9f46af4f78682a113db0102ede70525d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65

 Evaluation of Suspected Valvular Heart Disease in the Outpatient Setting Richard J Gordon, MD. , FACC No Financial Relationships to Disclose
Evaluation of Suspected Valvular Heart Disease in the Outpatient Setting Richard J Gordon, MD. , FACC No Financial Relationships to Disclose
 Case The patient is a 75 year old woman who goes to see her PCP for a routine visit and is found on cardiac exam to have a murmur. The patient is relatively inactive and the most she does is walk around her house. She sometimes feels “weak” but does not report any obvious shortness of breath, angina, palpitations or syncope. She denies any significant PMH and no previous surgery. What to do next?
Case The patient is a 75 year old woman who goes to see her PCP for a routine visit and is found on cardiac exam to have a murmur. The patient is relatively inactive and the most she does is walk around her house. She sometimes feels “weak” but does not report any obvious shortness of breath, angina, palpitations or syncope. She denies any significant PMH and no previous surgery. What to do next?
 Approach History ****Physical Exam**** Electrocardiogram Chest x ray ****ECHO**** Stress test MRI/CT/Cardiac Catheterization
Approach History ****Physical Exam**** Electrocardiogram Chest x ray ****ECHO**** Stress test MRI/CT/Cardiac Catheterization
 HISTORY
HISTORY
 History of Present Illness/Family History May or may not be helpful Clinical scenario helpful (IV drug abuse, h/o rheumatic fever or MVP) Shortness of breath, syncope, palpitations, angina FH of congenital heart disease Previous procedures (i. e. , previous valve replacement)
History of Present Illness/Family History May or may not be helpful Clinical scenario helpful (IV drug abuse, h/o rheumatic fever or MVP) Shortness of breath, syncope, palpitations, angina FH of congenital heart disease Previous procedures (i. e. , previous valve replacement)
 Physical Examination
Physical Examination
