227be5ab5e3631446e042bdd5d9c9f73.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Europe. Aid Training Seminar: EC support to governance in partner countries – with a focus on the African continent Political economy and governance in operations July 6 th, 2011
Europe. Aid Training Seminar: EC support to governance in partner countries – with a focus on the African continent Political economy and governance in operations July 6 th, 2011
 Europe. Aid Part A What is PE, and why is it important to DEVCO operations?
Europe. Aid Part A What is PE, and why is it important to DEVCO operations?
 Why political economy analysis? The argument for PEA: years of mistakes and waste in aid programming misunderstandings of country systems – political incentives, informal rules, the reality behind the façade Rationale for DEVCO: • these realities strongly affect development outcomes: • Basing country and sector strategies, and programme design, implementation and monitoring on a clearer understanding should result in greater development effectiveness and aid effectiveness (i. e. better results) Europe. Aid
Why political economy analysis? The argument for PEA: years of mistakes and waste in aid programming misunderstandings of country systems – political incentives, informal rules, the reality behind the façade Rationale for DEVCO: • these realities strongly affect development outcomes: • Basing country and sector strategies, and programme design, implementation and monitoring on a clearer understanding should result in greater development effectiveness and aid effectiveness (i. e. better results) Europe. Aid
 What is political economy analysis? (a) PE analysis is concerned with the interaction of political and economic processes in a society: the distribution of power and wealth between different groups and individuals, and the processes that create, sustain and transform these relationships over time. It highlights: • Politics --- contestation and bargaining over rights and resources • Economic processes that generate wealth and influence politics • Dynamic context – processes of change over time. . . /cont’d Europe. Aid
What is political economy analysis? (a) PE analysis is concerned with the interaction of political and economic processes in a society: the distribution of power and wealth between different groups and individuals, and the processes that create, sustain and transform these relationships over time. It highlights: • Politics --- contestation and bargaining over rights and resources • Economic processes that generate wealth and influence politics • Dynamic context – processes of change over time. . . /cont’d Europe. Aid
 What is political economy analysis? (b) Highlights (cont’d): • Pathways of change (‘theories of change’): what determines these, and how (if at all) can aid influence them? • Interests and incentives and how these generate policy outcomes • Role of formal institutions and informal social, political and cultural norms Useful when: • thinking about the feasibility/likelihood (or ‘political traction’) of policy / institutional change • Considering risks to a country strategy and programmes Europe. Aid
What is political economy analysis? (b) Highlights (cont’d): • Pathways of change (‘theories of change’): what determines these, and how (if at all) can aid influence them? • Interests and incentives and how these generate policy outcomes • Role of formal institutions and informal social, political and cultural norms Useful when: • thinking about the feasibility/likelihood (or ‘political traction’) of policy / institutional change • Considering risks to a country strategy and programmes Europe. Aid
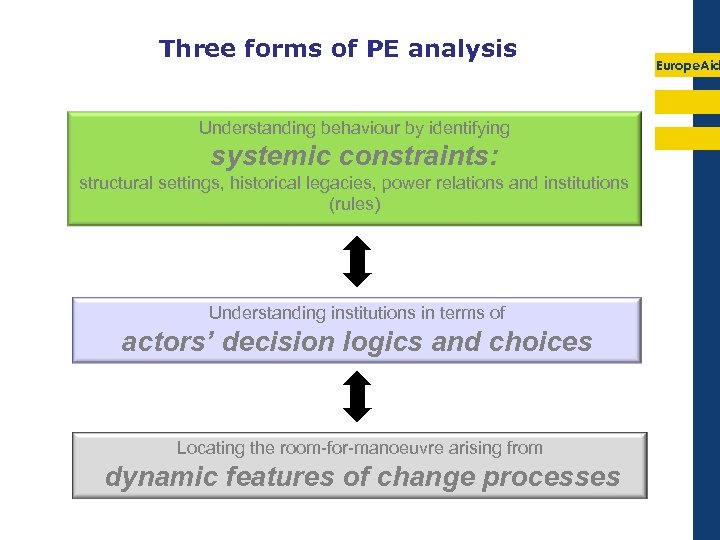 Three forms of PE analysis Understanding behaviour by identifying systemic constraints: structural settings, historical legacies, power relations and institutions (rules) Understanding institutions in terms of actors’ decision logics and choices Locating the room-for-manoeuvre arising from dynamic features of change processes Europe. Aid
Three forms of PE analysis Understanding behaviour by identifying systemic constraints: structural settings, historical legacies, power relations and institutions (rules) Understanding institutions in terms of actors’ decision logics and choices Locating the room-for-manoeuvre arising from dynamic features of change processes Europe. Aid
 Part B How is PEA carried out? An overview of frameworks for political economy analysis It is not a hard science; there are different intellectual traditions; there is no single method Europe. Aid
