97e6433f997d53575e6146e648312571.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

European Licensing System A harmonised symbol for Europe Tunde Koltai AOECS Board, Chair

Questions • 1 who produces only GF • 2 who doesn’t have HACCP • 3 who has Quality management for GF production (IFS, BRC, AHA, …) • 4 who had last year a turnover 100 000 EUR • 5 who had last year export sales > 15% and where? • 6 who uses now the Czech symbol and when the contract will expire • 7 who was asked already to join ELS • 8 who has a reps for HU

AOECS Ø European umbrella organisation of national coeliac societies in Europe Ø Independent NGO Ø Established in 1988 Ø Registered seat in Brussels Ø 5 Board members Ø 35 members from 29 European countries Ø Represents more than 300. 000 coeliacs across Europe

AOECS Ø Member of International networks: European Patients’ Forum (EPF), International Alliance of Patients’ Organisations (IAPO), International Society for the Study of Celiac Disease (ISSCD) Ø Partner scientific projects: PREVENTCD, CDMEDICS, TRAFOON, MEDICEL, Pro. Ce. DE Ø Partner of EU and national institutions

AOECS Aims Ø to increase awareness of coeliac disease Ø to facilitate the exchange of information relating to the coeliac condition Ø to increase the availability and easily identifiable labelling of gluten-free products
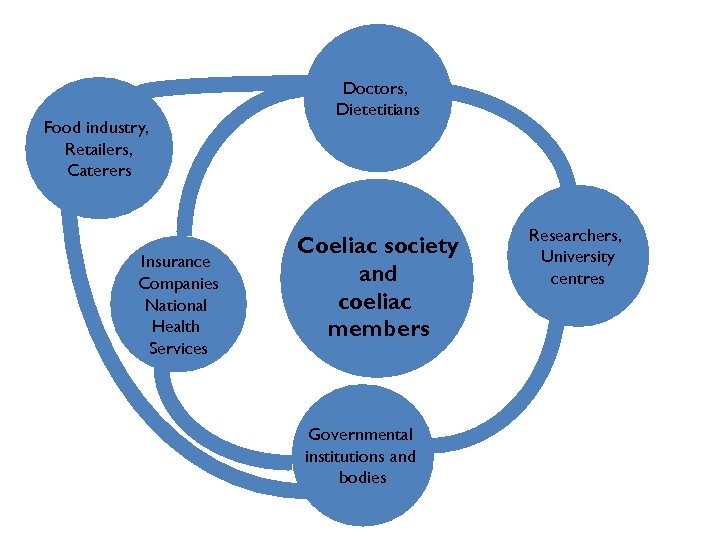
Food industry, Retailers, Caterers Insurance Companies National Health Services Doctors, Dietetitians Coeliac society and coeliac members Governmental institutions and bodies Researchers, University centres
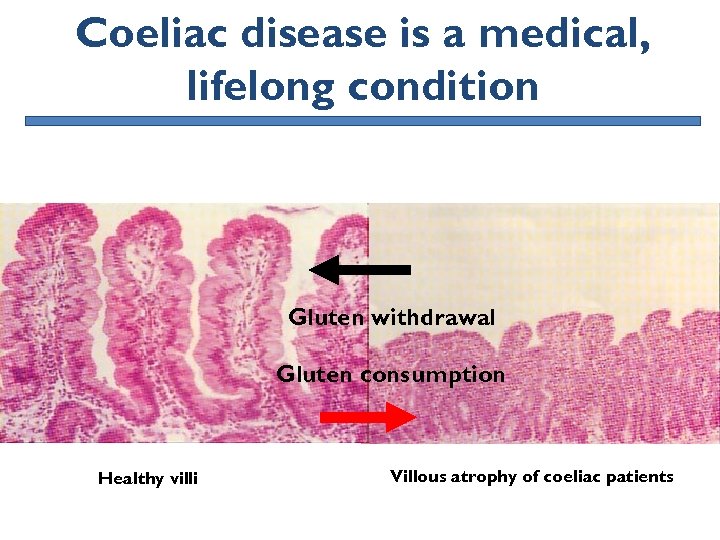
Coeliac disease is a medical, lifelong condition Gluten withdrawal Gluten consumption Healthy villi Villous atrophy of coeliac patients

Treatment The unique and evidence based treatment: Lifelong and strict gluten-free diet Never start a gluten-free diet before the diagnosis or exclusion of coeliac disease or cereal (protein) allergy

