710eda6735fd7692e9d302c0420b89f4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Europe-China Workshop on E-Learning and Games (Edutainment 2005) Middleware in Game Development Mr. Milo Yip (mcmilo@polyu. edu. hk)
Europe-China Workshop on E-Learning and Games (Edutainment 2005) Middleware in Game Development Mr. Milo Yip (mcmilo@polyu. edu. hk)
 Multimedia Innovation Centre Research & Development n n Games & Animation Education and Internet Technologies Hardware and Software Development Traditional and New Media Education n n Master of Science in Multimedia and Entertainment Technology (MSc. MET) Undergraduate (EIE, SD), High Diploma & SPEED Courses
Multimedia Innovation Centre Research & Development n n Games & Animation Education and Internet Technologies Hardware and Software Development Traditional and New Media Education n n Master of Science in Multimedia and Entertainment Technology (MSc. MET) Undergraduate (EIE, SD), High Diploma & SPEED Courses
 Overview 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Brief History of Game Development What & Why Middleware? Middleware Taxonomy MSMOG Development Platform Q&A
Overview 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Brief History of Game Development What & Why Middleware? Middleware Taxonomy MSMOG Development Platform Q&A
 1. Brief History of Game Development
1. Brief History of Game Development
 Brief History (50 s) 1958: “Tennis for Two” n n Willy Higginbotham (Brookhaven National Laboratories) Analog Computer, Oscilloscope
Brief History (50 s) 1958: “Tennis for Two” n n Willy Higginbotham (Brookhaven National Laboratories) Analog Computer, Oscilloscope
 Brief History (60 s) 1961: Spacewar n n Steve “Slug” Russel at MIT PDP-1 (USD 120, 000)
Brief History (60 s) 1961: Spacewar n n Steve “Slug” Russel at MIT PDP-1 (USD 120, 000)
 Brief History (70 s) 1972: Pong n n Allan Alcorn at Atari Entered home in 1975
Brief History (70 s) 1972: Pong n n Allan Alcorn at Atari Entered home in 1975
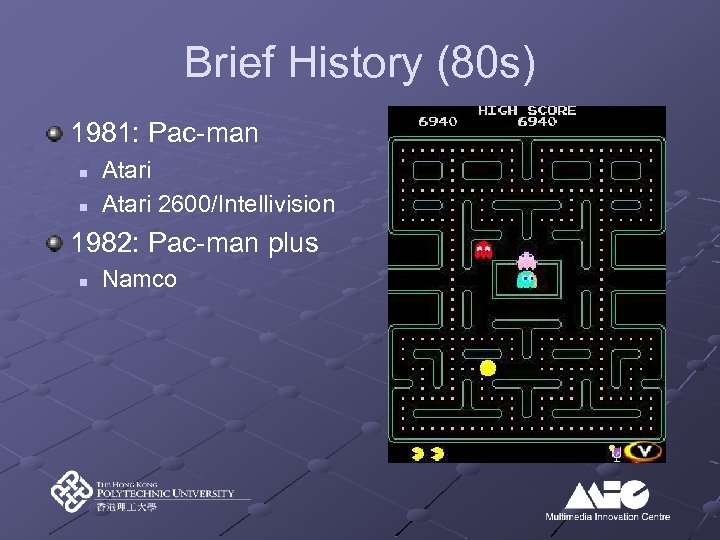 Brief History (80 s) 1981: Pac-man n n Atari 2600/Intellivision 1982: Pac-man plus n Namco
Brief History (80 s) 1981: Pac-man n n Atari 2600/Intellivision 1982: Pac-man plus n Namco
 Brief History (80 s) 1985: NES/Fami. Com n n n Nitendo Motorola 6502 (8 -bit) Popular Game Cartridge Super Mario Bros. Donkey Kong Zelda
