81122f27d9ebad24c3b47ab98df0db9b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation (European Commission) Veijo Ritola Head of Section Science, Technology and Innovation Statistics Eurostat – European Commission 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation
Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation (European Commission) Veijo Ritola Head of Section Science, Technology and Innovation Statistics Eurostat – European Commission 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation
 Outline of the presentation Short introduction to Eurostat in general Short briefing to the current policy needs Six sub-categories of the Science, Technology and Innovation Statistics Research and Development Innovation Patents Careers of Doctorate Holders High Tech Human Resources in Science and Technology 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 2
Outline of the presentation Short introduction to Eurostat in general Short briefing to the current policy needs Six sub-categories of the Science, Technology and Innovation Statistics Research and Development Innovation Patents Careers of Doctorate Holders High Tech Human Resources in Science and Technology 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 2
 What is Eurostat? n Eurostat is a Directorate General of the European Commission - Commissioner Joaquín Almunia n Eurostat is the central institution of the European Statistical System (ESS) - a network of National Statistical Institutes from all EU and EFTA Countries 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 3
What is Eurostat? n Eurostat is a Directorate General of the European Commission - Commissioner Joaquín Almunia n Eurostat is the central institution of the European Statistical System (ESS) - a network of National Statistical Institutes from all EU and EFTA Countries 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 3
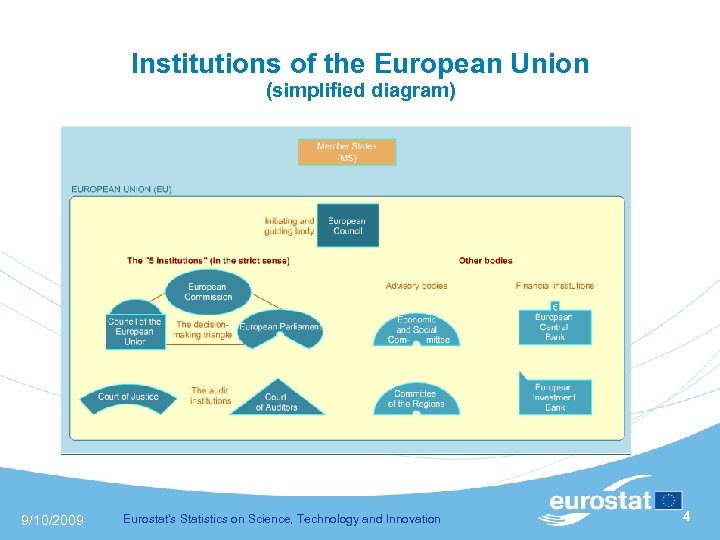 Institutions of the European Union (simplified diagram) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 4
Institutions of the European Union (simplified diagram) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 4
 European Commission: Directorates-General and Services 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 5
European Commission: Directorates-General and Services 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 5
 Eurostat’s organisation n Director General - Walter Radermacher n Deputy Director General - Marie Bohatá n Staff approximately 870 people n Seven Directorates – – – – 9/10/2009 Resources & Cooperation in the ESS Quality, methodology and information systems National and European accounts External cooperation, communication and key indicators Sectoral and regional statistics Social and information society statistics Business statistics Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 6
Eurostat’s organisation n Director General - Walter Radermacher n Deputy Director General - Marie Bohatá n Staff approximately 870 people n Seven Directorates – – – – 9/10/2009 Resources & Cooperation in the ESS Quality, methodology and information systems National and European accounts External cooperation, communication and key indicators Sectoral and regional statistics Social and information society statistics Business statistics Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 6
 Responsibilities of Eurostat n n Collect data from NSIs Harmonise methods, definitions & classifications Compile European aggregates – EU & Euro area Disseminate statistics n International relations – enlargement & development n Programme planning (coordinating national programmes) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 7
Responsibilities of Eurostat n n Collect data from NSIs Harmonise methods, definitions & classifications Compile European aggregates – EU & Euro area Disseminate statistics n International relations – enlargement & development n Programme planning (coordinating national programmes) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 7
 Eurostat credibility is based on n Independence n Impartiality n Objectivity 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 8
Eurostat credibility is based on n Independence n Impartiality n Objectivity 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 8
 Eurostat’s Website: http: //ec. europa. eu/eurostat 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 9
Eurostat’s Website: http: //ec. europa. eu/eurostat 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 9
 Science, Technology and Innovation statistics Establishment and development of harmonised Community statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) is important tool for Providing the necessary evidence basis for the definition, implementation and analysis of Community policies on Science, Technology and Innovation in Europe Regular monitoring the progress achieved towards development of Knowledge-based economy (Lisbon objectives) and realisation of the European Research Area Supplying the public and media with statistics needed to have an accurate picture of science and technology in Europe and to evaluate the performance of politicians and other actors 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 10
Science, Technology and Innovation statistics Establishment and development of harmonised Community statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) is important tool for Providing the necessary evidence basis for the definition, implementation and analysis of Community policies on Science, Technology and Innovation in Europe Regular monitoring the progress achieved towards development of Knowledge-based economy (Lisbon objectives) and realisation of the European Research Area Supplying the public and media with statistics needed to have an accurate picture of science and technology in Europe and to evaluate the performance of politicians and other actors 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 10
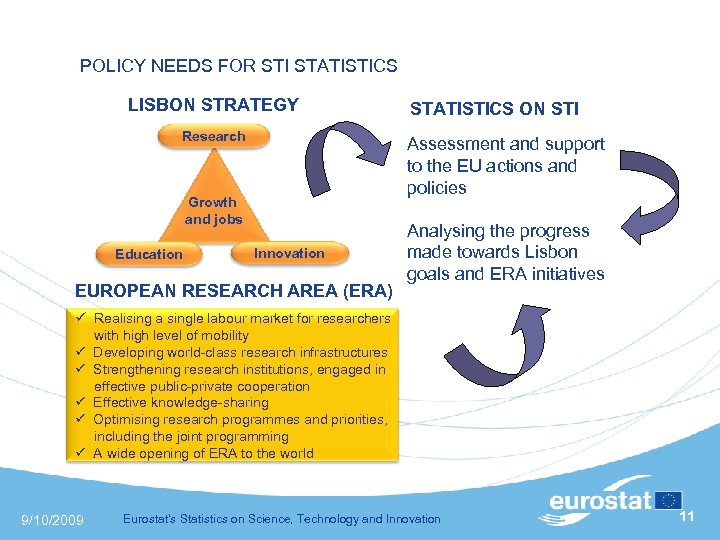 POLICY NEEDS FOR STI STATISTICS LISBON STRATEGY STATISTICS ON STI Research Assessment and support to the EU actions and policies Growth and jobs Education Innovation EUROPEAN RESEARCH AREA (ERA) Analysing the progress made towards Lisbon goals and ERA initiatives Realising a single labour market for researchers with high level of mobility Developing world-class research infrastructures Strengthening research institutions, engaged in effective public-private cooperation Effective knowledge-sharing Optimising research programmes and priorities, including the joint programming A wide opening of ERA to the world 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 11
POLICY NEEDS FOR STI STATISTICS LISBON STRATEGY STATISTICS ON STI Research Assessment and support to the EU actions and policies Growth and jobs Education Innovation EUROPEAN RESEARCH AREA (ERA) Analysing the progress made towards Lisbon goals and ERA initiatives Realising a single labour market for researchers with high level of mobility Developing world-class research infrastructures Strengthening research institutions, engaged in effective public-private cooperation Effective knowledge-sharing Optimising research programmes and priorities, including the joint programming A wide opening of ERA to the world 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 11