Medication?
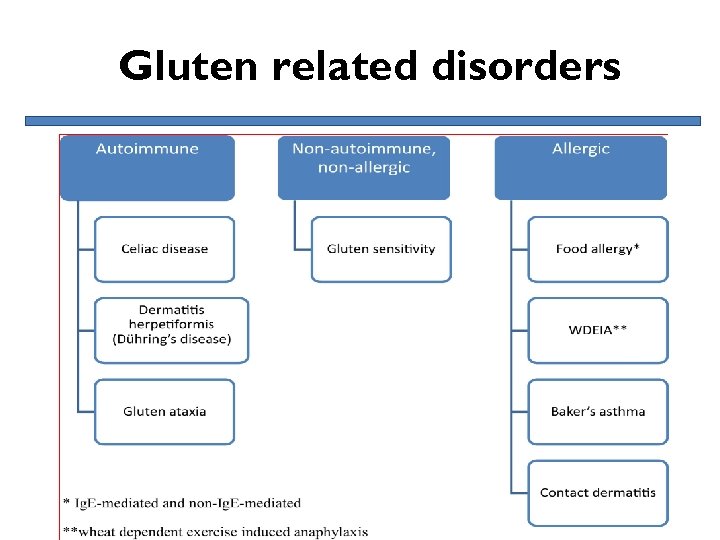
Gluten related disorders

![Gluten Storage protein of cereals: wheat, rye, barley and [oats*] Can cause • Intolerance Gluten Storage protein of cereals: wheat, rye, barley and [oats*] Can cause • Intolerance](https://present5.com/presentation/97e6433f997d53575e6146e648312571/image-12.jpg)
Gluten Storage protein of cereals: wheat, rye, barley and [oats*] Can cause • Intolerance Threshold: 10 mg/day • Allergy (is species specific) Threshold: 0 (? !)/different sensitivity levels * Oats can be tolerated by most but not all people who are intolerant to gluten. Therefore, the allowance of oats that are not contaminated with wheat, rye or barley in foods covered by this standard may be determined at the national level.
![Gluten Storage protein of cereals: wheat, rye, barley and [oats*] Can cause • Intolerance Gluten Storage protein of cereals: wheat, rye, barley and [oats*] Can cause • Intolerance](https://present5.com/presentation/97e6433f997d53575e6146e648312571/image-13.jpg)
Gluten Storage protein of cereals: wheat, rye, barley and [oats*] Can cause • Intolerance Threshold: 10 mg/day • Allergy (is species specific) Threshold: 0 (? !)/different sensitivity levels * Oats can be tolerated by most but not all people who are intolerant to gluten. Therefore, the allowance of oats that are not contaminated with wheat, rye or barley in foods covered by this standard may be determined at the national level.

Gluten-free regulation

Gluten-free foods Gluten content < 20 mg/kg

2008: Codex Standard 118 -1979 World-wide „Codex Standard for foods for special dietary use for persons intolerant to gluten”

EU regulations COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 41/2009 of 20 January 2009 concerning the composition and labelling of foodstuffs suitable for people intolerant to gluten

1169/2011 regulation (FIC) Regulation (EU) 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and the Council of 25 October 2011 on the provision of food information to consumers, amending Regulations (EC) No 1924/2006 and (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and repealing Commission Directive 87/250/EEC, Council Directive 90/496/EEC, Commission Directive 1999/10/EC, Directive 2000/13/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Directives 2002/67/EC and 2008/5/EC and Commission Regulation (EC) No 608/2004

1169/2011 regulation (FIC) Brings together existing regulations regarding • Labelling • Nutrition • Allergen information Not only for pre-packed food

1169/2011 regulation (FIC) Regulation (EU) 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and the Council of 25 October 2011 Starting from 20 July 2016 the ‘glutenfree’ foods are fully regulated only by this regulation

