997f3949f6133c2279503f65d10ad5f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

European Payload Operations Service for the Double Star Project Command Request Interface Document Dr. T. G. Dimbylow, RAL Third Chinese-European DSP Interface Meeting CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 1
Contents Purpose of the CRID Significance of Compliance Type of Mission General Aspects of Interface High Level EPOS Architecture Summary of Interface Files Details of Interface Files DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 2
Purpose of the CRID • To describe all the operational command related interface files transferred between the EPOS and DOMC/DSAS • Closely based on Cluster CRID, 3 drafts to date: – – Draft 1, 03/05/2002 Draft 2, 30/05/2002 Draft 3, 19/06/2002 Issue 1. 0, end of August internal review at RAL & ESTEC sent to DOMC/DSAS for review will contain all agreed changes • Defines the file format & content in detail • Operational activities between EPOS & DOMC/DSAS will be described in a separate ICD: – DOMC-EPOS Interface Agreement, DSP-RAL-ID-0003 – Will be closely based on the ESOC-JSOC Interface Agreement DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 3
Significance of Compliance • The DSP EPOS will be closely based on the existing Cluster JSOC: – Strict maintenance of the interface to the European PIs: • not directly impacted by the CRID • separate EPOS to PI ICD, DSP-RAL-ID-0002, based on the JSOC to PI ICD – Allows re-usability of core JSOC software & procedures – Differences taken care of by input/output shells – Modification of core code & database structures would be last option • Full CRID compliance minimizes changes to Cluster JSOC: – EPOS, DOMC/DSAS & ESTEC to agree on this interface – DOMC/DSAS to assess impact of strict compliance with CRID – EPOS to assess impact of deviation from CRID • CRID non-compliance will impact EPOS cost & schedule DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 4
One Two-Spacecraft Mission or Two Single-Spacecraft Missions • RAL has not fully analyzed the optimum way to command the European instruments in DSP: – Treat DSP as one mission with 2 spacecraft – Treat DSP as two missions each with one spacecraft • Each option: – Can be supported by a JSOC-like system – Advantages & disadvantages of either approach • Details of some of the CRID interface files might change depending on which option is chosen • Full analysis awaits contract from ESA DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 5
General Aspects of Interface • The file naming convention allows: – Some checking/verification at the level of the file name – Consistency checking with the file contents (standard file header) • The use of a standard end-of-file record – where applicable – is a check against processing an incomplete file: – FTP can terminate with a failure but give a “success” status – A break in an OBRQ between Observation Requests is still a “legal” OBRQ – Incomplete PI inputs did happen during Cluster-I testing, none during Cluster-II • An automated file transfer system (FTS) is assumed to exist between EPOS & DOMC/DSAS: – Based on CFTS (TBC), supplied for Cluster by ESOC – Details to be agreed between EPOS & DOMC/DSAS DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 6
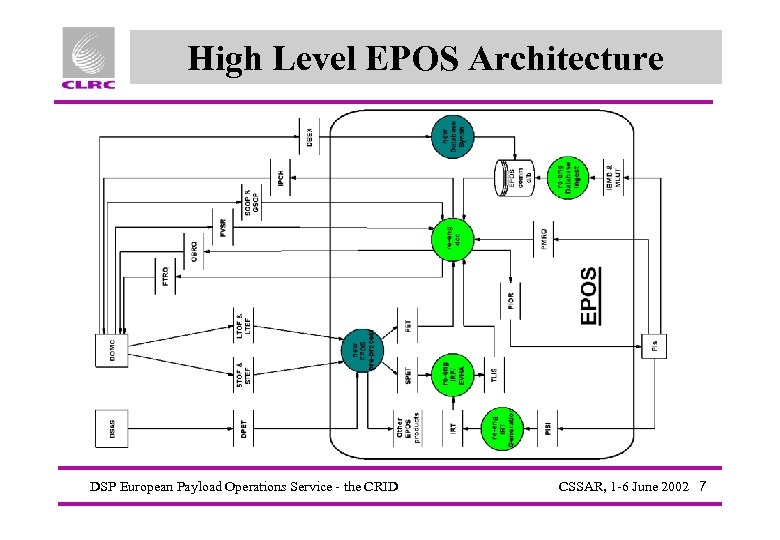
High Level EPOS Architecture DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 7
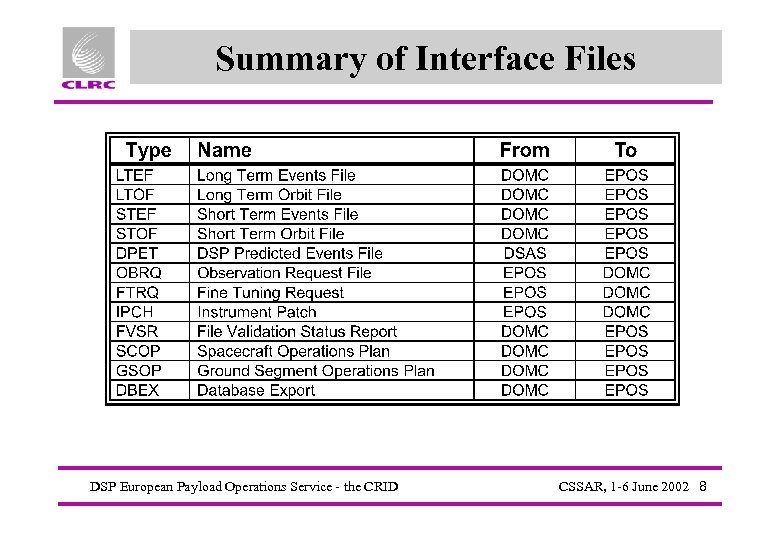
Summary of Interface Files DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 8
LTEF, LTOF, STEF, STOF • Long Term Event File, Long Term Orbit File, Short Term Event File, Short Term Orbit File – produced by DOMC: – LTEF/LTOF produced pre-launch and after final orbit manoeuvres (TBC) – STEF/STOF produced in-orbit at least once per week (TBC) • Details are specified in the Data Delivery Interface Document, DDID, because these files are part of the data set made available to all PIs • EPOS: – Ingests these files into its Oracle Planning Database – The timing information is used: • to resolve relative times in PIORs into absolute times in OBRQs • in catalogue generation • in other core EPOS activities DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 9