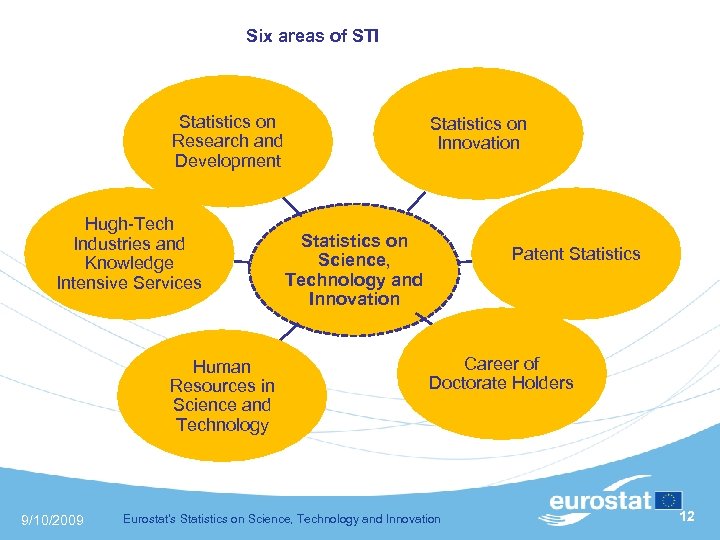 Six areas of STI Statistics on Research and Development Hugh-Tech Industries and Knowledge Intensive Services Human Resources in Science and Technology 9/10/2009 Statistics on Innovation Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation Patent Statistics Career of Doctorate Holders Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 12
Six areas of STI Statistics on Research and Development Hugh-Tech Industries and Knowledge Intensive Services Human Resources in Science and Technology 9/10/2009 Statistics on Innovation Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation Patent Statistics Career of Doctorate Holders Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 12
 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS LEGAL BASE Framework legal act: Decision № 1608/2003/EC of the EP and of the Council concerning the production and development of Community statistics on S&T Legal implementation measure: Commission Regulation № 753/2004 implementing Decision № 1608/2003/EC as regards statistics on S&T R&D INDICATORS Intramural R&D expenditure (GERD) R&D personnel Government budget appropriations or outlays on R&D (GBAORD) HARMONISED R&D CONCEPTS, DEFINITIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Proposed Standard Practice for Surveys on R&D - Frascati Manual, OECD, 2002 available at: http: //www. oecd. org/document/6/0, 3343, en_2649_34451_33828550_1_1, 00. html DATA SOURCES IN MEMBER STATES Sample/census surveys, administrative sources or others of equivalent quality, or their mixtures, subsidiary principle 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 13
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS LEGAL BASE Framework legal act: Decision № 1608/2003/EC of the EP and of the Council concerning the production and development of Community statistics on S&T Legal implementation measure: Commission Regulation № 753/2004 implementing Decision № 1608/2003/EC as regards statistics on S&T R&D INDICATORS Intramural R&D expenditure (GERD) R&D personnel Government budget appropriations or outlays on R&D (GBAORD) HARMONISED R&D CONCEPTS, DEFINITIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Proposed Standard Practice for Surveys on R&D - Frascati Manual, OECD, 2002 available at: http: //www. oecd. org/document/6/0, 3343, en_2649_34451_33828550_1_1, 00. html DATA SOURCES IN MEMBER STATES Sample/census surveys, administrative sources or others of equivalent quality, or their mixtures, subsidiary principle 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 13
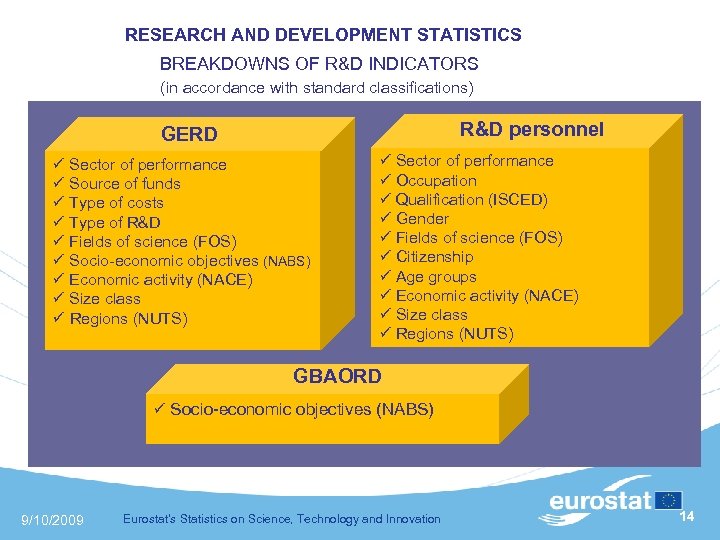 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS BREAKDOWNS OF R&D INDICATORS (in accordance with standard classifications) R&D personnel GERD Sector of performance Source of funds Type of costs Type of R&D Fields of science (FOS) Socio-economic objectives (NABS) Economic activity (NACE) Size class Regions (NUTS) Sector of performance Occupation Qualification (ISCED) Gender Fields of science (FOS) Citizenship Age groups Economic activity (NACE) Size class Regions (NUTS) GBAORD Socio-economic objectives (NABS) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 14
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS BREAKDOWNS OF R&D INDICATORS (in accordance with standard classifications) R&D personnel GERD Sector of performance Source of funds Type of costs Type of R&D Fields of science (FOS) Socio-economic objectives (NABS) Economic activity (NACE) Size class Regions (NUTS) Sector of performance Occupation Qualification (ISCED) Gender Fields of science (FOS) Citizenship Age groups Economic activity (NACE) Size class Regions (NUTS) GBAORD Socio-economic objectives (NABS) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 14
 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS STANDARD CLASSIFICATIONS - available on Eurostat's Metadata Server RAMON http: //ec. europa. eu/eurostat/ramon/index. cfm? Target. Url=DSP_PUB_WELS TYPE OF R&D INDICATORS Obligatory Preliminary R&D (T+10) / Provisional GBAORD (T+6) Optional Final R&D (T+18) / Final GBAORD (T+12) FREQUENCY OF INDICATORS Annual - GERD by sectors of performance, R&D personnel and Researchers in FTE Biannual (on each odd year) - vast majority of indicators Four yearly - gender disaggregation of some indicators DEADLINES FOR DATA COLLECTION BY EUROSTAT Annually three rounds of data collection covering all data sets required, including revisions of the time series: In June: final R&D and provisional GBAORD data In October: preliminary R&D yearly data In December: final GBAORD data 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 15
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS STANDARD CLASSIFICATIONS - available on Eurostat's Metadata Server RAMON http: //ec. europa. eu/eurostat/ramon/index. cfm? Target. Url=DSP_PUB_WELS TYPE OF R&D INDICATORS Obligatory Preliminary R&D (T+10) / Provisional GBAORD (T+6) Optional Final R&D (T+18) / Final GBAORD (T+12) FREQUENCY OF INDICATORS Annual - GERD by sectors of performance, R&D personnel and Researchers in FTE Biannual (on each odd year) - vast majority of indicators Four yearly - gender disaggregation of some indicators DEADLINES FOR DATA COLLECTION BY EUROSTAT Annually three rounds of data collection covering all data sets required, including revisions of the time series: In June: final R&D and provisional GBAORD data In October: preliminary R&D yearly data In December: final GBAORD data 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 15
 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS STANDARDISED APPROACH FOR DATA COLLECTION JOINT OECD/EUROSTAT HARMONISED R&D QUESTIONNAIRE Comprises 3 modules: Common Core OECD/Eurostat module ESTAT supplementary module OECD supplementary module Goes beyond the requirements of EU legal base Contains around 50 Tables in two Excel workbooks Data validation rules in place within the questionnaire Confidential data provision Received from 33 countries: 27 MSs; HR, TR, CH, IS, NO and RU Transmission media - e. DAMIS Transmission format - Excel EVALUATION OF DATA QUALITY Data validation by Eurostat at the delivery point National Quality Reports - covering standard quality criteria: Relevance, Accuracy, Timelines and Punctuality, Accessibility and Clarity, Comparability, Coherence, Cost and Burden 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 16
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS STANDARDISED APPROACH FOR DATA COLLECTION JOINT OECD/EUROSTAT HARMONISED R&D QUESTIONNAIRE Comprises 3 modules: Common Core OECD/Eurostat module ESTAT supplementary module OECD supplementary module Goes beyond the requirements of EU legal base Contains around 50 Tables in two Excel workbooks Data validation rules in place within the questionnaire Confidential data provision Received from 33 countries: 27 MSs; HR, TR, CH, IS, NO and RU Transmission media - e. DAMIS Transmission format - Excel EVALUATION OF DATA QUALITY Data validation by Eurostat at the delivery point National Quality Reports - covering standard quality criteria: Relevance, Accuracy, Timelines and Punctuality, Accessibility and Clarity, Comparability, Coherence, Cost and Burden 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 16
