 11; 5: 193. 8: Jóźwiak P, Forma E, Bryś M, Krześlak A. O-Glc. NAcylation and Metabolic Reprograming in Cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Sep 9; 5: 145. 9: de Queiroz RM, Carvalho E, Dias WB. O-Glc. NAcylation: The Sweet Side of the Cancer. Front Oncol. 2014 Jun 3; 4: 132. 10: Ma Z, Vosseller K. O-Glc. NAc in cancer biology. Amino Acids. 2013 Oct; 45(4): 719 -33. 11: Slawson C, Copeland RJ, Hart GW. O-Glc. NAc signaling: a metabolic link between diabetes and cancer? Trends Biochem Sci. 2010 Oct; 35(10): 547 -55. 33 12: Chou TY, Hart GW. O-linked N-acetylglucosamine and cancer: messages from the glycosylation of c-Myc. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001; 491: 413 -8.
 Glycans play a key role in infectious disease and in vaccine development.
Glycans play a key role in infectious disease and in vaccine development.
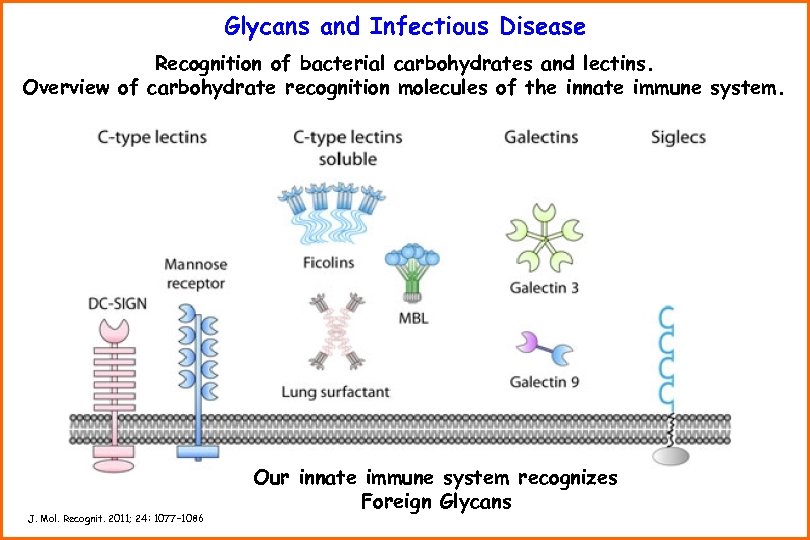 Glycans and Infectious Disease Recognition of bacterial carbohydrates and lectins. Overview of carbohydrate recognition molecules of the innate immune system. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011; 24: 1077– 1086 Our innate immune system recognizes Foreign Glycans
Glycans and Infectious Disease Recognition of bacterial carbohydrates and lectins. Overview of carbohydrate recognition molecules of the innate immune system. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011; 24: 1077– 1086 Our innate immune system recognizes Foreign Glycans
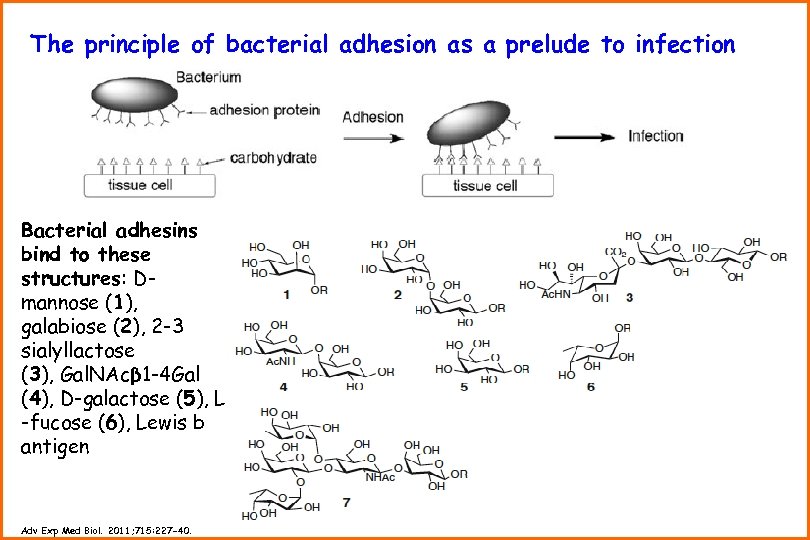 The principle of bacterial adhesion as a prelude to infection Bacterial adhesins bind to these structures: Dmannose (1), galabiose (2), 2 -3 sialyllactose (3), Gal. NAcβ 1 -4 Gal (4), D-galactose (5), L -fucose (6), Lewis b antigen Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011; 715: 227 -40.
The principle of bacterial adhesion as a prelude to infection Bacterial adhesins bind to these structures: Dmannose (1), galabiose (2), 2 -3 sialyllactose (3), Gal. NAcβ 1 -4 Gal (4), D-galactose (5), L -fucose (6), Lewis b antigen Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011; 715: 227 -40.
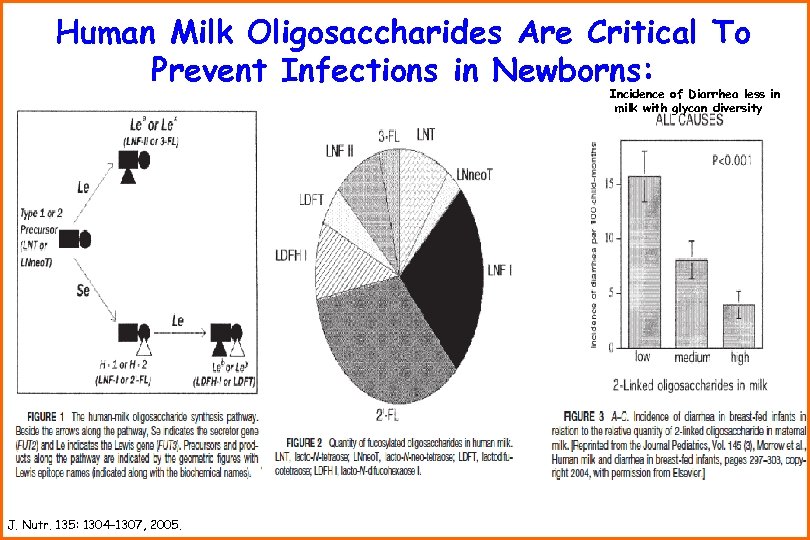 Human Milk Oligosaccharides Are Critical To Prevent Infections in Newborns: Incidence of Diarrhea less in milk with glycan diversity J. Nutr. 135: 1304– 1307, 2005.
Human Milk Oligosaccharides Are Critical To Prevent Infections in Newborns: Incidence of Diarrhea less in milk with glycan diversity J. Nutr. 135: 1304– 1307, 2005.
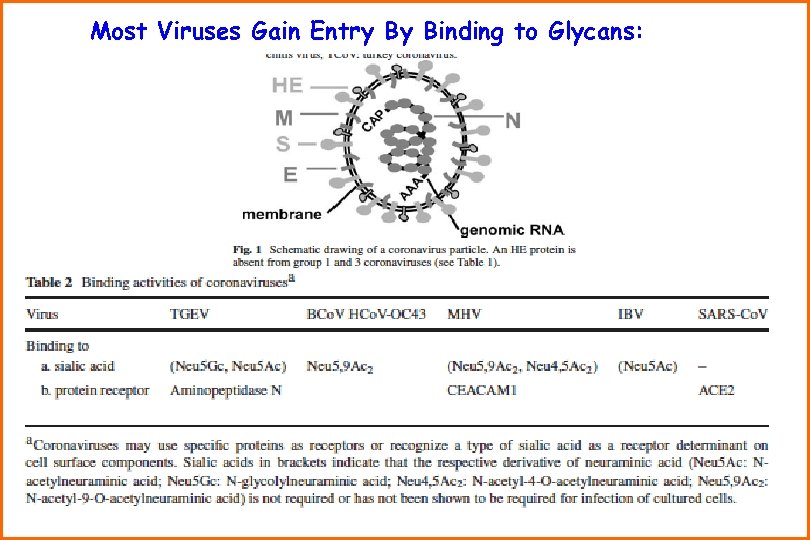 Most Viruses Gain Entry By Binding to Glycans:
Most Viruses Gain Entry By Binding to Glycans:
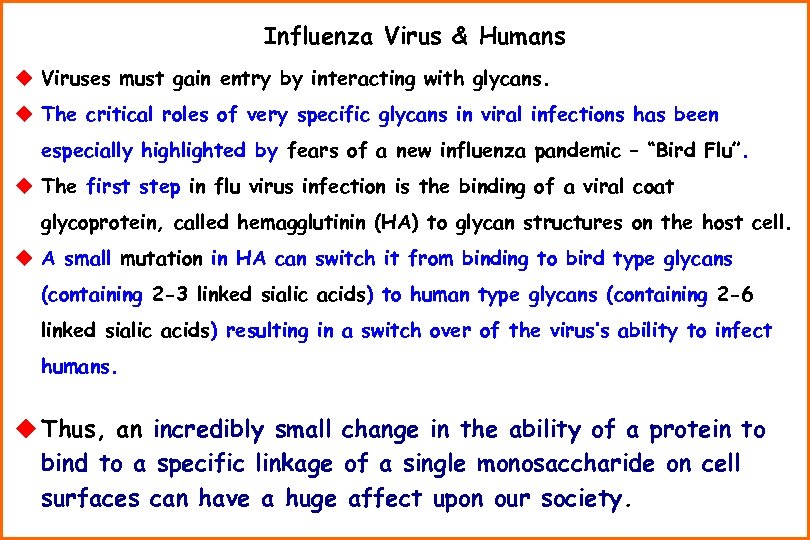 Influenza Virus & Humans u Viruses must gain entry by interacting with glycans. u The critical roles of very specific glycans in viral infections has been especially highlighted by fears of a new influenza pandemic – “Bird Flu”. u The first step in flu virus infection is the binding of a viral coat glycoprotein, called hemagglutinin (HA) to glycan structures on the host cell. u A small mutation in HA can switch it from binding to bird type glycans (containing 2 -3 linked sialic acids) to human type glycans (containing 2 -6 linked sialic acids) resulting in a switch over of the virus’s ability to infect humans. u Thus, an incredibly small change in the ability of a protein to bind to a specific linkage of a single monosaccharide on cell surfaces can have a huge affect upon our society.
Influenza Virus & Humans u Viruses must gain entry by interacting with glycans. u The critical roles of very specific glycans in viral infections has been especially highlighted by fears of a new influenza pandemic – “Bird Flu”. u The first step in flu virus infection is the binding of a viral coat glycoprotein, called hemagglutinin (HA) to glycan structures on the host cell. u A small mutation in HA can switch it from binding to bird type glycans (containing 2 -3 linked sialic acids) to human type glycans (containing 2 -6 linked sialic acids) resulting in a switch over of the virus’s ability to infect humans. u Thus, an incredibly small change in the ability of a protein to bind to a specific linkage of a single monosaccharide on cell surfaces can have a huge affect upon our society.
