3a4210828aacf848ecba146076dad78b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 85
 Europe Religion, Colonialism, Changes and Conflict
Europe Religion, Colonialism, Changes and Conflict
 Christianity • Romans • Allowed the Jews to worship freely, only thing they cared about was being loyal to Emperor • Jesus: Christianity is based off his teachings (a lot of Jewish principles as well) • Romans feared Jesus, though teachings might cause an uprising • Pontius Pilate: Roman governor, arrested Jesus and had him crucified • Christians believe that Jesus rose from the dead and that through faith all believers could be saved.
Christianity • Romans • Allowed the Jews to worship freely, only thing they cared about was being loyal to Emperor • Jesus: Christianity is based off his teachings (a lot of Jewish principles as well) • Romans feared Jesus, though teachings might cause an uprising • Pontius Pilate: Roman governor, arrested Jesus and had him crucified • Christians believe that Jesus rose from the dead and that through faith all believers could be saved.
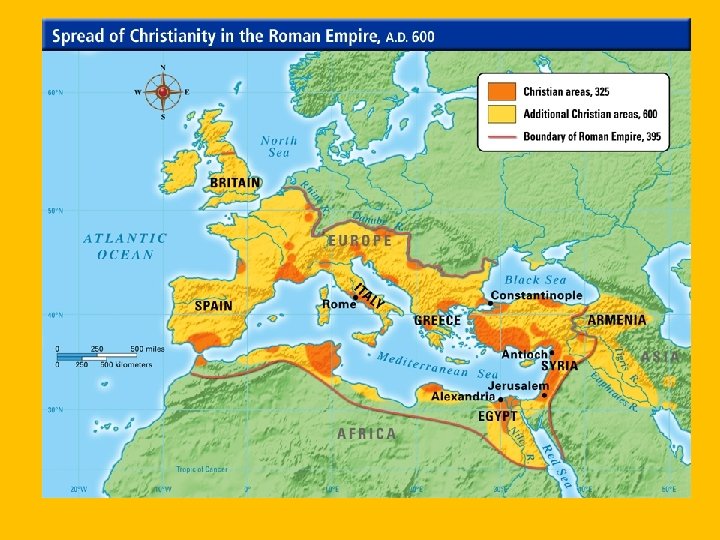
 Christianity • Romans • Christianity started to spread slowly throughout the Roman Empire. Eventually the Roman Empire began to see it as a threat. • Christianity became more popular in times of struggle (wealth and social status also did not matter) • By 300 AD, Christianity had grown so much that the Roman Empire was forced to accept Christianity as a religion. • Constantine supported Christianity, by 391 AD Christianity was adapted as the official religion of Roman Empire.
Christianity • Romans • Christianity started to spread slowly throughout the Roman Empire. Eventually the Roman Empire began to see it as a threat. • Christianity became more popular in times of struggle (wealth and social status also did not matter) • By 300 AD, Christianity had grown so much that the Roman Empire was forced to accept Christianity as a religion. • Constantine supported Christianity, by 391 AD Christianity was adapted as the official religion of Roman Empire.
 Christianity • Roman Religious Structure • • • Priest: Local Levels Bishops: Head of all churches in an large city/area Pope: Supreme power over all the church Holy Trinity: Father, Son, Holy Spirit. Structure resembles the Catholic Church today A TON of conflict between the power of bishops, popes and political leaders (Kings, Queens, etc)
Christianity • Roman Religious Structure • • • Priest: Local Levels Bishops: Head of all churches in an large city/area Pope: Supreme power over all the church Holy Trinity: Father, Son, Holy Spirit. Structure resembles the Catholic Church today A TON of conflict between the power of bishops, popes and political leaders (Kings, Queens, etc)
 Christianity • Crusades: • Cause: Muslims from Central Asia gained control of Palestine (Israel today). Also they threatened Christians in the Byzantine Empire (Turkey) • Pope Urban II: Decided to reclaim the holy land • Over 10, 000 Europeans took up this cause of numerous military expeditions. • Why did so many people go: Save Souls, gain land wealth, make money through trade
Christianity • Crusades: • Cause: Muslims from Central Asia gained control of Palestine (Israel today). Also they threatened Christians in the Byzantine Empire (Turkey) • Pope Urban II: Decided to reclaim the holy land • Over 10, 000 Europeans took up this cause of numerous military expeditions. • Why did so many people go: Save Souls, gain land wealth, make money through trade
 Christianity • 1 st Crusade • French and Italian leaders sent out armies • Successful in attacking and capturing the holy city of Jerusalem. (Massacred Jewish and Muslim residents) • Positive in that it set up trade between Europe and the Middle East. • Muslims and Christians lived along side of each other • Europeans had some control of the Middle East
Christianity • 1 st Crusade • French and Italian leaders sent out armies • Successful in attacking and capturing the holy city of Jerusalem. (Massacred Jewish and Muslim residents) • Positive in that it set up trade between Europe and the Middle East. • Muslims and Christians lived along side of each other • Europeans had some control of the Middle East
 Christianity • 2 nd Crusade • The Turks began to unite their forces and took back cities that the European’s had won • German and French forces failed to win back Damascus • 3 rd Crusade • Muslims gained control of Jerusalem • Red Beard (HRE), Phillip II (France), Richard I (England) all united to fight back • Red Beard drowned leading his army, Phillip and Richard fought with each other…. did not win city back
Christianity • 2 nd Crusade • The Turks began to unite their forces and took back cities that the European’s had won • German and French forces failed to win back Damascus • 3 rd Crusade • Muslims gained control of Jerusalem • Red Beard (HRE), Phillip II (France), Richard I (England) all united to fight back • Red Beard drowned leading his army, Phillip and Richard fought with each other…. did not win city back
 Christianity • 4 th Crusade • Pope Innocent III organized it • Italians troops attacked Christian cities of Zadar and Constantinople • Children’s Crusades • Young people from across Europe marched on the Holy Land to regain it for Christianity. • Many were killed or sold into slavery • Results • Last Crusade ended in 1291 when Muslims captured the city of Acre • All but the 1 st Crusades were a failure • Gunpowder, crossbows, etc • Church became more powerful • Exchange of goods and ideas boosted trade
Christianity • 4 th Crusade • Pope Innocent III organized it • Italians troops attacked Christian cities of Zadar and Constantinople • Children’s Crusades • Young people from across Europe marched on the Holy Land to regain it for Christianity. • Many were killed or sold into slavery • Results • Last Crusade ended in 1291 when Muslims captured the city of Acre • All but the 1 st Crusades were a failure • Gunpowder, crossbows, etc • Church became more powerful • Exchange of goods and ideas boosted trade

