85edd904dcc40533755b010457efcd38.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

EU Conformity assessment procedures “Fresh Produce” including traceability Dr. Friedrich Lüdeke, GLOBALG. A. P. Cairo, 11 June 2012

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE • Introduction • EU 178/2002 • RASSF • EU Control schemes • Summary © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 2

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE HELP ! I want to export to the EU, what rules apply? © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 3

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Safety Freedom from unacceptable risk of harm State in which the risk of harm (to persons) or damage is limited to an acceptable level DIN EN 45020: 1994 DIN EN ISO 8402: 1995 © GLOBALG. A. P. SECRETARIAT | PAGE 4

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 5

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE • Introduction • EU 178/2002 • RASSF • EU Control schemes • Summary © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 6

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE REGULATION (EC) No 178/2002 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 28 January 2002 laying down the general principles and requirements of food law, establishing the European Food Safety Authority and laying down procedures in matters of food safety © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 7

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE 12) In order to ensure the safety of food, it is necessary to consider all aspects of the food production chain as a continuum from and including primary production and the production of animal feed up to and including sale or supply of food to the consumer because each element may have a potential impact on food safety. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 8

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE What is ‘food’ ? Food’ shall not include: • live animals unless they are prepared for placing on the market for human consumption; • plants prior to harvesting; © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 9

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Article 6 Risk analysis 1. In order to achieve the general objective of a high level of protection of human health and life, food law shall be based on risk analysis except where this is not appropriate to the circumstances or the nature of the measure. 2. Risk assessment shall be based on the available scientific evidence and undertaken in an independent, objective and transparent manner. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 10

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Consumer © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 11

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE ‘Food business operator’ means the natural or legal persons responsible for ensuring that the requirements of food law are met within the feed business under their control; © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 12
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE • Introduction • EU 178/2002 • RASSF • EU Control schemes • Summary © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 13