 Physical Exam Heart Sounds Pulses and pulse pressures, differential, bounding Cyanosis/clubbing Hepatomegaly Palpable thrill ***Murmur***
Physical Exam Heart Sounds Pulses and pulse pressures, differential, bounding Cyanosis/clubbing Hepatomegaly Palpable thrill ***Murmur***
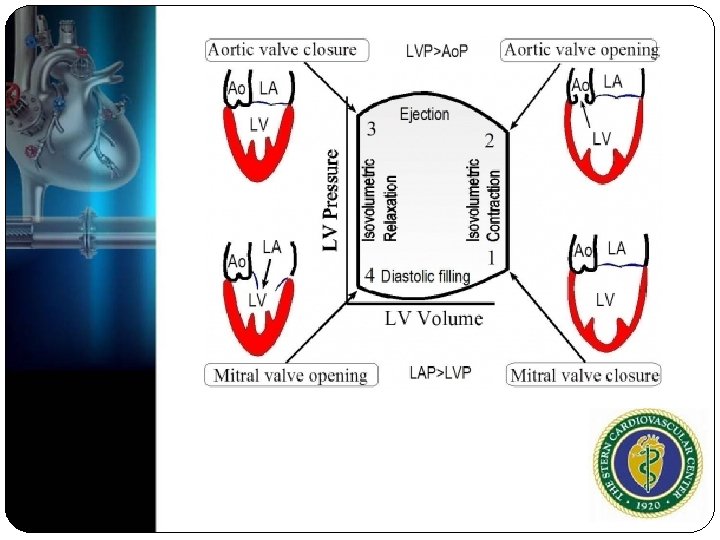
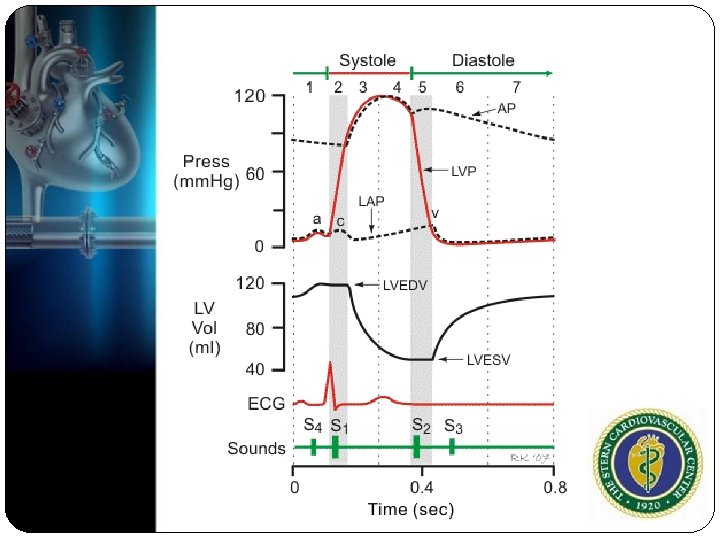
 Origin of Murmur Forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or chamber (stenosis) Backward flow through an incompetent valve(regurgitation) High blood flow through a normal or abnormal valve
Origin of Murmur Forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or chamber (stenosis) Backward flow through an incompetent valve(regurgitation) High blood flow through a normal or abnormal valve

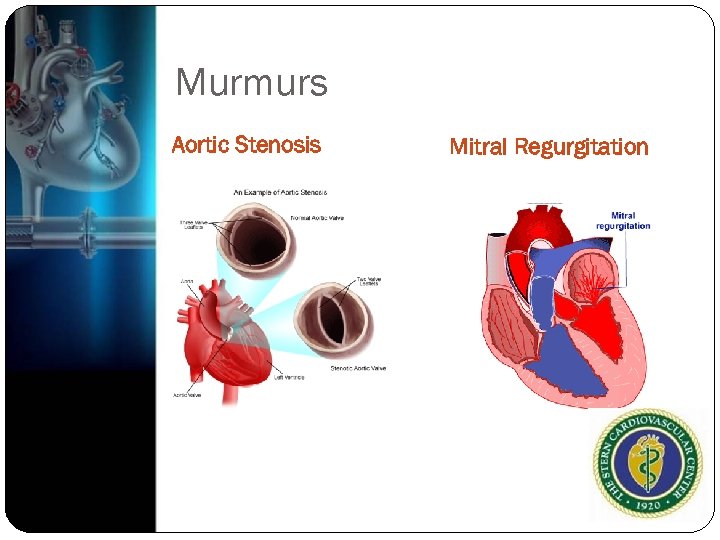 Murmurs Aortic Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation
Murmurs Aortic Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation
 Murmur Pathologic Innocent Diastolic High flow (younger pts, Some systolic murmurs anemia, thyrotoxicosis) Venous hums Mammary souffles Trivial or minimal systolic murmur
Murmur Pathologic Innocent Diastolic High flow (younger pts, Some systolic murmurs anemia, thyrotoxicosis) Venous hums Mammary souffles Trivial or minimal systolic murmur
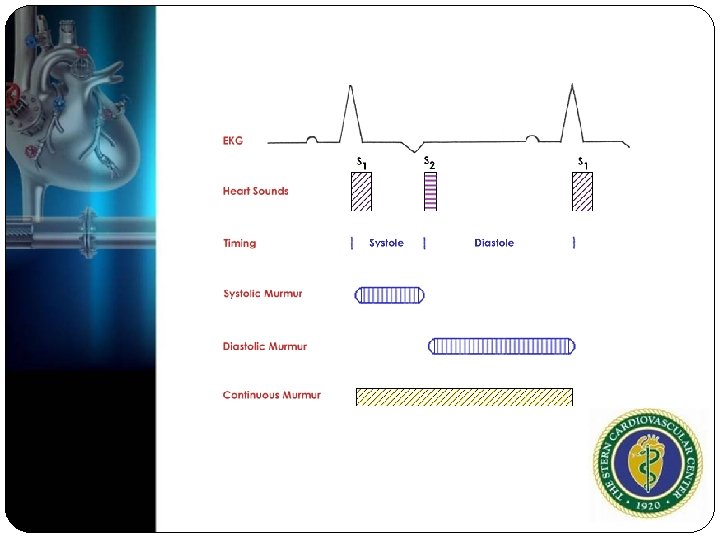
 Murmur Systolic Diastolic Pansystolic Early high-pitched (holosystolic) Systolic ejection (midsystolic) Early systolic Mid to late systolic murmurs Continuous murmurs diastolic murmurs Middiastolic murmurs Presystolic murmurs Continuous murmurs
Murmur Systolic Diastolic Pansystolic Early high-pitched (holosystolic) Systolic ejection (midsystolic) Early systolic Mid to late systolic murmurs Continuous murmurs diastolic murmurs Middiastolic murmurs Presystolic murmurs Continuous murmurs

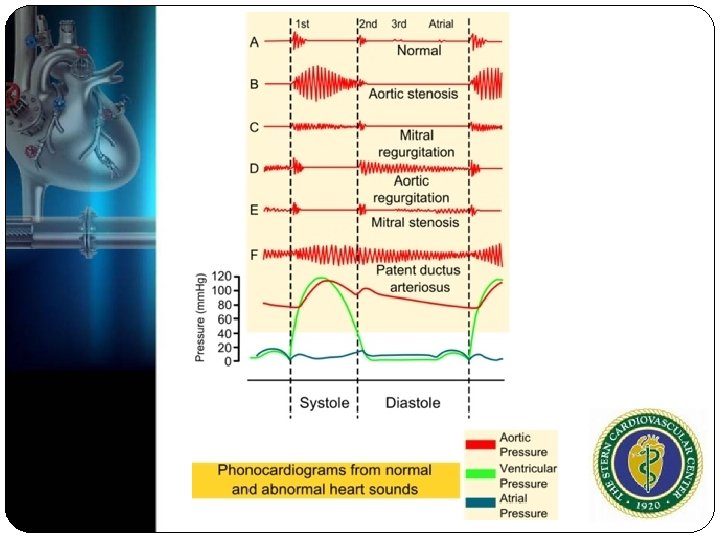
 8 Characteristics of Heart Murmur Timing in cardiac cycle Intensity (1 barely audible, 2 quiet but obvious, 3 moderate, 4 loud, 5 louder heard with stethoscope barely off chest, 6 very loud heart without a stethoscope) Location of maximal intensity Shape (crescendo, decrescendo, crescendodecrescendo, plateau) Duration (pan-systolic, mid-systolic, etc) Radiation(axillary, carotids) Quality (blowing, musical, rumbling, machinery) Pitch (high, medium or low)