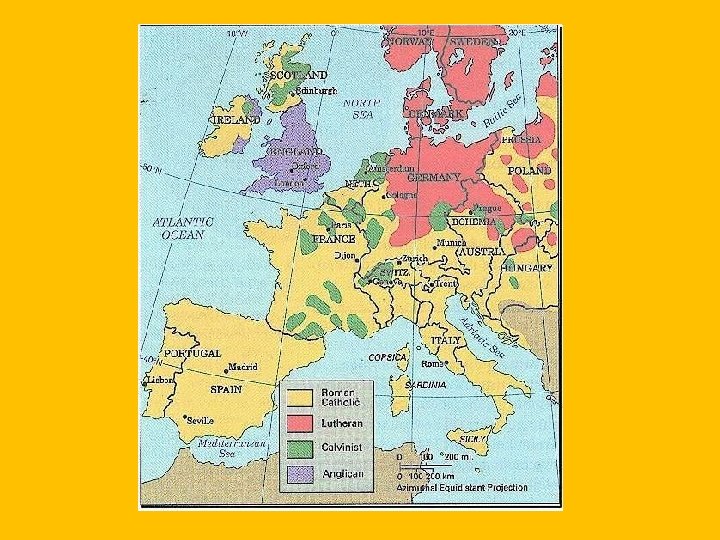
 Reformation • Split of the Roman Catholic Church in Western Europe • Why • People felt the Church was focusing too much on money and power • Start • Independent German states began to do their own thing religiously. • Pope Leo X tried to force these states to pay money for committing a sin…. angered a lot of people
Reformation • Split of the Roman Catholic Church in Western Europe • Why • People felt the Church was focusing too much on money and power • Start • Independent German states began to do their own thing religiously. • Pope Leo X tried to force these states to pay money for committing a sin…. angered a lot of people
 Reformation • Martin Luther • Monk who was struggling with his personal religious struggle • Belief: ceremonies and good deeds made no difference in saving a sinner. Only thing that mattered was inner faith with God. “Justification by grace through faith” • He shocked everyone by challenging the Church • Pope declared him a heretic and kicked him out of Church • Luther was declared an outlaw and he hid @ the Wartburg Castle in Eisenach Germany. There he translated the Bible into German. • Followers of Luther’s teachings were called Protestants
Reformation • Martin Luther • Monk who was struggling with his personal religious struggle • Belief: ceremonies and good deeds made no difference in saving a sinner. Only thing that mattered was inner faith with God. “Justification by grace through faith” • He shocked everyone by challenging the Church • Pope declared him a heretic and kicked him out of Church • Luther was declared an outlaw and he hid @ the Wartburg Castle in Eisenach Germany. There he translated the Bible into German. • Followers of Luther’s teachings were called Protestants

 Spread of Protestantism • German Issues • Charles V tried to stop Protestantism from spreading • He was unsuccessful, each German ruler had the right to choose the type of Christianity for their state. • England • Henry VIII: Created the Anglican Church to get away from the Roman Catholic Church • Henry did this because he wanted a divorce because his wife only gave him a daughter (Mary I). There had never been a Queen before. • Pope did not allow the divorce, so Henry VIII formed his own Church (Anglican Church of England). • Church kept same practices but did open the door for Protestantism in England
Spread of Protestantism • German Issues • Charles V tried to stop Protestantism from spreading • He was unsuccessful, each German ruler had the right to choose the type of Christianity for their state. • England • Henry VIII: Created the Anglican Church to get away from the Roman Catholic Church • Henry did this because he wanted a divorce because his wife only gave him a daughter (Mary I). There had never been a Queen before. • Pope did not allow the divorce, so Henry VIII formed his own Church (Anglican Church of England). • Church kept same practices but did open the door for Protestantism in England
 Calvinism • John Calvin • Became the leader of the movement in Switzerland • Similar to the Protestants in that it relied heavily on faith and the Bible • Predestination: God decided who to save @ the beginning of time. • Theocracy: Government ruled by a religious leader • Calvinist: Righteous Living, very strict • Huguenots: French nobles who began to covert to Calvinism. Fought Civil Wars with French Catholics for 30 years (1562 -1598). Eventually given religious freedom.
Calvinism • John Calvin • Became the leader of the movement in Switzerland • Similar to the Protestants in that it relied heavily on faith and the Bible • Predestination: God decided who to save @ the beginning of time. • Theocracy: Government ruled by a religious leader • Calvinist: Righteous Living, very strict • Huguenots: French nobles who began to covert to Calvinism. Fought Civil Wars with French Catholics for 30 years (1562 -1598). Eventually given religious freedom.
 European Exploration • Foundations • Needed better maps, navigation tools (compass) and ships to effectively sail to the riches of India and China • Joint-Stock Companies: helped to fund explorations all throughout the world. • Banks began to be more modern (lending, etc) • European Countries (Spain, Portugal, France, and England) began to build overseas Empires. • Mercantilism: countries wanted to get as much gold and silver possible to have more wealth. A favorable balance of trade with its colonies would help this. • Renaissance (curiosity), Religion (freedom), Land Fame all led to more people wanted to explore
European Exploration • Foundations • Needed better maps, navigation tools (compass) and ships to effectively sail to the riches of India and China • Joint-Stock Companies: helped to fund explorations all throughout the world. • Banks began to be more modern (lending, etc) • European Countries (Spain, Portugal, France, and England) began to build overseas Empires. • Mercantilism: countries wanted to get as much gold and silver possible to have more wealth. A favorable balance of trade with its colonies would help this. • Renaissance (curiosity), Religion (freedom), Land Fame all led to more people wanted to explore
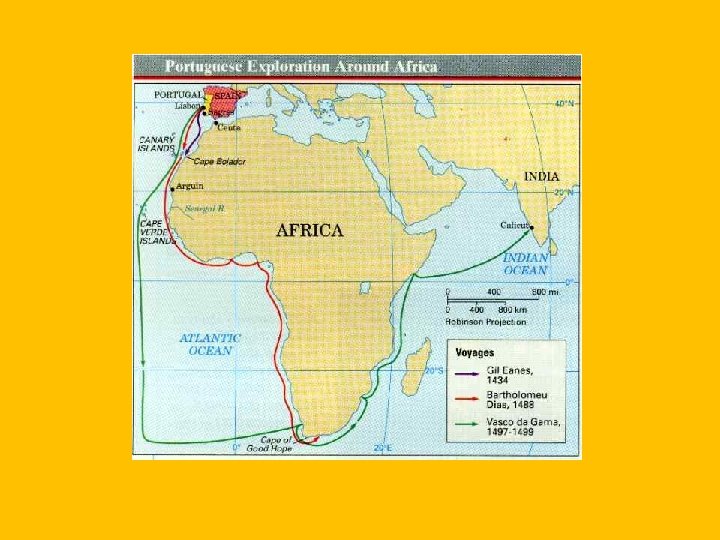
 Portugal • Explorers • Prince Henry: Henry the Navigator, sent people around Africa, looking for gold and trade • Bartolomeu Dias: Sailed around the Cape of Good Hope • Vasco da Gama: Sailed to India. • Opened the door to great wealth for Portugal • Pedro Cabral: Tried sailing west, landed in Brazil • Treaty of Tordesillas: Imaginary line that divided Spain’s conquests from Portugal's • Also expanded into SE Asia (Sri Lanka, Japan, China) • Began Slave Trade • Portugal could not keep up, eventually overrun by Spain
Portugal • Explorers • Prince Henry: Henry the Navigator, sent people around Africa, looking for gold and trade • Bartolomeu Dias: Sailed around the Cape of Good Hope • Vasco da Gama: Sailed to India. • Opened the door to great wealth for Portugal • Pedro Cabral: Tried sailing west, landed in Brazil • Treaty of Tordesillas: Imaginary line that divided Spain’s conquests from Portugal's • Also expanded into SE Asia (Sri Lanka, Japan, China) • Began Slave Trade • Portugal could not keep up, eventually overrun by Spain
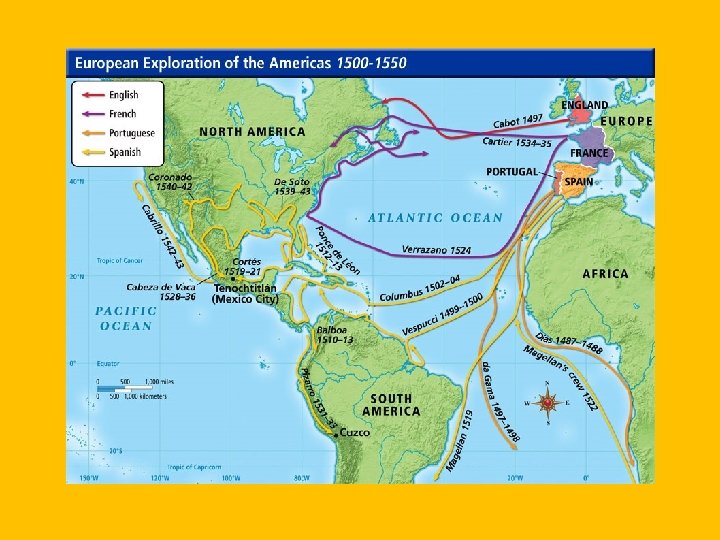
 Spain • Christopher Columbus • Shorter route to Asia by sailing Westward (Ptolemy and Marco Polo) • Made 4 total voyages to the West Indies, believed he had founded a completely new land. • Columbian Exchange: Exchange of goods between products, plants, animals, and even disease • Made Spain very wealthy
Spain • Christopher Columbus • Shorter route to Asia by sailing Westward (Ptolemy and Marco Polo) • Made 4 total voyages to the West Indies, believed he had founded a completely new land. • Columbian Exchange: Exchange of goods between products, plants, animals, and even disease • Made Spain very wealthy
 Spain • Explorers • Amerigo Vespucci (Italian): Sailed for Spain and Portugal (America’s namesake) • Ferdinand Magellan (Portugese): Sailed for Spain, made the first journey around the world in 1522. • Ponce De Leon: Florida and Fountain of Youth • Hernan Cortes: Mexico, captured Aztec leader Montezuma and destroyed Empire w/ small pox • Francisco Pizarro: Claimed Ecuador to Chile for Spain, destroyed thee Incan Empire • Fore a time the colonies produced great wealth for Spain. • The Empire was attached a lot by other countries
Spain • Explorers • Amerigo Vespucci (Italian): Sailed for Spain and Portugal (America’s namesake) • Ferdinand Magellan (Portugese): Sailed for Spain, made the first journey around the world in 1522. • Ponce De Leon: Florida and Fountain of Youth • Hernan Cortes: Mexico, captured Aztec leader Montezuma and destroyed Empire w/ small pox • Francisco Pizarro: Claimed Ecuador to Chile for Spain, destroyed thee Incan Empire • Fore a time the colonies produced great wealth for Spain. • The Empire was attached a lot by other countries
 Dutch • Early Ties w/ Spain • The Netherlands were part of Spain’s control. Phillips II ruined that by treating them poorly b/c of Calvinism • William of Orange led a successful revolt against Spanish influence by using guerilla warfare. • Dutch Exploration • Dutch were very tolerant of others, always had been sea going people. • Dutch East India Trading Company • Purchased Manhattan Island from natives…NYC • Dutch were looking to make money, had settlements in North America, South America and Asia.
Dutch • Early Ties w/ Spain • The Netherlands were part of Spain’s control. Phillips II ruined that by treating them poorly b/c of Calvinism • William of Orange led a successful revolt against Spanish influence by using guerilla warfare. • Dutch Exploration • Dutch were very tolerant of others, always had been sea going people. • Dutch East India Trading Company • Purchased Manhattan Island from natives…NYC • Dutch were looking to make money, had settlements in North America, South America and Asia.
 Great Britain's Empire • Summary • Started during the 1600 s, by 1760 Great Britain had the strongest colonial empire in the world • Start • King Henry VII sent John Cabot to explore the west in 1497 (explored Newfoundland Nova Scotia) • Elizabeth I: Sent out many explorers (Drake, Hawkins, Raleigh) that claimed new lands and made the Spanish mad by pirating their ships. • Defeating the Spanish Armada gave England confidence to colonize.
Great Britain's Empire • Summary • Started during the 1600 s, by 1760 Great Britain had the strongest colonial empire in the world • Start • King Henry VII sent John Cabot to explore the west in 1497 (explored Newfoundland Nova Scotia) • Elizabeth I: Sent out many explorers (Drake, Hawkins, Raleigh) that claimed new lands and made the Spanish mad by pirating their ships. • Defeating the Spanish Armada gave England confidence to colonize.
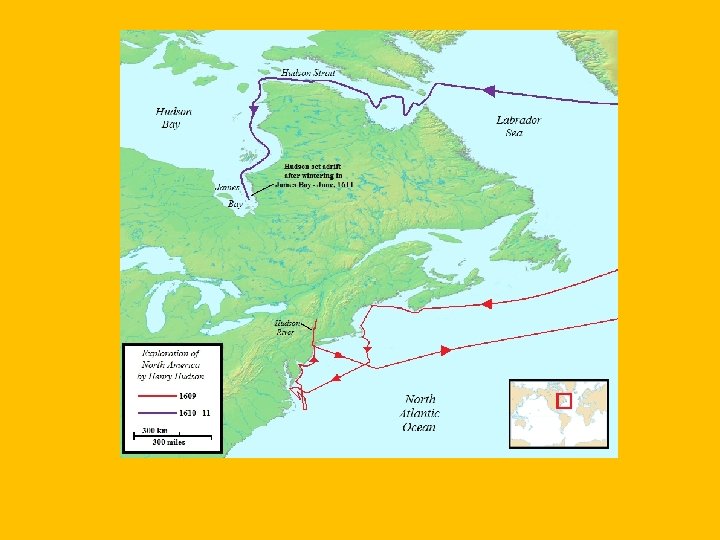
 Great Britain’s Empire • Colonization • Queen Elizabeth grated a charter to a group known as the British East India Trading Co…involved with India for 260 years. Most powerful company in world (1700 s) • America • First looking for Northwest Passage • Henry Hudson (explored of both Dutch and English). . never found the Northwest Passage • First settlements in Jamestown and Plymouth
Great Britain’s Empire • Colonization • Queen Elizabeth grated a charter to a group known as the British East India Trading Co…involved with India for 260 years. Most powerful company in world (1700 s) • America • First looking for Northwest Passage • Henry Hudson (explored of both Dutch and English). . never found the Northwest Passage • First settlements in Jamestown and Plymouth

