a254186dbb11c4c575ca2d7fdca179f7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 EU experience regarding communication with animal welfare stakeholders Amman, 04 -06 October 2009 Friedhelm Jaeger, CVO, North-Rhine Westphalia / Germany
EU experience regarding communication with animal welfare stakeholders Amman, 04 -06 October 2009 Friedhelm Jaeger, CVO, North-Rhine Westphalia / Germany
 Animal welfare – what does it mean? § Is this animal welfare ? § Is this welfare oriented animal husbandry ? § Is this species-appropriate husbandry ?
Animal welfare – what does it mean? § Is this animal welfare ? § Is this welfare oriented animal husbandry ? § Is this species-appropriate husbandry ?
 Animal welfare – what does it mean? (II) EU = ethical value (Lisbon treaty: sentinent beings) (= „because of itself“) Ø instructions throughout the EU: → standardization → socio-economic value (trade) Ø reflection of the society and the generally consensus of values Ø permanent advancement → input of NGO‘s → influence of globalization
Animal welfare – what does it mean? (II) EU = ethical value (Lisbon treaty: sentinent beings) (= „because of itself“) Ø instructions throughout the EU: → standardization → socio-economic value (trade) Ø reflection of the society and the generally consensus of values Ø permanent advancement → input of NGO‘s → influence of globalization
 Animal welfare – what does it mean? (III) Economic aspects: ▪ husbandry → consumer expection ▪ animals for slaughter → meat quality ▪ laboratory animals → pharmaceutical research
Animal welfare – what does it mean? (III) Economic aspects: ▪ husbandry → consumer expection ▪ animals for slaughter → meat quality ▪ laboratory animals → pharmaceutical research
 Animal welfare – what does it mean? (IV) All questions concerning: - laws - cultural aspects - perceptions - and social aspects have to be considered in animal welfare The outcome of this leads to the essential question: Is it possible to talk about THE animal welfare?
Animal welfare – what does it mean? (IV) All questions concerning: - laws - cultural aspects - perceptions - and social aspects have to be considered in animal welfare The outcome of this leads to the essential question: Is it possible to talk about THE animal welfare?
 = It does not exist THE only animal welfare But: a global concerted comprehension on the standards of animal welfare is necessary for a common ethical approach & successful and durable trade connections
= It does not exist THE only animal welfare But: a global concerted comprehension on the standards of animal welfare is necessary for a common ethical approach & successful and durable trade connections
 OIE-guidelines: Aims: - to improve and to harmonize methods of production - science-based standards - no construction of trade barriers (no protectionism) - support of all nations foundation of bilateral contracts between the EU and third countries (import of animals & foods)
OIE-guidelines: Aims: - to improve and to harmonize methods of production - science-based standards - no construction of trade barriers (no protectionism) - support of all nations foundation of bilateral contracts between the EU and third countries (import of animals & foods)
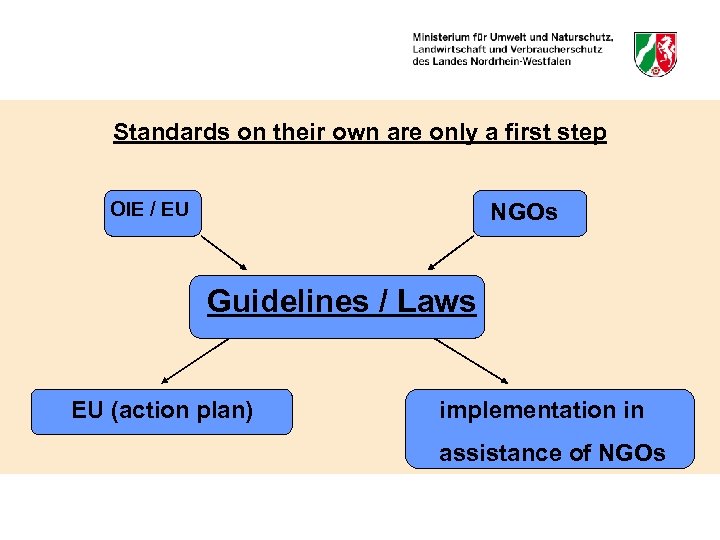 Standards on their own are only a first step OIE / EU NGOs Guidelines / Laws EU (action plan) implementation in assistance of NGOs
Standards on their own are only a first step OIE / EU NGOs Guidelines / Laws EU (action plan) implementation in assistance of NGOs
 Animal welfare and NGO‘s § collaboration is important for: politics / administration consumer expections (reactions) („Mc Donald‘s“) § collective consensus of values (concept of sentience) also important for the market collective principles (international) (implicate NGO‘s; „Burger King“ [eggs; meat])
Animal welfare and NGO‘s § collaboration is important for: politics / administration consumer expections (reactions) („Mc Donald‘s“) § collective consensus of values (concept of sentience) also important for the market collective principles (international) (implicate NGO‘s; „Burger King“ [eggs; meat])
 Animal welfare and NGO‘s § collaboration of: government, economy and NGO‘s § approximation of international / intercultural perceptions (globalization) § agreement on principles for ethical values & efficient trade relations => it`s just functional „together“ not „against“
