916afebfe44a788fade1117d2b9efc3e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Europe
Europe
 Introduction v Hearth of Western civilization v Global imperialism v Industrial revolution v History of fragmentation and integration v Nationalism: Nation-state v Regional integration: E. U.
Introduction v Hearth of Western civilization v Global imperialism v Industrial revolution v History of fragmentation and integration v Nationalism: Nation-state v Regional integration: E. U.

 Environmental Geography
Environmental Geography
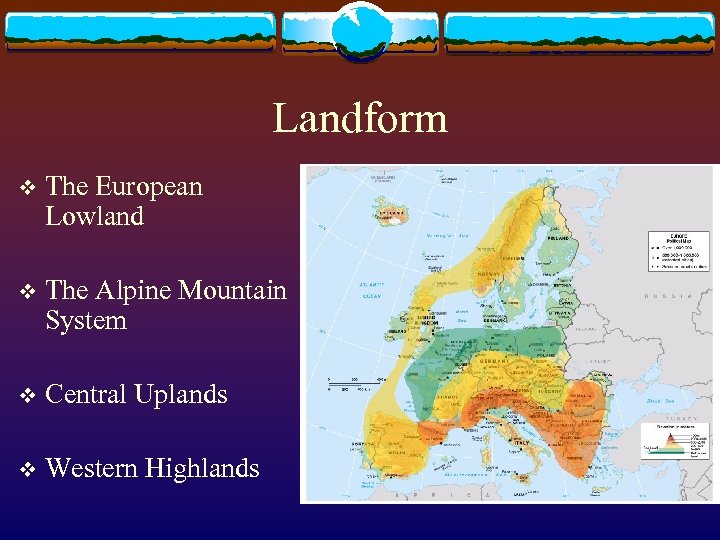 Landform v The European Lowland v The Alpine Mountain System v Central Uplands v Western Highlands
Landform v The European Lowland v The Alpine Mountain System v Central Uplands v Western Highlands
 The European Lowland v Support v Major high population density rivers v Ports v Glacial in estuaries forces north of the Rhine River delta v affects soil fertility and land forms (eg. moraines)
The European Lowland v Support v Major high population density rivers v Ports v Glacial in estuaries forces north of the Rhine River delta v affects soil fertility and land forms (eg. moraines)
 The Alpine Mountain System v The northward movement of the African Plate against the Eurasian Plate v Pyrenees, Alps, Carpathian Mountains, Dinaric Alps, and Balkan Ranges
The Alpine Mountain System v The northward movement of the African Plate against the Eurasian Plate v Pyrenees, Alps, Carpathian Mountains, Dinaric Alps, and Balkan Ranges
 Central Uplands v Between v Raw the Alps and the European Lowland materials for Europe’s industrial areas Steel industry in Germany and France
Central Uplands v Between v Raw the Alps and the European Lowland materials for Europe’s industrial areas Steel industry in Germany and France
 Western Highlands v Portugal – Northwestern British Isles – Scandinavia v Fjords A long, narrow, deep inlet of the sea between steep slopes v Western coastline of Norway v v Shield landscape Oldest rock formation by the erosion of ice sheets v Fenno-Scandian Shield v
Western Highlands v Portugal – Northwestern British Isles – Scandinavia v Fjords A long, narrow, deep inlet of the sea between steep slopes v Western coastline of Norway v v Shield landscape Oldest rock formation by the erosion of ice sheets v Fenno-Scandian Shield v
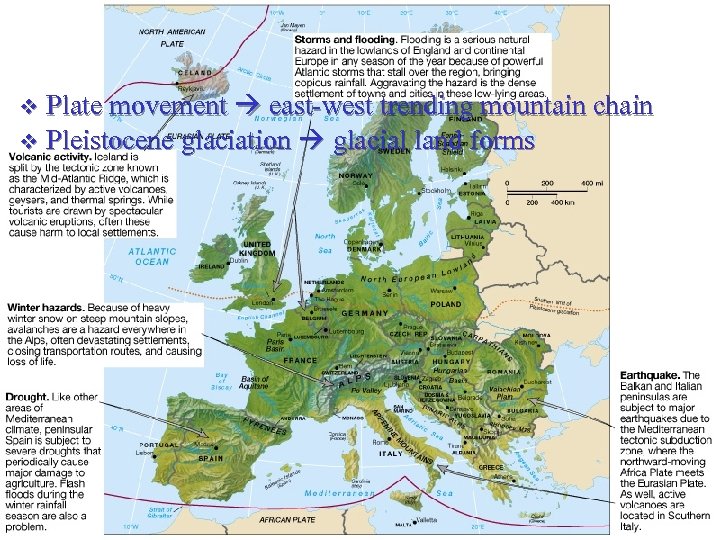 Plate movement east-west trending mountain chain v Pleistocene glaciation glacial land forms v
Plate movement east-west trending mountain chain v Pleistocene glaciation glacial land forms v
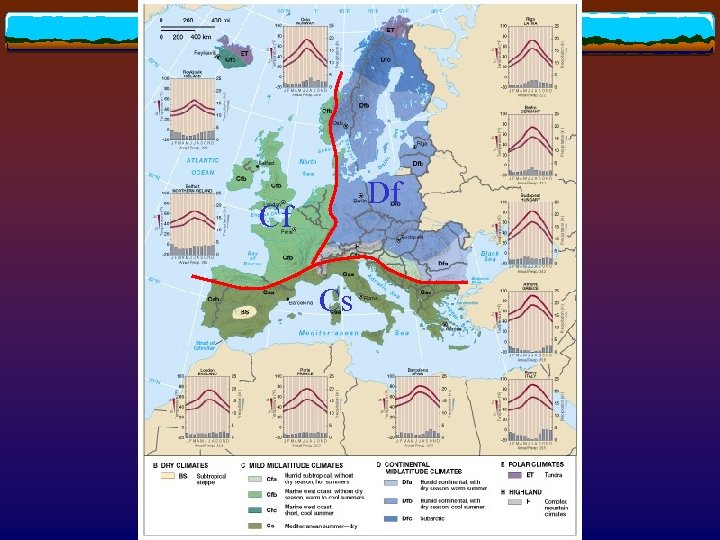 Df Cf Cs
Df Cf Cs
 Climate controls v Why is western Europe warmer than comparable latitudes? Mild North Atlantic current