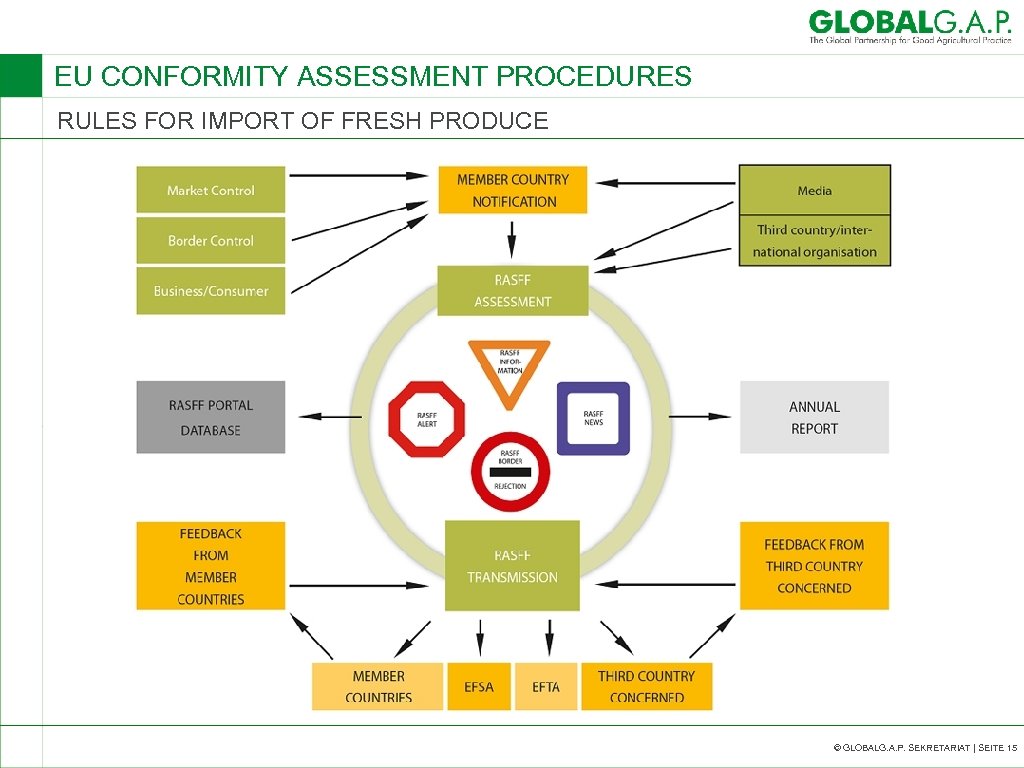
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE RAPID ALERT SYSTEM FOR FOOD AND FEED (RASFF) The legal basis of the system is Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 laying down the general principles and requirements of food law, establishing the European Food Safety Authority and laying down procedures in matters of food safety (O. J. No L 31 of 1 February 2002). The purpose of the rapid alert system for food and feed (RASFF) is to provide the control authorities with an effective tool for exchange of information on measures taken to ensure food safety. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 14
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 15
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Alert Notifications • Food or feed for which a serious risk has been identified • Product is on the market • Immediate action is required by members of the network Information Notifications Food or feed for