Animal welfare and NGO‘s § collaboration of: government, economy and NGO‘s § approximation of international / intercultural perceptions (globalization) § agreement on principles for ethical values & efficient trade relations => it`s just functional „together“ not „against“
 Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) Example 1: WSPA (World Society for the Protection of Animals) § global alliance of animal welfare organisations § 950 Member Organisations (150 countries) § aim: support the global implementation of OIE Standards § 2007: formal agreement with OIE § Evolution – not Revolution (cooperation)
Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) Example 1: WSPA (World Society for the Protection of Animals) § global alliance of animal welfare organisations § 950 Member Organisations (150 countries) § aim: support the global implementation of OIE Standards § 2007: formal agreement with OIE § Evolution – not Revolution (cooperation)
 Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) Example 2: Animals Angels § no gain § livestock transports, animal markets, slaughterhouses, … § § aim: claim of regulations and control of their compliance close collaboration with many institutions international work no sensationalism
Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) Example 2: Animals Angels § no gain § livestock transports, animal markets, slaughterhouses, … § § aim: claim of regulations and control of their compliance close collaboration with many institutions international work no sensationalism
 Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) Example 3: People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA) § § worldwide greatest organization of animal rights charitable organization 2006: 187 employees against: factory farming, fur bearing animal husbandry and animal experiments § focus on sensationalism
Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) Example 3: People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA) § § worldwide greatest organization of animal rights charitable organization 2006: 187 employees against: factory farming, fur bearing animal husbandry and animal experiments § focus on sensationalism
 Animal welfare – Collaboration with NGO‘s (examples) Animal welfare in livestock husbandry Animal welfare for animals for slaughter (transport) Animal welfare for animal experiments Animal welfare for the inspection
Animal welfare – Collaboration with NGO‘s (examples) Animal welfare in livestock husbandry Animal welfare for animals for slaughter (transport) Animal welfare for animal experiments Animal welfare for the inspection
 Animal welfare – Livestock husbandry (I) general requirements: 5 freedoms optimize husbandry conditions on focus of the NGO`s
Animal welfare – Livestock husbandry (I) general requirements: 5 freedoms optimize husbandry conditions on focus of the NGO`s
 Animal welfare – Livestock husbandry (II) NGO‘s announce: → grievances in the production of food → system immanent problems (i. e laying hens) customer reacts: boycott food industry reacts: phasing out of „critical“ products
Animal welfare – Livestock husbandry (II) NGO‘s announce: → grievances in the production of food → system immanent problems (i. e laying hens) customer reacts: boycott food industry reacts: phasing out of „critical“ products
 Animal welfare – slaughtering (I) transport of animals for slaughter Animal welfare Standards must be understood and accepted in the daily work (world-wide)
Animal welfare – slaughtering (I) transport of animals for slaughter Animal welfare Standards must be understood and accepted in the daily work (world-wide)
 Animal welfare – slaughtering (II) transport of animals for slaughter greatest attention by NGO‘s: - easy (official) to control and to document - distribution of grievances via internet, mass medias => great effect (trade & economy)
Animal welfare – slaughtering (II) transport of animals for slaughter greatest attention by NGO‘s: - easy (official) to control and to document - distribution of grievances via internet, mass medias => great effect (trade & economy)
 Animal welfare (III) transport of animals for slaughter Publicity !!!
