369350ed8cb5d67388e49fd474792a65.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Evaluating Risk Management Tools John D. Lawrence Extension Livestock Economist Iowa State University 1
Evaluating Risk Management Tools John D. Lawrence Extension Livestock Economist Iowa State University 1
 Tools • • • Futures Forward contracts Options Livestock Revenue Protection Livestock Gross Margin Option combinations 2
Tools • • • Futures Forward contracts Options Livestock Revenue Protection Livestock Gross Margin Option combinations 2
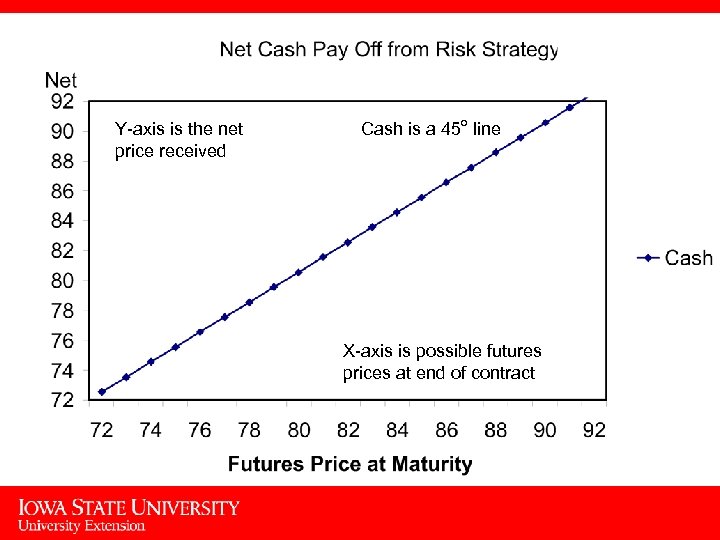 Y-axis is the net price received Cash is a 45 o line X-axis is possible futures prices at end of contract 3
Y-axis is the net price received Cash is a 45 o line X-axis is possible futures prices at end of contract 3
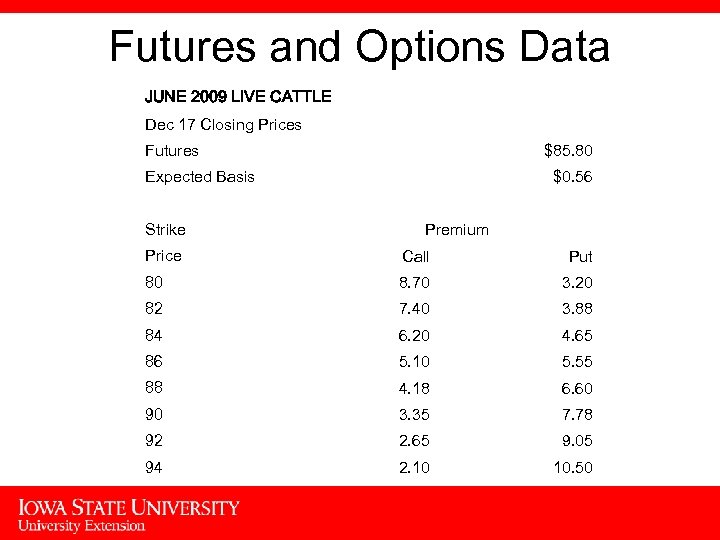 Futures and Options Data JUNE 2009 LIVE CATTLE Dec 17 Closing Prices Futures $85. 80 Expected Basis Strike $0. 56 Premium Price Call Put 80 8. 70 3. 20 82 7. 40 3. 88 84 6. 20 4. 65 86 5. 10 5. 55 88 4. 18 6. 60 90 3. 35 7. 78 92 2. 65 9. 05 94 2. 10 10. 50 4
Futures and Options Data JUNE 2009 LIVE CATTLE Dec 17 Closing Prices Futures $85. 80 Expected Basis Strike $0. 56 Premium Price Call Put 80 8. 70 3. 20 82 7. 40 3. 88 84 6. 20 4. 65 86 5. 10 5. 55 88 4. 18 6. 60 90 3. 35 7. 78 92 2. 65 9. 05 94 2. 10 10. 50 4
