f20591a20f8bbc14baf23809a17239bd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

EUMEDGRID & EUChina. GRID Federico Ruggieri EB INFN-GRID Bologna 29 Agosto 2006

Obiettivi Principali • Esportare le Griglie ed il Middleware di EGEE in altre regioni o paesi (Area Mediterraneo e Cina). • Stimolare la creazione di infrastrutture GRID regionali (Mediterraneo) • Supportare l’interoperabilità delle infrastrutture GRID esistenti e nascenti (Cina e Mediterraneo). • Supportare l’estensione delle applicazioni Grid. Enabled di EGEE (LHC, ecc. ) alle aree di interesse. • Abilitare nuove comunità scientifiche all’uso di tecnologie ed infrastrutture GRID. • Favorire l’uso di nuove applicazioni che siano GRIDEnabled.

Status & Numbers • Entrambi i Progetti sono Specific Support Action (SSA). • Sono partiti il 1 Gennaio 2006. • La durata è di 24 Mesi (finiranno il 31. 12. 2007). • Alcuni partners in comune: INFN, CERN, GARR, GRNET. • Contributo EU di 1, 646, 500 € (EUMEDGRID) e 1, 299, 998 € (EUChina. GRID). • Sedi INFN direttamente coinvolte: Roma 3, Catania, CNAF.
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024

![[Empowering e. Science across the Mediterranean] EUMEDGRID FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 www. eumedgrid. [Empowering e. Science across the Mediterranean] EUMEDGRID FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 www. eumedgrid.](https://present5.com/presentation/f20591a20f8bbc14baf23809a17239bd/image-6.jpg)
[Empowering e. Science across the Mediterranean] EUMEDGRID FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 www. eumedgrid. org
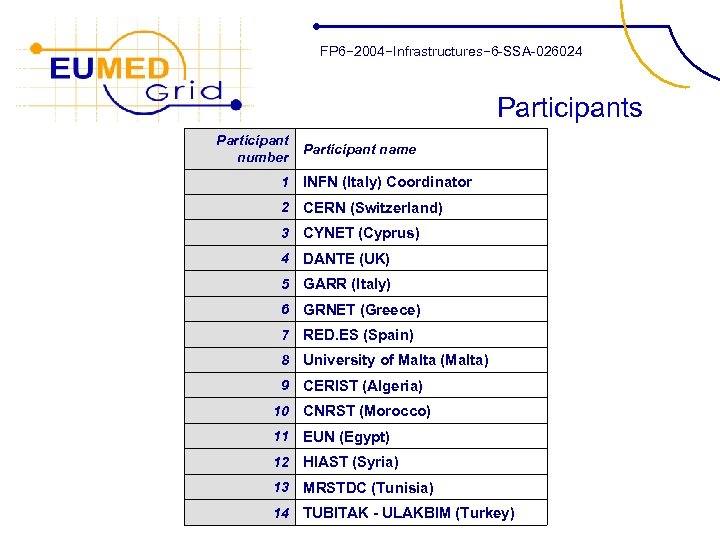
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 Participants Participant number Participant name 1 INFN (Italy) Coordinator 2 CERN (Switzerland) 3 CYNET (Cyprus) 4 DANTE (UK) 5 GARR (Italy) 6 GRNET (Greece) 7 RED. ES (Spain) 8 University of Malta (Malta) 9 CERIST (Algeria) 10 CNRST (Morocco) 11 EUN (Egypt) 12 HIAST (Syria) 13 MRSTDC (Tunisia) 14 TUBITAK - ULAKBIM (Turkey)
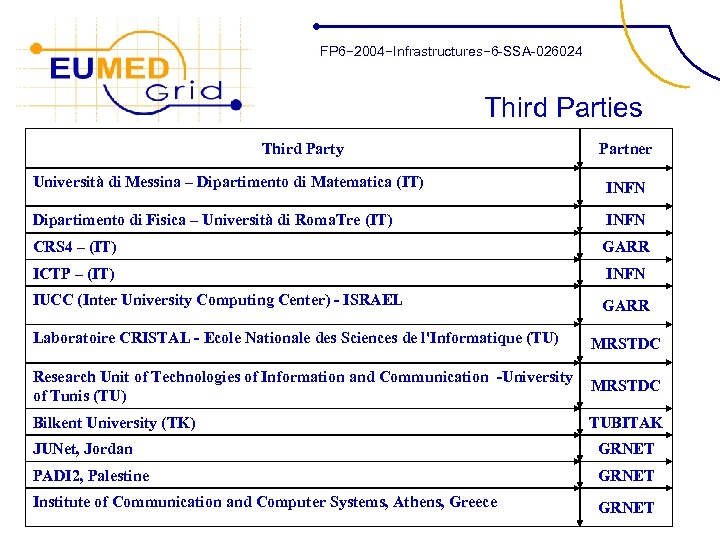
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 Third Parties Third Party Partner Università di Messina – Dipartimento di Matematica (IT) INFN Dipartimento di Fisica – Università di Roma. Tre (IT) INFN CRS 4 – (IT) GARR ICTP – (IT) INFN IUCC (Inter University Computing Center) - ISRAEL GARR Laboratoire CRISTAL - Ecole Nationale des Sciences de l'Informatique (TU) MRSTDC Research Unit of Technologies of Information and Communication -University of Tunis (TU) MRSTDC Bilkent University (TK) TUBITAK JUNet, Jordan GRNET PADI 2, Palestine GRNET Institute of Communication and Computer Systems, Athens, Greece GRNET

FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 EUMEDGRID WP’s 4 WP 1: Project administrative and technical management 4 WP 2: Requirement capture and analysis • User profiles and Applications • Universities & Research Centres potentially interested 4 WP 3: Pilot infrastructure deployment and operations • Support pilot national grid infrastructure and services. 4 WP 4: Applications support • EGEE supported applications (LHC, Bio. Med, etc. ) • Regional applications (Geology, Management of water, etc. ) • New applications (to be discovered by WP 2). 4 WP 5: Training and dissemination
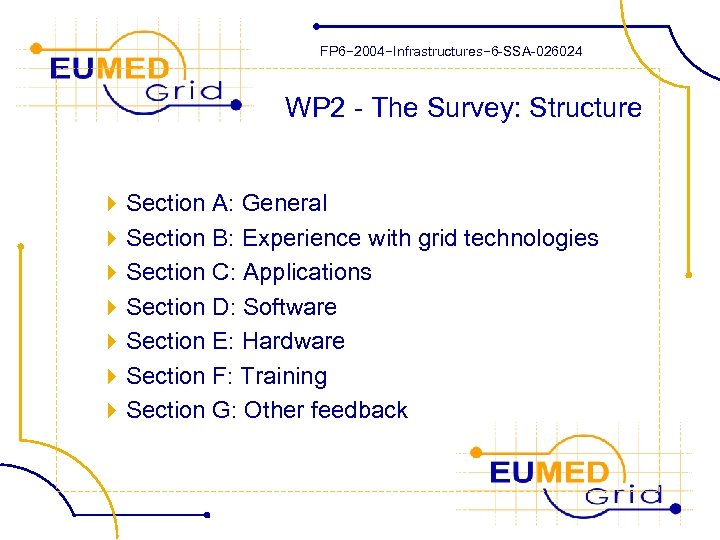
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 WP 2 - The Survey: Structure 4 Section A: General 4 Section B: Experience with grid technologies 4 Section C: Applications 4 Section D: Software 4 Section E: Hardware 4 Section F: Training 4 Section G: Other feedback
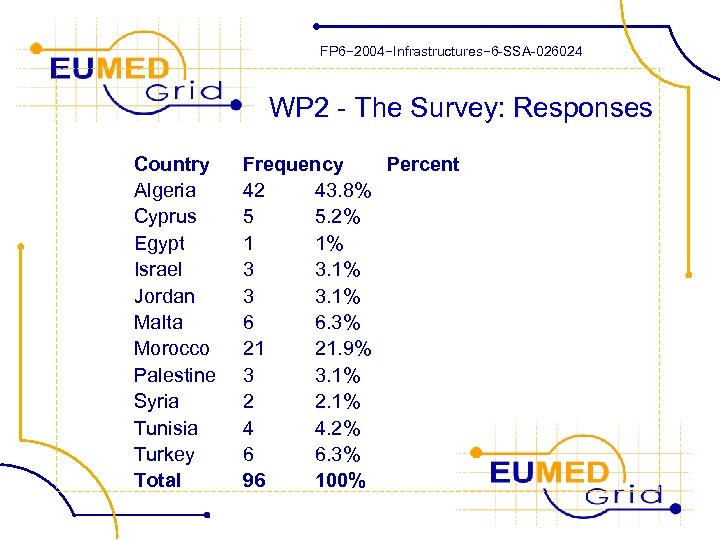
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 WP 2 - The Survey: Responses Country Algeria Cyprus Egypt Israel Jordan Malta Morocco Palestine Syria Tunisia Turkey Total Frequency Percent 42 43. 8% 5 5. 2% 1 1% 3 3. 1% 6 6. 3% 21 21. 9% 3 3. 1% 2 2. 1% 4 4. 2% 6 6. 3% 96 100%
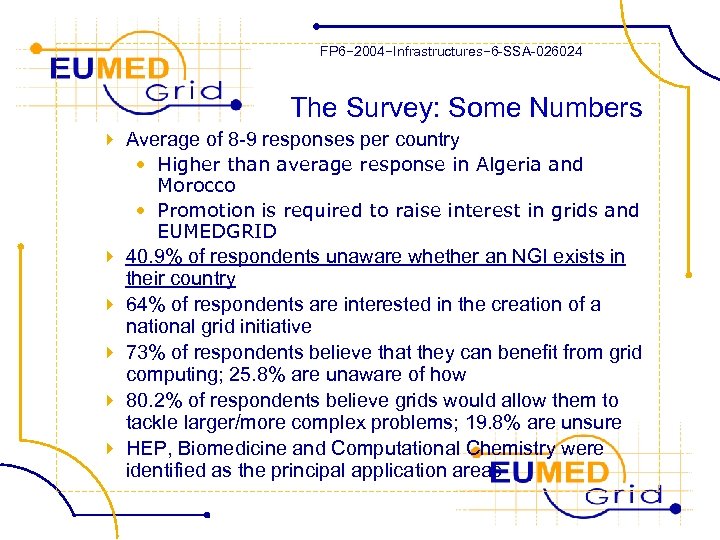
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 The Survey: Some Numbers 4 Average of 8 -9 responses per country • Higher than average response in Algeria and Morocco • Promotion is required to raise interest in grids and EUMEDGRID 4 40. 9% of respondents unaware whether an NGI exists in their country 4 64% of respondents are interested in the creation of a national grid initiative 4 73% of respondents believe that they can benefit from grid computing; 25. 