2EU Institutions.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
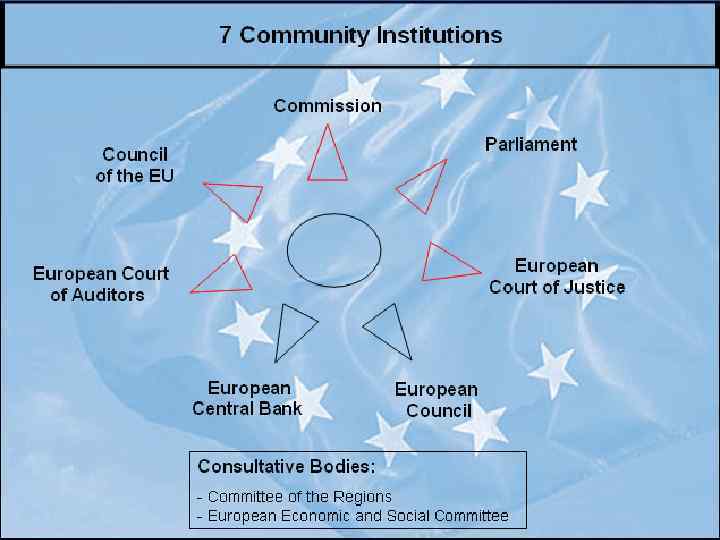
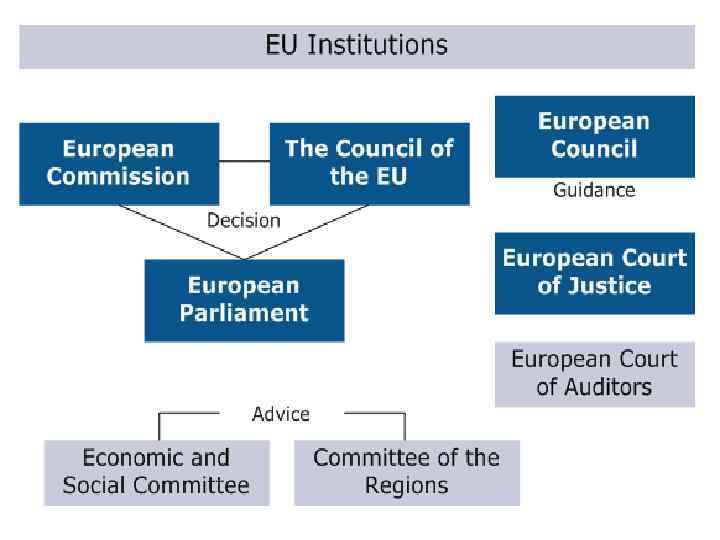
 EU Institutions
EU Institutions
 Principles of EU law n n n Supremacy (EU law dominates any national law). Costa vs Enel. Direct action (EU law applies to citizens, companies too, not only countries) Van Gend En Loos. Common principles (Democracy, freedom, human rights and so on) Special principles (Polluter pays, budget law) Subsidiarity (EU law should not be applied to matters, which national law can handle) Proportionality (EU law actions will be proportional to their aims)
Principles of EU law n n n Supremacy (EU law dominates any national law). Costa vs Enel. Direct action (EU law applies to citizens, companies too, not only countries) Van Gend En Loos. Common principles (Democracy, freedom, human rights and so on) Special principles (Polluter pays, budget law) Subsidiarity (EU law should not be applied to matters, which national law can handle) Proportionality (EU law actions will be proportional to their aims)
 Sources of EU law n Primary law • Constitutive and international treaties, revision treaties, acts of joining n Secondary • Regulations (laws) • Directions (change national law) + Decisions, Recommendations, Opinions q Case law / jurisprudence
Sources of EU law n Primary law • Constitutive and international treaties, revision treaties, acts of joining n Secondary • Regulations (laws) • Directions (change national law) + Decisions, Recommendations, Opinions q Case law / jurisprudence
 Europarliament
Europarliament
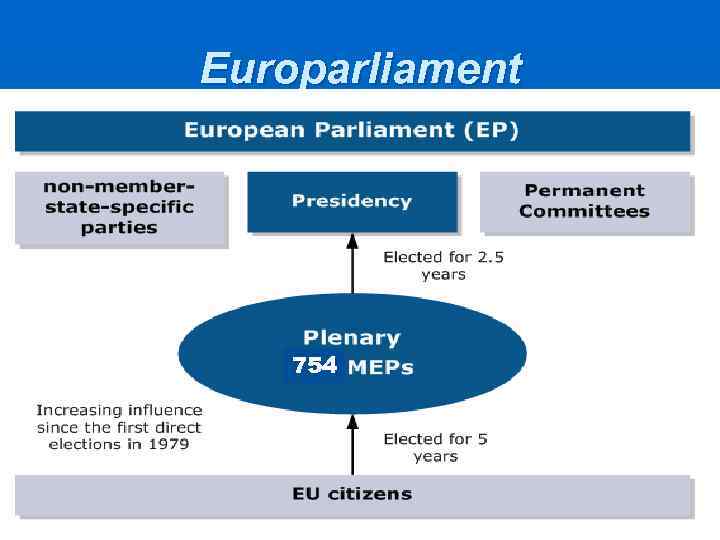 Europarliament 754
Europarliament 754
 Europarliament
Europarliament
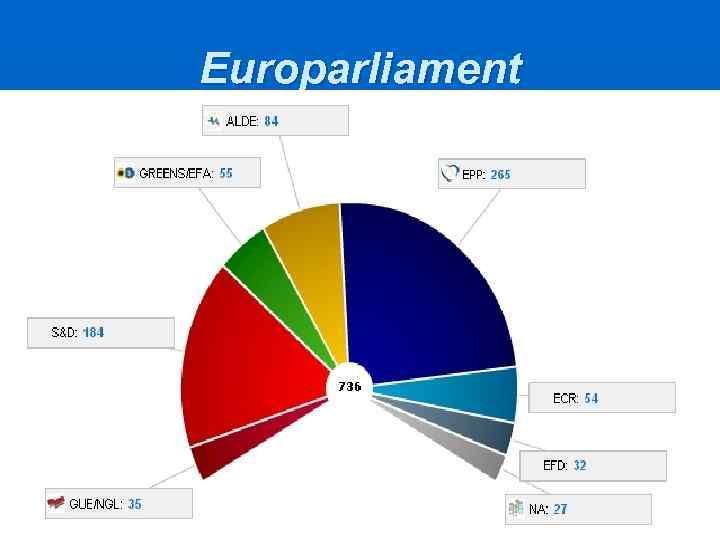
 Europarliament n n n n European People's Party - 265 Members Group of the Progressive Alliance of Socialists & Democrats -184 Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe – 84 The Greens / European Free Alliance – 55 European Conservatives and Reformists Group – 54 Confederal Group of the European United Left / Nordic Green Left – 35 Europe of Freedom and Democracy Group – 32 Non-attached members - 27