Brief History (80 s) 1985: NES/Fami. Com n n n Nitendo Motorola 6502 (8 -bit) Popular Game Cartridge Super Mario Bros. Donkey Kong Zelda
 Brief History (90 s) 1991: Wolfenstein 3 D n n id Software (John Carmack) PC (386 33 Mhz), VGA 1996: Tomb Raider n n n Eidos PC (Pentium 133 Mhz) 4 MB Ram SVGA, 3 D Acceleration Windows 95
Brief History (90 s) 1991: Wolfenstein 3 D n n id Software (John Carmack) PC (386 33 Mhz), VGA 1996: Tomb Raider n n n Eidos PC (Pentium 133 Mhz) 4 MB Ram SVGA, 3 D Acceleration Windows 95
 Brief History (Today) Gaming Platforms: n n PC (Pentium 4, Display card with Shader 3. 0) Consoles Sony Playstation 2 Microsoft XBox Game. Cube n Mobiles Game. Boy Advance/DS PDA (Palm. OS, Windows. CE) Mobile Phone (Symbian, J 2 ME) n Arcade
Brief History (Today) Gaming Platforms: n n PC (Pentium 4, Display card with Shader 3. 0) Consoles Sony Playstation 2 Microsoft XBox Game. Cube n Mobiles Game. Boy Advance/DS PDA (Palm. OS, Windows. CE) Mobile Phone (Symbian, J 2 ME) n Arcade
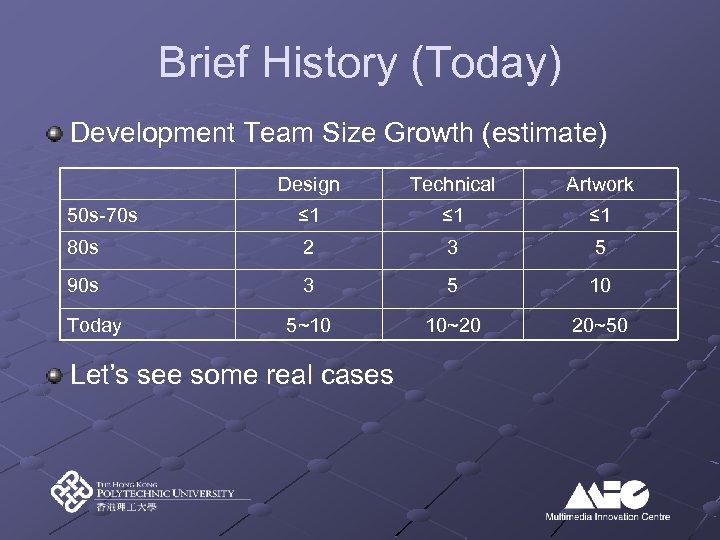 Brief History (Today) Development Team Size Growth (estimate) Design Technical Artwork 50 s-70 s ≤ 1 ≤ 1 80 s 2 3 5 90 s 3 5 10 5~10 10~20 20~50 Today Let’s see some real cases
Brief History (Today) Development Team Size Growth (estimate) Design Technical Artwork 50 s-70 s ≤ 1 ≤ 1 80 s 2 3 5 90 s 3 5 10 5~10 10~20 20~50 Today Let’s see some real cases
 Black & White By Lionhead Studios USD ~ 5. 7 M budget 25 full-time developers 3 contractors ~3 years ~2 M lines of code In-house technology
Black & White By Lionhead Studios USD ~ 5. 7 M budget 25 full-time developers 3 contractors ~3 years ~2 M lines of code In-house technology
 Neverwinter Night By Bioware Corp 75 developers at peek (~160 man-years of development) 40 QAs 5 sound contractors 20 translators ~5 years In-house technology
Neverwinter Night By Bioware Corp 75 developers at peek (~160 man-years of development) 40 QAs 5 sound contractors 20 translators ~5 years In-house technology
 Splinter Cell (PS 2 version) By Ubisoft Entertainment 76 full-time developers 18 contractors 5 months Uses Unreal. Engine as Middleware
Splinter Cell (PS 2 version) By Ubisoft Entertainment 76 full-time developers 18 contractors 5 months Uses Unreal. Engine as Middleware
