ec868e1db44ad4358d66d938b5c64c7f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 90

Euro. Docsis Introduction A short course about the introduction of Euro. Docsis 1. 1 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 1 Version:
Why this course? • Euro. Docsis 1. 1 is new • A lot of previous systems exist in Casema e. g. Demos, DVB, COM 21 • A lot of related subjects such as TPA, SI, SP, different OS IHN, EMC, LVD AAA, Qo. S but what does it mean? (even if you know them all, this presentation may be interesting for you) PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 2 Version:
Agenda for today • Euro. Docsis introduction – planning, – some features, – COM 21, DVB, Docsis, Euro. Docsis comparison • System Issues – NGP, implementation of other market areas, – system calculations (capacity, line price), – linking to the PC • Implementation issues – Suppliers comparison, – Self installation and provisioning PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 3 Version:

Our goals • Roll out without major surprises. • Broad knowledge about Euro. Docsis 1. 1 (not only technical possibilities and blockings, also the market related ones must be known) • Low line price (what the hell is line price!) (everybody knows its importance, nobody uses it, somebody calculated it, anybody does it his way) • Get a modem system that is cheaper and more flexible than COM 21's system today PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 4 Version:
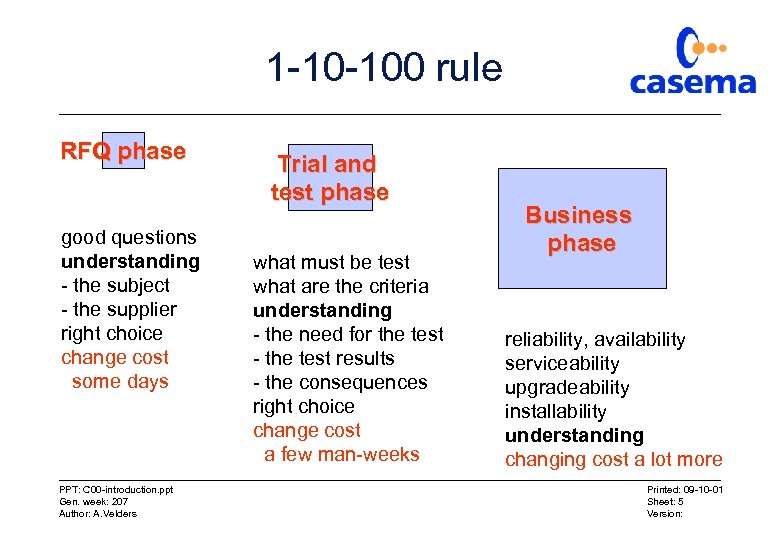
1 -10 -100 rule RFQ phase good questions understanding - the subject - the supplier right choice change cost some days PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Trial and test phase what must be test what are the criteria understanding - the need for the test - the test results - the consequences right choice change cost a few man-weeks Business phase reliability, availability serviceability upgradeability installability understanding changing cost a lot more Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 5 Version:

Issues that are (partly) not covered • Regulatory issues If it is mandatory, only the board can and must decide since the president (and his MT) is mostly personally responsible. Examples: – – LT Legal Tapping, government must be able to tap EMC Radiation & interfering other systems like air traffic LDV Low-Voltage Directive, Safety due to mains voltage IHN Configurations and responsibility (only TPA aspects) basis for seminar is: Cable operator is not responsible for IHN AOP + NTU + modem together, no usage of existing IHN for interactive traffic, Ethernet from modem to the PC 09 -10 -01 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt SI = Self installation Printed: Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Sheet: 6 Version:

Development of Euro-DOCSIS in Time Cursus voor niet-technici 3 mei 2002 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 7 Version:
Cable. Labs • In 1988, Cable. Labs was founded in the USA • Cable. Labs serves the cable television industry by: • researching and identifying new broadband technologies; • authoring specifications, certifying products and spreading information. • Cable. Labs benefits the cable television industry and consumers by: • enabling interoperability among different cable systems; • facilitating retail availability of cable modems and advanced services; and helping cable operators deploy innovative broadband technologies PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 8 Version:
DOCSIS summary Website: www. cablelabs. com PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 9 Version:
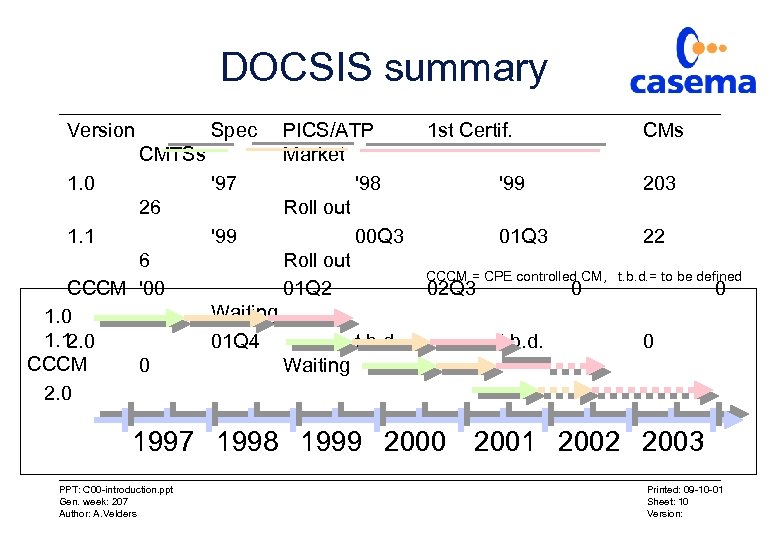
DOCSIS summary Version Spec CMTSs 1. 0 '97 26 1. 1 '99 6 CCCM '00 1. 1 2. 0 CCCM 0 2. 0 PICS/ATP Market '98 Roll out 00 Q 3 Roll out 01 Q 2 Waiting 01 Q 4 t. b. d. 1 st Certif. CMs '99 203 01 Q 3 22 CCCM = CPE controlled CM, t. b. d. = to be defined 02 Q 3 0 t. b. d. 0 0 Waiting 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 10 Version:
History of Euro-DOCSIS • In October 1999, TOCOF was founded and selected Ghent University to establish and conduct Euro-DOCSIS interoperability and certification program • In February 2000, Euro-DOCSIS annex N is approved • In May 2000, t. Com. Labs at Ghent and Euro-DOCSIS Certification Board (ECB) were founded • In June 2000, first certification wave for Euro-DOCSIS 1. 0 products by t. Com. Labs PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 11 Version:
Euro. DOCSIS summary Website: www. tcomlabs. com PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 12 Version:
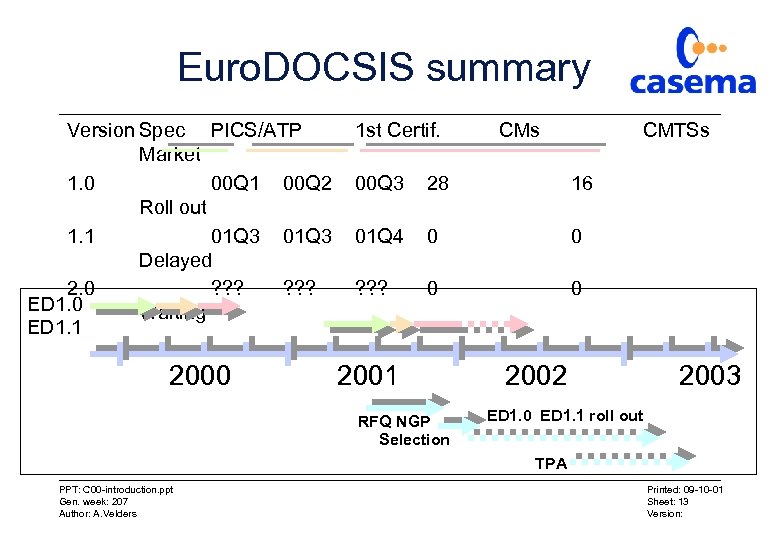
Euro. DOCSIS summary Version Spec PICS/ATP Market 1. 0 00 Q 1 00 Q 2 Roll out 1. 1 01 Q 3 Delayed 2. 0 ? ? ? ED 1. 0 Waiting ED 1. 1 2000 1 st Certif. CMs CMTSs 00 Q 3 28 16 01 Q 4 0 0 ? ? ? 0 0 2001 RFQ NGP Selection 2002 2003 ED 1. 0 ED 1. 1 roll out TPA PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 13 Version:

Euro-Docsis Technische inleiding PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 14 Version:
DOCSIS • • • Data Over Cable Services Interface Specifications PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 15 Version:

DOCSIS • Amerikaanse standaard • Gestandaardiseerde apparatuur • CM ( kabelmodem) en CMTS (netwerkapparatuur) mogen van een verschillende fabrikant zijn PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 16 Version:

Euro. DOCSIS • Europese versie van DOCSIS • Aanpassingen aan Europese kabelnetten – Kanaalbandbreedte – Upstream frequency range – Downstream frequency range PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 17 Version:
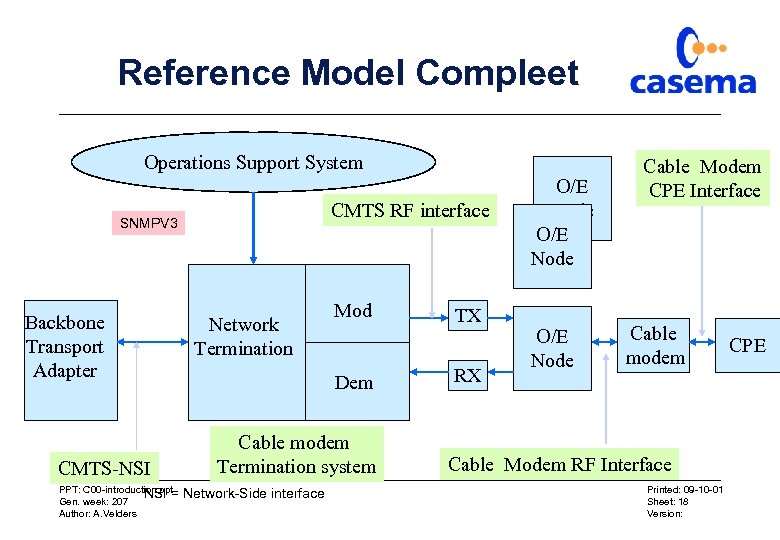
Reference Model Compleet Operations Support System CMTS RF interface SNMPV 3 Backbone Transport Adapter CMTS-NSI PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt NSI = Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Network Termination Mod Dem Cable modem Termination system Network-Side interface TX RX O/E Node Cable Modem CPE Interface Cable modem Cable Modem RF Interface Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 18 Version: CPE
Operations Support System • DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server • Time of Day Server • TFTP(Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 19 Version:

DHCP • De DHCP server zorgt voor: – Het IP adres van het Modem – Het IP adres van de Time of day server – Het IP adres van de TFTP server – Naam van de Config file – DCHP lease: tijd dat IP adres aan het modem is toegekend PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 20 Version:

Time of day Server • Zorgt voor: – de tijdsindicatie – samen met offset wordt dat de juiste lokale tijd PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 21 Version:
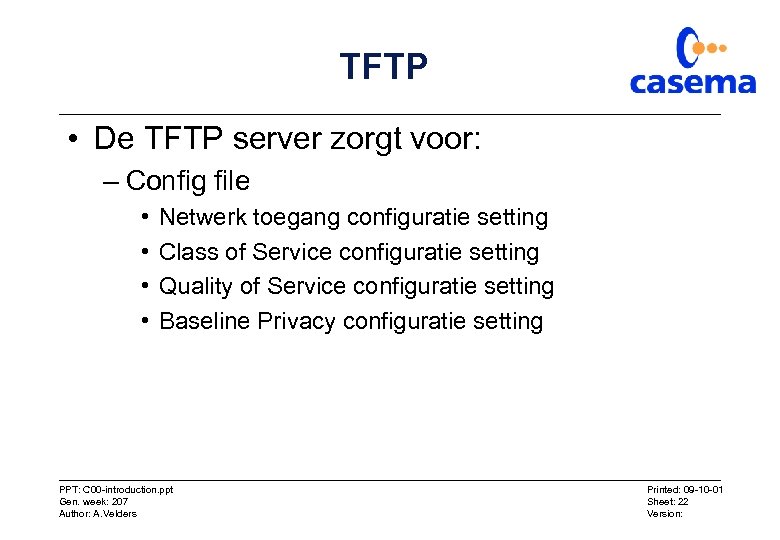
TFTP • De TFTP server zorgt voor: – Config file • • Netwerk toegang configuratie setting Class of Service configuratie setting Quality of Service configuratie setting Baseline Privacy configuratie setting PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 22 Version:

TPA • Toegang via derde partijen – Modem maakt verbinding met Casema – CPE (PC) maakt verbinding met ISP • Twee afzonderlijke procedures – CPE(PC) heeft IP adres – Modem heeft IP adres PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 23 Version:

Baseline Privacy • Bied een zeker niveau van versleuteling • Authenticiteit van CM en CTMS – Docsis 1. 0 BPI Niet voor CM – Docsis 1. 1 BPI Voor CM via digitale handtekening • Zorgt dat CM alleen toegang heeft tot diensten waarvoor het is geautoriseerd – Docsis 1. 0 via MAC adres PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 24 Version:

Baseline Privacy • Zorgt dat CM alleen toegang heeft tot diensten waarvoor het is geautoriseerd – Docsis 1. 0 via MAC adres – Docsis 1. 1 via MAC adres en Digitale handtekening. PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 25 Version:
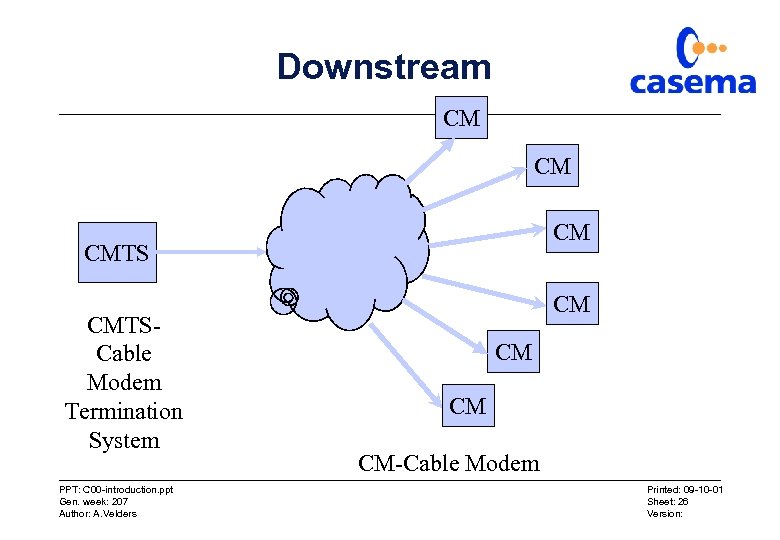
Downstream CM CMTSCable Modem Termination System PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders CM CM-Cable Modem Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 26 Version:
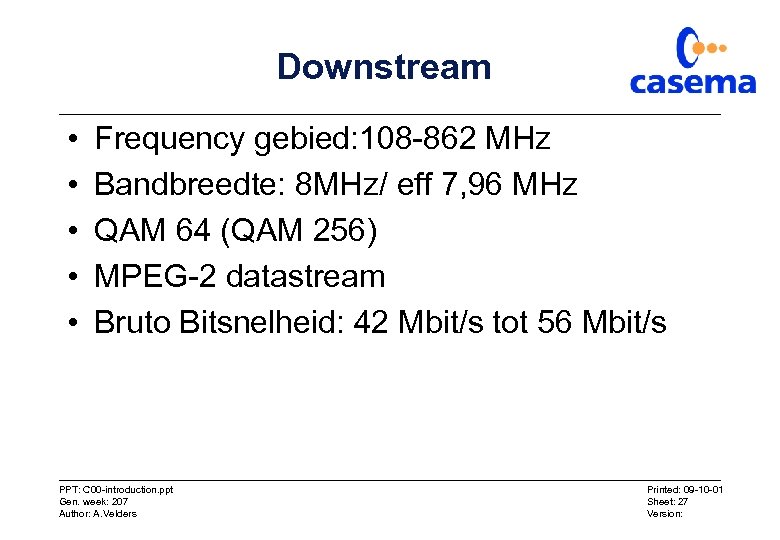
Downstream • • • Frequency gebied: 108 -862 MHz Bandbreedte: 8 MHz/ eff 7, 96 MHz QAM 64 (QAM 256) MPEG-2 datastream Bruto Bitsnelheid: 42 Mbit/s tot 56 Mbit/s PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 27 Version:
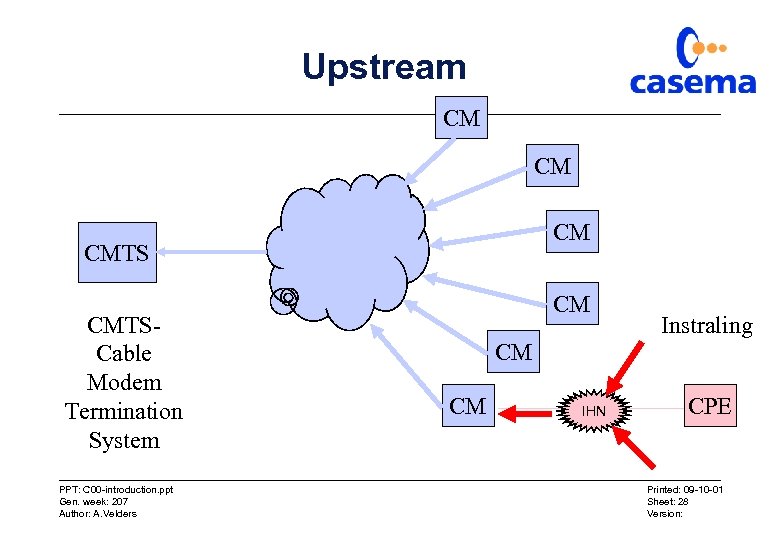
Upstream CM CMTSCable Modem Termination System PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders CM Instraling CM CM IHN CPE Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 28 Version:
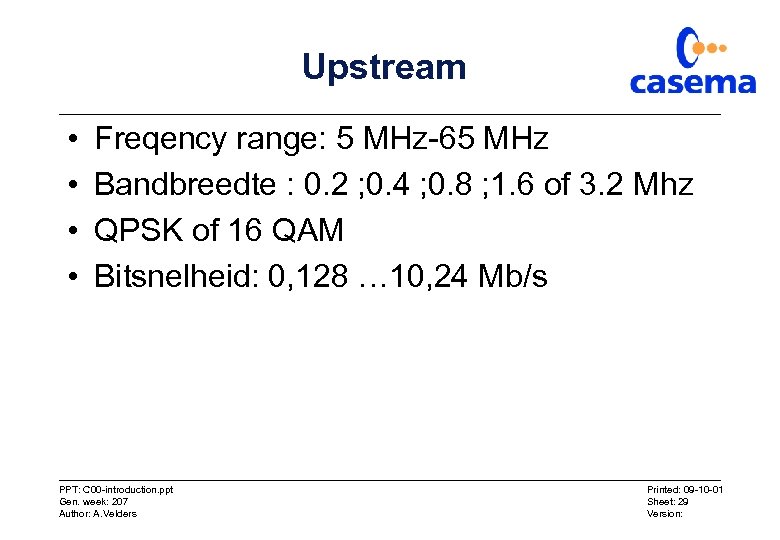
Upstream • • Freqency range: 5 MHz-65 MHz Bandbreedte : 0. 2 ; 0. 4 ; 0. 8 ; 1. 6 of 3. 2 Mhz QPSK of 16 QAM Bitsnelheid: 0, 128 … 10, 24 Mb/s PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 29 Version:
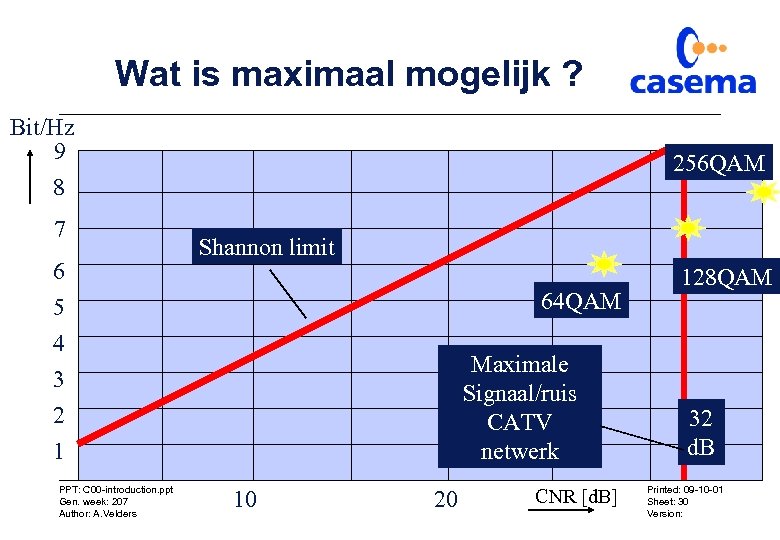
Wat is maximaal mogelijk ? Bit/Hz 9 8 7 6 256 QAM Shannon limit 64 QAM 5 4 3 2 1 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Maximale Signaal/ruis CATV netwerk 10 20 CNR [d. B] 128 QAM 32 d. B Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 30 Version:
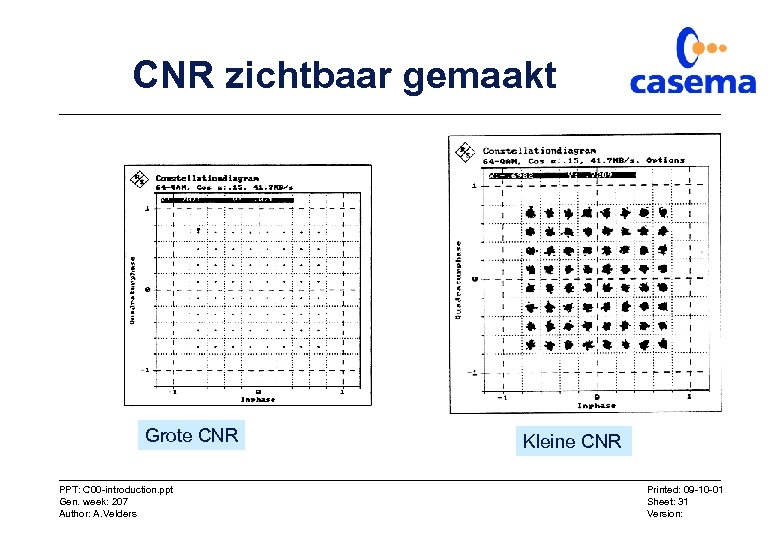
CNR zichtbaar gemaakt Grote CNR PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Kleine CNR Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 31 Version:

(Euro)Docsis to DVB/COM 21 issues the A short course about differences between DVB COM 21 and (Euro-)DOCSIS PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 32 Version:
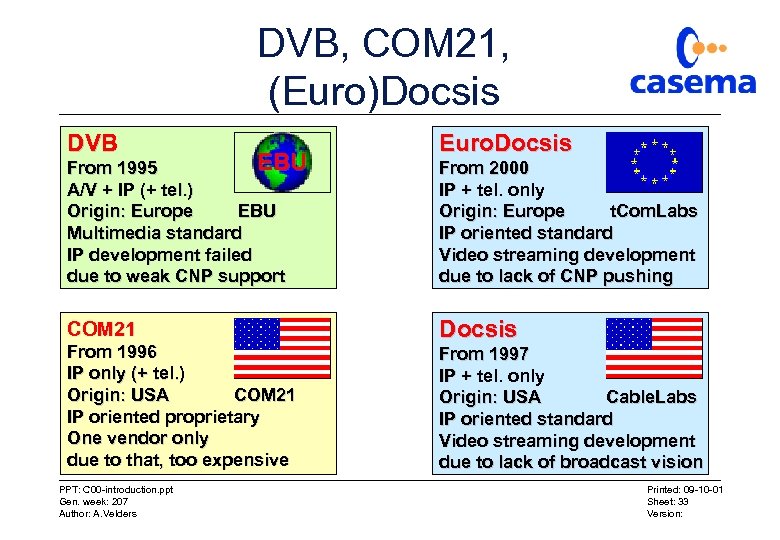
DVB, COM 21, (Euro)Docsis DVB EBU From 1995 A/V + IP (+ tel. ) Origin: Europe EBU Multimedia standard IP development failed due to weak CNP support COM 21 From 1996 IP only (+ tel. ) Origin: USA COM 21 IP oriented proprietary One vendor only due to that, too expensive PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Euro. Docsis From 2000 IP + tel. only Origin: Europe t. Com. Labs IP oriented standard Video streaming development due to lack of CNP pushing Docsis From 1997 IP + tel. only Origin: USA Cable. Labs IP oriented standard Video streaming development due to lack of broadcast vision Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 33 Version:
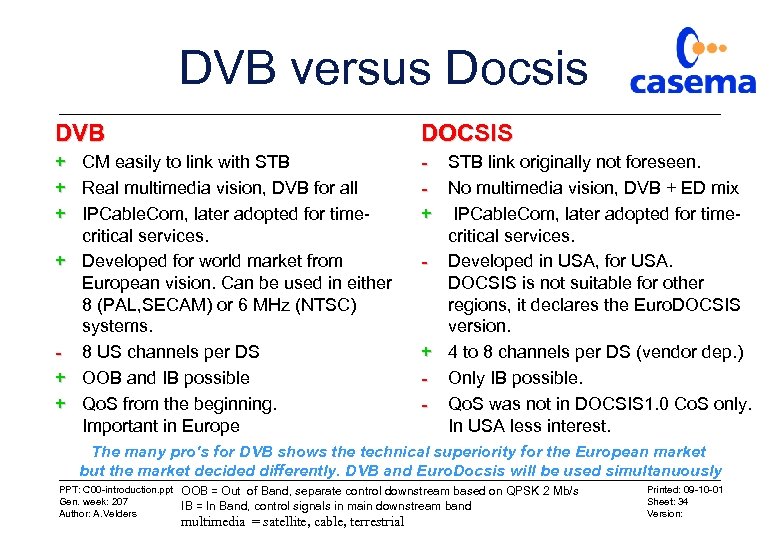
DVB versus Docsis DVB DOCSIS + CM easily to link with STB + Real multimedia vision, DVB for all + IPCable. Com, later adopted for timecritical services. + Developed for world market from European vision. Can be used in either 8 (PAL, SECAM) or 6 MHz (NTSC) systems. - 8 US channels per DS + OOB and IB possible + Qo. S from the beginning. Important in Europe - STB link originally not foreseen. - No multimedia vision, DVB + ED mix + IPCable. Com, later adopted for timecritical services. - Developed in USA, for USA. DOCSIS is not suitable for other regions, it declares the Euro. DOCSIS version. + 4 to 8 channels per DS (vendor dep. ) - Only IB possible. - Qo. S was not in DOCSIS 1. 0 Co. S only. In USA less interest. The many pro's for DVB shows the technical superiority for the European market but the market decided differently. DVB and Euro. Docsis will be used simultanuously PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders OOB = Out of Band, separate control downstream based on QPSK 2 Mb/s IB = In Band, control signals in main downstream band multimedia = satellite, cable, terrestrial Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 34 Version:
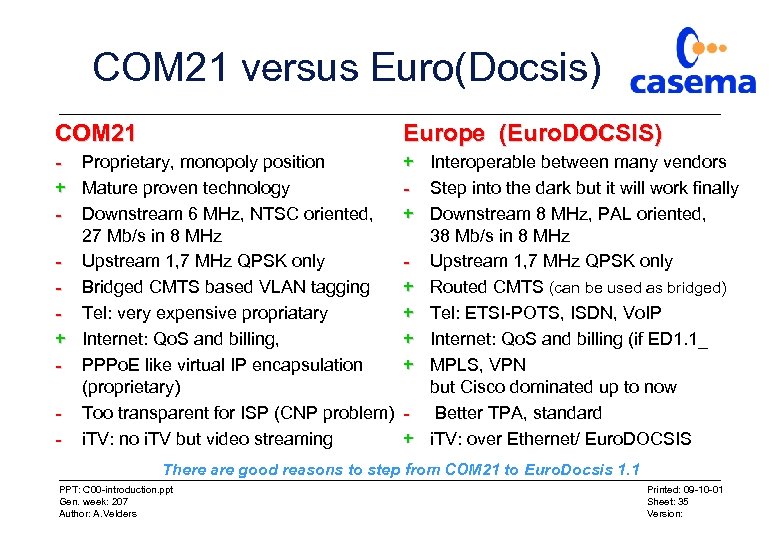
COM 21 versus Euro(Docsis) COM 21 Europe (Euro. DOCSIS) - Proprietary, monopoly position + Mature proven technology - Downstream 6 MHz, NTSC oriented, 27 Mb/s in 8 MHz - Upstream 1, 7 MHz QPSK only - Bridged CMTS based VLAN tagging - Tel: very expensive propriatary + Internet: Qo. S and billing, - PPPo. E like virtual IP encapsulation (proprietary) - Too transparent for ISP (CNP problem) - i. TV: no i. TV but video streaming + Interoperable between many vendors - Step into the dark but it will work finally + Downstream 8 MHz, PAL oriented, 38 Mb/s in 8 MHz - Upstream 1, 7 MHz QPSK only + Routed CMTS (can be used as bridged) + Tel: ETSI-POTS, ISDN, Vo. IP + Internet: Qo. S and billing (if ED 1. 1_ + MPLS, VPN but Cisco dominated up to now - Better TPA, standard + i. TV: over Ethernet/ Euro. DOCSIS There are good reasons to step from COM 21 to Euro. Docsis 1. 1 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 35 Version:
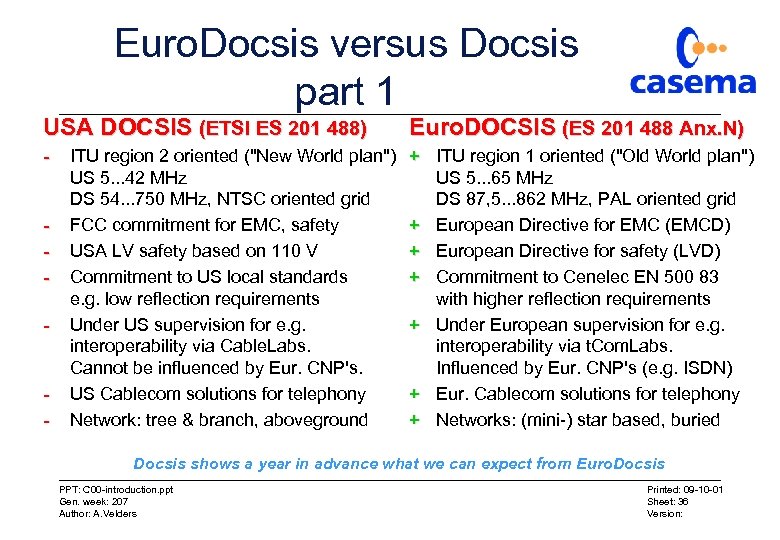
Euro. Docsis versus Docsis part 1 USA DOCSIS (ETSI ES 201 488) Euro. DOCSIS (ES 201 488 Anx. N) - + ITU region 1 oriented ("Old World plan") US 5. . . 65 MHz DS 87, 5. . . 862 MHz, PAL oriented grid + European Directive for EMC (EMCD) + European Directive for safety (LVD) + Commitment to Cenelec EN 500 83 with higher reflection requirements + Under European supervision for e. g. interoperability via t. Com. Labs. Influenced by Eur. CNP's (e. g. ISDN) + Eur. Cablecom solutions for telephony + Networks: (mini-) star based, buried - - ITU region 2 oriented ("New World plan") US 5. . . 42 MHz DS 54. . . 750 MHz, NTSC oriented grid FCC commitment for EMC, safety USA LV safety based on 110 V Commitment to US local standards e. g. low reflection requirements Under US supervision for e. g. interoperability via Cable. Labs. Cannot be influenced by Eur. CNP's. US Cablecom solutions for telephony Network: tree & branch, aboveground Docsis shows a year in advance what we can expect from Euro. Docsis PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 36 Version:
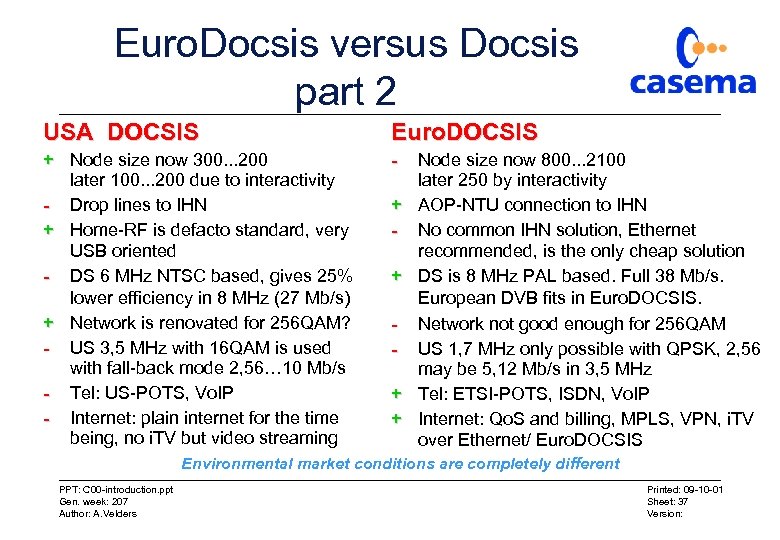
Euro. Docsis versus Docsis part 2 USA DOCSIS Euro. DOCSIS + Node size now 300. . . 200 later 100. . . 200 due to interactivity - Drop lines to IHN + Home-RF is defacto standard, very USB oriented - DS 6 MHz NTSC based, gives 25% lower efficiency in 8 MHz (27 Mb/s) + Network is renovated for 256 QAM? - US 3, 5 MHz with 16 QAM is used with fall-back mode 2, 56… 10 Mb/s - Tel: US-POTS, Vo. IP - Internet: plain internet for the time being, no i. TV but video streaming + + Node size now 800. . . 2100 later 250 by interactivity AOP-NTU connection to IHN No common IHN solution, Ethernet recommended, is the only cheap solution DS is 8 MHz PAL based. Full 38 Mb/s. European DVB fits in Euro. DOCSIS. Network not good enough for 256 QAM US 1, 7 MHz only possible with QPSK, 2, 56 may be 5, 12 Mb/s in 3, 5 MHz Tel: ETSI-POTS, ISDN, Vo. IP Internet: Qo. S and billing, MPLS, VPN, i. TV over Ethernet/ Euro. DOCSIS Environmental market conditions are completely different PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 37 Version:
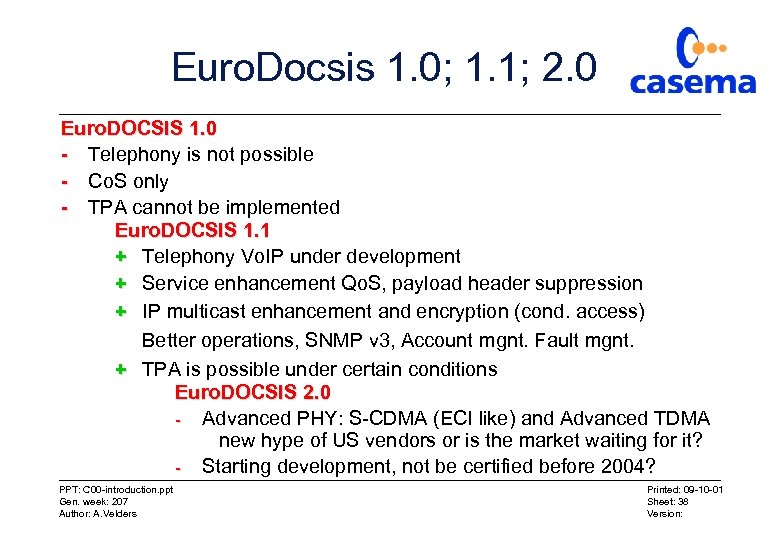
Euro. Docsis 1. 0; 1. 1; 2. 0 Euro. DOCSIS 1. 0 - Telephony is not possible - Co. S only - TPA cannot be implemented Euro. DOCSIS 1. 1 + Telephony Vo. IP under development + Service enhancement Qo. S, payload header suppression + IP multicast enhancement and encryption (cond. access) Better operations, SNMP v 3, Account mgnt. Fault mgnt. + TPA is possible under certain conditions Euro. DOCSIS 2. 0 - Advanced PHY: S-CDMA (ECI like) and Advanced TDMA new hype of US vendors or is the market waiting for it? - Starting development, not be certified before 2004? PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 38 Version:

Euro-DOCSIS and Telephony Cursus voor niet-technici 3 Mei 2002 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 39 Version:

Vo. IP / IP Telephony / Internet Telephony • Gedachten van Vo. IP varieren van persoon tot persoon • 3 verschillende voorbeelden Vo. IP / IP Telephony: - Voice-over-Internet meestal ‘PC-to-PC’ of ‘PC-to-Phone’ - Corporate Vo. IP bedrijfstelefonie, o. a. PBX - Carrier-grade Vo. IP gebruikelijke analoge telefoon De verschillen worden bepaald door type IP netwerk, toegepaste protocollen, apparatuur, e. d. PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 40 Version:
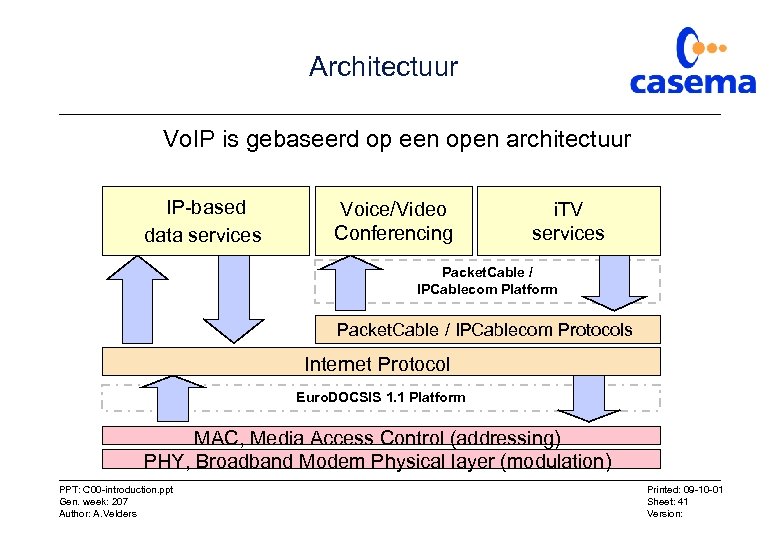
Architectuur Vo. IP is gebaseerd op een open architectuur IP-based data services Voice/Video Conferencing i. TV services Packet. Cable / IPCablecom Platform Packet. Cable / IPCablecom Protocols Internet Protocol Euro. DOCSIS 1. 1 Platform MAC, Media Access Control (addressing) PHY, Broadband Modem Physical layer (modulation) PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 41 Version:
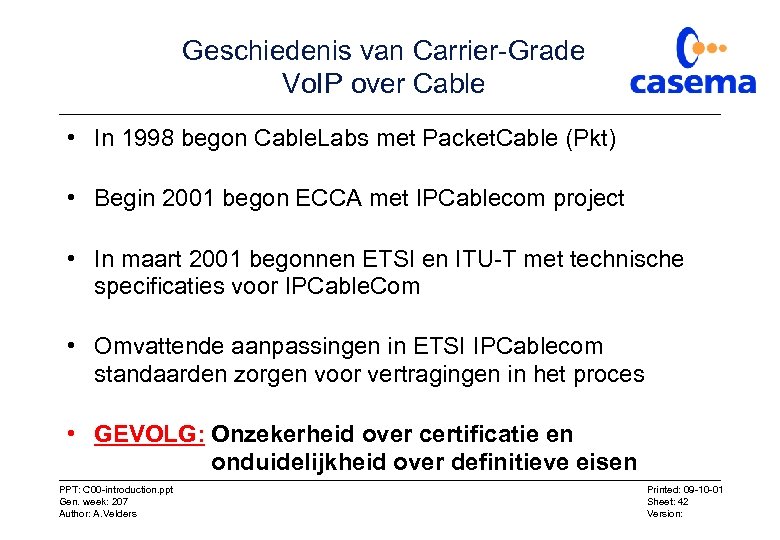
Geschiedenis van Carrier-Grade Vo. IP over Cable • In 1998 begon Cable. Labs met Packet. Cable (Pkt) • Begin 2001 begon ECCA met IPCablecom project • In maart 2001 begonnen ETSI en ITU-T met technische specificaties voor IPCable. Com • Omvattende aanpassingen in ETSI IPCablecom standaarden zorgen voor vertragingen in het proces • GEVOLG: Onzekerheid over certificatie en onduidelijkheid over definitieve eisen PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 42 Version:
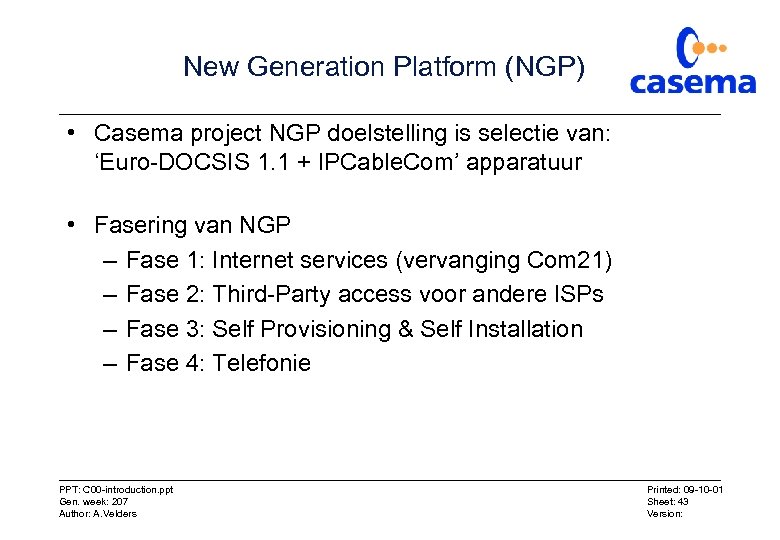
New Generation Platform (NGP) • Casema project NGP doelstelling is selectie van: ‘Euro-DOCSIS 1. 1 + IPCable. Com’ apparatuur • Fasering van NGP – Fase 1: Internet services (vervanging Com 21) – Fase 2: Third-Party access voor andere ISPs – Fase 3: Self Provisioning & Self Installation – Fase 4: Telefonie PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 43 Version:

Voice-over-NGP I • 2 architecturen gedefinieerd in IPCable. Com: – Fully Vo. IP (softswitch-gebaseerd) – Switched Vo. IP (gebruikmakend van PSTN switch) Casema heeft voor de ‘switched Vo. IP’ architectuur gekozen! PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 44 Version:
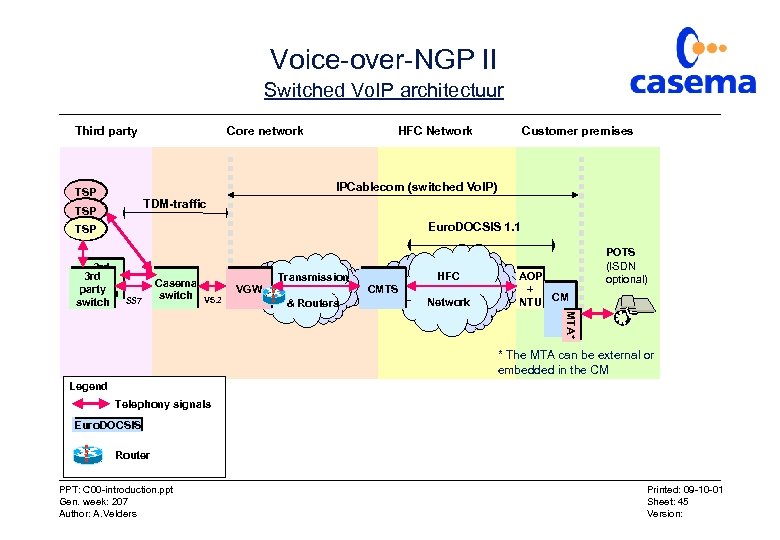
Voice-over-NGP II Switched Vo. IP architectuur Third party Core network HFC Network Customer premises IPCablecom (switched Vo. IP) TSP TDM-traffic TSP Euro. DOCSIS 1. 1 TSP 3 rd party switch SS 7 Casema switch V 5. 2 VGW Transmission Network AOP + NTU CM MTA* MTA & Routers HFC CMTS POTS (ISDN optional) * The MTA can be external or embedded in the CM Legend Telephony signals Euro. DOCSIS Router PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 45 Version:
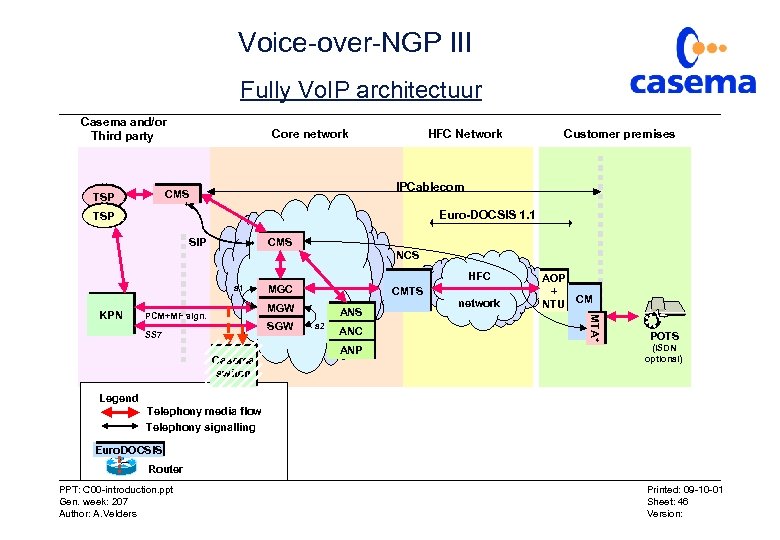
Voice-over-NGP III Fully Vo. IP architectuur Casema and/or Third party Core network Customer premises IPCablecom CMS TSP HFC Network Euro-DOCSIS 1. 1 TSP CMS SIP NCS HFC a 1 CMTS MGW PCM+MF sign. SGW SS 7 Casema switch ANS a 2 ANC ANP network AOP + NTU CM MTA* MTA KPN MGC POTS (ISDN optional) Legend Telephony media flow Telephony signalling Euro. DOCSIS Router PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 46 Version:

Het i. TV platform in NGP 3 mei 2002

Behandeld zal worden 1. Mogelijkheden van het gebruik van het i. TV platform in relatie tot NGP 2. Aandachtspunten c. q. mogelijk te verwachten problemen PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 48 Version:

Algemeen Twee scenario's voor transport interactieve data: • Via telefoonlijn dmv POTS modem in de STB: – Via KPN – Via MTA in het kabelmodem • Via kabel, down- and upstream via het HFC netwerk. Twee verschillende stromen: • A/V broadcast = het oversturen van het digitale video, audio en extra programma informatie, uitgezonden in een DVB-downstream kanaal. PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 49 Version:
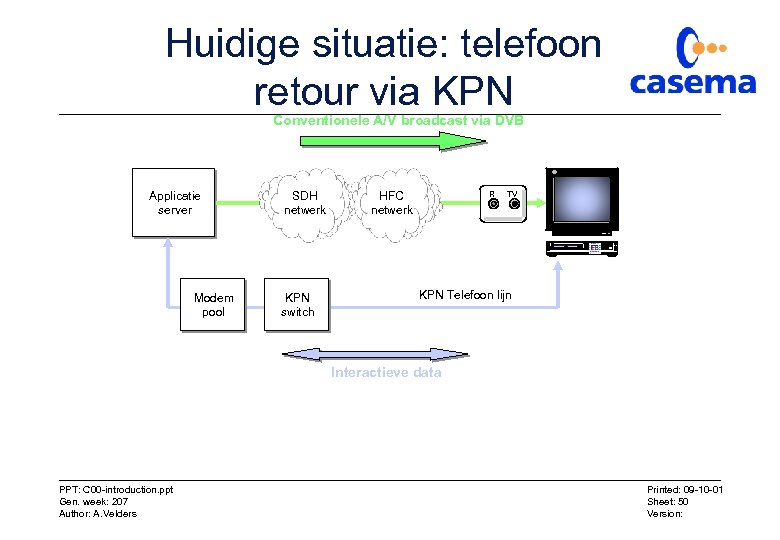
Huidige situatie: telefoon retour via KPN Conventionele A/V broadcast via DVB Applicatie server Modem pool SDH netwerk KPN switch HFC netwerk R TV KPN Telefoon lijn Interactieve data PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 50 Version:
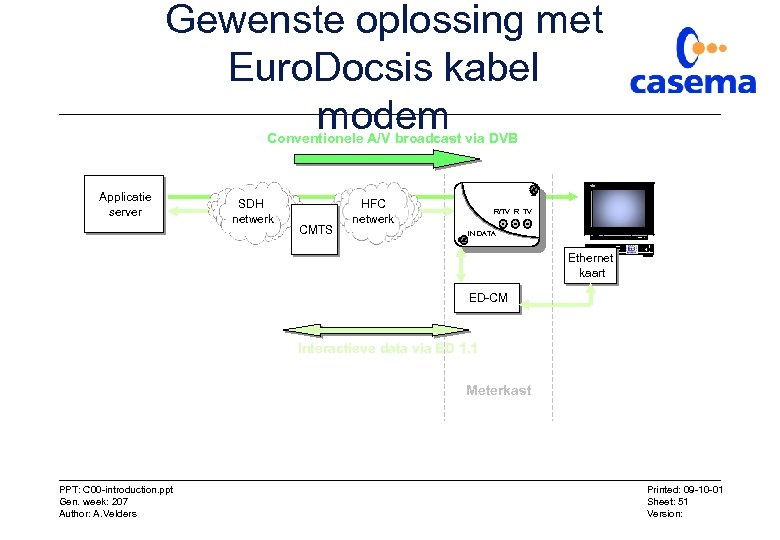
Gewenste oplossing met Euro. Docsis kabel modem Conventionele A/V broadcast via DVB Applicatie server SDH netwerk CMTS HFC netwerk R/TV R TV IN DATA Ethernet kaart ED-CM Interactieve data via ED 1. 1 Meterkast PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 51 Version:
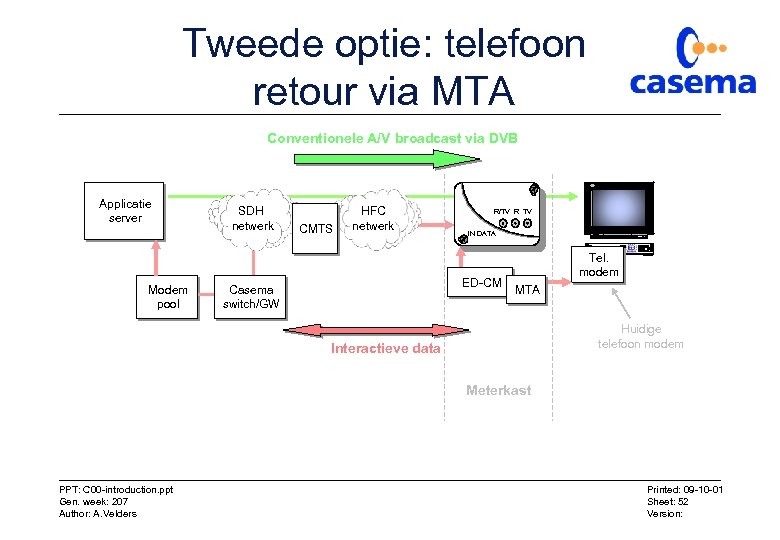
Tweede optie: telefoon retour via MTA Conventionele A/V broadcast via DVB Applicatie server Modem pool SDH netwerk CMTS HFC netwerk R/TV R TV IN DATA ED-CM Casema switch/GW Tel. modem MTA Huidige telefoon modem Interactieve data Meterkast PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 52 Version:
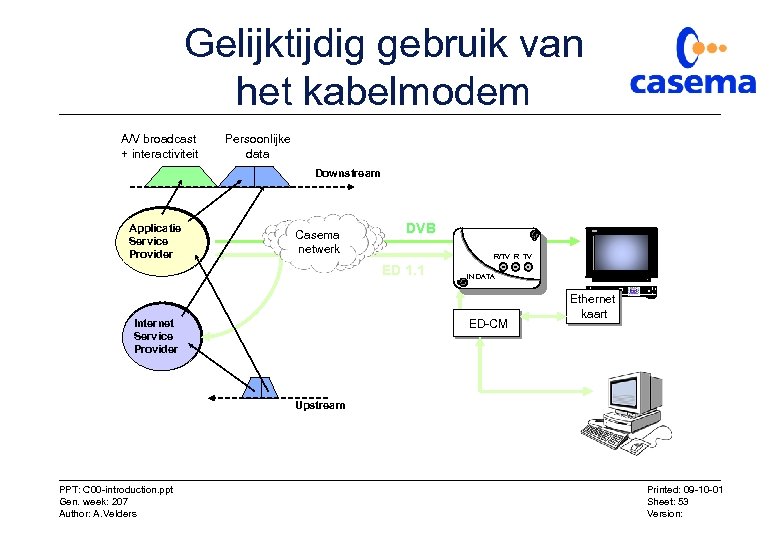
Gelijktijdig gebruik van het kabelmodem A/V broadcast + interactiviteit Persoonlijke data Downstream Applicatie Service Provider Casema netwerk DVB R/TV R TV ED 1. 1 IN DATA ED-CM Internet Service Provider Ethernet kaart Upstream PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 53 Version:
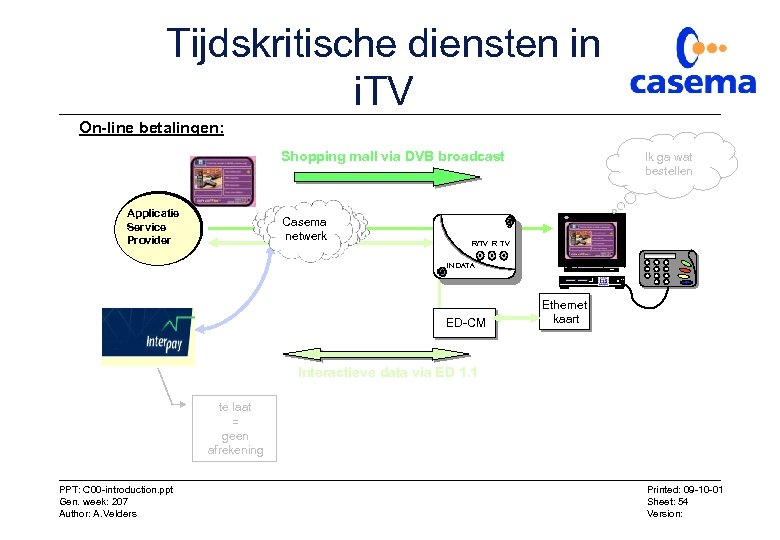
Tijdskritische diensten in i. TV On-line betalingen: Shopping mall via DVB broadcast Applicatie Service Provider Casema netwerk Ik ga wat bestellen R/TV R TV IN DATA ED-CM Ethernet kaart Interactieve data via ED 1. 1 te laat = geen afrekening PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 54 Version:
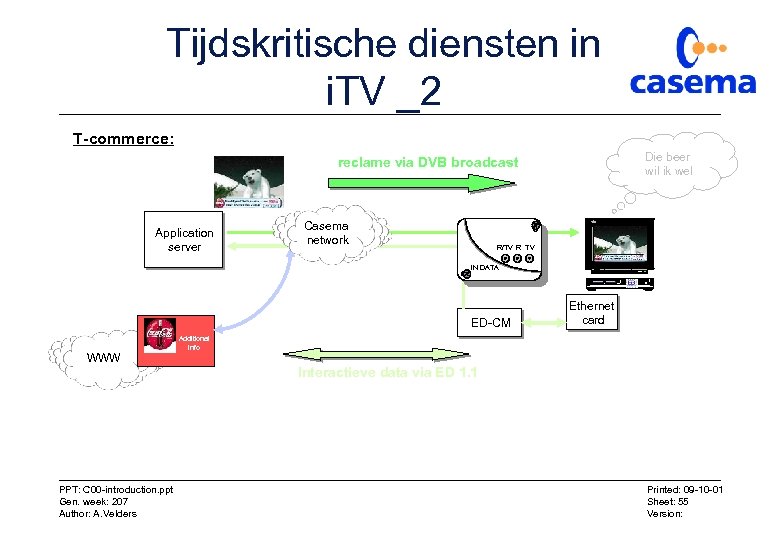
Tijdskritische diensten in i. TV _2 T-commerce: Die beer wil ik wel reclame via DVB broadcast Application server Casema network R/TV R TV IN DATA ED-CM WWW Ethernet card Additional info Interactieve data via ED 1. 1 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 55 Version:

Samengevat • i. TV mogelijk in het ED NGP – via het Internetplatform – via het Telefonie platform • Een aantal zaken zullen goed uitgezocht moeten worden – gelijktijdig gebruik PC en STB met de data communicatie tussen verschillende SP’s – het correct laten verlopen van tijdskritische diensten PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 56 Version:

Verschillen DVB en ED in relatie tot i. TV Mei, 2002

Algemeen • De DVB standaard is ontwikkeld voor digitale audio en video broadcast waaraan later een module is toegevoegd waarin interactiviteit geregeld wordt. Deze standaard is hierdoor uitermate bruikbaar voor de STB. • DOCSIS is ontwikkeld voor de internet omgeving maar wordt inmiddels ook gebruikt in de STB. PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 58 Version:

Verschillen in de downstream Euro. Docsis: • Modulatietechniek identiek aan DVB • MPEG transport alleen mogelijk via IP over ED. Aangezien dit zorgt voor timingproblemen is dit voor MPEG transport geen optie. DVB: • Twee methoden in de downstream: Out-Of-Band (OOB) and In-band (IB): – OOB: QPSK modulatie met een bandbreedte van 2 MHz met 3 Mb/s, is PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 59 Version:

Verschillen in de upstream Euro. Docsis: • De US modulatie kan QPSK zijn en 16 QAM. De standaard laat data snelheden toe* van 128 kb/s tot 10 Mb/s in zeven stappen. DVB: • US modulatie is QPSK. Mogelijke data snelheden zijn 256 kb/s tot 6 Mb/s in stappen van vier. Voor beide standaarden geldt dat de toegang naar de gedeelde US bandbreedte wordt geregeld via de MAC protocollen. De controllers in het HE regelen de toewijzing van de US bandbreedte, de manier PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 60 Version:

Belangrijkste punten • DVB: – Multimedia oplossing, bruikbaar in kabel, satelliet en terrestrial netwerken en voor audio/ video, internet en telefonie diensten. – Voor broadcast van audio en video in de downstream is DVB via Europese regelgeving verplicht gesteld. • Euro. Docsis: – Alleen te gebruiken in kabelnetwerk en voor de internet en telefonie diensten. i. TV PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 61 Version:

Euro. Docsis System calculations Short calculations you must know for Euro. Docsis 1. 1: speed, capacity, CMs/CMTS, line price PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 62 Version:
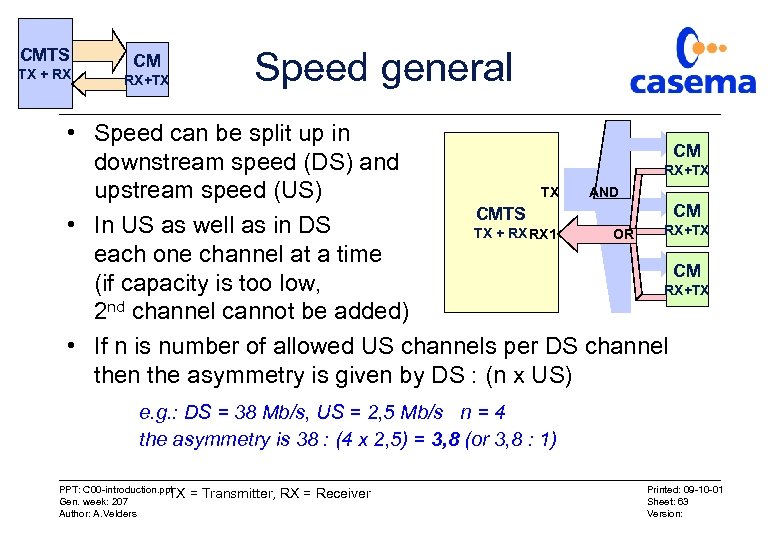
CMTS TX + RX CM RX+TX Speed general • Speed can be split up in CM downstream speed (DS) and RX+TX TX AND upstream speed (US) CM CMTS • In US as well as in DS RX+TX TX + RX RX 1 OR each one channel at a time CM (if capacity is too low, RX+TX 2 nd channel cannot be added) • If n is number of allowed US channels per DS channel then the asymmetry is given by DS : (n x US) e. g. : DS = 38 Mb/s, US = 2, 5 Mb/s n = 4 the asymmetry is 38 : (4 x 2, 5) = 3, 8 (or 3, 8 : 1) PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt TX Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders = Transmitter, RX = Receiver Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 63 Version:
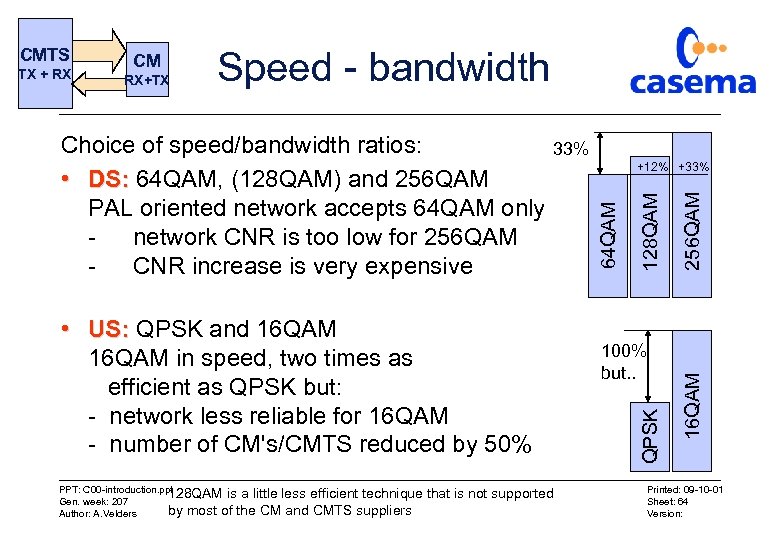
Speed - bandwidth 33% • US: QPSK and 16 QAM in speed, two times as efficient as QPSK but: - network less reliable for 16 QAM - number of CM's/CMTS reduced by 50% PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt 128 QAM is a little less efficient technique Gen. week: 207 by most of the CM and CMTS suppliers Author: A. Velders that is not supported +12% +33% 100% but. . 256 QAM Choice of speed/bandwidth ratios: • DS: 64 QAM, (128 QAM) and 256 QAM PAL oriented network accepts 64 QAM only network CNR is too low for 256 QAM CNR increase is very expensive 16 QAM RX+TX 128 QAM CM QPSK TX + RX 64 QAM CMTS Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 64 Version:
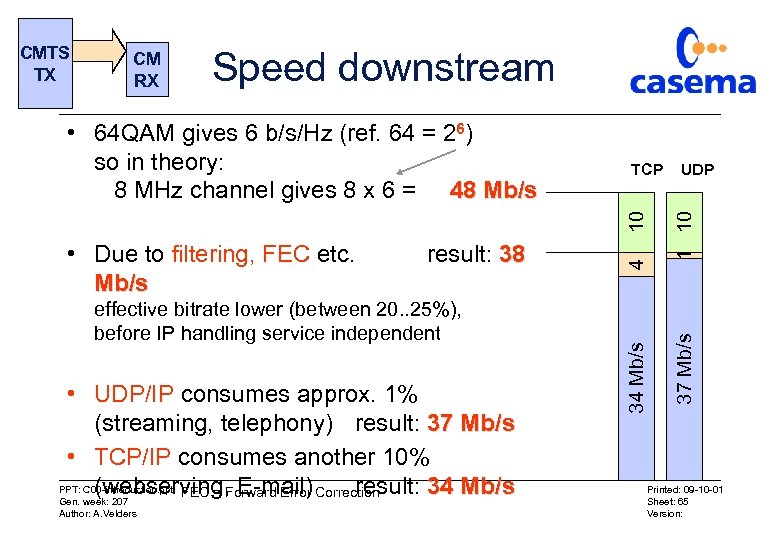
Speed downstream result: 38 effective bitrate lower (between 20. . 25%), before IP handling service independent • UDP/IP consumes approx. 1% (streaming, telephony) result: 37 Mb/s • TCP/IP consumes another 10% PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt FEC = Forward Error Correction (webserving, E-mail) result: 34 Mb/s Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders 1 10 • Due to filtering, FEC etc. Mb/s UDP 37 Mb/s TCP 10 • 64 QAM gives 6 b/s/Hz (ref. 64 = 26) so in theory: 8 MHz channel gives 8 x 6 = 48 Mb/s 4 CM RX 34 Mb/s CMTS TX Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 65 Version:

Speed upstream effective bitrate is lower (approx. 35%), before IP handling service independent • UDP/IP consumes approx. 5% (due to asymmetry) (streaming, telephony) result: 2, 5 Mb/s • TCP/IP consumes another 40% (due to asymmetry) (web serving, E-mail) result: 1, 5 Mb/s PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders 0, 84 0, 06 result: 2, 56 2, 5 Mb/s • Due to filtering, FEC etc. Mb/s TCP UDP 0, 84 • QPSK gives 2 b/s/Hz (ref. 4 = 22) so in theory: 1, 7 MHz channel gives 1, 7 x 2 = 3, 4 Mb/s 1, 06 Mb/s CM TX 1, 5 Mb/s CMTS RX Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 66 Version:
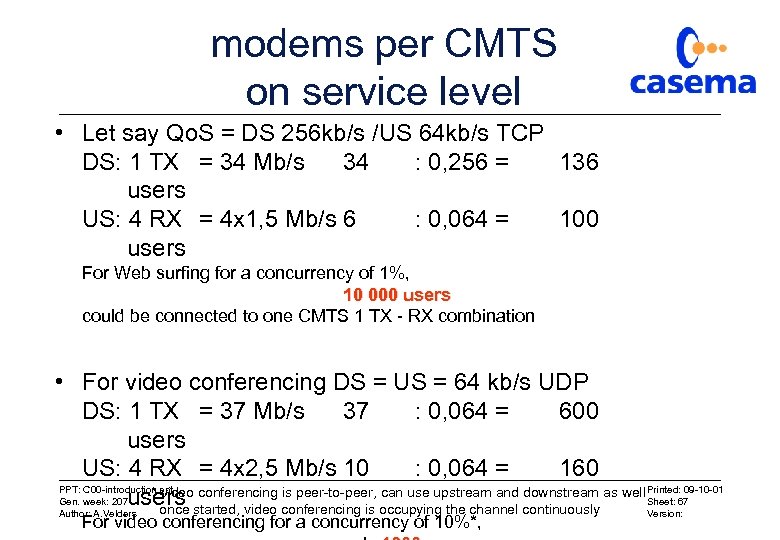
modems per CMTS on service level • Let say Qo. S = DS 256 kb/s /US 64 kb/s TCP DS: 1 TX = 34 Mb/s 34 : 0, 256 = 136 users US: 4 RX = 4 x 1, 5 Mb/s 6 : 0, 064 = 100 users For Web surfing for a concurrency of 1%, 10 000 users could be connected to one CMTS 1 TX - RX combination • For video conferencing DS = US = 64 kb/s UDP DS: 1 TX = 37 Mb/s 37 : 0, 064 = 600 users US: 4 RX = 4 x 2, 5 Mb/s 10 : 0, 064 = 160 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt * video conferencing is peer-to-peer, can use upstream and downstream as well Printed: 09 -10 -01 Gen. week: 207 users Sheet: 67 once started, video conferencing is occupying the channel continuously Author: A. Velders Version: For video conferencing for a concurrency of 10%*,
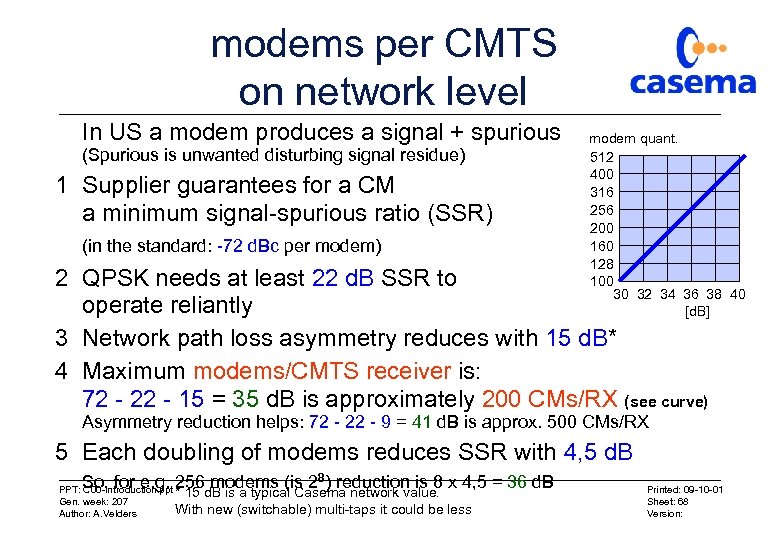
modems per CMTS on network level In US a modem produces a signal + spurious (Spurious is unwanted disturbing signal residue) 1 Supplier guarantees for a CM a minimum signal-spurious ratio (SSR) (in the standard: -72 d. Bc per modem) modem quant. 512 400 316 256 200 160 128 100 30 32 34 36 38 40 [d. B] 2 QPSK needs at least 22 d. B SSR to operate reliantly 3 Network path loss asymmetry reduces with 15 d. B* 4 Maximum modems/CMTS receiver is: 72 - 22 - 15 = 35 d. B is approximately 200 CMs/RX (see curve) Asymmetry reduction helps: 72 - 22 - 9 = 41 d. B is approx. 500 CMs/RX 5 Each doubling of modems reduces SSR with 4, 5 d. B So, for e. g. 256 modems (is 28) reduction is 8 x 4, 5 = 36 d. B PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt * 15 d. B is a typical Casema network value. Gen. week: 207 With new (switchable) multi-taps it could be Author: A. Velders less Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 68 Version:
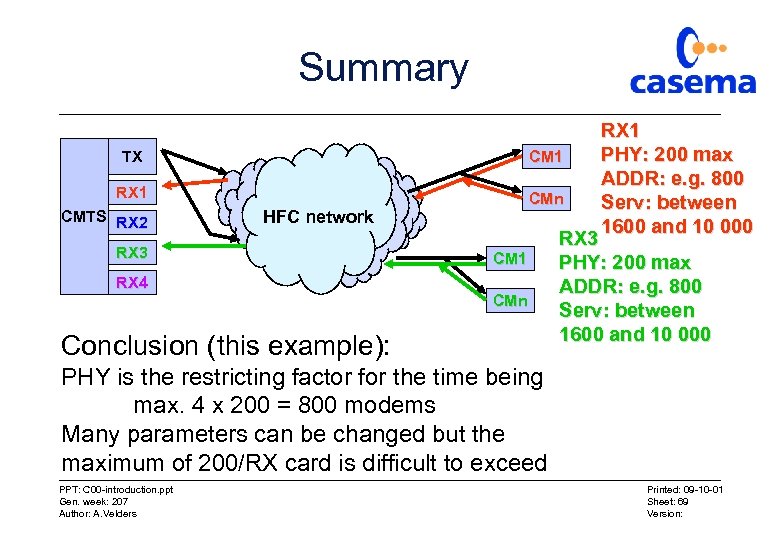
Summary TX CM 1 RX 1 CMn CMTS RX 2 HFC network RX 3 RX 4 CM 1 CMn Conclusion (this example): RX 1 PHY: 200 max ADDR: e. g. 800 Serv: between 1600 and 10 000 RX 3 PHY: 200 max ADDR: e. g. 800 Serv: between 1600 and 10 000 PHY is the restricting factor for the time being max. 4 x 200 = 800 modems Many parameters can be changed but the maximum of 200/RX card is difficult to exceed PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 69 Version:
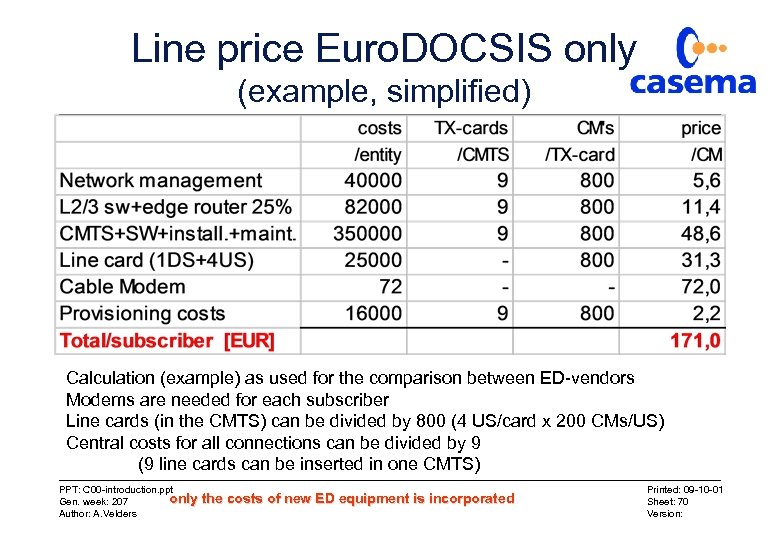
Line price Euro. DOCSIS only (example, simplified) Calculation (example) as used for the comparison between ED-vendors Modems are needed for each subscriber Line cards (in the CMTS) can be divided by 800 (4 US/card x 200 CMs/US) Central costs for all connections can be divided by 9 (9 line cards can be inserted in one CMTS) PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt only Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders the costs of new ED equipment is incorporated Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 70 Version:
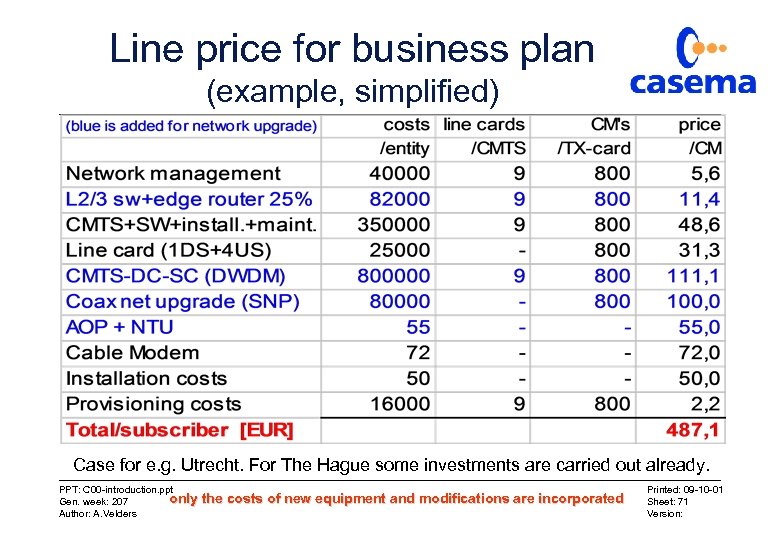
Line price for business plan (example, simplified) Case for e. g. Utrecht. For The Hague some investments are carried out already. PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt only Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders the costs of new equipment and modifications are incorporated Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 71 Version:

Conclusions • Line-price increase not for internet only. If telephony and interactive TV can use the same platform, the line-price increase of EUR 487 is an investment for all these services. • Why so much? – CATV was designed for connecting one R/TV only – Network quality increase was always used for capacity increase – Lot of investments were postponed until now (SNP) • But there is a moment that limits are reached PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 72 Version:

Euro. Docsis and TPA Third Party Access The consequences and some special issues (SI and SP) PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 73 Version:
Is TPA for internet only? modem/ SP • On the IP platform, TPA is a All over one modem, orthe modem? Who delivers Who owns the modem? hot issue at the moment but: Who cares…? CM • It was already an issue years a go Tel nd operators) CM for telephony as well (2 Tel STB • It was already an issue years ago on STB pay-TV (Channel+). This will become more important with introduction of interactive TV • Today we study TPA for the IP platform since the government presses us to open our network for other SP's (third parties). PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders SP is generic name for Service Provider ISP is specific Provider for Internet-Services Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 74 Version:

Casema only? • Casema is studying TPA for internal knowledge improvement • Casema is working together with Essent and UPC to get common sense and to get one standpoint in the direction of the government. • Projectname: Sh. AP (Shared Access Project) splitted in WG technology and WG business. Casema will commit to the result of Sh. AP study. • TPA for Euro. Docsis only because of step-to-ED policy and uniform SLA for all ISP's PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Internal TPA group: Fred v. Let, Maria Gen. week: 207 Sh. AP: Fred van Let, Hans Velders, . . . Author: A. Velders Klessens Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 75 Version:

TPA dualism • Cable Network Provider Business group sets conditions (CNP) is leading, tries to • Sets up Business plans • Select business model that can set the Standard for the work with Techn. group conditions SLA once and for all. • Makes SLA between CNP and ISP • Internet Service Provider (ISP) must feel happy with such SLA Technical group sets conditions • Physical parameters (NTU) • Government (OPTA) • IP platform parameters (MPLS) must accept construction • NMS, AAA, SI, SP • Eliminate all impossible models PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt NMS = Network Management System Gen. week: 207 AAA = Authentication, Authorization, Accounting Author: A. Velders SP = Self Provisioning SI = Self Installation Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 76 Version:
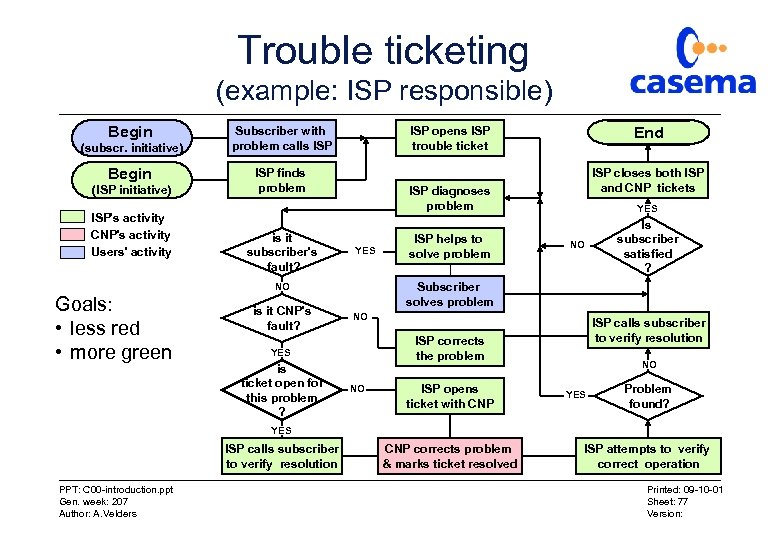
Trouble ticketing (example: ISP responsible) Begin (subscr. initiative) Begin (ISP initiative) ISP's activity CNP's activity Users' activity Subscriber with problem calls ISP finds problem is it subscriber's fault? is it CNP's fault? YES ISP helps to solve problem YES NO Is subscriber satisfied ? Subscriber solves problem NO ISP calls subscriber to verify resolution ISP corrects the problem YES is ticket open for this problem ? ISP closes both ISP and CNP tickets ISP diagnoses problem NO Goals: • less red • more green End ISP opens ISP trouble ticket NO ISP opens ticket with CNP NO YES Problem found? YES ISP calls subscriber to verify resolution PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders CNP corrects problem & marks ticket resolved ISP attempts to verify correct operation Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 77 Version:
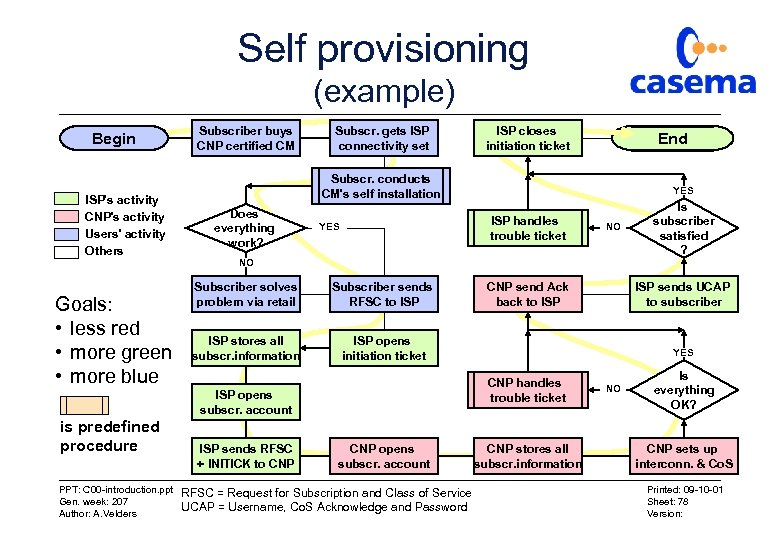
Self provisioning (example) Begin ISP's activity CNP's activity Users' activity Others Goals: • less red • more green • more blue Subscriber buys CNP certified CM Subscr. gets ISP connectivity set PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders End Subscr. conducts CM's self installation Does everything work? YES ISP handles trouble ticket YES NO Is subscriber satisfied ? NO Subscriber solves problem via retail Subscriber sends RFSC to ISP stores all subscr. information ISP opens initiation ticket ISP sends RFSC + INITICK to CNP send Ack back to ISP CNP opens subscr. account RFSC = Request for Subscription and Class of Service UCAP = Username, Co. S Acknowledge and Password ISP sends UCAP to subscriber YES CNP handles trouble ticket ISP opens subscr. account is predefined procedure ISP closes initiation ticket CNP stores all subscr. information NO Is everything OK? CNP sets up interconn. & Co. S Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 78 Version:
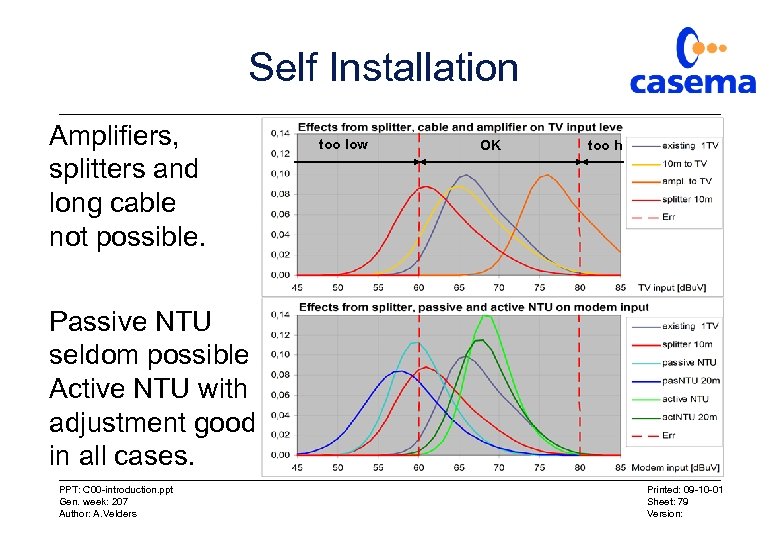
Self Installation Amplifiers, splitters and long cable not possible. too low OK too h Passive NTU seldom possible Active NTU with adjustment good in all cases. PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 79 Version:
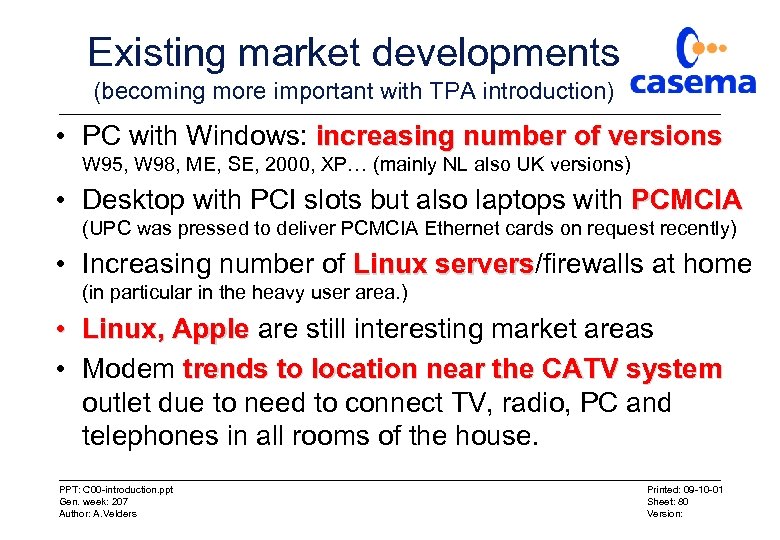
Existing market developments (becoming more important with TPA introduction) • PC with Windows: increasing number of versions W 95, W 98, ME, SE, 2000, XP… (mainly NL also UK versions) • Desktop with PCI slots but also laptops with PCMCIA (UPC was pressed to deliver PCMCIA Ethernet cards on request recently) • Increasing number of Linux servers/firewalls at home servers (in particular in the heavy user area. ) • Linux, Apple are still interesting market areas • Modem trends to location near the CATV system outlet due to need to connect TV, radio, PC and telephones in all rooms of the house. PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 80 Version:

Summary • Third Party Access asks for a very good co-operation between CNP and ISP. • Self provisioning is seldom a problem but a good scenario must be chosen. • Self installation is a Capex problem. Is it possible to ask the retailer with (its connections to installers) to control correct installation and to keep the installation costs separated from our line price. PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 81 Version:

Comparison of Euro-DOCSIS Vendors Cursus voor niet-technici 3 Mei 2002 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 82 Version:
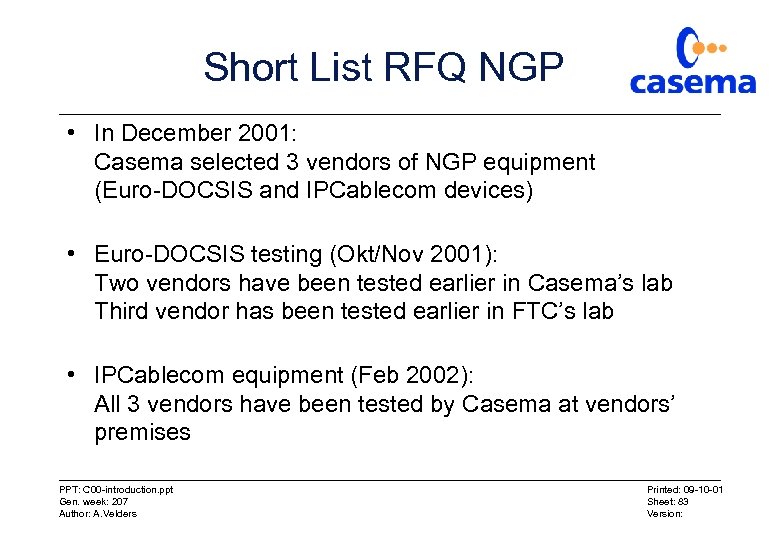
Short List RFQ NGP • In December 2001: Casema selected 3 vendors of NGP equipment (Euro-DOCSIS and IPCablecom devices) • Euro-DOCSIS testing (Okt/Nov 2001): Two vendors have been tested earlier in Casema’s lab Third vendor has been tested earlier in FTC’s lab • IPCablecom equipment (Feb 2002): All 3 vendors have been tested by Casema at vendors’ premises PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 83 Version:
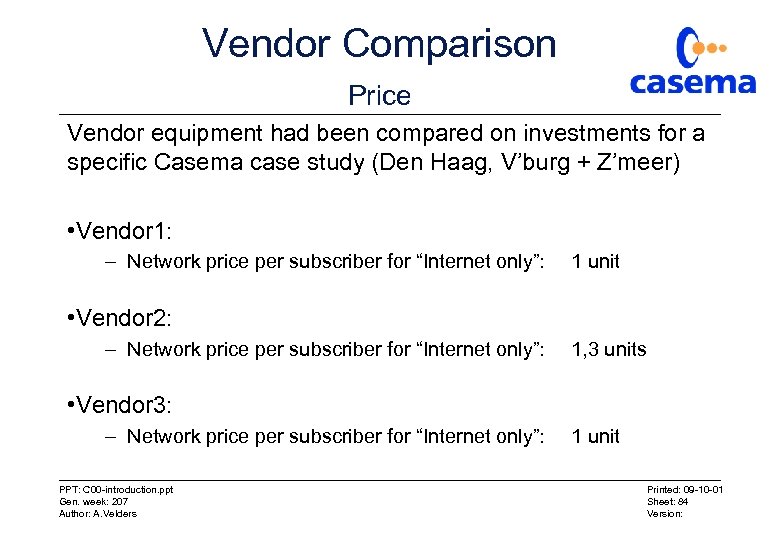
Vendor Comparison Price Vendor equipment had been compared on investments for a specific Casema case study (Den Haag, V’burg + Z’meer) • Vendor 1: – Network price per subscriber for “Internet only”: 1 unit • Vendor 2: – Network price per subscriber for “Internet only”: 1, 3 units • Vendor 3: – Network price per subscriber for “Internet only”: PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders 1 unit Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 84 Version:
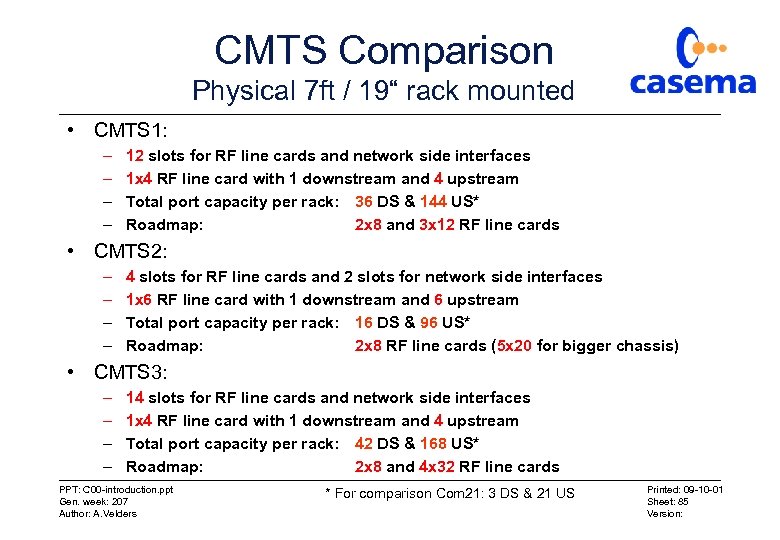
CMTS Comparison Physical 7 ft / 19“ rack mounted • CMTS 1: – – 12 slots for RF line cards and network side interfaces 1 x 4 RF line card with 1 downstream and 4 upstream Total port capacity per rack: 36 DS & 144 US* Roadmap: 2 x 8 and 3 x 12 RF line cards • CMTS 2: – – 4 slots for RF line cards and 2 slots for network side interfaces 1 x 6 RF line card with 1 downstream and 6 upstream Total port capacity per rack: 16 DS & 96 US* Roadmap: 2 x 8 RF line cards (5 x 20 for bigger chassis) • CMTS 3: – – 14 slots for RF line cards and network side interfaces 1 x 4 RF line card with 1 downstream and 4 upstream Total port capacity per rack: 42 DS & 168 US* Roadmap: 2 x 8 and 4 x 32 RF line cards PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders * For comparison Com 21: 3 DS & 21 US Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 85 Version:
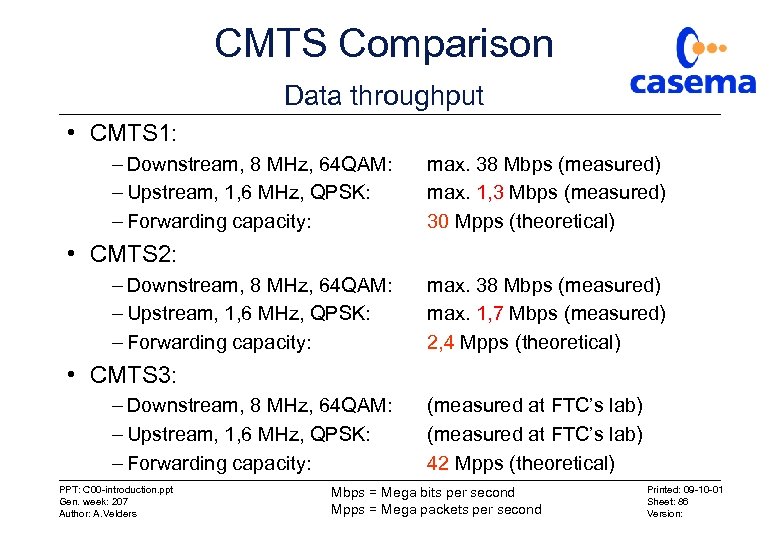
CMTS Comparison Data throughput • CMTS 1: – Downstream, 8 MHz, 64 QAM: – Upstream, 1, 6 MHz, QPSK: – Forwarding capacity: max. 38 Mbps (measured) max. 1, 3 Mbps (measured) 30 Mpps (theoretical) • CMTS 2: – Downstream, 8 MHz, 64 QAM: – Upstream, 1, 6 MHz, QPSK: – Forwarding capacity: max. 38 Mbps (measured) max. 1, 7 Mbps (measured) 2, 4 Mpps (theoretical) • CMTS 3: – Downstream, 8 MHz, 64 QAM: – Upstream, 1, 6 MHz, QPSK: – Forwarding capacity: PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders (measured at FTC’s lab) 42 Mpps (theoretical) Mbps = Mega bits per second Mpps = Mega packets per second Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 86 Version:
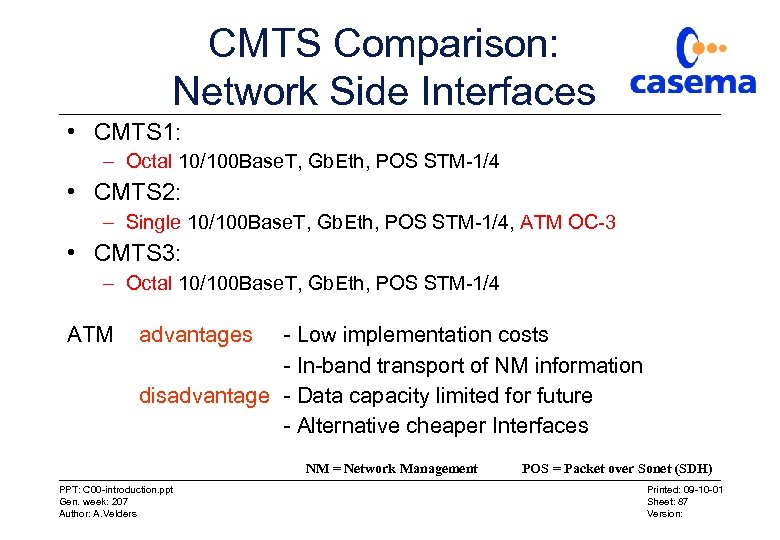
CMTS Comparison: Network Side Interfaces • CMTS 1: – Octal 10/100 Base. T, Gb. Eth, POS STM-1/4 • CMTS 2: – Single 10/100 Base. T, Gb. Eth, POS STM-1/4, ATM OC-3 • CMTS 3: – Octal 10/100 Base. T, Gb. Eth, POS STM-1/4 ATM advantages - Low implementation costs - In-band transport of NM information disadvantage - Data capacity limited for future - Alternative cheaper Interfaces NM = Network Management PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders POS = Packet over Sonet (SDH) Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 87 Version:
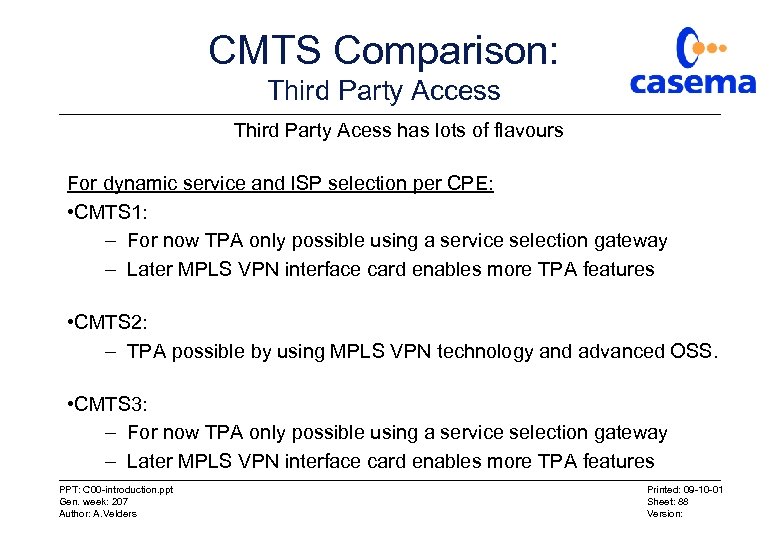
CMTS Comparison: Third Party Access Third Party Acess has lots of flavours For dynamic service and ISP selection per CPE: • CMTS 1: – For now TPA only possible using a service selection gateway – Later MPLS VPN interface card enables more TPA features • CMTS 2: – TPA possible by using MPLS VPN technology and advanced OSS. • CMTS 3: – For now TPA only possible using a service selection gateway – Later MPLS VPN interface card enables more TPA features PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 88 Version:
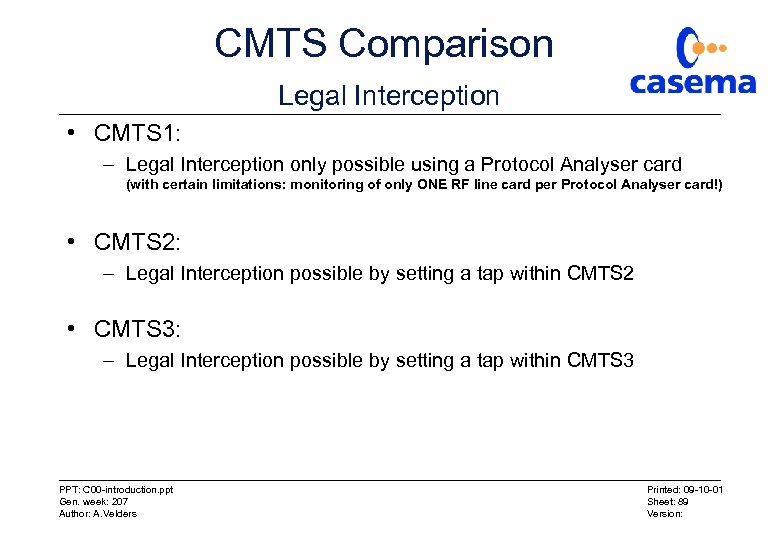
CMTS Comparison Legal Interception • CMTS 1: – Legal Interception only possible using a Protocol Analyser card (with certain limitations: monitoring of only ONE RF line card per Protocol Analyser card!) • CMTS 2: – Legal Interception possible by setting a tap within CMTS 2 • CMTS 3: – Legal Interception possible by setting a tap within CMTS 3 PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 89 Version:
Conclusion • Many factors (financial, service, technical, time-to-market) have an impact on the equipment selection • Comparison of equipment is not always straightforward because of many hidden pitfalls • Every vendor has strong and weak points depending on service (Internet, Telephony, …. ) PPT: C 00 -introduction. ppt Gen. week: 207 Author: A. Velders Printed: 09 -10 -01 Sheet: 90 Version:
ec868e1db44ad4358d66d938b5c64c7f.ppt