Climate controls v Why is western Europe warmer than comparable latitudes? Mild North Atlantic current
 Seas v Baltic Sea v North Sea v Atlantic Ocean v Mediterranean Sea v Black Sea v Skagerrak v Strait & Kattegat of Gibraltar v Bosporous Strait & Dardanelles
Seas v Baltic Sea v North Sea v Atlantic Ocean v Mediterranean Sea v Black Sea v Skagerrak v Strait & Kattegat of Gibraltar v Bosporous Strait & Dardanelles
 Rivers v Rivers of the European Lowland Loire, Seine, Rhine, Elbe, and Vistula River v Flow into Atlantic and Baltic Sea v v Danube River Longest river in Europe v Connects between central and eastern Europe v v In general, Europe is a region of navigable rivers connected by canals and locks
Rivers v Rivers of the European Lowland Loire, Seine, Rhine, Elbe, and Vistula River v Flow into Atlantic and Baltic Sea v v Danube River Longest river in Europe v Connects between central and eastern Europe v v In general, Europe is a region of navigable rivers connected by canals and locks
 Ports v Developed at the mouths of rivers v Transshipment points for inland waterway v Bordeux, Le Havre, London, Rotterdam, Hamburg, and Gdansk
Ports v Developed at the mouths of rivers v Transshipment points for inland waterway v Bordeux, Le Havre, London, Rotterdam, Hamburg, and Gdansk
 Polders v Protected and reclaimed landscapes (diked agricultural settlements) in the Netherlands v Windmills are used to pump water from low-lying wetlands
Polders v Protected and reclaimed landscapes (diked agricultural settlements) in the Netherlands v Windmills are used to pump water from low-lying wetlands
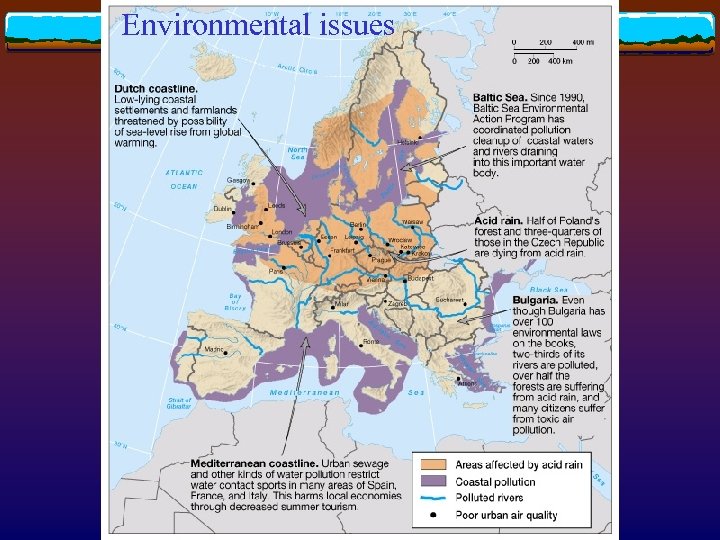 Environmental issues
Environmental issues
 Environmental protection in western Europe v Environmental problems cross national boundaries v Formation of E. U. aided in addressing problems v Heightened environmental sensitivity v “Red-Green Coalition” in Germany v Greenhouse gas emission reduction
Environmental protection in western Europe v Environmental problems cross national boundaries v Formation of E. U. aided in addressing problems v Heightened environmental sensitivity v “Red-Green Coalition” in Germany v Greenhouse gas emission reduction
 Environmental protection in eastern Europe v Legacy of Soviet economic planning (1945 -90) v Post-1990 economic and political transition Acid rain and forest death Bohemia, Czech Republic
Environmental protection in eastern Europe v Legacy of Soviet economic planning (1945 -90) v Post-1990 economic and political transition Acid rain and forest death Bohemia, Czech Republic
 Settlement and Population
Settlement and Population