 2. What & Why Middleware?
2. What & Why Middleware?
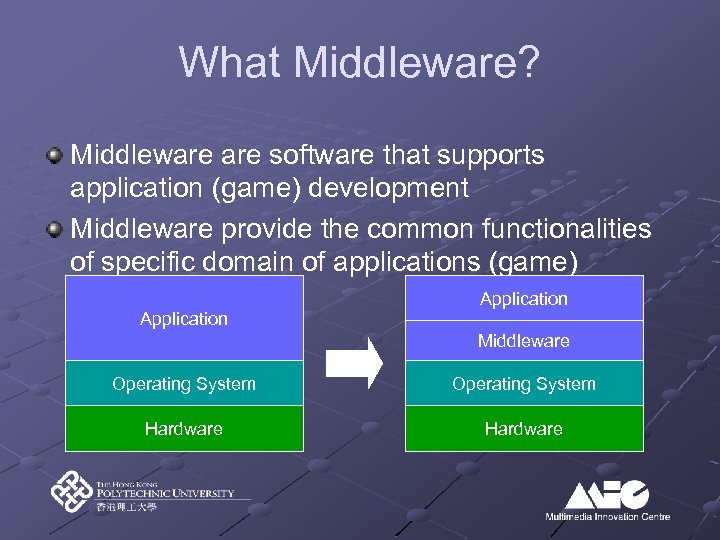 What Middleware? Middleware software that supports application (game) development Middleware provide the common functionalities of specific domain of applications (game) Application Middleware Operating System Hardware
What Middleware? Middleware software that supports application (game) development Middleware provide the common functionalities of specific domain of applications (game) Application Middleware Operating System Hardware
 Why Middleware? Prevent re-inventing the wheel Game system becomes more and more complicated: n real-time, interactive, networked, persisted, massive users, virtual reality system Game development requires a vast domains of expertise nowadays To use technologies with success stories
Why Middleware? Prevent re-inventing the wheel Game system becomes more and more complicated: n real-time, interactive, networked, persisted, massive users, virtual reality system Game development requires a vast domains of expertise nowadays To use technologies with success stories
 Why Middleware? (cont. ) Developing a game from ground up is: n Expensive Need to hire many domain experts Train developers with latest technologies n Slow Market changes rapidly Publishers want shorter development time n Risky Development of high-end technologies is very risky
Why Middleware? (cont. ) Developing a game from ground up is: n Expensive Need to hire many domain experts Train developers with latest technologies n Slow Market changes rapidly Publishers want shorter development time n Risky Development of high-end technologies is very risky
 Why Middleware? (cont. ) However, there a few disadvantages: n n Licensing may be a big investment Middleware may not be fully suitable to the project, customization may be needed Difficult to integrate with existing assets Developing in-house technologies makes The game having unique features Possible to re-use in future Possible to sell to third parties (as middleware)
Why Middleware? (cont. ) However, there a few disadvantages: n n Licensing may be a big investment Middleware may not be fully suitable to the project, customization may be needed Difficult to integrate with existing assets Developing in-house technologies makes The game having unique features Possible to re-use in future Possible to sell to third parties (as middleware)
 3. Middleware Taxonomy
3. Middleware Taxonomy
 Middleware Taxonomy Graphics Rendering Audio Rendering Physics Simulation Artificial Intelligence Multiplayer Mathematics Special (e. g. Plant, Planet synthesis) All-in-one (3 D Game Engine)
Middleware Taxonomy Graphics Rendering Audio Rendering Physics Simulation Artificial Intelligence Multiplayer Mathematics Special (e. g. Plant, Planet synthesis) All-in-one (3 D Game Engine)
 Middleware Taxonomy Middleware products normally include: n n n Application Programming Interface (API), normally in C/C++ Runtime Components (e. g. DLLs) Tools Documentation Examples Some products are cross-platform
Middleware Taxonomy Middleware products normally include: n n n Application Programming Interface (API), normally in C/C++ Runtime Components (e. g. DLLs) Tools Documentation Examples Some products are cross-platform
 Graphics Rendering Visual quality and fluency is very important to games Most games nowadays requires 3 D realtime computer graphics Famous products: n Criterion’s Render. Ware Graphics
Graphics Rendering Visual quality and fluency is very important to games Most games nowadays requires 3 D realtime computer graphics Famous products: n Criterion’s Render. Ware Graphics
 Graphics Rendering Features n n n Lighting/Material, Shadowing Scene Management (indoor/outdoor) Camera Control Animation (objects, character, facial) Special Effects (particles, lens flare, etc) Workflow Tools (e. g. exporting 3 D models from 3 D Studio Max, Maya)
