f0db46e9cb252c5aec15d96a0ef33222.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 ETO: Accounting for Engineering Trade-Offs in Decision-making Kenneth R. Stone Engineering Trade-Offs Team Leader
ETO: Accounting for Engineering Trade-Offs in Decision-making Kenneth R. Stone Engineering Trade-Offs Team Leader
 Presentation Outline Overview of Environmental and Economic Approaches Life Cycle Engineering – Precursor to Engineering Trade-Offs (ETO) The ETO Concept Program Plans
Presentation Outline Overview of Environmental and Economic Approaches Life Cycle Engineering – Precursor to Engineering Trade-Offs (ETO) The ETO Concept Program Plans
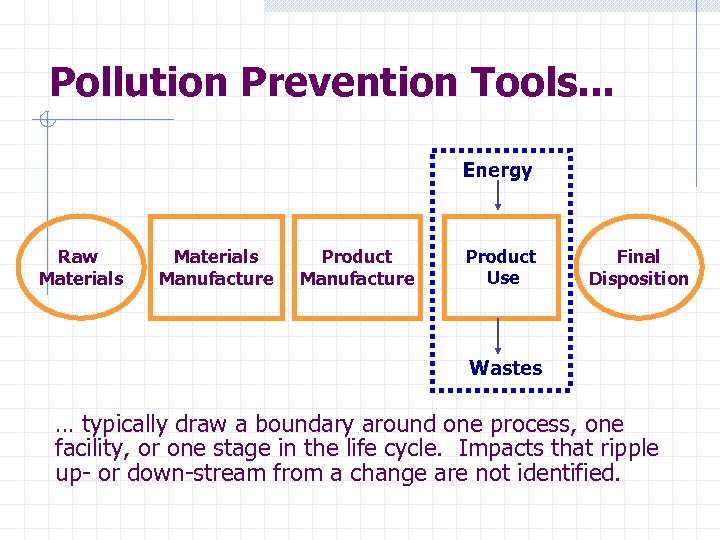 Pollution Prevention Tools. . . Energy Raw Materials Manufacture Product Use Final Disposition Wastes … typically draw a boundary around one process, one facility, or one stage in the life cycle. Impacts that ripple up- or down-stream from a change are not identified.
Pollution Prevention Tools. . . Energy Raw Materials Manufacture Product Use Final Disposition Wastes … typically draw a boundary around one process, one facility, or one stage in the life cycle. Impacts that ripple up- or down-stream from a change are not identified.
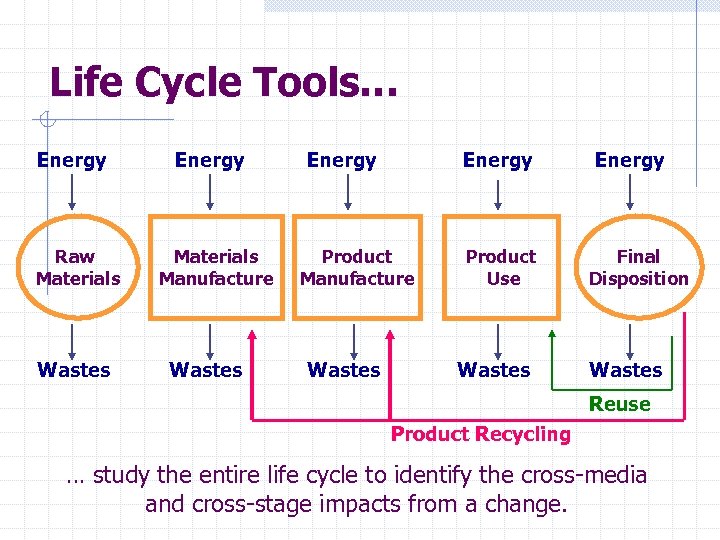 Life Cycle Tools… Energy Raw Materials Wastes Energy Materials Manufacture Wastes Energy Product Manufacture Wastes Product Use Wastes Energy Final Disposition Wastes Reuse Product Recycling … study the entire life cycle to identify the cross-media and cross-stage impacts from a change.