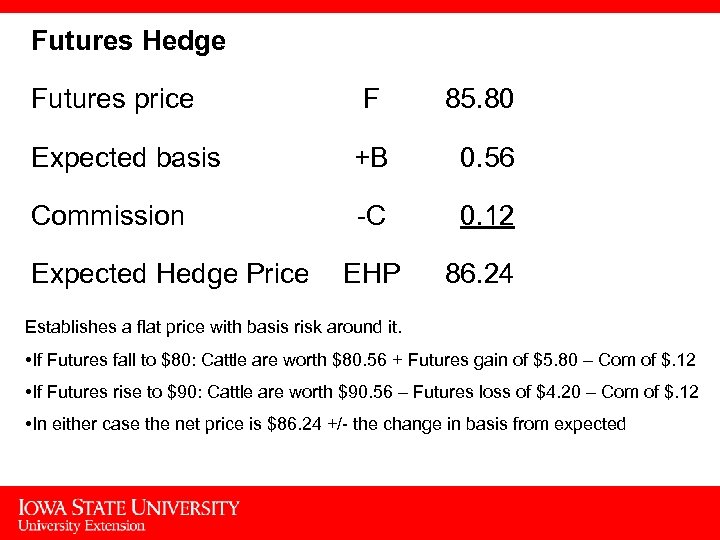 Futures Hedge Futures price F 85. 80 Expected basis +B 0. 56 Commission -C 0. 12 EHP 86. 24 Expected Hedge Price Establishes a flat price with basis risk around it. • If Futures fall to $80: Cattle are worth $80. 56 + Futures gain of $5. 80 – Com of $. 12 • If Futures rise to $90: Cattle are worth $90. 56 – Futures loss of $4. 20 – Com of $. 12 • In either case the net price is $86. 24 +/- the change in basis from expected 5
Futures Hedge Futures price F 85. 80 Expected basis +B 0. 56 Commission -C 0. 12 EHP 86. 24 Expected Hedge Price Establishes a flat price with basis risk around it. • If Futures fall to $80: Cattle are worth $80. 56 + Futures gain of $5. 80 – Com of $. 12 • If Futures rise to $90: Cattle are worth $90. 56 – Futures loss of $4. 20 – Com of $. 12 • In either case the net price is $86. 24 +/- the change in basis from expected 5
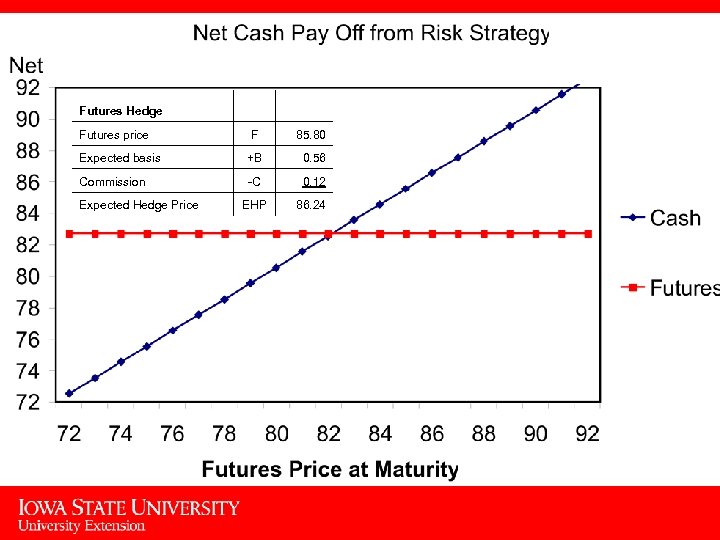 Futures Hedge Futures price F 85. 80 Expected basis +B 0. 56 Commission -C 0. 12 EHP 86. 24 Expected Hedge Price 6
Futures Hedge Futures price F 85. 80 Expected basis +B 0. 56 Commission -C 0. 12 EHP 86. 24 Expected Hedge Price 6
 Forward Contract v. Futures • They look the same on the graph • Flat price • Difference: Forward contact – Contract with buyer – Must deliver commodity (deliver specs) – Basis is known and no basis risk – No margin calls – Typically flexible sizes 7
Forward Contract v. Futures • They look the same on the graph • Flat price • Difference: Forward contact – Contract with buyer – Must deliver commodity (deliver specs) – Basis is known and no basis risk – No margin calls – Typically flexible sizes 7