“Big 14” food allergens Annex II Gluten containing cereals Crustaceans Nuts Celery Egg Mustard Fish Peanuts Soybeans Milk (casein and lactose) Sesame seed Lupin Molluscs SO 2 and sulfits
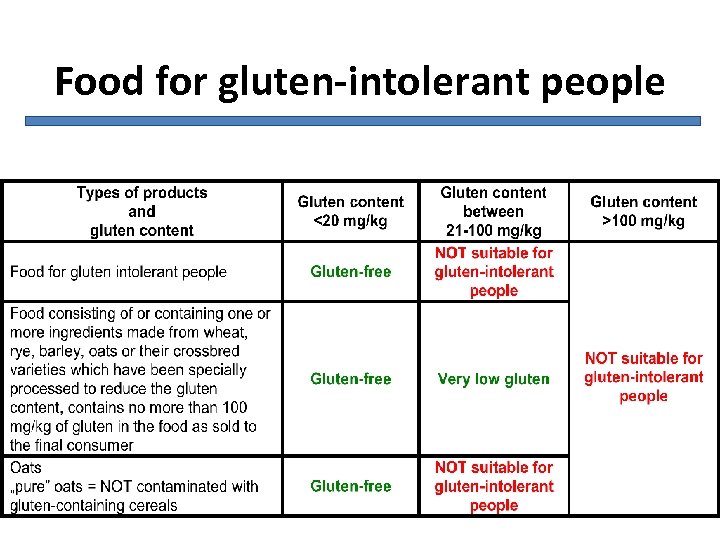
Food for gluten-intolerant people


Coeliacs need and wish - Safe Good Cheap Available products which comply with the international and local standards


What is the Crossed Grain Symbol? • Created in 1969 by a member of Coeliac UK • Today it is the internationally recognised symbol for gluten-free food needed by people with coeliac disease • Registered by coeliac societies at national and European levels • Outside Europe: contact to Coeliac UK
International Trade Mark • Harmonised system for equality in Europe • Trust/confidence of the customers • Guidelines for the local/small producers • Advises for local/small producers For quality and safe gluten-free products
European Charta Determines ü Obligations of all the partners ü Definitions ü Technical requirements ü Quality criteria
European Licensing System (ELS) ELS components consist of: • AOECS Standard • AOECS Charta • AOECS-Member society license contract for the sub-licensing of the Crossed Grain symbol • AOECS Member-Producer license contract for the use of the Crossed Grain symbol

European Licensing System (ELS) License numbering Country code-license code-product code CZ-100 -001 OATS-CZ-100 -001

European Licensing System (ELS) ü The ELS Charta was accepted by the AOECS General Assembly in Malta in 2009 ü Regulates the use of the Crossed Grain Symbol on gf food products across all countries in which AOECS Member societies are located (AOECS territory) ü Permits the use of the Symbol across the entire AOECS territory with one license contract

European Licensing System (ELS) ü The Crossed Grain symbol conveys a safety guarantee for coeliacs by communicating that licensed gluten-free products must comply with the AOECS Standard ü Provides unified licensing conditions across AOECS territory ü Increases availability of gluten-free food products featuring the Symbol across Europe

European Licensing System (ELS) • One licencor in each AOECS-member countries (= national societies) • International producers: • Sales of licenced products > 100. 001 € and • Export sales > 15 % • Local producers: • Sales of licenced products <100. 000 € and/or • Export sales < 15 %

European Licensing System (ELS) Data as per 31 December 2014 • 21 Member societies have signed the AOECS Charta • +300 producer contracts signed • +5000 gluten-free products licensed


Our aim is common: the happy and satisfied coeliac customer/patient/guest

Certification procedure 1. step: contact of CS and a producer, information 2. step: application - Certificate of gluten analysis Packaging/labelling to place on the symbol Proving documentation 3. step: - Audit of the production site(s)

Certification procedure 4. Audit can be fulfilled - by employing qualified staff of the society - by deploying a service provider - by using the existing/acceptable assurance scheme of the producer (recognising the AOECS Standard too) The minimum quality criteria from the producer: to have an appropriate HACCP System The main goal: to avoid/prevent gluten contamination