Part B How is PEA carried out? An overview of frameworks for political economy analysis It is not a hard science; there are different intellectual traditions; there is no single method Europe. Aid
 Terminology: frameworks and tools Framework: a broad approach to political economy analysis which includes a structured set of questions to be addressed Tool: a means of addressing one or more of the questions set out in the framework (e. g. stakeholder analysis) Europe. Aid
Terminology: frameworks and tools Framework: a broad approach to political economy analysis which includes a structured set of questions to be addressed Tool: a means of addressing one or more of the questions set out in the framework (e. g. stakeholder analysis) Europe. Aid
 Some frameworks Drivers of change Strategic Governance and Corruption Assessment (SGACA) SIDA Power Analysis Democratic Governance Assessment (US) And now: new concept paper of the EC …. . They are evolving all the time, but they share common features…. Europe. Aid
Some frameworks Drivers of change Strategic Governance and Corruption Assessment (SGACA) SIDA Power Analysis Democratic Governance Assessment (US) And now: new concept paper of the EC …. . They are evolving all the time, but they share common features…. Europe. Aid
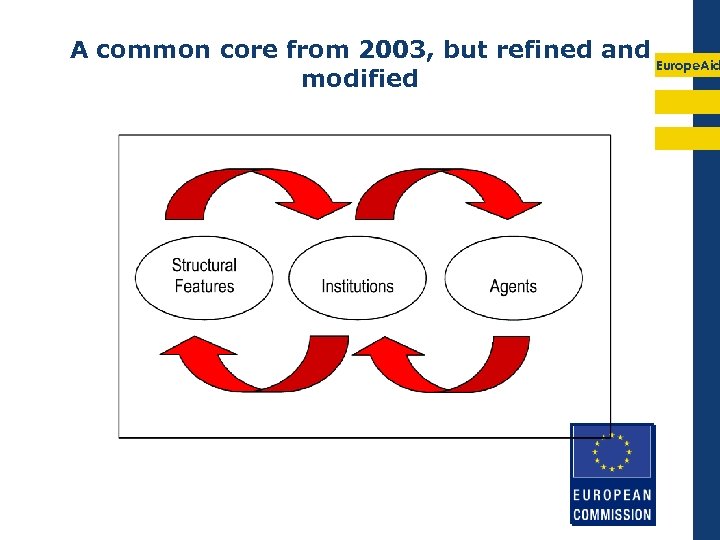 A common core from 2003, but refined and Europe. Aid modified
A common core from 2003, but refined and Europe. Aid modified
 Example 1: Drivers of Change What does it cover? 1. Basic country analysis 2. Medium-term dynamics 3. External forces, including donors 4. Link between change and poverty outcomes 5. Operational implications 6. How agencies work --- internal incentives Europe. Aid
Example 1: Drivers of Change What does it cover? 1. Basic country analysis 2. Medium-term dynamics 3. External forces, including donors 4. Link between change and poverty outcomes 5. Operational implications 6. How agencies work --- internal incentives Europe. Aid
 Europe. Aid Example 2: SGACA Power and change analysis: 1. Structured method 2. Framework of analysis and detailed questions 3. Workshops -- test, internalise 4. Rapid
Europe. Aid Example 2: SGACA Power and change analysis: 1. Structured method 2. Framework of analysis and detailed questions 3. Workshops -- test, internalise 4. Rapid
 SGACA – the framework • Foundational factors – Territorial integrity; state formation; revenue; social and economic structures; geo-strategic; geography • Rules of the game – Formal, informal; political competition; institutionalisation; distribution of power; statesociety relations; trends • Here and now – Context; actors • Operational implications – Most important challenges; how they explain performance; incentives for change; opportunities and threats for donors Europe. Aid
SGACA – the framework • Foundational factors – Territorial integrity; state formation; revenue; social and economic structures; geo-strategic; geography • Rules of the game – Formal, informal; political competition; institutionalisation; distribution of power; statesociety relations; trends • Here and now – Context; actors • Operational implications – Most important challenges; how they explain performance; incentives for change; opportunities and threats for donors Europe. Aid
 Applied at three levels PEA has been applied at three levels: • Country/macro-level • Sectoral/thematic • Project-level or micro Analysis at each of these can be more contextual or more problem-focussed • Problem-focussed: geared to understanding and resolving a particular problem at any level (projectspecific, or in relation to a policy issue e. g. growth or public financial management reform. ) Europe. Aid
Applied at three levels PEA has been applied at three levels: • Country/macro-level • Sectoral/thematic • Project-level or micro Analysis at each of these can be more contextual or more problem-focussed • Problem-focussed: geared to understanding and resolving a particular problem at any level (projectspecific, or in relation to a policy issue e. g. growth or public financial management reform. ) Europe. Aid
 Europe. Aid Level 1: Country/macro To enhance general sensitivity to country context and understanding of the broad Political-economy environment useful to inform country planning processes and the overall strategic direction of country programmes Links outward to international and regional context. . .