which a serious risk has been identified but no rapid action required on the product Or Not a serious risk but useful for food/feed control in other member countries Border Rejection Notifications Any rejection, related to a direct or indirect risk, of a batch, container or cargo of food or feed at a border post News Notifications Information related to the safety of food/feed Not communicated as an ‘alert’ or an ‘information’ But judged as interesting for the control authorities © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 16
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 17
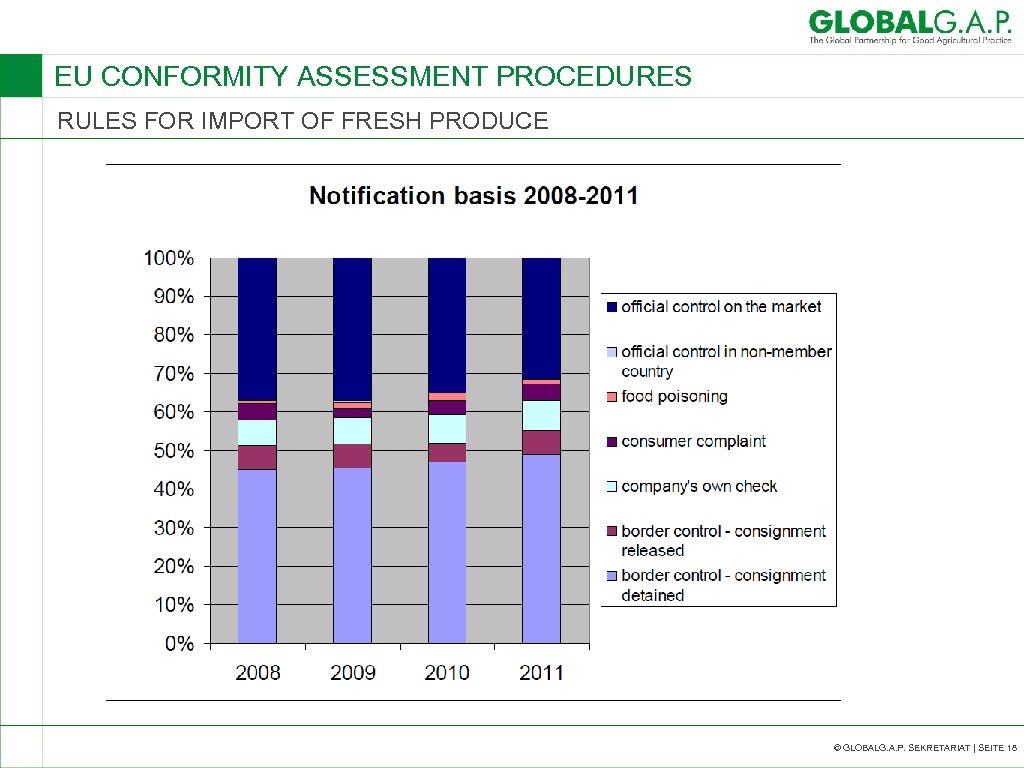
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 18
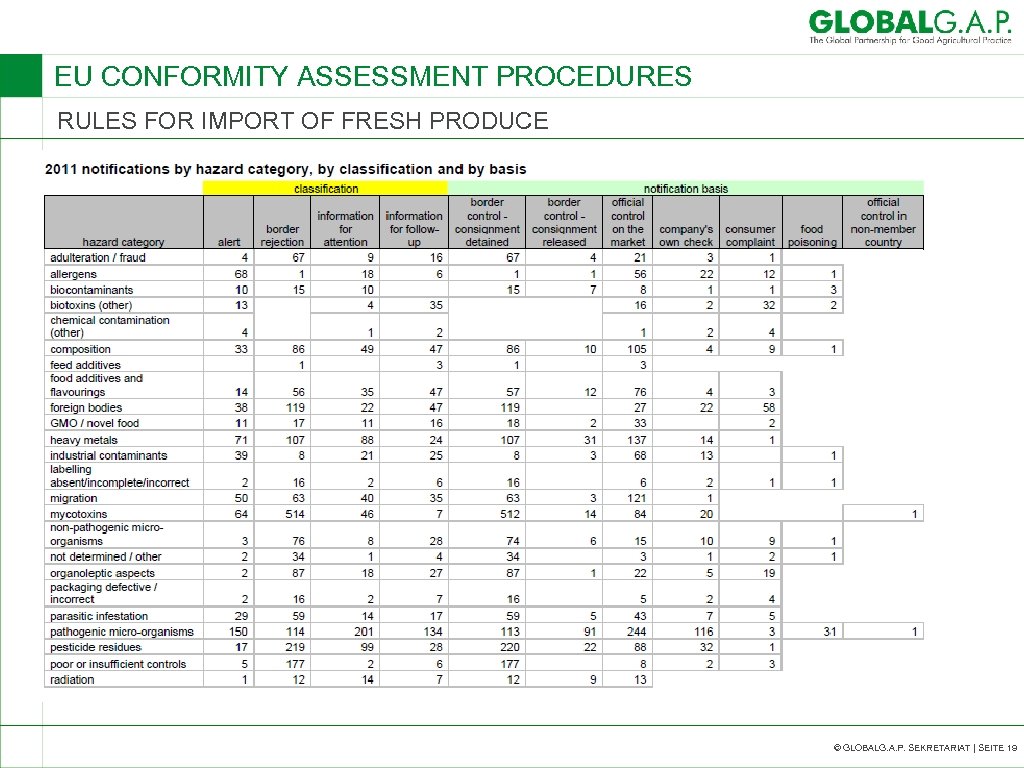
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 19
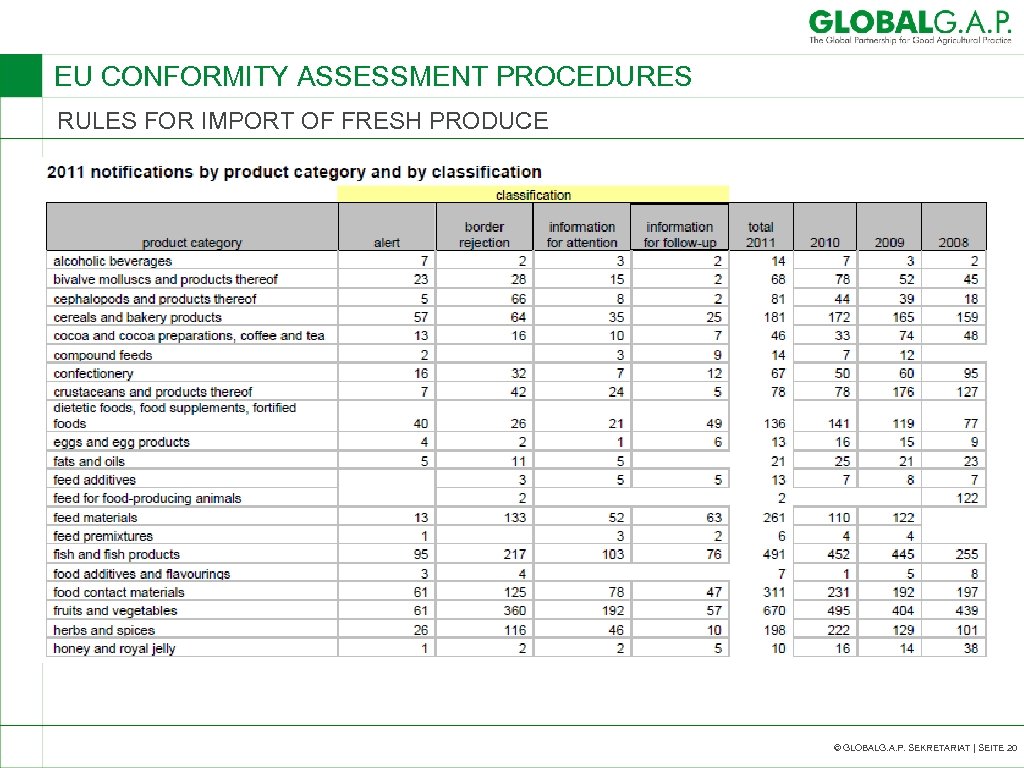
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 20
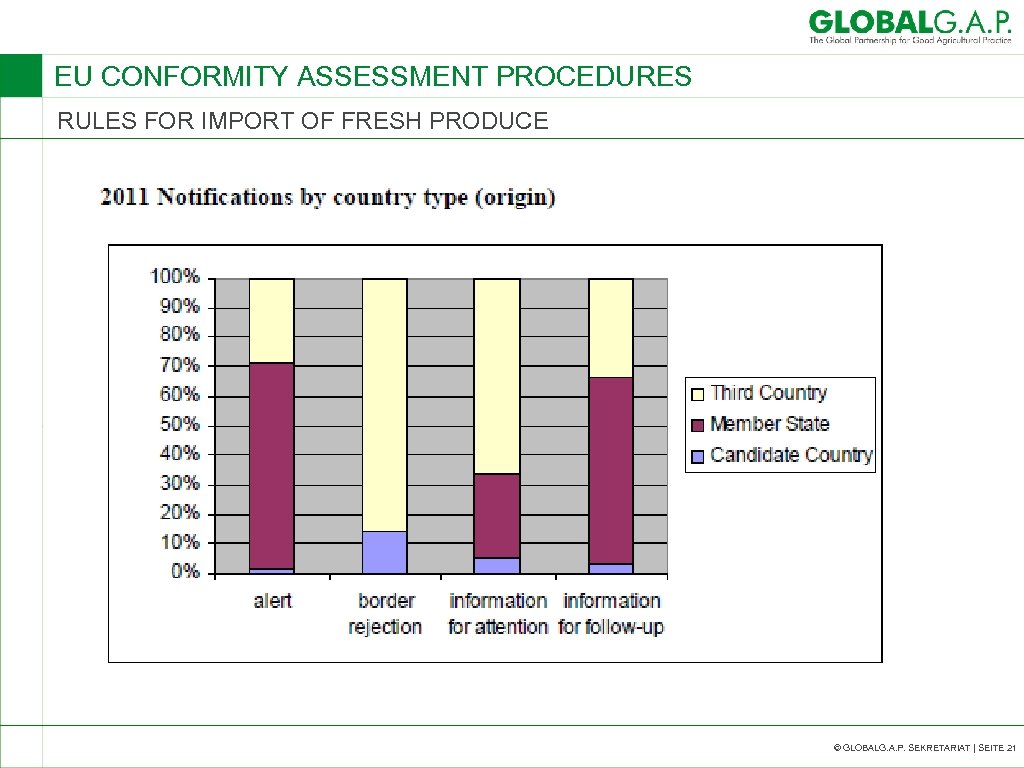
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 21