 Changes to GB Empire • America won its independence in 1781 • Canada • Canadian settlers wanted more self rule in the early 1800 s. GB just let them have their independence • Australia • James Cook claimed the land in 1770 for Australia, GB sent prisoners to live there. • Aborigines: Native people to Australia • All parts of Australia united in 1901. • New Zealand • British took control in 1840. • Maori: Native people of New Zealand • By 1907 New Zealand had joined the British Empire.
Changes to GB Empire • America won its independence in 1781 • Canada • Canadian settlers wanted more self rule in the early 1800 s. GB just let them have their independence • Australia • James Cook claimed the land in 1770 for Australia, GB sent prisoners to live there. • Aborigines: Native people to Australia • All parts of Australia united in 1901. • New Zealand • British took control in 1840. • Maori: Native people of New Zealand • By 1907 New Zealand had joined the British Empire.
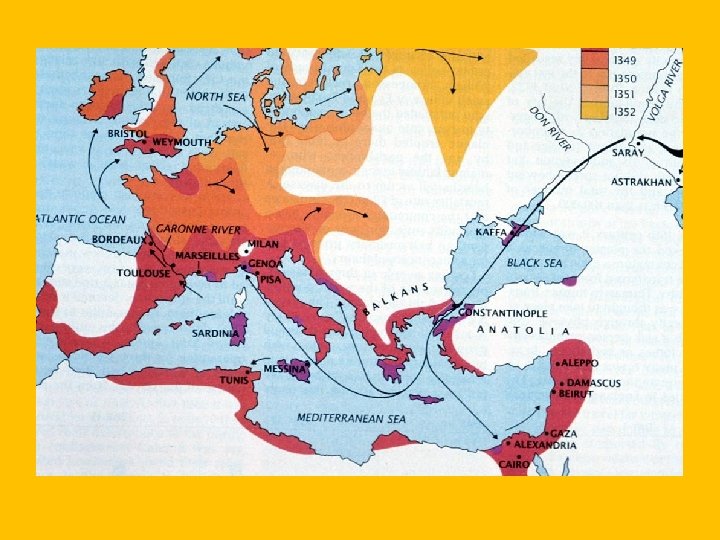
 Social Changes • Bad Living Conditions • Cities were dirty, unsafe, and unhealthy • People did not go out alone at night, no police, etc • Disease was easily able to spread b/c of waste everywhere • Black Death • • Plague that started from Asian trade routes (1347) Carried by black rats on ships Around 25 million people died (1/3 of all Europe population) People lost faith in God, workers wanted more wages, etc
Social Changes • Bad Living Conditions • Cities were dirty, unsafe, and unhealthy • People did not go out alone at night, no police, etc • Disease was easily able to spread b/c of waste everywhere • Black Death • • Plague that started from Asian trade routes (1347) Carried by black rats on ships Around 25 million people died (1/3 of all Europe population) People lost faith in God, workers wanted more wages, etc
 New Ways of Thinking • Renaissance • Philosophical and Artistic Movement. • Renewed by studying the works of ancient civilizations. . got the idea from the Byzantines during the Crusades. • Believed in the power of human reason (thinking) • Niccolo Machiavelli • Writer who believed that political rulers should be only concerned about power and political success
New Ways of Thinking • Renaissance • Philosophical and Artistic Movement. • Renewed by studying the works of ancient civilizations. . got the idea from the Byzantines during the Crusades. • Believed in the power of human reason (thinking) • Niccolo Machiavelli • Writer who believed that political rulers should be only concerned about power and political success
 New Ways of Thinking • Inventions • • Thomas Edison: Light bulb and harnessing electricity Alexander Graham Bell: Human voice on electrical circuit Henry Ford, Karl Benz, Etienne Lenoir: Cars Wilbur and Orville Wright: Airplane • New Thinkers • Charles Darwin: Theory of Evolution. Those who survive have the best natural characteristics to survive. • Gregor Mendel: Founded Genetics • Edward Jenner: small pox vaccine (coxpox) • Louis Pasteur: Pasteurization…. found out that bacteria cause illness • Dmitry Mendeleyev: Classified Elements • Albert Einstein: German Scientist
New Ways of Thinking • Inventions • • Thomas Edison: Light bulb and harnessing electricity Alexander Graham Bell: Human voice on electrical circuit Henry Ford, Karl Benz, Etienne Lenoir: Cars Wilbur and Orville Wright: Airplane • New Thinkers • Charles Darwin: Theory of Evolution. Those who survive have the best natural characteristics to survive. • Gregor Mendel: Founded Genetics • Edward Jenner: small pox vaccine (coxpox) • Louis Pasteur: Pasteurization…. found out that bacteria cause illness • Dmitry Mendeleyev: Classified Elements • Albert Einstein: German Scientist
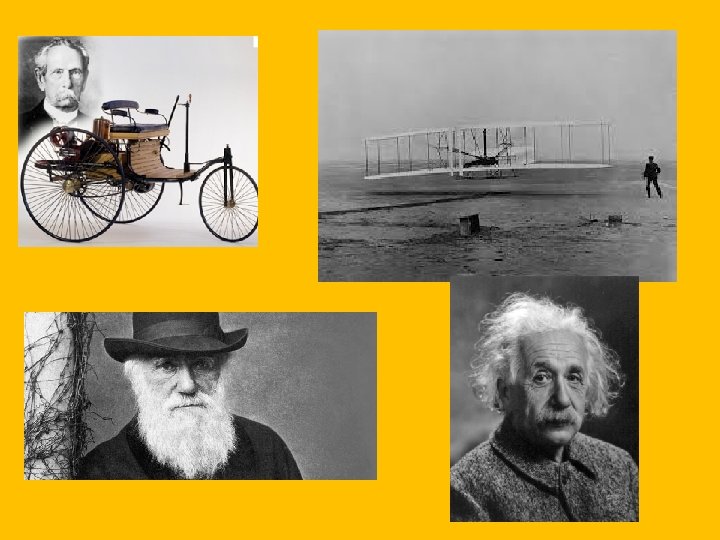


