9ac7234230ce5d1cf7f615663c7103b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Evaluation of Corneal Parameters and Spherical Aberration After DSAEK Measured with Pentacam System Orkun Muftuoglu, Pawan Prasher, R. Wayne Bowman, Steven M. Verity, H. Dwight Cavanagh, James P. Mc. Culley V. Vinod Mootha MD University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, Texas

Financial Disclosure ► ► ► UT Southwestern Medical Center & Aston Ophthalmology Clinic, Dallas, TX. Drs. Bowman, Verity, and Mc. Culley receive consultant reimbursement from Alcon Inc. Dr. Cavanagh receives research reimbursements from Ciba Inc and Menion Inc. None of the authors have financial interest in the subject matter of this poster. Acknowledgements: Supported in part by an unrestricted research grant from Research to Prevent Blindness, Inc. , New York.

Introduction ► ► DSAEK is a technique for selective replacement of dysfunctional endothelium § Rapid recovery of vision § Minimal induced astigmatism and anisometropia § Enhanced resistance to trauma § Less risk of expulsive choroidal hemorrhage § Fewer ocular surface problems Despite favorable visual outcomes, fewer patients than expected achieve BCVA of 20/20. Probable limiting factors: subepithelial scarring, interface changes, increased corneal thickness and increased higher order aberrations Hyperopic shift- Anatomical changes induced to posterior corneal surface? ? ?
Purpose ► Compare corneal parameters of the eyes that underwent DSAEK with age-matched controls using rotating Scheimpflug imaging system

Materials and Methods 32 eyes (28 patients) who underwent DSAEK 32 eyes (32 patients) age-matched controls (no previous ocular surgery) Pentacam § Study group had Scheimpflug images (Pentacam, Oculus, Germany) taken after 3 months post -operatively § Scheimpflug camera and a monochromatic light source § The system rotates 180 degrees and takes 25 -50 images of the anterior segment in about 2 seconds § Calculates a 3 -dimensional model of