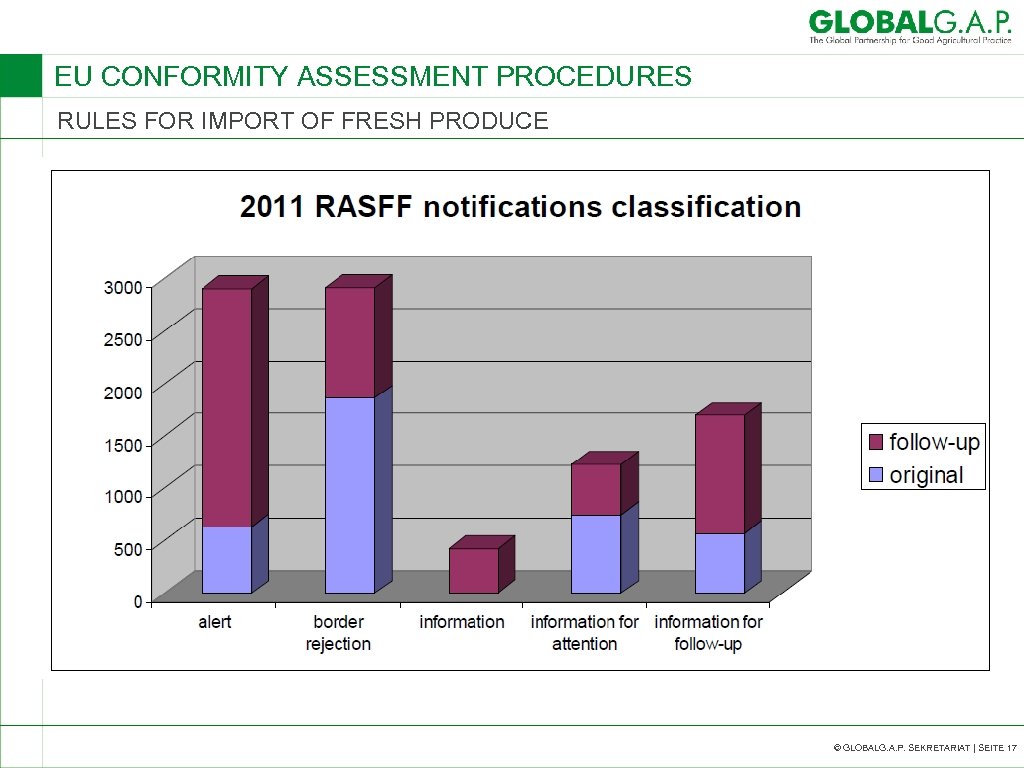
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Criteria for notification by risk • Prohibited substances or ingredients • Unauthorised substances or ingredients • Exceeding of legal limits • Unauthorised establishment for food of animal origin • Unauthorised novel food / GM food • Physical risk (foreign bodies) • Incorrect labelling implying health risk • Other risk based on risk assessment © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 22
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE • Introduction • EU 178/2002 • RASSF • EU Control schemes • Summary © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 23