 New Ways of Thinking • New Thinkers cont. . • • Ivan Pavlov and Sigmund Freud: Psychology Beethoven: German Composer James Fennimore Cooper: American Writer Pyotr Ilich Tchaikovsky: ballets, operas • Sports • Became organized and popular during the 1800 s. • Soccer and baseball were some of the earliest
New Ways of Thinking • New Thinkers cont. . • • Ivan Pavlov and Sigmund Freud: Psychology Beethoven: German Composer James Fennimore Cooper: American Writer Pyotr Ilich Tchaikovsky: ballets, operas • Sports • Became organized and popular during the 1800 s. • Soccer and baseball were some of the earliest
 Economic Changes • Domestic System/Barter • Old way of doing things were manufacturing took place within the home. Separate workers would complete tasks at home. . come together to produce final product • Barter: Trade • Money Changers were the first bankers. They exchanged money and gave out loans. Many Jews held this role in Middle Ages b/c they could not own land • People also began to invest money
Economic Changes • Domestic System/Barter • Old way of doing things were manufacturing took place within the home. Separate workers would complete tasks at home. . come together to produce final product • Barter: Trade • Money Changers were the first bankers. They exchanged money and gave out loans. Many Jews held this role in Middle Ages b/c they could not own land • People also began to invest money
 Economic Change • Industrial Revolution • Rapid industrial development caused by available land natural resources, available money to invest and available workers. • Mechanization: Automatic machines (silk spinning first) • Richard Arkwright: Use of water to power machine. . started the first factory system. • Demand for cotton increased, England got most from the Southern United States (4 million to 100 million pounds per year) • Cotton Gin (Eli Whitney): machine that cleaned cotton, made it easier to mass produce it
Economic Change • Industrial Revolution • Rapid industrial development caused by available land natural resources, available money to invest and available workers. • Mechanization: Automatic machines (silk spinning first) • Richard Arkwright: Use of water to power machine. . started the first factory system. • Demand for cotton increased, England got most from the Southern United States (4 million to 100 million pounds per year) • Cotton Gin (Eli Whitney): machine that cleaned cotton, made it easier to mass produce it
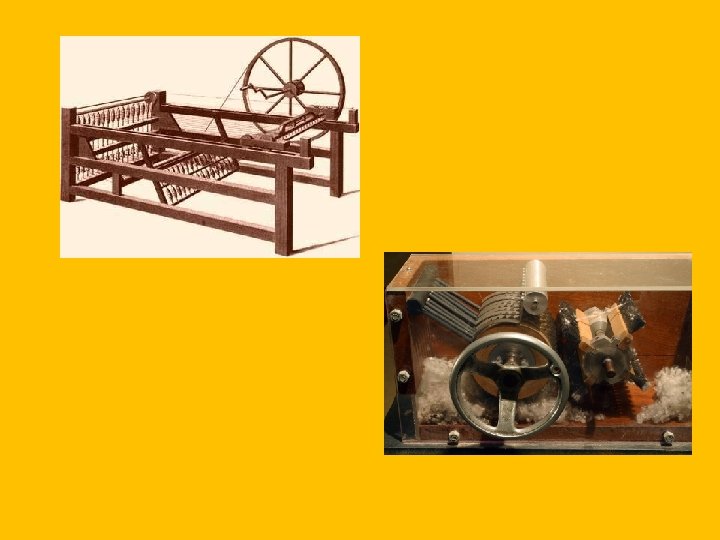