 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS DERIVED R&D VARIABLES (RATIO INDICATORS) produced by Eurostat DERIVED R&D VARIABLES R&D expenditure as а percentage of GDP (R&D intensity) For 2007: EU-27 = 1. 85 % - still below the Lisbon target of 3% In two MS: > 3 % - SE (3. 60%) FI (3. 47%) In four MS: (2 % - 3%) - DE, FR, AT, DK GBAORD as а percentage of GDP GBAORD as а percentage general government expenditure R&D expenditure and GBAORD in Euro per inhabitant R&D personnel/Researchers as а percentage of active population R&D personnel/Researchers as а percentage of total employment EU AGGREGATES calculated by Eurostat: EU-27, EU-15, EA-16 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 17
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS DERIVED R&D VARIABLES (RATIO INDICATORS) produced by Eurostat DERIVED R&D VARIABLES R&D expenditure as а percentage of GDP (R&D intensity) For 2007: EU-27 = 1. 85 % - still below the Lisbon target of 3% In two MS: > 3 % - SE (3. 60%) FI (3. 47%) In four MS: (2 % - 3%) - DE, FR, AT, DK GBAORD as а percentage of GDP GBAORD as а percentage general government expenditure R&D expenditure and GBAORD in Euro per inhabitant R&D personnel/Researchers as а percentage of active population R&D personnel/Researchers as а percentage of total employment EU AGGREGATES calculated by Eurostat: EU-27, EU-15, EA-16 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 17
 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS CURRENT CHALLENGES DEVELOPMENT OF NEW INDICATORS FOR MONITORING EUROPEAN RESEARCH AREA (ERA) National public funding to trans-nationally coordinated research National contributions to trans-national public R&D performers (CERN, ILL, ERSF, EMBL, EMBO, ESO, JRC) National contributions to Europe-wide trans-national public R&D programmes (ERA-NETs, ESA, EFDA, EUREKA, COST etc. ) National contributions to bi- or multi-lateral public R&D programmes established between MSs governments Total amount of Structural Funds for R&D (national and EU funding) Breakdown of R&D expenditure financed by abroad by type of source (including EU/non-EU origin of source) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 18
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS CURRENT CHALLENGES DEVELOPMENT OF NEW INDICATORS FOR MONITORING EUROPEAN RESEARCH AREA (ERA) National public funding to trans-nationally coordinated research National contributions to trans-national public R&D performers (CERN, ILL, ERSF, EMBL, EMBO, ESO, JRC) National contributions to Europe-wide trans-national public R&D programmes (ERA-NETs, ESA, EFDA, EUREKA, COST etc. ) National contributions to bi- or multi-lateral public R&D programmes established between MSs governments Total amount of Structural Funds for R&D (national and EU funding) Breakdown of R&D expenditure financed by abroad by type of source (including EU/non-EU origin of source) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 18
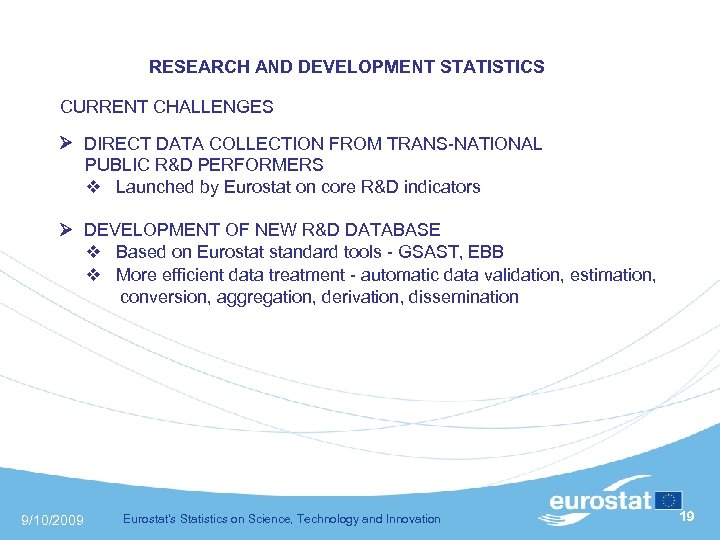 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS CURRENT CHALLENGES DIRECT DATA COLLECTION FROM TRANS-NATIONAL PUBLIC R&D PERFORMERS Launched by Eurostat on core R&D indicators DEVELOPMENT OF NEW R&D DATABASE Based on Eurostat standard tools - GSAST, EBB More efficient data treatment - automatic data validation, estimation, conversion, aggregation, derivation, dissemination 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 19
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT STATISTICS CURRENT CHALLENGES DIRECT DATA COLLECTION FROM TRANS-NATIONAL PUBLIC R&D PERFORMERS Launched by Eurostat on core R&D indicators DEVELOPMENT OF NEW R&D DATABASE Based on Eurostat standard tools - GSAST, EBB More efficient data treatment - automatic data validation, estimation, conversion, aggregation, derivation, dissemination 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 19
 INNOVATION STATISTICS LEGAL BASE Framework legal act: Decision № 1608/2003/EC of the EP and of the Council concerning the production and development of Community statistics on S&T Legal implementation measure: Commission Regulation № 1450/2004 implementing Decision № 1608/2003/EC concerning the production and development of Community statistics on innovation (amended by CR № 540/2009) INDICATORS EVERY TWO YEARS Innovation active enterprises Innovating enterprises that introduced new or significantly improved products, new to the market Turnover from innovation, related to new or significantly improved products, new to the firm, but not new to the market Innovation active enterprises involved in innovation cooperation - by type of cooperation 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 20
INNOVATION STATISTICS LEGAL BASE Framework legal act: Decision № 1608/2003/EC of the EP and of the Council concerning the production and development of Community statistics on S&T Legal implementation measure: Commission Regulation № 1450/2004 implementing Decision № 1608/2003/EC concerning the production and development of Community statistics on innovation (amended by CR № 540/2009) INDICATORS EVERY TWO YEARS Innovation active enterprises Innovating enterprises that introduced new or significantly improved products, new to the market Turnover from innovation, related to new or significantly improved products, new to the firm, but not new to the market Innovation active enterprises involved in innovation cooperation - by type of cooperation 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 20
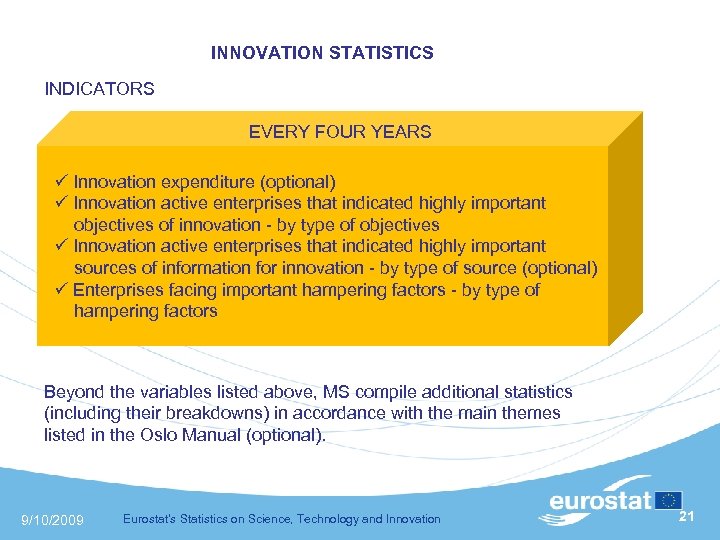 INNOVATION STATISTICS INDICATORS EVERY FOUR YEARS Innovation expenditure (optional) Innovation active enterprises that indicated highly important objectives of innovation - by type of objectives Innovation active enterprises that indicated highly important sources of information for innovation - by type of source (optional) Enterprises facing important hampering factors - by type of hampering factors Beyond the variables listed above, MS compile additional statistics (including their breakdowns) in accordance with the main themes listed in the Oslo Manual (optional). 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 21
INNOVATION STATISTICS INDICATORS EVERY FOUR YEARS Innovation expenditure (optional) Innovation active enterprises that indicated highly important objectives of innovation - by type of objectives Innovation active enterprises that indicated highly important sources of information for innovation - by type of source (optional) Enterprises facing important hampering factors - by type of hampering factors Beyond the variables listed above, MS compile additional statistics (including their breakdowns) in accordance with the main themes listed in the Oslo Manual (optional). 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 21
 INNOVATION STATISTICS HARMONISED CONCEPTS, DEFINITIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Guidelines for Collecting and Interpreting Innovation Data - Oslo Manual, OECD, 2005 available at: http: //lysander. sourceoecd. org/vl=1764186/cl=11/nw=1/rpsv/cgibin/fulltextew. pl? prpsv=/ij/oecdthemes/99980134/v 2005 n 18/s 1/p 1 l. idx DATA SOURCES IN MEMBER STATES Combination of different sources - sample surveys, administrative data or others of equivalent quality TYPE OF INDICATORS Obligatory Optional FREQUENCY OF INDICATORS Biannual, on each even year - 5 obligatory variables Four yearly - 7 obligatory and 2 optional variables (plus more) DEADLINE FOR DATA COLLECTION BY EUROSTAT 18 months after the end of the calendar year of the reference period 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 22