Life Cycle Tools… Energy Raw Materials Wastes Energy Materials Manufacture Wastes Energy Product Manufacture Wastes Product Use Wastes Energy Final Disposition Wastes Reuse Product Recycling … study the entire life cycle to identify the cross-media and cross-stage impacts from a change.
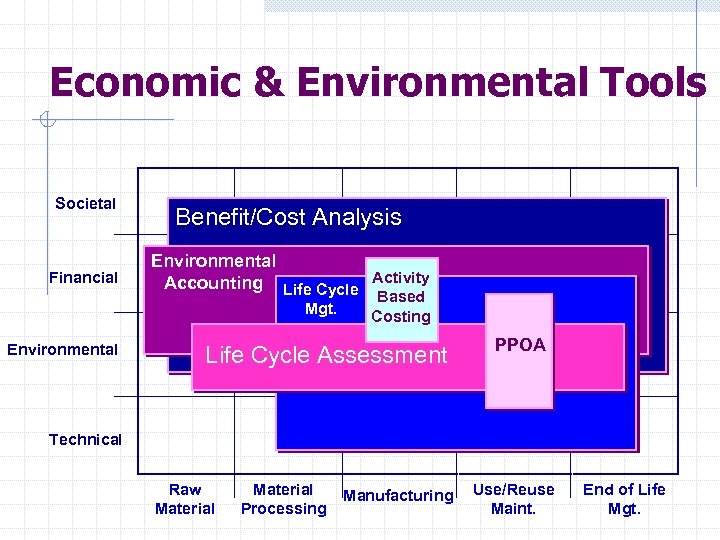 Economic & Environmental Tools Societal Financial Benefit/Cost Analysis Environmental Accounting Life Cycle Activity Based Mgt. Environmental Costing Life Cycle Assessment PPOA Technical Raw Material Processing Manufacturing Use/Reuse Maint. End of Life Mgt.
Economic & Environmental Tools Societal Financial Benefit/Cost Analysis Environmental Accounting Life Cycle Activity Based Mgt. Environmental Costing Life Cycle Assessment PPOA Technical Raw Material Processing Manufacturing Use/Reuse Maint. End of Life Mgt.
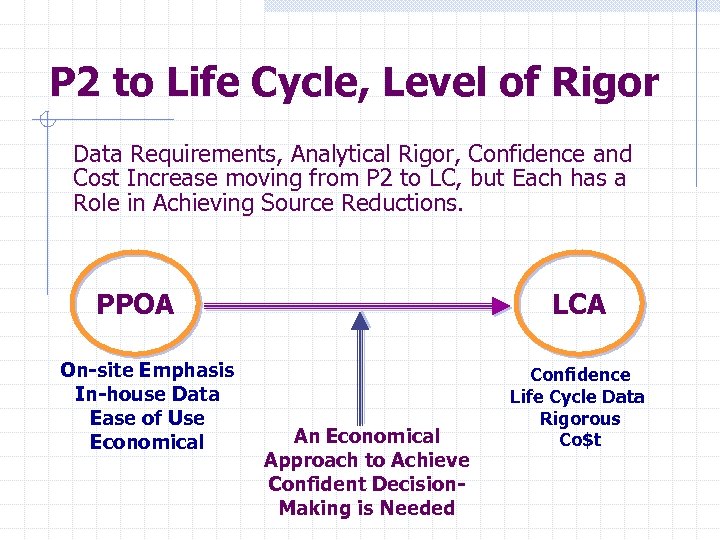 P 2 to Life Cycle, Level of Rigor Data Requirements, Analytical Rigor, Confidence and Cost Increase moving from P 2 to LC, but Each has a Role in Achieving Source Reductions. PPOA On-site Emphasis In-house Data Ease of Use Economical LCA An Economical Approach to Achieve Confident Decision. Making is Needed Confidence Life Cycle Data Rigorous Co$t
P 2 to Life Cycle, Level of Rigor Data Requirements, Analytical Rigor, Confidence and Cost Increase moving from P 2 to LC, but Each has a Role in Achieving Source Reductions. PPOA On-site Emphasis In-house Data Ease of Use Economical LCA An Economical Approach to Achieve Confident Decision. Making is Needed Confidence Life Cycle Data Rigorous Co$t
 CARC is used on military vehicles & equipment to prevent penetration by a chemical agent, which allows contaminated vehicles to be cleaned in the field. CARC paints use heavy metals and volatile organic solvents.