Graphics Rendering Features n n n Lighting/Material, Shadowing Scene Management (indoor/outdoor) Camera Control Animation (objects, character, facial) Special Effects (particles, lens flare, etc) Workflow Tools (e. g. exporting 3 D models from 3 D Studio Max, Maya)

 Audio Rendering Audio in games has very important effect to gamer’s emotion Famous products: n Render. Ware Audio
Audio Rendering Audio in games has very important effect to gamer’s emotion Famous products: n Render. Ware Audio
 Audio Rendering Features n n Mono/Stereo playback 3 D Surround Sound Emulation Effect filters (e. g. echo, chorus, reverb, etc. ) Streaming
Audio Rendering Features n n Mono/Stereo playback 3 D Surround Sound Emulation Effect filters (e. g. echo, chorus, reverb, etc. ) Streaming
 Physics Simulation Traditional games have little use of physics simulation n Collision Detection (preventing penetration among objects and environment) Physics become more important in game development recently Physics simulation add realism to games Famous Products: n n n Havok Novedex Open Dynamics Engine
Physics Simulation Traditional games have little use of physics simulation n Collision Detection (preventing penetration among objects and environment) Physics become more important in game development recently Physics simulation add realism to games Famous Products: n n n Havok Novedex Open Dynamics Engine
 Physics Simulation Features n n n Collision Detection Kinematics Simulation Rigid-body Dynamics Simulation Hinge, ball, slider joints n Special domains Vehicle simulation Ragdoll simulation
Physics Simulation Features n n n Collision Detection Kinematics Simulation Rigid-body Dynamics Simulation Hinge, ball, slider joints n Special domains Vehicle simulation Ragdoll simulation
 Artificial Intelligence (AI) adds behavior to Non. Playable Characters (NPCs) Behavior can be low- or high-level n n Low-level behavior such as finding a path from current position to target is vital to games High-level behavior such as decision making adds realism to human (or human-like) NPCs Famous Products n Renderware AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) adds behavior to Non. Playable Characters (NPCs) Behavior can be low- or high-level n n Low-level behavior such as finding a path from current position to target is vital to games High-level behavior such as decision making adds realism to human (or human-like) NPCs Famous Products n Renderware AI
 Artificial Intelligence Features n World/Perception Modeling Mobility (Where NPCs can move through) Visibility (What NPCs can see) Audibility (What NPCs can here) n n Path-Finding Behavior Modeling Finite-State Machine (FSM) Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Rule-based Systems n Team Collaboration
Artificial Intelligence Features n World/Perception Modeling Mobility (Where NPCs can move through) Visibility (What NPCs can see) Audibility (What NPCs can here) n n Path-Finding Behavior Modeling Finite-State Machine (FSM) Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Rule-based Systems n Team Collaboration
 Multiplayer games continue to grow n n Lobby Games Massively Multiplayer Online Game (MMOG) Multiplayer games are complicated to design and implement (relative to single player games) n n In research, it is Networked Virtual Environment (NVE) NVE can be applied on military simulation Famous Products: n n n Net-Z/Eterna Terazona Butterfly. net (Distributed Architecture)
Multiplayer games continue to grow n n Lobby Games Massively Multiplayer Online Game (MMOG) Multiplayer games are complicated to design and implement (relative to single player games) n n In research, it is Networked Virtual Environment (NVE) NVE can be applied on military simulation Famous Products: n n n Net-Z/Eterna Terazona Butterfly. net (Distributed Architecture)