INNOVATION STATISTICS HARMONISED CONCEPTS, DEFINITIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Guidelines for Collecting and Interpreting Innovation Data - Oslo Manual, OECD, 2005 available at: http: //lysander. sourceoecd. org/vl=1764186/cl=11/nw=1/rpsv/cgibin/fulltextew. pl? prpsv=/ij/oecdthemes/99980134/v 2005 n 18/s 1/p 1 l. idx DATA SOURCES IN MEMBER STATES Combination of different sources - sample surveys, administrative data or others of equivalent quality TYPE OF INDICATORS Obligatory Optional FREQUENCY OF INDICATORS Biannual, on each even year - 5 obligatory variables Four yearly - 7 obligatory and 2 optional variables (plus more) DEADLINE FOR DATA COLLECTION BY EUROSTAT 18 months after the end of the calendar year of the reference period 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 22
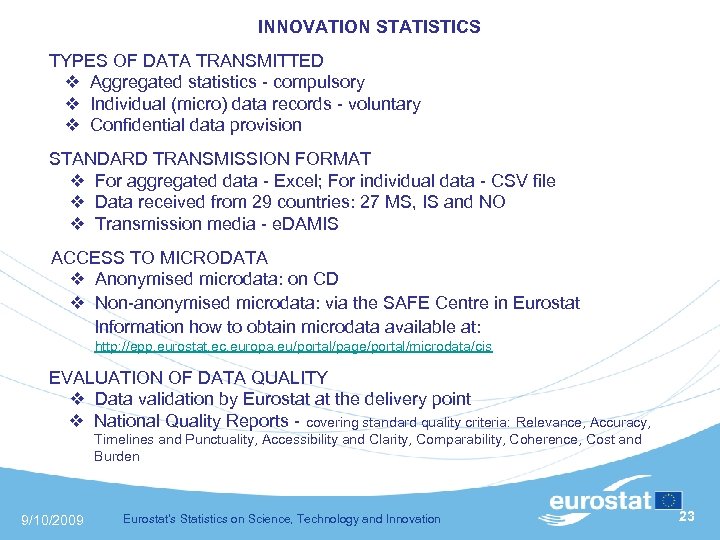 INNOVATION STATISTICS TYPES OF DATA TRANSMITTED Aggregated statistics - compulsory Individual (micro) data records - voluntary Confidential data provision STANDARD TRANSMISSION FORMAT For aggregated data - Excel; For individual data - CSV file Data received from 29 countries: 27 MS, IS and NO Transmission media - e. DAMIS ACCESS TO MICRODATA Anonymised microdata: on CD Non-anonymised microdata: via the SAFE Centre in Eurostat Information how to obtain microdata available at: http: //epp. eurostat. ec. europa. eu/portal/page/portal/microdata/cis EVALUATION OF DATA QUALITY Data validation by Eurostat at the delivery point National Quality Reports - covering standard quality criteria: Relevance, Accuracy, Timelines and Punctuality, Accessibility and Clarity, Comparability, Coherence, Cost and Burden 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 23
INNOVATION STATISTICS TYPES OF DATA TRANSMITTED Aggregated statistics - compulsory Individual (micro) data records - voluntary Confidential data provision STANDARD TRANSMISSION FORMAT For aggregated data - Excel; For individual data - CSV file Data received from 29 countries: 27 MS, IS and NO Transmission media - e. DAMIS ACCESS TO MICRODATA Anonymised microdata: on CD Non-anonymised microdata: via the SAFE Centre in Eurostat Information how to obtain microdata available at: http: //epp. eurostat. ec. europa. eu/portal/page/portal/microdata/cis EVALUATION OF DATA QUALITY Data validation by Eurostat at the delivery point National Quality Reports - covering standard quality criteria: Relevance, Accuracy, Timelines and Punctuality, Accessibility and Clarity, Comparability, Coherence, Cost and Burden 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 23
 INNOVATION STATISTICS STANDARDISED APPROACH FOR DATA COLLECTION COMMUNITY INNOVATION SURVEY (CIS) HARMONISED METHODOLOGICAL RECOMMENDATIONS Target population (NACE and size class coverage, statistical unit, observation period) Survey methodology (sampling frame, type of survey, stratification variables, sample size, sample selection and allocation) Collecting and processing the data (survey questionnaire, data collection and data editing) Data quality (response rate, non- response survey, precision of results, imputation, weighting and calibration) Transmission of data (types of data, output tabulation scheme, deadlines, transmission tool) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 24
INNOVATION STATISTICS STANDARDISED APPROACH FOR DATA COLLECTION COMMUNITY INNOVATION SURVEY (CIS) HARMONISED METHODOLOGICAL RECOMMENDATIONS Target population (NACE and size class coverage, statistical unit, observation period) Survey methodology (sampling frame, type of survey, stratification variables, sample size, sample selection and allocation) Collecting and processing the data (survey questionnaire, data collection and data editing) Data quality (response rate, non- response survey, precision of results, imputation, weighting and calibration) Transmission of data (types of data, output tabulation scheme, deadlines, transmission tool) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 24
 INNOVATION STATISTICS COMMUNITY INNOVATION SURVEY (CIS) STANDARD SURVEY QUESTIONNAIRE (CIS 2008) 1/ General information about the enterprise 2/ Product innovation (good or service) 3/ Process innovation 4/ Ongoing or abandoned innovation activities for process and product innovations 5/ Innovation activities and expenditures for process and product innovations 6/ Sources of information and co-operation for innovation activities 7/ Innovation objectives during 2006 - 2008 8/ Organisational innovation 9/ Marketing innovation 10/ Innovations with environmental benefits 11/ Basic economic information on the enterprise (turnover, employees) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 25
INNOVATION STATISTICS COMMUNITY INNOVATION SURVEY (CIS) STANDARD SURVEY QUESTIONNAIRE (CIS 2008) 1/ General information about the enterprise 2/ Product innovation (good or service) 3/ Process innovation 4/ Ongoing or abandoned innovation activities for process and product innovations 5/ Innovation activities and expenditures for process and product innovations 6/ Sources of information and co-operation for innovation activities 7/ Innovation objectives during 2006 - 2008 8/ Organisational innovation 9/ Marketing innovation 10/ Innovations with environmental benefits 11/ Basic economic information on the enterprise (turnover, employees) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 25
 INNOVATION STATISTICS CURRENT CHALLENGES REVISION OF THE REGULATION 1450/2004 Extension to the organisational and marketing innovation Revision/extension of the economic activities covered Introduction of one-off modules Introduction of the quality annex From voluntary to mandatory microdata deliveries Frequency of the variables MODULE SELECTION FOR CIS 2010 User driven innovation Creativity and skills to innovate TRACKING ENTERPRISES IN CONSECUTIVE MICRODATA SETS OBSERVATION PERIOD (2/3 YEARS) MEASUREMENT OF THE DESIGN IN THE INNOVATION SURVEYS EVALUATION OF THE NATIONAL QUESTIONNAIRES 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 26
INNOVATION STATISTICS CURRENT CHALLENGES REVISION OF THE REGULATION 1450/2004 Extension to the organisational and marketing innovation Revision/extension of the economic activities covered Introduction of one-off modules Introduction of the quality annex From voluntary to mandatory microdata deliveries Frequency of the variables MODULE SELECTION FOR CIS 2010 User driven innovation Creativity and skills to innovate TRACKING ENTERPRISES IN CONSECUTIVE MICRODATA SETS OBSERVATION PERIOD (2/3 YEARS) MEASUREMENT OF THE DESIGN IN THE INNOVATION SURVEYS EVALUATION OF THE NATIONAL QUESTIONNAIRES 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 26
 PATENT STATISTICS Patent statistics measure Research output Innovation activities Technological progress Capacity to exploit knowledge DATA SOURCES One single raw database (PATSTAT) compiled on the basis of input from European Patent Office (EPO) US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) Japanese Patent Office (JPO) HARMONISED R&D CONCEPTS, DEFINITIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Patent Statistics Manual, OECD, 2009, available at: http: //www. oecd. org/document/29/0, 3343, en_2649_34451_42168029_1_1, 00. html International Patent Classification (IPC) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 27