CARC is used on military vehicles & equipment to prevent penetration by a chemical agent, which allows contaminated vehicles to be cleaned in the field. CARC paints use heavy metals and volatile organic solvents.
 CARC PPOA, Ft. Eustis In 1992, in support of TIPPP, NRMRL conducted a PPOA on CARC Painting operations at Ft. Eustis. The PPOA recommended: Upgrades to the Paint Booth Recovery of Paint Thinner Installation of HVLP Spray Guns
CARC PPOA, Ft. Eustis In 1992, in support of TIPPP, NRMRL conducted a PPOA on CARC Painting operations at Ft. Eustis. The PPOA recommended: Upgrades to the Paint Booth Recovery of Paint Thinner Installation of HVLP Spray Guns
 Short Term Results Ft. Eustis switched over to commercial HVLP spray guns to reduce environmental impacts. Short term results were: Overspray was reduced by 60% CARC paint purchases cut by 40% Net annual savings = $6, 700
Short Term Results Ft. Eustis switched over to commercial HVLP spray guns to reduce environmental impacts. Short term results were: Overspray was reduced by 60% CARC paint purchases cut by 40% Net annual savings = $6, 700
 CARC LCE, Ft. Eustis Environment LCC Decision T&E Performance LCA Cost In 1993, NRMRL instituted the Life Cycle Engineering & Design (LCED) Program and in 1994 revisited Ft. Eustis. Because the LCE Approach inherently captures Trade-Offs – due to the emphasis on integrating Performance, Cost and Environment – a new picture had emerged.
CARC LCE, Ft. Eustis Environment LCC Decision T&E Performance LCA Cost In 1993, NRMRL instituted the Life Cycle Engineering & Design (LCED) Program and in 1994 revisited Ft. Eustis. Because the LCE Approach inherently captures Trade-Offs – due to the emphasis on integrating Performance, Cost and Environment – a new picture had emerged.
 Actual Trade-Offs CARC is a Do. D-specialty paint, more viscous and has higher solids content than commercial paints. It clogged up the HVLPs: HVLPs were harder to use & maintain Topcoat had to be thinned (up to 20%) Solvent use & VOC emissions increased Labor increased & Operations suffered
Actual Trade-Offs CARC is a Do. D-specialty paint, more viscous and has higher solids content than commercial paints. It clogged up the HVLPs: HVLPs were harder to use & maintain Topcoat had to be thinned (up to 20%) Solvent use & VOC emissions increased Labor increased & Operations suffered