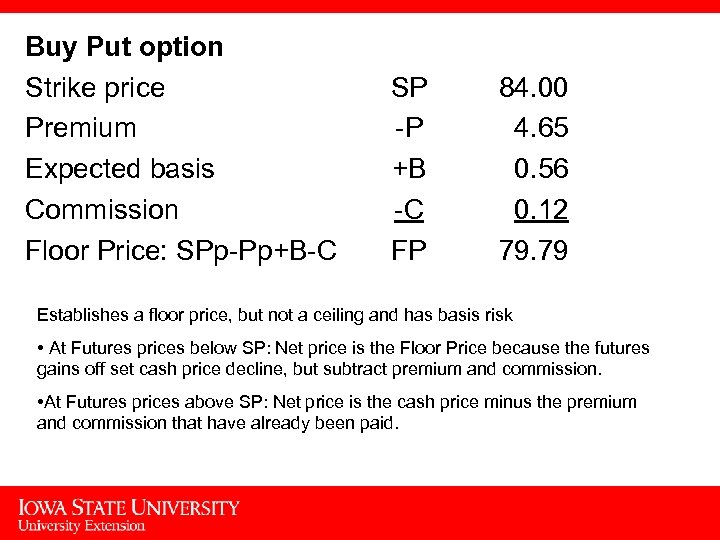 Buy Put option Strike price Premium Expected basis Commission Floor Price: SPp-Pp+B-C SP -P +B -C FP 84. 00 4. 65 0. 56 0. 12 79. 79 Establishes a floor price, but not a ceiling and has basis risk • At Futures prices below SP: Net price is the Floor Price because the futures gains off set cash price decline, but subtract premium and commission. • At Futures prices above SP: Net price is the cash price minus the premium and commission that have already been paid. 8
Buy Put option Strike price Premium Expected basis Commission Floor Price: SPp-Pp+B-C SP -P +B -C FP 84. 00 4. 65 0. 56 0. 12 79. 79 Establishes a floor price, but not a ceiling and has basis risk • At Futures prices below SP: Net price is the Floor Price because the futures gains off set cash price decline, but subtract premium and commission. • At Futures prices above SP: Net price is the cash price minus the premium and commission that have already been paid. 8
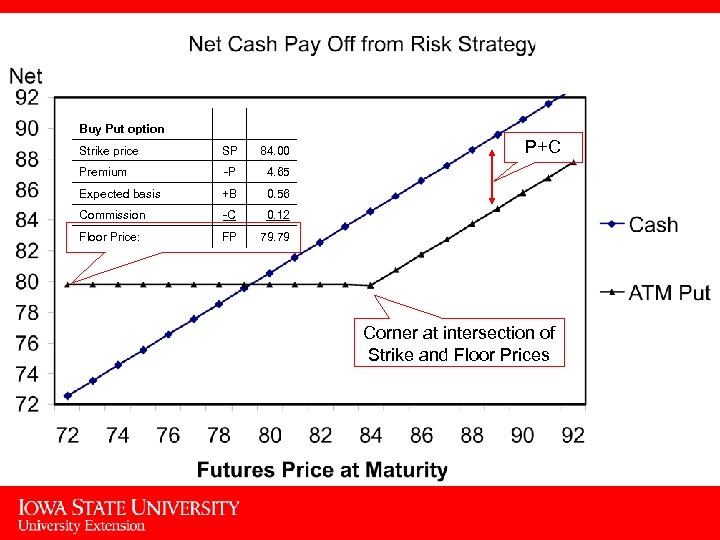 Buy Put option Strike price SP 84. 00 Premium -P 4. 65 Expected basis +B 0. 56 Commission -C 0. 12 Floor Price: FP P+C 79. 79 Corner at intersection of Strike and Floor Prices 9
Buy Put option Strike price SP 84. 00 Premium -P 4. 65 Expected basis +B 0. 56 Commission -C 0. 12 Floor Price: FP P+C 79. 79 Corner at intersection of Strike and Floor Prices 9