Europarliament n n n n European People's Party - 265 Members Group of the Progressive Alliance of Socialists & Democrats -184 Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe – 84 The Greens / European Free Alliance – 55 European Conservatives and Reformists Group – 54 Confederal Group of the European United Left / Nordic Green Left – 35 Europe of Freedom and Democracy Group – 32 Non-attached members - 27
 Europarliament n n n Features Representatives of nations All European parties (over 5%) Not bound by national parliaments
Europarliament n n n Features Representatives of nations All European parties (over 5%) Not bound by national parliaments
 Europarliament n n Functions Legislative function (Joining, Common decision and consultancy) Political function (represents people, appoint major executives) Monitoring function (Comission and Ombudsman) Budgetary functions (together with Council)
Europarliament n n Functions Legislative function (Joining, Common decision and consultancy) Political function (represents people, appoint major executives) Monitoring function (Comission and Ombudsman) Budgetary functions (together with Council)
 Europarliament n n Organization Population size, 6 – 96 MEPs 11 sessions, with 30% quorum Simple and Qualified Majority vote President, 14 vice-presidents • Quaestors (finance and administration) • Bureau (budget and organisation) • Conference of Presidents (heads of parties)
Europarliament n n Organization Population size, 6 – 96 MEPs 11 sessions, with 30% quorum Simple and Qualified Majority vote President, 14 vice-presidents • Quaestors (finance and administration) • Bureau (budget and organisation) • Conference of Presidents (heads of parties)
 Europarliament n n n Brussels = meet within parliamentary committees and political groups Strasbourg = plenary sittings. Constituencies = parallel.