the anterior eye segment from as many as 25, 000 true elevation points ► Paremeters evaluated § Mean anterior keratometry (Ka) § Mean posterior keratometry (Kp) § Mean anterior radius of curvature (Ra) § Mean posterior radius of curvature (Rp) § True net power (TNP) § Central corneal thickness (CCT) § Corneal volume (CV) § Keratometric Power Deviation (KPD) § Mean anterior and posterior astigmatism § Equivalent K Readings (EKR) in 2, 4 and 6 mm zone § HOAs data up to 6 th order from anterior and posterior surface in the central 6. 0 mm zone § Corneal densitometry ► DSAEK- 16 eyes ► Phacoemulsification with DSAEK- 14 eyes ► DSAEK with IOL exchange- 2 eyes ► 17 clear corneal and 15 scleral tunnel ► Graft size was 8. 0 mm or larger in all cases ► ►
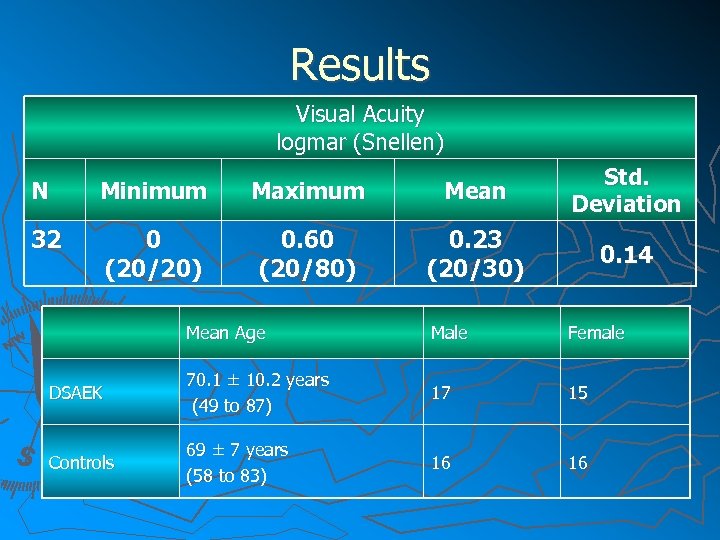
Results Visual Acuity logmar (Snellen) N Minimum Maximum Mean Std. Deviation 32 0 (20/20) 0. 60 (20/80) 0. 23 (20/30) 0. 14 Mean Age Male Female DSAEK 70. 1 ± 10. 2 years (49 to 87) 17 15 Controls 69 ± 7 years (58 to 83) 16 16
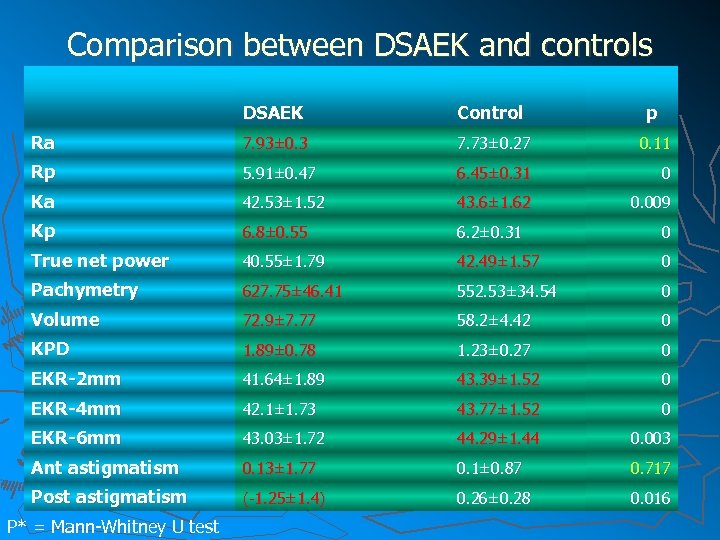
Comparison between DSAEK and controls DSAEK Control p Ra 7. 93± 0. 3 7. 73± 0. 27 0. 11 Rp 5. 91± 0. 47 6. 45± 0. 31 0 Ka 42. 53± 1. 52 43. 6± 1. 62 0. 009 Kp 6. 8± 0. 55 6. 2± 0. 31 0 True net power 40. 55± 1. 79 42. 49± 1. 57 0 Pachymetry 627. 75± 46. 41 552. 53± 34. 54 0 Volume 72. 9± 7. 77 58. 2± 4. 42 0 KPD 1. 89± 0. 78 1. 23± 0. 27 0 EKR-2 mm 41. 64± 1. 89 43. 39± 1. 52 0 EKR-4 mm 42. 1± 1. 73 43. 77± 1. 52 0 EKR-6 mm 43. 03± 1. 72 44. 29± 1. 44 0. 003 Ant astigmatism 0. 13± 1. 77 0. 1± 0. 87 0. 717 Post astigmatism (-1. 25± 1. 4) 0. 26± 0. 28 0. 016 P* = Mann-Whitney U test
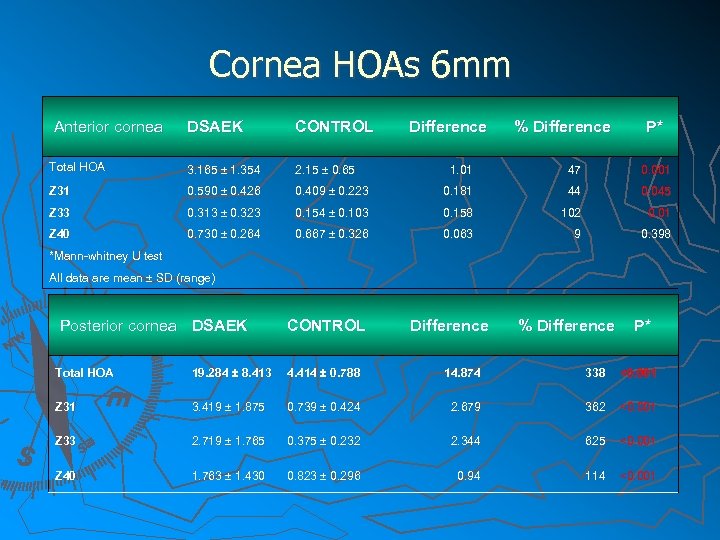
Cornea HOAs 6 mm Anterior cornea DSAEK CONTROL Total HOA 3. 165 ± 1. 354 2. 15 ± 0. 65 Z 31 0. 590 ± 0. 426 Z 33 Z 40 Difference % Difference P* 1. 01 47 0. 001 0. 409 ± 0. 223 0. 181 44 0. 045 0. 313 ± 0. 323 0. 154 ± 0. 103 0. 158 102 0. 01 0. 730 ± 0. 264 0. 667 ± 0. 326 0. 063 9 0. 