Certification procedure 5. Step 6. step: 7. step: 8. step: the contracts can be signed and the products register inform AOECS inform socety’s members via magazin and webpage License fee - information from the company - invoicing the amount - paying the invoice Sharing the money with AOECS
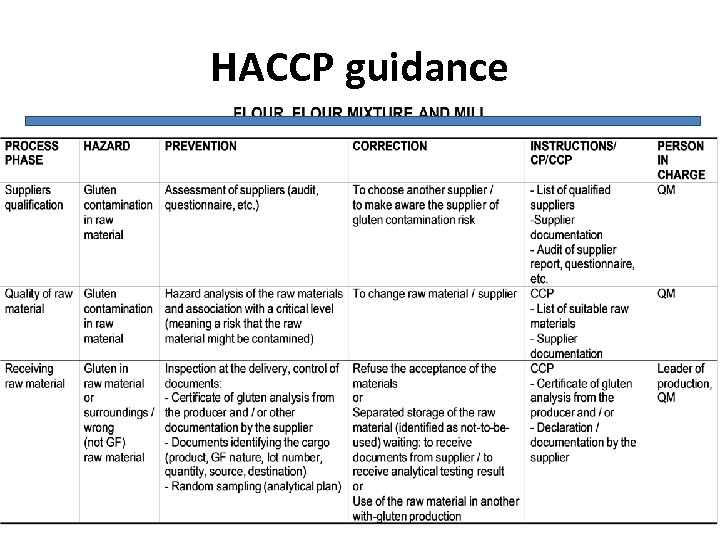
HACCP guidance

Foods not to be licensed UNPROCESSED CEREAL GRAINS AND PSEUDOCEREALS • Rice • Maize MEAT, FISH AND EGGS • All sorts of fresh or frozen meat and fish not processed • Tinned or canned fish with water/vegetable oil and salt, without additives or other • substances • Eggs

Foods not to be licensed MILK AND MILK-DERIVATES • Fresh milk, UHT milk, sterilized milk without additives, vitamins or other substances • Infant formula • Yogurt without additives, vitamins or other substances • Fresh milk cream and UHT milk cream • Cheese VEGETABLES AND LEGUMES • All sorts of plain, fresh, frozen, canned or dried vegetables and legumes

Foods not to be licensed NUTS AND SEEDS All sorts of nuts and seeds, with or without shells, not processed FRUITS All sorts of plain, fresh, frozen, canned or dried fruits DRINKS • Fruit juices • Soft drinks • Mineral waters • Tea, pure coffee • Wine • Distillates for spirits

Foods not to be licensed SWEETS • Honey, sugar • Marmalade and jam DRESSINGS AND OTHERS • • Butter, bacon fat, lard Vegetable Oil Vinegar Spices and aromatic herbs not processed

GOOD GLUTEN-FREE Majority of (daily) gluten-free products contain more salt, sugar and fat than regular products

Food allergy across EUROPE − Up to 25% of European population reacts to food − About 17 million Europeans suffer from food allergies, 3. 5 million aged less than 25 − 8% of allergic patients produce acute anaphylaxis considered potentially fatal − Over the past ten years, number of allergic children younger than 5 years has redoubled + emergency room visits for anaphylactic reactions have increased seven-fold * * Source: European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (EAACI)

