c986e514a12fafa0ace782cad6fac2b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 Introduction to IT audits PART II IT Audit International Standards, Practices & Guidance Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 Monique Garsoux ISACA Chapter Vice-President Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 1

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 Introduction • The MIS has to be : – – – Reliable Continuous Secure Efficient/effective Compliant • All authorities need an independent IT audit because – It is their responsibility – They should have reports on the IT risks evaluation based on objective assessment criteria – Their IT system should be effective Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 2

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 The association of IT auditors : ISACA • The IT audit is an internationnally regulated profession. • Founded in 1969, as the EDP Auditors Association (EDPAA) • More than 86, 000 members in 160 countries • Members include internal & external auditors, Chief Information Officers, Information security and control professionals and IT consultants • More than 175 chapters worldwide • 33 Chapters in Europe Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 3

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 The IT Auditors team • The IT auditor has to respect professional standards, certification, skills and expertise. • The IT auditor should be qualified for the work. • The IT auditor has frameworks and best practices as the support for his work. Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 4

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 IT auditor has to be competent • Hold certifications – Certified Information Systems Auditor™ (CISA®) – Certified Information Security Manager® (CISM®) – Certified in the Governance of Enterprise IT® (CGEIT®) • Apply Standards and Frameworks – IS auditing standards, guidelines, procedures, IS control standards – Frameworks to be used : Cobi. T & IT Assurance Guide and more… • Keep informed and trained : – Conferences and education – Information : K-NET® – Publications Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 5