 Population density in the Core and Periphery v Population pattern is linked to areas of early industrialization v Urban-industrial v Low core is characterized by natural growth rates v Target area for migrants
Population density in the Core and Periphery v Population pattern is linked to areas of early industrialization v Urban-industrial v Low core is characterized by natural growth rates v Target area for migrants

 Continued slow natural growth v Why? v Highly urbanized and industrialized population in western Europe shortage after WWII in eastern Europe need for female labor government promotes family planning and birth control v Labor
Continued slow natural growth v Why? v Highly urbanized and industrialized population in western Europe shortage after WWII in eastern Europe need for female labor government promotes family planning and birth control v Labor

 Migration into Europe v So far, industrialized countries in Europe have received many immigrants because of Open-door immigration policy to alleviate labor shortage during the postwar period (eg. guest works in Germany) v Influx of migrants from former European colonies v Flight from post-1989 economic and political turmoil v
Migration into Europe v So far, industrialized countries in Europe have received many immigrants because of Open-door immigration policy to alleviate labor shortage during the postwar period (eg. guest works in Germany) v Influx of migrants from former European colonies v Flight from post-1989 economic and political turmoil v
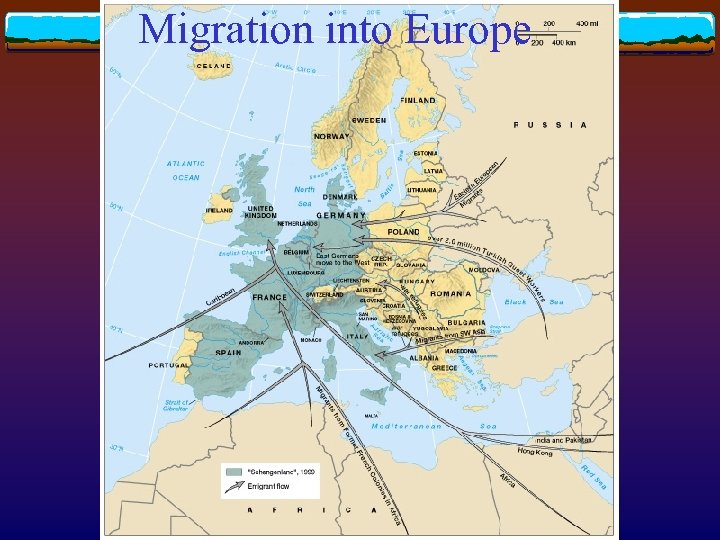 Migration into Europe
Migration into Europe
 Schengen Agreement v EU declaration of intent to reduce border formalities for travelers moving between western Europe (1985) v Resulted in strict border controls between EU and non-EU countries – “Fortress Europe”
Schengen Agreement v EU declaration of intent to reduce border formalities for travelers moving between western Europe (1985) v Resulted in strict border controls between EU and non-EU countries – “Fortress Europe”
 Urban landscapes Contemporary landscape expresses different historical periods v Medieval period (900 -1500) v v v Renaissance-Baroque period (1500 -1800) v v Narrow, winding streets, and crowded masonry buildings with little setback from the street Urban planning, high stories girdled by city walls Industrial period (1800 -present) v Industrial districts clustered along transportation lines, often outside the fortifications
Urban landscapes Contemporary landscape expresses different historical periods v Medieval period (900 -1500) v v v Renaissance-Baroque period (1500 -1800) v v Narrow, winding streets, and crowded masonry buildings with little setback from the street Urban planning, high stories girdled by city walls Industrial period (1800 -present) v Industrial districts clustered along transportation lines, often outside the fortifications