Europe. Aid Level 1: Country/macro To enhance general sensitivity to country context and understanding of the broad Political-economy environment useful to inform country planning processes and the overall strategic direction of country programmes Links outward to international and regional context. . .
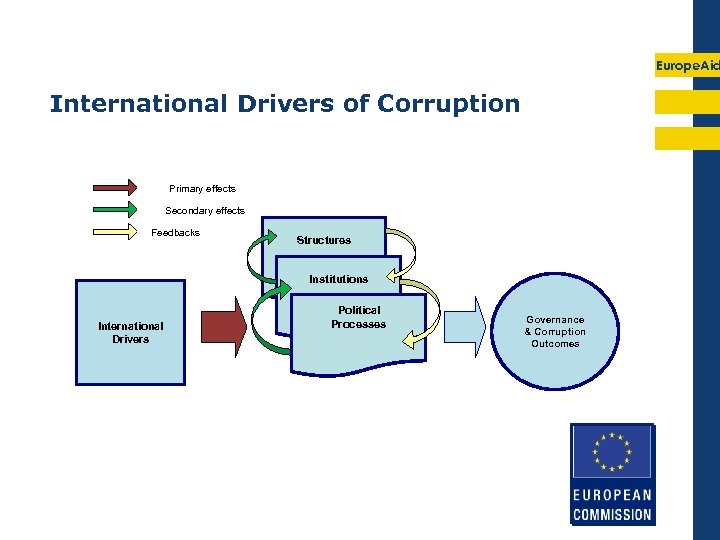 Europe. Aid International Drivers of Corruption Primary effects Secondary effects Feedbacks Structures Institutions International Drivers Political Processes Governance & Corruption Outcomes
Europe. Aid International Drivers of Corruption Primary effects Secondary effects Feedbacks Structures Institutions International Drivers Political Processes Governance & Corruption Outcomes
 Level 2: Sectoral/thematic Sector-level analysis: • to identify specific barriers and opportunities within particular sectors where DEVCO is working e. g. health, education, roads. Thematic: • To examine issues arising in relation to one of the enduring non-sectoral challenges of development (e. g. promotion of well-distributed economic growth) or cross-cutting issues (e. g. gender, environment or accountability) Europe. Aid
Level 2: Sectoral/thematic Sector-level analysis: • to identify specific barriers and opportunities within particular sectors where DEVCO is working e. g. health, education, roads. Thematic: • To examine issues arising in relation to one of the enduring non-sectoral challenges of development (e. g. promotion of well-distributed economic growth) or cross-cutting issues (e. g. gender, environment or accountability) Europe. Aid
 Sectoral (continued) ODI/DFID: 1. Start with country analysis 2. Define sector: players, relations 3. Political analysis of sector (roles, structures, leadership, finance, incentives) 4. How players influence policy 5. Operational implications Also: Jean Bossuyt presentation Europe. Aid
Sectoral (continued) ODI/DFID: 1. Start with country analysis 2. Define sector: players, relations 3. Political analysis of sector (roles, structures, leadership, finance, incentives) 4. How players influence policy 5. Operational implications Also: Jean Bossuyt presentation Europe. Aid
 Level 3: Project/micro To apply PEA to issues of project/programme design and implementation, or in a specific locality, so as to: • identify opportunities and barriers, and • maximise likelihood of political traction Project/micro will often be more problemfocussed than contextual Europe. Aid
Level 3: Project/micro To apply PEA to issues of project/programme design and implementation, or in a specific locality, so as to: • identify opportunities and barriers, and • maximise likelihood of political traction Project/micro will often be more problemfocussed than contextual Europe. Aid
 Europe. Aid PART C Two experiences of applying PEA to governance: Rwanda and Bangladesh
Europe. Aid PART C Two experiences of applying PEA to governance: Rwanda and Bangladesh
 Why governance, when we are considering PE? This is PE applied to a routine part of the cycle of analysis and decisions of most DPs – it is not something separate PE adds value to the ‘What? ’ of governance analysis by asking • ‘Why? ’ • ‘How promote change? ’ Europe. Aid