 Additional Trade-Offs Two Do. D Bases were Using the Wrong Thinner n Direct Impact: Shortened Topcoat Lifespan Operations Changed Dramatically Among Sites n n MILSPECs & Tech Orders Ignored Safety Gear Varied
Additional Trade-Offs Two Do. D Bases were Using the Wrong Thinner n Direct Impact: Shortened Topcoat Lifespan Operations Changed Dramatically Among Sites n n MILSPECs & Tech Orders Ignored Safety Gear Varied
 Problem Statement P 2 Tools can Fall Short n Process Inefficiencies can be Missed n Trade-offs among Critical Areas not Highlighted n Full Environmental Effect not Assessed LCA Tools cannot be Internalized n High Level of Effort and Cost n Data Uncertainties n Off-site Information & Externalities not Valued
Problem Statement P 2 Tools can Fall Short n Process Inefficiencies can be Missed n Trade-offs among Critical Areas not Highlighted n Full Environmental Effect not Assessed LCA Tools cannot be Internalized n High Level of Effort and Cost n Data Uncertainties n Off-site Information & Externalities not Valued
 Research Needs Target Middle Ground of P 2/LCA n Illustrate True Efficiencies n Capture Trade-offs n Identify Environmental Issues with Confidence Focus on Lower Tier Decision-makers n Moderate Cost n Exploit Data in Hand n Emphasize Site Issues
Research Needs Target Middle Ground of P 2/LCA n Illustrate True Efficiencies n Capture Trade-offs n Identify Environmental Issues with Confidence Focus on Lower Tier Decision-makers n Moderate Cost n Exploit Data in Hand n Emphasize Site Issues
 Common Trade-Off Decisions Buying a Car: n Capacity, Power, Utility, Comfort, Color, Cost, MPG, Emissions, Status, etc. Purchasing a House: n Location, Lot Layout, Structure, Condition, Cost, Cosmetics, Amenities, School System, Shopping, Congestion, Police & Fire Service, Ethnicity, Social Status, Environment, etc.
Common Trade-Off Decisions Buying a Car: n Capacity, Power, Utility, Comfort, Color, Cost, MPG, Emissions, Status, etc. Purchasing a House: n Location, Lot Layout, Structure, Condition, Cost, Cosmetics, Amenities, School System, Shopping, Congestion, Police & Fire Service, Ethnicity, Social Status, Environment, etc.
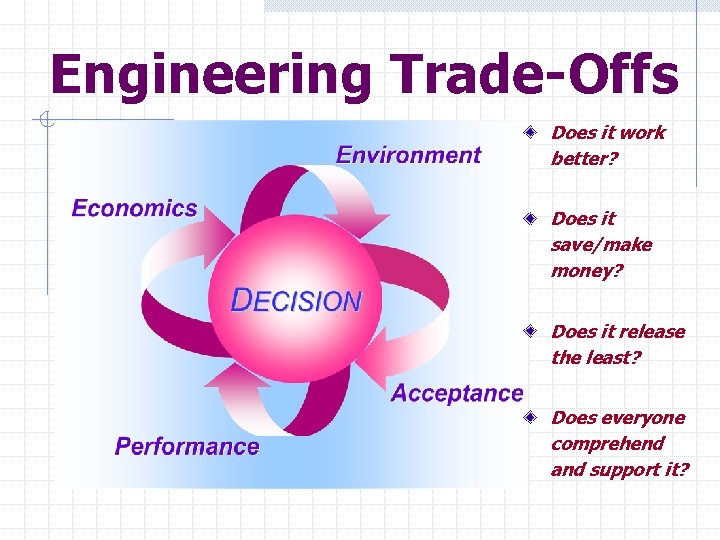 Engineering Trade-Offs Does it work better? Does it save/make money? Does it release the least? Does everyone comprehend and support it?
Engineering Trade-Offs Does it work better? Does it save/make money? Does it release the least? Does everyone comprehend and support it?