398 *Mann-whitney U test Mann- whitney U test All data are mean ± SD (range) Posterior cornea DSAEK CONTROL Difference % Difference P* Total HOA 19. 284 ± 8. 413 4. 414 ± 0. 788 14. 874 338 <0. 001 Z 31 3. 419 ± 1. 875 0. 739 ± 0. 424 2. 679 362 <0. 001 Z 33 2. 719 ± 1. 765 0. 375 ± 0. 232 2. 344 625 <0. 001 Z 40 1. 763 ± 1. 430 0. 823 ± 0. 296 0. 94 114 <0. 001
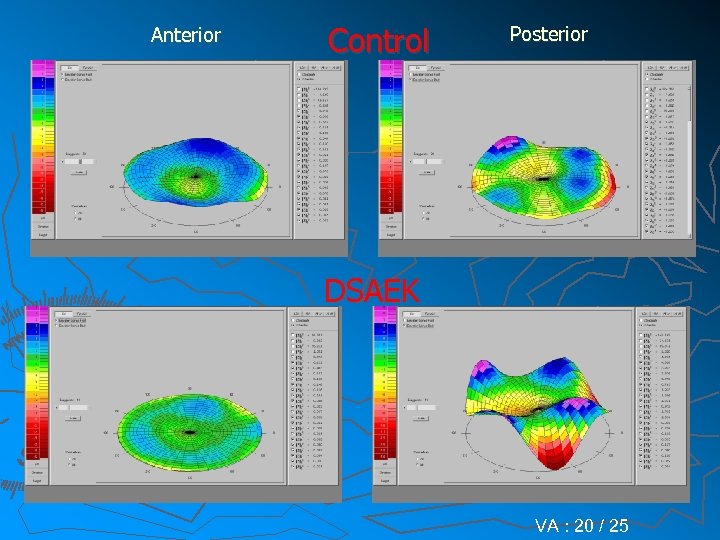
Anterior Control Posterior DSAEK VA : 20 / 25
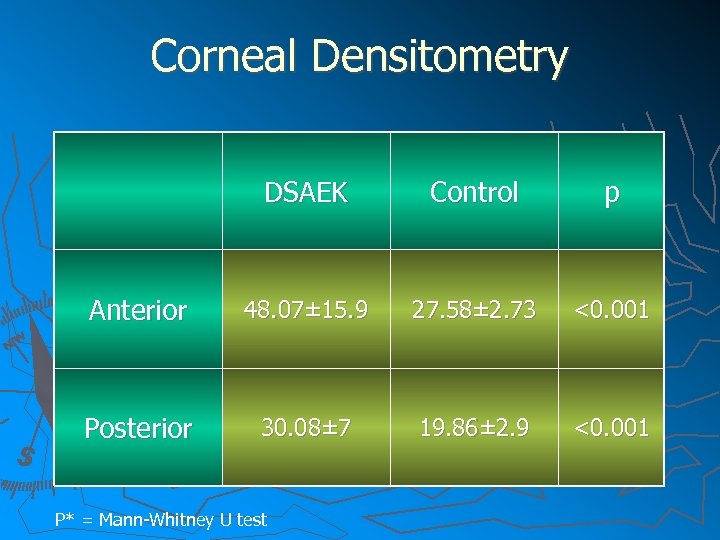
Corneal Densitometry DSAEK Control p Anterior 48. 07± 15. 9 27. 58± 2. 73 <0. 001 Posterior 30. 08± 7 19. 86± 2. 9 <0. 001 P* = Mann-Whitney U test

Discussion DSAEK surgery► Creation of a new steeper endothelial surface ► Meniscus shaped endothelial graft ► Alteration of physiological relationship between anterior and posterior surface ► Placido based imaging systems could produce erroneous measurements of corneal power ► Measures both anterior and posterior surface ► Calculates true net power based on thick lens formula ► Incorporates refractive indices at each interface along with anterior and posterior curvature and corneal thickness ► Has been shown to be useful in studying changes in posterior curvature and give repeatable measurements of corneal thickness- the parameters most affected in DSAEK Changes induced by DSAEK ► Increased corneal thickness and volume § additional stromal tissue ► Lower radius of curvature of posterior surface (relative steepening) § Meniscus shaped graft thicker in the periphery ► Higher radius of curvature of anterior surface (relative flattening) § Wound related? § Alteration of curvature on resolution of bullous changes? ? ► Lower true net power in DSAEK corneas
Conclusions ► Pentacam measurements show lower true net power in DSAEK as compared to controls likely due to § increased posterior curvature (increased minus lens effect) § Decreased anterior curvature (decreased plus lens effect)? ? ► Spherical surgery. aberration is variable after DSAEK
9ac7234230ce5d1cf7f615663c7103b5.ppt