8% are unaware of how 4 80. 2% of respondents believe grids would allow them to tackle larger/more complex problems; 19. 8% are unsure 4 HEP, Biomedicine and Computational Chemistry were identified as the principal application areas
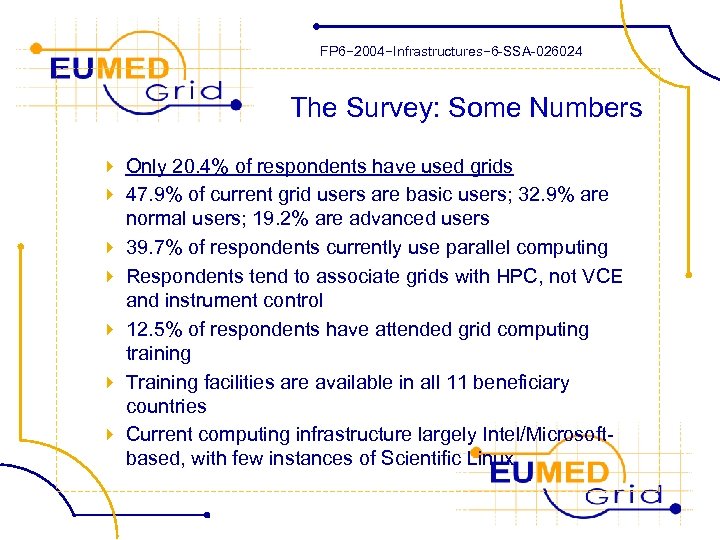
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 The Survey: Some Numbers 4 Only 20. 4% of respondents have used grids 4 47. 9% of current grid users are basic users; 32. 9% are normal users; 19. 2% are advanced users 4 39. 7% of respondents currently use parallel computing 4 Respondents tend to associate grids with HPC, not VCE and instrument control 4 12. 5% of respondents have attended grid computing training 4 Training facilities are available in all 11 beneficiary countries 4 Current computing infrastructure largely Intel/Microsoftbased, with few instances of Scientific Linux
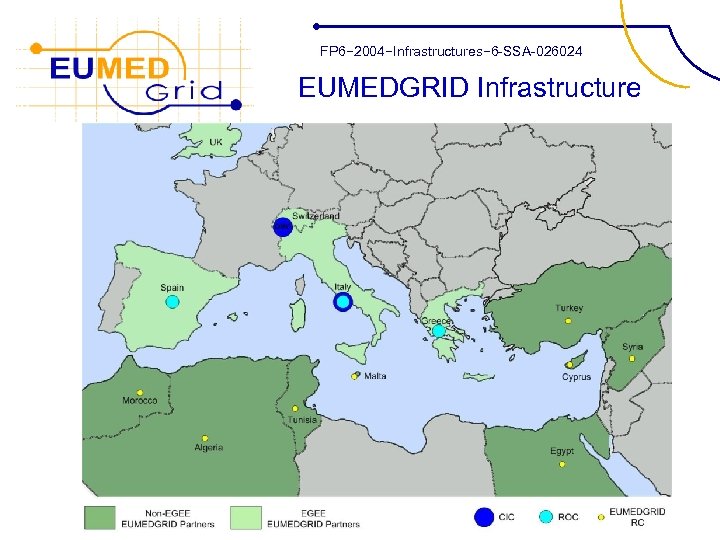
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 EUMEDGRID Infrastructure
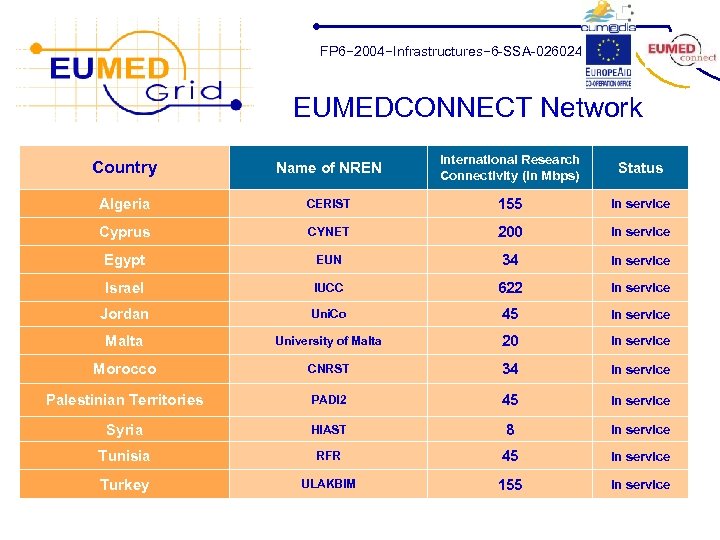
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 EUMEDCONNECT Network Country Name of NREN International Research Connectivity (in Mbps) Status Algeria CERIST 155 In service Cyprus CYNET 200 In service Egypt EUN 34 In service Israel IUCC 622 In service Jordan Uni. Co 45 In service Malta University of Malta 20 In service Morocco CNRST 34 In service Palestinian Territories PADI 2 45 In service Syria HIAST 8 In service Tunisia RFR 45 In service Turkey ULAKBIM 155 In service
Guided User Registration procedure FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024

FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 WP 2 4 Questionnaire for requirements capture and analysis finalized and widely advertised. 4 97 answers received in less than two months (the number of answers varies a lot as a function of countries). 4 First draft of D 2. 1 already circulated by our colleagues at Uo. M. It’s a monumental work! Etremely good “inventory” of e-Science in the Mediterranean Area.
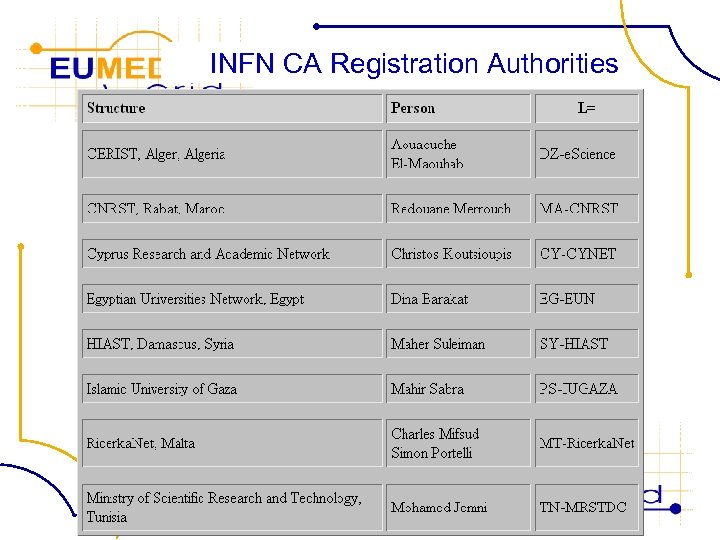
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 INFN CA Registration Authorities
Documentation for sysadmins FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024
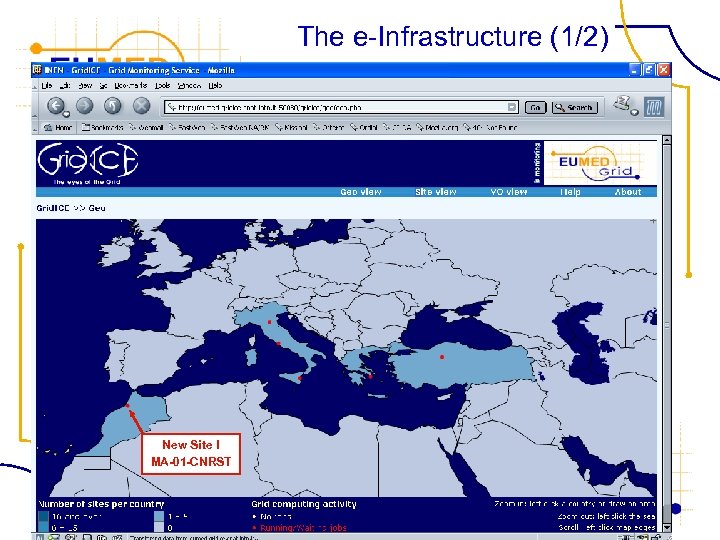
The e-Infrastructure (1/2) FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 New Site ! MA-01 -CNRST
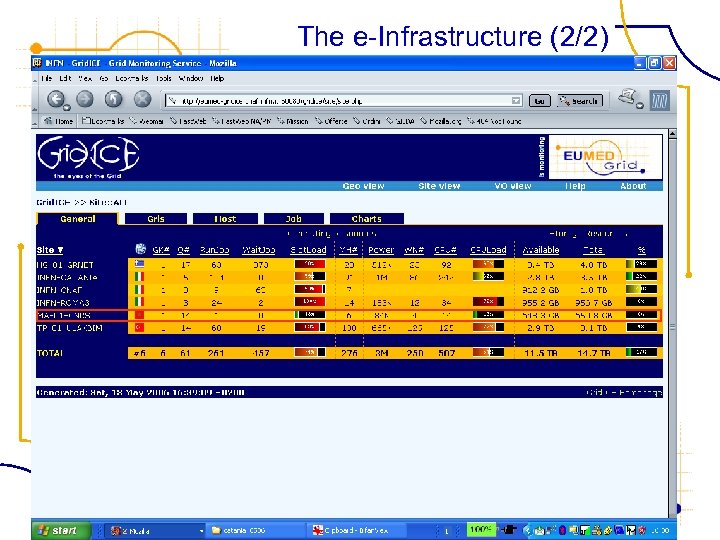
The e-Infrastructure (2/2) FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024
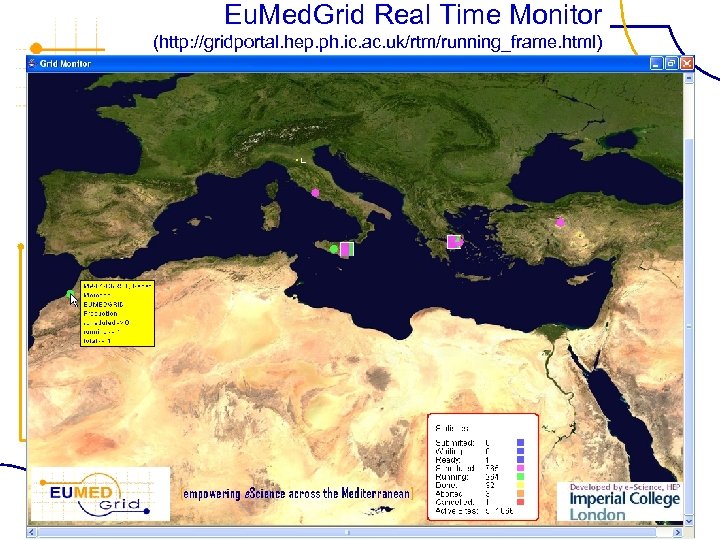
Eu. Med. Grid Real Time Monitor (http: //gridportal. hep. ph. ic. ac. uk/rtm/running_frame. html) FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024
Eu. Med. Grid Acceptable Use Policy FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024
Eu. Med. Grid VOMS FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 (https: //voms 2. cnaf. infn. it: 8443/voms/eumed/)
Users’ and Sysadmins’ Support System FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024

FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 Applications 4 WP 4 was not expected to work while WP 2 was acting but we need anyway to prepare the roadmap for the next months. 4 In particular, we need to: • authorize the EGEE VO’s of the applications we need/want to deploy on all Eu. Med. Grid sites; • deploy the EGEE applications; • deploy the Eu. Med. Grid-specific applications already identified; • define the process to get new applications “on board”.

FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 Known applications 4 SPECFEM 3 D: simulates global and regional (continental-scale) seismic wave propagation 4 Groundwater Hydrology Application: Modeling seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers 4 Grid. SPN: Tool for the analysis of Non-Markovian Stochastic Petri Nets (NMSPN) 4 GRIDVideo: To adopt Grid technologies to deliver services to end users
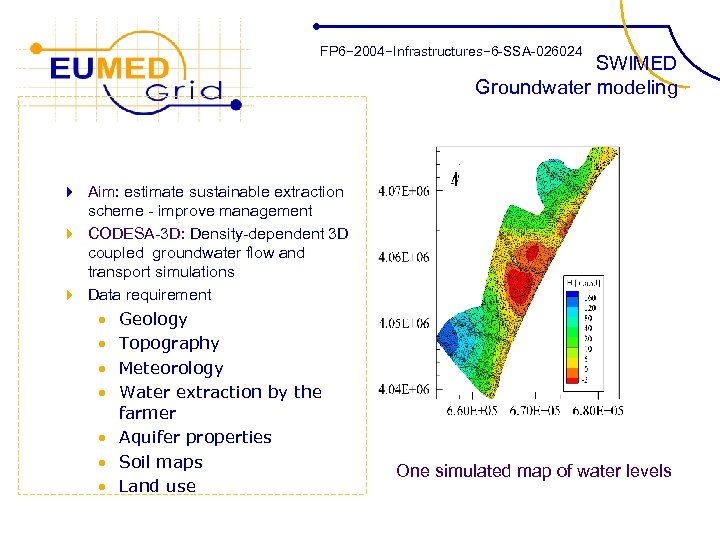
FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 SWIMED Groundwater modeling 4 Aim: estimate sustainable extraction scheme - improve management 4 CODESA-3 D: Density-dependent 3 D coupled groundwater flow and transport simulations 4 Data requirement • Geology • Topography • Meteorology • Water extraction by the farmer • Aquifer properties • Soil maps • Land use One simulated map of water levels

FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA-026024 Dissemination material 4 Several documents advertising the Project have been produced (http: //documents. eumedgrid. org/? c=Disseminati on+materials&as=0&ln=en). 4 Official brochure and poster have been prepared expressly for TNC 2006 (have a look at them at the Eu. Med. Grid booth). 4 First Project’s gadgets produced (don’t forget to take one to bring back home).

EUChina. GRID FP 6− 2004−Infrastructures− 6 -SSA 026634 http: //www. euchinagrid. org

Participants 1 Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare – INFN (IT) (coordinator) 2 European Organisation for Nuclear Research CERN (CH) 3 Dipartimento di Biologia - Università di Roma Tre (IT) 4 Consortium GARR (IT) 5 Greek Research & Technology Network (GR) 6 Jagiellonian University, Cracow (PL) 7 School of Computer Science and Engineering – Beihang University Beijing (CN) 8 Computer Network Information Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences – Beijing (CN) 9 Institute of High Energy Physics, Beijing (CN) 10 Peking University – Beijing (CN)

Third Parties 4 ACADEMIA SINICA GRID COMPUTING CENTRE (ASGC), TAIPEI (Partner: CERN) 4 Physics Department – UNIVERSITÀ DI ROMATRE – ROMA (Partner: INFN)

EUChina. GRID WP’s 4 WP 1 – Project Administrative and Technical Management 4 WP 2 – Network planning and interoperability study • Specific activity to study IPv 4/IPv 6 GRID interoperability. 4 WP 3 – Pilot infrastructure operational support • Specific activity to study interoperability between EGEE & CNGrid. 4 WP 4 – Applications • EGEE applications (LHC, Bio, etc. ) • ARGO-YBJ and Gamma Ray Bursts • Never Born Proteins 4 WP 5 – Dissemination • Dissemination of advanced knowledge on Grid technologies.
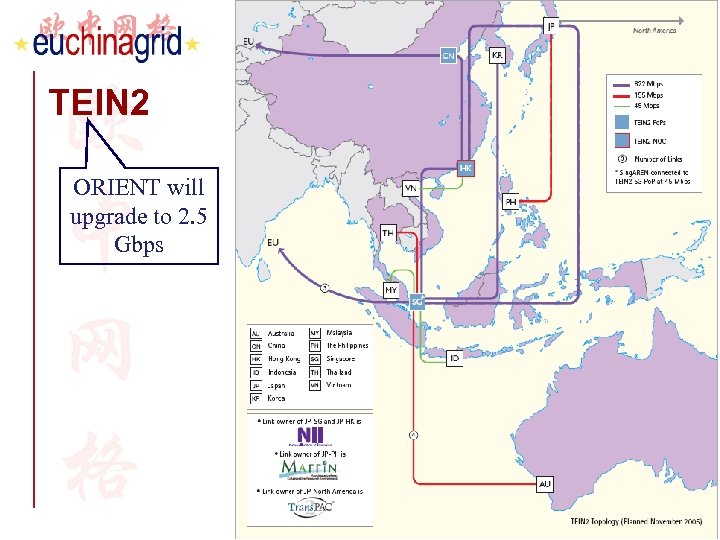
TEIN 2 ORIENT will upgrade to 2. 5 Gbps
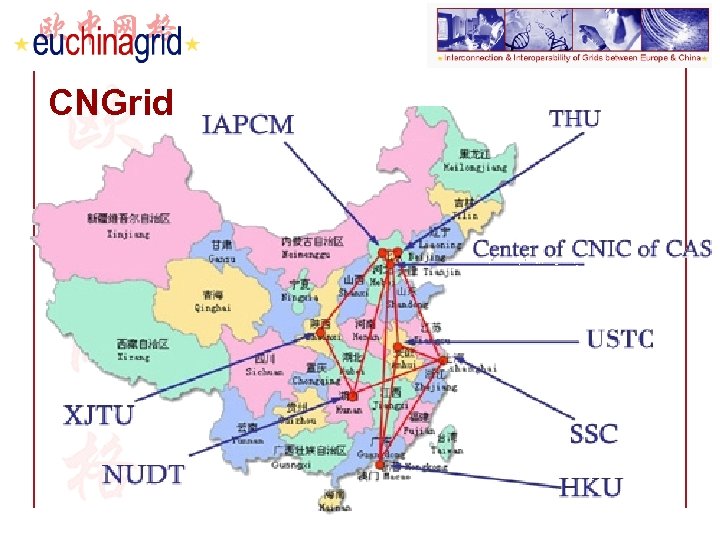
CNGrid