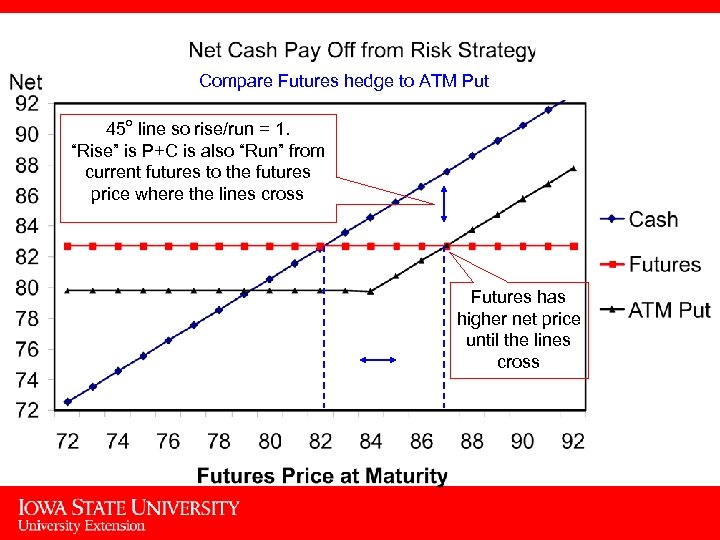 Compare Futures hedge to ATM Put 45 o line so rise/run = 1. “Rise” is P+C is also “Run” from current futures to the futures price where the lines cross Futures has higher net price until the lines cross 10
Compare Futures hedge to ATM Put 45 o line so rise/run = 1. “Rise” is P+C is also “Run” from current futures to the futures price where the lines cross Futures has higher net price until the lines cross 10
 11
11
 Livestock Revenue Protection • Looks like buying put option on graph • Floor price with upside potential • Difference: LRP – Is both through insurance agent – Flexible size of contract – Expiration time is fixed – Cannot be resold – Basis is slightly different as is basis risk 12
Livestock Revenue Protection • Looks like buying put option on graph • Floor price with upside potential • Difference: LRP – Is both through insurance agent – Flexible size of contract – Expiration time is fixed – Cannot be resold – Basis is slightly different as is basis risk 12
 Livestock Gross Margin • Protect a “margin” – Revenue – feed cost – feeder cost – Budgeted quantities and weights – Uses futures prices • Focus on profits not price • Flexible size • Purchased from insurance agents 13
Livestock Gross Margin • Protect a “margin” – Revenue – feed cost – feeder cost – Budgeted quantities and weights – Uses futures prices • Focus on profits not price • Flexible size • Purchased from insurance agents 13