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE If you export fresh fruit and vegetables (FFV) to the EU you have to make sure that your products comply with the following kinds of market access requirements: • Health control (food law, hygiene, microbiological criteria, contaminants, pesticides); • Plant health (phytosanitary) control (harmful organisms); • Marketing standards (general or specific); • Other requirements (food additives, food contact materials, food irradiation, novel foods, radioactivity, quick frozen foods, GMO’s, labelling and organic products). © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 24

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE REGULATION (EC) No 852/2004 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 29 April 2004 on the hygiene of foodstuffs Article 10 Imports Food business operators shall ensure that all stages of production, processing and distribution of food under their control satisfy the relevant hygiene requirements laid down in this Regulation Food business operators shall, as appropriate, adopt the following specific hygiene measures: • compliance with microbiological criteria for foodstuffs; • procedures necessary to meet targets set to achieve the objectives of this Regulation; • compliance with temperature control requirements for foodstuffs; • maintenance of the cold chain; • sampling and analysis. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 25

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Hazard analysis and critical control points The HACCP principles referred to in paragraph 1 consist of the following: • identifying any hazards that must be prevented, eliminated or reduced to acceptable levels; • identifying the critical control points at the step or steps at which control is essential to prevent or eliminate a hazard or to reduce it to acceptable levels; • establishing critical limits at critical control points which separate acceptability from unacceptability for the prevention, elimination or reduction of identified hazards; • establishing and implementing effective monitoring procedures at critical control points; • establishing corrective actions when monitoring indicates that a critical control point is not under control; • establishing procedures, which shall be carried out regularly, to verify that the measures outlined are working effectively; • establishing documents and records commensurate with the nature and size of the food business to demonstrate the effective application of the measures outlined © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 26

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE REGULATION (EC) No 852/2004 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 29 April 2004 on the hygiene of foodstuffs Article 6 Official controls, registration and approval Food business operators shall cooperate with the competent authorities in accordance with other applicable Community legislation or, if it does not exist, with national law. Food business operators shall also ensure that the competent authority always has up-to-date information on establishments, including by notifying any significant change in activities and any closure of an existing establishment. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 27
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE http: //ec. europa. eu/sanco_pesticides/public/index. cfm © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 28

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING REGULATION (EU) No 543/2011 of 7 June 2011 laying down detailed rules for the application of Council Regulation (EC) No 1234/2007 in respect of the fruit and vegetables and processed fruit and vegetables sectors Feed and food of non-animal origin subject to an increased level of official controls at the designated point of entry Egypt Fruit CN Code Oranges (fresh or dryed) Peaches (exept Nectarines) Pomgranates Strawberries Green Beans 0805 10 20; 0805 10 80 0809 30 90 ex 0810 90 95 0810 10 00 Sample size = 10% Pesticide residues analysed with Multi-methodes on the basis of. GCMS and LC-MS or individual methodes © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 29

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Council Directive 2000/29/EC of 8 May 2000 on protective measures against the introduction into the Community of organisms harmful to plants or plant products and against their spread within the Community Phytosanitary Import Control The task of phytosanitary import control is upon carrying out plant health control on the State border, to prevent from bringing into the European Union of harmful organisms thus increasing output and productivity of agriculture as well as protection of environment. Subject of phytosanitary control are: • standing trees and other plants, tubers, roots • cut flowers and ornamental plants • seed material • wood and wood packaging material • fruits and vegetables © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 30
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 31

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE What are ‘marketing standards’? Marketing standards are requirements that intend to guarantee EU consumers a particular minimum quality of the products they buy. Furthermore, they intend to enable comparison among products. As such, the EU marketing standards are mainly related to quality and labelling of products at the retail stage. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 32

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Marketing standards may in particular relate to quality, grading into classes, sizing, packaging, wrapping, storage, transport, presentation, marketing and labelling The holder of products covered by the adopted marketing standards may not display such products or offer them for sale or deliver or market them in any manner within the Community other than in conformity with those standards. The holder shall be responsible for ensuring such conformity . © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 33

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Marketing standards Regulation (EC) No 1221/2008 has introduced the new implementing rules regarding marketing standards and associated checks, following the reform of the common market organization for the fruit and vegetables sector © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 34

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE (18) Fruit and vegetables checked for conformity with the marketing standards should be subject to the same type of check at all stages of marketing. To this end, the inspection guidelines recommended by the UNECE in line with the relevant OECD recommendations, should be applied. Specific arrangements should, however, be laid down for checks at the retail sale stage. EN L 157/2 Official Journal of the European Union 15. 6. 2011 © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 35