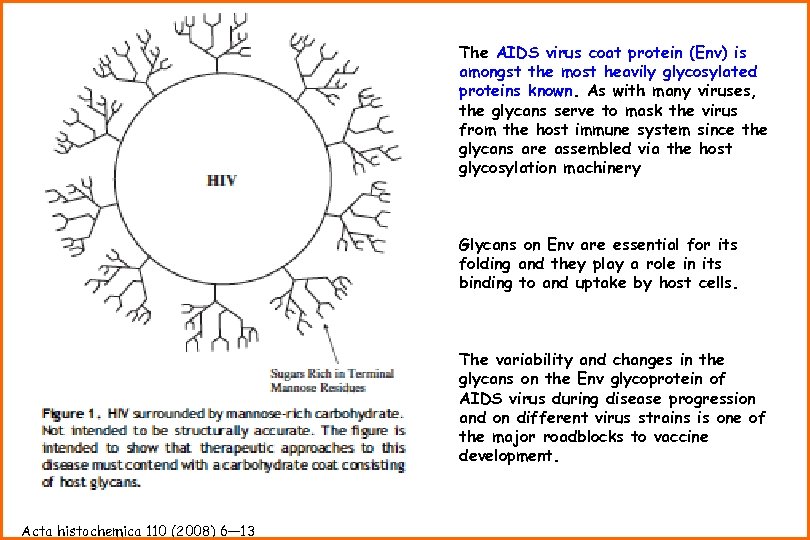 The AIDS virus coat protein (Env) is amongst the most heavily glycosylated proteins known. As with many viruses, the glycans serve to mask the virus from the host immune system since the glycans are assembled via the host glycosylation machinery Glycans on Env are essential for its folding and they play a role in its binding to and uptake by host cells. The variability and changes in the glycans on the Env glycoprotein of AIDS virus during disease progression and on different virus strains is one of the major roadblocks to vaccine development. Acta histochemica 110 (2008) 6— 13
The AIDS virus coat protein (Env) is amongst the most heavily glycosylated proteins known. As with many viruses, the glycans serve to mask the virus from the host immune system since the glycans are assembled via the host glycosylation machinery Glycans on Env are essential for its folding and they play a role in its binding to and uptake by host cells. The variability and changes in the glycans on the Env glycoprotein of AIDS virus during disease progression and on different virus strains is one of the major roadblocks to vaccine development. Acta histochemica 110 (2008) 6— 13
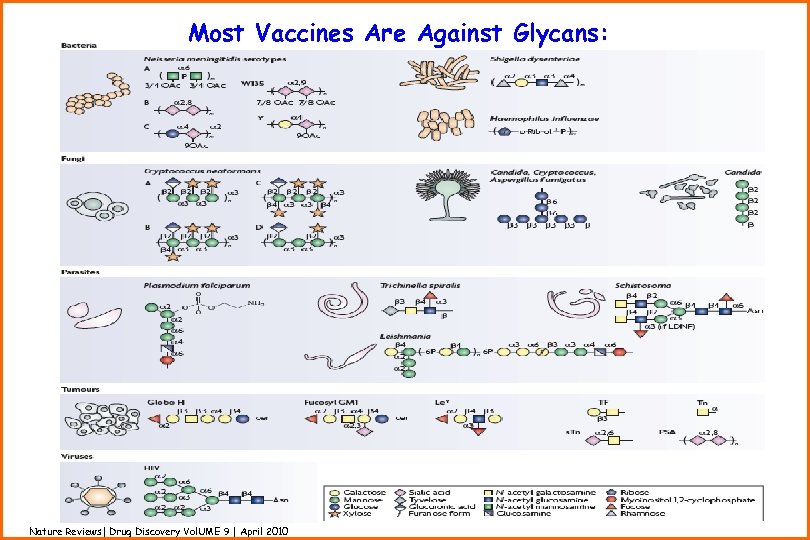 Most Vaccines Are Against Glycans: Nature Reviews| Drug Discovery Vol. UME 9 | April 2010
Most Vaccines Are Against Glycans: Nature Reviews| Drug Discovery Vol. UME 9 | April 2010
 Both Intracellular and extracellular glycans underlie molecular mechanisms leading to chronic disease, such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.
Both Intracellular and extracellular glycans underlie molecular mechanisms leading to chronic disease, such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.
 O-Glc. NAc and Diabetes Since 1950 s, ~1400 Papers Linking Hexosamine Metabolism to Diabetes. Marshall et al. and Mc. Clain et al. Established Direct Link Between Insulin Resistance and Conversion of Glucose to Glucosamine (GFAT) (eg. JBC 266, 4706; PNAS 99, 10695). 266, 99, Hyperglycemia, Hyperinsulinemia and Hyperlipidemia Increases O-Glc. NAcylation on Many Proteins in All Cell Types Examined - OGT is a Subtrate for IR and is Activated by Tyrosine Phosphorylation. Hyper-O-Glc. NAcylation of SP 1 Plays a Role in Glucose Toxicity. (several papers) Increased O-Glc. NAcylation Directly Blocks Insulin Signaling in Adipocytes & Muscle. O-Glc. NAcylation Blocks Akt Activation of e. NOS and Reduces Insulin’s activation of Glycogen Synthase - Blocks Phosphorylation (Brownlee et al. & Mc. Clain et al. ) O-Glc. NAcylation of PDX-1, Neuro. D 1, MAF-1 Directly Regulate Insulin Transcription by -cells. Targeted Over-Expression of OGT to Muscle or Fat Causes Diabetic Phenotype in Mice. (Hanover & Mc. Clain) A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) in MGEA 5 (O-Glc. NAcase) correlates with Diabetes in a human population.
O-Glc. NAc and Diabetes Since 1950 s, ~1400 Papers Linking Hexosamine Metabolism to Diabetes. Marshall et al. and Mc. Clain et al. Established Direct Link Between Insulin Resistance and Conversion of Glucose to Glucosamine (GFAT) (eg. JBC 266, 4706; PNAS 99, 10695). 266, 99, Hyperglycemia, Hyperinsulinemia and Hyperlipidemia Increases O-Glc. NAcylation on Many Proteins in All Cell Types Examined - OGT is a Subtrate for IR and is Activated by Tyrosine Phosphorylation. Hyper-O-Glc. NAcylation of SP 1 Plays a Role in Glucose Toxicity. (several papers) Increased O-Glc. NAcylation Directly Blocks Insulin Signaling in Adipocytes & Muscle. O-Glc. NAcylation Blocks Akt Activation of e. NOS and Reduces Insulin’s activation of Glycogen Synthase - Blocks Phosphorylation (Brownlee et al. & Mc. Clain et al. ) O-Glc. NAcylation of PDX-1, Neuro. D 1, MAF-1 Directly Regulate Insulin Transcription by -cells. Targeted Over-Expression of OGT to Muscle or Fat Causes Diabetic Phenotype in Mice. (Hanover & Mc. Clain) A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) in MGEA 5 (O-Glc. NAcase) correlates with Diabetes in a human population.
 O-Glc. NAc is Important to “Glucose Toxicity” u. Hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and hyperinsulinema all increase O-Glc. NAcylation of many proteins. Possible Mechanisms: u. Transcription Factors and Histones – Altered Promoter Activities. u. Translation Factors and Ribosomes. u. Signaling Molecules & Kinases – Balance with Phosphorylation is Disrupted. u. Mitochondrial Electron Transport Proteins – ROS Production? ? ? . . . ROS in-turn increases O-Glc. NAcylation.
O-Glc. NAc is Important to “Glucose Toxicity” u. Hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and hyperinsulinema all increase O-Glc. NAcylation of many proteins. Possible Mechanisms: u. Transcription Factors and Histones – Altered Promoter Activities. u. Translation Factors and Ribosomes. u. Signaling Molecules & Kinases – Balance with Phosphorylation is Disrupted. u. Mitochondrial Electron Transport Proteins – ROS Production? ? ? . . . ROS in-turn increases O-Glc. NAcylation.
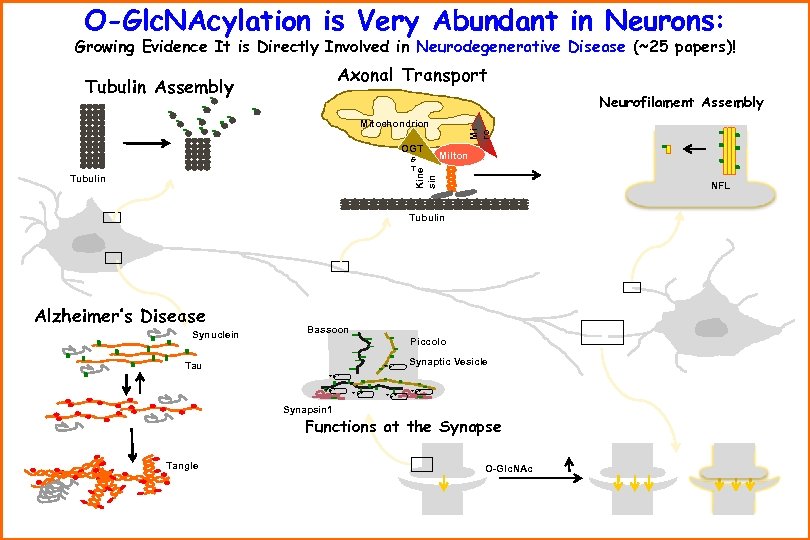 O-Glc. NAcylation is Very Abundant in Neurons: Growing Evidence It is Directly Involved in Neurodegenerative Disease (~25 papers)! Axonal Transport Tubulin Assembly Neurofilament Assembly OGT O Milton Kine sin G T Mi ro Mitochondrion Tubulin NFL Tubulin Alzheimer’s Disease Synuclein Tau Bassoon Piccolo + ++ Synaptic Vesicle + ++ + ++ Synapsin 1 Functions at the Synapse Tangle O-Glc. NAc
O-Glc. NAcylation is Very Abundant in Neurons: Growing Evidence It is Directly Involved in Neurodegenerative Disease (~25 papers)! Axonal Transport Tubulin Assembly Neurofilament Assembly OGT O Milton Kine sin G T Mi ro Mitochondrion Tubulin NFL Tubulin Alzheimer’s Disease Synuclein Tau Bassoon Piccolo + ++ Synaptic Vesicle + ++ + ++ Synapsin 1 Functions at the Synapse Tangle O-Glc. NAc
 Evidence That O-Glc. NAc Might Be Important for Neurodegenerative Disease: ü Virtually all proteins involved in AD are O-Glc. NAcylated/phosphorylated. ü Glucose Metabolism is Impaired in AD Neurons - Reducing O-Glc. NAc. (Science 291, 2376; BBA 1761, 599) (Am. J. Psychiatry 159, 738) ü Tau is Extensively O-Glc. NAcylated in Normal Brain & Hyper-Phos. In AD ü Amyloid Precursor Protein is O-Glc. NAcylated in its Cytosolic Domain. ü Studies in Neuronal Cells Document Interplay Between O-Glc. NAc & Phosphate on Tau ü Starved Mice have Hyperphosphorylated/Hypo-O-Glc. NAcylated Tau & others; Reversed by Feeding. ü O-Glc. NAcylation is Reduced in Human AD Brain Tissue ü OGase Gene Maps to 10 q 24. 1 (late onset AD Locus); OGT maps to X 13 (Parkinson Dystonia locus) ü Over-Exp. of OGT in Neurons Increases Tau O-Glc. NAcylation; Decreases Tau Phos. at Sites Important to AD ü Cre-Lox brain-targeted deletion of OGT in mice led to Tau Hyperphosphorylation Prior to Neuron Death. ü Proteasome is Important in AD; O-Glc. NAcylation Shuts Off the Proteasome ü Synaptic Loss Occurs in AD. Myriad Synaptosomal Proteins are Dynamically O-Glc. NAcylated ü O-Glc. NAcylation of Clathrin Assembly Proteins AP-180 & AP-3 Decreased in AD Brains ü Neurodegen. Assoc. Protein Ataxin-10 interacts with OGT in Brain, increases O-Glc. NAcylation ü Neurofilaments H, L, M Extensively O-Glc. NAcylated; Reduced in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (JBC 271, 28741) (J. Neurosci. Res. 41, 270. ) (BBA 1619, 167; PNAS 101, 1084) (Eur. J. Neuroscience 23, 2078) (PNAS 101, 1084). (Science 290, 2302; JBC 276, 9838) (PNAS 101, 1084). (Mol. Cell Biol. 24, 1680) (Biochem. Soc. Trans. 34, 743; Curr Alz. Res. 2, 19; Cell 115, 715) (J. Neurochem. 73, 418 & 79, 1080) (Neurosci. Lett. 252, 33; J. Neurosci. 18, 2399) (JBC 281, 20263) (JBC 268, 16679; 271, 20845; 280, 31648) üO-Glc. NAc on Neurofilaments M is Reduced in AD Concomitant with Increased Phos. (FASEB J. on-line 8/8/07; Gong et al. ) ü O-Glc. NAcylation Protects Cells from Apoptosis. (JBC 279, 30133)
Evidence That O-Glc. NAc Might Be Important for Neurodegenerative Disease: ü Virtually all proteins involved in AD are O-Glc. NAcylated/phosphorylated. ü Glucose Metabolism is Impaired in AD Neurons - Reducing O-Glc. NAc. (Science 291, 2376; BBA 1761, 599) (Am. J. Psychiatry 159, 738) ü Tau is Extensively O-Glc. NAcylated in Normal Brain & Hyper-Phos. In AD ü Amyloid Precursor Protein is O-Glc. NAcylated in its Cytosolic Domain. ü Studies in Neuronal Cells Document Interplay Between O-Glc. NAc & Phosphate on Tau ü Starved Mice have Hyperphosphorylated/Hypo-O-Glc. NAcylated Tau & others; Reversed by Feeding. ü O-Glc. NAcylation is Reduced in Human AD Brain Tissue ü OGase Gene Maps to 10 q 24. 1 (late onset AD Locus); OGT maps to X 13 (Parkinson Dystonia locus) ü Over-Exp. of OGT in Neurons Increases Tau O-Glc. NAcylation; Decreases Tau Phos. at Sites Important to AD ü Cre-Lox brain-targeted deletion of OGT in mice led to Tau Hyperphosphorylation Prior to Neuron Death. ü Proteasome is Important in AD; O-Glc. NAcylation Shuts Off the Proteasome ü Synaptic Loss Occurs in AD. Myriad Synaptosomal Proteins are Dynamically O-Glc. NAcylated ü O-Glc. NAcylation of Clathrin Assembly Proteins AP-180 & AP-3 Decreased in AD Brains ü Neurodegen. Assoc. Protein Ataxin-10 interacts with OGT in Brain, increases O-Glc. NAcylation ü Neurofilaments H, L, M Extensively O-Glc. NAcylated; Reduced in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (JBC 271, 28741) (J. Neurosci. Res. 41, 270. ) (BBA 1619, 167; PNAS 101, 1084) (Eur. J. Neuroscience 23, 2078) (PNAS 101, 1084). (Science 290, 2302; JBC 276, 9838) (PNAS 101, 1084). (Mol. Cell Biol. 24, 1680) (Biochem. Soc. Trans. 34, 743; Curr Alz. Res. 2, 19; Cell 115, 715) (J. Neurochem. 73, 418 & 79, 1080) (Neurosci. Lett. 252, 33; J. Neurosci. 18, 2399) (JBC 281, 20263) (JBC 268, 16679; 271, 20845; 280, 31648) üO-Glc. NAc on Neurofilaments M is Reduced in AD Concomitant with Increased Phos. (FASEB J. on-line 8/8/07; Gong et al. ) ü O-Glc. NAcylation Protects Cells from Apoptosis. (JBC 279, 30133)
 Glycans play a critical role in the bioactivity and pharmacokinetics of drugs and Development of New Drugs.