 Economic Changes • Industrial Revolution • Water (river power) was unpredictable, tried to harness steam power (James Watt) • Bessemer Process: Process to inject air into pure Iron to remove impurities. This made steel easier to use. • Charles Goodyear: Vulcanization (made rubber less sticky) • Robert Fulton: Steam Engine on boat. . changed water travel • Samuel Morse: Morse Code and Telegraph • Great Britain was the European leader in Industrialization • Factory System developed a wage system and Middle Class • Women also began to work more
Economic Changes • Industrial Revolution • Water (river power) was unpredictable, tried to harness steam power (James Watt) • Bessemer Process: Process to inject air into pure Iron to remove impurities. This made steel easier to use. • Charles Goodyear: Vulcanization (made rubber less sticky) • Robert Fulton: Steam Engine on boat. . changed water travel • Samuel Morse: Morse Code and Telegraph • Great Britain was the European leader in Industrialization • Factory System developed a wage system and Middle Class • Women also began to work more

 Economic Changes • Capitalism • Economic system where individuals or corporations control what and how much gets produced (not govts) • Division of Labor: Economic principle that increased the rate of production…. each person specialized in a certain job. • Eli Whitney invented interchangeable parts…machines that made things that were all alike…easier to fix • Mass Production: Producing large numbers of identical items. • Business began to become corporations (people could buy stock in them)
Economic Changes • Capitalism • Economic system where individuals or corporations control what and how much gets produced (not govts) • Division of Labor: Economic principle that increased the rate of production…. each person specialized in a certain job. • Eli Whitney invented interchangeable parts…machines that made things that were all alike…easier to fix • Mass Production: Producing large numbers of identical items. • Business began to become corporations (people could buy stock in them)
 Economic Changes • Supply-Demand • Item is scarce and has high demand=high prices paid. When supply goes down, prices rise • Item is not scarce and has low demand=lower prices paid • Smith’s Theory: Manufacturers that compete with other companies must reduce prices to be competitive (but not too low or they will go out of business). • System of Free Enterprise (no government control)
Economic Changes • Supply-Demand • Item is scarce and has high demand=high prices paid. When supply goes down, prices rise • Item is not scarce and has low demand=lower prices paid • Smith’s Theory: Manufacturers that compete with other companies must reduce prices to be competitive (but not too low or they will go out of business). • System of Free Enterprise (no government control)
 Economic Changes • Conditions: • • Were bad for workers Humanitarians: People who tried to help (Charles Dickens) Strikes: effective way to protest working conditions Unions: organizations created to protect the rights of workers
Economic Changes • Conditions: • • Were bad for workers Humanitarians: People who tried to help (Charles Dickens) Strikes: effective way to protest working conditions Unions: organizations created to protect the rights of workers
 Economic Changes • Socialism • Some people felt that the laissez-faire approach would not work (let it be) • Felt they need to change who owned the means of production • Means of Production: money and equipment used to produce and exchange goods (land, RR, mines, factories, stores, banks) • Definition: government owns the means of production and operates them for the benefit of all people, not just the wealthy. Everyone should share in the profits • Utopian Socialists: People who believed that people could live peacefully together in small communities where everyone would work for the common good of all
Economic Changes • Socialism • Some people felt that the laissez-faire approach would not work (let it be) • Felt they need to change who owned the means of production • Means of Production: money and equipment used to produce and exchange goods (land, RR, mines, factories, stores, banks) • Definition: government owns the means of production and operates them for the benefit of all people, not just the wealthy. Everyone should share in the profits • Utopian Socialists: People who believed that people could live peacefully together in small communities where everyone would work for the common good of all
 Theories • Karl Marx • Wrote the Communist Manifesto (1848) • Thought that capitalism created a conflict between workers and business owners. His thoughts were that a few owners made a ton of money of the hard work of the workers. • Marx predicted that the workers would eventually unite and overthrow the capitalistic areas and create a socialist revolution. • Believed that people would learn the benefits of working together and a classless society would emerge. . pure communism
Theories • Karl Marx • Wrote the Communist Manifesto (1848) • Thought that capitalism created a conflict between workers and business owners. His thoughts were that a few owners made a ton of money of the hard work of the workers. • Marx predicted that the workers would eventually unite and overthrow the capitalistic areas and create a socialist revolution. • Believed that people would learn the benefits of working together and a classless society would emerge. . pure communism


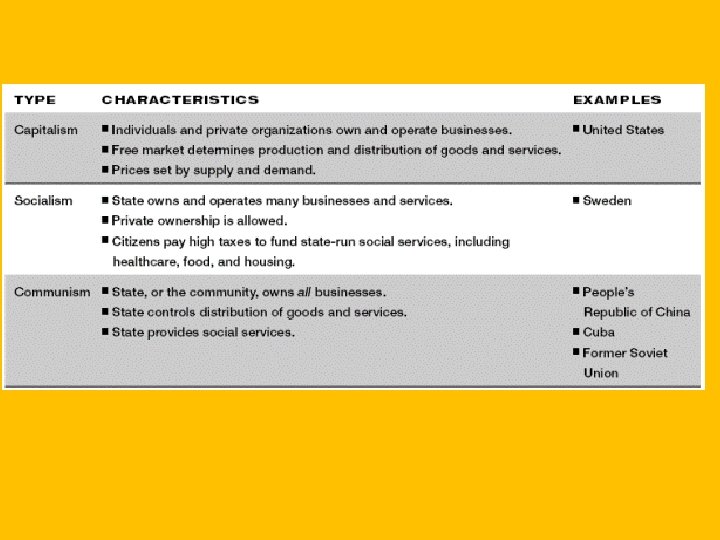
 Theories • Communism • Government that owns the means of production and all economic planning (and all other aspects of daily life). • Democratic Socialism • People retain partial control over economic planning through the election of government officials • Marx’s Ideas • Had an important affect in parts of Northern and Western Europe. Huge impact in Russia
Theories • Communism • Government that owns the means of production and all economic planning (and all other aspects of daily life). • Democratic Socialism • People retain partial control over economic planning through the election of government officials • Marx’s Ideas • Had an important affect in parts of Northern and Western Europe. Huge impact in Russia
 New Conflicts and Problems • WWI • Nationalism, Imperialism, Militarism, • Triple Alliance: Italy, Germany and Austria-Hungary (made by Bismarck during the 1880 s) • Triple Entente: France, Russia, and GB • Serbs wanted Bosnia (Controlled by Austria) to be part of a Slavic Empire • Assassination of Franz Ferdinand (AH prince) by a Serbian nationalist set off the alliances. • Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, Ottoman Empire • Allied Powers: Great Britain, France, Russia, and others
New Conflicts and Problems • WWI • Nationalism, Imperialism, Militarism, • Triple Alliance: Italy, Germany and Austria-Hungary (made by Bismarck during the 1880 s) • Triple Entente: France, Russia, and GB • Serbs wanted Bosnia (Controlled by Austria) to be part of a Slavic Empire • Assassination of Franz Ferdinand (AH prince) by a Serbian nationalist set off the alliances. • Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, Ottoman Empire • Allied Powers: Great Britain, France, Russia, and others