 Performance Must be able to Demonstrate an Improvement: Development & Demonstration n Verify Physical Attributes n Prove Results are Achievable Level of Performance n A Good Substitute is not Good Enough n Contributes to a Competitive Product
Performance Must be able to Demonstrate an Improvement: Development & Demonstration n Verify Physical Attributes n Prove Results are Achievable Level of Performance n A Good Substitute is not Good Enough n Contributes to a Competitive Product
 Environment Focus on Smallest Environmental Footprint: Release the Least n Follow Releases n Do not Develop Impact Categories Quantify and Qualify n Quantify On-site Releases n Qualify Up- and Down-stream Issues
Environment Focus on Smallest Environmental Footprint: Release the Least n Follow Releases n Do not Develop Impact Categories Quantify and Qualify n Quantify On-site Releases n Qualify Up- and Down-stream Issues
 Economics A Measurable Economic Benefit: Dollar Value n Increased Profit n Lowered Cost Intangible Value n Reputation/Goodwill n Internal Effects/Morale
Economics A Measurable Economic Benefit: Dollar Value n Increased Profit n Lowered Cost Intangible Value n Reputation/Goodwill n Internal Effects/Morale
 Acceptance The Impact of Human Error and Will: Human Error n Personal Limitations n Poor Information, Training or Judgment n Individual Technical Belief Human Will n Agreement/Support n Disagreement/Passivity n Resentment/Resistance n Indifference/Independence
Acceptance The Impact of Human Error and Will: Human Error n Personal Limitations n Poor Information, Training or Judgment n Individual Technical Belief Human Will n Agreement/Support n Disagreement/Passivity n Resentment/Resistance n Indifference/Independence
 How Does ETO Relate to LCE? Evolved From the LCE Program n Integrated Cost & Performance with Environment n Case Studies Emphasized the Value of Trade-offs Based on LCE Lessons Learned n Many of the P 2 “Ripples” were On-site n Emphasize Site Issues Highlighted Human Factors n Human Potential to Avoid Perverse Outcomes n Human Contribution to Perverse Outcomes
How Does ETO Relate to LCE? Evolved From the LCE Program n Integrated Cost & Performance with Environment n Case Studies Emphasized the Value of Trade-offs Based on LCE Lessons Learned n Many of the P 2 “Ripples” were On-site n Emphasize Site Issues Highlighted Human Factors n Human Potential to Avoid Perverse Outcomes n Human Contribution to Perverse Outcomes
 HVLP Trade-Offs by ETO Issue Performance n n Transfer Efficiency was Good Operational Efficiency was Poor Environment n Increased VOC Emissions Economics n n Reduced Topcoat Purchases Increased Solvent Purchases, Net Loss Acceptance n n Painters did not report Problems, made In-house Fixes Painters Typically Ignore “Unsound” Policies