8 Characteristics of Heart Murmur Timing in cardiac cycle Intensity (1 barely audible, 2 quiet but obvious, 3 moderate, 4 loud, 5 louder heard with stethoscope barely off chest, 6 very loud heart without a stethoscope) Location of maximal intensity Shape (crescendo, decrescendo, crescendodecrescendo, plateau) Duration (pan-systolic, mid-systolic, etc) Radiation(axillary, carotids) Quality (blowing, musical, rumbling, machinery) Pitch (high, medium or low)
 Holosystolic Murmur Wide pressure gradient throughout systole Mitral regurgitation/Tricuspid Regurgitation High pitched blowing, holosystolic heard best at apex, radiating to axilla
Holosystolic Murmur Wide pressure gradient throughout systole Mitral regurgitation/Tricuspid Regurgitation High pitched blowing, holosystolic heard best at apex, radiating to axilla
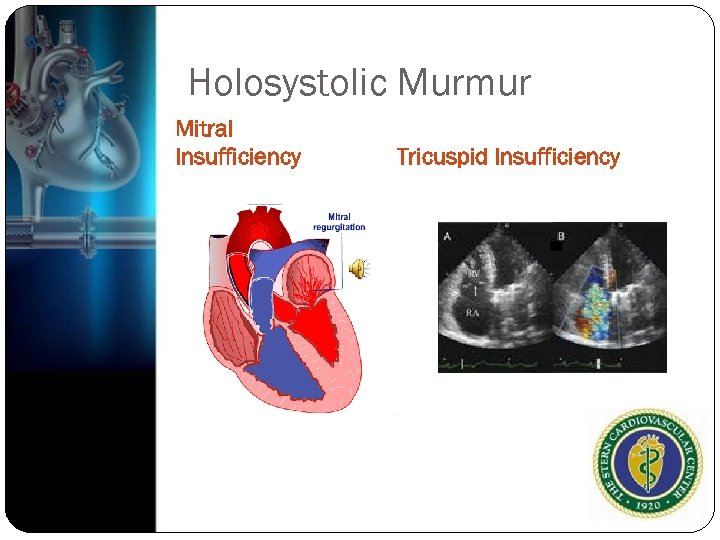 Holosystolic Murmur Mitral Insufficiency Tricuspid Insufficiency
Holosystolic Murmur Mitral Insufficiency Tricuspid Insufficiency
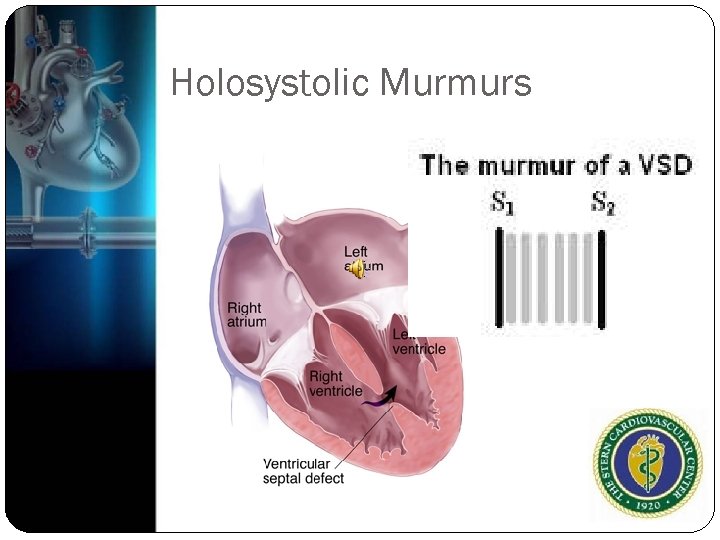 Holosystolic Murmurs
Holosystolic Murmurs
 Midsystolic Usually crescendo-decrescendo murmurs With increased ejection the murmur is louder, and subsides with relaxation High flow rates with increased cardiac output Harsh systolic, crescendo-decrescendo murmur heard right upper sternal border, radiates to carotids
Midsystolic Usually crescendo-decrescendo murmurs With increased ejection the murmur is louder, and subsides with relaxation High flow rates with increased cardiac output Harsh systolic, crescendo-decrescendo murmur heard right upper sternal border, radiates to carotids
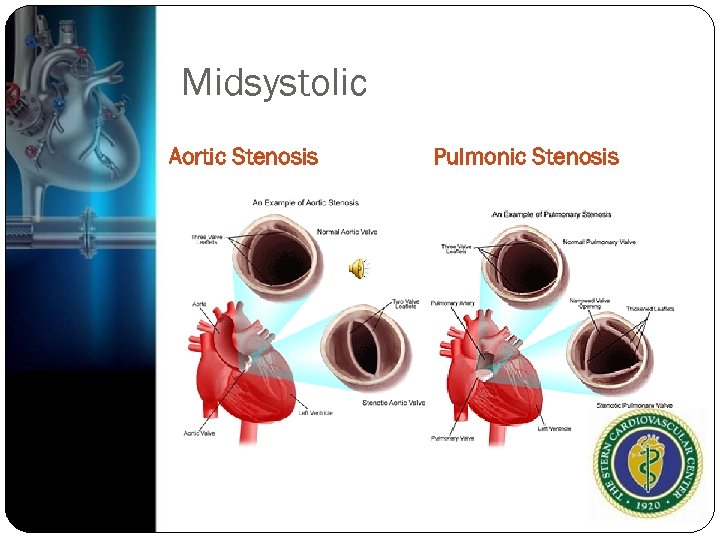 Midsystolic Aortic Stenosis Pulmonic Stenosis
Midsystolic Aortic Stenosis Pulmonic Stenosis
 Early Systolic Murmur Much less common and may be difficult to hear Acute MR
Early Systolic Murmur Much less common and may be difficult to hear Acute MR