Glycans play a critical role in the bioactivity and pharmacokinetics of drugs and Development of New Drugs.
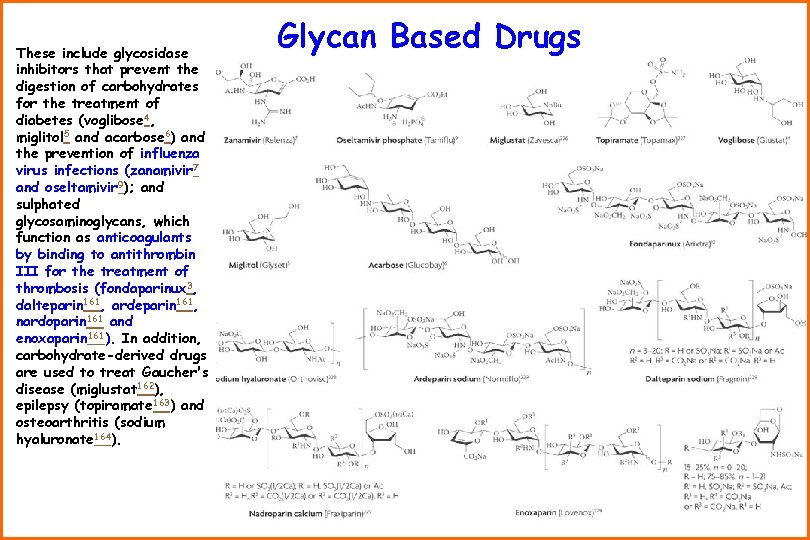 These include glycosidase inhibitors that prevent the digestion of carbohydrates for the treatment of diabetes (voglibose 4, miglitol 5 and acarbose 6) and the prevention of influenza virus infections (zanamivir 7 and oseltamivir 9); and sulphated glycosaminoglycans, which function as anticoagulants by binding to antithrombin III for the treatment of thrombosis (fondaparinux 3, dalteparin 161, ardeparin 161, nardoparin 161 and enoxaparin 161). In addition, carbohydrate-derived drugs are used to treat Gaucher's disease (miglustat 162), epilepsy (topiramate 163) and osteoarthritis (sodium hyaluronate 164). Glycan Based Drugs
These include glycosidase inhibitors that prevent the digestion of carbohydrates for the treatment of diabetes (voglibose 4, miglitol 5 and acarbose 6) and the prevention of influenza virus infections (zanamivir 7 and oseltamivir 9); and sulphated glycosaminoglycans, which function as anticoagulants by binding to antithrombin III for the treatment of thrombosis (fondaparinux 3, dalteparin 161, ardeparin 161, nardoparin 161 and enoxaparin 161). In addition, carbohydrate-derived drugs are used to treat Gaucher's disease (miglustat 162), epilepsy (topiramate 163) and osteoarthritis (sodium hyaluronate 164). Glycan Based Drugs
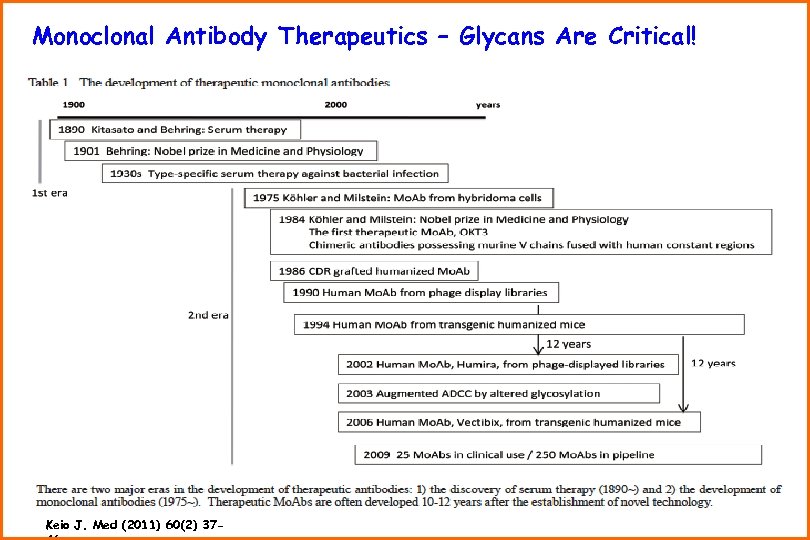 Monoclonal Antibody Therapeutics – Glycans Are Critical! Keio J. Med (2011) 60(2) 37 -
Monoclonal Antibody Therapeutics – Glycans Are Critical! Keio J. Med (2011) 60(2) 37 -
 Glycans play a multi-faceted role in cardiovascular disease.
Glycans play a multi-faceted role in cardiovascular disease.
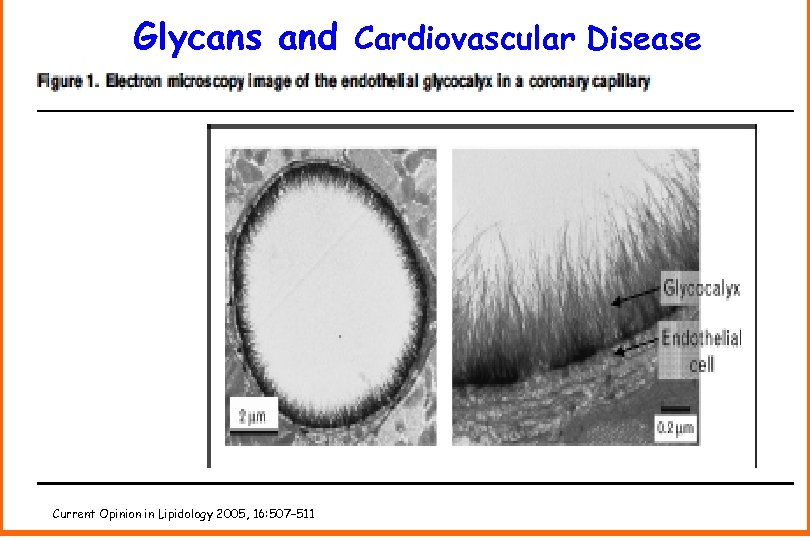 Glycans and Cardiovascular Disease Current Opinion in Lipidology 2005, 16: 507– 511
Glycans and Cardiovascular Disease Current Opinion in Lipidology 2005, 16: 507– 511
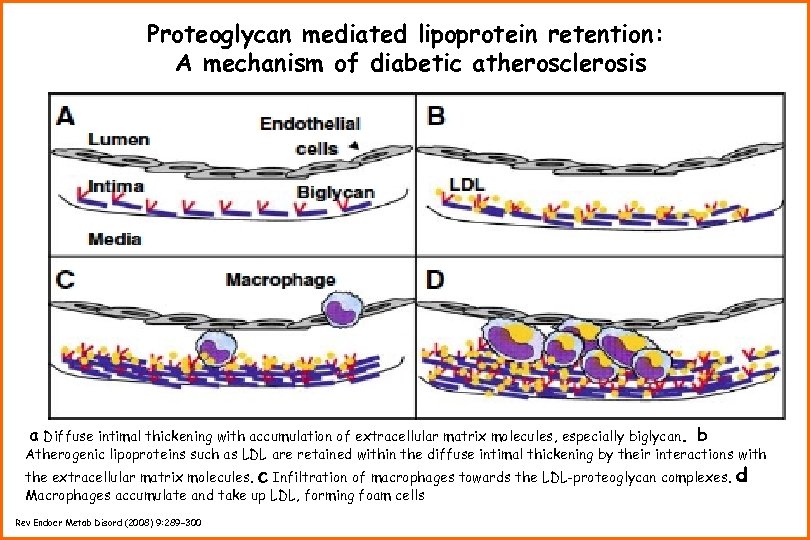 Proteoglycan mediated lipoprotein retention: A mechanism of diabetic atherosclerosis a Diffuse intimal thickening with accumulation of extracellular matrix molecules, especially biglycan. b Atherogenic lipoproteins such as LDL are retained within the diffuse intimal thickening by their interactions with the extracellular matrix molecules. c Infiltration of macrophages towards the LDL-proteoglycan complexes. Macrophages accumulate and take up LDL, forming foam cells Rev Endocr Metab Disord (2008) 9: 289– 300 d
Proteoglycan mediated lipoprotein retention: A mechanism of diabetic atherosclerosis a Diffuse intimal thickening with accumulation of extracellular matrix molecules, especially biglycan. b Atherogenic lipoproteins such as LDL are retained within the diffuse intimal thickening by their interactions with the extracellular matrix molecules. c Infiltration of macrophages towards the LDL-proteoglycan complexes. Macrophages accumulate and take up LDL, forming foam cells Rev Endocr Metab Disord (2008) 9: 289– 300 d
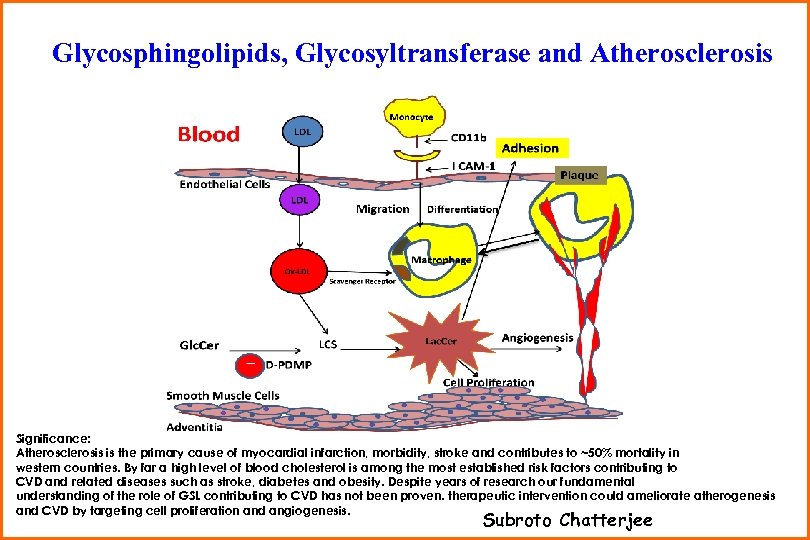 Glycosphingolipids, Glycosyltransferase and Atherosclerosis Project 5 Significance: Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of myocardial infarction, morbidity, stroke and contributes to ~50% mortality in western countries. By far a high level of blood cholesterol is among the most established risk factors contributing to CVD and related diseases such as stroke, diabetes and obesity. Despite years of research our fundamental understanding of the role of GSL contributing to CVD has not been proven. therapeutic intervention could ameliorate atherogenesis and CVD by targeting cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Subroto Chatterjee
Glycosphingolipids, Glycosyltransferase and Atherosclerosis Project 5 Significance: Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of myocardial infarction, morbidity, stroke and contributes to ~50% mortality in western countries. By far a high level of blood cholesterol is among the most established risk factors contributing to CVD and related diseases such as stroke, diabetes and obesity. Despite years of research our fundamental understanding of the role of GSL contributing to CVD has not been proven. therapeutic intervention could ameliorate atherogenesis and CVD by targeting cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Subroto Chatterjee
 Cardiovascular Disease and Glycans u Endothelial Cell Glycocalyx Plays a Critical Role in Cardiovascular Disease u Damage to Glycocalyx Directly Involved in Atheroslcerosis. u In diabetes, the abnormal expression of proteoglycans or glycosaminoglycans contributes to the binding of cholesterol rich lipoprotein particles at sites in the vascular endothelium. u Heparan sulfate proteoglycans play an important role in the clearance of lipoprotein particles from the circulation by the liver. u O-Glc. NAc plays an important role in diabetic cardiomyopathy
Cardiovascular Disease and Glycans u Endothelial Cell Glycocalyx Plays a Critical Role in Cardiovascular Disease u Damage to Glycocalyx Directly Involved in Atheroslcerosis. u In diabetes, the abnormal expression of proteoglycans or glycosaminoglycans contributes to the binding of cholesterol rich lipoprotein particles at sites in the vascular endothelium. u Heparan sulfate proteoglycans play an important role in the clearance of lipoprotein particles from the circulation by the liver. u O-Glc. NAc plays an important role in diabetic cardiomyopathy
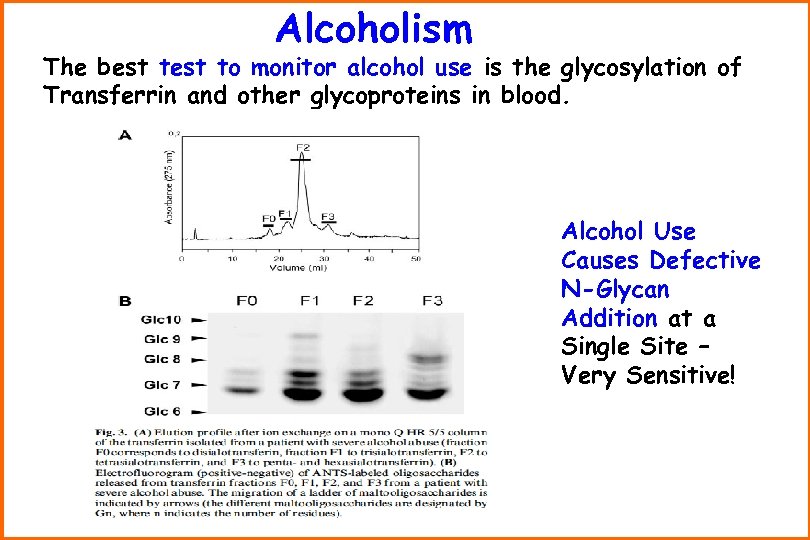 Alcoholism The best to monitor alcohol use is the glycosylation of Transferrin and other glycoproteins in blood. Alcohol Use Causes Defective N-Glycan Addition at a Single Site – Very Sensitive!