DPET • DSP Predicted Event Timeline file produced by DSAS (TBC): – At least one DPET is produced per planning period – Produced 5 weeks (TBC) before start of execution of the planning period – Might be produced by DOMC (TBC) • This is the core interface file from DSAS input into EPOS: – Based on/derived from the MSOP – EPOS will ingest this file together with the STOF/STEF – EPOS will produce internal interface files which will feed into the reengineered JSOC system • EPOS & DOMC/DSAS to agree on: – The content of this file – The Event Types actually appropriate/needed for DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 10
OBRQ • Observation Request file produced by EPOS: – At least one OBRQ will be produced per planning period – Produced 4 weeks (TBC) before start of execution of the planning period – Expect that commanding for DSP-1 & DSP-2 will be in same file (TBC) • This is the core interface file from EPOS input into DOMC: – Contains sequences of instantiated Command Sequences with resolved parameter values – Time tags are absolute UTCs • The number of OBRQ instantiations per planning period and their delivery schedule are TBC DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 11
FTQR • Fine Tuning Request file produced by EPOS: – Produced on an “as required” basis – Allows changes to instrument commanding at the parameter level, after receipt of final OBRQ at DOMC – Only allowed if no negative impact on spacecraft resources • EPOS: – Has a defined interface with PIs to receive requested changes for nominated parameters (agreed between PIs, DOMC & EPOS) – Updates its own database for future use – If within agreed time window for planning period, FTRQ generated and sent to DOMC • The requirement for this facility for DSP is TBC DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 12
IPCH • Instrument Patch File produced by EPOS: – Produced infrequently for non-critical changes to on-board software & tables for the European instruments • EPOS: – Has a defined interface with PIs to receive requested changes – Performs format & checksum checks – but not content checks • The requirement for this facility for DSP is TBC • For Cluster the PIs also had a direct interface with ESOC for critical on-board patching activities DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 13
FVSR • File Validation Status Report file produced by DOMC – One FVSR will be generated by DOMC for every file sent from EPOS: • For every OBRQ • For every FTRQ • For every IPCH • DOMC checks syntax/semantics of each file received from EPOS • FVSR contains the status, either: – “VALID” – “INVALID” with an error report • EPOS uses FVSR to: – Respond to OBRQs, FTRQs or IPCHs which are in error – Track the reception & ingestion of OBRQs, FTRQs or IPCHs at DOMC DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 14
SCOP • Spacecraft Operations file produced by DOMC: – Produced for each OBRQ received from EPOS • The SCOP reports on a deeper analysis of the OBRQ, constraint checking Observation Request execution against: – – Spacecraft operations Spacecraft power SSMM capacity Data/telemetry mode (TBC) • All anomalies due to the European instrument commanding will have to be rectified by EPOS: – May involve interaction/iteration with European PIs – May involve interaction/iteration with PS or PS decision DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 15
GSOP • Ground Segment Operations file produced by DOMC: – Produced for each OBRQ received from EPOS • The GSOP reports on a deeper analysis of the OBRQ, globally constraint checking against: – – Allowable downlink telemetry rates Ground station availability (the 2 Chinese ground stations & VILSPA) Spacecraft power SSMM capacity • All anomalies due to the European instrument commanding will have to be rectified by EPOS: – May involve interaction/iteration with European PIs – May involve interaction/iteration with PS or PS decision DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 16
DBEX • Database Export File produced by DOMC – Frequency of production is TBS • EPOS Command Database is an Oracle database: – Contains details of the Command Sequences (CSEQ) & CSEQ Parameters – Is a sub-set of the information held in the DOMC Command Database • There is no requirement from EPOS on the DBMS & database structure at DOMC • EPOS will process/ingest the DBEX to ensure EPOS database remains synchronised with the DOMC database: – CSEQ changes – Parameter changes DSP European Payload Operations Service - the CRID CSSAR, 1 -6 June 2002 17
997f3949f6133c2279503f65d10ad5f8.ppt