 Cultural Coherence and Diversity
Cultural Coherence and Diversity
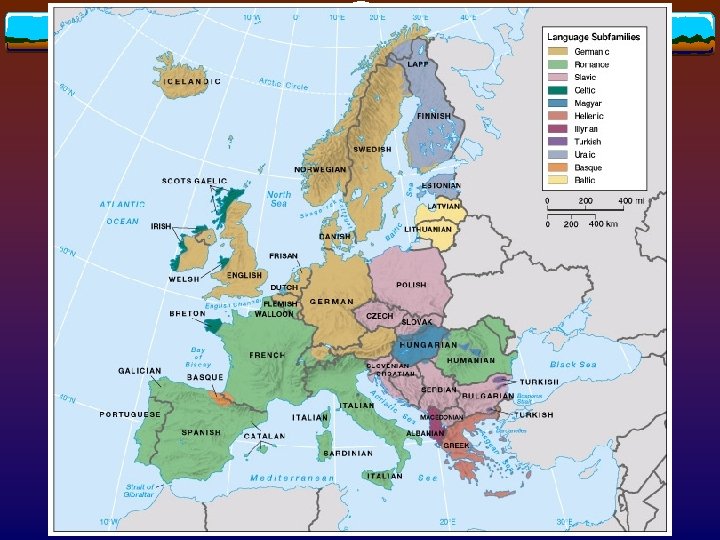
 Language v Major Indo-European language (90%) v Germanic language v German, v Romance v Italian, v Slavic English, Dutch, Flemish, Scandinavian, and Icelandic language French, Spanish, Portuguese, Romanian, and Moldavian language v Polish, Czech, Slovakian – Latin Alphabet v Serbo-Croatian, Bularian, Macedonian, Slovenian – Cyrillic Alphabet
Language v Major Indo-European language (90%) v Germanic language v German, v Romance v Italian, v Slavic English, Dutch, Flemish, Scandinavian, and Icelandic language French, Spanish, Portuguese, Romanian, and Moldavian language v Polish, Czech, Slovakian – Latin Alphabet v Serbo-Croatian, Bularian, Macedonian, Slovenian – Cyrillic Alphabet
 Language v Minor Indo-European language Celtic language - Breton, Welsh, Scots Gaelic, Irish v Hellenic language - Greek v Baltic language - Lettish, Lithuanian v v Non-Indo-European language Uralic language - Magyar (Hungarian), Finns, Estonian v Altaic language - Turkish minorities in southeastern Europe v Etc… - Basque v
Language v Minor Indo-European language Celtic language - Breton, Welsh, Scots Gaelic, Irish v Hellenic language - Greek v Baltic language - Lettish, Lithuanian v v Non-Indo-European language Uralic language - Magyar (Hungarian), Finns, Estonian v Altaic language - Turkish minorities in southeastern Europe v Etc… - Basque v
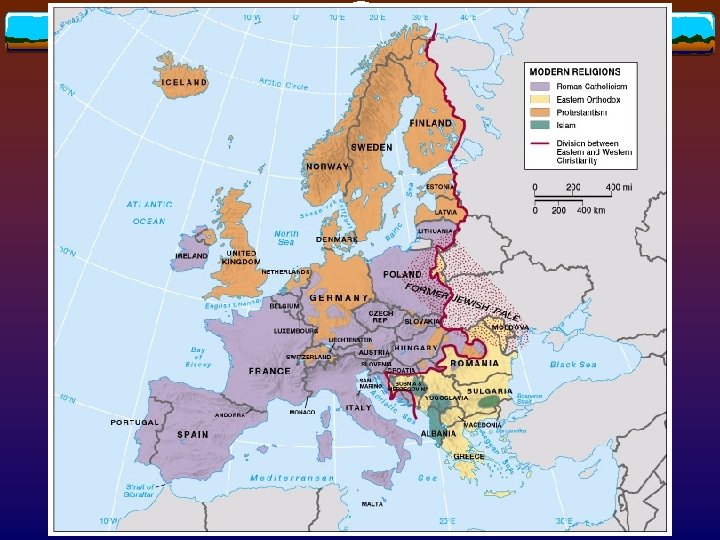
 Religion v Historical geography of religious complexity is essential to understanding today’s cultural tension such as v Cultural borders in eastern Europe and Balkans v Northern Ireland v Ethnic cleansing in Yugoslavia
Religion v Historical geography of religious complexity is essential to understanding today’s cultural tension such as v Cultural borders in eastern Europe and Balkans v Northern Ireland v Ethnic cleansing in Yugoslavia
 Historical geography of religion v Adoption of Christianity Edict of Tolerance (A. D. 313) v Hierarchical diffusion v v Schism between western and eastern Christianity v v Official split of the eastern church from Rome (1054) Conflicts with Islam Presence of Ottoman Empire in southeastern Europe (16 c ~ early 20 c) v Muslim incursion into Spain (8 c ~ 15 c) v
Historical geography of religion v Adoption of Christianity Edict of Tolerance (A. D. 313) v Hierarchical diffusion v v Schism between western and eastern Christianity v v Official split of the eastern church from Rome (1054) Conflicts with Islam Presence of Ottoman Empire in southeastern Europe (16 c ~ early 20 c) v Muslim incursion into Spain (8 c ~ 15 c) v