 Combination Option Strategies • Buy one option and sell another – Income from option sold raises the floor – Get premium, but give up something else • Option sellers – Must establish an margin account and will get margin calls if futures price moves against you 14
Combination Option Strategies • Buy one option and sell another – Income from option sold raises the floor – Get premium, but give up something else • Option sellers – Must establish an margin account and will get margin calls if futures price moves against you 14
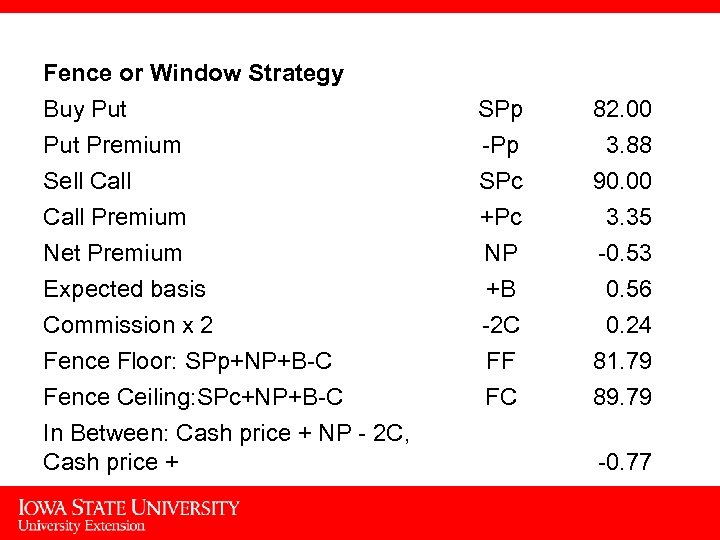 Fence or Window Strategy Buy Put Premium Sell Call Premium Net Premium Expected basis Commission x 2 Fence Floor: SPp+NP+B-C Fence Ceiling: SPc+NP+B-C In Between: Cash price + NP - 2 C, Cash price + SPp -Pp 82. 00 3. 88 SPc +Pc NP +B -2 C FF FC 90. 00 3. 35 -0. 53 0. 56 0. 24 81. 79 89. 79 -0. 77 15
Fence or Window Strategy Buy Put Premium Sell Call Premium Net Premium Expected basis Commission x 2 Fence Floor: SPp+NP+B-C Fence Ceiling: SPc+NP+B-C In Between: Cash price + NP - 2 C, Cash price + SPp -Pp 82. 00 3. 88 SPc +Pc NP +B -2 C FF FC 90. 00 3. 35 -0. 53 0. 56 0. 24 81. 79 89. 79 -0. 77 15
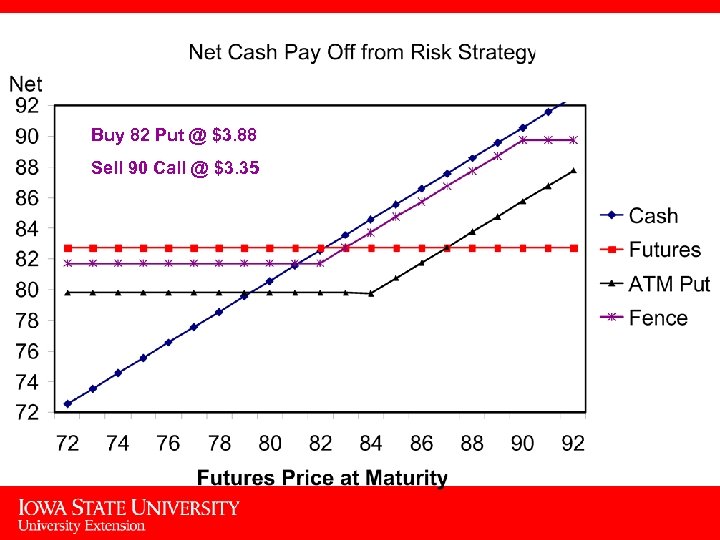 Buy 82 Put @ $3. 88 Sell 90 Call @ $3. 35 16
Buy 82 Put @ $3. 88 Sell 90 Call @ $3. 35 16