HVLP Trade-Offs by ETO Issue Performance n n Transfer Efficiency was Good Operational Efficiency was Poor Environment n Increased VOC Emissions Economics n n Reduced Topcoat Purchases Increased Solvent Purchases, Net Loss Acceptance n n Painters did not report Problems, made In-house Fixes Painters Typically Ignore “Unsound” Policies
 ETO Issues Performance n n Requires Access to Technology or Product for Testing On-site or Vendor’s Site Environment n n Up to Date Data on Environmental Characteristics Known Circumstances under which Data was Collected Economics n n Quantitative On-site Cost Impacts Life Cycle Qualitative Evaluation of Enviro/Economic Risk Acceptance n n Identification and Characterization of User Community Development of Implementation Strategy with Community
ETO Issues Performance n n Requires Access to Technology or Product for Testing On-site or Vendor’s Site Environment n n Up to Date Data on Environmental Characteristics Known Circumstances under which Data was Collected Economics n n Quantitative On-site Cost Impacts Life Cycle Qualitative Evaluation of Enviro/Economic Risk Acceptance n n Identification and Characterization of User Community Development of Implementation Strategy with Community
 Engineering Trade-Offs Small Business, Community or Facility-level Support Informed Decision-making Comparative Assessment Releases-based, not Impacts-based Quantify Gate-to-Gate Operations & Releases Qualify Releases Outside Gates
Engineering Trade-Offs Small Business, Community or Facility-level Support Informed Decision-making Comparative Assessment Releases-based, not Impacts-based Quantify Gate-to-Gate Operations & Releases Qualify Releases Outside Gates
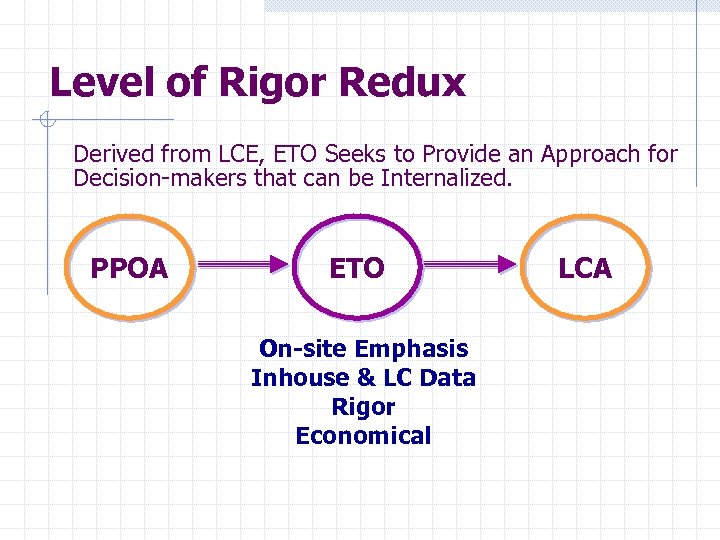 Level of Rigor Redux Derived from LCE, ETO Seeks to Provide an Approach for Decision-makers that can be Internalized. PPOA ETO On-site Emphasis Inhouse & LC Data Rigor Economical LCA
Level of Rigor Redux Derived from LCE, ETO Seeks to Provide an Approach for Decision-makers that can be Internalized. PPOA ETO On-site Emphasis Inhouse & LC Data Rigor Economical LCA
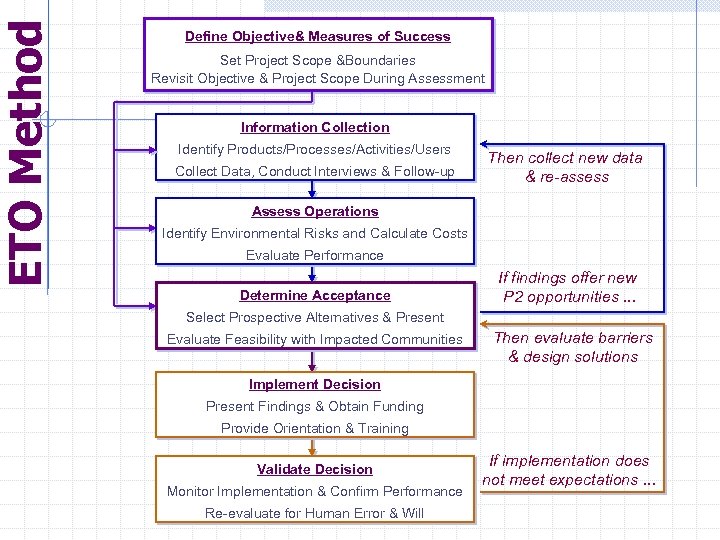 ETO Method Define Objective& Measures of Success Set Project Scope &Boundaries Revisit Objective & Project Scope During Assessment Information Collection Identify Products/Processes/Activities/Users Collect Data, Conduct Interviews & Follow-up Then collect new data & re-assess Assess Operations Identify Environmental Risks and Calculate Costs Evaluate Performance Determine Acceptance If findings offer new P 2 opportunities. . . Select Prospective Alternatives & Present Evaluate Feasibility with Impacted Communities Then evaluate barriers & design solutions Implement Decision Present Findings & Obtain Funding Provide Orientation & Training Validate Decision Monitor Implementation & Confirm Performance Re-evaluate for Human Error & Will If implementation does not meet expectations. . .