 Historical geography of religion v Protestant Revolt (16 c) v v Creates north-south boundary between Protestant and Catholic Europe Geography of Judaism Forced dispersal of Jews from Palestine during the Roman Empire v Mediterranean cities Iberian Peninsula (10 c) “Jewish Pale” in eastern Europe (15 c) North America (19 c~) Israel (1948~) Germany (1990~) v
Historical geography of religion v Protestant Revolt (16 c) v v Creates north-south boundary between Protestant and Catholic Europe Geography of Judaism Forced dispersal of Jews from Palestine during the Roman Empire v Mediterranean cities Iberian Peninsula (10 c) “Jewish Pale” in eastern Europe (15 c) North America (19 c~) Israel (1948~) Germany (1990~) v
 Patterns of contemporary religion v Roman Catholics (250 million) in southern half except for Ireland Poland v Protestants (100 million) in northern half v Secularization in western Europe after WWII
Patterns of contemporary religion v Roman Catholics (250 million) in southern half except for Ireland Poland v Protestants (100 million) in northern half v Secularization in western Europe after WWII
 Geopolitical Framework
Geopolitical Framework
 From Empire to Nation-State v Legacy of the Roman Empire (B. C 300 - A. D. 400) v v Cities connected by highway (eg. London, Paris, Frankfurt) Feudal territories (9 c - 15 c) Urban power of a merchant class (eg. Hamburg, Venice) v Rural polity based on feudalism (formal relation between a superior and a vassal) v v Nation-states (15 c - 18 c) Geopolitical entity fostered by ethnic and cultural nationalism v Congruence between a shared culture and political space v
From Empire to Nation-State v Legacy of the Roman Empire (B. C 300 - A. D. 400) v v Cities connected by highway (eg. London, Paris, Frankfurt) Feudal territories (9 c - 15 c) Urban power of a merchant class (eg. Hamburg, Venice) v Rural polity based on feudalism (formal relation between a superior and a vassal) v v Nation-states (15 c - 18 c) Geopolitical entity fostered by ethnic and cultural nationalism v Congruence between a shared culture and political space v
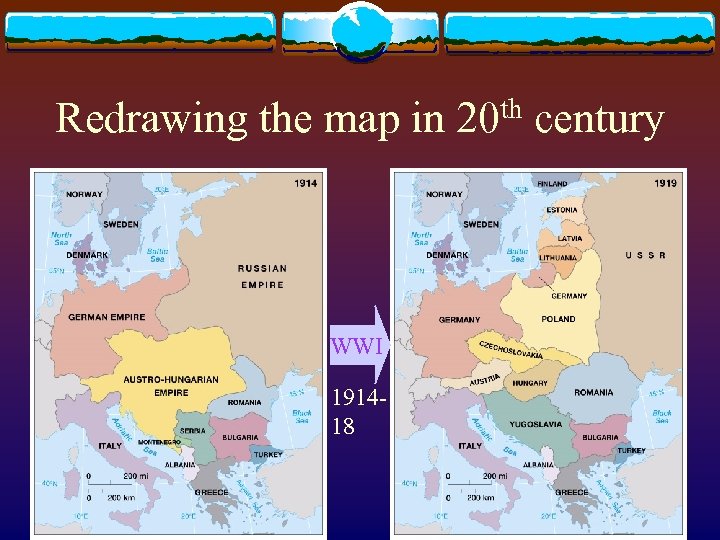 Redrawing the map in 20 th century WWI 191418
Redrawing the map in 20 th century WWI 191418
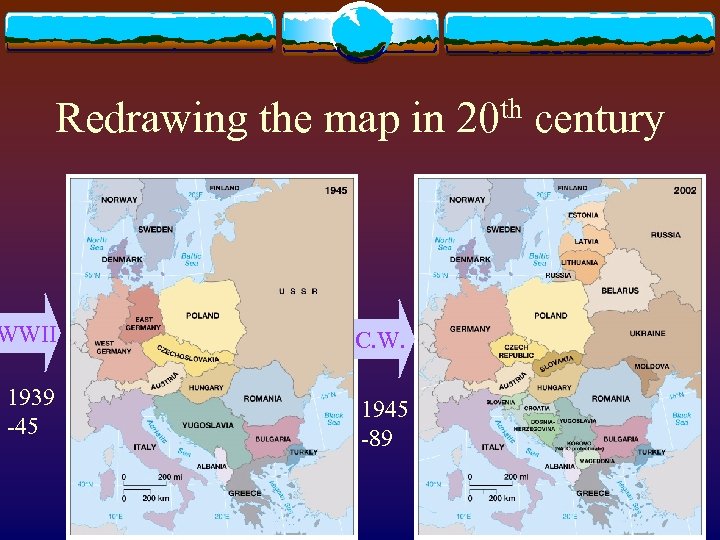 Redrawing the map in 20 th century WWII C. W. 1939 -45 1945 -89
Redrawing the map in 20 th century WWII C. W. 1939 -45 1945 -89
 Scale of tensions in the Balkans v Local/regional tensions v v Tensions between Yugoslavia and its neighboring states v v Macedonia, Albania, Bosnia, Croatia, and Slovenia Relations with the rest of Europe v v Provinces of Serbia, Montenegro, and Kosovo E. U. , NATO Global implications v U. N.