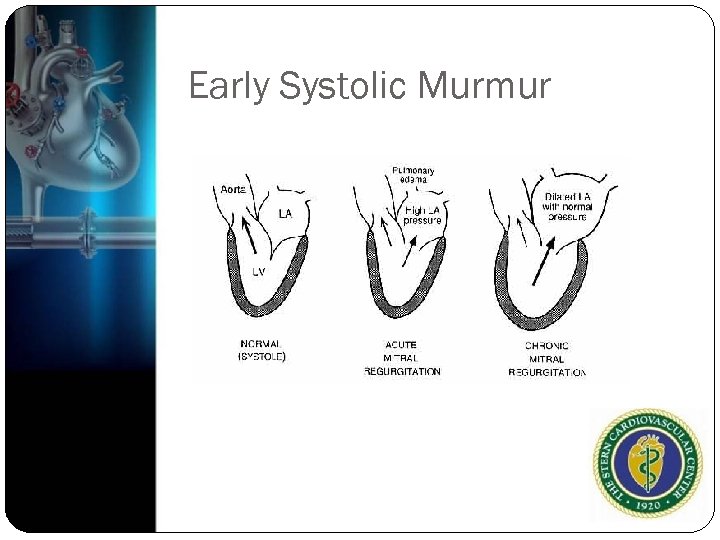 Early Systolic Murmur
Early Systolic Murmur
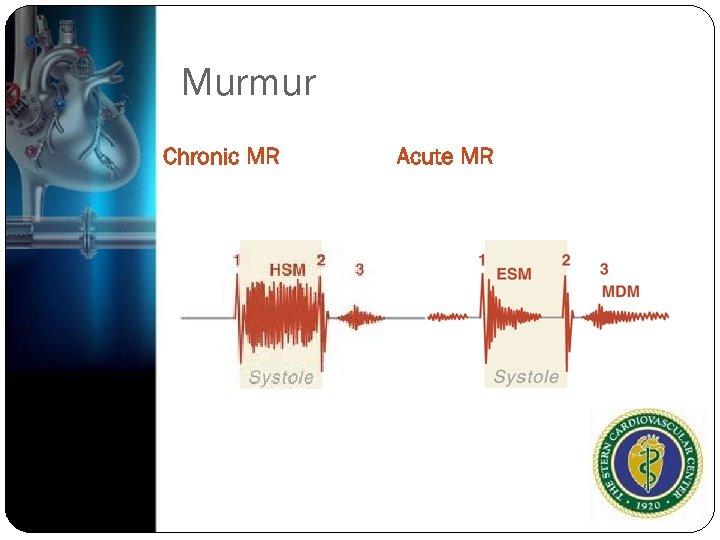 Murmur Chronic MR Acute MR
Murmur Chronic MR Acute MR
 Late Systolic Murmur Soft or moderately loud, high pitched sounds at LV apex Malcoaptation of mitral leaflets MVP late systolic murmurs with a click Advanced aortic stenosis with decreased or absent S 2 and often S 4
Late Systolic Murmur Soft or moderately loud, high pitched sounds at LV apex Malcoaptation of mitral leaflets MVP late systolic murmurs with a click Advanced aortic stenosis with decreased or absent S 2 and often S 4
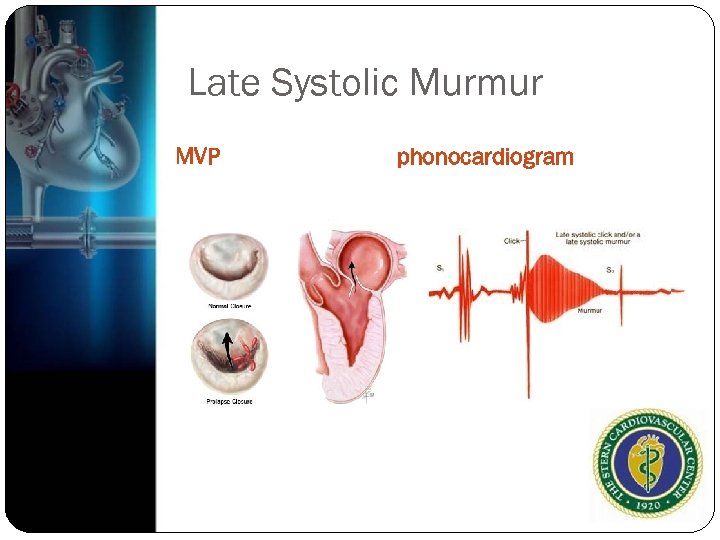 Late Systolic Murmur MVP phonocardiogram
Late Systolic Murmur MVP phonocardiogram

 Early Diastolic Murmur Occurs shortly after S 2 when intraventricular pressure drops below aortic or pulmonary pressures Aortic regurgitation or pulmonary regurgitation Decrescendo murmurs, soft and in early diastole, high pitched, often faint and blowing quality Heard best at left upper sternal border when patient is seated forward and during expiration
Early Diastolic Murmur Occurs shortly after S 2 when intraventricular pressure drops below aortic or pulmonary pressures Aortic regurgitation or pulmonary regurgitation Decrescendo murmurs, soft and in early diastole, high pitched, often faint and blowing quality Heard best at left upper sternal border when patient is seated forward and during expiration
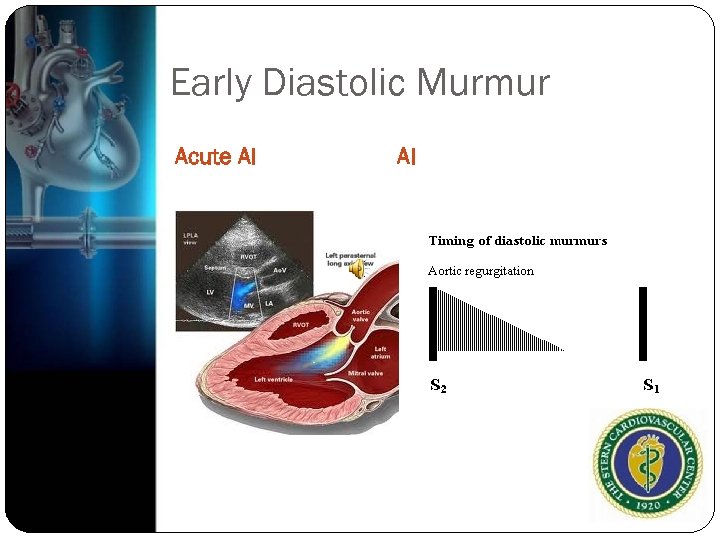 Early Diastolic Murmur Acute AI AI
Early Diastolic Murmur Acute AI AI
 Middiastolic murmur Mismatch between diastolic flow and valve size Mitral stenosis/Tricuspid stenosis ASD Severe, chronic AR( Austin Flint) Left lateral lying position
Middiastolic murmur Mismatch between diastolic flow and valve size Mitral stenosis/Tricuspid stenosis ASD Severe, chronic AR( Austin Flint) Left lateral lying position
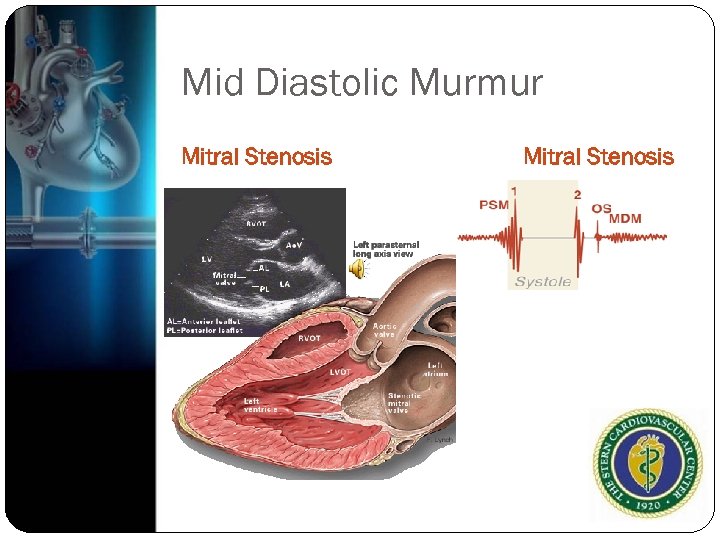 Mid Diastolic Murmur Mitral Stenosis
Mid Diastolic Murmur Mitral Stenosis
 Presystolic Sound heard after atrial contraction in diastole Usually occur with mitral or tricuspid stenosis Myxoma