Europarliament n n n Brussels = meet within parliamentary committees and political groups Strasbourg = plenary sittings. Constituencies = parallel.
 Europarliament Conference of Community and European Affairs Committees of Parliaments of the European Union (COSAC) Aims : n Contacts between Members of National Parliaments and Members of EU Parliament n Information exchanges
Europarliament Conference of Community and European Affairs Committees of Parliaments of the European Union (COSAC) Aims : n Contacts between Members of National Parliaments and Members of EU Parliament n Information exchanges
 Council of Ministers
Council of Ministers
 Council of Ministers
Council of Ministers
 Council of Ministers n n Features 9 professional formations with relevant ministers Bound by member-states
Council of Ministers n n Features 9 professional formations with relevant ministers Bound by member-states
 Council of Ministers Formations n n n n n General Affairs (common denominator), Foreign Affairs; Economic and Financial Affairs (including budget); Justice and Home Affairs (including civil protection); Employment, Social Policy, Health and Consumer Affairs; Competitiveness (Internal Market, Industry and Research, including tourism); Transport, Telecommunications and Energy; Agriculture and Fisheries; Environment; Education, Youth and Culture (including audiovisual affairs)
Council of Ministers Formations n n n n n General Affairs (common denominator), Foreign Affairs; Economic and Financial Affairs (including budget); Justice and Home Affairs (including civil protection); Employment, Social Policy, Health and Consumer Affairs; Competitiveness (Internal Market, Industry and Research, including tourism); Transport, Telecommunications and Energy; Agriculture and Fisheries; Environment; Education, Youth and Culture (including audiovisual affairs)
 Council of Ministers n n n Functions Legislative function (Approving common law, often together with Parliament) Political function (represents governments, appoints executives) Budget drafting and acceptance General member states economic policies coordination Definition and implementation of common foreign and security policy issues
Council of Ministers n n n Functions Legislative function (Approving common law, often together with Parliament) Political function (represents governments, appoints executives) Budget drafting and acceptance General member states economic policies coordination Definition and implementation of common foreign and security policy issues
 Council of Ministers Organization n n 100 sessions Qualified majority voting (50%, 74%, 62%) Special committees in each area COREPER (Permanent Representatives Committee) • Preparing the work of the Council and for carrying out the tasks assigned to it by the Council • If agreed by COREPER, Council accepts the provision automatically
Council of Ministers Organization n n 100 sessions Qualified majority voting (50%, 74%, 62%) Special committees in each area COREPER (Permanent Representatives Committee) • Preparing the work of the Council and for carrying out the tasks assigned to it by the Council • If agreed by COREPER, Council accepts the provision automatically
 Council of Ministers Votes in Council: n n n n n Germany, France, Italy and UK – 29 Spain and Poland – 27 Romania – 14 Netherlands – 13 Belgium, Czech Republic, Greece, Hungary and Portugal – 12 Austria, Bulgaria and Sweden – 10 Denmark, Ireland, Lithuania, Slovakia and Finland – 7 Cyprus, Estonia, Latvia, Luxembourg and Slovenia – 4 Malta – 3
Council of Ministers Votes in Council: n n n n n Germany, France, Italy and UK – 29 Spain and Poland – 27 Romania – 14 Netherlands – 13 Belgium, Czech Republic, Greece, Hungary and Portugal – 12 Austria, Bulgaria and Sweden – 10 Denmark, Ireland, Lithuania, Slovakia and Finland – 7 Cyprus, Estonia, Latvia, Luxembourg and Slovenia – 4 Malta – 3