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Specific marketing standards exist for the following products: (a) apples, (b) citrus fruit, (c) kiwifruit, (d) lettuces, curled leaved and broad-leaved endives, (e) peaches and nectarines, (f) pears, (g) strawberries, (h) sweet peppers, (i) table grapes, (j) tomatoes. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 36
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE http: //www. unece. org/trade/agr/standard/fresh/ffv-standardse. html © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 37
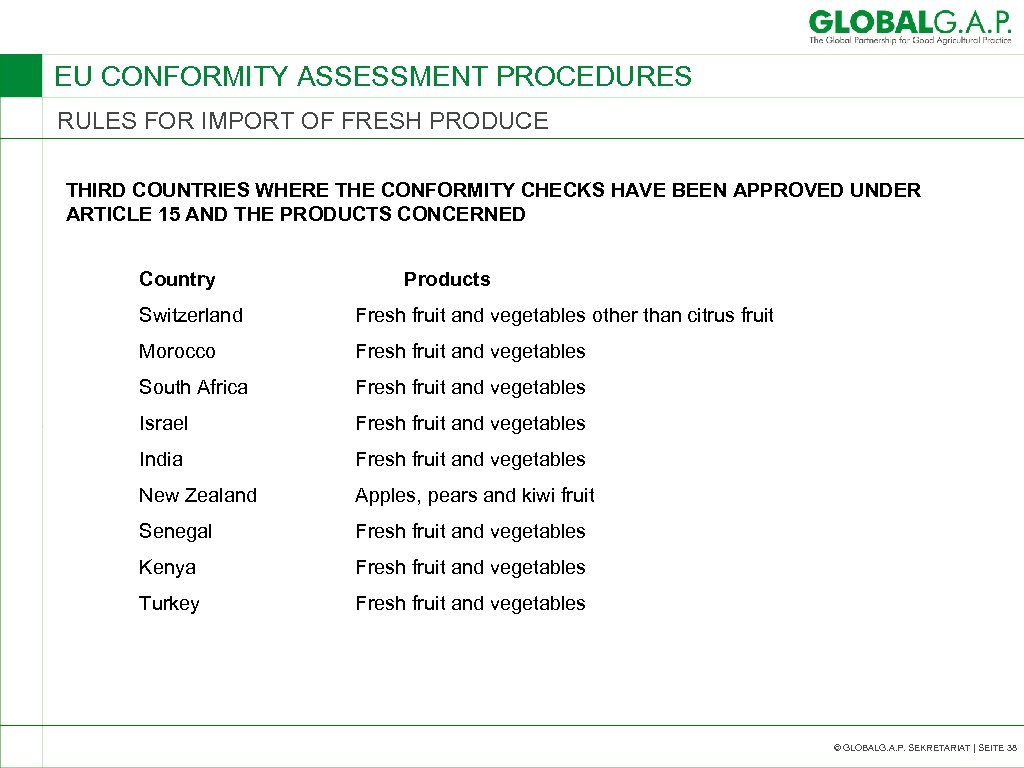
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE THIRD COUNTRIES WHERE THE CONFORMITY CHECKS HAVE BEEN APPROVED UNDER ARTICLE 15 AND THE PRODUCTS CONCERNED Country Products Switzerland Fresh fruit and vegetables other than citrus fruit Morocco Fresh fruit and vegetables South Africa Fresh fruit and vegetables Israel Fresh fruit and vegetables India Fresh fruit and vegetables New Zealand Apples, pears and kiwi fruit Senegal Fresh fruit and vegetables Kenya Fresh fruit and vegetables Turkey Fresh fruit and vegetables © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 38
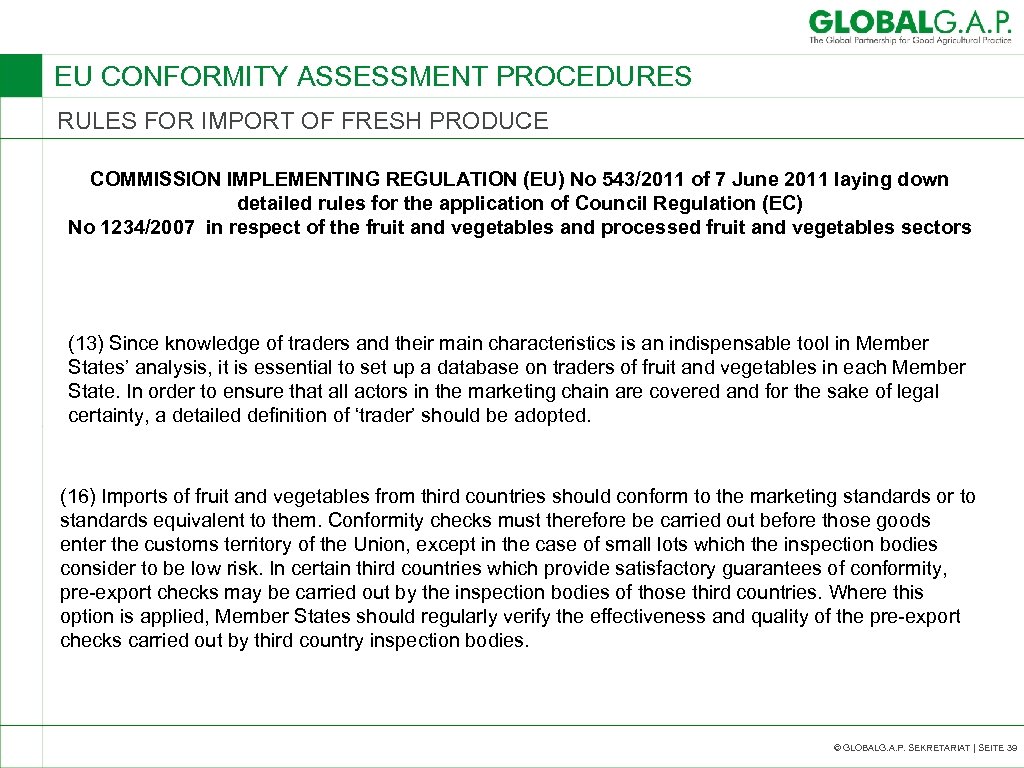
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING REGULATION (EU) No 543/2011 of 7 June 2011 laying down detailed rules for the application of Council Regulation (EC) No 1234/2007 in respect of the fruit and vegetables and processed fruit and vegetables sectors (13) Since knowledge of traders and their main characteristics is an indispensable tool in Member States’ analysis, it is essential to set up a database on traders of fruit and vegetables in each Member State. In order to ensure that all actors in the marketing chain are covered and for the sake of legal certainty, a detailed definition of ‘trader’ should be adopted. (16) Imports of fruit and vegetables from third countries should conform to the marketing standards or to standards equivalent to them. Conformity checks must therefore be carried out before those goods enter the customs territory of the Union, except in the case of small lots which the inspection bodies consider to be low risk. In certain third countries which provide satisfactory guarantees of conformity, pre-export checks may be carried out by the inspection bodies of those third countries. Where this option is applied, Member States should regularly verify the effectiveness and quality of the pre-export checks carried out by third country inspection bodies. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 39