Presystolic Sound heard after atrial contraction in diastole Usually occur with mitral or tricuspid stenosis Myxoma
 Continuous Murmurs Occur in of systole and persist the into all are part of diastole High to low pressure gradients that are present for end of systole and beginning of diastole Persistent, Patent ductus arteriosis Intracardias Shunts
Continuous Murmurs Occur in of systole and persist the into all are part of diastole High to low pressure gradients that are present for end of systole and beginning of diastole Persistent, Patent ductus arteriosis Intracardias Shunts
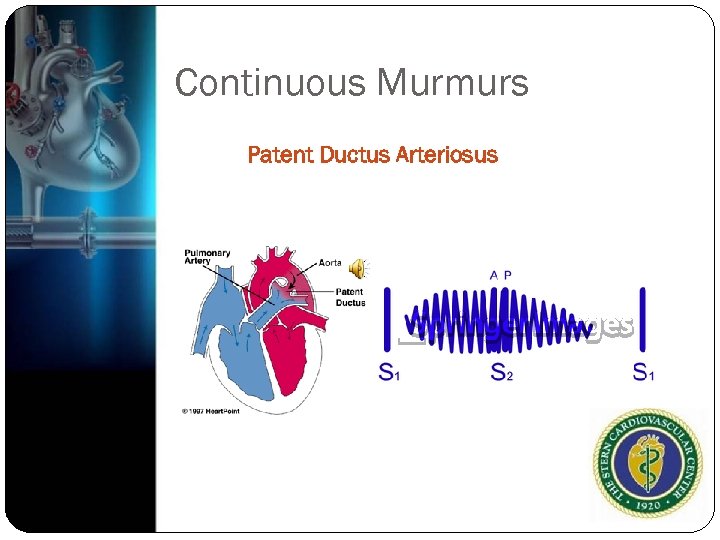 Continuous Murmurs Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Continuous Murmurs Patent Ductus Arteriosus

 Benign systolic murmur
Benign systolic murmur

 Echocardiography 2 D 3 D Color flow Doppler (CW and PW) TDI
Echocardiography 2 D 3 D Color flow Doppler (CW and PW) TDI
 Echocardiography Valve Morphology Function Associated chamber sizes Ventricular function Associated hypertrophy Pulmonary vein and hepatic vein flow Pulmonary pressures
Echocardiography Valve Morphology Function Associated chamber sizes Ventricular function Associated hypertrophy Pulmonary vein and hepatic vein flow Pulmonary pressures
 Purpose of Echocardiography Identify the primary source of murmur Define pressure gradients/hemodynamics Detect secondary lesions Establish a reference for comparisons Chamber size and function In association with exercise in select cases
Purpose of Echocardiography Identify the primary source of murmur Define pressure gradients/hemodynamics Detect secondary lesions Establish a reference for comparisons Chamber size and function In association with exercise in select cases
 When Echo is probably not necessary Grade 1 or 2 murmur in absence of suspected endocarditis Normal systolic ejection pattern Normal heart sounds No suggestion of more severe heart disease with provocative maneuvers
When Echo is probably not necessary Grade 1 or 2 murmur in absence of suspected endocarditis Normal systolic ejection pattern Normal heart sounds No suggestion of more severe heart disease with provocative maneuvers