Scale of tensions in the Balkans v Local/regional tensions v v Tensions between Yugoslavia and its neighboring states v v Macedonia, Albania, Bosnia, Croatia, and Slovenia Relations with the rest of Europe v v Provinces of Serbia, Montenegro, and Kosovo E. U. , NATO Global implications v U. N.
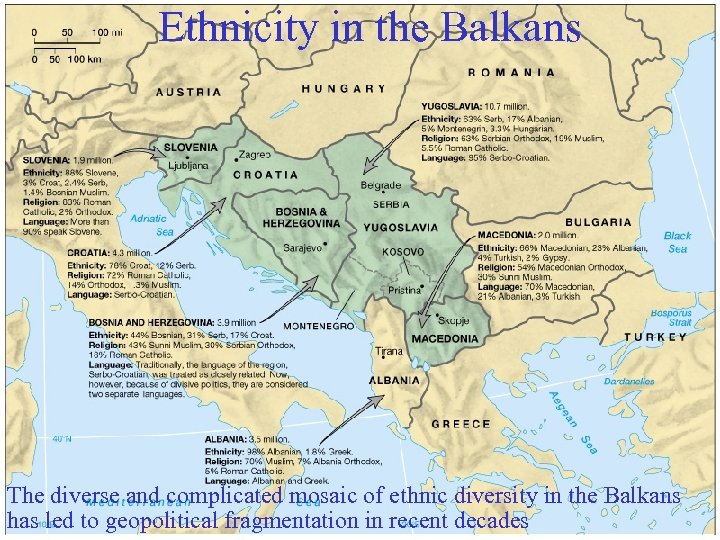 Ethnicity in the Balkans v Fragmented geopolitical processes involved with small-scale independence movements and the phenomenon of mininationalism as it develops along ethnic fault lines The diverse and complicated mosaic of ethnic diversity in the Balkans has led to geopolitical fragmentation in recent decades
Ethnicity in the Balkans v Fragmented geopolitical processes involved with small-scale independence movements and the phenomenon of mininationalism as it develops along ethnic fault lines The diverse and complicated mosaic of ethnic diversity in the Balkans has led to geopolitical fragmentation in recent decades
 Geopolitical issues in Europe
Geopolitical issues in Europe
 Economic and Social Development
Economic and Social Development
 v Birthplace of industrial revolution v Economic integration – E. U. v Chaotic economic transition in eastern Europe
v Birthplace of industrial revolution v Economic integration – E. U. v Chaotic economic transition in eastern Europe
 Industrial revolution v Human labor replaced by machine v Machines powered by inanimate energy sources v Began in England between 1730 and 1850 v eg. Wool Textile manufacturing by steam-powered mechanized looms