ETO Method Define Objective& Measures of Success Set Project Scope &Boundaries Revisit Objective & Project Scope During Assessment Information Collection Identify Products/Processes/Activities/Users Collect Data, Conduct Interviews & Follow-up Then collect new data & re-assess Assess Operations Identify Environmental Risks and Calculate Costs Evaluate Performance Determine Acceptance If findings offer new P 2 opportunities. . . Select Prospective Alternatives & Present Evaluate Feasibility with Impacted Communities Then evaluate barriers & design solutions Implement Decision Present Findings & Obtain Funding Provide Orientation & Training Validate Decision Monitor Implementation & Confirm Performance Re-evaluate for Human Error & Will If implementation does not meet expectations. . .
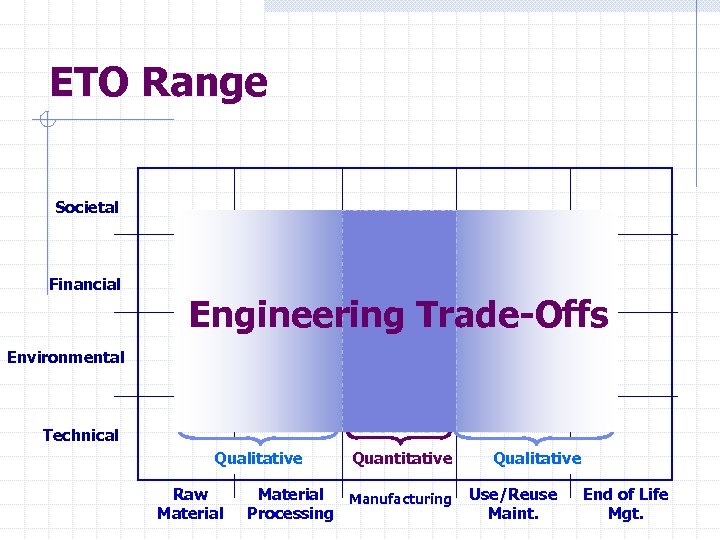 ETO Range Societal Financial Engineering Trade-Offs Environmental Technical Qualitative Raw Material Quantitative Material Manufacturing Processing Qualitative Use/Reuse Maint. End of Life Mgt.
ETO Range Societal Financial Engineering Trade-Offs Environmental Technical Qualitative Raw Material Quantitative Material Manufacturing Processing Qualitative Use/Reuse Maint. End of Life Mgt.
 The Questions PPOA can Answer How can I Improve Housekeeping Habits? n Low-hanging fruit, Simple Improvements Where can I Find Ways to Refine Operations? n Seeks out P 2 Techniques and Technologies How can I Identify Hazards & Avoid MOVs? n Problems Often come to Light During a PPOA How can I Develop Higher ESOH Awareness? n Identifies Needs, Communicates Priorities What can I Do to Change Staff Perspectives? n Creates Inhouse Capability, Recognizes Results
The Questions PPOA can Answer How can I Improve Housekeeping Habits? n Low-hanging fruit, Simple Improvements Where can I Find Ways to Refine Operations? n Seeks out P 2 Techniques and Technologies How can I Identify Hazards & Avoid MOVs? n Problems Often come to Light During a PPOA How can I Develop Higher ESOH Awareness? n Identifies Needs, Communicates Priorities What can I Do to Change Staff Perspectives? n Creates Inhouse Capability, Recognizes Results
 The Questions ETO can Answer: Which Product/Process should I Purchase? n Provides an Integrated Evaluation, Capturing Trade-offs How should I Redesign or Retrofit an Existing System? n Illustrates Trade-offs, Anticipates Perverse Outcomes How Do I Implement a P 2 Technology Solution? n Emphasizes On-site Issues, Operator Acceptance Where should We Site the Recycling Center? n Identifies Enviro/Economic Issues and Human Factors What Services/Product/Process Choices Do We Face? n Illustrates the Local Effects of a Decision