 Echocardiography: Indications Level 1 C Asymptomatic patients with diastolic murmurs, continuous murmurs, holosystolic, late systolic murmurs, murmurs associated with ejection clicks or murmurs that radiate to the neck or back Murmurs with associated sxs or signs of heart disease Asymptomatic with grade 3 or louder midpeaking systolic murmur
Echocardiography: Indications Level 1 C Asymptomatic patients with diastolic murmurs, continuous murmurs, holosystolic, late systolic murmurs, murmurs associated with ejection clicks or murmurs that radiate to the neck or back Murmurs with associated sxs or signs of heart disease Asymptomatic with grade 3 or louder midpeaking systolic murmur
 Class IIa Useful for evaluation of asymp pts with murmur associated with other abnl cardiac physical findings (abnormal EKG or CXR) Can be useful in patients whose signs/sxs are likely noncardiac in origin but cannot rule out cardiac basis
Class IIa Useful for evaluation of asymp pts with murmur associated with other abnl cardiac physical findings (abnormal EKG or CXR) Can be useful in patients whose signs/sxs are likely noncardiac in origin but cannot rule out cardiac basis
 Class III Grade 2 or softer midsystolic murmur (innocent murmurs)
Class III Grade 2 or softer midsystolic murmur (innocent murmurs)
 National Center for Health Statistics 1999 -2009 The number of transthoracic echoes have grown by 90 % and TEE by 70% JACC Vol. 60 Suppl No. 25, 2012
National Center for Health Statistics 1999 -2009 The number of transthoracic echoes have grown by 90 % and TEE by 70% JACC Vol. 60 Suppl No. 25, 2012

 Case The patient is a 75 yo woman who goes to see her PCP for a routine visit and is found on cardiac exam to have a murmur. The patient is relatively inactive and the most she does is walk around her house. She sometimes feels “weak” but does not report any obvious shortness of breath, angina, palpitations or syncope. She denies any significant PMH and no previous surgery. What to do next?