Alcoholism The best to monitor alcohol use is the glycosylation of Transferrin and other glycoproteins in blood. Alcohol Use Causes Defective N-Glycan Addition at a Single Site – Very Sensitive!
 Genetic diseases of glycosylation and inborn errors of glycan metabolism illustrate the critical roles of glycans in human development.
Genetic diseases of glycosylation and inborn errors of glycan metabolism illustrate the critical roles of glycans in human development.
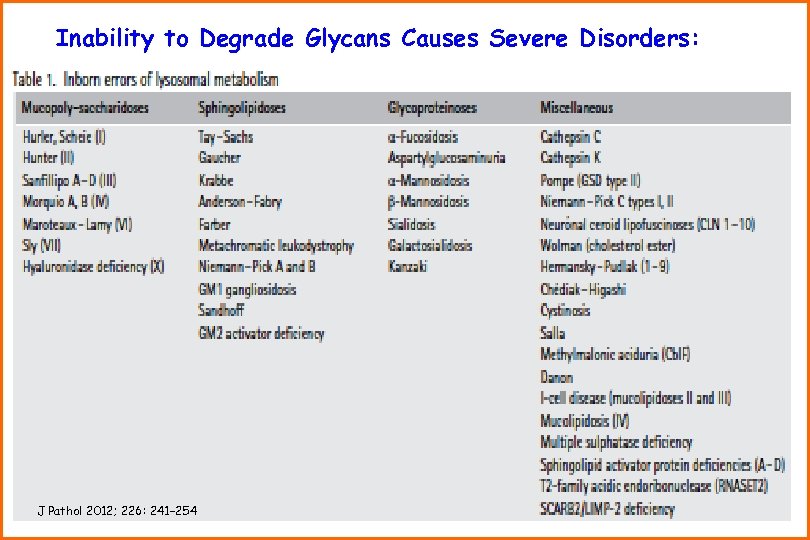 Inability to Degrade Glycans Causes Severe Disorders: J Pathol 2012; 226: 241– 254
Inability to Degrade Glycans Causes Severe Disorders: J Pathol 2012; 226: 241– 254
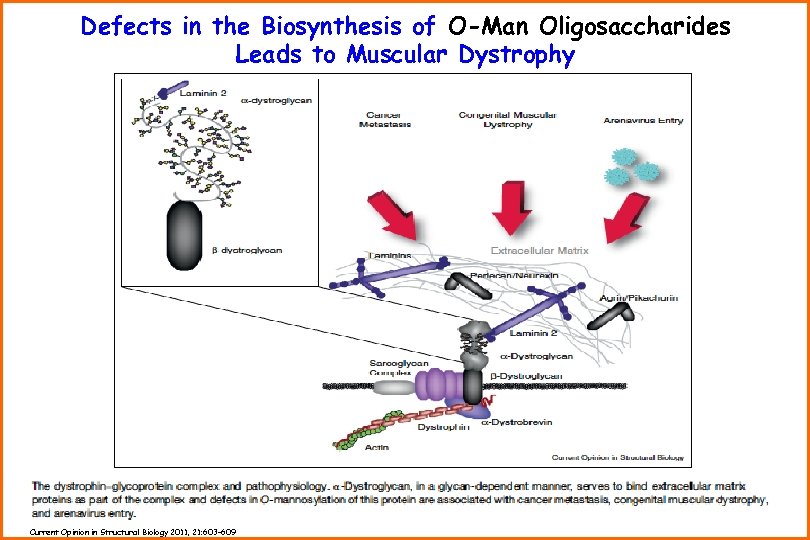 Defects in the Biosynthesis of O-Man Oligosaccharides Leads to Muscular Dystrophy Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2011, 21: 603– 609
Defects in the Biosynthesis of O-Man Oligosaccharides Leads to Muscular Dystrophy Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2011, 21: 603– 609
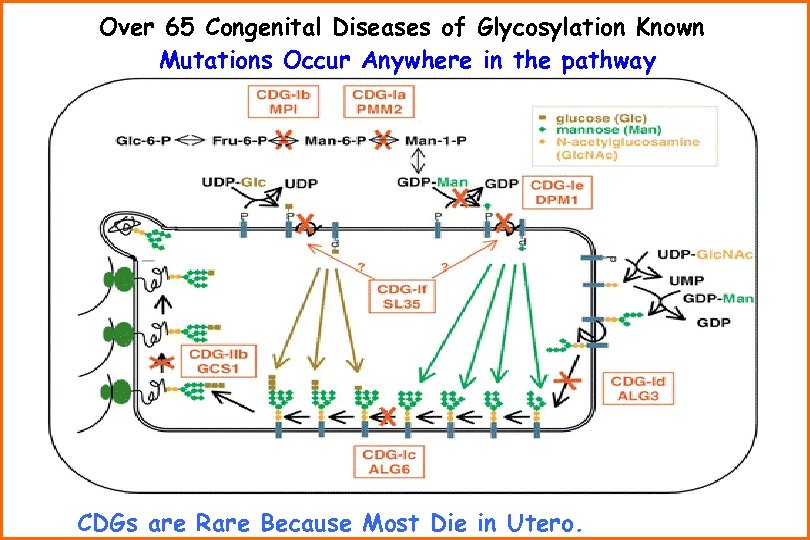 Over 65 Congenital Diseases of Glycosylation Known Mutations Occur Anywhere in the pathway CDGs are Rare Because Most Die in Utero.
Over 65 Congenital Diseases of Glycosylation Known Mutations Occur Anywhere in the pathway CDGs are Rare Because Most Die in Utero.
 Conclusions: Glycans Are Involved in Every Human Disease! • Inflammation, which underlies cellular damage associated with most diseases, is regulated by glycans. • Glycans play an essential role in the regulation of the immune system • Glycans play a direct role in cancer progression and as biomarkers for early detection of cancer • Glycans play a key role in infectious disease and in vaccine development. • Both Intracellular and extracellular glycans underlie molecular mechanisms leading to chronic disease, such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. • Glycans play a critical role in the bioactivity and pharmacokinetics of drugs. • Glycans play a multi-faceted role in cardiovascular disease. • Genetic diseases of glycosylation and inborn errors of glycan metabolism illustrate the critical roles of glycans in human development. u Too few People trained to do Glycosciences, glycans no less important to human health than proteins or DNA! u Glycoscience is the next big thing! – NIH, DOE, FDA, NSF, NIST a high priority. u Biomedical Research in Glycosciences involves expertise in many disciplines – Biology is at the Organism Level!
Conclusions: Glycans Are Involved in Every Human Disease! • Inflammation, which underlies cellular damage associated with most diseases, is regulated by glycans. • Glycans play an essential role in the regulation of the immune system • Glycans play a direct role in cancer progression and as biomarkers for early detection of cancer • Glycans play a key role in infectious disease and in vaccine development. • Both Intracellular and extracellular glycans underlie molecular mechanisms leading to chronic disease, such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. • Glycans play a critical role in the bioactivity and pharmacokinetics of drugs. • Glycans play a multi-faceted role in cardiovascular disease. • Genetic diseases of glycosylation and inborn errors of glycan metabolism illustrate the critical roles of glycans in human development. u Too few People trained to do Glycosciences, glycans no less important to human health than proteins or DNA! u Glycoscience is the next big thing! – NIH, DOE, FDA, NSF, NIST a high priority. u Biomedical Research in Glycosciences involves expertise in many disciplines – Biology is at the Organism Level!