PATENT STATISTICS Patent statistics measure Research output Innovation activities Technological progress Capacity to exploit knowledge DATA SOURCES One single raw database (PATSTAT) compiled on the basis of input from European Patent Office (EPO) US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) Japanese Patent Office (JPO) HARMONISED R&D CONCEPTS, DEFINITIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Patent Statistics Manual, OECD, 2009, available at: http: //www. oecd. org/document/29/0, 3343, en_2649_34451_42168029_1_1, 00. html International Patent Classification (IPC) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 27
 PATENT STATISTICS APPROACH FOR COMPILATION OF PATENT STATISTICS Data extracted from a single patent statistics raw database (PATSTAT), held by the European Patent Office (EPO) and further edited, aggregated and disseminated by Eurostat for all EU Member States, Candidate Countries, EFTA members and other countries Eurostat’s database contains data on: Patents in high-technology fields Patent applications to the EPO Patents granted by the USPTO Triadic patent families (based on raw patent data from OECD) High-tech patents ICT patents Biotechnology patents Nanotechnology patents 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 28
PATENT STATISTICS APPROACH FOR COMPILATION OF PATENT STATISTICS Data extracted from a single patent statistics raw database (PATSTAT), held by the European Patent Office (EPO) and further edited, aggregated and disseminated by Eurostat for all EU Member States, Candidate Countries, EFTA members and other countries Eurostat’s database contains data on: Patents in high-technology fields Patent applications to the EPO Patents granted by the USPTO Triadic patent families (based on raw patent data from OECD) High-tech patents ICT patents Biotechnology patents Nanotechnology patents 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 28
 PATENT STATISTICS TYPES OF INDICATORS Patent applications to EPO by priority year Patent applications to the EPO by priority year at the national level Patent applications to the EPO by priority year at the regional level Ownership of inventions European and international co-patenting Patent citations Patents granted by the USPTO by priority year at the national level Ownership of inventions European and international co-patenting Patent citations Triadic patent families by earliest priority year 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 29
PATENT STATISTICS TYPES OF INDICATORS Patent applications to EPO by priority year Patent applications to the EPO by priority year at the national level Patent applications to the EPO by priority year at the regional level Ownership of inventions European and international co-patenting Patent citations Patents granted by the USPTO by priority year at the national level Ownership of inventions European and international co-patenting Patent citations Triadic patent families by earliest priority year 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 29
 PATENT STATISTICS BREAKDOWNS OF PATENT INDICATORS BREAKDOWNS Institutional sector IPC sections and classes, Economic activities (NACE classes) Type of ownership Inventors’/ applicants' country of residence DERIVED PATENT VARIABLES (RATIO INDICATORS) DERIVED VARIABLES FOR EPO AND USPTO PATENTS 9/10/2009 Per million inhabitants Per million labour force Relative to Gross domestic product (GDP) in euro Relative to Gross domestic expenditure on R&D (GERD) Relative to Expenditure on R&D in Business enterprise sector Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 30
PATENT STATISTICS BREAKDOWNS OF PATENT INDICATORS BREAKDOWNS Institutional sector IPC sections and classes, Economic activities (NACE classes) Type of ownership Inventors’/ applicants' country of residence DERIVED PATENT VARIABLES (RATIO INDICATORS) DERIVED VARIABLES FOR EPO AND USPTO PATENTS 9/10/2009 Per million inhabitants Per million labour force Relative to Gross domestic product (GDP) in euro Relative to Gross domestic expenditure on R&D (GERD) Relative to Expenditure on R&D in Business enterprise sector Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 30
 PATENT STATISTICS FIELDS OF INVESTIGATION PATENTS IN NUCLEAR TECHNOLOGY Nuclear Reactor Technique Radiation Acceleration Technique PATENTS IN WIND ENERGY Wind Motors Relevant surrounding techniques (Circuit arrangements or systems for supplying or distributing electric powers, Control or regulation of electric motors, generators, or dynamo-electric converters, Dynamo-electric machines) PATENTS IN ENVIRONMENTAL RELATED ENERGY Environmental Related Renewable Energy Automobile Pollution Control Technology 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 31
PATENT STATISTICS FIELDS OF INVESTIGATION PATENTS IN NUCLEAR TECHNOLOGY Nuclear Reactor Technique Radiation Acceleration Technique PATENTS IN WIND ENERGY Wind Motors Relevant surrounding techniques (Circuit arrangements or systems for supplying or distributing electric powers, Control or regulation of electric motors, generators, or dynamo-electric converters, Dynamo-electric machines) PATENTS IN ENVIRONMENTAL RELATED ENERGY Environmental Related Renewable Energy Automobile Pollution Control Technology 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 31
 PATENT STATISTICS CURRENT CHALLENGES CREATE NEW INDICATORS AND MORE BREAKDOWNS Specific technological sectors Triadic patent families Regional level SEARCH WAYS TO COMBINE PATENT STATISTICS WITH THE BUSINESS DATA 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 32
PATENT STATISTICS CURRENT CHALLENGES CREATE NEW INDICATORS AND MORE BREAKDOWNS Specific technological sectors Triadic patent families Regional level SEARCH WAYS TO COMBINE PATENT STATISTICS WITH THE BUSINESS DATA 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 32
 CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS CDH 2006 VOLUNTARY SURVEY (NO LEGAL BASE) Widely supported project (EU Commission, OECD, UNESCO) Measuring the mobility, careers and expectations of research educated people PARTICIPATING COUNTRIES 21 EU MSs, Australia, Switzerland, Iceland, Norway and USA REFERENCE YEAR 2006 (except for Belgium, Netherlands, Norway: 2005, Italy, Malta: 2007) CARRIED OUT In 2007 - 2008 DATA SOURCES IN MS Variety of sources for compiling the target population (registers, administrative data, census of population etc. ) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 33
CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS CDH 2006 VOLUNTARY SURVEY (NO LEGAL BASE) Widely supported project (EU Commission, OECD, UNESCO) Measuring the mobility, careers and expectations of research educated people PARTICIPATING COUNTRIES 21 EU MSs, Australia, Switzerland, Iceland, Norway and USA REFERENCE YEAR 2006 (except for Belgium, Netherlands, Norway: 2005, Italy, Malta: 2007) CARRIED OUT In 2007 - 2008 DATA SOURCES IN MS Variety of sources for compiling the target population (registers, administrative data, census of population etc. ) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 33
 CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS STANDARDISED APPROACH FOR DATA COLLECTION CORE MODEL QUESTIONNAIRE INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR COMPLETING THE QUESTIONNAIRE METHODOLOGICAL GUIDELINES OUTPUT INDICATORS TEMPLATE VARIABLES IN PROPOSED TABULATIONS - definitions and sources CORE MODEL QUESTIONNAIRE Module EDU - Doctoral education Module REC - Recent graduates Module POS - POSTDOCS Module EMP - Employment situation Module MOB - International mobility Module CAR - Career related experience and scientific productivity Module PER - Personal characteristics 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 34
CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS STANDARDISED APPROACH FOR DATA COLLECTION CORE MODEL QUESTIONNAIRE INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR COMPLETING THE QUESTIONNAIRE METHODOLOGICAL GUIDELINES OUTPUT INDICATORS TEMPLATE VARIABLES IN PROPOSED TABULATIONS - definitions and sources CORE MODEL QUESTIONNAIRE Module EDU - Doctoral education Module REC - Recent graduates Module POS - POSTDOCS Module EMP - Employment situation Module MOB - International mobility Module CAR - Career related experience and scientific productivity Module PER - Personal characteristics 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 34
 CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS MAIN CHARACTERISTICS Personal characteristics Gender Age Country of birth Type of citizenship/residential status Educational characteristics Country of doctorate award Field of doctorate award Work perception Employment characteristics Occupation Researcher function / non - Earnings Length of stay with current employer 9/10/2009 Job qualification Perception to salary Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 35
CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS MAIN CHARACTERISTICS Personal characteristics Gender Age Country of birth Type of citizenship/residential status Educational characteristics Country of doctorate award Field of doctorate award Work perception Employment characteristics Occupation Researcher function / non - Earnings Length of stay with current employer 9/10/2009 Job qualification Perception to salary Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 35
 CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS GROSSING-UP - applied by all countries except for Belgium, Czech Republic, Poland, Romania and Slovak Republic FIRST RESULTS Presented in the December 2008 Brussels meeting Lack of comparability, mainly due to coverage inconsistencies Additional request for ‘restricted’ data on specific set of output tables Restriction 1: ISCED 6 graduates aged below 70 years old Restriction 2: ISCED 6 graduates awarded after 1990 Revised data was gathered in March 2009 - comparability issues are still apparent 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 36
CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS GROSSING-UP - applied by all countries except for Belgium, Czech Republic, Poland, Romania and Slovak Republic FIRST RESULTS Presented in the December 2008 Brussels meeting Lack of comparability, mainly due to coverage inconsistencies Additional request for ‘restricted’ data on specific set of output tables Restriction 1: ISCED 6 graduates aged below 70 years old Restriction 2: ISCED 6 graduates awarded after 1990 Revised data was gathered in March 2009 - comparability issues are still apparent 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 36
 CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS SELECTED FINDINGS Male doctorate holders are in general more than female doctorate holders (more than 60% in most of the countries) Most doctorate holders have been awarded in the reporting country (exceptions are CY IS MT) Most popular occupation is teaching profession Doctorate holders are most employed as researchers than non researchers in all countries (exceptions are BE NL RO) Doctorate holders are generally far better paid compared to the total population (SES 2006 results) Doctorate holders tend to stay with the same employer for more than 5 years and in many countries for more than 10 years (except for DK) Most employed doctorate holders have a job that is related to their doctoral degree (except for AT) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 37
CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS SELECTED FINDINGS Male doctorate holders are in general more than female doctorate holders (more than 60% in most of the countries) Most doctorate holders have been awarded in the reporting country (exceptions are CY IS MT) Most popular occupation is teaching profession Doctorate holders are most employed as researchers than non researchers in all countries (exceptions are BE NL RO) Doctorate holders are generally far better paid compared to the total population (SES 2006 results) Doctorate holders tend to stay with the same employer for more than 5 years and in many countries for more than 10 years (except for DK) Most employed doctorate holders have a job that is related to their doctoral degree (except for AT) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 37
 CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS UPCOMING CHALLENGES Voluntary countries participation in CDH 2009. Financial support (grants) from Eurostat Revision of the CDH technical documents - end of September 2009 CDH 2009 national data collection: Preparation phase at country level - end of 2009 Data collection - 2010 Output tables to UIS/OECD/Eurostat before end 2010 Data publication and analysis 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 38
CAREERS OF DOCTORATE HOLDERS UPCOMING CHALLENGES Voluntary countries participation in CDH 2009. Financial support (grants) from Eurostat Revision of the CDH technical documents - end of September 2009 CDH 2009 national data collection: Preparation phase at country level - end of 2009 Data collection - 2010 Output tables to UIS/OECD/Eurostat before end 2010 Data publication and analysis 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 38
 HIGH-TECH STATISTICS MAIN APPROACHES IN COMPILATION OF HIGH-TECH STATISTICS SECTORAL APPROACH n Sectors identified following the Statistical Classification of Economic Activities in the European Community (NACE) PRODUCT APPROACH n Products identified following the Standard International Trade Classification (SITC) Sectors identified according to the technological intensity: R&D expenditure/value added Products identified according to the high value of R&D intensity: R&D expenditure/total sales PATENTS High-tech and biotechnology patents identified according to International Patent Classification (IPC 8 th edition) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 39
HIGH-TECH STATISTICS MAIN APPROACHES IN COMPILATION OF HIGH-TECH STATISTICS SECTORAL APPROACH n Sectors identified following the Statistical Classification of Economic Activities in the European Community (NACE) PRODUCT APPROACH n Products identified following the Standard International Trade Classification (SITC) Sectors identified according to the technological intensity: R&D expenditure/value added Products identified according to the high value of R&D intensity: R&D expenditure/total sales PATENTS High-tech and biotechnology patents identified according to International Patent Classification (IPC 8 th edition) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 39