Industrial revolution v Human labor replaced by machine v Machines powered by inanimate energy sources v Began in England between 1730 and 1850 v eg. Wool Textile manufacturing by steam-powered mechanized looms
 Locational factors of early industrial areas v Access to coalfields v Coke replaced charcoal as a fuel to make iron and steel v eg. The English Midlands, The Ruhr, Saar-Lorraine v Exceptions v London, to this are and Po Plain
Locational factors of early industrial areas v Access to coalfields v Coke replaced charcoal as a fuel to make iron and steel v eg. The English Midlands, The Ruhr, Saar-Lorraine v Exceptions v London, to this are and Po Plain
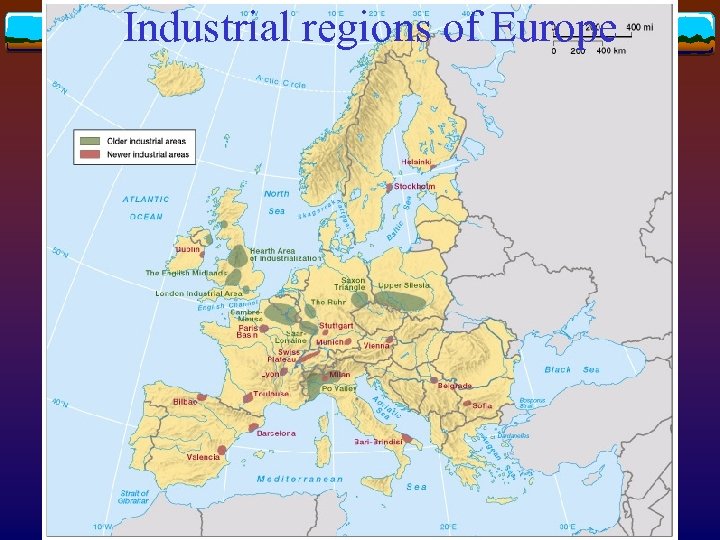 Industrial regions of Europe
Industrial regions of Europe
 Economic integration in the West v ECSC (European Coal and Steel Community) in 1952 v v EEC (European Economic Community) in 1957 v v Coordinate coal and steel production by a supranational authority Foster the free movement of goods, labor, and capital EC (European Community) in 1965 v Add political union to the economic community
Economic integration in the West v ECSC (European Coal and Steel Community) in 1952 v v EEC (European Economic Community) in 1957 v v Coordinate coal and steel production by a supranational authority Foster the free movement of goods, labor, and capital EC (European Community) in 1965 v Add political union to the economic community