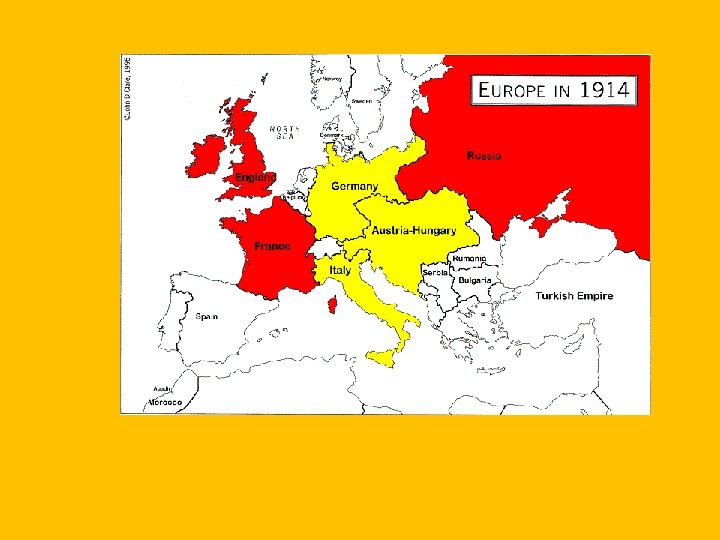

 Newer Conflicts and Problems • WWI • • • U Boats Propaganda Trench Warfare US Involvement (Lusitania and Zimmerman Note) Eventually the Allies won due to American help and Austria/Hungary falling apart • Costs of WWI • 8. 5 -10 million dead, 21 million wounded, 300 Billion • 14 pts • Wilson’s attempt to make the world safe for democracy • League of Nations: A world organization to maintain peace…what the UN would become. Not strong after WWI • Treaty of Versailles: Punished Germany for actions in WWI and caused WWII. (No resolution of problems, Germany poor)
Newer Conflicts and Problems • WWI • • • U Boats Propaganda Trench Warfare US Involvement (Lusitania and Zimmerman Note) Eventually the Allies won due to American help and Austria/Hungary falling apart • Costs of WWI • 8. 5 -10 million dead, 21 million wounded, 300 Billion • 14 pts • Wilson’s attempt to make the world safe for democracy • League of Nations: A world organization to maintain peace…what the UN would become. Not strong after WWI • Treaty of Versailles: Punished Germany for actions in WWI and caused WWII. (No resolution of problems, Germany poor)
 New Conflicts • Great Depression • • Black Tuesday: Oct 29, 1929, stock market crash Market Speculation: Risky Investments Great Depression: 30 million unemployed by 1932 Major effect in GB, France, and Germany (destroy govt) • France WWII Difficulties • Maginot Line (defending from France). . $$$$ • France signed treaties w/ Czech and Poland • Great Britain Struggles • • Struggle to find people jobs during 1920 s-1930 s Irish nationals revolted in 1916 (Easter Rising) IRA: Irish Republic Army. Compromise: Catholic Southern Ireland (Republic of Ireland) would be independent, 6 Northern counties (Protestant) remained a part of the UK
New Conflicts • Great Depression • • Black Tuesday: Oct 29, 1929, stock market crash Market Speculation: Risky Investments Great Depression: 30 million unemployed by 1932 Major effect in GB, France, and Germany (destroy govt) • France WWII Difficulties • Maginot Line (defending from France). . $$$$ • France signed treaties w/ Czech and Poland • Great Britain Struggles • • Struggle to find people jobs during 1920 s-1930 s Irish nationals revolted in 1916 (Easter Rising) IRA: Irish Republic Army. Compromise: Catholic Southern Ireland (Republic of Ireland) would be independent, 6 Northern counties (Protestant) remained a part of the UK

 Newer Problems • Eastern Europe • Most of Eastern European Countries were very weak • Austria, Poland, Hungary, etc • Italian Fascism • Benito Mussolini: Leader of fascist Italy • Fascism: Totalitarian dictatorship, opposed to democracies and communism (very much nationalistic) • Communism appealed to the workers, Fascism appealed to the middle/upper class because they were guaranteed to keep their power. Protect private property and middle class • Black Shirts: Mussolini’s military branch that eliminated all things socialist or democratic
Newer Problems • Eastern Europe • Most of Eastern European Countries were very weak • Austria, Poland, Hungary, etc • Italian Fascism • Benito Mussolini: Leader of fascist Italy • Fascism: Totalitarian dictatorship, opposed to democracies and communism (very much nationalistic) • Communism appealed to the workers, Fascism appealed to the middle/upper class because they were guaranteed to keep their power. Protect private property and middle class • Black Shirts: Mussolini’s military branch that eliminated all things socialist or democratic