 HIGH-TECH STATISTICS SECTORAL APPROACH BASED ON NACE common EU classification of economic activities covers a whole range of economic activities 4 -digit level Manufacturing and services classified according to: the level of technological intensity R&D expenditure/value added the share of the highest educated staff Manufacturing sector – High-technology manufacturing – Medium-high technology manufacturing – Medium-low technology manufacturing – Low-technology manufacturing Services Classification is relative to variables used the data of the countries used the time the data refer to threshold set 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation – Knowledge intensive services – Less knowledge intensive services 40
HIGH-TECH STATISTICS SECTORAL APPROACH BASED ON NACE common EU classification of economic activities covers a whole range of economic activities 4 -digit level Manufacturing and services classified according to: the level of technological intensity R&D expenditure/value added the share of the highest educated staff Manufacturing sector – High-technology manufacturing – Medium-high technology manufacturing – Medium-low technology manufacturing – Low-technology manufacturing Services Classification is relative to variables used the data of the countries used the time the data refer to threshold set 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation – Knowledge intensive services – Less knowledge intensive services 40
 HIGH-TECH STATISTICS PRODUCT APPROACH BASED ON SITC HIGH-TECH PRODUCTS Aerospace Armament Computers-Office machines Electronics-Telecommunication Pharmacy Scientific instruments Electrical machinery Non-electrical machinery Chemistry Data collection – Traders’ customs declarations (extra. EU 27) – Direct enterprise declarations (intra. EU 27) Indicators – Import/export in Mio Euro – World shares – Ratio of country’s high-tech trade in its total trade – Share of intra-EU trade Classification is less relative as the products are assumed to be more homogeneous (than the sectors) and therefore less dependent on the set of countries used Data source and coverage – Comext database - EU trade – Comtrade database - World trade 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 41
HIGH-TECH STATISTICS PRODUCT APPROACH BASED ON SITC HIGH-TECH PRODUCTS Aerospace Armament Computers-Office machines Electronics-Telecommunication Pharmacy Scientific instruments Electrical machinery Non-electrical machinery Chemistry Data collection – Traders’ customs declarations (extra. EU 27) – Direct enterprise declarations (intra. EU 27) Indicators – Import/export in Mio Euro – World shares – Ratio of country’s high-tech trade in its total trade – Share of intra-EU trade Classification is less relative as the products are assumed to be more homogeneous (than the sectors) and therefore less dependent on the set of countries used Data source and coverage – Comext database - EU trade – Comtrade database - World trade 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 41
 HIGH-TECH STATISTICS INDICATORS AND SOURCES FOR HIGH-TECH SECTORS (NACE) SECTORAL APPROACH n R&D personnel and expenditure R&D survey n Employment statistics for high-tech sectors Innovation activities Structural business statistics (number of enterprises, turnover, value added at factor costs, production value, social security costs etc) Mean annual earnings by sex, age and level of education Venture capital investment by stage of development (for all sectors) Labour Force Survey (LFS) n n 9/10/2009 Community Innovation Survey (CIS) Structural Business Survey (SBS) Structure of Earnings Survey (SES) European Private Equity and Venture Capital Association (EVCA) Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 42
HIGH-TECH STATISTICS INDICATORS AND SOURCES FOR HIGH-TECH SECTORS (NACE) SECTORAL APPROACH n R&D personnel and expenditure R&D survey n Employment statistics for high-tech sectors Innovation activities Structural business statistics (number of enterprises, turnover, value added at factor costs, production value, social security costs etc) Mean annual earnings by sex, age and level of education Venture capital investment by stage of development (for all sectors) Labour Force Survey (LFS) n n 9/10/2009 Community Innovation Survey (CIS) Structural Business Survey (SBS) Structure of Earnings Survey (SES) European Private Equity and Venture Capital Association (EVCA) Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 42
 HIGH-TECH STATISTICS INDICATORS AND SOURCES FOR HIGH-TECH TRADE (SITC) – PRODUCT APPROACH Import and export of high-tech group of products Comext / Comtrade Patent indicators (IPC) EPO, USPTO High-tech patents in high-technology fields and biotechnology patents 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 43
HIGH-TECH STATISTICS INDICATORS AND SOURCES FOR HIGH-TECH TRADE (SITC) – PRODUCT APPROACH Import and export of high-tech group of products Comext / Comtrade Patent indicators (IPC) EPO, USPTO High-tech patents in high-technology fields and biotechnology patents 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 43
 HIGH-TECH STATISTICS UPCOMING CHALLENGES Establishment of transitional definitions to accommodate the revised NACE Rev. 2 source data More in-depth revision waits the R&D intensity data with NACE 2 (2011) and more recent OECD's input-output tables (2009 -2010) Updating the High-Tech classifications Presently both main High-Tech classifications (in terms of economic activities and in terms of products) are based on 'old' reference data for very limited set of (more developed) countries Development of new sectoral classification based on the knowledge intensity, measured through LFS data on the share of tertiary educated employed, by economic activity (NACE) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 44
HIGH-TECH STATISTICS UPCOMING CHALLENGES Establishment of transitional definitions to accommodate the revised NACE Rev. 2 source data More in-depth revision waits the R&D intensity data with NACE 2 (2011) and more recent OECD's input-output tables (2009 -2010) Updating the High-Tech classifications Presently both main High-Tech classifications (in terms of economic activities and in terms of products) are based on 'old' reference data for very limited set of (more developed) countries Development of new sectoral classification based on the knowledge intensity, measured through LFS data on the share of tertiary educated employed, by economic activity (NACE) 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 44
 HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) HRST STATISTICS HRST statistics review the supply of and demand for highly qualified staff in a broad sense Statistics show stocks and flows of HRST at EU, national and regional level DATA SOURCES Data extracted from two Eurostat sources (Labour force survey and Statistics on education) and edited, aggregated and disseminated by Eurostat for all EU 27 (+) HARMONISED CONCEPTS, DEFINITIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Manual on the measurement of Human Resources devoted to S&T - Canberra Manual, OECD, 1995 available at: http: //www. oecd. org/dataoecd/34/0/2096025. pdf 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 45
HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) HRST STATISTICS HRST statistics review the supply of and demand for highly qualified staff in a broad sense Statistics show stocks and flows of HRST at EU, national and regional level DATA SOURCES Data extracted from two Eurostat sources (Labour force survey and Statistics on education) and edited, aggregated and disseminated by Eurostat for all EU 27 (+) HARMONISED CONCEPTS, DEFINITIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS Manual on the measurement of Human Resources devoted to S&T - Canberra Manual, OECD, 1995 available at: http: //www. oecd. org/dataoecd/34/0/2096025. pdf 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 45
 HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) DEFINITION Definition based on the cross tabulation of education and occupation, used often as proxy for ‘researchers’ Human Resources in S&T are all individuals who fulfil at least one of the following conditions: Have successfully completed tertiary-level education and/or Work in S&T occupation as professionals or technicians, where the above qualifications are normally required The conditions of the above educational or occupational requirements are considered according to internationally harmonised standards: - International Standard Classification of Occupation - ISCO - International Standard Classification of Education - ISCED 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 46
HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) DEFINITION Definition based on the cross tabulation of education and occupation, used often as proxy for ‘researchers’ Human Resources in S&T are all individuals who fulfil at least one of the following conditions: Have successfully completed tertiary-level education and/or Work in S&T occupation as professionals or technicians, where the above qualifications are normally required The conditions of the above educational or occupational requirements are considered according to internationally harmonised standards: - International Standard Classification of Occupation - ISCO - International Standard Classification of Education - ISCED 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 46
 HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) HRST SUB - CATEGORIES HRSTC - individuals who have successfully completed tertiary-level education and work in an S&T occupation as professionals or technicians HRSTE - individuals who have successfully completed tertiary-level education HRSTO - individuals who work in an S&T occupation as professionals or technicians HRSTU - individuals who have successfully completed tertiary-level education but are unemployed 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 47
HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) HRST SUB - CATEGORIES HRSTC - individuals who have successfully completed tertiary-level education and work in an S&T occupation as professionals or technicians HRSTE - individuals who have successfully completed tertiary-level education HRSTO - individuals who work in an S&T occupation as professionals or technicians HRSTU - individuals who have successfully completed tertiary-level education but are unemployed 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 47
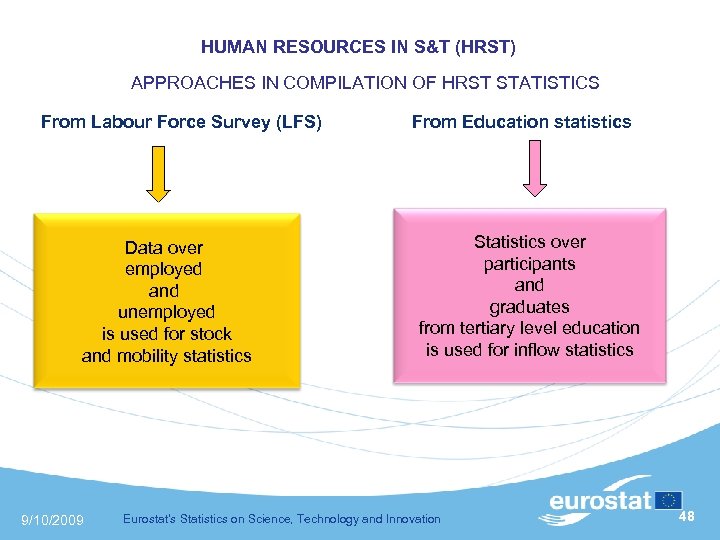 HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) APPROACHES IN COMPILATION OF HRST STATISTICS From Labour Force Survey (LFS) Data over employed and unemployed is used for stock and mobility statistics 9/10/2009 From Education statistics Statistics over participants and graduates from tertiary level education is used for inflow statistics Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 48
HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) APPROACHES IN COMPILATION OF HRST STATISTICS From Labour Force Survey (LFS) Data over employed and unemployed is used for stock and mobility statistics 9/10/2009 From Education statistics Statistics over participants and graduates from tertiary level education is used for inflow statistics Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 48
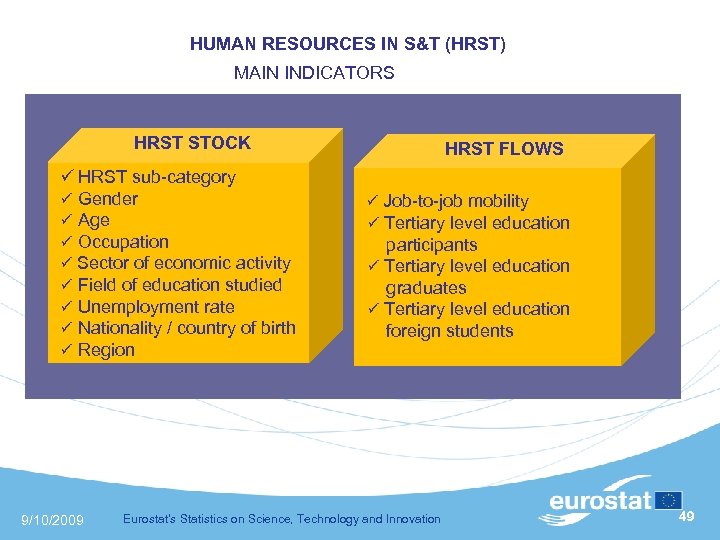 HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) MAIN INDICATORS HRST STOCK HRST sub-category Gender Age Occupation Sector of economic activity Field of education studied Unemployment rate Nationality / country of birth Region 9/10/2009 HRST FLOWS Job-to-job mobility Tertiary level education participants Tertiary level education graduates Tertiary level education foreign students Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 49
HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) MAIN INDICATORS HRST STOCK HRST sub-category Gender Age Occupation Sector of economic activity Field of education studied Unemployment rate Nationality / country of birth Region 9/10/2009 HRST FLOWS Job-to-job mobility Tertiary level education participants Tertiary level education graduates Tertiary level education foreign students Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 49
 HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) UPCOMING CHALLENGES Updating the Canberra Manual HRST concept and definitions are based on the OECD's Canberra Manual which was published more than 20 years ago. Since then both underlying classifications has been revised, International Standard Classification of Occupation (ISCO) and International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED 97). 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 50
HUMAN RESOURCES IN S&T (HRST) UPCOMING CHALLENGES Updating the Canberra Manual HRST concept and definitions are based on the OECD's Canberra Manual which was published more than 20 years ago. Since then both underlying classifications has been revised, International Standard Classification of Occupation (ISCO) and International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED 97). 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 50
 WHERE TO FIND S&T&I STATISTICS? WEB PUBLICATIONS – Eurostat/Science, Technology and Innovation http: //epp. eurostat. ec. europa. eu – OECD database http: //www. oecd. org/statsportal/ – DG Research http: //ec. europa. eu/research/ 9/10/2009 – Eurostat collections Statistical Book on Science, technology and innovation – 2009 Pocketbook on Science, technology and innovation – 2008 Statistics in Focus News release – DG Research Key figures on Science, technology and competitiveness 2008/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 51
WHERE TO FIND S&T&I STATISTICS? WEB PUBLICATIONS – Eurostat/Science, Technology and Innovation http: //epp. eurostat. ec. europa. eu – OECD database http: //www. oecd. org/statsportal/ – DG Research http: //ec. europa. eu/research/ 9/10/2009 – Eurostat collections Statistical Book on Science, technology and innovation – 2009 Pocketbook on Science, technology and innovation – 2008 Statistics in Focus News release – DG Research Key figures on Science, technology and competitiveness 2008/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 51
 Thank you ! 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 52
Thank you ! 9/10/2009 Eurostat's Statistics on Science, Technology and Innovation 52