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Minimum quality requirements Subject to the tolerances allowed, the products shall be: • intact, • sound; products affected by rotting or deterioration such as to make them unfit for consumption are excluded, • clean, practically free of any visible foreign matter, • practically free from pests, • practically free from damage caused by pests affecting the flesh, • free of abnormal external moisture, • free of any foreign smell and/or taste. The condition of the products must be such as to enable them: • to withstand transport and handling, • to arrive in satisfactory condition at the place of destination. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 40

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Tolerance A tolerance of 10 % by number or weight of product not satisfying the minimum quality requirements shall be permitted in each lot. Within this tolerance not more than 2 per cent in total may consist of produce affected by decay. Marking of origin of produce Full name of the country of origin. This shall be in any language understandable by the consumers of the country of destination. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 41
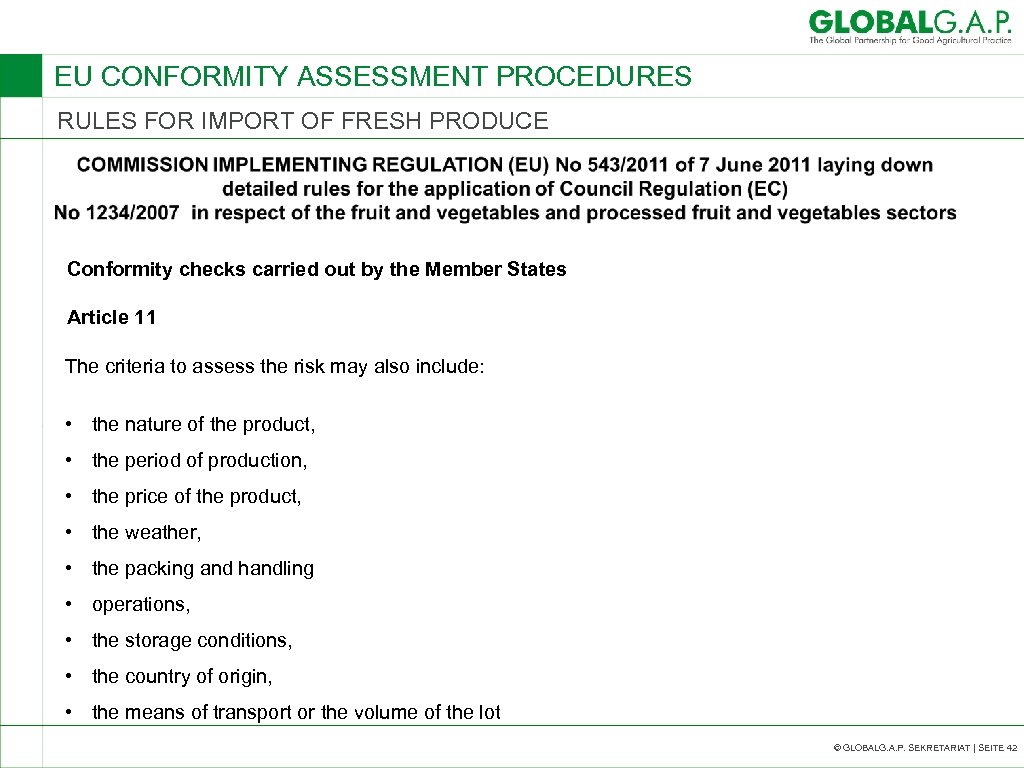
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Conformity checks carried out by the Member States Article 11 The criteria to assess the risk may also include: • the nature of the product, • the period of production, • the price of the product, • the weather, • the packing and handling • operations, • the storage conditions, • the country of origin, • the means of transport or the volume of the lot © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 42