 Newer Problems • Germany • Nazis: Extreme Nationalism, anti-semitic (Jew) and anticommunist. Began around 1920 • Hitler’s views began to shape Nazi Party. • Through elections the Nazi’s were able to take gain a majority in the Reichstag (Parliament). Hitler became the emergency dictator when the Reichstag burnt down in 1933. • After that Hitler began to used the SS to round up Jews, forcing them to ghettos, work camps, and eventually concentration camps. • Hitler believed in the Third Reich (3 rd Empire) • Began to rebuild the Army (illegal) and made a secret alliance with Italy
Newer Problems • Germany • Nazis: Extreme Nationalism, anti-semitic (Jew) and anticommunist. Began around 1920 • Hitler’s views began to shape Nazi Party. • Through elections the Nazi’s were able to take gain a majority in the Reichstag (Parliament). Hitler became the emergency dictator when the Reichstag burnt down in 1933. • After that Hitler began to used the SS to round up Jews, forcing them to ghettos, work camps, and eventually concentration camps. • Hitler believed in the Third Reich (3 rd Empire) • Began to rebuild the Army (illegal) and made a secret alliance with Italy
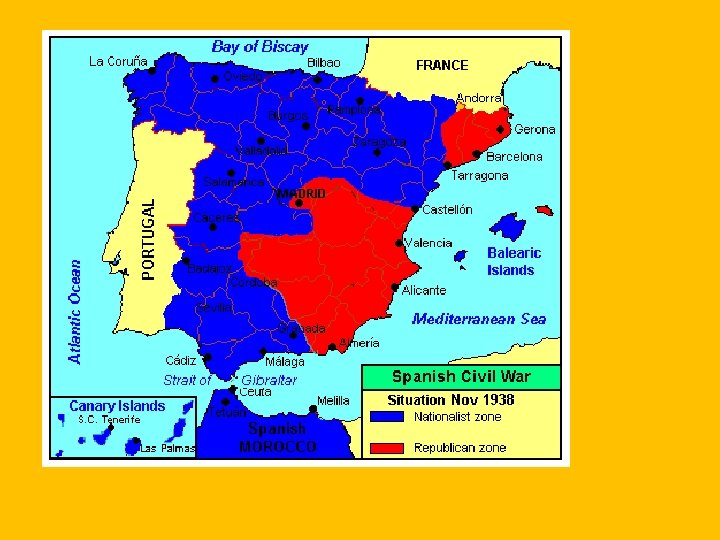
 New Problems • Spanish Civil War • Many changes following WWI • Nationalist: Fascist group called Falange (Francisco Franco) • Loyalist: Supporters of the old Republic • Germany and Italy helped the Nationalist, Soviets helped the Loyalists. • People the movement’s would spread throughout all of Europe • Nationalists won and Franco set up a government that looked a lot like Italy’s
New Problems • Spanish Civil War • Many changes following WWI • Nationalist: Fascist group called Falange (Francisco Franco) • Loyalist: Supporters of the old Republic • Germany and Italy helped the Nationalist, Soviets helped the Loyalists. • People the movement’s would spread throughout all of Europe • Nationalists won and Franco set up a government that looked a lot like Italy’s
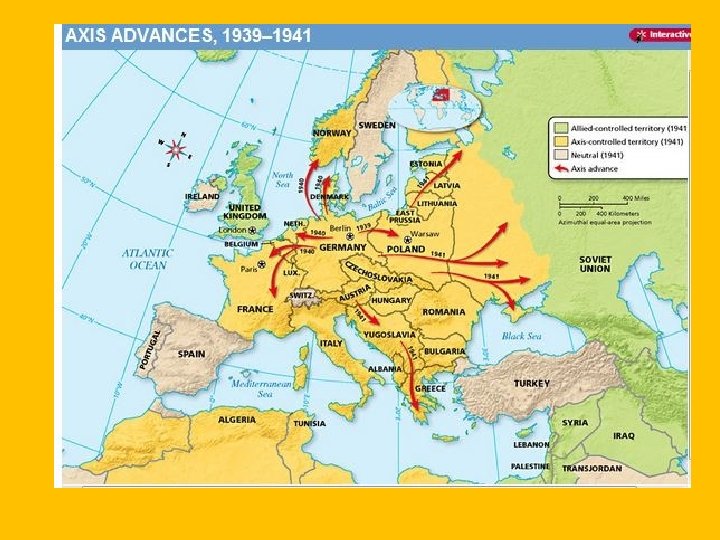
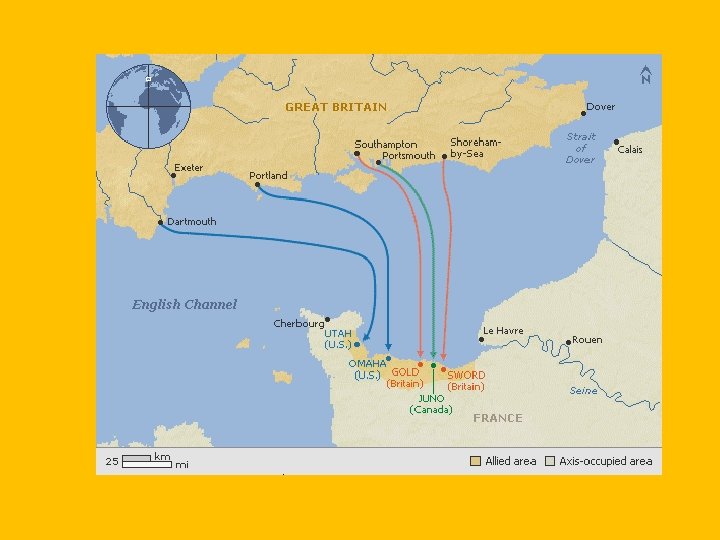
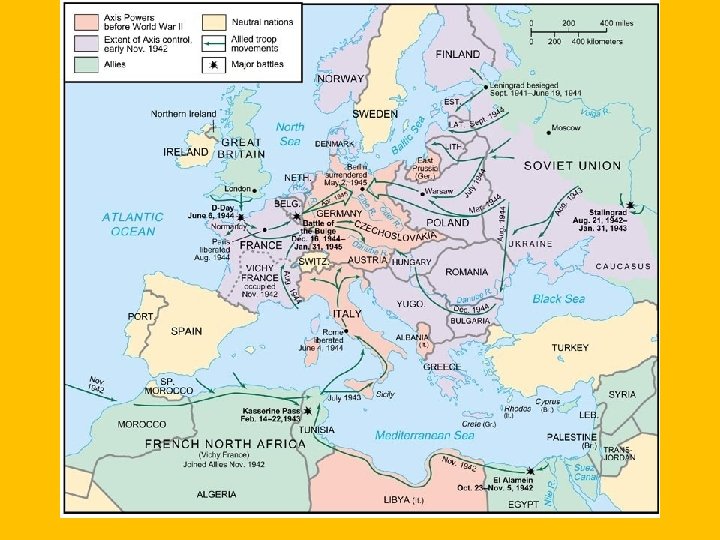
 New Problems • WWII: • Began with Hitler's Aggression – Austria, Czechoslovakia, Poland, Scandinavia and Low Countries, USSR, France • Hitler was not able to fully capture USSR and never invaded Great Britain. • Allies: GB, France, USSR, USA • Axis: Germany, Italy, Japan • Hitler’s attack on the Soviet Union was similar to Napoleon’s failed attempt. Too big and cold. • Hitler began to kill the Jews in 1941. • Famous concentration camps like Auschwitz were built • D-Day: Allied Invasion of France…. would mark the end for Hitler and the German Army
New Problems • WWII: • Began with Hitler's Aggression – Austria, Czechoslovakia, Poland, Scandinavia and Low Countries, USSR, France • Hitler was not able to fully capture USSR and never invaded Great Britain. • Allies: GB, France, USSR, USA • Axis: Germany, Italy, Japan • Hitler’s attack on the Soviet Union was similar to Napoleon’s failed attempt. Too big and cold. • Hitler began to kill the Jews in 1941. • Famous concentration camps like Auschwitz were built • D-Day: Allied Invasion of France…. would mark the end for Hitler and the German Army
 World After WWII • United Nations • Created to keep peace throughout the world, don’t make the same mistakes that happened post WWI • Yalta Conference • Divided up Germany into 4 states (3 controlled by the West and 1 controlled by the USSR) • Cold War • Began after WWII. The Soviet Army never really left the lands that they had conquered between Germany and USSR. • Marshall Plan: US gave over 13 billion dollars to 17 Western European countries to prevent communism from spreading • Truman Doctrine: USA would support any country in their fight against communism (Greece and Turkey were first)
World After WWII • United Nations • Created to keep peace throughout the world, don’t make the same mistakes that happened post WWI • Yalta Conference • Divided up Germany into 4 states (3 controlled by the West and 1 controlled by the USSR) • Cold War • Began after WWII. The Soviet Army never really left the lands that they had conquered between Germany and USSR. • Marshall Plan: US gave over 13 billion dollars to 17 Western European countries to prevent communism from spreading • Truman Doctrine: USA would support any country in their fight against communism (Greece and Turkey were first)

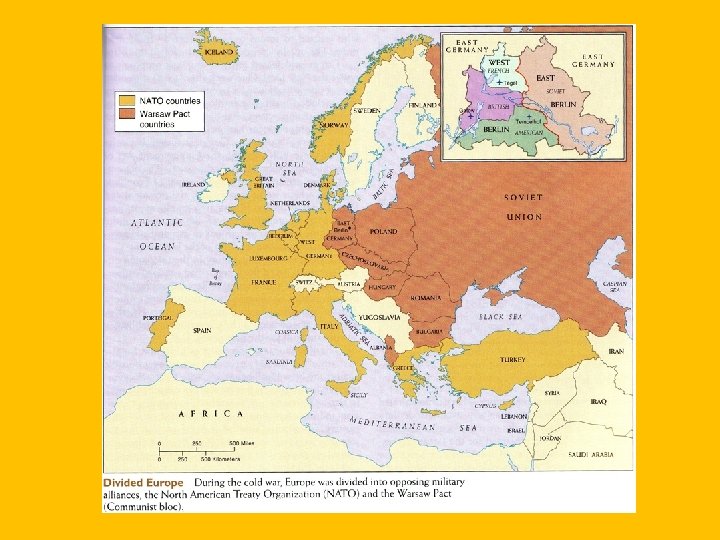
 World After WWII • Berlin Airlift • City of Berlin (in east Berlin) was divided by East and West. The Soviets shut off access to outside world • US and GB dropped food and supplies into West Berlin • Eventually the Berlin was created to prevent people moving from East to West. • NATO • Military Alliance of European countries. . Warsaw Pact was the same thing except involving Soviets and the countries they controlled
World After WWII • Berlin Airlift • City of Berlin (in east Berlin) was divided by East and West. The Soviets shut off access to outside world • US and GB dropped food and supplies into West Berlin • Eventually the Berlin was created to prevent people moving from East to West. • NATO • Military Alliance of European countries. . Warsaw Pact was the same thing except involving Soviets and the countries they controlled
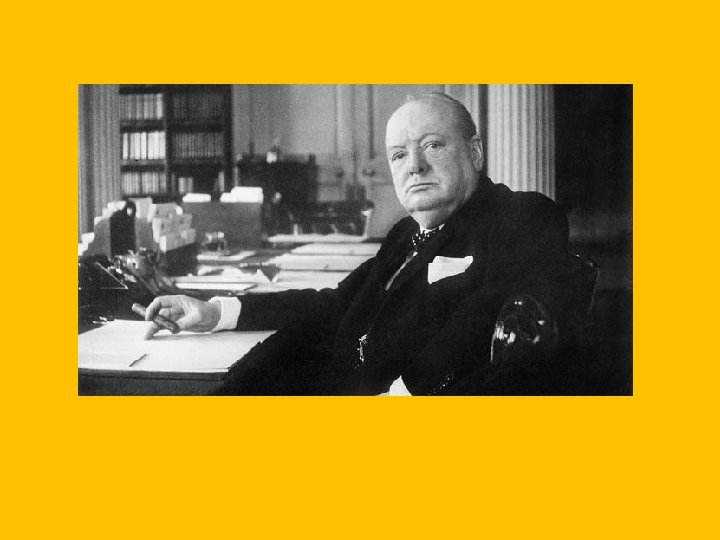
 Great Britain • Prime Ministers • Neville Chamberlain • Winston Churchill (during WWII) • Economics • Struggled between welfare state and non welfare state • One of the least industrialized countries by 1960 • Major problems from the destruction of WWII
Great Britain • Prime Ministers • Neville Chamberlain • Winston Churchill (during WWII) • Economics • Struggled between welfare state and non welfare state • One of the least industrialized countries by 1960 • Major problems from the destruction of WWII