 Additional Reading 1. Varki, A. , Cummings, R. D. , Esko, J. D. , Freeze, H. H. , Stanley, P. , Bertozzi, C. R. , Hart, G. W. , and Etzler, M. E. (2009) Essentials of Glycobiology, 2 nd ed. , Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 2. Hart, G. W. , and Copeland, R. J. (2010) Glycomics hits the big time Cell 143, 672 -676 3. Barreiro, O. , and Sanchez-Madrid, F. (2009) Molecular basis of leukocyte-endothelium interactions during the inflammatory response Revista espanola de cardiologia 62, 552 -562 4. Kobayashi, M. , Fukuda, M. , and Nakayama, J. (2009) Role of sulfated O-glycans expressed by high endothelial venule-like vessels in pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 32, 774 -779 5. Celie, J. W. , Beelen, R. H. , and van den Born, J. (2009) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans in extravasation: assisting leukocyte guidance Frontiers in bioscience : a journal and virtual library 14, 4932 -4949 6. Langer, H. F. , and Chavakis, T. (2009) Leukocyte-endothelial interactions in inflammation Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 13, 1211 -1220 7. Sperandio, M. , Gleissner, C. A. , and Ley, K. (2009) Glycosylation in immune cell trafficking Immunological Reviews 230, 97 -113 8. Schauer, R. (2009) Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions Current Opinion in Structural Biology 19, 507 -514 9. Mc. Ever, R. P. , and Zhu, C. (2010) Rolling cell adhesion Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 26, 363 -396 10. Mc. Ever, R. P. (2010) Rolling back neutrophil adhesion Nature Immunology 11, 282 -284 11. Zarbock, A. , Ley, K. , Mc. Ever, R. P. , and Hidalgo, A. (2011) Leukocyte ligands for endothelial selectins: specialized glycoconjugates that mediate rolling and signaling under flow Blood 118, 6743 -6751 12. Korpos, E. , Wu, C. , and Sorokin, L. (2009) Multiple roles of the extracellular matrix in inflammation Current Pharmaceutical Design 15, 1349 -1357 13. Sorokin, L. (2010) The impact of the extracellular matrix on inflammation Nature reviews. Immunology 10, 712 -723 14. Laubli, H. , and Borsig, L. (2010) Selectins promote tumor metastasis Seminars in Cancer Biology 20, 169 -177 15. St Hill, C. A. (2012) Interactions between endothelial selectins and cancer cells regulate metastasis Frontiers in bioscience : a journal and virtual library 17, 3233 -3251 16. Dube, D. H. , and Bertozzi, C. R. (2005) Glycans in cancer and inflammation--potential for therapeutics and diagnostics Nature reviews. Drug discovery 4, 477 -488 17. Ernst, B. , and Magnani, J. L. (2009) From carbohydrate leads to glycomimetic drugs Nature reviews. Drug discovery 8, 661 -677 18. Magnani, J. L. , and Ernst, B. (2009) Glycomimetic drugs--a new source of therapeutic opportunities Discovery medicine 8, 247 -252 19. Imberty, A. , Chabre, Y. M. , and Roy, R. (2008) Glycomimetics and glycodendrimers as high affinity microbial anti-adhesins Chemistry 14, 74907499 20. Garber, K. C. , Wangkanont, K. , Carlson, E. E. , and Kiessling, L. L. (2010) A general glycomimetic strategy yields non-carbohydrate inhibitors of DCSIGN Chemical communications 46, 6747 -6749 21. Chabre, Y. M. , Giguere, D. , Blanchard, B. , Rodrigue, J. , Rocheleau, S. , Neault, M. , Rauthu, S. , Papadopoulos, A. , Arnold, A. A. , Imberty, A. , and Roy, R. (2011) Combining glycomimetic and multivalent strategies toward designing potent bacterial lectin inhibitors Chemistry 17, 6545 -6562 22. Drozdova, A. , Bojarova, P. , Krenek, K. , Weignerova, L. , Henssen, B. , Elling, L. , Christensen, H. , Jensen, H. H. , Pelantova, H. , Kuzma, M. , Bezouska, K. , Krupova, M, Adamek, D. , Slamova, K. , and Kren, V. (2011) Enzymatic synthesis of dimeric glycomimetic ligands of NK cell activation receptors Carbohydrate research 346, 1599 -1609 23. Jandus, C. , Simon, H. U. , and von Gunten, S. (2011) Targeting siglecs--a novel pharmacological strategy for immuno- and glycotherapy Biochemical Pharmacology 82, 323 -332 24. Sackstein, R. (2011) The biology of CD 44 and HCELL in hematopoiesis: the 'step 2 -bypass pathway' and other emerging perspectives Current opinion in hematology 18, 239 -248
Additional Reading 1. Varki, A. , Cummings, R. D. , Esko, J. D. , Freeze, H. H. , Stanley, P. , Bertozzi, C. R. , Hart, G. W. , and Etzler, M. E. (2009) Essentials of Glycobiology, 2 nd ed. , Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 2. Hart, G. W. , and Copeland, R. J. (2010) Glycomics hits the big time Cell 143, 672 -676 3. Barreiro, O. , and Sanchez-Madrid, F. (2009) Molecular basis of leukocyte-endothelium interactions during the inflammatory response Revista espanola de cardiologia 62, 552 -562 4. Kobayashi, M. , Fukuda, M. , and Nakayama, J. (2009) Role of sulfated O-glycans expressed by high endothelial venule-like vessels in pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 32, 774 -779 5. Celie, J. W. , Beelen, R. H. , and van den Born, J. (2009) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans in extravasation: assisting leukocyte guidance Frontiers in bioscience : a journal and virtual library 14, 4932 -4949 6. Langer, H. F. , and Chavakis, T. (2009) Leukocyte-endothelial interactions in inflammation Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 13, 1211 -1220 7. Sperandio, M. , Gleissner, C. A. , and Ley, K. (2009) Glycosylation in immune cell trafficking Immunological Reviews 230, 97 -113 8. Schauer, R. (2009) Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions Current Opinion in Structural Biology 19, 507 -514 9. Mc. Ever, R. P. , and Zhu, C. (2010) Rolling cell adhesion Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 26, 363 -396 10. Mc. Ever, R. P. (2010) Rolling back neutrophil adhesion Nature Immunology 11, 282 -284 11. Zarbock, A. , Ley, K. , Mc. Ever, R. P. , and Hidalgo, A. (2011) Leukocyte ligands for endothelial selectins: specialized glycoconjugates that mediate rolling and signaling under flow Blood 118, 6743 -6751 12. Korpos, E. , Wu, C. , and Sorokin, L. (2009) Multiple roles of the extracellular matrix in inflammation Current Pharmaceutical Design 15, 1349 -1357 13. Sorokin, L. (2010) The impact of the extracellular matrix on inflammation Nature reviews. Immunology 10, 712 -723 14. Laubli, H. , and Borsig, L. (2010) Selectins promote tumor metastasis Seminars in Cancer Biology 20, 169 -177 15. St Hill, C. A. (2012) Interactions between endothelial selectins and cancer cells regulate metastasis Frontiers in bioscience : a journal and virtual library 17, 3233 -3251 16. Dube, D. H. , and Bertozzi, C. R. (2005) Glycans in cancer and inflammation--potential for therapeutics and diagnostics Nature reviews. Drug discovery 4, 477 -488 17. Ernst, B. , and Magnani, J. L. (2009) From carbohydrate leads to glycomimetic drugs Nature reviews. Drug discovery 8, 661 -677 18. Magnani, J. L. , and Ernst, B. (2009) Glycomimetic drugs--a new source of therapeutic opportunities Discovery medicine 8, 247 -252 19. Imberty, A. , Chabre, Y. M. , and Roy, R. (2008) Glycomimetics and glycodendrimers as high affinity microbial anti-adhesins Chemistry 14, 74907499 20. Garber, K. C. , Wangkanont, K. , Carlson, E. E. , and Kiessling, L. L. (2010) A general glycomimetic strategy yields non-carbohydrate inhibitors of DCSIGN Chemical communications 46, 6747 -6749 21. Chabre, Y. M. , Giguere, D. , Blanchard, B. , Rodrigue, J. , Rocheleau, S. , Neault, M. , Rauthu, S. , Papadopoulos, A. , Arnold, A. A. , Imberty, A. , and Roy, R. (2011) Combining glycomimetic and multivalent strategies toward designing potent bacterial lectin inhibitors Chemistry 17, 6545 -6562 22. Drozdova, A. , Bojarova, P. , Krenek, K. , Weignerova, L. , Henssen, B. , Elling, L. , Christensen, H. , Jensen, H. H. , Pelantova, H. , Kuzma, M. , Bezouska, K. , Krupova, M, Adamek, D. , Slamova, K. , and Kren, V. (2011) Enzymatic synthesis of dimeric glycomimetic ligands of NK cell activation receptors Carbohydrate research 346, 1599 -1609 23. Jandus, C. , Simon, H. U. , and von Gunten, S. (2011) Targeting siglecs--a novel pharmacological strategy for immuno- and glycotherapy Biochemical Pharmacology 82, 323 -332 24. Sackstein, R. (2011) The biology of CD 44 and HCELL in hematopoiesis: the 'step 2 -bypass pathway' and other emerging perspectives Current opinion in hematology 18, 239 -248
 Additional Reading Continued: 25. Morgan, W. T. , and Watkins, W. M. (1969) Genetic and biochemical aspects of human blood-group A-, B-, H-, Le-a- and Le-b-specificity British Medical Bulletin 25, 30 -34 26. Lux, A. , and Nimmerjahn, F. (2011) Impact of differential glycosylation on Ig. G activity Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 780, 113 -124 27. Raju, T. S. (2008) Terminal sugars of Fc glycans influence antibody effector functions of Ig. Gs Current Opinion in Immunology 20, 471 -478 28. Marth, J. D. , and Grewal, P. K. (2008) Mammalian glycosylation in immunity Nature reviews. Immunology 8, 874 -887 29. Erbacher, A. , Gieseke, F. , Handgretinger, R. , and Muller, I. (2009) Dendritic cells: functional aspects of glycosylation and lectins Human Immunology 70, 308 -312 30. Silva, Z. , Konstantopoulos, K. , and Videira, P. A. (2011) The Role of Sugars in Dendritic Cell Trafficking Annals of Biomedical Engineering 31. Lee, S. U. , Grigorian, A. , Pawling, J. , Chen, I. J. , Gao, G. , Mozaffar, T. , Mc. Kerlie, C. , and Demetriou, M. (2007) N-glycan processing deficiency promotes spontaneous inflammatory demyelination and neurodegeneration The Journal of biological chemistry 282, 33725 -33734 32. Rabinovich, G. A. , and Toscano, M. A. (2009) Turning 'sweet' on immunity: galectin-glycan interactions in immune tolerance and inflammation Nature reviews. Immunology 9, 338 -352 33. Demotte, N. , Stroobant, V. , Courtoy, P. J. , Van Der Smissen, P. , Colau, D. , Luescher, I. F. , Hivroz, C. , Nicaise, J. , Squifflet, J. L. , Mourad, M. , Godelaine, D. , Boon, T. , and van der Bruggen, P. (2008) Restoring the association of the T cell receptor with CD 8 reverses anergy in human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes Immunity 28, 414 -424 34. Rabinovich, G. A. , Toscano, M. A. , Jackson, S. S. , and Vasta, G. R. (2007) Functions of cell surface galectin-glycoprotein lattices Current Opinion in Structural Biology 17, 513 -520 35. Pillai, S. , Netravali, I. A. , Cariappa, A. , and Mattoo, H. (2011) Siglecs and Immune Regulation Annual Review of Immunology 36. Crocker, P. R. , Paulson, J. C. , and Varki, A. (2007) Siglecs and their roles in the immune system Nature reviews. Immunology 7, 255 -266 37. Crocker, P. R. , and Redelinghuys, P. (2008) Siglecs as positive and negative regulators of the immune system Biochemical Society Transactions 36, 1467 -1471 38. O'Reilly, M. K. , and Paulson, J. C. (2009) Siglecs as targets for therapy in immune-cell-mediated disease Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 30, 240 -248 39. Hart, G. W. , Slawson, C. , Ramirez-Correa, G. A. , and Lagerlof, O. (2011) Cross Talk Between O-Glc. NAcylation and Phosphorylation: Roles in Signaling, Transcription, and Chronic Disease Annu Rev Biochem 80, 825 -858 40. Golks, A. , Tran, T. T. , Goetschy, J. F. , and Guerini, D. (2007) Requirement for O-linked N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase in lymphocytes activation The EMBO journal 26, 4368 -4379 41. Kolarich, D. , Lepenies, B. , and Seeberger, P. H. (2012) Glycomics, glycoproteomics and the immune system Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 42. Hakomori, S. (2002) Glycosylation defining cancer malignancy: new