Grid Middleware and IPv 6 4 Mini-Workshop held on 13 June 2006 at IHEP (Beijing). 4 EGEE MW is not at all IPv 6 compliant due to both internal and external code. 4 Dedicated workshop in the next EGEE conference in Geneva (25 -29 September ’ 06) 4 CNGrid MW is not yet IPv 6 compliant but code modification and external packages update is under work to reach complete compatibility. 4 A Web Portal will contain: 4 A list of the mw components and external packages that are declared to be IPv 6 compliant. 4 A short manual on how to produce IPv 6 compliant software 4 A simple code checker that will allow to discover non-compliant parts of code in a source file.

EGEE and CNGRID interoperability 4 g. Lite and GOS are based on a completely different architecture. 4 A gateway will be developed in Beihang University to allow the job submission service as a first trial. 4 Interoperation is in preliminary study phase.

ARGO – YBJ Laboratory • Unique High Altitude Cosmic Ray Laboratory (4300 m) Tibet, 90 km North to Lhasa. Chinese-Italian collaboration. • The Experiment data rate to be transferred is 250 TB/Year requiring a steady transfer rate of the order of 100 Mbps to Beijing and from there to Italy.

Never Born Proteins 4 The number of natural proteins on Earth, although apparently large, is only a tiny fraction of the possible ones: • with 20 different co-monomers (the 20 different natural amino- acids), a polypeptide chain with 60 residues (n=60) can exist in 2060 different chain structures. • In nature, we have around 1013 -14 different proteins, so that the ratio between the possible and the actual number is staggeringly large. 4 This means that there is an astronomically large number of proteins that have never been seen on Earth - an incredibly large number of “never born proteins” (NBP). 4 The present research in the field is based on a computational approach to study a large library of NBP (109 protein sequences) to the aim of clarifying the structural principles that characterize them and of selecting a reasonable number of sequences which can potentially give rise to stably folded proteins.
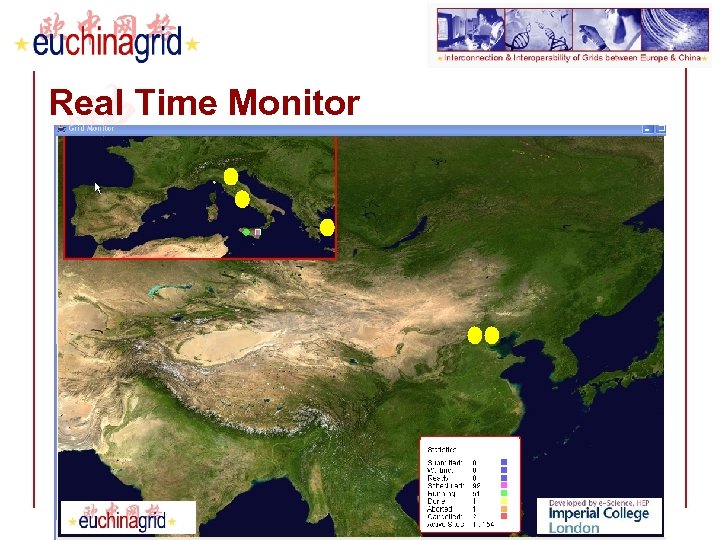
Real Time Monitor
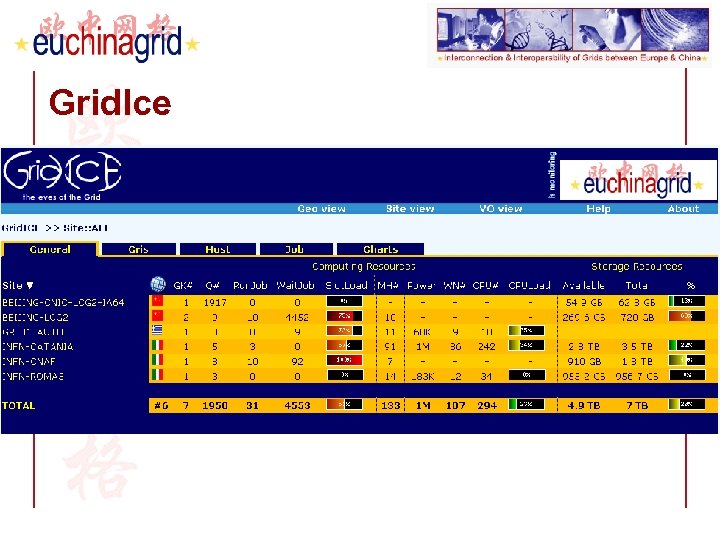
Grid. Ice