 France • Problems • Destroyed, much like Great Britain from fighting in WWII • Had trouble holding on to foreign possessions like Algeria and French Indochina (Vietnam) • Charles De Gaulle • French President after WWII. • Let go of possessions, believed in NATO, etc • Economy never got better and he resigned
France • Problems • Destroyed, much like Great Britain from fighting in WWII • Had trouble holding on to foreign possessions like Algeria and French Indochina (Vietnam) • Charles De Gaulle • French President after WWII. • Let go of possessions, believed in NATO, etc • Economy never got better and he resigned

 Other European Countries • Denmark, Norway, Sweden • All had solid democracies in place • All prospered in the times after WWII • Very little rebuilding occurred • Greece, Portugal, Spain • Turned to free-enterprise systems of economy • Portugal and Spain remained Authoritarian Govts
Other European Countries • Denmark, Norway, Sweden • All had solid democracies in place • All prospered in the times after WWII • Very little rebuilding occurred • Greece, Portugal, Spain • Turned to free-enterprise systems of economy • Portugal and Spain remained Authoritarian Govts
 Modern Times • Great Britain • Margaret Thatcher: Became the first female Prime Minister in Britain’s History • Reduced government funding of many social programs (like Republicanism) • Poll Tax: Replaced income tax, charged everyone the same…led to problems…she resigned in 1990 • John Major: More moderate, had many scandals • Tony Blair: Elected in 1997 • Northern Ireland (Protestant aligned with GB) • Battles between the Catholics (IRA) and Protestants • Wanted to drive the Protestants out of Ireland (unite) • Still an issue today
Modern Times • Great Britain • Margaret Thatcher: Became the first female Prime Minister in Britain’s History • Reduced government funding of many social programs (like Republicanism) • Poll Tax: Replaced income tax, charged everyone the same…led to problems…she resigned in 1990 • John Major: More moderate, had many scandals • Tony Blair: Elected in 1997 • Northern Ireland (Protestant aligned with GB) • Battles between the Catholics (IRA) and Protestants • Wanted to drive the Protestants out of Ireland (unite) • Still an issue today


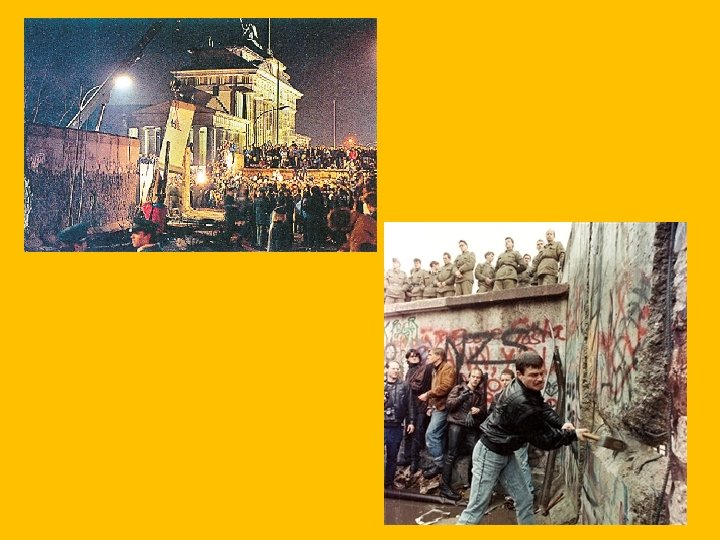
 Modern Times • France • Many different leaders (Pompidou, d’Estaing, Mitterand, Chirac) • Continued to struggle with economic problems and foreign relations. • Germany • West Germany became a major economic power while East Germany struggled • Helmut Kohl: Conservative (Reagan and Thatcher) kept close times with GB and USA • USSR collapsed and Germany was re-united as one country in 1992.
Modern Times • France • Many different leaders (Pompidou, d’Estaing, Mitterand, Chirac) • Continued to struggle with economic problems and foreign relations. • Germany • West Germany became a major economic power while East Germany struggled • Helmut Kohl: Conservative (Reagan and Thatcher) kept close times with GB and USA • USSR collapsed and Germany was re-united as one country in 1992.

 Modern Times • NATO • United most of Western Europe (small countries) • Belgium, Luxemburg, Netherlands, Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Finland, Sweden, Austria, Switzerland all were either supportive of Western ideas or neutral • Italy • Divided between political parties and industrial/wealthy Northern Italy vs poor/rural Southern Italy • Situation improved during the 1990 s • Spain • Juan Carlos: King in 1975 • Troubles with economy during the 1970 s and 80 s • By 2000, Spain was in much better shape
Modern Times • NATO • United most of Western Europe (small countries) • Belgium, Luxemburg, Netherlands, Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Finland, Sweden, Austria, Switzerland all were either supportive of Western ideas or neutral • Italy • Divided between political parties and industrial/wealthy Northern Italy vs poor/rural Southern Italy • Situation improved during the 1990 s • Spain • Juan Carlos: King in 1975 • Troubles with economy during the 1970 s and 80 s • By 2000, Spain was in much better shape
 Modern Times • European Cooperation • Helsinki Accords: 35 European Nations (and USA/USSR) met to discuss security and cooperation among countries • Called on all nations to respect basic human rights, such as speech and worship…helped usher in democracy of the 1980’s • NATO: started to include Eastern European countries (Czech, Poland, Hungary) in 1997 • European Economic Community: Economic cooperation between countries to include common taxation, trade and currency • European Union: 1993, ended trade barriers between countries. Where the Euro came from (common currency)
Modern Times • European Cooperation • Helsinki Accords: 35 European Nations (and USA/USSR) met to discuss security and cooperation among countries • Called on all nations to respect basic human rights, such as speech and worship…helped usher in democracy of the 1980’s • NATO: started to include Eastern European countries (Czech, Poland, Hungary) in 1997 • European Economic Community: Economic cooperation between countries to include common taxation, trade and currency • European Union: 1993, ended trade barriers between countries. Where the Euro came from (common currency)