wine in an old bottle Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99, 10231 -10233 43. Reis, C. A. , Osorio, H. , Silva, L. , Gomes, C. , and David, L. (2010) Alterations in glycosylation as biomarkers for cancer detection Journal of Clinical Pathology 63, 322 -329 44. Drake, P. M. , Cho, W. , Li, B. , Prakobphol, A. , Johansen, E. , Anderson, N. L. , Regnier, F. E. , Gibson, B. W. , and Fisher, S. J. (2010) Sweetening the pot: adding glycosylation to the biomarker discovery equation Clinical Chemistry 56, 223 -236 45. Li, D. , Mallory, T. , and Satomura, S. (2001) AFP-L 3: a new generation of tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry 313, 15 -19 46. Meany, D. L. , and Chan, D. W. (2011) Aberrant glycosylation associated with enzymes as cancer biomarkers Clinical proteomics 8, 7 47. Dennis, J. W. , Granovsky, M. , and Warren, C. E. (1999) Glycoprotein glycosylation and cancer progression Biochimica et biophysica acta 1473, 21 -34 48. Adamczyk, B. , Tharmalingam, T. , and Rudd, P. M. (2011) Glycans as cancer biomarkers Biochimica et biophysica acta 49. Heimburg-Molinaro, J. , Lum, M. , Vijay, G. , Jain, M. , Almogren, A. , and Rittenhouse-Olson, K. (2011) Cancer vaccines and carbohydrate epitopes Vaccine 29, 88028826 50. Li, M. , Song, L. , and Qin, X. (2010) Glycan changes: cancer metastasis and anti-cancer vaccines Journal of biosciences 35, 665 -673 51. Rambaruth, N. D. , and Dwek, M. V. (2011) Cell surface glycan-lectin interactions in tumor metastasis Acta histochemica 113, 591 -600 52. Pinho, S. S. , Seruca, R. , Gartner, F. , Yamaguchi, Y. , Gu, J. , Taniguchi, N. , and Reis, C. A. (2011) Modulation of E-cadherin function and dysfunction by Nglycosylation Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 68, 1011 -1020
Additional Reading Continued: 25. Morgan, W. T. , and Watkins, W. M. (1969) Genetic and biochemical aspects of human blood-group A-, B-, H-, Le-a- and Le-b-specificity British Medical Bulletin 25, 30 -34 26. Lux, A. , and Nimmerjahn, F. (2011) Impact of differential glycosylation on Ig. G activity Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 780, 113 -124 27. Raju, T. S. (2008) Terminal sugars of Fc glycans influence antibody effector functions of Ig. Gs Current Opinion in Immunology 20, 471 -478 28. Marth, J. D. , and Grewal, P. K. (2008) Mammalian glycosylation in immunity Nature reviews. Immunology 8, 874 -887 29. Erbacher, A. , Gieseke, F. , Handgretinger, R. , and Muller, I. (2009) Dendritic cells: functional aspects of glycosylation and lectins Human Immunology 70, 308 -312 30. Silva, Z. , Konstantopoulos, K. , and Videira, P. A. (2011) The Role of Sugars in Dendritic Cell Trafficking Annals of Biomedical Engineering 31. Lee, S. U. , Grigorian, A. , Pawling, J. , Chen, I. J. , Gao, G. , Mozaffar, T. , Mc. Kerlie, C. , and Demetriou, M. (2007) N-glycan processing deficiency promotes spontaneous inflammatory demyelination and neurodegeneration The Journal of biological chemistry 282, 33725 -33734 32. Rabinovich, G. A. , and Toscano, M. A. (2009) Turning 'sweet' on immunity: galectin-glycan interactions in immune tolerance and inflammation Nature reviews. Immunology 9, 338 -352 33. Demotte, N. , Stroobant, V. , Courtoy, P. J. , Van Der Smissen, P. , Colau, D. , Luescher, I. F. , Hivroz, C. , Nicaise, J. , Squifflet, J. L. , Mourad, M. , Godelaine, D. , Boon, T. , and van der Bruggen, P. (2008) Restoring the association of the T cell receptor with CD 8 reverses anergy in human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes Immunity 28, 414 -424 34. Rabinovich, G. A. , Toscano, M. A. , Jackson, S. S. , and Vasta, G. R. (2007) Functions of cell surface galectin-glycoprotein lattices Current Opinion in Structural Biology 17, 513 -520 35. Pillai, S. , Netravali, I. A. , Cariappa, A. , and Mattoo, H. (2011) Siglecs and Immune Regulation Annual Review of Immunology 36. Crocker, P. R. , Paulson, J. C. , and Varki, A. (2007) Siglecs and their roles in the immune system Nature reviews. Immunology 7, 255 -266 37. Crocker, P. R. , and Redelinghuys, P. (2008) Siglecs as positive and negative regulators of the immune system Biochemical Society Transactions 36, 1467 -1471 38. O'Reilly, M. K. , and Paulson, J. C. (2009) Siglecs as targets for therapy in immune-cell-mediated disease Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 30, 240 -248 39. Hart, G. W. , Slawson, C. , Ramirez-Correa, G. A. , and Lagerlof, O. (2011) Cross Talk Between O-Glc. NAcylation and Phosphorylation: Roles in Signaling, Transcription, and Chronic Disease Annu Rev Biochem 80, 825 -858 40. Golks, A. , Tran, T. T. , Goetschy, J. F. , and Guerini, D. (2007) Requirement for O-linked N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase in lymphocytes activation The EMBO journal 26, 4368 -4379 41. Kolarich, D. , Lepenies, B. , and Seeberger, P. H. (2012) Glycomics, glycoproteomics and the immune system Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 42. Hakomori, S. (2002) Glycosylation defining cancer malignancy: new wine in an old bottle Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99, 10231 -10233 43. Reis, C. A. , Osorio, H. , Silva, L. , Gomes, C. , and David, L. (2010) Alterations in glycosylation as biomarkers for cancer detection Journal of Clinical Pathology 63, 322 -329 44. Drake, P. M. , Cho, W. , Li, B. , Prakobphol, A. , Johansen, E. , Anderson, N. L. , Regnier, F. E. , Gibson, B. W. , and Fisher, S. J. (2010) Sweetening the pot: adding glycosylation to the biomarker discovery equation Clinical Chemistry 56, 223 -236 45. Li, D. , Mallory, T. , and Satomura, S. (2001) AFP-L 3: a new generation of tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry 313, 15 -19 46. Meany, D. L. , and Chan, D. W. (2011) Aberrant glycosylation associated with enzymes as cancer biomarkers Clinical proteomics 8, 7 47. Dennis, J. W. , Granovsky, M. , and Warren, C. E. (1999) Glycoprotein glycosylation and cancer progression Biochimica et biophysica acta 1473, 21 -34 48. Adamczyk, B. , Tharmalingam, T. , and Rudd, P. M. (2011) Glycans as cancer biomarkers Biochimica et biophysica acta 49. Heimburg-Molinaro, J. , Lum, M. , Vijay, G. , Jain, M. , Almogren, A. , and Rittenhouse-Olson, K. (2011) Cancer vaccines and carbohydrate epitopes Vaccine 29, 88028826 50. Li, M. , Song, L. , and Qin, X. (2010) Glycan changes: cancer metastasis and anti-cancer vaccines Journal of biosciences 35, 665 -673 51. Rambaruth, N. D. , and Dwek, M. V. (2011) Cell surface glycan-lectin interactions in tumor metastasis Acta histochemica 113, 591 -600 52. Pinho, S. S. , Seruca, R. , Gartner, F. , Yamaguchi, Y. , Gu, J. , Taniguchi, N. , and Reis, C. A. (2011) Modulation of E-cadherin function and dysfunction by Nglycosylation Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 68, 1011 -1020
 Additional Reading Continued: 53. Slawson, C. , Copeland, R. J. , and Hart, G. W. (2010) O-Glc. NAc signaling: a metabolic link between diabetes and cancer? Trends Biochem Sci 35, 547 -555 54. Slawson, C. , and Hart, G. W. (2011) O-Glc. NAc signalling: implications for cancer cell biology Nature reviews. Cancer 11, 678 -684 55. Bardoel, B. W. , and Strijp, J. A. (2011) Molecular battle between host and bacterium: recognition in innate immunity Journal of molecular recognition : JMR 24, 1077 -1086 56. Pieters, R. J. (2011) Carbohydrate mediated bacterial adhesion Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 715, 227 -240 57. Kobayashi, M. , Lee, H. , Nakayama, J. , and Fukuda, M. (2009) Roles of gastric mucin-type O-glycans in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection Glycobiology 19, 453 -461 58. Newburg, D. S. , Ruiz-Palacios, G. M. , and Morrow, A. L. (2005) Human milk glycans protect infants against enteric pathogens Annual Review of Nutrition 25, 37 -58 59. Tao, N. , Wu, S. , Kim, J. , An, H. J. , Hinde, K. , Power, M. L. , Gagneux, P. , German, J. B. , and Lebrilla, C. B. (2011) Evolutionary glycomics: characterization of milk oligosaccharides in primates Journal of proteome research 10, 1548 -1557 60. Chichlowski, M. , German, J. B. , Lebrilla, C. B. , and Mills, D. A. (2011) The influence of milk oligosaccharides on microbiota of infants: opportunities formulas Annual review of food science and technology 2, 331 -351 61. Karlsson, K. A. (1998) Meaning and therapeutic potential of microbial recognition of host glycoconjugates Molecular Microbiology 29, 1 -11 62. Viswanathan, K. , Chandrasekaran, A. , Srinivasan, A. , Raman, R. , Sasisekharan, V. , and Sasisekharan, R. (2010) Glycans as receptors for influenza pathogenesis Glycoconjugate journal 27, 561 -570 63. Stevens, J. , Blixt, O. , Paulson, J. C. , and Wilson, I. A. (2006) Glycan microarray technologies: tools to survey host specificity of influenza viruses Nat Rev Microbiol 4, 857 -864 64. Tumpey, T. M. , Maines, T. R. , Van Hoeven, N. , Glaser, L. , Solorzano, A. , Pappas, C. , Cox, N. J. , Swayne, D. E. , Palese, P. , Katz, J. M. , and Garcia-Sastre, A. (2007) A two-amino acid change in the hemagglutinin of the 1918 influenza virus abolishes transmission Science 315, 655659 65. Raska, M. , and Novak, J. (2010) Involvement of envelope-glycoprotein glycans in HIV-1 biology and infection Archivum immunologiae et therapiae experimentalis 58, 191 -208 66. Mc. Lellan, J. S. , Pancera, M. , Carrico, C. , Gorman, J. , Julien, J. P. , Khayat, R. , Louder, R. , Pejchal, R. , Sastry, M. , Dai, K. , O'Dell, S. , Patel, N. , Shahzad-ul-Hussan, S. , Yang, Y. , Zhang, B. , Zhou, T. , Zhu, J. , Boyington, J. C. , Chuang, G. Y. , Diwanji, D. , Georgiev, I. , Kwon, Y. D. , Lee, D. , Louder, M. K. , Moquin, S. , Schmidt, S. D. , Yang, Z. Y. , Bonsignori, M. , Crump, J. A. , Kapiga, S. H. , Sam, N. E. , Haynes, B. F. , Burton, D. R. , Koff, W. C. , Walker, L. M. , Phogat, S. , Wyatt, R. , Orwenyo, J. , Wang, L. X. , Arthos, J. , Bewley, C. A. , Mascola, J. R. , Nabel, G. J. , Schief, W. R. , Ward, A. B. , Wilson, I. A. , and Kwong, P. D. (2011) Structure of HIV-1 gp 120 V 1/V 2 domain with broadly neutralizing antibody PG 9 Nature 480, 336 -343 67. Pejchal, R. , Doores, K. J. , Walker, L. M. , Khayat, R. , Huang, P. S. , Wang, S. K. , Stanfield, R. L. , Julien, J. P. , Ramos, A. , Crispin, M. , Depetris, R. , Katpally, U. , Marozsan, A. , Cupo, A. , Maloveste, S. , Liu, Y. , Mc. Bride, R. , Ito, Y. , Sanders, R. W. , Ogohara, C. , Paulson, J. C. , Feizi, T. , Scanlan, C. N. , Wong, C. H. , Moore, J. P. , Olson, W. C. , Ward, A. B. , Poignard, P. , Schief, W. R. , Burton, D. R. , and Wilson, I. A. (2011) A potent and broad neutralizing antibody recognizes and penetrates the HIV glycan shield Science 334, 1097 -1103