Case The patient is a 75 yo woman who goes to see her PCP for a routine visit and is found on cardiac exam to have a murmur. The patient is relatively inactive and the most she does is walk around her house. She sometimes feels “weak” but does not report any obvious shortness of breath, angina, palpitations or syncope. She denies any significant PMH and no previous surgery. What to do next?
 Physical Exam BP 140/80 pulse 75 Carotid Upstroke is delayed and weak (pulsus tardus) Mid to late peaking murmur is heard at RUSB radiating to carotids. S 1 normal, S 2 absent, and S 4 heard
Physical Exam BP 140/80 pulse 75 Carotid Upstroke is delayed and weak (pulsus tardus) Mid to late peaking murmur is heard at RUSB radiating to carotids. S 1 normal, S 2 absent, and S 4 heard

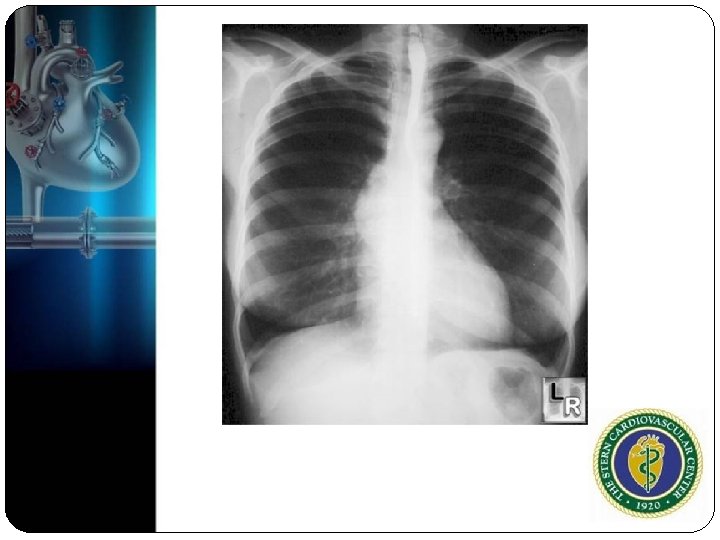
 Should we get an echo? What’s the diagnosis?
Should we get an echo? What’s the diagnosis?
 Case The patient is a 75 yo woman who goes to see her PCP for a routine visit and is found on cardiac exam to have a murmur. The patient is relatively inactive and the most she does is walk around her house. She sometimes feels “weak” and does report shortness of breath. She denies any significant PMH and no previous surgery. What to do next?
Case The patient is a 75 yo woman who goes to see her PCP for a routine visit and is found on cardiac exam to have a murmur. The patient is relatively inactive and the most she does is walk around her house. She sometimes feels “weak” and does report shortness of breath. She denies any significant PMH and no previous surgery. What to do next?