Animal welfare (III) transport of animals for slaughter Publicity !!!
 Animal welfare – slaughtering (IV) transport of animals for slaughter grievances (shown by NGO‘s) Ø boycott of the products Ø challenge for the politics Ø influence of the trade connections
Animal welfare – slaughtering (IV) transport of animals for slaughter grievances (shown by NGO‘s) Ø boycott of the products Ø challenge for the politics Ø influence of the trade connections
 Animal welfare – slaughtering (V) Ø public & NGO‘s: critical (not „if“, but „how“) Ø optimization and transparency • • develop a link to NGO‘s → commissioner of animal welfare (impartial) → no „concealment“ • economic advantage because …
Animal welfare – slaughtering (V) Ø public & NGO‘s: critical (not „if“, but „how“) Ø optimization and transparency • • develop a link to NGO‘s → commissioner of animal welfare (impartial) → no „concealment“ • economic advantage because …
 Animal welfare – slaughtering (VI) § consumers ask for animal products from: - welfare oriented animal husbandries and - welfare oriented handling / slaughtering § NGO`s = effect on the behaviour of the consumers
Animal welfare – slaughtering (VI) § consumers ask for animal products from: - welfare oriented animal husbandries and - welfare oriented handling / slaughtering § NGO`s = effect on the behaviour of the consumers
 Animal welfare for laboratory animals § necessary for research § Focus of public interest commissioner of animal welfare: → „control“ → impartial → „interlink“ to other NGO‘s § governmental permission: assessment by ethics committees
Animal welfare for laboratory animals § necessary for research § Focus of public interest commissioner of animal welfare: → „control“ → impartial → „interlink“ to other NGO‘s § governmental permission: assessment by ethics committees
 Animal welfare and control (I) § NGO: QS = own (In house-) control system for food § (QS = „ensure quality“) § QS = 30 % of the criteria are concerning the animal welfare utilization for the governmental control system
Animal welfare and control (I) § NGO: QS = own (In house-) control system for food § (QS = „ensure quality“) § QS = 30 % of the criteria are concerning the animal welfare utilization for the governmental control system
 Animal welfare and control (II) § QS-certification mark: - meat and sausage - fruits & vegetables § condition: compliance of the selected requirements across all stages of the production § 23 test criteria
Animal welfare and control (II) § QS-certification mark: - meat and sausage - fruits & vegetables § condition: compliance of the selected requirements across all stages of the production § 23 test criteria
 Animal welfare and control (III) § official controls → risk oriented (targeted checks) § criteria - governmental „findings“ (offences, claims; risks) audits from QS Ø very efficient Ø transparency, confidence
Animal welfare and control (III) § official controls → risk oriented (targeted checks) § criteria - governmental „findings“ (offences, claims; risks) audits from QS Ø very efficient Ø transparency, confidence
 Summary (I) Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) § impatial § take part in implementation and further development of the animal welfare § documentation and report about contraventions: force of governmental actions effect of trade connections
Summary (I) Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) § impatial § take part in implementation and further development of the animal welfare § documentation and report about contraventions: force of governmental actions effect of trade connections
 Summary (II) – „to do“ 1. establishment of collective basics ( - Ø international; intercultural Ø importance for the trade 2. NGO‘s: Ø development of principles Ø control; advise 3. transparency & collaboration )
Summary (II) – „to do“ 1. establishment of collective basics ( - Ø international; intercultural Ø importance for the trade 2. NGO‘s: Ø development of principles Ø control; advise 3. transparency & collaboration )
 Summary (III) – „to do“ 1. Standards at their own: Ø only 1. step Ø international; intercultural acceptance Ø opportunity for transparent information from farmer to consumer 2. Standards must be implemented (training schemes, visits…) : Ø OIE / EU /competent authorities Ø NGO‘s 3. step by step (togehter; win-win)
Summary (III) – „to do“ 1. Standards at their own: Ø only 1. step Ø international; intercultural acceptance Ø opportunity for transparent information from farmer to consumer 2. Standards must be implemented (training schemes, visits…) : Ø OIE / EU /competent authorities Ø NGO‘s 3. step by step (togehter; win-win)
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!