Why governance, when we are considering PE? This is PE applied to a routine part of the cycle of analysis and decisions of most DPs – it is not something separate PE adds value to the ‘What? ’ of governance analysis by asking • ‘Why? ’ • ‘How promote change? ’ Europe. Aid
 What was done (1) Rwanda? • Came from Kagame in DPs/GOR retreat late 2006. Fed up with multiple and inconsistent analyses; DPs too not happy with multiplication • Joint and equal ownership (Government and DPs): reflected in oversight – Steering group, technical group • Objectives: rigorous credible review of institutions laws, processes bearing on governance, and make recommendations; indicators; monitoring system • Implementation 2008: competitive tender; TORs’ multiple aims; coverage (Ruling Justly, Govt effectiveness; investment environment); 3 phases – methodology; implementation; presentation of draft; finalisation. Mid-term adjustment; Cabinet approval • 2010 follow-up on monitoring indicators; discussion on full JGA re-run in 2012. Europe. Aid
What was done (1) Rwanda? • Came from Kagame in DPs/GOR retreat late 2006. Fed up with multiple and inconsistent analyses; DPs too not happy with multiplication • Joint and equal ownership (Government and DPs): reflected in oversight – Steering group, technical group • Objectives: rigorous credible review of institutions laws, processes bearing on governance, and make recommendations; indicators; monitoring system • Implementation 2008: competitive tender; TORs’ multiple aims; coverage (Ruling Justly, Govt effectiveness; investment environment); 3 phases – methodology; implementation; presentation of draft; finalisation. Mid-term adjustment; Cabinet approval • 2010 follow-up on monitoring indicators; discussion on full JGA re-run in 2012. Europe. Aid
 What was done (2): Bangladesh Europe. Aid • Harmonisation: all donors in governance group • But stated aspiration is to do it with Govt. • Objectives: common understanding among DPs; shared vision, basis for action; basis for dialogue with Govt; NO recommendations for govt. • Ownership is with consultancy team; but if DPs want to take it over, OK • Implementation 2010: Steering Group (technical not political); local organisation plus international • Three stages: methodology; implementation; workshop – presentation / implications • Content: solid PE core; chapter on DPs • Shared analysis – little/no disagreement • How much follow-up? Don’t yet know.
What was done (2): Bangladesh Europe. Aid • Harmonisation: all donors in governance group • But stated aspiration is to do it with Govt. • Objectives: common understanding among DPs; shared vision, basis for action; basis for dialogue with Govt; NO recommendations for govt. • Ownership is with consultancy team; but if DPs want to take it over, OK • Implementation 2010: Steering Group (technical not political); local organisation plus international • Three stages: methodology; implementation; workshop – presentation / implications • Content: solid PE core; chapter on DPs • Shared analysis – little/no disagreement • How much follow-up? Don’t yet know.