The Questions ETO can Answer: Which Product/Process should I Purchase? n Provides an Integrated Evaluation, Capturing Trade-offs How should I Redesign or Retrofit an Existing System? n Illustrates Trade-offs, Anticipates Perverse Outcomes How Do I Implement a P 2 Technology Solution? n Emphasizes On-site Issues, Operator Acceptance Where should We Site the Recycling Center? n Identifies Enviro/Economic Issues and Human Factors What Services/Product/Process Choices Do We Face? n Illustrates the Local Effects of a Decision
 The Questions LCE can Answer: How should I Design Long Term Systems? n Identifies Lowest Life Cycle Impact, Lowest Cost What Purchasing Guidelines should I Set? n Provides Basis for Integrated Management How can I Reduce Liability Risk? n Captures Downstream Impacts, Risk Exposure How can I Ensure No Future Surprises? n Captures Up-stream Risk that May Later Raise Costs How can I Validate an Environmental Success? n Provides a Data-based Rationale for “Green-ness”
The Questions LCE can Answer: How should I Design Long Term Systems? n Identifies Lowest Life Cycle Impact, Lowest Cost What Purchasing Guidelines should I Set? n Provides Basis for Integrated Management How can I Reduce Liability Risk? n Captures Downstream Impacts, Risk Exposure How can I Ensure No Future Surprises? n Captures Up-stream Risk that May Later Raise Costs How can I Validate an Environmental Success? n Provides a Data-based Rationale for “Green-ness”
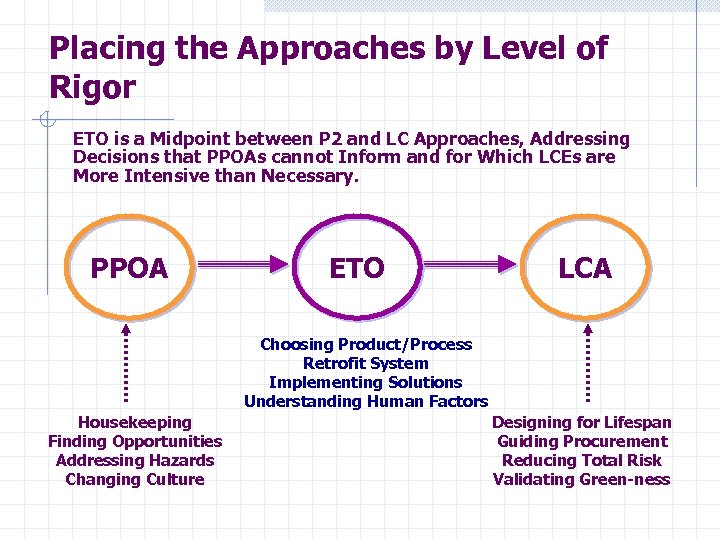 Placing the Approaches by Level of Rigor ETO is a Midpoint between P 2 and LC Approaches, Addressing Decisions that PPOAs cannot Inform and for Which LCEs are More Intensive than Necessary. PPOA ETO LCA Choosing Product/Process Retrofit System Implementing Solutions Understanding Human Factors Housekeeping Finding Opportunities Addressing Hazards Changing Culture Designing for Lifespan Guiding Procurement Reducing Total Risk Validating Green-ness
Placing the Approaches by Level of Rigor ETO is a Midpoint between P 2 and LC Approaches, Addressing Decisions that PPOAs cannot Inform and for Which LCEs are More Intensive than Necessary. PPOA ETO LCA Choosing Product/Process Retrofit System Implementing Solutions Understanding Human Factors Housekeeping Finding Opportunities Addressing Hazards Changing Culture Designing for Lifespan Guiding Procurement Reducing Total Risk Validating Green-ness
 Contact: stone. kenneth@epa. gov Kenneth R. Stone ETO Team Leader NATIONAL RISK MANAGEMENT RESEARCH LABORATORY 26 W. Martin Luther King Cincinnati OH 45268 513 -569 -7474
Contact: stone. kenneth@epa. gov Kenneth R. Stone ETO Team Leader NATIONAL RISK MANAGEMENT RESEARCH LABORATORY 26 W. Martin Luther King Cincinnati OH 45268 513 -569 -7474