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Comformity checks carried out by the Member States Article 11 The criteria to assess the risk may also include: • the size of the traders, • their position in the marketing chain, • the volume or value marketed by them, • their product range, • the delivery area or the type of business carried out such as storage, sorting, packing or sale; • findings made during previous checks including the number and type of defects found, the usual quality of products marketed, the level of technical equipment used; • reliability of traders’ quality assurance systems or self- checking systems related to the conformity to marketing standards; • the place where the check is carried out, in particular if it is the point of first entry into the Union, or the place where the products are being packed or loaded; • any other information that might indicate a risk of non- compliance. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 43
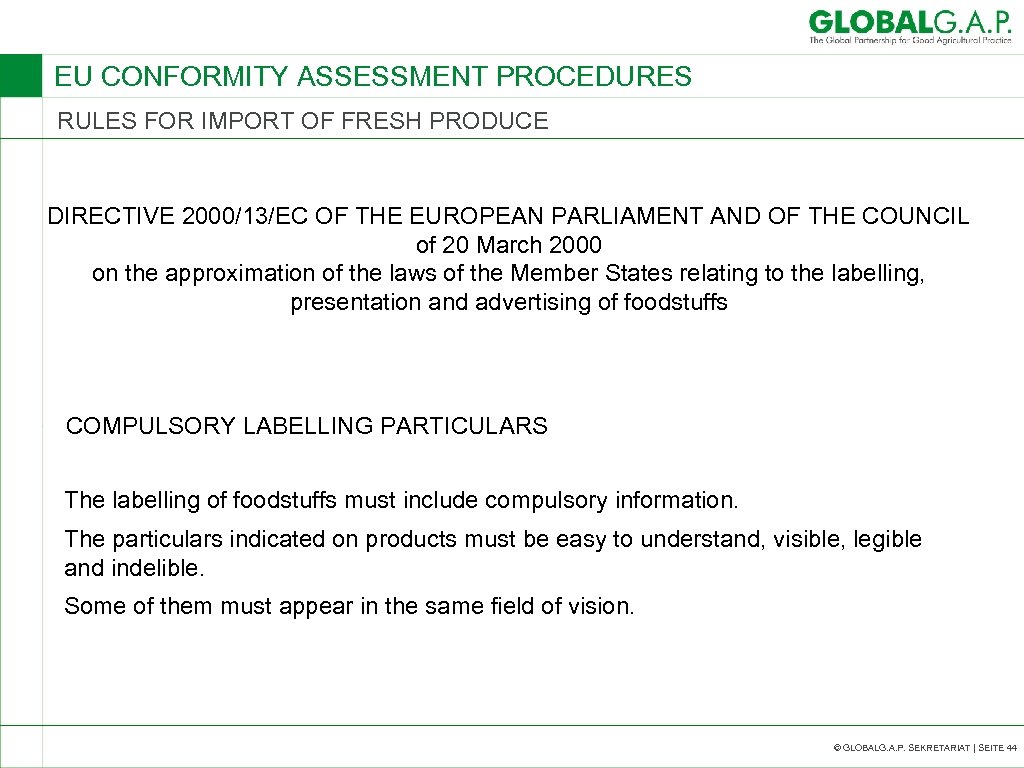
EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE DIRECTIVE 2000/13/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 20 March 2000 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to the labelling, presentation and advertising of foodstuffs COMPULSORY LABELLING PARTICULARS The labelling of foodstuffs must include compulsory information. The particulars indicated on products must be easy to understand, visible, legible and indelible. Some of them must appear in the same field of vision. © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 44

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 45

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 46

EU CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES RULES FOR IMPORT OF FRESH PRODUCE Summary • Export to the EU is complex • Hygiene and traceability are key • Use of Plant Protection Products according to regulations • Export is a great opportunity © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 47

THANK YOR FOR YOUR ATTENTION! QUESTIONS - DISCUSSION - CONTACT DR. FRIEDRICH LÜDEKE E-MAIL: LUEDEKE@GLOBALGAP. ORG WWW. GLOBALGAP. ORG © GLOBALG. A. P. SEKRETARIAT | SEITE 48
85edd904dcc40533755b010457efcd38.ppt