 Physical Exam Anxious and tachypnic BP 170/100 120, irreg RR 25 Brisk, irregular, and sharp, but weak carotid upstroke Lungs: Rales heard throughout lung fields Cardiac: Irregularly, Irregular and rapid, high pitched , blowing holosystolic 3/6 systolic murmur heard best at the apex
Physical Exam Anxious and tachypnic BP 170/100 120, irreg RR 25 Brisk, irregular, and sharp, but weak carotid upstroke Lungs: Rales heard throughout lung fields Cardiac: Irregularly, Irregular and rapid, high pitched , blowing holosystolic 3/6 systolic murmur heard best at the apex

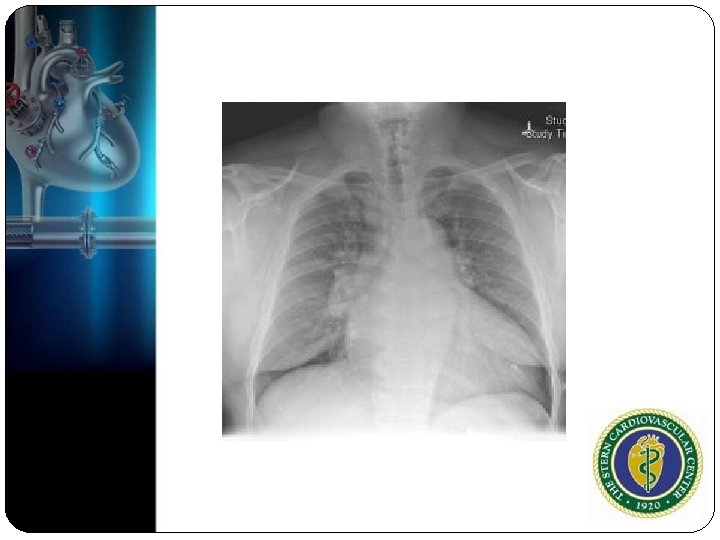
 Do you want to get an echo? What’s the diagnosis?
Do you want to get an echo? What’s the diagnosis?
 Case The patient is a 75 yo woman who goes to see her PCP for a routine visit and is found on cardiac exam to have a murmur. The patient is relatively inactive and the most she does is walk around her house. She sometimes feels “weak” but does not report shortness of breath, angina, palpitations or syncope. She denies any significant PMH and no previous surgery. What to do next?
Case The patient is a 75 yo woman who goes to see her PCP for a routine visit and is found on cardiac exam to have a murmur. The patient is relatively inactive and the most she does is walk around her house. She sometimes feels “weak” but does not report shortness of breath, angina, palpitations or syncope. She denies any significant PMH and no previous surgery. What to do next?
 Physical Exam 120/80 pulse 60, regular Normal Carotid upstroke Regularly Rhythm Early Systolic ejection murmur heard at RUSB 2/6
Physical Exam 120/80 pulse 60, regular Normal Carotid upstroke Regularly Rhythm Early Systolic ejection murmur heard at RUSB 2/6
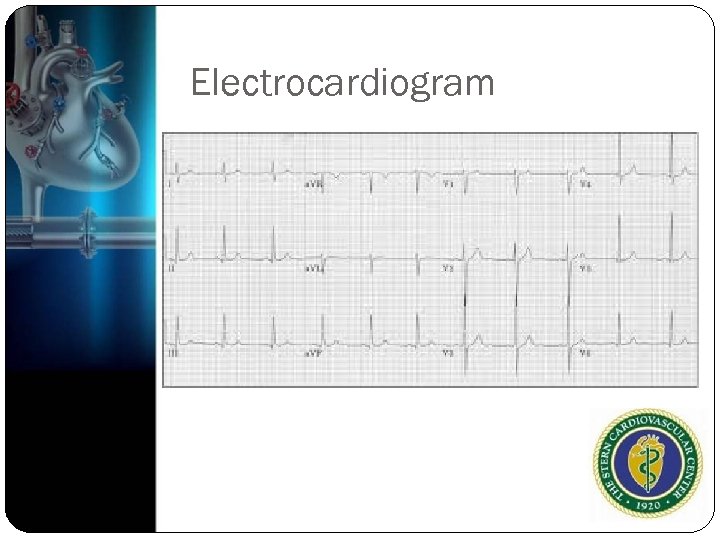 Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram
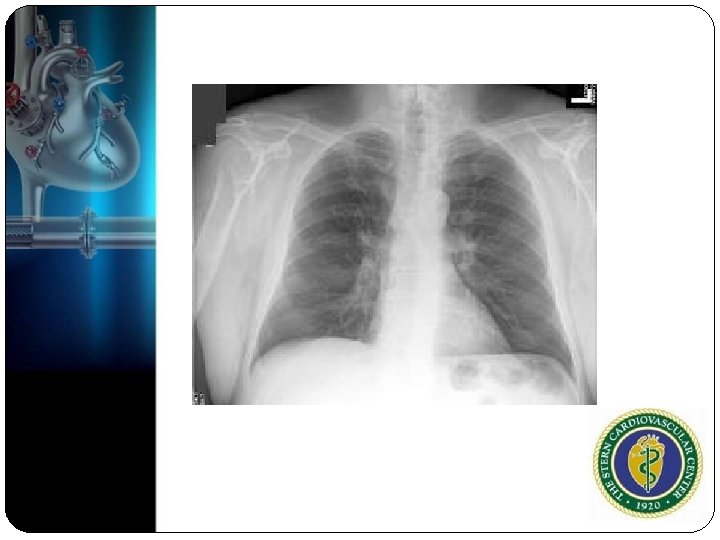
 Do we need an echo?
Do we need an echo?
 Questions?
Questions?