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 What the IT auditor does … • A formal, independent and systematic assessment of the IT system that must meet specific criteria (effectiveness, integrity, confidentiality, completeness, availability, compliance, reliability). • He produces a written report on risks, weaknesses, findings and recommendations. He follows the action plans from the auditees. • Code of Professional Ethics : guides the professional and personal conduct of IT Auditors (Independence and Objectivity, Reasonable Expectation, Management’s Acknowledgement, Training and Proficiency, Knowledge of the Subject Matter; Due Professional Care). Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 6| 6
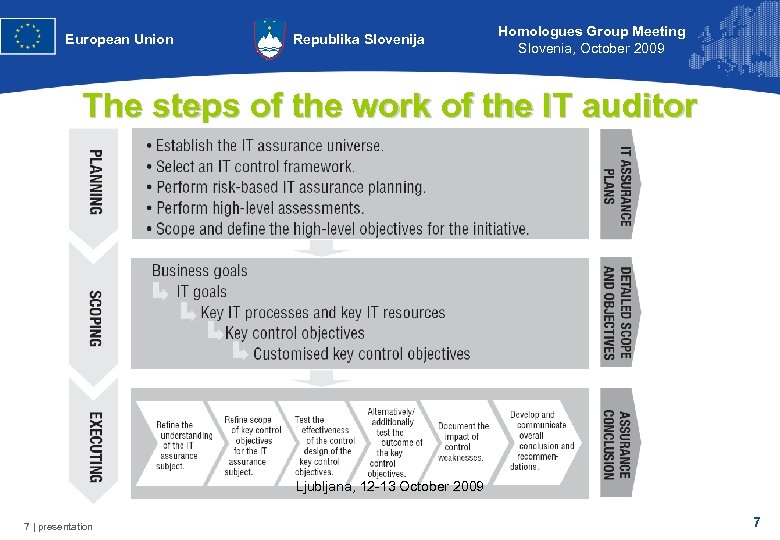
European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 The steps of the work of the IT auditor Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 7 | presentation 7
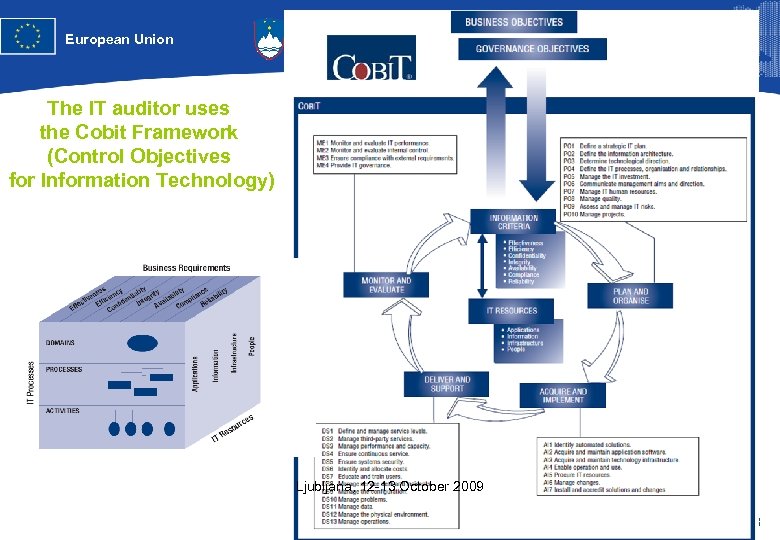
European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 The IT auditor uses the Cobit Framework (Control Objectives for Information Technology) Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 8
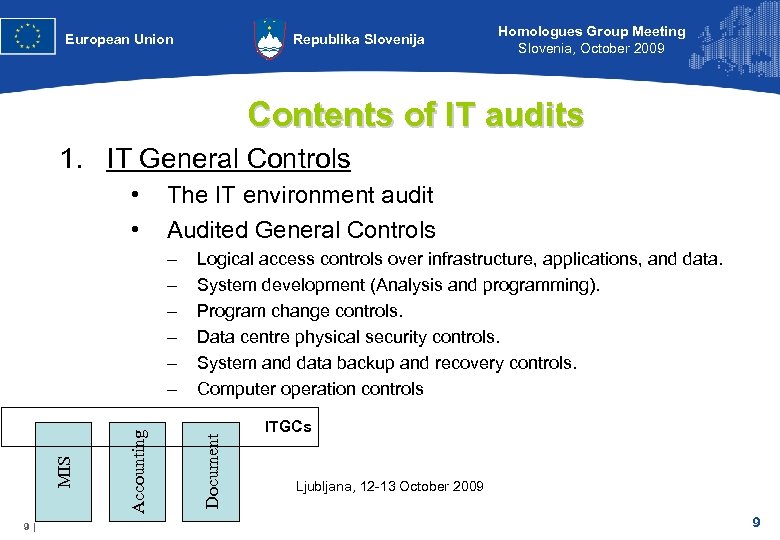
European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 Contents of IT audits 1. IT General Controls The IT environment audit Audited General Controls 9| Accounting MIS – – – Logical access controls over infrastructure, applications, and data. System development (Analysis and programming). Program change controls. Data centre physical security controls. System and data backup and recovery controls. Computer operation controls Document • • ITGCs Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 9
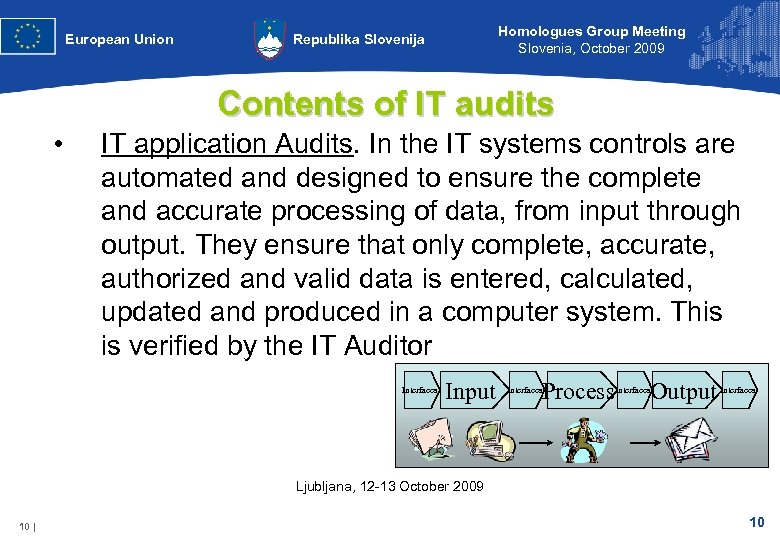
European Union Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 Republika Slovenija Contents of IT audits • IT application Audits. In the IT systems controls are automated and designed to ensure the complete and accurate processing of data, from input through output. They ensure that only complete, accurate, authorized and valid data is entered, calculated, updated and produced in a computer system. This is verified by the IT Auditor Interfaces Input Process Interfaces Output Interfaces Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 10 | 10

• European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 AC 1 Source document preparation & authorisation Example of the IT audit Framework Example of tests from Cobit to be realized by the IT auditor Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 11

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 Reporting done by the IT Auditor – Reports consist of a written text accompanied with detailed information. – It is organised in such a manner as to permit the reader to understand, in greater depth, the areas included in the scope of the report; the work performed; the findings obtained (audit opinion); and the issues, concerns, risks, etc. , identified. – The report is based on the findings and the recommendations themselves substantiated by the tests and investigations performed Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 12 | 12

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 References • WWW. ISACA. ORG for Cobit and the Assurance Guide and IT assurance framework -> free downloadable • For information on IT audit &Training Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 13

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 Conclusion • IT audit is a mature and regulated profession with available tools and techniques from ISACA. Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 14

European Union Republika Slovenija Homologues Group Meeting Slovenia, October 2009 Thank you for your attention! Email : M. Garsoux@QAP. EU Tel: + 32 472739836 Ljubljana, 12 -13 October 2009 15
c986e514a12fafa0ace782cad6fac2b5.ppt