Additional Reading Continued: 53. Slawson, C. , Copeland, R. J. , and Hart, G. W. (2010) O-Glc. NAc signaling: a metabolic link between diabetes and cancer? Trends Biochem Sci 35, 547 -555 54. Slawson, C. , and Hart, G. W. (2011) O-Glc. NAc signalling: implications for cancer cell biology Nature reviews. Cancer 11, 678 -684 55. Bardoel, B. W. , and Strijp, J. A. (2011) Molecular battle between host and bacterium: recognition in innate immunity Journal of molecular recognition : JMR 24, 1077 -1086 56. Pieters, R. J. (2011) Carbohydrate mediated bacterial adhesion Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 715, 227 -240 57. Kobayashi, M. , Lee, H. , Nakayama, J. , and Fukuda, M. (2009) Roles of gastric mucin-type O-glycans in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection Glycobiology 19, 453 -461 58. Newburg, D. S. , Ruiz-Palacios, G. M. , and Morrow, A. L. (2005) Human milk glycans protect infants against enteric pathogens Annual Review of Nutrition 25, 37 -58 59. Tao, N. , Wu, S. , Kim, J. , An, H. J. , Hinde, K. , Power, M. L. , Gagneux, P. , German, J. B. , and Lebrilla, C. B. (2011) Evolutionary glycomics: characterization of milk oligosaccharides in primates Journal of proteome research 10, 1548 -1557 60. Chichlowski, M. , German, J. B. , Lebrilla, C. B. , and Mills, D. A. (2011) The influence of milk oligosaccharides on microbiota of infants: opportunities formulas Annual review of food science and technology 2, 331 -351 61. Karlsson, K. A. (1998) Meaning and therapeutic potential of microbial recognition of host glycoconjugates Molecular Microbiology 29, 1 -11 62. Viswanathan, K. , Chandrasekaran, A. , Srinivasan, A. , Raman, R. , Sasisekharan, V. , and Sasisekharan, R. (2010) Glycans as receptors for influenza pathogenesis Glycoconjugate journal 27, 561 -570 63. Stevens, J. , Blixt, O. , Paulson, J. C. , and Wilson, I. A. (2006) Glycan microarray technologies: tools to survey host specificity of influenza viruses Nat Rev Microbiol 4, 857 -864 64. Tumpey, T. M. , Maines, T. R. , Van Hoeven, N. , Glaser, L. , Solorzano, A. , Pappas, C. , Cox, N. J. , Swayne, D. E. , Palese, P. , Katz, J. M. , and Garcia-Sastre, A. (2007) A two-amino acid change in the hemagglutinin of the 1918 influenza virus abolishes transmission Science 315, 655659 65. Raska, M. , and Novak, J. (2010) Involvement of envelope-glycoprotein glycans in HIV-1 biology and infection Archivum immunologiae et therapiae experimentalis 58, 191 -208 66. Mc. Lellan, J. S. , Pancera, M. , Carrico, C. , Gorman, J. , Julien, J. P. , Khayat, R. , Louder, R. , Pejchal, R. , Sastry, M. , Dai, K. , O'Dell, S. , Patel, N. , Shahzad-ul-Hussan, S. , Yang, Y. , Zhang, B. , Zhou, T. , Zhu, J. , Boyington, J. C. , Chuang, G. Y. , Diwanji, D. , Georgiev, I. , Kwon, Y. D. , Lee, D. , Louder, M. K. , Moquin, S. , Schmidt, S. D. , Yang, Z. Y. , Bonsignori, M. , Crump, J. A. , Kapiga, S. H. , Sam, N. E. , Haynes, B. F. , Burton, D. R. , Koff, W. C. , Walker, L. M. , Phogat, S. , Wyatt, R. , Orwenyo, J. , Wang, L. X. , Arthos, J. , Bewley, C. A. , Mascola, J. R. , Nabel, G. J. , Schief, W. R. , Ward, A. B. , Wilson, I. A. , and Kwong, P. D. (2011) Structure of HIV-1 gp 120 V 1/V 2 domain with broadly neutralizing antibody PG 9 Nature 480, 336 -343 67. Pejchal, R. , Doores, K. J. , Walker, L. M. , Khayat, R. , Huang, P. S. , Wang, S. K. , Stanfield, R. L. , Julien, J. P. , Ramos, A. , Crispin, M. , Depetris, R. , Katpally, U. , Marozsan, A. , Cupo, A. , Maloveste, S. , Liu, Y. , Mc. Bride, R. , Ito, Y. , Sanders, R. W. , Ogohara, C. , Paulson, J. C. , Feizi, T. , Scanlan, C. N. , Wong, C. H. , Moore, J. P. , Olson, W. C. , Ward, A. B. , Poignard, P. , Schief, W. R. , Burton, D. R. , and Wilson, I. A. (2011) A potent and broad neutralizing antibody recognizes and penetrates the HIV glycan shield Science 334, 1097 -1103
 Additional Reading Continued: 68. Walker, L. M. , Huber, M. , Doores, K. J. , Falkowska, E. , Pejchal, R. , Julien, J. P. , Wang, S. K. , Ramos, A. , Chan-Hui, P. Y. , Moyle, M. , Mitcham, J. L. , Hammond, P. W. , Olsen, O. A. , Phung, P. , Fling, S. , Wong, C. H. , Phogat, S. , Wrin, T. , Simek, M. D. , Koff, W. C. , Wilson, I. A. , Burton, D. R. , and Poignard, P. (2011) Broad neutralization coverage of HIV by multiple highly potent antibodies Nature 477, 466 -470 69. Tillett, W. S. , and Francis, T. (1929) Cutaneous Reactions to the Polysaccharides and Proteins of Pneumococcus in Lobar Pneumonia The Journal of experimental medicine 50, 687 -701 70. Astronomo, R. D. , and Burton, D. R. (2010) Carbohydrate vaccines: developing sweet solutions to sticky situations? Nature reviews. Drug discovery 9, 308 -324 71. Seeberger, P. H. , and Werz, D. B. (2007) Synthesis and medical applications of oligosaccharides Nature 446, 1046 -1051 72. Lepenies, B. , and Seeberger, P. H. (2010) The promise of glycomics, glycan arrays and carbohydrate-based vaccines Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology 32, 196 -207 73. Huang, Y. L. , and Wu, C. Y. (2010) Carbohydrate-based vaccines: challenges and opportunities Expert review of vaccines 9, 1257 -1274 74. Nyame, A. K. , Kawar, Z. S. , and Cummings, R. D. (2004) Antigenic glycans in parasitic infections: implications for vaccines and diagnostics Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 426, 182 -200 75. Hart, G. W. , Housley, M. P. , and Slawson, C. (2007) Cycling of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins Nature 446, 10171022 76. Copeland, R. J. , Bullen Jr, J. W. , and Hart, G. W. (2008) Crosstalk Between Glc. NAcylation and Phosphorylation: Roles in Insulin Resistance and Glucose Toxicity American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism • Teo, C. F. , Wollaston-Hayden, E. E. , and Wells, L. (2010) Hexosamine flux, the O-Glc. NAc modification, and the development of insulin resistance in adipocytes Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 318, 44 -53 78. Solomon, S. S. , Majumdar, G. , Martinez-Hernandez, A. , and Raghow, R. (2008) A critical role of Sp 1 transcription factor in regulating gene expression in response to insulin and other hormones Life Sci 83, 305 -312 79. Clark, R. J. , Mc. Donough, P. M. , Swanson, E. , Trost, S. U. , Suzuki, M. , Fukuda, M. , and Dillmann, W. H. (2003) Diabetes and the accompanying hyperglycemia impairs cardiomyocyte calcium cycling through increased nuclear O-Glc. NAcylation J Biol Chem 278, 44230 -44237 80. Kudlow, J. E. (2006) Post-translational modification by O-Glc. NAc: another way to change protein function J Cell Biochem 98, 1062 -1075 81. Hu, Y. , Suarez, J. , Fricovsky, E. , Wang, H. , Scott, B. T. , Trauger, S. A. , Han, W. , Oyeleye, M. O. , and Dillmann, W. H. (2009) Increased Enzymatic OGlc. NAcylation of Mitochondrial Proteins Impairs Mitochondrial Function in Cardiac Myocytes Exposed to High Glucose J Biol Chem 284, 547 -555 82. Dias, W. B. , and Hart, G. W. (2007) O-Glc. NAc modification in diabetes and Alzheimer's disease Mol Biosyst 3, 766 -772 83. Lazarus, B. D. , Love, D. C. , and Hanover, J. A. (2009) O-Glc. NAc cycling: implications for neurodegenerative disorders The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology 41, 2134 -2146 84. Skorobogatko, Y. V. , Deuso, J. , Adolf-Bergfoyle, J. , Nowak, M. G. , Gong, Y. , Lippa, C. F. , and Vosseller, K. (2010) Human Alzheimer's disease synaptic O -Glc. NAc site mapping and i. TRAQ expression proteomics with ion trap mass spectrometry Amino Acids 85. Tallent, M. K. , Varghis, N. , Skorobogatko, Y. , Hernandez-Cuebas, L. , Whelan, K. , Vocadlo, D. J. , and Vosseller, K. (2009) In vivo modulation of OGlc. NAc levels regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity through interplay with phosphorylation J Biol Chem 284, 174 -181
Additional Reading Continued: 68. Walker, L. M. , Huber, M. , Doores, K. J. , Falkowska, E. , Pejchal, R. , Julien, J. P. , Wang, S. K. , Ramos, A. , Chan-Hui, P. Y. , Moyle, M. , Mitcham, J. L. , Hammond, P. W. , Olsen, O. A. , Phung, P. , Fling, S. , Wong, C. H. , Phogat, S. , Wrin, T. , Simek, M. D. , Koff, W. C. , Wilson, I. A. , Burton, D. R. , and Poignard, P. (2011) Broad neutralization coverage of HIV by multiple highly potent antibodies Nature 477, 466 -470 69. Tillett, W. S. , and Francis, T. (1929) Cutaneous Reactions to the Polysaccharides and Proteins of Pneumococcus in Lobar Pneumonia The Journal of experimental medicine 50, 687 -701 70. Astronomo, R. D. , and Burton, D. R. (2010) Carbohydrate vaccines: developing sweet solutions to sticky situations? Nature reviews. Drug discovery 9, 308 -324 71. Seeberger, P. H. , and Werz, D. B. (2007) Synthesis and medical applications of oligosaccharides Nature 446, 1046 -1051 72. Lepenies, B. , and Seeberger, P. H. (2010) The promise of glycomics, glycan arrays and carbohydrate-based vaccines Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology 32, 196 -207 73. Huang, Y. L. , and Wu, C. Y. (2010) Carbohydrate-based vaccines: challenges and opportunities Expert review of vaccines 9, 1257 -1274 74. Nyame, A. K. , Kawar, Z. S. , and Cummings, R. D. (2004) Antigenic glycans in parasitic infections: implications for vaccines and diagnostics Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 426, 182 -200 75. Hart, G. W. , Housley, M. P. , and Slawson, C. (2007) Cycling of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins Nature 446, 10171022 76. Copeland, R. J. , Bullen Jr, J. W. , and Hart, G. W. (2008) Crosstalk Between Glc. NAcylation and Phosphorylation: Roles in Insulin Resistance and Glucose Toxicity American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism • Teo, C. F. , Wollaston-Hayden, E. E. , and Wells, L. (2010) Hexosamine flux, the O-Glc. NAc modification, and the development of insulin resistance in adipocytes Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 318, 44 -53 78. Solomon, S. S. , Majumdar, G. , Martinez-Hernandez, A. , and Raghow, R. (2008) A critical role of Sp 1 transcription factor in regulating gene expression in response to insulin and other hormones Life Sci 83, 305 -312 79. Clark, R. J. , Mc. Donough, P. M. , Swanson, E. , Trost, S. U. , Suzuki, M. , Fukuda, M. , and Dillmann, W. H. (2003) Diabetes and the accompanying hyperglycemia impairs cardiomyocyte calcium cycling through increased nuclear O-Glc. NAcylation J Biol Chem 278, 44230 -44237 80. Kudlow, J. E. (2006) Post-translational modification by O-Glc. NAc: another way to change protein function J Cell Biochem 98, 1062 -1075 81. Hu, Y. , Suarez, J. , Fricovsky, E. , Wang, H. , Scott, B. T. , Trauger, S. A. , Han, W. , Oyeleye, M. O. , and Dillmann, W. H. (2009) Increased Enzymatic OGlc. NAcylation of Mitochondrial Proteins Impairs Mitochondrial Function in Cardiac Myocytes Exposed to High Glucose J Biol Chem 284, 547 -555 82. Dias, W. B. , and Hart, G. W. (2007) O-Glc. NAc modification in diabetes and Alzheimer's disease Mol Biosyst 3, 766 -772 83. Lazarus, B. D. , Love, D. C. , and Hanover, J. A. (2009) O-Glc. NAc cycling: implications for neurodegenerative disorders The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology 41, 2134 -2146 84. Skorobogatko, Y. V. , Deuso, J. , Adolf-Bergfoyle, J. , Nowak, M. G. , Gong, Y. , Lippa, C. F. , and Vosseller, K. (2010) Human Alzheimer's disease synaptic O -Glc. NAc site mapping and i. TRAQ expression proteomics with ion trap mass spectrometry Amino Acids 85. Tallent, M. K. , Varghis, N. , Skorobogatko, Y. , Hernandez-Cuebas, L. , Whelan, K. , Vocadlo, D. J. , and Vosseller, K. (2009) In vivo modulation of OGlc. NAc levels regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity through interplay with phosphorylation J Biol Chem 284, 174 -181