Richieste 2007 • EUChina. GRID ed EUMEDGRID hanno un forte coinvolgimento estero e necessitano di una quantità di Missioni Est. abbastanza rilevante. • Continuerà l’attività di tutoraggio (soprattutto nei primi sei mesi); cercheremo di effettuare un certo numero di training in Italia. • L’attività critica sarà quella del supporto alle applicazioni. • Per EUMED sarà critico lo sviluppo di iniziative Grid Nazionali. • Per EUChina sono fondamentali le attività di compatibilità IPv 6 e di interoperabilità g. Lite-GOS.
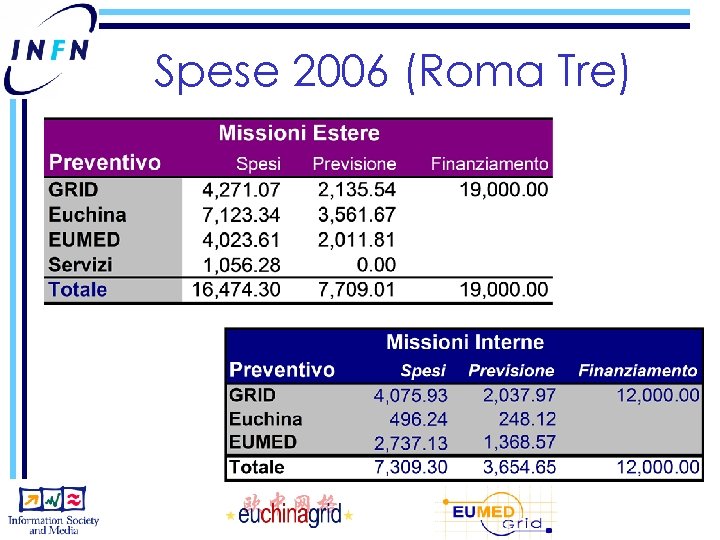
Spese 2006 (Roma Tre)
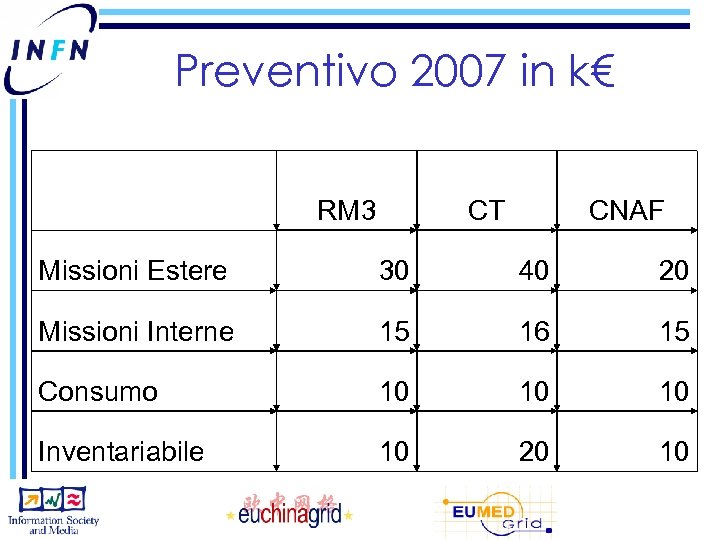
Preventivo 2007 in k€ RM 3 CT CNAF Missioni Estere 30 40 20 Missioni Interne 15 16 15 Consumo 10 10 10 Inventariabile 10 20 10
f20591a20f8bbc14baf23809a17239bd.ppt