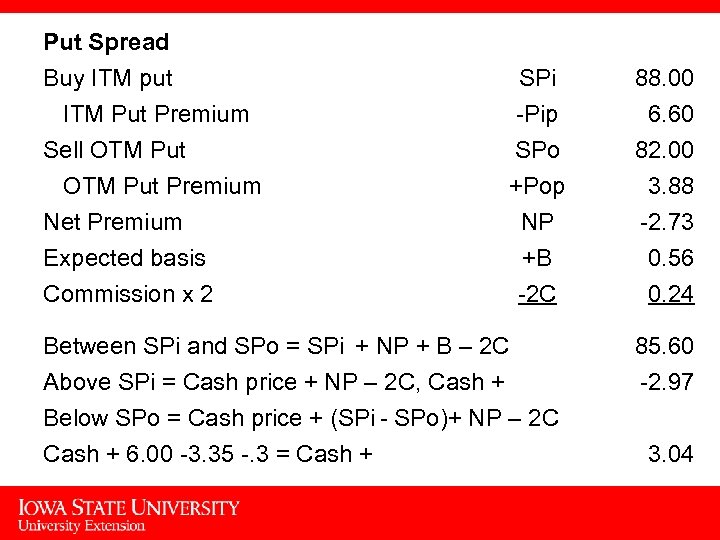 Put Spread Buy ITM put SPi 88. 00 ITM Put Premium -Pip 6. 60 Sell OTM Put Premium Net Premium Expected basis Commission x 2 SPo +Pop NP +B -2 C 82. 00 3. 88 -2. 73 0. 56 0. 24 Between SPi and SPo = SPi + NP + B – 2 C Above SPi = Cash price + NP – 2 C, Cash + Below SPo = Cash price + (SPi - SPo)+ NP – 2 C Cash + 6. 00 -3. 35 -. 3 = Cash + 85. 60 -2. 97 3. 04 17
Put Spread Buy ITM put SPi 88. 00 ITM Put Premium -Pip 6. 60 Sell OTM Put Premium Net Premium Expected basis Commission x 2 SPo +Pop NP +B -2 C 82. 00 3. 88 -2. 73 0. 56 0. 24 Between SPi and SPo = SPi + NP + B – 2 C Above SPi = Cash price + NP – 2 C, Cash + Below SPo = Cash price + (SPi - SPo)+ NP – 2 C Cash + 6. 00 -3. 35 -. 3 = Cash + 85. 60 -2. 97 3. 04 17
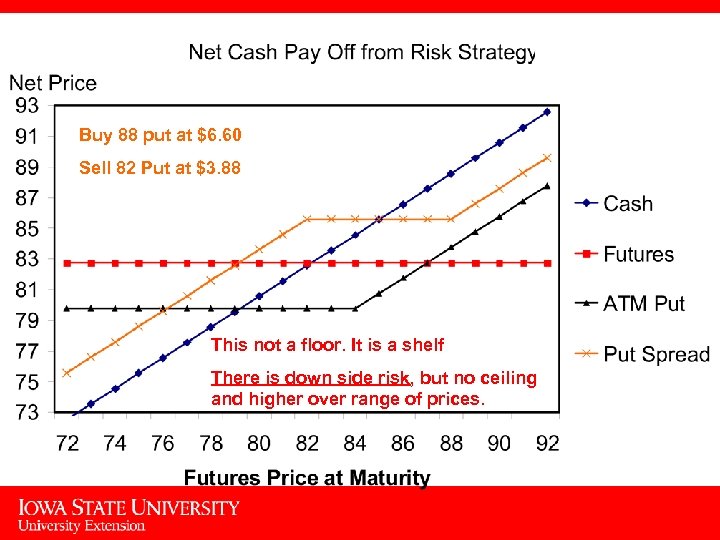 Buy 88 put at $6. 60 Sell 82 Put at $3. 88 This not a floor. It is a shelf There is down side risk, but no ceiling and higher over range of prices. 18
Buy 88 put at $6. 60 Sell 82 Put at $3. 88 This not a floor. It is a shelf There is down side risk, but no ceiling and higher over range of prices. 18
 Summary • Tools are available to include into a well developed marketing plan • Tools have different strengths and weaknesses to achieve different objectives • Understand the math and basis first • Marketing clubs are good ways to learn 19
Summary • Tools are available to include into a well developed marketing plan • Tools have different strengths and weaknesses to achieve different objectives • Understand the math and basis first • Marketing clubs are good ways to learn 19