 European Commission
European Commission
 European Commission
European Commission
 European Commission n Features 27 Commissioners (“Ministers”) Not bound by national governments Appointed by Parliament and Council
European Commission n Features 27 Commissioners (“Ministers”) Not bound by national governments Appointed by Parliament and Council
 European Commission n n Functions Initiative (legal acts proposal, common policies development) Protective (fulfilment of Member States obligations under the treaties) Executive (administration, regulation and directive enforcement Representative (representation of EU in 3 d countries and other)
European Commission n n Functions Initiative (legal acts proposal, common policies development) Protective (fulfilment of Member States obligations under the treaties) Executive (administration, regulation and directive enforcement Representative (representation of EU in 3 d countries and other)
 European Commission n n Organisation Sectoral departments (Directorates. General) 33033 permanent officials Executive agencies General Secretariat Interpreter service (20% of total)
European Commission n n Organisation Sectoral departments (Directorates. General) 33033 permanent officials Executive agencies General Secretariat Interpreter service (20% of total)
 European Commission Comitology
European Commission Comitology
 European Council
European Council
 European Council
European Council
 European Council n n n Features Heads of States Consensus Do not adopt formally binding legal acts
European Council n n n Features Heads of States Consensus Do not adopt formally binding legal acts
 European Council n n n Functions A forum for free and informal exchanges of views Strategic development issues Change of constitutive treaties
European Council n n n Functions A forum for free and informal exchanges of views Strategic development issues Change of constitutive treaties
 European Council n n Organization Meet 2 times a year Brussels or presiding member state
European Council n n Organization Meet 2 times a year Brussels or presiding member state
 European Court of Justice
European Court of Justice
 European Court of Justice
European Court of Justice
 European Court of Justice n Highest court in EU law, does not deal with national law The General Court n private individuals, companies and cases relating to competition law Specialised courts n CJ works in plenary sessions, Grand Chambers of 13 judges, or in chambers of three - five judges
European Court of Justice n Highest court in EU law, does not deal with national law The General Court n private individuals, companies and cases relating to competition law Specialised courts n CJ works in plenary sessions, Grand Chambers of 13 judges, or in chambers of three - five judges
 European Court of Justice European Court on Human Rights n n n NOT within EU legal system, separate European Convention on protection of Human Right 1950 Last place to apply, after all other means Infringer pays damages, size varies Personal, political and property rights
European Court of Justice European Court on Human Rights n n n NOT within EU legal system, separate European Convention on protection of Human Right 1950 Last place to apply, after all other means Infringer pays damages, size varies Personal, political and property rights
 European Court of Justice n Who applies to Court of Justice Commission • If a state is in breach of EU law, the Commission investigates and demands the state to correct the mistake • If resisted, it makes the “default of obligation” lawsuit. • All necessary measures or fine.
European Court of Justice n Who applies to Court of Justice Commission • If a state is in breach of EU law, the Commission investigates and demands the state to correct the mistake • If resisted, it makes the “default of obligation” lawsuit. • All necessary measures or fine.