 Lessons (1) 1. Clarity of purpose and scope essential o Different in the two cases o Range of possible purposes: Inform ourselves; Share understanding among DPs; Basis for dialogue with Govt; Determine financial flows? o Both were country/macro 2. How much appetite for PE? o Rwanda: Not much on part of Govt o Bangladesh – much more – but owned by consultants 3. Oversight arrangements o Inclusive o Need to be manageable / efficient o Rwanda – Govt and DPs had to negotiate using oversight forum o Consultants need close contact Europe. Aid
Lessons (1) 1. Clarity of purpose and scope essential o Different in the two cases o Range of possible purposes: Inform ourselves; Share understanding among DPs; Basis for dialogue with Govt; Determine financial flows? o Both were country/macro 2. How much appetite for PE? o Rwanda: Not much on part of Govt o Bangladesh – much more – but owned by consultants 3. Oversight arrangements o Inclusive o Need to be manageable / efficient o Rwanda – Govt and DPs had to negotiate using oversight forum o Consultants need close contact Europe. Aid
 Lessons (2) 4. Role / composition of consultancy team o Can it be done in-house? If so, good o Build in DP staff if possible o Rwanda: technical input / challenge / facilitation o Bangladesh: owned product; more straightforward o Local / international o Within team: structure questions; specialist country/sector knowledge 5. Consultative process o External • Rwanda – big public forum, and district meetings • Bangladesh: used literature more, so meetings were supplementary – some group meetings, e. g. private business. o Internal with DPs in Bangladesh – important for drawing out operational implications Europe. Aid
Lessons (2) 4. Role / composition of consultancy team o Can it be done in-house? If so, good o Build in DP staff if possible o Rwanda: technical input / challenge / facilitation o Bangladesh: owned product; more straightforward o Local / international o Within team: structure questions; specialist country/sector knowledge 5. Consultative process o External • Rwanda – big public forum, and district meetings • Bangladesh: used literature more, so meetings were supplementary – some group meetings, e. g. private business. o Internal with DPs in Bangladesh – important for drawing out operational implications Europe. Aid
 Lessons (3) 6. How normative? o Rwanda: local conditions as starting point + explicit international norms o Bangladesh: starting point local conditions also; ‘prevailing’ expectations 7. Indicators o Rwanda: 45; quite tough; monitored 2010/11 o Bangladesh: • No recommendations for Government, therefore no indicators; • set out international experiences; critique of existing Bangladesh indicators 8. How public to be (trade-off) o Depends on aim, type of analysis o Use consultants’ name and deniability 9. Build and use local organisations for sustainability Europe. Aid
Lessons (3) 6. How normative? o Rwanda: local conditions as starting point + explicit international norms o Bangladesh: starting point local conditions also; ‘prevailing’ expectations 7. Indicators o Rwanda: 45; quite tough; monitored 2010/11 o Bangladesh: • No recommendations for Government, therefore no indicators; • set out international experiences; critique of existing Bangladesh indicators 8. How public to be (trade-off) o Depends on aim, type of analysis o Use consultants’ name and deniability 9. Build and use local organisations for sustainability Europe. Aid
 Europe. Aid Part D What effects has applying PEA had?
Europe. Aid Part D What effects has applying PEA had?
 What use has been made of PEA? Some effect, but uptake limited overall. Several areas to go further: • Thinking • Strategy • Dialogue / Operations • Development effectiveness, aid effectiveness Europe. Aid
What use has been made of PEA? Some effect, but uptake limited overall. Several areas to go further: • Thinking • Strategy • Dialogue / Operations • Development effectiveness, aid effectiveness Europe. Aid
 Evidence of impact on development effectiveness and aid effectiveness? No review (yet) of overall impact of PEA; there’s a good case for one Europe. Aid
Evidence of impact on development effectiveness and aid effectiveness? No review (yet) of overall impact of PEA; there’s a good case for one Europe. Aid
 Challenges to adoption of PEA (1) Europe. Aid Supply side: get product right, get message across • Clarify aim; beyond contextual analysis • Big-picture issues, but more problem-focussed • Positive approach; avoid ‘dismal science of constraints’ • Manage expectations • ‘Sell’ approach better
Challenges to adoption of PEA (1) Europe. Aid Supply side: get product right, get message across • Clarify aim; beyond contextual analysis • Big-picture issues, but more problem-focussed • Positive approach; avoid ‘dismal science of constraints’ • Manage expectations • ‘Sell’ approach better
 Challenges to adoption of PEA (2) The PE of development agencies • hard to explain to governments and publics • pressure to disburse funds • short time horizons • pressure from domestic lobbies • the need to tell positive story • complex motivations • costs and risks for staff Europe. Aid
Challenges to adoption of PEA (2) The PE of development agencies • hard to explain to governments and publics • pressure to disburse funds • short time horizons • pressure from domestic lobbies • the need to tell positive story • complex motivations • costs and risks for staff Europe. Aid
 Challenges to adoption of PEA (3) Europe. Aid Organisational culture, values and beliefs • pressure to get things done • wishful thinking • preference for experts • inflated view of donors’ importance • preference formal institutions and lack of understanding of the informal • models putting capacity at the centre • rapid staff turnover; institutional memory weak Legitimacy and sensitivity – sovereignty issues
Challenges to adoption of PEA (3) Europe. Aid Organisational culture, values and beliefs • pressure to get things done • wishful thinking • preference for experts • inflated view of donors’ importance • preference formal institutions and lack of understanding of the informal • models putting capacity at the centre • rapid staff turnover; institutional memory weak Legitimacy and sensitivity – sovereignty issues