 Multiplayer Features n Communication TCP/UDP, Encryption, Compression Session Management n Object World Management, Transaction, Persistency Remote Method Invocation (RMI) n Synchronization Management Optimistic/Pessimistic Dead-Reckoning Models Interest Management (reduce synchronization traffic) n Lobby and User Management
Multiplayer Features n Communication TCP/UDP, Encryption, Compression Session Management n Object World Management, Transaction, Persistency Remote Method Invocation (RMI) n Synchronization Management Optimistic/Pessimistic Dead-Reckoning Models Interest Management (reduce synchronization traffic) n Lobby and User Management
 Special - Plant simulation and rendering Famous products n n Speed. Tree. RT Real. NAT
Special - Plant simulation and rendering Famous products n n Speed. Tree. RT Real. NAT
 Special - Planet synthesis n n Terrain, water, atmosphere, satellites Very huge and detailed game worlds Famous Products: n Mojo. World (not yet provide as middleware for public licensing)
Special - Planet synthesis n n Terrain, water, atmosphere, satellites Very huge and detailed game worlds Famous Products: n Mojo. World (not yet provide as middleware for public licensing)
 All-in-one (3 D Game Engine) 3 D Game Engines provide all-in-one solutions to game development Normally 3 D Game Engines contain integrated workflow tools Famous Products n n n Unreal Technology (Unreal Tournament) Source Engine (Half-life 2) Jupiter (No One Lives Forever) Renderware Studio Net. Immerse
All-in-one (3 D Game Engine) 3 D Game Engines provide all-in-one solutions to game development Normally 3 D Game Engines contain integrated workflow tools Famous Products n n n Unreal Technology (Unreal Tournament) Source Engine (Half-life 2) Jupiter (No One Lives Forever) Renderware Studio Net. Immerse
 All-in-one (3 D Game Engine) Features n n n n 3 D Graphics/Audio Rendering Input Handling Graphical User Interface (GUI) Physics Simulation Artificial Intelligence Script Engine Integrated Tools Multiplayer (for lobby type only)
All-in-one (3 D Game Engine) Features n n n n 3 D Graphics/Audio Rendering Input Handling Graphical User Interface (GUI) Physics Simulation Artificial Intelligence Script Engine Integrated Tools Multiplayer (for lobby type only)
 4. MSMOG Development Platform http: //micn. polyu. edu. hk/~msmog/
4. MSMOG Development Platform http: //micn. polyu. edu. hk/~msmog/
 MSMOG Development Platform Mini-Scale Multiplayer Online Game Development Platform (MSMOG DP) n n n Funded by SME Development Fund (10/2003 - 3/2005, 18 months, HKD ~2 M) Developed by MIC, Poly. U Aimed at enabling game companies to develop MSMOGs in a more rapid, efficient, secure and affordable way
MSMOG Development Platform Mini-Scale Multiplayer Online Game Development Platform (MSMOG DP) n n n Funded by SME Development Fund (10/2003 - 3/2005, 18 months, HKD ~2 M) Developed by MIC, Poly. U Aimed at enabling game companies to develop MSMOGs in a more rapid, efficient, secure and affordable way
 MSMOG Types of online game nowadays n n 2 -16 players lobby game 1000 -10000 players Massively Multiplayer Online Game (MMOG), persist world MSMOG is a new type of online game for n n <200 players in controlled network environment (e. g. Cyber café) Fast interaction games (e. g. fighting, racing, sports)
MSMOG Types of online game nowadays n n 2 -16 players lobby game 1000 -10000 players Massively Multiplayer Online Game (MMOG), persist world MSMOG is a new type of online game for n n <200 players in controlled network environment (e. g. Cyber café) Fast interaction games (e. g. fighting, racing, sports)
 MSMOG Rationales for MSMOG n n n Asia have a huge number of cyber cafés No games are designed for this market New opportunity for Hong Kong game industry!
MSMOG Rationales for MSMOG n n n Asia have a huge number of cyber cafés No games are designed for this market New opportunity for Hong Kong game industry!