 European Court of Justice Prejudicial applications n n n Inquiry to interpret (explain) Validity of legal acts (collision between an act and a treaty) Conformity of national laws and EU Law
European Court of Justice Prejudicial applications n n n Inquiry to interpret (explain) Validity of legal acts (collision between an act and a treaty) Conformity of national laws and EU Law
 European Court of Justice Who else applies to Court of Justice n n n Annulment actions (if EU regulations seem to breach the Treaties) Direct actions (individuals against EU) Failures to act (EU institutions sued for non-actions when supposed to)
European Court of Justice Who else applies to Court of Justice n n n Annulment actions (if EU regulations seem to breach the Treaties) Direct actions (individuals against EU) Failures to act (EU institutions sued for non-actions when supposed to)
 European Court of Justice n n n Advocates-General Make independent investigations Advisory character, no legal binding Impartial Fired only by unanimous CJ decision Germany, UK, France, Italy and Spain
European Court of Justice n n n Advocates-General Make independent investigations Advisory character, no legal binding Impartial Fired only by unanimous CJ decision Germany, UK, France, Italy and Spain
 European Court of Justice Organization n n Written Oral stage Advocates give opinion, if it seems like a new point of law Majority decision read outloud General courts – basically the same
European Court of Justice Organization n n Written Oral stage Advocates give opinion, if it seems like a new point of law Majority decision read outloud General courts – basically the same
 Court of Auditors A single financial control body in EU Provides control over the accounts and budget, checks the income and expenses. Audition inspections of accounting documentation in institutions. CA issues a special and annual reports, as well as conclusions, but cannot penalize the violators. 27 members, 500 officers.
Court of Auditors A single financial control body in EU Provides control over the accounts and budget, checks the income and expenses. Audition inspections of accounting documentation in institutions. CA issues a special and annual reports, as well as conclusions, but cannot penalize the violators. 27 members, 500 officers.
 European Ombudsman 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Parliamentary authorized person controlling the administrative bodies. Sole person appointed for 5 years. Independent, answers to Court only. Institutions must provide him with necessary info upon request, and should not hinder the questioning of their staff (except top-secret issues). Mediator, voluntary dispute settlement
European Ombudsman 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Parliamentary authorized person controlling the administrative bodies. Sole person appointed for 5 years. Independent, answers to Court only. Institutions must provide him with necessary info upon request, and should not hinder the questioning of their staff (except top-secret issues). Mediator, voluntary dispute settlement
 European Ombudsman n n EU citizen or entity can complain about administrative irregularities, unfairness, discrimination, abuse of power, failure to reply, refusal of information or unnecessary delay. Can also investigate the violation of procedures and incidents voluntary
European Ombudsman n n EU citizen or entity can complain about administrative irregularities, unfairness, discrimination, abuse of power, failure to reply, refusal of information or unnecessary delay. Can also investigate the violation of procedures and incidents voluntary
 European Ombudsman n Cannot help in case of: Problems with national, regional or local authorities inside EU countries (even when the complaints are about EU matters). n Problems with companies or private individuals. n Problems with national courts or ombudsmen. Not an appeals body for decisions taken by these entities.
European Ombudsman n Cannot help in case of: Problems with national, regional or local authorities inside EU countries (even when the complaints are about EU matters). n Problems with companies or private individuals. n Problems with national courts or ombudsmen. Not an appeals body for decisions taken by these entities.
 European Ombudsman n n If you make complaint: An Ombudsman call to the problematic institution, body, office or agency can be enough. If not working – tries to find a compromise solution. If the institution is stubborn – Ombudsman makes recommendations to it. If it does not accept it - he makes a report to the European Parliament. If the Ombudsman cannot deal with a complaint – advise will follow.
European Ombudsman n n If you make complaint: An Ombudsman call to the problematic institution, body, office or agency can be enough. If not working – tries to find a compromise solution. If the institution is stubborn – Ombudsman makes recommendations to it. If it does not accept it - he makes a report to the European Parliament. If the Ombudsman cannot deal with a complaint – advise will follow.
 Europol and Eurojust Europol Coordination and cooperation body for member-states police service. Prevention and investigation. Mostly information support. Eurojust National Prosecutors coordinator Deal with serious organized crime Make investigations and prosecutions covering the territory of more than one Member State
Europol and Eurojust Europol Coordination and cooperation body for member-states police service. Prevention and investigation. Mostly information support. Eurojust National Prosecutors coordinator Deal with serious organized crime Make investigations and prosecutions covering the territory of more than one Member State