 Additional Reading Continued: 86. Rexach, J. E. , Clark, P. M. , Mason, D. E. , Neve, R. L. , Peters, E. C. , and Hsieh-Wilson, L. C. (2012) Dynamic O-Glc. NAc modification regulates CREB-mediated gene expression and memory formation Nature Chemical Biology 8, 253 -261 87. Yuzwa, S. A. , Shan, X. , Macauley, M. S. , Clark, T. , Skorobogatko, Y. , Vosseller, K. , and Vocadlo, D. J. (2012) Increasing O-Glc. NAc slows neurodegeneration and stabilizes tau against aggregation Nature Chemical Biology 88. Ohtsubo, K. , Chen, M. Z. , Olefsky, J. M. , and Marth, J. D. (2011) Pathway to diabetes through attenuation of pancreatic beta cell glycosylation and glucose transport Nature Medicine 17, 1067 -1075 89. Wang, A. , de la Motte, C. , Lauer, M. , and Hascall, V. (2011) Hyaluronan matrices in pathobiological processes The FEBS journal 278, 1412 -1418 90. Jokela, T. A. , Makkonen, K. M. , Oikari, S. , Karna, R. , Koli, E. , Hart, G. W. , Tammi, R. H. , Carlberg, C. , and Tammi, M. I. (2011) Cellular content of UDP-Nacetylhexosamines controls hyaluronan synthase 2 expression and correlates with O-linked N-acetylglucosamine modification of transcription factors YY 1 and SP 1 The Journal of biological chemistry 286, 33632 -33640 91. Jiang, D. , Liang, J. , and Noble, P. W. (2011) Hyaluronan as an immune regulator in human diseases Physiological Reviews 91, 221 -264 92. Galan, M. C. , Benito-Alifonso, D. , and Watt, G. M. (2011) Carbohydrate chemistry in drug discovery Organic & biomolecular chemistry 9, 3598 -3610 93. Shriver, Z. , Raguram, S. , and Sasisekharan, R. (2004) Glycomics: a pathway to a class of new and improved therapeutics Nature reviews. Drug discovery 3, 863 -873 94. Butters, T. D. (2007) Gaucher disease Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 11, 412 -418 95. Cummings, R. D. (2009) The repertoire of glycan determinants in the human glycome Mol Biosyst 5, 1087 -1104 96. Smith, D. F. , Song, X. , and Cummings, R. D. (2010) Use of glycan microarrays to explore specificity of glycan-binding proteins Methods Enzymol 480, 417 -444 97. Liang, P. H. , Wu, C. Y. , Greenberg, W. A. , and Wong, C. H. (2008) Glycan arrays: biological and medical applications Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 12, 86 -92 98. Wu, C. Y. , Liang, P. H. , and Wong, C. H. (2009) New development of glycan arrays Organic & biomolecular chemistry 7, 2247 -2254 99. Yamada, T. (2011) Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies The Keio journal of medicine 60, 37 -46 100. Ghaderi, D. , Taylor, R. E. , Padler-Karavani, V. , Diaz, S. , and Varki, A. (2010) Implications of the presence of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in recombinant therapeutic glycoproteins Nature Biotechnology 28, 863 -867 101. Nieuwdorp, M. , Meuwese, M. C. , Vink, H. , Hoekstra, J. B. , Kastelein, J. J. , and Stroes, E. S. (2005) The endothelial glycocalyx: a potential barrier between health and vascular disease Current opinion in lipidology 16, 507 -511 102. Broekhuizen, L. N. , Mooij, H. L. , Kastelein, J. J. , Stroes, E. S. , Vink, H. , and Nieuwdorp, M. (2009) Endothelial glycocalyx as potential diagnostic and therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease Current opinion in lipidology 20, 57 -62 103. Tannock, L. R. , and King, V. L. (2008) Proteoglycan mediated lipoprotein retention: a mechanism of diabetic atherosclerosis Reviews in Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders 9, 289 -300 104. Stanford, K. I. , Bishop, J. R. , Foley, E. M. , Gonzales, J. C. , Niesman, I. R. , Witztum, J. L. , and Esko, J. D. (2009) Syndecan-1 is the primary heparan sulfate proteoglycan mediating hepatic clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in mice The Journal of clinical investigation 119, 3236 -3245 105. Fulop, N. , Mason, M. M. , Dutta, K. , Wang, P. , Davidoff, A. J. , Marchase, R. B. , and Chatham, J. C. (2007) Impact of Type 2 diabetes and aging on cardiomyocyte function and O-linked N-acetylglucosamine levels in the heart American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 292, C 1370 -1378
Additional Reading Continued: 86. Rexach, J. E. , Clark, P. M. , Mason, D. E. , Neve, R. L. , Peters, E. C. , and Hsieh-Wilson, L. C. (2012) Dynamic O-Glc. NAc modification regulates CREB-mediated gene expression and memory formation Nature Chemical Biology 8, 253 -261 87. Yuzwa, S. A. , Shan, X. , Macauley, M. S. , Clark, T. , Skorobogatko, Y. , Vosseller, K. , and Vocadlo, D. J. (2012) Increasing O-Glc. NAc slows neurodegeneration and stabilizes tau against aggregation Nature Chemical Biology 88. Ohtsubo, K. , Chen, M. Z. , Olefsky, J. M. , and Marth, J. D. (2011) Pathway to diabetes through attenuation of pancreatic beta cell glycosylation and glucose transport Nature Medicine 17, 1067 -1075 89. Wang, A. , de la Motte, C. , Lauer, M. , and Hascall, V. (2011) Hyaluronan matrices in pathobiological processes The FEBS journal 278, 1412 -1418 90. Jokela, T. A. , Makkonen, K. M. , Oikari, S. , Karna, R. , Koli, E. , Hart, G. W. , Tammi, R. H. , Carlberg, C. , and Tammi, M. I. (2011) Cellular content of UDP-Nacetylhexosamines controls hyaluronan synthase 2 expression and correlates with O-linked N-acetylglucosamine modification of transcription factors YY 1 and SP 1 The Journal of biological chemistry 286, 33632 -33640 91. Jiang, D. , Liang, J. , and Noble, P. W. (2011) Hyaluronan as an immune regulator in human diseases Physiological Reviews 91, 221 -264 92. Galan, M. C. , Benito-Alifonso, D. , and Watt, G. M. (2011) Carbohydrate chemistry in drug discovery Organic & biomolecular chemistry 9, 3598 -3610 93. Shriver, Z. , Raguram, S. , and Sasisekharan, R. (2004) Glycomics: a pathway to a class of new and improved therapeutics Nature reviews. Drug discovery 3, 863 -873 94. Butters, T. D. (2007) Gaucher disease Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 11, 412 -418 95. Cummings, R. D. (2009) The repertoire of glycan determinants in the human glycome Mol Biosyst 5, 1087 -1104 96. Smith, D. F. , Song, X. , and Cummings, R. D. (2010) Use of glycan microarrays to explore specificity of glycan-binding proteins Methods Enzymol 480, 417 -444 97. Liang, P. H. , Wu, C. Y. , Greenberg, W. A. , and Wong, C. H. (2008) Glycan arrays: biological and medical applications Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 12, 86 -92 98. Wu, C. Y. , Liang, P. H. , and Wong, C. H. (2009) New development of glycan arrays Organic & biomolecular chemistry 7, 2247 -2254 99. Yamada, T. (2011) Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies The Keio journal of medicine 60, 37 -46 100. Ghaderi, D. , Taylor, R. E. , Padler-Karavani, V. , Diaz, S. , and Varki, A. (2010) Implications of the presence of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in recombinant therapeutic glycoproteins Nature Biotechnology 28, 863 -867 101. Nieuwdorp, M. , Meuwese, M. C. , Vink, H. , Hoekstra, J. B. , Kastelein, J. J. , and Stroes, E. S. (2005) The endothelial glycocalyx: a potential barrier between health and vascular disease Current opinion in lipidology 16, 507 -511 102. Broekhuizen, L. N. , Mooij, H. L. , Kastelein, J. J. , Stroes, E. S. , Vink, H. , and Nieuwdorp, M. (2009) Endothelial glycocalyx as potential diagnostic and therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease Current opinion in lipidology 20, 57 -62 103. Tannock, L. R. , and King, V. L. (2008) Proteoglycan mediated lipoprotein retention: a mechanism of diabetic atherosclerosis Reviews in Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders 9, 289 -300 104. Stanford, K. I. , Bishop, J. R. , Foley, E. M. , Gonzales, J. C. , Niesman, I. R. , Witztum, J. L. , and Esko, J. D. (2009) Syndecan-1 is the primary heparan sulfate proteoglycan mediating hepatic clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in mice The Journal of clinical investigation 119, 3236 -3245 105. Fulop, N. , Mason, M. M. , Dutta, K. , Wang, P. , Davidoff, A. J. , Marchase, R. B. , and Chatham, J. C. (2007) Impact of Type 2 diabetes and aging on cardiomyocyte function and O-linked N-acetylglucosamine levels in the heart American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 292, C 1370 -1378
 Additional Reading Continued: 105. Fulop, N. , Mason, M. M. , Dutta, K. , Wang, P. , Davidoff, A. J. , Marchase, R. B. , and Chatham, J. C. (2007) Impact of Type 2 diabetes and aging on cardiomyocyte function and O-linked N-acetylglucosamine levels in the heart American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 292, C 1370 -1378 106. Jones, S. P. (2005) A bittersweet modification: O-Glc. NAc and cardiac dysfunction Circ Res 96, 925 -926 107. Ramirez-Correa, G. A. , Jin, W. , Wang, Z. , Zhong, X. , Gao, W. D. , Dias, W. B. , Vecoli, C. , Hart, G. W. , and Murphy, A. M. (2008) O-Linked Glc. NAc Modification of Cardiac Myofilament Proteins. A Novel Regulator of Myocardial Contractile Function Circ Res 108. Hennet, T. (2012) Diseases of glycosylation beyond classical congenital disorders of glycosylation Biochimica et biophysica acta 109. Freeze, H. H. , and Ng, B. G. (2011) Golgi glycosylation and human inherited diseases Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 3, a 005371 110. Jaeken, J. (2011) Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG): it's (nearly) all in it! Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 34, 853 -858 111. Muntoni, F. , Torelli, S. , Wells, D. J. , and Brown, S. C. (2011) Muscular dystrophies due to glycosylation defects: diagnosis and therapeutic strategies Current opinion in neurology 24, 437 -442 112. Godfrey, C. , Foley, A. R. , Clement, E. , and Muntoni, F. (2011) Dystroglycanopathies: coming into focus Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 21, 278 -285 113. Cox, T. M. , and Cachon-Gonzalez, M. B. (2012) The cellular pathology of lysosomal diseases The Journal of pathology 226, 241 -254 114. Kornfeld, S. (2010) A fascination with sugars Molecular biology of the cell 21, 3773 -3775 115. Coutinho, M. F. , Lacerda, L. , and Alves, S. (2012) Glycosaminoglycan storage disorders: a review Biochemistry research international 2012, 471325 116. Schulze, H. , and Sandhoff, K. (2011) Lysosomal lipid storage diseases Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 3
Additional Reading Continued: 105. Fulop, N. , Mason, M. M. , Dutta, K. , Wang, P. , Davidoff, A. J. , Marchase, R. B. , and Chatham, J. C. (2007) Impact of Type 2 diabetes and aging on cardiomyocyte function and O-linked N-acetylglucosamine levels in the heart American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 292, C 1370 -1378 106. Jones, S. P. (2005) A bittersweet modification: O-Glc. NAc and cardiac dysfunction Circ Res 96, 925 -926 107. Ramirez-Correa, G. A. , Jin, W. , Wang, Z. , Zhong, X. , Gao, W. D. , Dias, W. B. , Vecoli, C. , Hart, G. W. , and Murphy, A. M. (2008) O-Linked Glc. NAc Modification of Cardiac Myofilament Proteins. A Novel Regulator of Myocardial Contractile Function Circ Res 108. Hennet, T. (2012) Diseases of glycosylation beyond classical congenital disorders of glycosylation Biochimica et biophysica acta 109. Freeze, H. H. , and Ng, B. G. (2011) Golgi glycosylation and human inherited diseases Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 3, a 005371 110. Jaeken, J. (2011) Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG): it's (nearly) all in it! Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 34, 853 -858 111. Muntoni, F. , Torelli, S. , Wells, D. J. , and Brown, S. C. (2011) Muscular dystrophies due to glycosylation defects: diagnosis and therapeutic strategies Current opinion in neurology 24, 437 -442 112. Godfrey, C. , Foley, A. R. , Clement, E. , and Muntoni, F. (2011) Dystroglycanopathies: coming into focus Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 21, 278 -285 113. Cox, T. M. , and Cachon-Gonzalez, M. B. (2012) The cellular pathology of lysosomal diseases The Journal of pathology 226, 241 -254 114. Kornfeld, S. (2010) A fascination with sugars Molecular biology of the cell 21, 3773 -3775 115. Coutinho, M. F. , Lacerda, L. , and Alves, S. (2012) Glycosaminoglycan storage disorders: a review Biochemistry research international 2012, 471325 116. Schulze, H. , and Sandhoff, K. (2011) Lysosomal lipid storage diseases Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 3