 MSMOG DP is an all-in-one middleware for game development MSMOG divides into two products: n n 3 D Game Engine Multiplayer Network Engine
MSMOG DP is an all-in-one middleware for game development MSMOG divides into two products: n n 3 D Game Engine Multiplayer Network Engine
 MSMOG - 3 D Game Engine provides: n n n n 3 D Graphics/Audio Rendering Input Handling Physics Simulation Artificial Intelligence (AI) Graphical User Interface (GUI) Mathematics Workflow Tools All of them are tightly integrated
MSMOG - 3 D Game Engine provides: n n n n 3 D Graphics/Audio Rendering Input Handling Physics Simulation Artificial Intelligence (AI) Graphical User Interface (GUI) Mathematics Workflow Tools All of them are tightly integrated



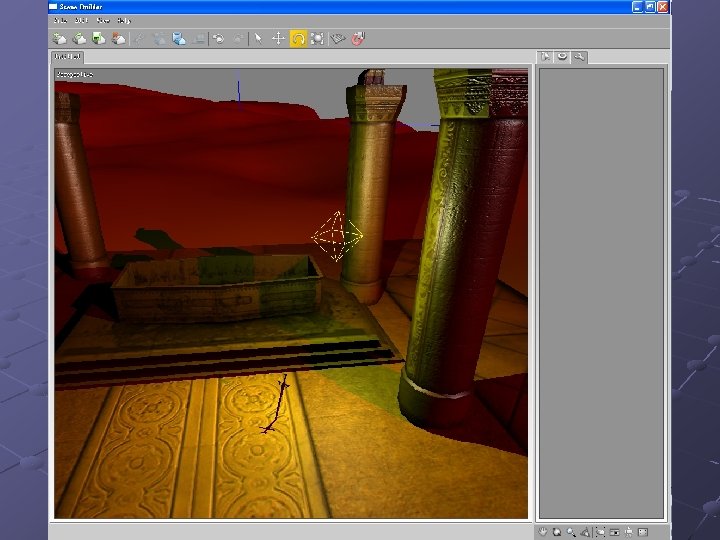
 MSMOG – Multiplayer Network Engine The Multiplayer Network Engine supports n n n World Management Interest Management Communication Synchronization Persistency Transaction Current performance profile n 400 concurrent users at 20 Hz sync.
MSMOG – Multiplayer Network Engine The Multiplayer Network Engine supports n n n World Management Interest Management Communication Synchronization Persistency Transaction Current performance profile n 400 concurrent users at 20 Hz sync.
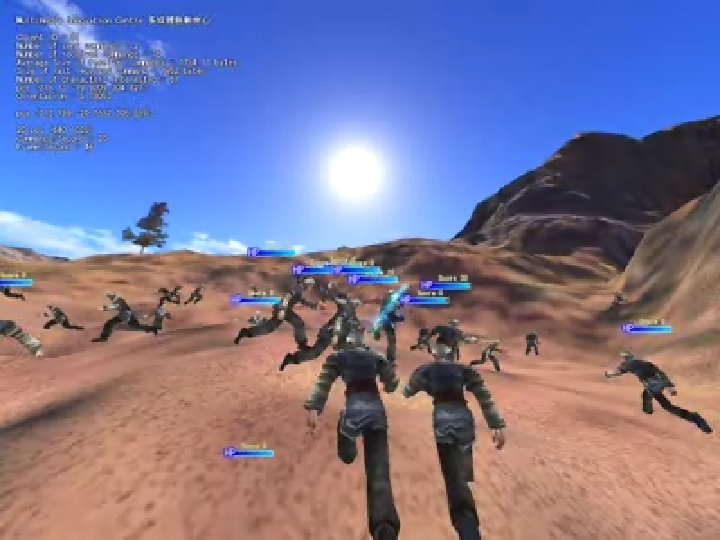
 MSMOG DP - Applications Benefits of using MSMOG DP n n n Latest high-end technologies Reducing development cost, time and risk Local support and training Applications n n Single player, Multiplayer games Education/Edutainment software 3 D Simulation Virtual/Mixed Reality applications
MSMOG DP - Applications Benefits of using MSMOG DP n n n Latest high-end technologies Reducing development cost, time and risk Local support and training Applications n n Single player, Multiplayer games Education/Edutainment software 3 D Simulation Virtual/Mixed Reality applications
 “Auroral Snare” Prototype - 3 D Multiplayer Action Game - 3 MSc. MET Students’ FYP - 3 Months of Development - Using MSMOG Development Platform
“Auroral Snare” Prototype - 3 D Multiplayer Action Game - 3 MSc. MET Students’ FYP - 3 Months of Development - Using MSMOG Development Platform
 5. Q&A
5. Q&A
 Thanks! http: //micn. polyu. edu. hk/~msmog/ Welcome to visit MIC! Please contact me or Ms. Cindy Yu (mccindy@polyu. edu. hk)
Thanks! http: //micn. polyu. edu. hk/~msmog/ Welcome to visit MIC! Please contact me or Ms. Cindy Yu (mccindy@polyu. edu. hk)