Gluten related disorders
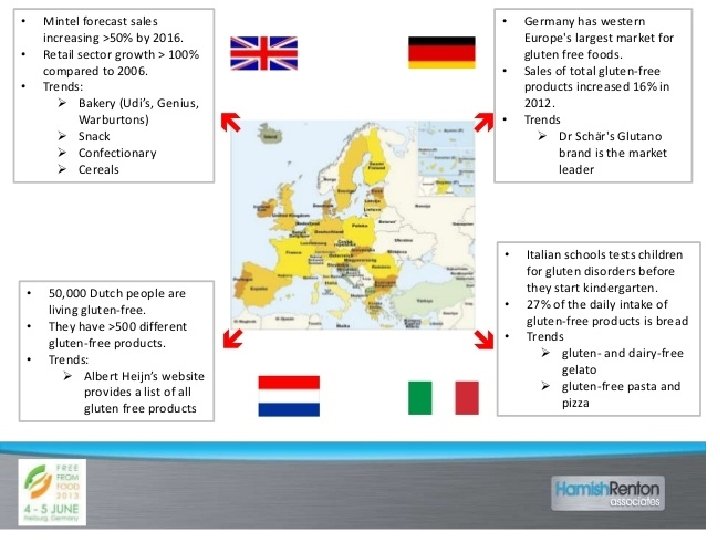
http: //image. slidesharecdn. com/finalfreefrompp-130530053441 -phpapp 02/95/free-from-presentation-9638. jpg? cb=1369892133
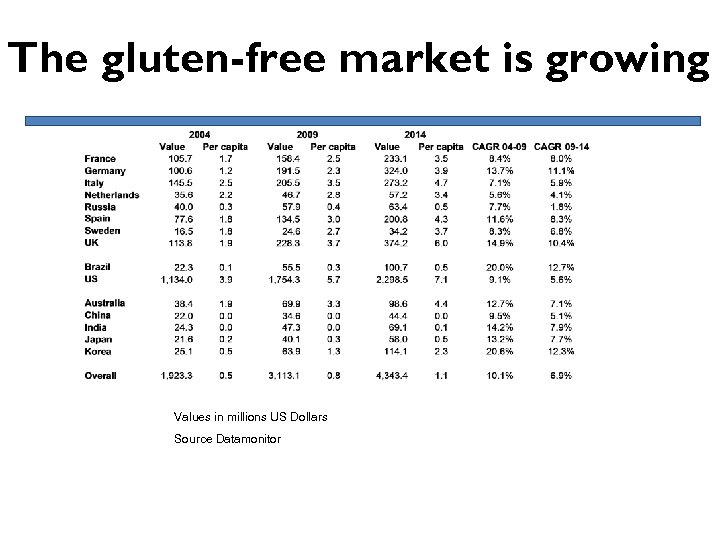
The gluten-free market is growing Values in millions US Dollars Source Datamonitor
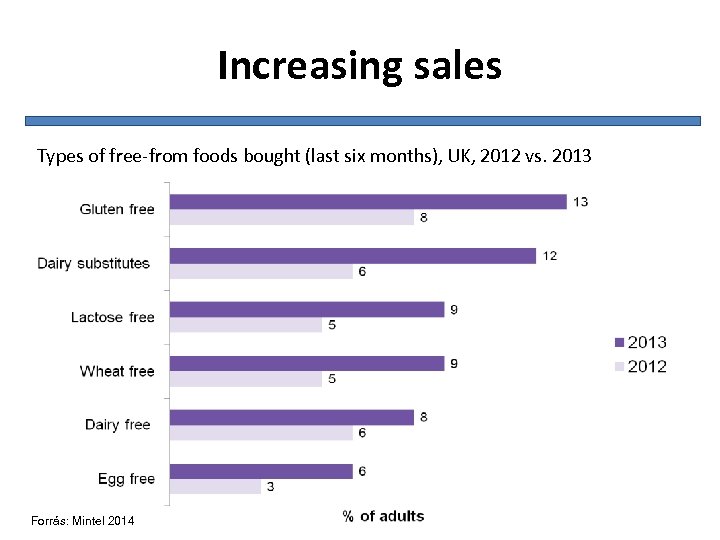
Increasing sales Types of free-from foods bought (last six months), UK, 2012 vs. 2013 Forrás: Mintel 2014

Increasing awareness Foods/ingredients avoided, UK, July 2013 Forrás: Mintel 2014
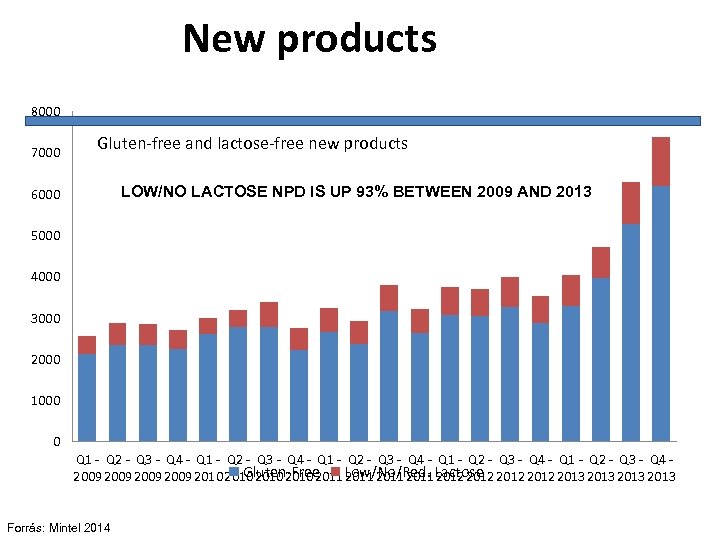
New products 8000 7000 Gluten-free and lactose-free new products LOW/NO LACTOSE NPD IS UP 93% BETWEEN 2009 AND 2013 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 Q 1 - Q 2 - Q 3 - Q 4 - Q 1 - Q 2 - Q 3 - Q 4 Gluten-Free 2009 2010 2011 Low/No/Red. Lactose 2012 2013 2011 2012 Forrás: Mintel 2014

Coeliac disease Our common challenge

Coeliac disease Our common challenge
97e6433f997d53575e6146e648312571.ppt