 Economic integration in the West v EU (European Union) in 1991 v Aimed at v Single currency through the European Monetary Union v Common foreign policies v Mutual security agreements v Currently 15 members v 11 Euroland members adopt a common currency (2002)
Economic integration in the West v EU (European Union) in 1991 v Aimed at v Single currency through the European Monetary Union v Common foreign policies v Mutual security agreements v Currently 15 members v 11 Euroland members adopt a common currency (2002)
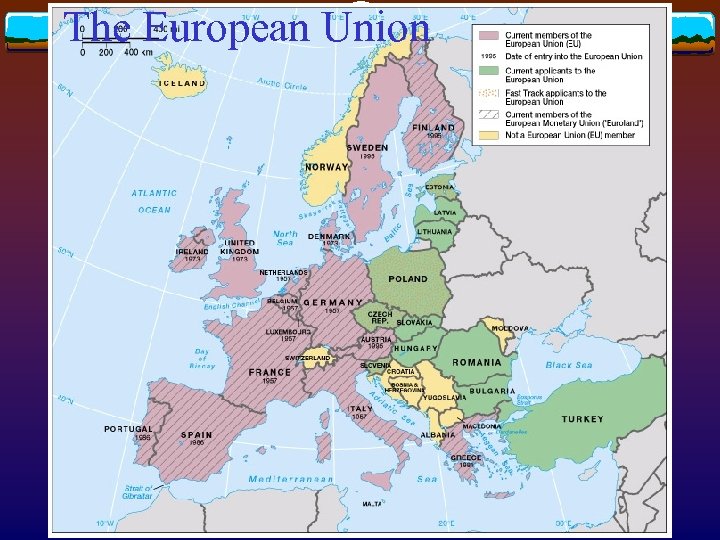 The European Union
The European Union
 Economic transition in eastern Europe v The Soviet Plan (1949 -1989) v CMEA (Council for Mutual Economic Assistance) v Command economy v Transitions since 1991 v Discontinuation of subsidies v Privatization of industry
Economic transition in eastern Europe v The Soviet Plan (1949 -1989) v CMEA (Council for Mutual Economic Assistance) v Command economy v Transitions since 1991 v Discontinuation of subsidies v Privatization of industry
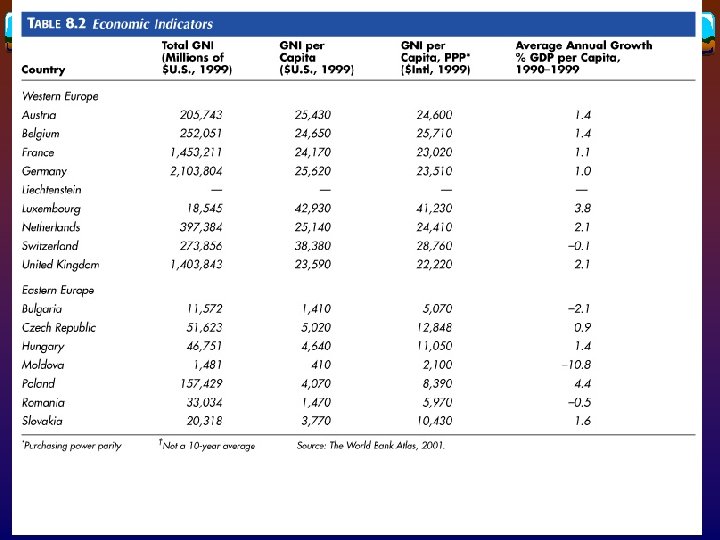
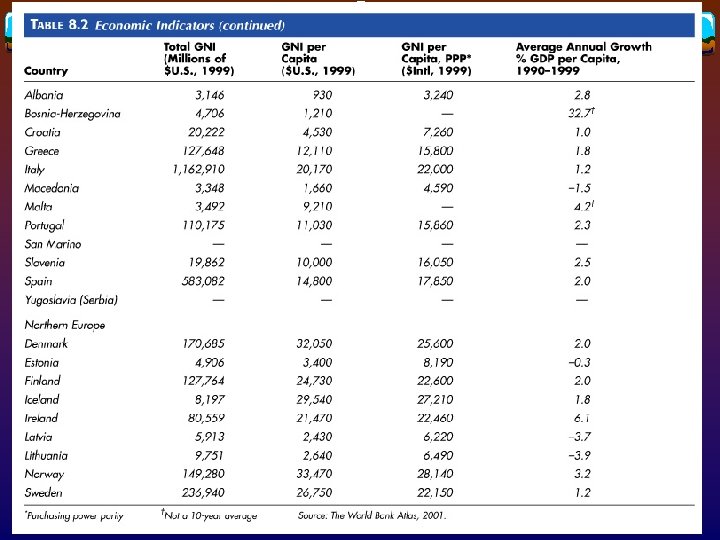

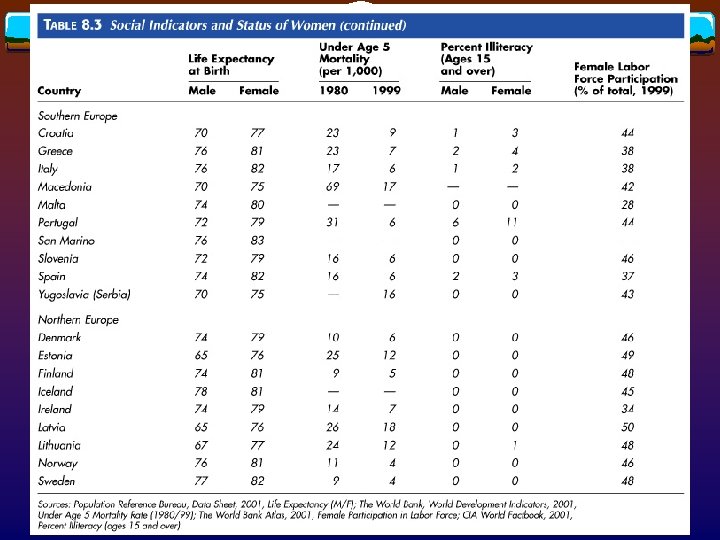
 v Regional disparities between western and eastern Europe v Regional v Czech disparities within eastern Europe Republic, Slovenia, Hungary, and Poland
v Regional disparities between western and eastern Europe v Regional v Czech disparities within eastern Europe Republic, Slovenia, Hungary, and Poland
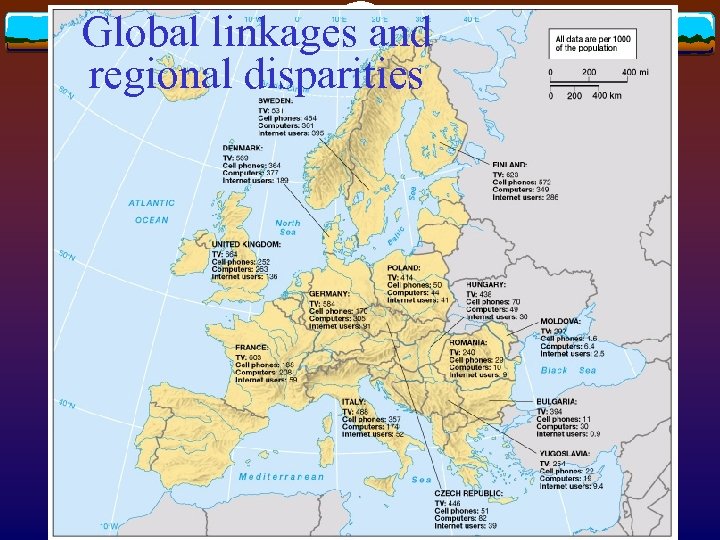 Global linkages and regional disparities
Global linkages and regional disparities


